Fingerprinting of Plum (Prunus domestica) Genotypes in Lithuania Using SSR Markers
Abstract
1. Introduction
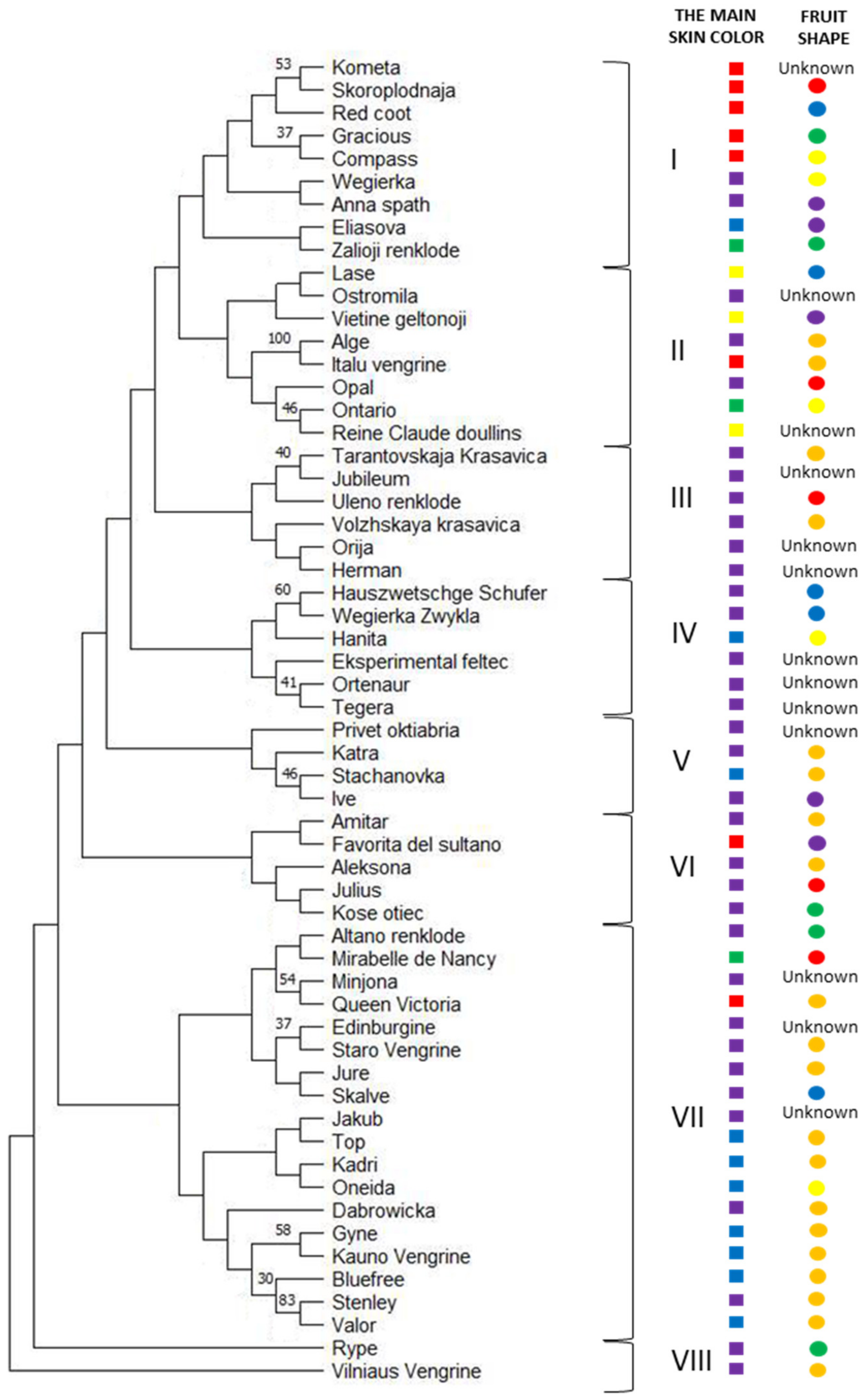
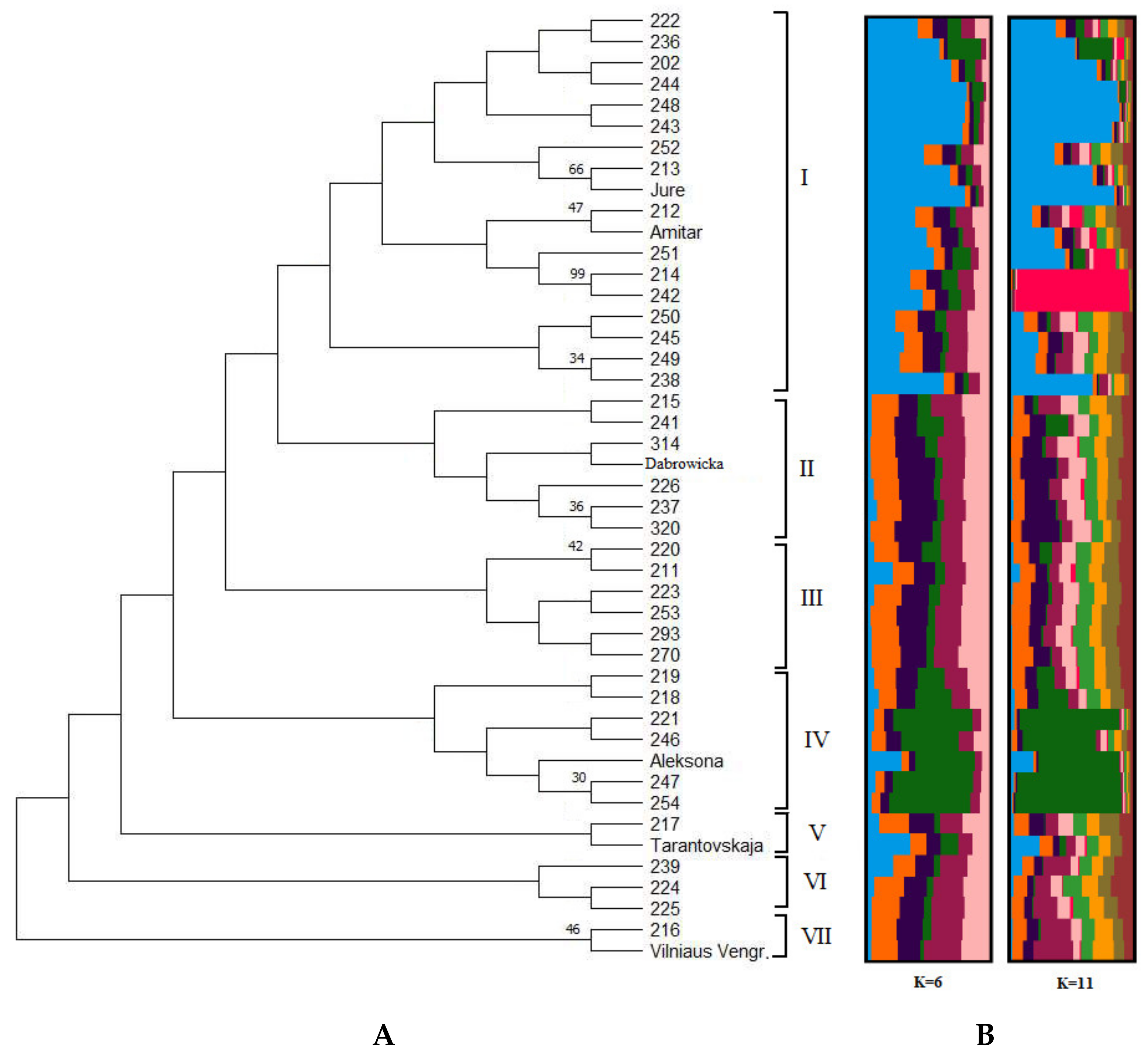
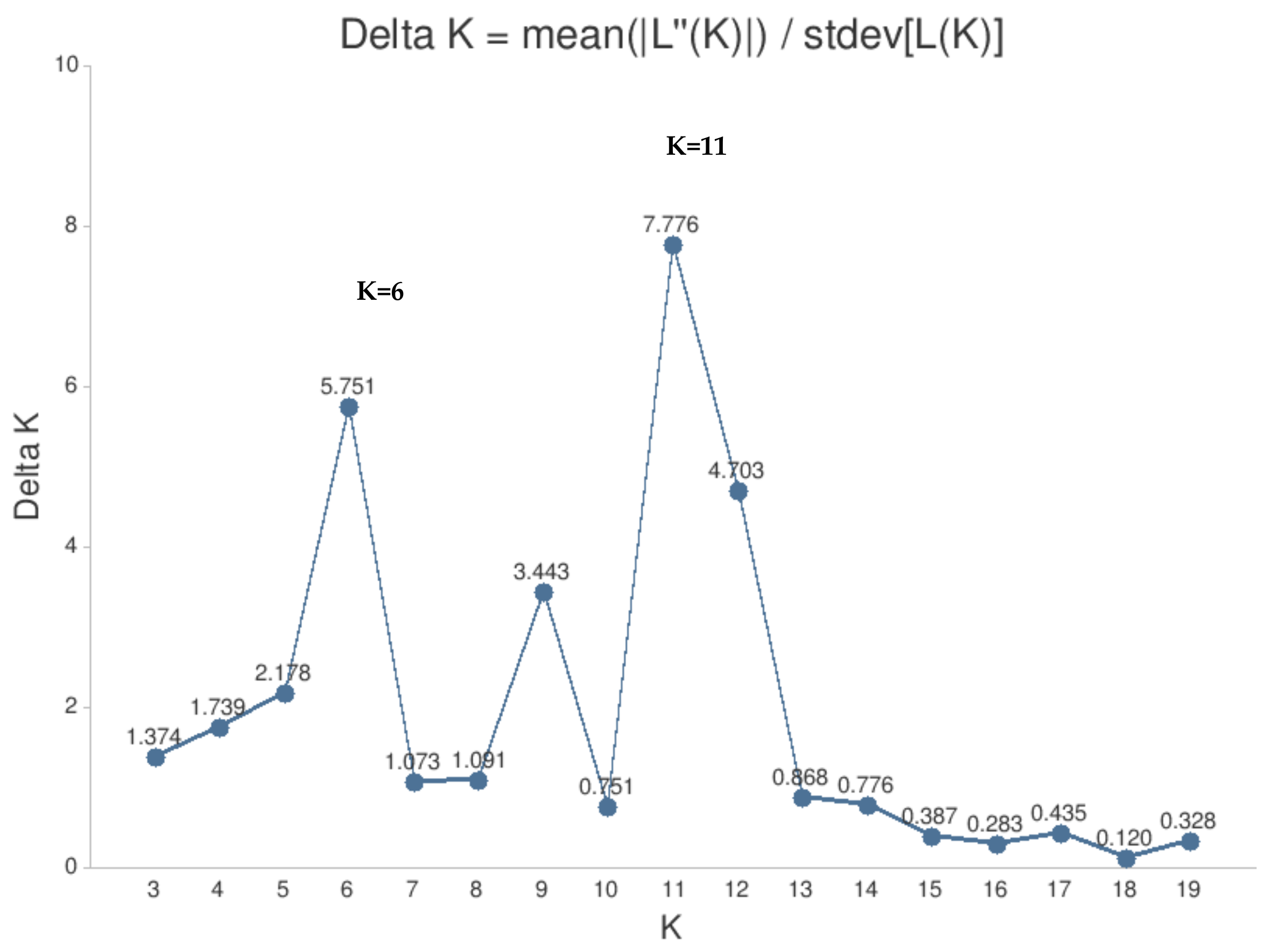
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Marker Name | Allele Size Range (bp) | Allele Number | Ho 1 | PIC 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | BPPCT040 | 115–155 | 27 | 0.991 | 0.232 |
| 2. | BPPCT034 | 216–258 | 24 | 0.981 | 0.213 |
| 3. | BPPCT039 | 124–177 | 24 | 1 | 0.239 |
| 4. | BPPCT014 | 185–225 | 18 | 0.869 | 0.182 |
| 5. | UDP98-407 | 164–233 | 24 | 0.766 | 0.139 |
| 6. | PacA33 | 168–223 | 30 | 0.832 | 0.136 |
| 7. | BPPCT007 | 124–161 | 20 | 0.832 | 0.282 |
| 8. | CPSCT026 | 166–213 | 24 | 0.991 | 0.235 |
| 9. | UDP96-005 | 96–154 | 28 | 0.757 | 0.162 |
| Average | 24.33 | 0.891 | 0.203 | ||
References
- Manco, R.; Chiaiese, P.; Basile, B.; Corrado, G. Comparative analysis of genomic- and EST-SSRs in European plum (Prunus domestica L.): Implications for the diversity analysis of polyploids. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butac, M. Plum Breeding. In Prunus, 2nd ed.; Küden, A., Ali, A., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Nybom, H.; Giovannini, D.; Ordidge, M.; Hjeltnes, S.H.; Grahić, J.; Gaši, F. ECPGR recommended SSR loci for analyses of European plum (Prunus domestica) collections. Genet. Resour. 2020, 1, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, M.; Lawrence, W. The Genetic of Garden Plants; Mac Millan: London, UK, 1934. [Google Scholar]
- Zhebentyayeva, T.; Shankar, V.; Scorza, R.; Callahan, A.; Ravelonandro, M.; Castro, S.; DeJong, T.; Saski, C.A.; Dardick, C. Genetic characterization of worldwide Prunus domestica (plum) germplasm using sequence-based genotyping. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaši, F.; Sehic, J.; Grahic, J.; Hjeltnes, S.H.; Ordidge, M.; Benedikova, D.; Blouin-Delmas, M.; Drogoudi, P.; Giovannini, D.; Höfer, M.; et al. Genetic assessment of the pomological classification of plum Prunus domestica L. accessions sampled across Europe. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2020, 67, 1137–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumüller, M. Fundamental and applied aspects of plum (Prunus domestica) breeding. Fruit Veg. Cereal Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 1, 139–156. [Google Scholar]
- Blažytė, A. Senosios Lietuviškos Vaismedžių Veislės: Mokomoji Priemonė; Spaudvita: Kėdainiai, Lithuania, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Stanys, V.; Šikšnianas, T.; Gelvonauskiene, D.; Sasnauskas, A. Genetiniai ir biotechnologiniai tyrimai sodo augalų veislėms kurti. In Augalų Selekcija Lietuvoje Amžių Sandūroje; Monografija; Lietuvos Agrarinių ir Miškų Mokslų Centras: Kėdainiai, Lithuania, 2022; p. 308. [Google Scholar]
- Gharbi, O.; Wünsch, A.; Rodrigo, J. Characterization of accessions of “Reine Claude Verte” plum using Prunus SRR and phenotypic traits. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 169, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrestarazu, J.; Errea, P.; Miranda, C.; Santesteban, L.G.; Pina, A. Genetic diversity of Spanish Prunus domestica L. germplasm reveals a complex genetic structure underlying. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, D.; Hartmann, W.; Stösser, R. Cultivar identification in Prunus domestica using random amplified polymorphic DNA markers. Acta Hortic. 1994, 359, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, A.M.; Igartua, E.; Balaguer, G.; Moreno, M.A. Genetic diversity of Prunus rootstocks analyzed by RAPD markers. Euphytica 1999, 110, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, H.; Uematsu, C. Structural analysis of chloroplast DNA in Prunus (Rosaceae): Evolution, genetic diversity and unequal mutations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 111, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdani, A.; Bouda, S.; Houmanat, K.; Outghouliast, H.; Razouk, R.; Adiba, A.; Charafi, J. Genetic diversity revealed via molecular analysis of moroccan and foreign plum (Prunus domestica; Prunus salicina) genotypes from an ex-situ collection. Vegetos 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decroocq, V.; Hagen, L.S.; Favé, M.G.; Eyquard, J.P.; Pierronnet, A. Microsatellite markers in the hexaploid Prunus domestica species and parentage lineage of three European plum cultivars using nuclear and chloroplast simple-sequence repeats. Mol. Breed. 2004, 13, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Halapija Kazija, D.; Vujević, P.; JelaČić, T.; Milinović, B.; Drkenda, P.; Gaŝi, F.; Kurtović, M.; Pejić, I.; Ŝimon, S.; Žulj, M.; et al. Genetic identification of “bistrica” and its synonyms “pož egača” and “hauszwetsche” (prunus domestica l.) using SSRs. Acta Hortic. 2013, 976, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, A.; Balsemin, E.; Barbot, J.C.; Christmann, H.; Manzano, G.; Reynet, P.; Laigret, F.; Mariette, S. Phenotypic variability and genetic structure in plum (Prunus domestica L.), cherry plum (P. cerasifera Ehrh.) and sloe (P. spinosa L.). Sci. Hortic. 2011, 129, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makovics-Zsohár, N.; Tóth, M.; Surányi, D.; Kovács, S.; Hegedűs, A.; Halász, J. Simple sequence repeat markers reveal Hungarian plum (Prunus domestica L.) germplasm as a valuable gene resource. HortScience 2017, 52, 1655–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manco, R.; Basile, B.; Capuozzo, C.; Scognamiglio, P.; Forlani, M.; Rao, R.; Corrado, G. Molecular and phenotypic diversity of traditional European plum (Prunus domestica L.) germplasm of Southern Italy. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkouropoulos, G.; Ganopoulos, I.; Tsaftaris, A.; Papadopoulos, I.; Drogoudi, P. Combination of high resolution melting (HRM) analysis and SSR molecular markers speeds up plum genotyping: Case study genotyping the Greek plum GeneBank collection. Plant Genet. Resour. Characterisation Util. 2017, 15, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnejja, M.; Garcia-Mas, J.; Howad, W.; Badenes, M.L.; Arus, P. Simple-sequence repeat (SSR) markers of Japanese plum (Prunus salicina Lindl.) are highly polymorphic and transferable to peach and almond. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2004, 4, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, R.; Hârţa, M.; Szabo, K.; Zănescu, M.; Sisea, C.R.; Cătană, C.; Pamfil, D. Genetic diversity and population structure of plum accessions from a Romanian germplasm collection assessed by simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. 2018, 46, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rallo, P.; López, C.; Suárez, M.P.; Morales-Sillero, A.M.; Casanova, L.; Jiménez, R.; Sánchez, A.; Guzmán, J.R. Molecular characterization of prunus accessions of traditional cultivars prospected in western andalusia, spain. Acta Hortic. 2011, 918, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suprun, I.I.; Stepanov, I.V.; Tokmakov, S.V.; Eremin, G.V. Study of Prunus domestica Genetic Diversity by Analysis of Microsatellite Loci. Russ. J. Genet. 2019, 55, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrestarazu, J.; Pina, A.; Errea, P. Diversity and genetic structure of European plum in mountainous areas of Northeastern Spain. Acta Hortic. 2017, 1172, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wünsch, A. SSR Markers for Fingerprinting Prunus Species. Acta Hortic. 2009, 814, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, H.; Spann, D.; Schlottmann, P.; Neumüller, M. Approaches to determine the origin of european plum (Prunus domestica) based on DNA nucleotide sequences. Acta Hortic. 2011, 918, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, K.A.; Hardigan, M.A.; Ragsdale, A.P.; Knapp, S.J.; VanBuren, R.; Edger, P.P. Diversification, spread, and admixture of octoploid strawberry in the Western Hemisphere. Am. J. Bot. 2021, 108, 2269–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanys, V.; Baniulis, D.; Morkunaite-Haimi, S.; Siksnianiene, J.B.; Frercks, B.; Gelvonauskiene, D.; Stepulaitiene, I.; Staniene, G.; Siksnianas, T. Characterising the genetic diversity of Lithuanian sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) cultivars using SSR markers. Sci. Hortic. 2012, 142, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software structure: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanauskas, J.; Kviklys, D.; Uselis, N.; Buskienė, L. Plum Cultivar Evaluation on Myrobalan Rootstock in Lithuania. Proc. Latv. Acad. Sci. Sect. B Nat. Exact Appl. Sci. 2019, 73, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janes, H.; Kahu, K. Winter Injuries of Plum Cultivars in Winters 2005–2007 in Estonia. In Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference Sustainable Fruit Growing: From Plant to Product, Jûrmala, Dobele, Latvia, 28–31 May 2008; pp. 149–153. [Google Scholar]
- Iezzoni, A.; Wünsch, A.; Höfer, M.; Giovannini, D.; Jensen, M.; Quero-García, J.; Campoy, J.A.; Vokurka, A.; Barreneche, T. Biodiversity, Germplasm Resources and Breeding Methods. In Cherries: Botany, Production and Uses; Quero-García, J., Iezzoni, A., Pulawska, J., Lang, G., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2017; pp. 36–59. [Google Scholar]
- Horak, J.; Peltanova, A.; Podavkova, A.; Safarova, L.; Bogusch, P.; Romport, D.; Zasadil, P. Biodiversity responses to land use in traditional fruit orchards of a rural agricultural landscape. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 178, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehic, J.; Nybom, H.; Hjeltnes, S.H.; Gasi, F. Genetic diversity and structure of Nordic plum germplasm preserved ex situ and on-farm. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 160, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 1990, 12, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Cipriani, G.; Lot, G.; Huang, W.G.; Marrazzo, M.T.; Peterlunger, E.; Testolin, R. AC/GT and AG/CT microsatellite repeats in peach [Prunus persica (L) Batsch]: Isolation, characterisation and cross-species amplification in Prunus. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1999, 99, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decroocq, V.; Fave, M.G.; Hagen, L.; Bordenave, L.; Decroocq, S. Development and transferability of apricot and grape EST microsatellite markers across taxa. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 106, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirlewanger, E.; Cosson, P.; Tavaud, M.; Aranzana, M.; Poizat, C.; Zanetto, A.; Arus, P.; Laigret, F. Development of microsatellite markers in peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] and their use in genetic diversity analysis in peach and sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 105, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán-Ruiz, I.; Dendauw, J.; Van Bockstaele, E.; Depicker, A.; De Loose, M. AFLP markers reveal high polymorphic rates in ryegrasses (Lolium spp.). Mol. Breed. 2000, 6, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botstein, D.; White, R.; Skolnick, M.; Davis, R.W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1980, 32, 314–331. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneath, P.H.A.; Sokal, R.R. Numerical Taxonomy: The Principles and Practice of Numerical Classification; WF Freeman & Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1973; p. 573. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11030–11035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porras-Hurtado, L.; Ruiz, Y.; Santos, C.; Phillips, C.; Carracedo, Á.; Lareu, M.V. An overview of STRUCTURE: Applications, parameter settings, and supporting software. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earl, D.A.; Holdt, B.M.V. Structure harvester: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2011, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Lithuanian-Origin Cultivars (LT Origin-Plum Group) | Reference Cultivars (R-Plum) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marker Name | Allele Size Range (bp) | Allele Number | Ho 1 | PIC 2 | Max. Number of Alleles in Genotype | Allele Size Range (bp) | Allele Number | Ho 1 | PIC 2 | Max. Number of Alleles in Genotype | |
| 1. | BPPCT040 | 115–155 | 21 | 1.00 | 0.274 | 6 | 116–147 | 8 | 1.00 | 0.410 | 5 |
| 2. | BPPCT034 | 216–258 | 17 | 1.00 | 0.256 | 6 | 216–258 | 13 | 1.00 | 0.308 | 4 |
| 3. | BPPCT039 | 126–171 | 15 | 1.00 | 0.286 | 5 | 126–177 | 13 | 1.00 | 0.368 | 5 |
| 4. | BPPCT014 | 185–225 | 12 | 0.71 | 0.243 | 5 | 185–225 | 9 | 1.00 | 0.358 | 5 |
| 5. | UDP98-407 | 168–197 | 11 | 0.71 | 0.258 | 3 | 164–194 | 6 | 0.33 | 0.343 | 3 |
| 6. | PacA33 | 175–213 | 13 | 0.79 | 0.265 | 6 | 168–210 | 11 | 1.00 | 0.333 | 4 |
| 7. | BPPCT007 | 124–161 | 14 | 1.00 | 0.374 | 6 | 124–149 | 11 | 1.00 | 0.369 | 6 |
| 8. | CPSCT026 | 166–213 | 18 | 1.00 | 0.280 | 6 | 166–210 | 13 | 1.00 | 0.368 | 3 |
| 9. | UDP96-005 | 96–154 | 19 | 0.71 | 0.240 | 6 | 104–152 | 11 | 0.83 | 0.414 | 5 |
| Average | 15.67 | 0.88 | 0.275 | 5.44 | 10.56 | 0.91 | 0.363 | 4.44 | |||
| Loci | Common Allele Lengths in bp (Frequencies in %) | Unique Allele Lengths in bp (Frequencies in %) * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithuanian Origin Cultivars | Reference Cultivars | ||
| BPPCT040 | 116 (20); 120 (25); 124 (35); 126 (50); 128 (50); 134 (30); 145 (25); 147 (40) | 115 (5); 118 (5); 119 (5); 131 (5); 136 (10); 138 (5); 140 (10); 141 (5); 144 (10); 149 (5); 150 (5); 153 (15); 155 (15) | - |
| BPPCT034 | 216 (75); 226 (25); 229 (10); 235 (20); 236 (15); 238 (10); 241 (55); 243 (20); 250 (15); 258 (15) | 222 (10); 227 (5); 232 (5); 234 (35); 237 (5); 246 (10); 247 (5) | 225 (5); 249 (5); 256 (5) |
| BPPCT039 | 126 (35); 129 (20); 131(15); 132 (30); 136 (25); 143 (25); 145 (15); 150 (15); 153 (70); 171 (25) | 128 (10); 130 (10); 141 (10); 163 (5); 167 (10) | 139 (5); 159 (5); 177 (10) |
| BPPCT014 | 185 (85); 202 (20); 204 (45); 214 (15); 215 (20); 216 (15); 218 (10); 223 (10); 225 (25) | 203 (15); 208 (5); 221 (5) | - |
| UDP98-407 | 181 (30); 187 (25); 194 (20) | 168 (10); 172 (5); 179 (25); 186 (5); 189 (5); 191 (15); 193 (15); 197 (5) | 164 (5); 177 (5); 185 (5) |
| PacA33 | 175 (50); 177 (15); 185 (30); 193 (15); 194 (30); 196 (10); 209 (10) | 179 (10); 183 (20); 191 (15); 192 (5); 202 (5); 213 (10) | 168 (5); 198 (5); 206 (5); 210 (5) |
| BPPCT007 | 124 (40); 126 (20); 128 (40); 130 (55); 134 (60); 136 (20); 138 (45); 140 (50); 142 (20); 144 (10); 149 (60) | 134 (10); 146 (10); 151 (30); 161 (5) | - |
| CPSCT026 | 166 (55); 175 (25); 183 (25); 188 (10); 189 (80); 193 (35); 196 (25); 199 (35); 200 (20); 202 (55); 204 (25); 210 (15) | 173 (5); 195 (15); 197 (15); 208 (5); 211 (5); 213 (5) | 185 (5) |
| UDP96-005 | 104 (25); 105 (10); 107 (20); 112 (30); 115 (20); 125 (15); 137 (15); 148 (35); 152 (30) | 96 (10); 120 (10); 124 (10); 128 (5); 130 (10); 132 (5); 134 (5); 139 (10); 142 (10); 154 (15) | 127 (5); 150 (10) |
| No. of alleles | 79 (50.3%) | 62 (39,5%) | 16 (10,2%) |
| No. of rare alleles | 8 (10,1%) | 50 (80,6%) | 16 (100%) |
| Hybrids | Parental Forms of Hybrids | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marker Name | Allele Size Range (bp) | Allele Number | Ho 1 | PIC 2 | Allele Size Range (bp) | Allele Number | Ho 1 | PIC 2 | |
| 1. | BPPCT040 | 115–155 | 26 | 1.00 | 0.253 | 117–155 | 17 | 1.00 | 0.333 |
| 2. | BPPCT034 | 216–256 | 22 | 1.00 | 0.221 | 216–250 | 15 | 1.00 | 0.352 |
| 3. | BPPCT039 | 124–177 | 23 | 1.00 | 0.251 | 126–177 | 13 | 1.00 | 0.363 |
| 4. | BPPCT014 | 185–225 | 14 | 0.95 | 0.225 | 185–221 | 9 | 1.00 | 0.284 |
| 5. | UDP98-407 | 164–225 | 17 | 0.80 | 0.179 | 164–198 | 9 | 0.50 | 0.358 |
| 6. | PacA33 | 168–221 | 26 | 0.82 | 0.157 | 168–194 | 8 | 0.83 | 0.347 |
| 7. | BPPCT007 | 124–161 | 18 | 1.00 | 0.279 | 124–161 | 12 | 1.00 | 0.352 |
| 8. | CPSCT026 | 166–211 | 20 | 1.00 | 0.260 | 166–211 | 13 | 1.00 | 0.333 |
| 9. | UDP96-005 | 96–154 | 25 | 0.77 | 0.179 | 96–154 | 13 | 0.83 | 0.355 |
| Average | 21.22 | 0.93 | 0.223 | 12.11 | 0.91 | 0.342 | |||
| Locus Name | DNA Sequence | Dye | Annealing Temp. °C | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UDP 98-407 | 5′-AGCGGCAGGCTAAATATCAA-3′ 5′-AATCGCCGATCAAAGCAAC-3′ | HEX | 58 | Cipriani et al. [38] |
| Pac A 33 | 5′-TCAGTCTCATCCTGCATACG-3′ 5′-CATGTGGCTCAAGGATCAAA-3′ | ATTO550 | 58 | Decroocq et al. [39] |
| CPSCT 026 | 5′-TCTCACACGCTTTCGTCAAC-3′ 5′-AAAAAGCCAAAAGGGGTTGT-3′ | 6-FAM | 46 | Mnejja et al. [22] |
| BPPCT 040 | 5′-ATGAGGACGTGTCTGAATGG-3′ 5′-AGCCAAACCCCTCTTATACG-3′ | 6-FAM | 58 | Dirlewanger et al. [40] |
| BPPCT 007 | 5′-TCATTGCTCGTCATCAGC-3′ 5′-CAGATTTCTGAAGTTAGCGGTA-3′ | HEX | 60 | Dirlewanger et al. [40] |
| BPPCT 034 | 5′-CTACCTGAAATAAGCAGAGCC AT-3′ 5′-CAATGGAGAATGGGGTGC-3′ | 6-FAM | 56 | Dirlewanger et al. [40] |
| UDP 96-005 | 5′-GTAACGCTCGCTACCACAAA-3′ 5′-CCTGCATATCACCACCCAG-3′ | HEX | 56 | Cipriani et al. [38] |
| BPPCT 039 | 5′-ATTACGTACCCTAAAGCTTCTGC-3′ 5′-GATGTCATGAAGATTGGAGAGG-3′ | HEX | 58 | Dirlewanger et al. [40] |
| BPPCT 014 | 5′-TTGTCTGCCTCTCATCTTAACC-3′ 5′-CATCGCAGAGAACTGAGAGC-3′ | 6-FAM | 58 | Dirlewanger et al. [40] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antanynienė, R.; Šikšnianienė, J.B.; Stanys, V.; Frercks, B. Fingerprinting of Plum (Prunus domestica) Genotypes in Lithuania Using SSR Markers. Plants 2023, 12, 1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12071538
Antanynienė R, Šikšnianienė JB, Stanys V, Frercks B. Fingerprinting of Plum (Prunus domestica) Genotypes in Lithuania Using SSR Markers. Plants. 2023; 12(7):1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12071538
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntanynienė, Raminta, Jūratė Bronė Šikšnianienė, Vidmantas Stanys, and Birutė Frercks. 2023. "Fingerprinting of Plum (Prunus domestica) Genotypes in Lithuania Using SSR Markers" Plants 12, no. 7: 1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12071538
APA StyleAntanynienė, R., Šikšnianienė, J. B., Stanys, V., & Frercks, B. (2023). Fingerprinting of Plum (Prunus domestica) Genotypes in Lithuania Using SSR Markers. Plants, 12(7), 1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12071538






