Different Impacts of Long-Term Tillage and Manure on Yield and N Use Efficiency, Soil Fertility, and Fungal Community in Rainfed Wheat in Loess Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Wheat Yield and N Use Efficiency
2.2. Soil Properties Analysis
2.3. Alpha Diversity of Soil Fungal Community
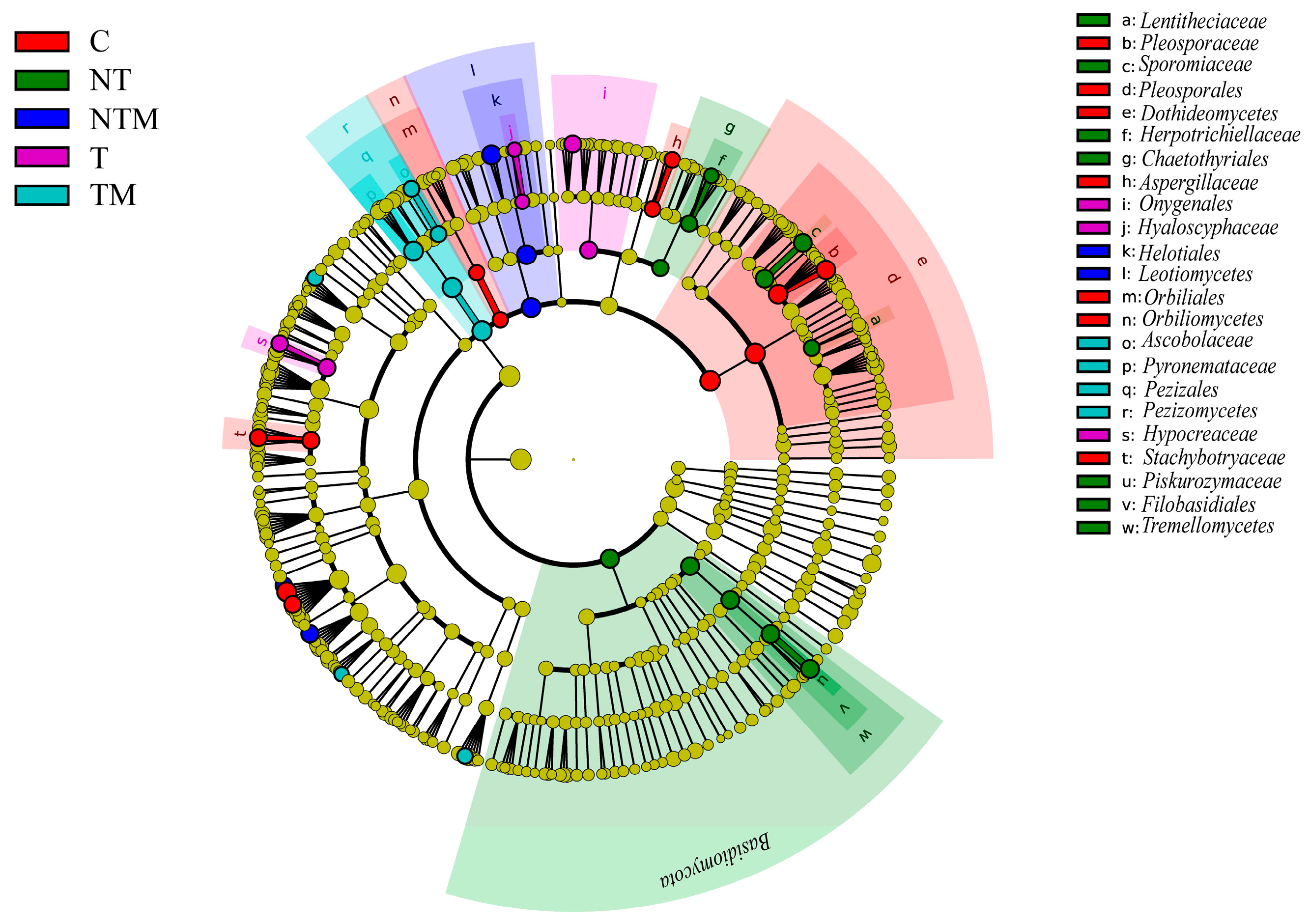
2.4. Composition of Fungal Community
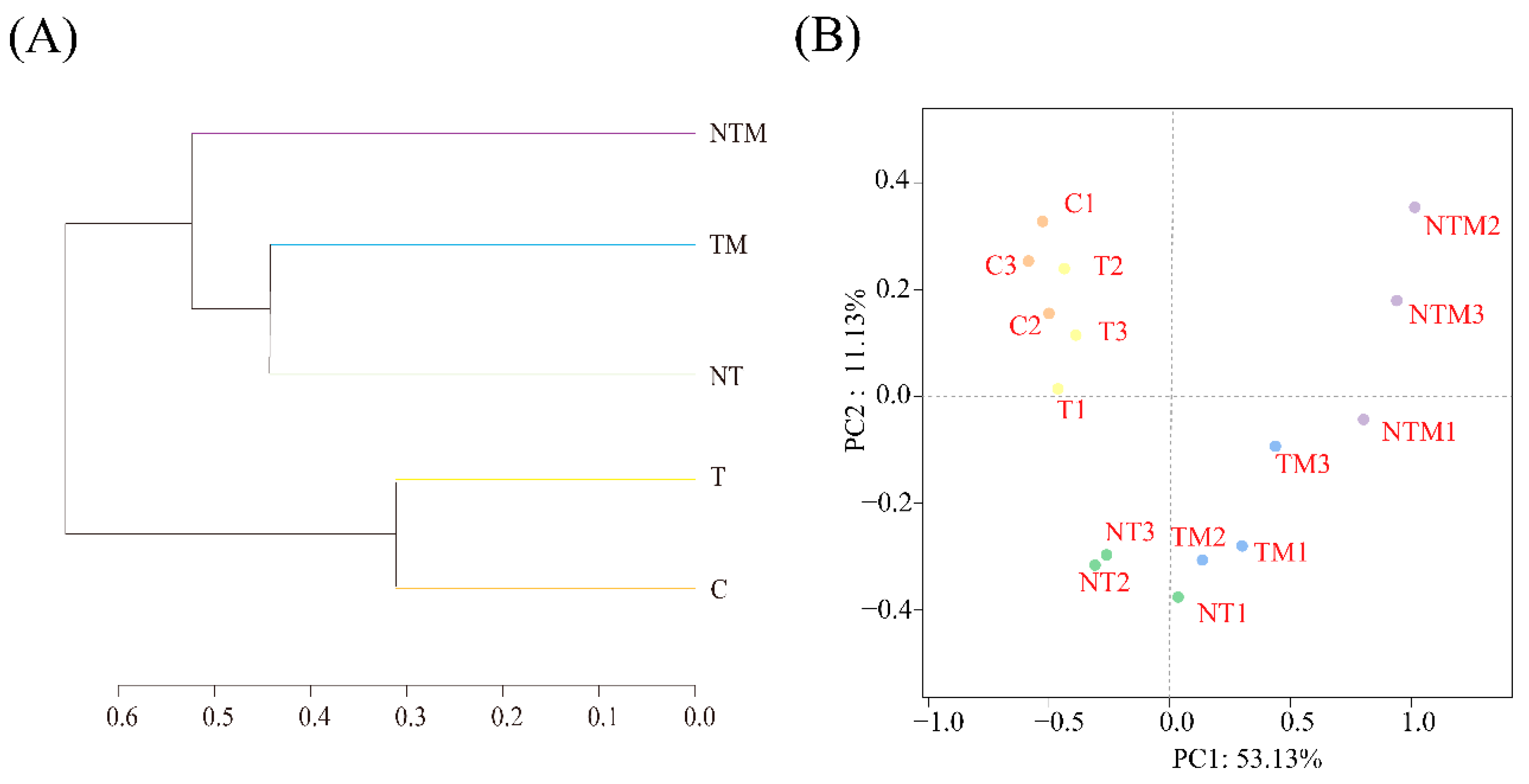
2.5. Beta Diversity of Soil Microbial Community
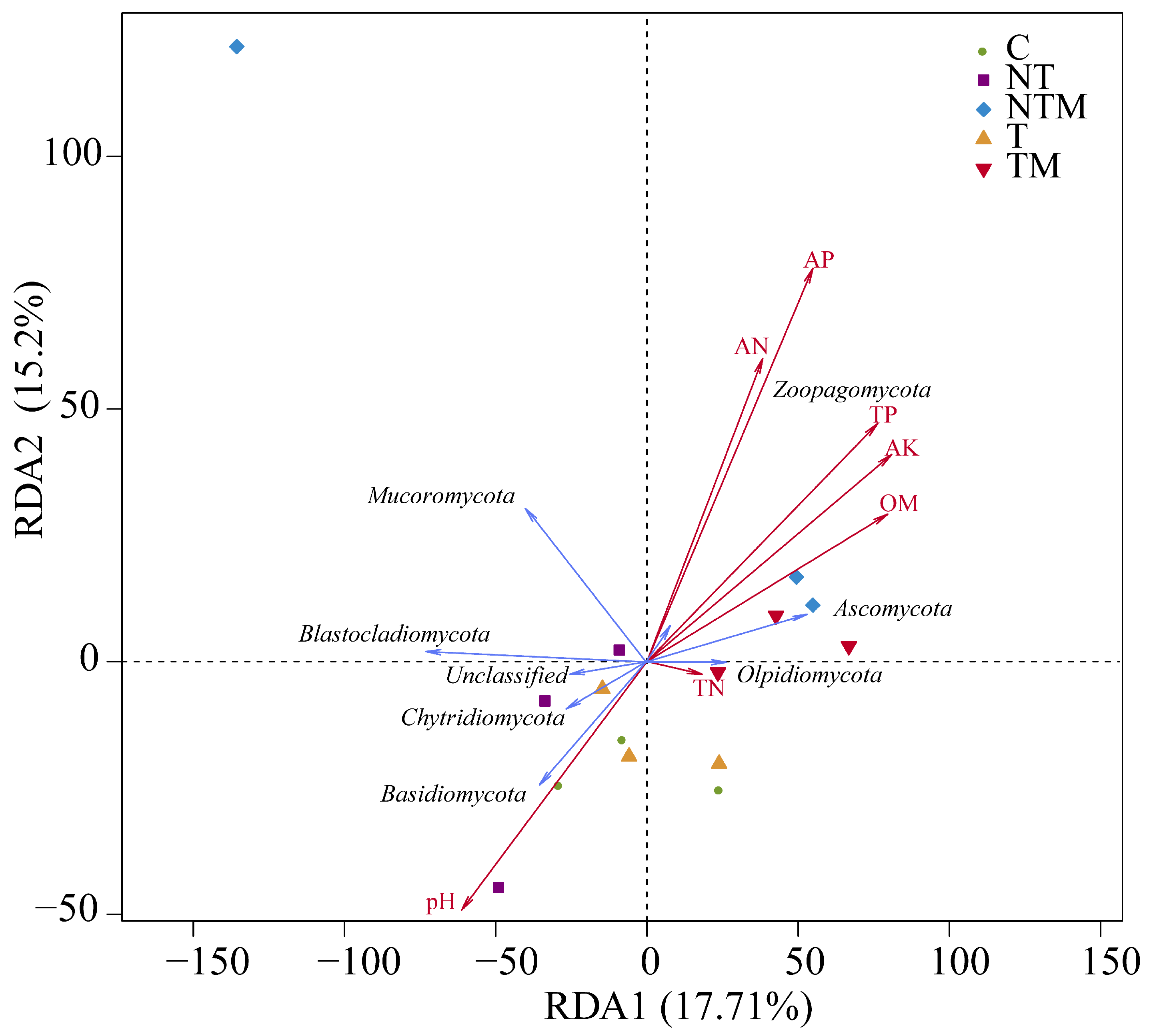
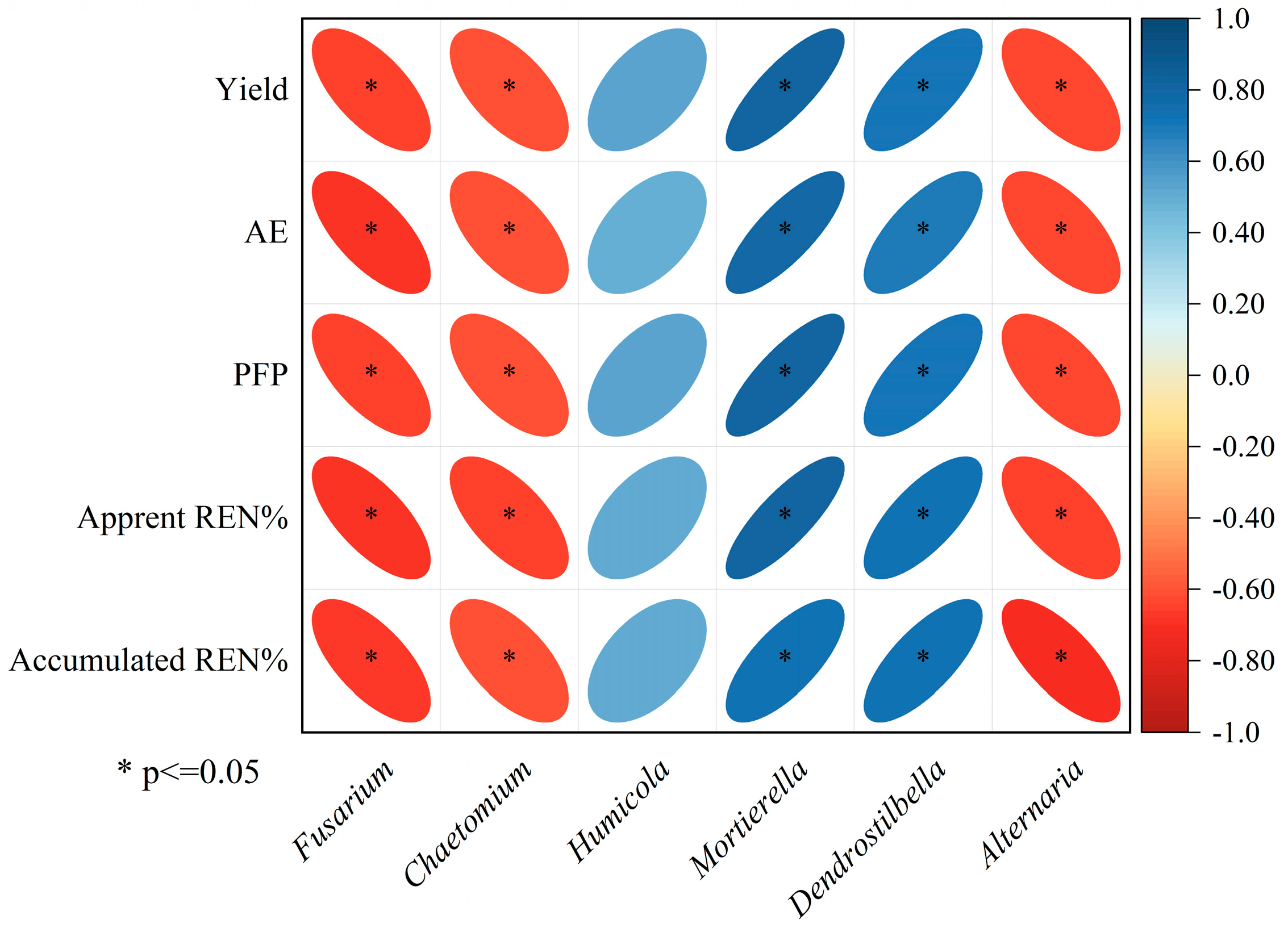
2.6. Relationship Between Fungal Community and Soil Properties, Yield, and NUE
3. Discussion
3.1. Effects of Long-Term Soil Tillage and Fertilization Management on Wheat Yield and N Use Efficiency
3.2. Effects of Long-Term Tillage and Fertilization Management on Soil Properties
3.3. Effects of Tillage and Fertilization Management on Soil Fungal Diversity
3.4. Effects of Tillage and Fertilization Management on Soil Fungal Compositions
3.5. Soil Fungi Association Analysis with Soil Environmental Factors, Yield, and NUE
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Site Description
4.2. Experimental Design and Sampling
4.3. Sampling and Measurements
4.4. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Francioli, D.; Schulz, E.; Lentendu, G.; Wubet, T.; Buscot, F.; Reitz, T. Mineral vs. organic amendments: Microbial community structure, activity and abundance of agriculturally relevant microbes are driven by long-term fertilization strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbell, F.; Reich, P.B.; Tilman, D.; Hobbie, S.E.; Polasky, S.; Binder, S. Nutrient enrichment, biodiversity loss, and consequent declines in ecosystem productivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2013, 110, 11911–11916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowler, D.; Bradshaw, B. Farmers’ adoption of conservation agriculture: A review and synthesis of recent research. Food Policy 2007, 32, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittelkow, C.M.; Linquist, B.A.; Lundy, M.E.; Liang, X.; Van Groenigen, K.J.; Lee, J.; Van Gestel, N.; Six, J.; Venterea, R.T.; Van Kessel, C. When does no-till yield more? A global meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2015, 183, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Singh, M.; Begam, A.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Meena, B.L.; Kumar, S. Improvement of growth, yield and soil fertility in wheat through tillage and nutrient management practices. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 5374–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Li, S.; Hu, W.; Wu, J.; Yang, Y. Simulating the effects of conventional tillage versus no-tillage on nitrogen uptake and utilization of winter wheat with RZWQM2 in a 7-year field experiment. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2022, 16, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veresoglou, S.D.; Chen, J.; Du, X.; Fu, Q.; Geng, Q.; Huang, C.; Huang, X.; Hu, N.; Hun, Y.; Li, G.C. No tillage outperforms conventional tillage under arid conditions and following fertilization. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2023, 5, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Luo, J.; Zou, J. Effects of no-till on upland crop yield and soil organic carbon: A global meta-analysis. Plant Soil 2024, 499, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuan, L.; He, P.; Pampolino, M.F.; Johnston, A.M.; Jin, J.; Xu, X.; Zhao, S.; Qiu, S.; Zhou, W. Establishing a scientific basis for fertilizer recommendations for wheat in China: Yield response and agronomic efficiency. Field Crops Res. 2013, 140, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Sun, P.; Waring, B.G. Nitrogen agronomic efficiency under nitrogen fertilization does not change over time in the long term: Evidence from 477 global studies. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 223, 105468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, J.; Gao, F.; Dong, S.; Liu, P.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J. Integrated agronomic practices management improve yield and nitrogen balance in double cropping of winter wheat-summer maize. Field Crops Res. 2018, 221, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, R. System based integrated nutrient management. Soil Use Manag. 2013, 29, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xia, H.; Jiang, C.; Riaz, M.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Fan, X.; Xia, X. 14 year applications of chemical fertilizers and crop straw effects on soil labile organic carbon fractions, enzyme activities and microbial community in rice-wheat rotation of middle China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-P.; Cui, Z.-L.; Vitousek, P.M.; Cassman, K.G.; Matson, P.A.; Bai, J.-S.; Meng, Q.-F.; Hou, P.; Yue, S.-C.; Römheld, V. Integrated soil–crop system management for food security. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2011, 108, 6399–6404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Lu, D.; Zhou, J.; Li, C. Changes in soil microbial community and organic carbon fractions under short-term straw return in a rice–wheat cropping system. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 165, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Liu, L.; Wen, X.; Liao, Y. Responses of soil fungi to 5-year conservation tillage treatments in the drylands of northern China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 101, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Chellemi, D.O.; Martin, K.J.; Graham, J.H.; Rosskopf, E.N. Discriminating the effects of agricultural land management practices on soil fungal communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 1139–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, Q.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Yu, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, T.; Su, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C. Effects of long-term no-tillage with different straw mulching frequencies on soil microbial community and the abundances of two soil-borne pathogens. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 148, 103488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Jia, S.; Zhang, S.; McLaughlin, N.B.; Zhang, X.; Liang, A.; Chen, X.; Wei, S.; Liu, S. Tillage, seasonal and depths effects on soil microbial properties in black soil of northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beare, M.H.; Hu, S.; Coleman, D.C.; Hendrix, P.F. Influences of mycelial fungi on soil aggregation and organic matter storage in conventional and no-tillage soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 1997, 5, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, S.D.; Elliott, E.T.; Paustian, K. Bacterial and fungal abundance and biomass in conventional and no-tillage agroecosystems along two climatic gradients. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, M.S.; Rousk, J. Considering fungal: Bacterial dominance in soils–methods, controls, and ecosystem implications. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Groenigen, K.-J.; Bloem, J.; Bååth, E.; Boeckx, P.; Rousk, J.; Bodé, S.; Forristal, D.; Jones, M.B. Abundance, production and stabilization of microbial biomass under conventional and reduced tillage. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Dai, Z.; Veach, A.M.; Zheng, J.; Xu, J.; Schadt, C.W. Global meta-analyses show that conservation tillage practices promote soil fungal and bacterial biomass. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 293, 106841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ma, K.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Negrete-Yankelevich, S. Effects of no-tillage and biologically-based organic fertilizer on soil arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities in winter wheat field. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 178, 104564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helgason, B.L.; Walley, F.L.; Germida, J.J. Fungal and bacterial abundance in long-term no-till and intensive-till soils of the Northern Great Plains. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardle, D.A. Impacts of disturbance on detritus food webs in agro-ecosystems of contrasting tillage and weed management practices. Adv. Ecol. Res. 1995, 26, 105–185. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Song, D.; Liang, S.; Dang, P.; Qin, X.; Liao, Y.; Siddique, K.H.M. Effect of no-tillage on soil bacterial and fungal community diversity: A meta-analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 204, 104721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Fan, J.; Fu, W.; Niu, X.; Yang, Q.; Hao, M. Changes in soil microbial community and co-occurrence network after long-term no-tillage and mulching in dryland farming. Plant Soil 2024, 495, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liang, L.; Li, H.; Han, W. Dynamics of soil bacteria and fungi communities of dry land for 8 years with soil conservation management. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Tang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Long-term organic fertilization reshapes the communities of bacteria and fungi and enhances the activities of C-and P-cycling enzymes in calcareous alluvial soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 194, 105204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, L.; Li, T.; Dou, Y.; Qiao, J.; Wang, Y.; An, S.; Chang, S.X. Nitrogen fertilization weakens the linkage between soil carbon and microbial diversity: A global meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 6446–6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, B.; Ma, M.; Guan, D.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; Cao, F.; Shen, D. Thirty four years of nitrogen fertilization decreases fungal diversity and alters fungal community composition in black soil in northeast China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 95, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Su, W.; Chen, H.; Barberán, A.; Zhao, H.; Yu, M.; Yu, L.; Brookes, P.C.; Schadt, C.W.; Chang, S.X. Long-term nitrogen fertilization decreases bacterial diversity and favors the growth of Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria in agro-ecosystems across the globe. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 3452–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, D.; Bai, E. Decreasing soil microbial diversity is associated with decreasing microbial biomass under nitrogen addition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Gu, S.; Xin, Y.; Bello, A.; Sun, W.; Xu, X. Compost addition enhanced hyphal growth and sporulation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi without affecting their community composition in the soil. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 312120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahter, T.; Sepp, S.K.; Astover, A.; Helm, A.; Kikas, T.; Liu, S.; Oja, J.; Öpik, M.; Penu, P.; Vasar, M. Landscapes, management practices and their interactions shape soil fungal diversity in arable fields–Evidence from a nationwide farmers’ network. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 168, 108652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morugán-Coronado, A.; Pérez-Rodríguez, P.; Insolia, E.; Soto-Gómez, D.; Fernández-Calvino, D.; Zornoza, R. The impact of crop diversification, tillage and fertilization type on soil total microbial, fungal and bacterial abundance: A worldwide meta-analysis of agricultural sites. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 329, 107867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Nie, Y.; Butterly, C.R.; Wang, L.; Chen, Q.; Tian, W.; Song, B.; Xi, Y.; Wang, Y. Fertilization alters microbial community composition and functional patterns by changing the chemical nature of soil organic carbon: A field study in a Halosol. Geoderma 2017, 292, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gougoulias, C.; Clark, J.M.; Shaw, L.J. The role of soil microbes in the global carbon cycle: Tracking the below-ground microbial processing of plant-derived carbon for manipulating carbon dynamics in agricultural systems. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 2362–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Dsouza, M.; Gilbert, J.A.; Guo, X.; Wang, D.; Guo, Z.; Ni, Y.; Chu, H. Fungal community composition in soils subjected to long-term chemical fertilization is most influenced by the type of organic matter. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 5137–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, Z. Assessing bacterial diversity in soil: A brief review. J. Soils Sediments 2008, 8, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Wu, J. Short-term effects of returning granulated straw on soil microbial community and organic carbon fractions in dryland farming. J. Microbiol. 2020, 58, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, C.; Yue, J.; Yao, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, T. Effects of different soil conservation tillage approaches on soil nutrients, water use and wheat-maize yield in rainfed dry-land regions of north China. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 81, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.; Okubo, A.; Sugiyama, S.; Mayland, H.F. Physical, chemical and microbiological properties of an Andisol as related to land use and tillage practice. Soil Tillage Res. 2008, 101, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyiwa, T.; Dikinya, O. Impact of tillage types on compaction and physical properties of soils of Sebele farms in Botswana. Plant Soil Environ. 2014, 33, 124–132. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Bonkowski, M.; Shen, Y.; Griffiths, B.S.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, B. Root ethylene mediates rhizosphere microbial community reconstruction when chemically detecting cyanide produced by neighbouring plants. Microbiome 2020, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.; Liu, E.; Yan, C.; Tian, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y. Impact of no tillage vs. conventional tillage on the soil bacterial community structure in a winter wheat cropping succession in northern China. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2017, 80, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazcano, C.; Gómez-Brandón, M.; Revilla, P.; Domínguez, J. Short-term effects of organic and inorganic fertilizers on soil microbial community structure and function: A field study with sweet corn. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2013, 49, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Guo, Q.; Yu, Z.; Yang, T.; Zhang, H. Long-term no-tillage and different residue amounts alter soil microbial community composition and increase the risk of maize root rot in northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 196, 104452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, M.; He, J. Long-term fertilization regimes affect bacterial community structure and diversity of an agricultural soil in northern China. J. Soils Sediments 2008, 8, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Wu, S.; Guan, Y.; Zhai, C.; Zhang, Z.; Bello, A.; Guo, X.; Yang, W. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community was affected by tillage practices rather than residue management in black soil of northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 198, 104552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma-Poudyal, D.; Schlatter, D.; Yin, C.; Hulbert, S.; Paulitz, T. Long-term no-till: A major driver of fungal communities in dryland wheat cropping systems. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, H.; Mao, Z.; Bao, X.; He, H.; Zhang, X.; Liang, C. Fungi determine increased soil organic carbon more than bacteria through their necromass inputs in conservation tillage croplands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 167, 108587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Säle, V.; Aguilera, P.; Laczko, E.; Mäder, P.; Berner, A.; Zihlmann, U.; van der Heijden, M.G.A.; Oehl, F. Impact of conservation tillage and organic farming on the diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 84, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Tu, C.; Hoyt, G.D.; DeForest, J.L.; Hu, S. Long-term no-tillage and organic input management enhanced the diversity and stability of soil microbial community. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Xu, C.; Kuzyakov, Y. Divergence in fungal abundance and community structure between soils under long-term mineral and organic fertilization. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 196, 104491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Hou, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, J.; Wei, G.; Lin, Y. Soil microbial diversity during 30 years of grassland restoration on the Loess Plateau, China: Tight linkages with plant diversity. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1172–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Berbel, N.; Ortega, R.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Solé-Benet, A.; Miralles, I. Long-term effects of two organic amendments on bacterial communities of calcareous mediterranean soils degraded by mining. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 271, 110920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, D.; Li, G.; Xiu, W. Variation of soil bacterial and fungal communities from fluvo-aquic soil under chemical fertilizer reduction combined with organic materials in north China Plain. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebber, D.P.; Richards, V.R. A meta-analysis of the effect of organic and mineral fertilizers on soil microbial diversity. Applied Soil Ecology 2022, 175, 104450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, M.; Yin, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Qin, W. Effect of organic material addition on active soil organic carbon and microbial diversity: A meta-analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 241, 106128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xin, X.; Zhu, A.; Yang, W.; Zhang, J.; Ding, S.; Mu, L.; Shao, L. Linking macroaggregation to soil microbial community and organic carbon accumulation under different tillage and residue managements. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 178, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shu, A.; Song, W.; Shi, W.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, G.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, S. Long-term organic fertilizer substitution increases rice yield by improving soil properties and regulating soil bacteria. Geoderma 2021, 404, 115287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liang, A.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; McLaughlin, N.B.; Gao, Y.; Jia, S. The impact of cropping system, tillage and season on shaping soil fungal community in a long-term field trial. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2021, 102, 103253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degrune, F.; Dufrêne, M.; Colinet, G.; Massart, S.; Taminiau, B.; Bodson, B.; Hiel, M.P.; Daube, G.; Nezer, C.; Vandenbol, M. A novel sub-phylum method discriminates better the impact of crop management on soil microbial community. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, W.; Yang, X.; Li, W.; Xia, Q.; Li, J.; Gao, Z.; Yang, Z. Rhizosphere soil properties, microbial community, and enzyme activities: Short-term responses to partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with organic manure. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs-Weber, E.; Aigle, A.; Prosser, J.I.; Gubry-Rangin, C. Oxygen preference of deeply-rooted mesophilic thaumarchaeota in forest soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 107848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Niu, W.; Cao, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z. Growth response of greenhouse-produced muskmelon and tomato to sub-surface drip irrigation and soil aeration management factors. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhen, W.; Li, H. Allelopathy of decomposed maize straw products on three soil-born diseases of wheat and the analysis by GC-MS. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flower, K.C.; Hüberli, D.; Collins, S.J.; Thomas, G.; Ward, P.R.; Cordingley, N. Progression of plant-parasitic nematodes and foliar and root diseases under no-tillage with different crop rotations. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 191, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, X.; Li, G.; Qin, P. Interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and phosphate-solubilizing fungus (Mortierella sp.) and their effects on Kostelelzkya virginica growth and enzyme activities of rhizosphere and bulk soils at different salinities. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2011, 47, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.Y.; Zienkiewicz, K.; Vande Pol, N.; Ostrom, N.E.; Benning, C.; Bonito, G.M. Algal-fungal symbiosis leads to photosynthetic mycelium. Elife 2019, 8, e47815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, T.; Wen, X.; Liu, Y.; Han, J.; Liao, Y.; DeBruyn, J.M. Fungal communities in rhizosphere soil under conservation tillage shift in response to plant growth. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannula, S.E.; Boschker, H.T.S.; de Boer, W.; Van Veen, J.A. 13C pulse-labeling assessment of the community structure of active fungi in the rhizosphere of a genetically starch-modified potato (Solanum tuberosum) cultivar and its parental isoline. New Phytol. 2012, 194, 784–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfante, P.; Venice, F.; Lanfranco, L. The mycobiota: Fungi take their place between plants and bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2019, 49, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodenhausen, N.; Somerville, V.; Desirò, A.; Walser, J.C.; Borghi, L.; van der Heijden, M.G.A.; Schlaeppi, K. Species-specific root microbiota dynamics in response to plant-available phosphorus. bioRxiv 2018, 400119. [Google Scholar]
- Baldrian, P. Wood-inhabiting ligninolytic basidiomycetes in soils: Ecology and constraints for applicability in bioremediation. Fungal Ecol. 2008, 1, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollister, E.B.; Hu, P.; Wang, A.S.; Hons, F.M.; Gentry, T.J. Differential impacts of brassicaceous and nonbrassicaceous oilseed meals on soil bacterial and fungal communities. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 83, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Andom, O.; Li, Y.; Cheng, C.; Deng, H.; Sun, L.; Li, Z. Responses of grape yield and quality, soil physicochemical and microbial properties to different planting years. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2024, 120, 103587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazan, K.; Gardiner, D.M. Fusarium crown rot caused by Fusarium pseudograminearum in cereal crops: Recent progress and future prospects. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 1547–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, L. Fusarium species associated with diseases of major tropical fruit crops. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, Z.A.; Shoaib, A.; Khan, K.A. Crosstalk of Zn in combination with other fertilizers underpins interactive effects and induces resistance in tomato plant against early blight disease. Plant Pathol. J. 2019, 35, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Berardis, S.; De Paola, E.L.; Montevecchi, G.; Garbini, D.; Masino, F.; Antonelli, A.; Melucci, D. Determination of four Alternaria alternata mycotoxins by QuEChERS approach coupled with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in tomato-based and fruit-based products. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; He, P.; Jia, L.; Ding, W.; Ullah, S.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Liu, M.; Zhou, W. Improving nitrogen use efficiency and reducing environmental cost with long-term nutrient expert management in a summer maize-winter wheat rotation system. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 213, 105117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
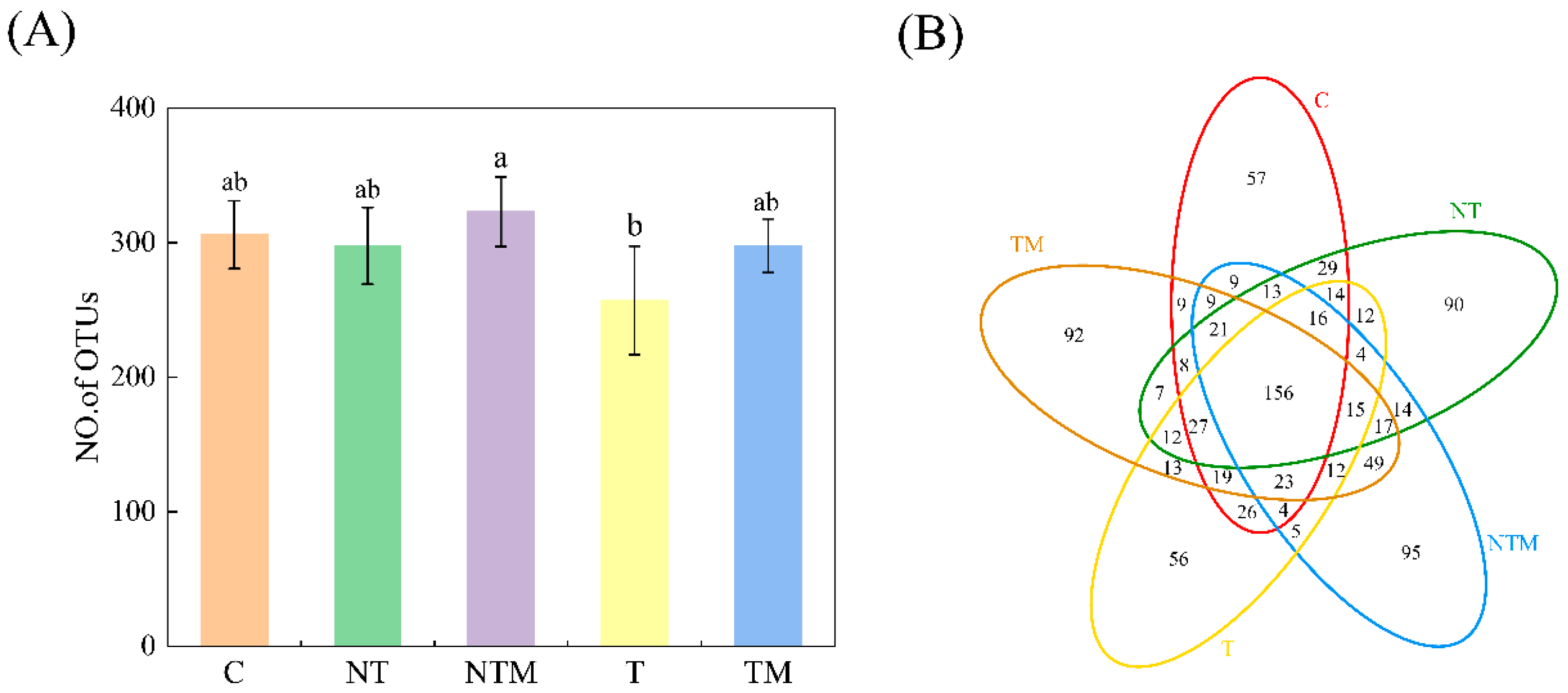
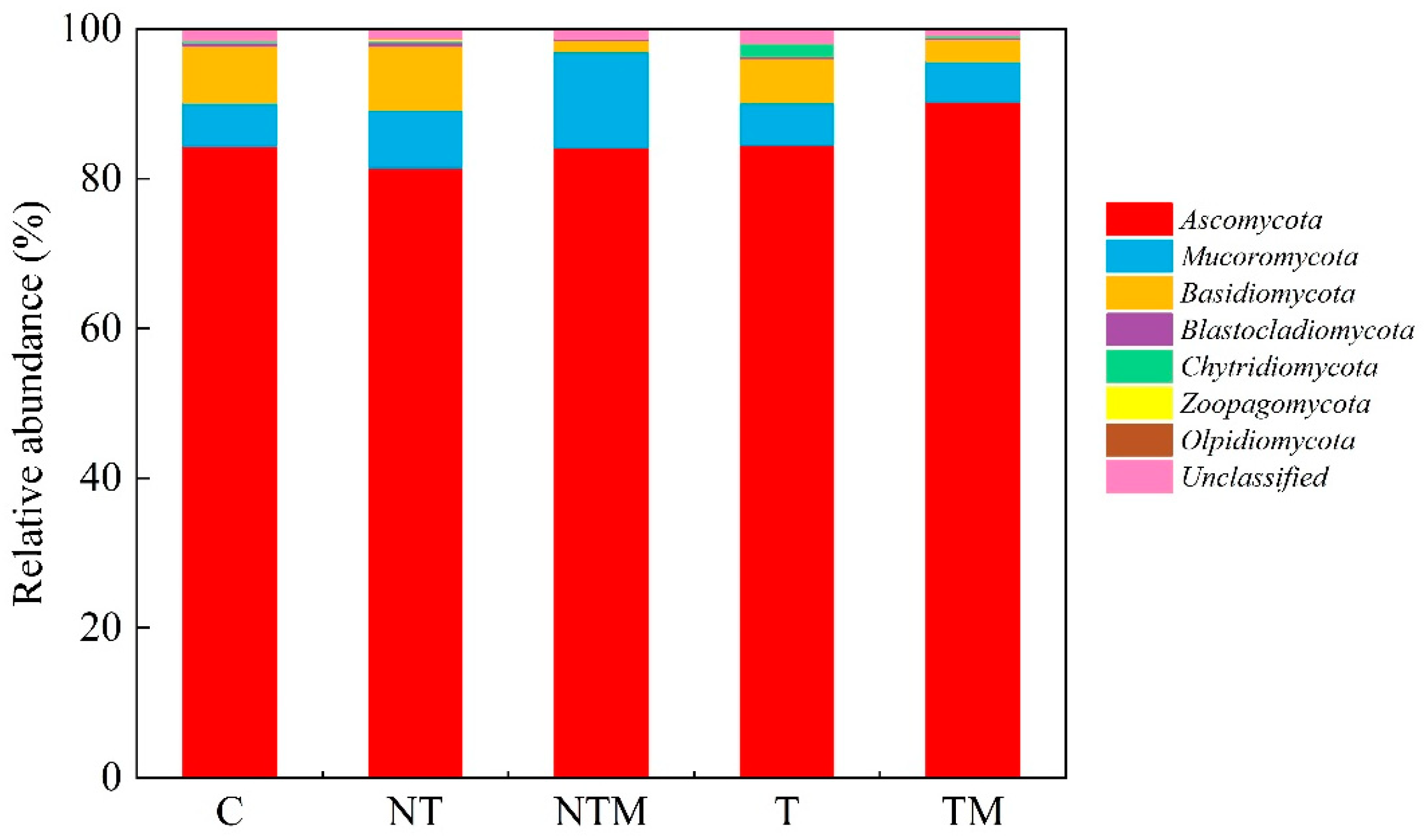
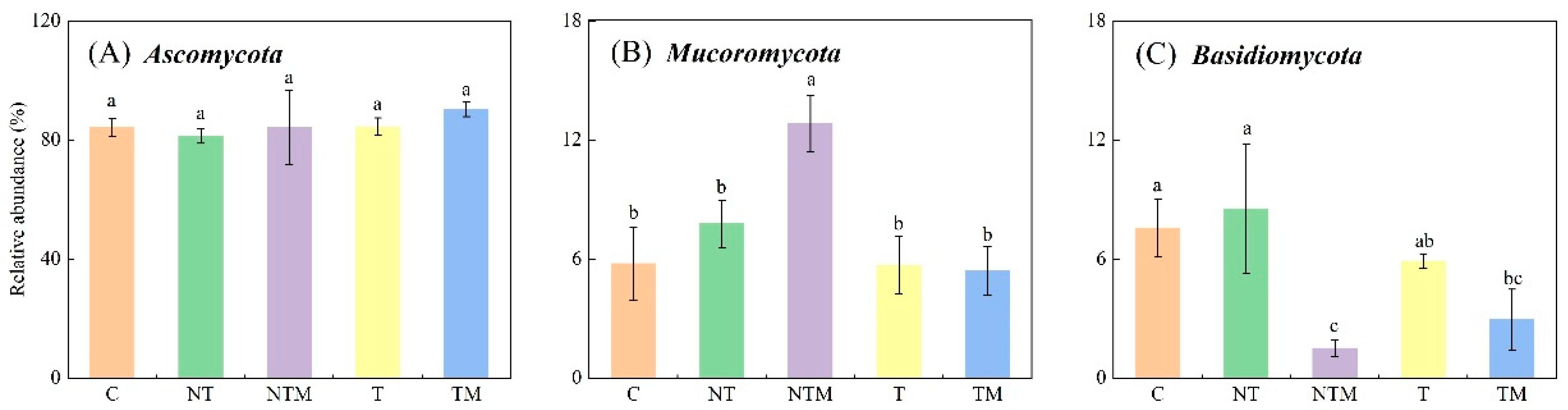
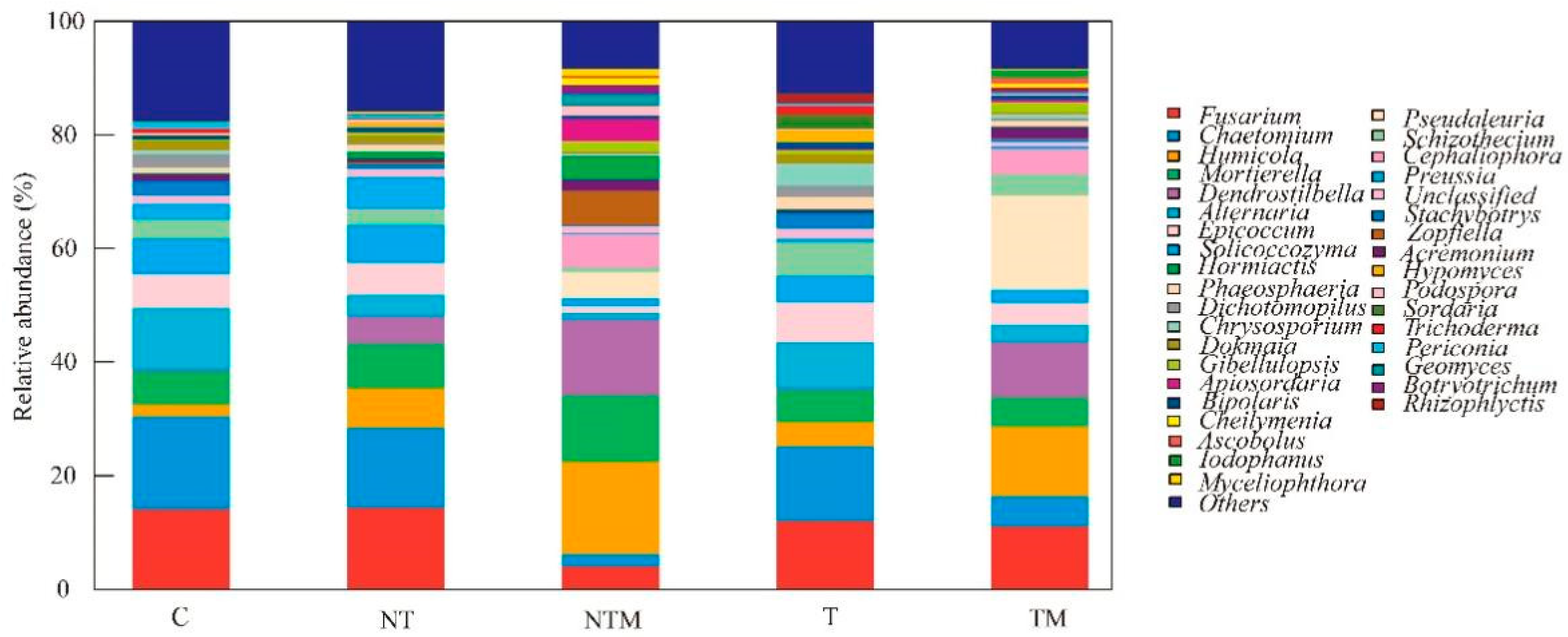

| Treatments | Grain Yield (kg/ha) | AEN (kg/kg) | PEPN (kg/kg) | Apparent REN (%) | Accumulated REN (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 1767.00 ± 55.90 c | - | - | - | - |
| NT | 2931.17 ± 564.76 b | 6.47 ± 3.12 b | 16.28 ±3.14 b | 23.69 ± 9.43 b | 46.85 ±10.22 bc |
| NTM | 3974.78 ± 165.60 a | 12.27 ± 1.13 a | 22.08 ± 0.92 a | 45.90 ± 3.52 a | 64.17 ± 2.39 a |
| T | 2504.65 ± 118.67 b | 4.10 ± 0.82 b | 13.91 ± 0.66 b | 15.27 ± 2.35 b | 37.29 ± 4.22 c |
| TM | 2985.62 ± 222.34 b | 6.77 ±1.06 b | 16.59 ± 1.24 b | 25.44 ± 3.33 b | 49.76 ± 2.86 b |
| Treatment | OM (g/kg) | TN (g/kg) | TP (g/kg) | AN (mg/kg) | AP (mg/kg) | AK (mg/kg) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 18.15 ± 1.37 c | 1.59 ± 0.16 a | 1.50 ± 0.06 d | 70.00 ± 7.00 c | 15.04 ± 1.67 d | 259.27 ± 2.79 c | 8.19 ± 0.02 a |
| NT | 22.64 ± 0.78 b | 0.93 ± 0.16 c | 2.10 ± 0.13 c | 88.67 ± 10.69 bc | 40.03 ± 5.36 c | 228.55 ± 1.34 e | 8.07 ± 0.02 c |
| NTM | 30.98 ± 1.45 a | 1.73 ± 0.09 a | 4.68 ± 0.48 a | 133.00 ± 14.00 a | 130.69 ± 18.33 a | 490.05 ± 7.87 a | 8.00 ± 0.01 d |
| T | 21.29 ± 1.02 b | 1.59 ± 0.16 a | 1.66 ± 0.18 d | 105.00 ± 14.00 b | 36.71 ± 0.77 c | 247.75 ± 5.42 d | 8.12 ± 0.01 b |
| TM | 22.94 ± 0.18 b | 1.31 ± 0.16 b | 3.00 ± 0.17 b | 128.33 ± 10.69 a | 115.66 ± 2.13 b | 335.08 ± 4.31 b | 8.06 ± 0.02 c |
| ANOVA | |||||||
| Tillage | 58.464 ** | 8.514 * | 157.842 ** | 12.195 ** | 142.463 ** | 1404.910 ** | 185.606 ** |
| Fertilizer | 99.431 ** | 14.080 ** | 77.378 ** | 30.071 ** | 171.685 ** | 1259.080 ** | 75.884 ** |
| Tillage × Fertilizer | 29.786 ** | 21.226 ** | 70.929 ** | 0.488 | 47.916 ** | 2339.443 ** | 0.152 |
| Treatment | Chaol Index | Shannon Index | Simpson Index | ACE Index | Evenness Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 330.54 ± 15.79 ab | 5.00 ± 0.29 c | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 351.43 ± 23.28 a | 0.60 ± 0.03 b |
| NT | 342.13 ± 21.36 ab | 5.89 ± 0.31 ab | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | 337.90 ± 39.75 a | 0.72 ± 0.03 a |
| NTM | 354.20 ± 19.55 a | 5.98 ± 0.09 a | 0.08 ± 0.01 a | 347.31 ± 30.81 a | 0.71 ± 0.02 a |
| T | 291.69 ± 41.53 b | 5.81 ± 0.18 ab | 0.04 ± 0.01 a | 294.40 ± 39.54 a | 0.72 ± 0.04 a |
| TM | 352.52 ± 34.93 a | 5.20 ± 0.67 bc | 0.09 ± 0.06 a | 327.90 ± 21.12 a | 0.63 ± 0.09 ab |
| ANOVA | |||||
| Tillage | 5.106 * | 6.399 * | 1.070 | 1.145 | 3.848 |
| Fertilizer | 2.459 | 2.570 | 3.488 | 0.861 | 2.801 |
| Tillage × Fertilizer | 2.412 | 3.031 | 2.204 | 3.258 | 4.876 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, M.; Yang, H.; Yang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Fan, Q.; Yang, N.; Wang, K.; Zhang, J.; et al. Different Impacts of Long-Term Tillage and Manure on Yield and N Use Efficiency, Soil Fertility, and Fungal Community in Rainfed Wheat in Loess Plateau. Plants 2024, 13, 3477. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13243477
Chen M, Yang H, Yang Q, Li Y, Wang H, Wang J, Fan Q, Yang N, Wang K, Zhang J, et al. Different Impacts of Long-Term Tillage and Manure on Yield and N Use Efficiency, Soil Fertility, and Fungal Community in Rainfed Wheat in Loess Plateau. Plants. 2024; 13(24):3477. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13243477
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Mengni, Hailiang Yang, Qingshan Yang, Yongshan Li, Hui Wang, Juanling Wang, Qiaolan Fan, Na Yang, Ke Wang, Jiancheng Zhang, and et al. 2024. "Different Impacts of Long-Term Tillage and Manure on Yield and N Use Efficiency, Soil Fertility, and Fungal Community in Rainfed Wheat in Loess Plateau" Plants 13, no. 24: 3477. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13243477
APA StyleChen, M., Yang, H., Yang, Q., Li, Y., Wang, H., Wang, J., Fan, Q., Yang, N., Wang, K., Zhang, J., Yuan, J., Dong, P., & Wang, L. (2024). Different Impacts of Long-Term Tillage and Manure on Yield and N Use Efficiency, Soil Fertility, and Fungal Community in Rainfed Wheat in Loess Plateau. Plants, 13(24), 3477. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13243477





