Functional Identification of Malus halliana MhbZIP23 Gene Demonstrates That It Enhances Saline–Alkali Stress Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Treatments
2.2. Saline–Alkali Stress Treatment of M. halliana Seedlings
2.3. Bioinformatic Analysis of bZIP23 Gene
2.4. Cloning and Expression Vector Construction of bZIP23 Gene
2.5. Treatment and Screening of Genetically Modified Arabidopsis
2.6. Transgenic Arabidopsis under Saline–Alkali Stress and Determination of Related Indicators
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the MhbZIP23 Gene
3.2. Protein Sequence Analysis of MhbZIP23 Gene
3.3. Phylogenetic Tree Evolutionary Analysis of the Apple MhbZIP23 Protein
3.4. Analysis of Cis-Acting Elements of MhbZIP23 Promoter
3.5. Response of MhbZIP23 to Saline–Alkali Stress in M. halliana Seedlings
3.6. Cloning of MhbZIP23 Gene
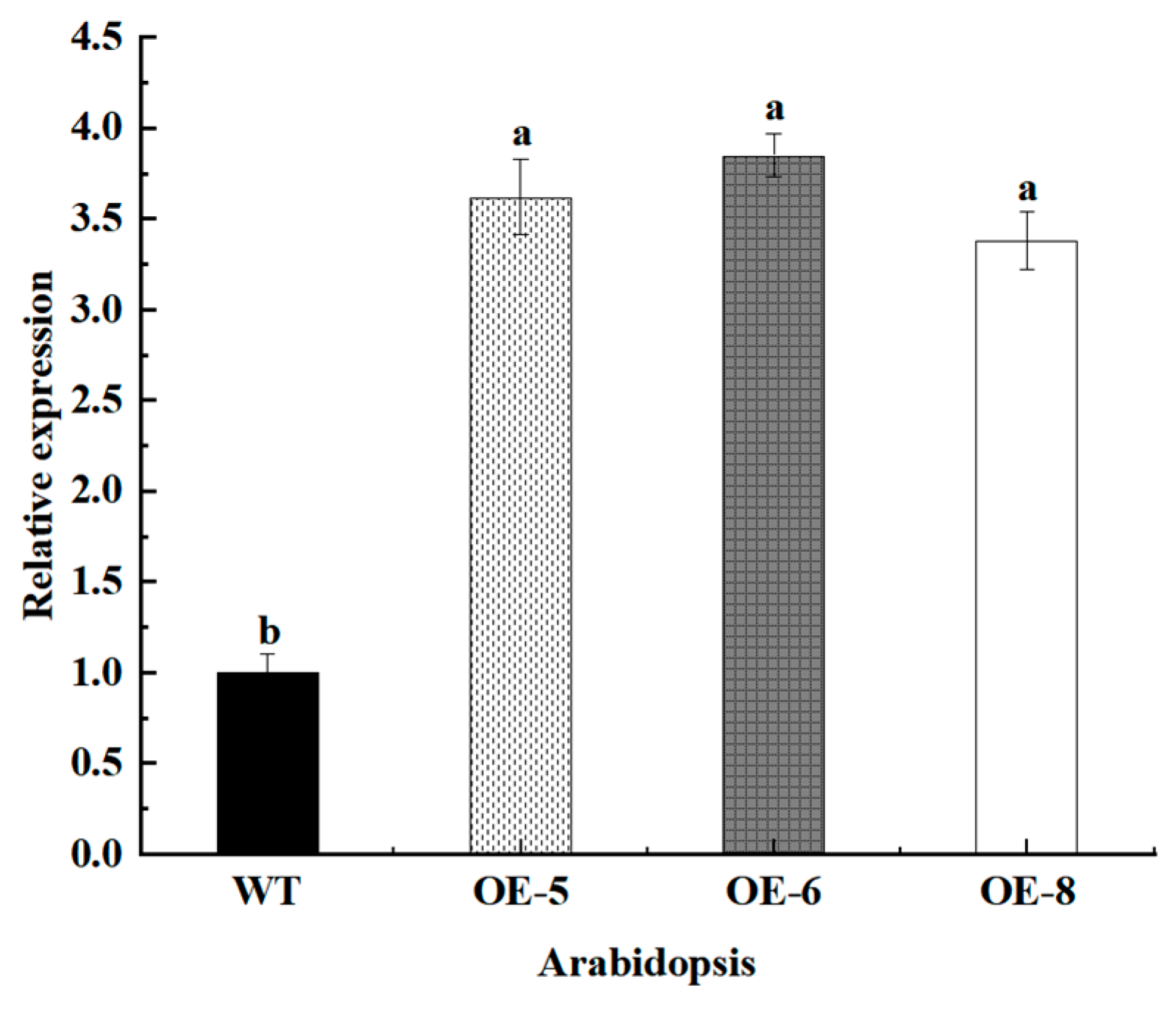
3.7. Screening and Identification of Transgenic Arabidopsis
3.8. Morphological Characteristics and Physiological Indicators of MhbZIP23 Transgenic Arabidopsis under Saline–Alkali Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schofield, R.V.; Kirkby, M.J. Application of salinization indicators and initial development of potential global soil salinization scenario under climatic change. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003, 17, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Min, W.; Shi, Y.; Tian, L.; Li, P.; Ma, T.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, C. Exogenous melatonin alleviates alkaline stress by removing reactive oxygen species and promoting antioxidant defence in rice seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 849553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, T.J.; Colmer, T.D. Salinity tolerance in halophytes. New Phytol. 2008, 1, 945–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, T.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.Q.; Chan, Z. Physiological and metabolomic responses of bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon) to alkali stress. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 171, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.; Zhai, H.; He, S.; Zhao, N.; Liu, Q. A novel sweetpotato bZIP transcription factor gene, IbbZIP1, is involved in salt and drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 2019, 38, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Huang, S.S.C.; Wise, A. A transcription factor hierarchy defines an environmental stress response network. Science 2016, 354, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.K. Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2002, 53, 247–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Guo, C.; Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Wang, D.; Xu, L.; Li, X.; Guo, Y. Identification and analysis of bZIP family genes in potato and their potential roles in stress responses. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 637343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolis, I.K.; McKay, D.J.; Mantouvalou, E.; Lomvardas, S.; Merika, M.; Thanos, D. Transcription factors mediate long-range enhancer–promoter interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20222–20227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tang, X.; Zhang, N.; Li, S.; Si, H. Role of bZIP transcription factors in plant salt stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caregnato, F.F.; Koller, C.E.; MacFarlane, G.R.; Moreira, J.C. The glutathione antioxidant system as a biomarker suite for the assessment of heavy metal exposure and effect in the grey mangrove, Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Xia, C.; Zhao, G.; Liu, J.; Jia, J.; Kong, X. A novel wheat bZIP transcription factor, TabZIP60, confers multiple abiotic stress tolerances in transgenic Arabidopsis. Physiol. Plant. 2015, 153, 538–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. ER-anchored transcription factors bZIP17 and bZIP28 regulate root elongation. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 2221–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.; Tang, N.; Du, H.; Ye, H.; Xiong, L. Characterization of OsbZIP23 as a key player of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family for conferring abscisic acid sensitivity and salinity and drought tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 1938–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.I.; Hong, J.H.; Ha, J.O.; Kang, J.Y.; Kim, S.Y. ABFs, a family of ABA-responsive element binding factors. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, H.; Baek, W.; Lim, C.W.; Lee, S.C. Post-translational modifications of bZIP transcription factors in abscisic acid signaling and drought responses. Curr. Genom. 2021, 22, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assunção, A.G.; Herrero, E.; Lin, Y.F.; Huettel, B.; Talukdar, S.; Smaczniak, C.; Immink, R.G.; Van Eldik, M.; Fiers, M.; Schat, H.; et al. Arabidopsis thaliana transcription factors bZIP19 and bZIP23 regulate the adaptation to zinc deficiency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 10296–10301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kwon, S.I.; Sheob Shin, I.; Cho, K.H.; Heo, S.; Kim, H.R. The Apple Rootstock Transgenic M.26 (Malus pumila) with Enhanced Rooting Ability. Korean J. Breed. Sci. 2009, 41, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.F.; Wu, Y.X.; Hu, Y.; Jia, X.M.; Zhao, T.; Cheng, L.; Wang, Y.X. Tolerance of two apple rootstocks to short-term salt stress: Focus on chlorophyll degradation, photosynthesis, hormone and leaf ultrastructures. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2019, 41, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Zhou, H. Plant salt response: Perception, signaling, and tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1053699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.X.; Wang, W.X.; Li, S.T.; Li, J.L.; Wang, Y.X. Functional identification of CCR1 gene in apple (Malus halliana) demonstrates that it enhances saline-alkali stress tolerance. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2024, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.X.; Wang, S.C.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Y.X. Identification of ANS from Malus halliana reveal flavonoid metabolic pathway involved in response to saline–alkali stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 99, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhu, Y.F.; Guo, A.X.; Jia, X.M.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, T.; Wang, Y.X. Transcriptome analysis in Malus halliana roots in response to iron deficiency reveals insight into sugar regulation. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2018, 293, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Du, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y. Functional identification of ZDS gene in apple (Malus halliana) and demonstration of it’s role in improving saline–alkali stress tolerance. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2023, 29, 799–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, B.; Zhang, S.; Yao, J.; Rahman, M.U.; Hanif, M.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X. Genomic organization of the B3-domain transcription factor family in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) and expression during seed development in seedless and seeded cultivars. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; et al. CDD/SPARCLE: The conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D265–D268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cheng, J.; Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Xian, X.; Li, C.; Wang, Y. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of MhHEC2-like genes in Malus halliana reveals it enhances Fe (iron) deficiency tolerance. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2022, 22, 1283–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.G.; Sun, M.H.; Sun, C.H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Zhao, J.; Hao, Y.J. Conserved vacuolar H+-ATPase subunit B1 improves salt stress tolerance in apple calli and tomato plants. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 197, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Zhao, T.; Wu, Y.X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zhang, D.; Wang, S.C.; Wang, Y.X. Identification of AP2/ERF genes in apple (Malus × domestica) and demonstration that MdERF017 enhances iron deficiency tolerance. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. PCTOC 2020, 143, 465–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira Júnior, D.C.; Gaion, L.A.; Sousa Júnior, G.S.; Santos, D.M.; Carvalho, R.F. Drought-induced proline synthesis depends on root-to-shoot communication mediated by light perception. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2018, 40, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajji, M.; Kinet, J.M.; Lutts, S. The use of the electrolyte leakage method for assessing cell membrane stability as a water stress tolerance test in durum wheat. Plant Growth Regul. 2002, 36, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Lv, L.; Meng, C.; Zhou, C.; Fu, J.; Shen, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y. Genome-wide analysis of abscisic acid biosynthesis, catabolism, and signaling in Sorghum bicolor under saline-alkali stress. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sornaraj, P.; Luang, S.; Lopato, S.; Hrmova, M. Basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors involved in abiotic stresses: A molecular model of a wheat bZIP factor and implications of its structure in function. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2016, 1860, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Dossa, K.; Yu, J.; Li, D.; Liu, A.; Mmadi, M.A.; Zhang, X.; You, J. Identification and characterization of the bZIP transcription factor family and its expression in response to abiotic stresses in sesame. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jindrich, K.; Degnan, B.M. The diversification of the basic leucine zipper family in eukaryotes correlates with the evolution of multicellularity. BMC Evol. Biol. 2016, 16, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakoby, M.; Weisshaar, B.; Dröge-Laser, W.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J.; Tiedemann, J.; Kroj, T.; Parcy, F. bZIP transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Meng, X.; Cai, J.; Li, G.; Dong, T.; Li, Z. Basic leucine zipper transcription factor SlbZIP1 mediates salt and drought stress tolerance in tomato. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Fujita, Y.; Maruyama, K.; Mogami, J.; Todaka, D.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.A. Four A rabidopsis AREB/ABF transcription factors function predominantly in gene expression downstream of SnRK2 kinases in abscisic acid signalling in response to osmotic stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Kang, J.Y.; Park, H.J.; Kim, M.D.; Bae, M.S.; Choi, H.I.; Kim, S.Y. DREB2C interacts with ABF2, a bZIP protein regulating abscisic acid-responsive gene expression, and its overexpression affects abscisic acid sensitivity. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, A.; Kirchler, T.; Fillinger, S.; Wanke, F.; Stadelhofer, B.; Stahl, M.; Chaban, C. Targeted manipulation of bZIP53 DNA-binding properties influences Arabidopsis metabolism and growth. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 5659–5671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tak, H.; Mhatre, M. Cloning and molecular characterization of a putative bZIP transcription factor VvbZIP23 from Vitis vinifera. Protoplasma 2013, 250, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Guo, R.; Guo, C.; Hou, H.; Wang, X.; Gao, H. Evolutionary and expression analyses of the apple basic leucine zipper transcription factor family. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, W.; Tang, N.; Yang, J.; Peng, L.; Ma, S.; Xu, Y.; Li, G.; Xiong, L. Feedback regulation of ABA signaling and biosynthesis by a bZIP transcription factor targets drought-resistance-related genes. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 2810–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Jeong, J.S.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Do Choi, Y.; Kim, J.K. OsbZIP23 and OsbZIP45, members of the rice basic leucine zipper transcription factor family, are involved in drought tolerance. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2015, 9, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dröge-Laser, W.; Snoek, B.L.; Snel, B.; Weiste, C. The Arabidopsis bZIP transcription factor family—An update. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 45, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, D.; Sofkova, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y. Genome-wide analysis of the bZIP gene lineage in apple and functional analysis of MhABF in Malus halliana. Planta 2021, 254, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M. Phylogenetic analysis in molecular evolutionary genetics. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1996, 30, 371–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Cho, J.I.; Han, M.; Ahn, C.H.; Jeon, J.S.; An, G.; Park, P.B. The ABRE-binding bZIP transcription factor OsABF2 is a positive regulator of abiotic stress and ABA signaling in rice. J. Plant Physiol. 2010, 167, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, L.; Pedrotti, L.; Weiste, C.; Fekete, A.; Schierstaedt, J.; Göttler, J.; Kempa, S.; Krischke, M.; Dietrich, K.; Mueller, M.J.; et al. Crosstalk between two bZIP signaling pathways orchestrates salt-induced metabolic reprogramming in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 2244–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, B. Lack of K-dependent oxidative stress in cotton roots following coronatine-induced ROS accumulation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, B.; Zhao, W.; An, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Song, L.; Guo, C. Overexpression of an alfalfa glutathione S-transferase gene improved the saline-alkali tolerance of transgenic tobacco. Biol. Open 2019, 8, bio043505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, K. Production and scavenging of reactive oxygen species in chloroplasts and their functions. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperdouli, I.; Moustakas, M. Interaction of proline, sugars, and anthocyanins during photosynthetic acclimation of Arabidopsis thaliana to drought stress. J. Plant Physiol. 2012, 169, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Hou, X.; Liang, X. Response mechanisms of plants under saline-alkali stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 667458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.Q.; Wang, W.J.; Zhu, H.; Shi, X.C.; Liu, X.L.; Zu, Y.G. Effects of salt-alkali stress on osmoregulation substance and active oxygen metabolism of Qingshan poplar (Populus pseudo-cathayana x P. deltoides). Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao = J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 20, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Han, L.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Nie, J. Dynamic degradation of penconazole and its effect on antioxidant enzyme activity and malondialdehyde content in apple fruit. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 300, 111053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Wang, J.; Xu, D.; Tao, S.; Chong, S.; Yan, D.; Li, Z.; Yuan, H.; Zheng, B. Melatonin regulates the functional components of photosynthesis, antioxidant system, gene expression, and metabolic pathways to induce drought resistance in grafted Carya cathayensis plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wu, C.; Luo, C.; Wei, M.; Qu, S.; Wang, S. Overexpression of MdCPK1a gene, a calcium dependent protein kinase in apple, increase tobacco cold tolerance via scavenging ROS accumulation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Chen, J.; Tao, L.; An, Y.; Cai, H.; Guo, C. Overexpression of the alfalfa WRKY11 gene enhances salt tolerance in soybean. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| MhbZIP23-F | ATGGACGACCAGGAGGTGT |
| MhbZIP23-R | TCAGTTTGCTGCTGCGGC |
| TYCZ-bZIP23-SF | CATATGCCCGTCGACCCCGGGATGGACGACCAGGAGGTGT |
| TYCZ-bZIP23-SR | TCAGAATTCGGATCCGGTACCTCAGTTTGCTGCTGCGGC |
| MhbZIP23-GFP-F | GGACAGGGTACCCGGGGATCCATGGACGACCAGGAGGTGT |
| MhbZIP23-GFP-R | CACCATGGTACTAGTGTCGACGTTTGCTGCTGCGGCACG |
| Gene ID | Gene Name | Size/aa | MW/KD | pI | Aliphatic Index | Instability Index | Hydrophilicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD05G1121500 | MhbZIP23 | 263 | 28.48 | 6.18 | 61.98 | 35.77 | −0.617 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Li, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y. Functional Identification of Malus halliana MhbZIP23 Gene Demonstrates That It Enhances Saline–Alkali Stress Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants 2024, 13, 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13131803
Liu W, Li P, Wang X, Zhang Z, Wang Y. Functional Identification of Malus halliana MhbZIP23 Gene Demonstrates That It Enhances Saline–Alkali Stress Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants. 2024; 13(13):1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13131803
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wenqing, Peng Li, Xiu Wang, Zhongxing Zhang, and Yanxiu Wang. 2024. "Functional Identification of Malus halliana MhbZIP23 Gene Demonstrates That It Enhances Saline–Alkali Stress Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana" Plants 13, no. 13: 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13131803
APA StyleLiu, W., Li, P., Wang, X., Zhang, Z., & Wang, Y. (2024). Functional Identification of Malus halliana MhbZIP23 Gene Demonstrates That It Enhances Saline–Alkali Stress Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants, 13(13), 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13131803





