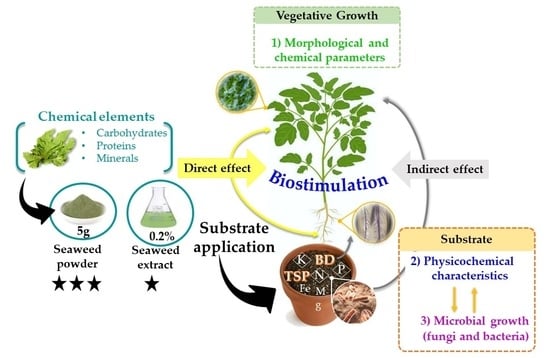
Application of Seaweed Generates Changes in the Substrate and Stimulates the Growth of Tomato Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. C, N, and Cell Wall Composition of U. ohnoi
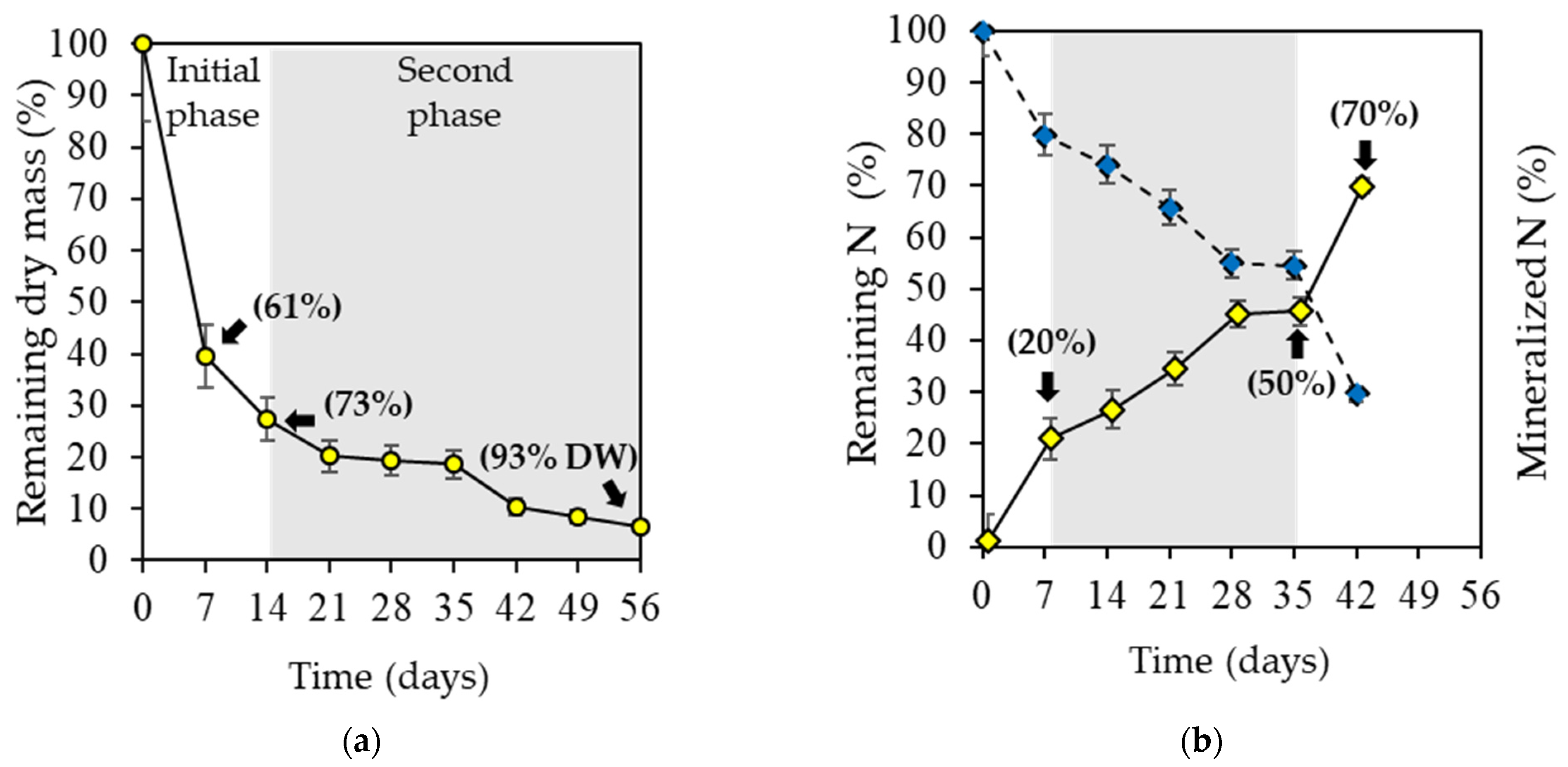
2.2. Algae Decomposition and N Mineralization
2.3. Physicochemical Analysis of U. ohnoi
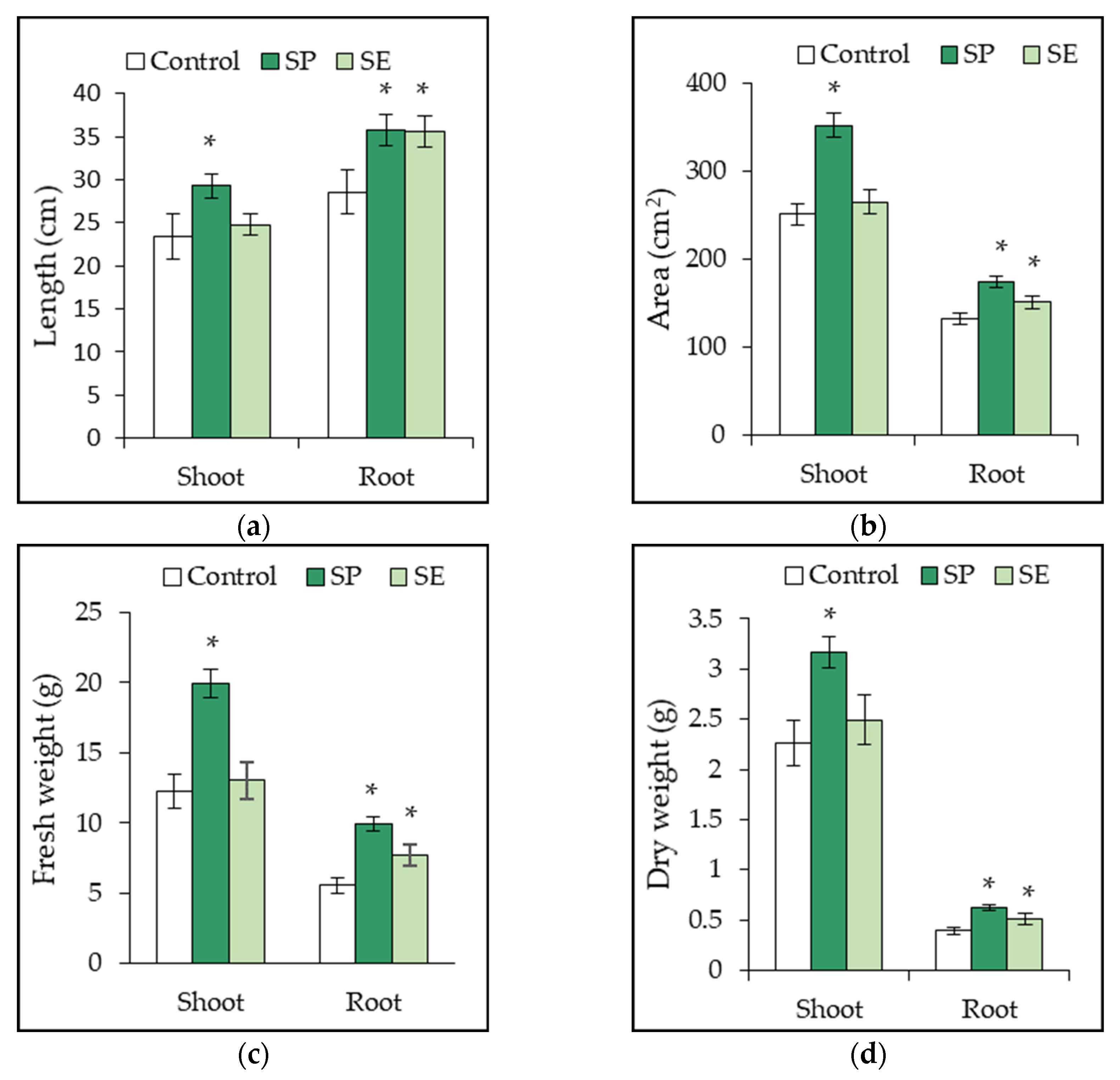
2.4. Growth Promotion of Tomato Plant by SP and SE
2.5. Mineral Composition and Chlorophyll Content
2.6. Physicochemical Properties of the Plant-Growth Substrate
2.7. Microbial Populations in the Plant-Growth Substrate
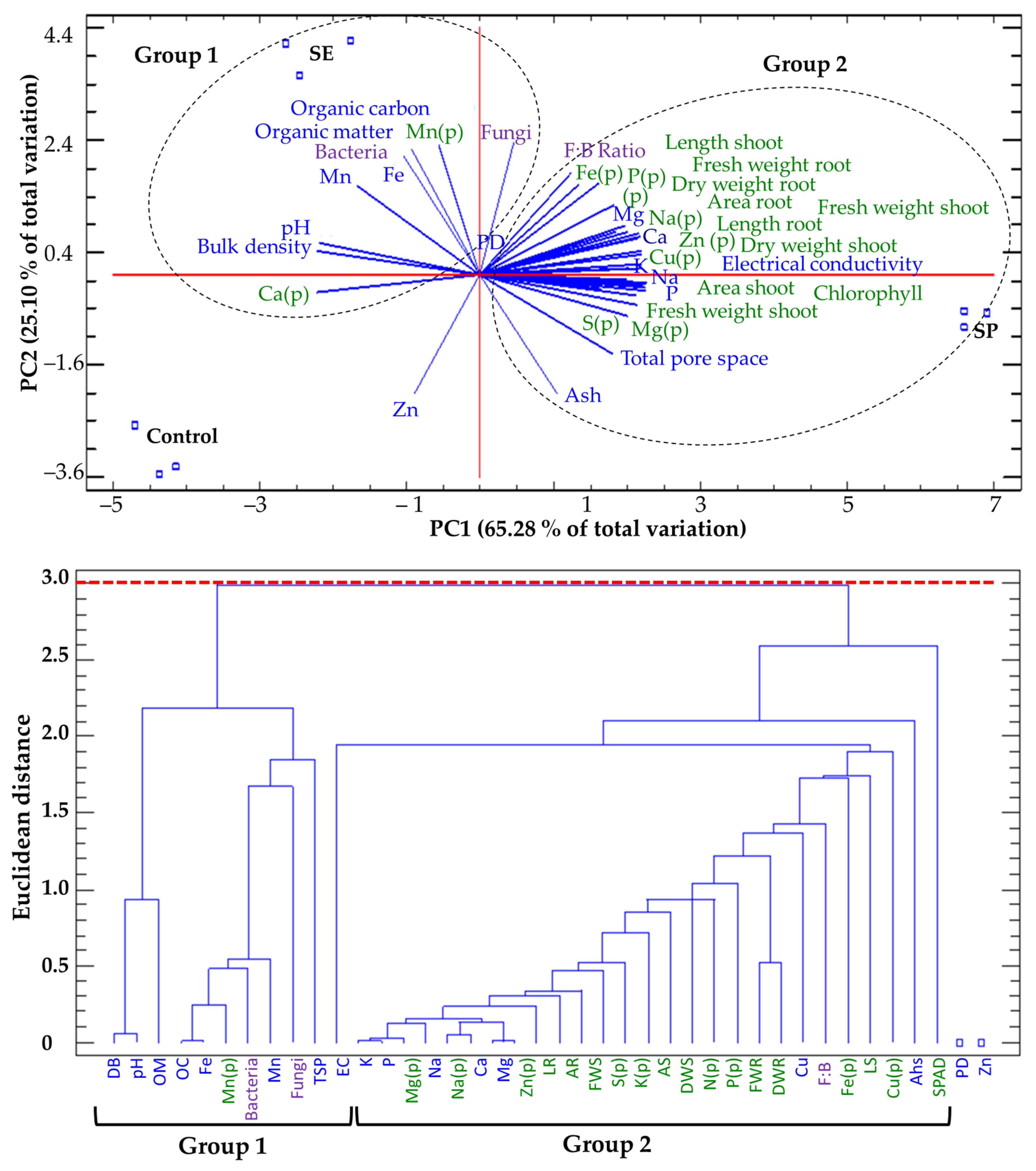
2.8. Principal Component Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Algae Material and Preparation of the Seaweed Extract
3.2. Algae Decomposition and Nitrogen Mineralization
3.3. Plant Material and Growth Conditions
3.4. Application of U. ohnoi SP and SE
3.5. Morphological Atributes and Chlorophyll Content of the Tomato Plants
3.6. Physicochemical Properties of the Substrate
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gruda, N.S. Increasing sustainability of growing media constituents and stand-alone substrates in soilless culture systems. Agronomy 2019, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL Boukhari, M.E.M.; Barakate, M.; Bouhia, Y.; Lyamlouli, K. Trends in Seaweed Extract Based Biostimulants: Manufacturing Process and Beneficial Effect on Soil-Plant Systems. Plants 2020, 9, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G. Biostimulants in agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- du Jardin, P. Plant biostimulants: Definition, concept, main categories and regulation. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhin, O.I.; Lubyanov, A.A.; Yakhin, I.A.; Brown, P.H. Biostimulants in Plant Science: A Global Perspective. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocira, A.; Świeca, M.; Kocira, S.; Złotek, U.; Jakubczyk, A. Enhancement of yield, nutritional and nutraceutical properties of two common bean cultivars following the application of seaweed extract (Ecklonia maxima). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannino, G.; Campobenedetto, C.; Vigliante, I.; Contartese, V.; Gentile, C.; Bertea, C.M. The application of a plant biostimulant based on seaweed and yeast extract improved tomato fruit development and quality. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannino, G.; Ricciardi, M.; Gatti, N.; Serio, G.; Vigliante, I.; Contartese, V.; Gentile, C.; Bertea, C.M. Changes in the Phytochemical Profile and Antioxidant Properties of Prunus persica Fruits after the Application of a Commercial Biostimulant Based on Seaweed and Yeast Extract. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aremu, A.O.; Makhaye, G.; Tesfay, S.Z.; Gerrano, A.S.; Du Plooy, C.P.; Amoo, S.O. Influence of Commercial Seaweed Extract and Microbial Biostimulant on Growth, Yield, Phytochemical Content, and Nutritional Quality of Five Abelmoschus esculentus Genotypes. Agronomy 2022, 12, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.A.; Illera-Vives, M.; Labrada, M.F.; Labandeira, S.S.; López-Mosquera, M.E. Improving growing substrates by adding the seaweed Cystoseira baccata. J. Appl. Phycol. 2022, 34, 3177–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gerrewey, T.; Vandecruys, M.; Ameloot, N.; Perneel, M.; Van Labeke, M.-C.; Boon, N.; Geelen, D. Microbe-Plant Growing Media Interactions Modulate the Effectiveness of Bacterial Amendments on Lettuce Performance Inside a Plant Factory with Artificial Lighting. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, R.I. Propiedades, uso y manejo de sustratos de cultivo para la producción de plantas en maceta. Rev. Chapingo. Ser. Hortic. 1999, 5, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabti, E.; Jha, B.C.; Hartmann, A. Impact of seaweeds on agricultural crop production as biofertilizer. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 1119–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, O.; Ramsubhag, A.; Jayaraman, J. Biostimulant properties of seaweed extracts in plants: Implications towards sustainable crop production. Plants 2021, 10, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craigie, J.S. Seaweed extract stimuli in plant science and agriculture. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 371–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illera-Vives, M.; Labandeira, S.S.; Fernández-Labrada, M.; López-Mosquera, M.E. Agricultural uses of seaweed. In Sustainable Seaweed Technologies: Cultivation, Biorefinery, and Applications; Torres, M.D., Kraan, S., Dominguez, H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 591–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, A.H.; Osman, M.E.; Gheda, S.F. Influence of the aqueous extracts of Ulva lactuca and Chlorella kessleri on growth and yield of Vicia faba. Algol. Stud. Arch. Für Hydrobiol. 2005, 116, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Herrera, R.A.; Santacruz-Ruvalcaba, F.; Ruiz-López, M.A.; Norrie, J.; Hernández-Carmona, G. Effect of liquid seaweed extracts on growth of tomato seedlings (Solanum lycopersicum L.). J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos-Barriga, L.G.; Santacruz-Ruvalcaba, F.; Hernández-Carmona, G.; Ramírez-Briones, E.; Hernández-Herrera, R.M. Effect of seaweed liquid extracts from Ulva lactuca on seedling growth of mung bean (Vigna radiata). J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 2479–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroud, S.; Tahrouch, S.; El Mehrach, K.; Sadki, I.; Fahmi, F.; Hatimi, A. Effect of brown algae on germination, growth and biochemical composition of tomato leaves (Solanum lycopersicum). J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2021, 20, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, R.A.; Hussein, M.H.; El-Naggar, N.E.A.; Karim-Eldeen, M.A.; Alamer, K.H.; Saleh, M.A.; Sharaf, E.M.; El-Azeem, R.M.A. Promoting effect of soluble polysaccharides extracted from Ulva spp. on Zea mays L. growth. Molecules 2022, 27, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battacharyya, D.; Babgohari, M.Z.; Rathor, P.; Prithiviraj, B. Seaweed extracts as biostimulants in horticulture. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Song, W.; Yang, J.; Ren, C.; Du, H.; Tang, T.; Qin, S.; Liu, Z.; Cui, H. The role and mechanism of commercial macroalgae for soil conditioner and nutrient uptake catalyzer. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 97, 455–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billard, V.; Etienne, P.; Jannin, L.; Garnica, M.; Cruz, F.; Garcia-Mina, J.-M.; Yvin, J.-C.; Ourry, A. Two Biostimulants Derived from Algae or Humic Acid Induce Similar Responses in the Mineral Content and Gene Expression of Winter Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L.). J. Plant Growth Regul. 2014, 33, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Kaur, I.; Bhatnagar, A.K. Enhancing soil health and productivity of Lycopersicon esculentum Mill. using Sargassum johnstonii Setchell & Gardner as a soil conditioner and fertilizer. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, I.J.; Álvarez, S.H.; Ibañez, A.L.; Rodríguez, A. Macroalgae as Soil Conditioners or Growth Promoters of Pisum sativum (L). Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2018, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, J.G.; Barrios, E.; Kass, D.C.L.; Thomas, R.J. Decomposition and nutrient release by green manures in a tropical hillside agroecosystem. Plant Soil 2002, 240, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulbry, W.; Kondrad, S.; Pizarro, C. Biofertilizers from algal treatment of dairy and swine manure effluents: Characterization of algal biomass as a slow release fertilizer. J. Veg. Sci. 2007, 12, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell, W.J.; McCarty, P.L. Aerobic decomposition of algae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1971, 5, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartino, M.L.; Vazquez, S.C.; Latorre, G.E.J.; Mac Cormack, W.P. Possible role of bacteria in the degradation of macro algae Desmarestia anceps Montagne (Phaeophyceae) in Antarctic marine waters. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2015, 47, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Sánchez, T.; Piñón-Gimate, A.; Melton III, J.T.; López-Bautista, J.M.; Casas-Valdez, M. First report, along with nomenclature adjustments, of Ulva ohnoi, U. tepida and U. torta (Ulvaceae, Ulvales, Chlorophyta) from northwestern Mexico. Bot. Mar. 2019, 62, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, M.; Shimada, S.; Uenosono, M.; Masuda, M. A new green-tide-forming alga, Ulva ohnoi Hiraoka et Shimada sp. nov. (Ulvales, Ulvophyceae) from Japan. Phycol. Res. 2004, 51, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Sánchez, T.; Piñón-Gimate, A.; Casas-Valdez, M. Normal, the Blob, and El Niño conditions: Effects on macroalgal blooms in a subtropical zone of the Gulf of California. Estuar. Coast. Shelf. Sci. 2022, 268, 107787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, L.; Magnusson, M.; Paul, N.A.; de Nys, R. The intensive land-based production of the green seaweeds Derbesia tenuissima and Ulva ohnoi: Biomass and bioproducts. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla-Lovano, S.; Sandoval-Gil, J.M.; Zertuche-González, J.A.; Belando-Torrentes, M.D.; Bernardeau-Esteller, J.; Rangel-Mendoza, L.K.; Ferreira-Arrieta, A.; Guzmán-Calderón, J.M.; Camacho-Ibar, V.F.; Muñiz-Salazar, R.; et al. Physiological responses and productivity of the seaweed Ulva ohnoi (Chlorophyta) under changing cultivation conditions in pilot large land-based ponds. Algal. Res. 2022, 56, 102316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, A.J.; Roberts, D.A.; Garside, A.L.; de Nys, R.; Paul, N.A. Seaweed compost for agricultural crop production. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, M.; Carl, C.; Mata, L.; de Nys, R.; Paul, N.A. Seaweed salt from Ulva: A novel first step in a cascading biorefinery model. Algal. Res. 2016, 16, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnuolo, D.; Prisa, D. Evaluation of Growth Parameters on Carpobrotus edulis, Kalanchoe daigremontiana and Kalanchoe tubiflora in Relation to Different Seaweed Liquid Fertilizer (SLF) as a Biostimulant. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2021, 10, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Farrell, A.; Ramsubhag, A.; Jayaraman, J. The effect of Ascophyllum nodosum extract on the growth, yield and fruit quality of tomato grown under tropical conditions. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu, N.J.; Bujang, J.S.; Zakaria, M.H.; Zulkifly, S. Use of Ulva reticulata as a growth supplement for tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, J. Tomato Plant Culture: In the Field, Greenhouse, and Home Garden; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bodale, I.; Mihalache, G.; Achitei, V.; Teliban, G.-C.; Cazacu, A.; Stoleru, V. Evaluation of the Nutrients Uptake by Tomato Plants in Different Phenological Stages Using an Electrical Conductivity Technique. Agriculture 2021, 11, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, H.I.; Kasinadhuni, N.; Arioli, T. The effect of seaweed extract on tomato plant growth, productivity and soil. J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 33, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-González, M.I.; Pérez-Gil, F.; Pérez-Estrella, S.; Carrillo-Domínguez, S. Composición química del alga verde Ulva lactuca. Cienc. Mar. 1996, 22, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaich, H.; Garna, H.; Besbes, S.; Paquot, M.; Blecker, C.; Attia, H. Chemical composition and functional properties of Ulva lactuca seaweed collected in Tunisia. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karberg, N.J.; Scott, N.A.; Giardina, C.P. Methods for estimating litter decomposition. In Field Measurements for Forest Carbon Monitoring: A Landscape-Scale Approach; Hoover, C.M., Ed.; Springer Science + Business Media B.V.: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, E.D.S.; Moura, W.D.M.; Guimarães, G.P.; Burak, D.L. Nutrient release from green manure under different sun-exposed faces. Coffee Sci. 2017, 13, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akila, V.; Manikandan, A.; Sukeetha, D.S.; Balakrishnan, S.; Ayyasamy, P.M.; Rajakumar, S. Biogas and biofertilizer production of marine macroalgae: An effective anaerobic digestion of Ulva sp. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 101035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Sundman, V.; Soininvaara, O.; Meriläinen, A. Effect of chemical composition on the release of nitrogen from agricultural plant materials decomposing in soil under field conditions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1988, 6, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanlauwe, B.; Diels, J.; Sanginga, N.; Merckx, R. Residue quality and decomposition: An unsteady relationship? In Driven by Nature: Plant Litter Quality and Decomposition; Cadisch, G., Giller, K.E., Eds.; CAB International: Oxon, UK, 1997; pp. 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Nyberg, G.; Ekblad, A.; Buresh, R.; Högberg, P. Short-term patterns of carbon and nitrogen mineralization in a fallow field amended with green manures from agroforestry trees. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2002, 36, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masunga, R.H.; Uzokwe, V.N.; Mlay, P.D.; Odeh, I.; Singh, A.; Buchan, D.; De Neve, S. Nitrogen mineralization dynamics of different valuable organic amendments commonly used in agriculture. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 101, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCurdy, J.D.; McElroy, J.S.; Guertal, E.A.; Wood, C.W. Dynamics of White Clover Decomposition in a Southeastern Bermudagrass Lawn. Agron. J. 2013, 105, 1277–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.; Cintra-Buenrostro, C.E.; Fierro-Cabo, A. Decomposition and nitrogen dynamics of turtle grass (Thalassia testudinum) in a subtropical estuarine system. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 25, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, R.R.; Brady, N.C. The Nature and Properties of Soils, 15th ed.; Pearson Education, Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 526–559. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.R.; Singh, J.S. The effect of plant species, weather variables and chemical composition of plant material on decomposition in a tropical grassland. Plant Soil 1981, 59, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahaye, M.; Robic, A. Structure and functional properties of ulvan, a polysaccharide from green seaweeds. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Bourgaugnon, N.; Deslandes, E. Carbohydrates from Seaweeds. In Seaweed in Health and Disease Prevention; Fleurence, J., Levine, I., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 223–274. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, B. Litter decomposition and organic matter turnover in northern forest soils. For. Ecol. Manag. 2000, 133, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordovil, C.M.S.; Coutinho, J.; Goss, M.; Cabral, F. Potentially mineralizable nitrogen from organic materials applied to a sandy soil: Fitting the one-pool exponential model. Soil Use Manag. 2005, 21, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioretto, A.; Di Nardo, C.; Papa, S.; Fuggi, A. Lignin and cellulose degradation and nitrogen dynamics during decomposition of three leaf litter species in a Mediterranean ecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahdat, E.; Nourbakhsh, F.; Basiri, M. Lignin content of range plant residues controls N mineralization in soil. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2011, 47, 243e246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänsch, R.; Mendel, R.R. Physiological functions of mineral micronutrients (cu, Zn, Mn, Fe, Ni, Mo, B, cl). Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanthini, K.M.-P.; Stanley-Raja, V.; Thanigaivel, A.; Karthi, S.; Palanikani, R.; Shyam Sundar, N.; Sivanesh, H.; Soranam, R.; Senthil-Nathan, S. Sustainable Agronomic Strategies for Enhancing the Yield and Nutritional Quality of Wild Tomato, Solanum lycopersicum (L.) Var Cerasiforme Mill. Agronomy 2019, 9, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirian, K.; Piri, K.; Sohrabipour, J.; Blomster, J. Three species of Ulva (Ulvophyceae) from the Persian Gulf as potential sources of protein, essential amino acids and fatty acids. Phycol. Res. 2018, 66, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Chaski, C.; Polyzos, N.; Petropoulos, S.A. Biostimulants application: A low input cropping management tool for sustainable farming of vegetables. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Herrera, R.M.; Santacruz-Ruvalcaba, F.; Zañudo-Hernández, J.; Hernández-Carmona, G. Activity of seaweed extracts and polysaccharide-enriched extracts from Ulva lactuca and Padina gymnospora as growth promoters of tomato and mung bean plants. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 2549–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, D.A.E.A.; Gheda, S.F.; Ismail, G.A. Efficacy of two seaweeds dry mass in bioremediation of heavy metal polluted soil and growth of radish (Raphanus sativus L.) plant. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 12831–12846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhouna, D.; Kies, F.; Elegbede, I.O.; Matemilola, S.; Zorriehzahra, J.; Hussein, E.K. Potential assay of two green algae Ulva lactuca and Ulva intestinalisas biofertilizers. Sustain. Agri Food Environ. Res. 2021, 9, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez-García, I.; Dueñas Ledezma, A.K.; Martínez Montaño, E.; Salazar Leyva, J.A.; Carrera, E.; Osuna Ruiz, I. Identification and quantification of plant growth regulators and antioxidant compounds in aqueous extracts of Padina durvillaei and Ulva lactuca. Agronomy 2020, 10, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnie, J.F.; Van Staden, J. Effect of seaweed concentrate and applied hormones on in vitro cultured tomato roots. J. Plant Physiol. 1985, 120, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Rengasamy, R. The effects of Seaweed Liquid Fertilizer of Ulva lactuca on Capsicum annum. Algol. Stud. 2012, 138, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugnai, S.; Azzarello, E.; Pandolfi, C.; Salamagne, S.; Briand, X.; Mancuso, S. Enhancement of ammonium and potassium root influxes by the application of marine bioactive substances positively affects Vitis vinifera plant growth. J. Appl. Phycol. 2008, 20, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baligar, V.C.; Fageria, N.K.; He, Z.L. Nutrient use efficiency in plants. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2001, 32, 921–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popko, M.; Michalak, I.; Wilk, R.; Gramza, M.; Chojnacka, K.; Górecki, H. Effect of the New Plant Growth Biostimulants Based on Amino Acids on Yield and Grain Quality of Winter Wheat. Molecules 2018, 23, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemkemeyer, M.; Schwalb, S.A.; Heinze, S.; Joergensen, R.G.; Wichern, F. Functions of elements in soil microorganisms. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 252, 126832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes-Blackburn, D.; Giles, C.; Darch, T.; George, T.S.; Blackwell, M.; Stutter, M.; Shand, C.; Lumsdond, C.P.; Wendler, R.; Brown, L.; et al. Opportunities for mobilizing recalcitrant phosphorus from agricultural soils: A review. Plant Soil 2018, 427, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higo, M.; Azuma, M.; Kamiyoshihara, Y.; Kanda, A.; Tatewaki, Y.; Isobe, K. Impact of Phosphorus Fertilization on Tomato Growth and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungal Communities. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.D.; Duigan, S.P.; Berlyn, G.P. An evaluation of noninvasive methods to estimate foliar chlorophyll content. New Phytol. 2002, 153, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunden, G.; Jenkins, T.; Liu, Y.W. Enhanced leaf chlorophyll levels in plants treated with seaweed extract. J. Appl. Phycol. 1996, 8, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad-Berjon, M.; Noguera-Murray, P.; Carrión-Benedito, C. Los sustratos en los cultivos sin suelo. In Cultivo sin Suelo; Urrestarazu-Gavilán, P., Ed.; Editorial Mundi-Prensa: Madrid, España, 2004; pp. 113–158. [Google Scholar]
- Cordell, D.; Drangert, J.O.; White, S. The story of phosphorus: Global food security and food for thought. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2009, 19, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkar, V.; Thirumalaikumar, V.P.; Xue, G.P.; Vallarino, J.G.; Turěcková, V.; Strnad, M.; Fernie, A.R.; Hoefgen, R.; Mueller-Roeber, B.; Balazadeh, S. Multifaceted regulatory function of tomato SlTAF1 in the response to salinity stress. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1681–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, M.K.; Aduayi, E.A. Effects of sodium and potassium application on water content and yield of tomato in Southwestern Nigeria. J. Plant Nutr. 2006, 29, 2131–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Mao, Z. Effects of seaweed fertilizer on the Malus hupehensis Rehd. seedlings growth and soil microbial numbers under continue cropping. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Official Methods of Analysis, 15th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lourenço, S.O.; Barbarino, E.; De Paula, J.C.; Pereira, L.O.D.S.; Marquez, U.M.L. Amino acid composition, protein content and calculation of nitrogen-to-protein conversion factors for 19 tropical seaweeds. Physiol. Res. 2002, 50, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wider, R.K.; Lang, G.E. A Critique of the Analytical Methods Used in Examining Decomposition Data Obtained from Litter Bags. Ecology 1982, 63, 1636–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, E.; Katayama, A.; Hishi, T. Effects of declining understory vegetation on leaf litter decomposition in a Japanese cool-temperate forest. J. For. Res. 2020, 25, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, J.S. Energy storage and the balance of producers and decomposers in ecological. Ecology 1963, 44, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerril-Espinosa, A.; Hernández-Herrera, R.M.; Meza-Canales, I.D.; Perez-Ramirez, R.; Rodríguez-Zaragoza, F.A.; Méndez-Morán, L.; Sánchez-Hernández, C.V.; Palmeros-Suárez, P.A.; Palacios, O.A.; Choix, F.J.; et al. Habitat-adapted heterologous symbiont Salinispora arenicola promotes growth and alleviates salt stress in tomato crop plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 920881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriels, R.; Van Keirsbulck, W.; Engels, H. A rapid method for the determination of physical properties of growing media. Acta Hortic. 1993, 342, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boodt, M.; Verdonck, O.; Cappaert, I. Methods for measuring the water release curve of organic substrates. Acta Hortic. 1974, 37, 2054–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales (SEMARNAT). Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-021-RECNAT-2000. Que Establece las Especificaciones de Fertilidad, Salinidad y Clasificación de Suelos. Estudios, Muestreo y Análisis; Oficial de la Federación: Ciudad de México, México, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, W.M. AOAC Methods for the Determination of Phosphorus in Fertilizers. J. Assoc. Off. Agric. Chem. 1964, 47, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkley, A.J.; Black, I.A. Estimation of soil organic carbon by the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.R. Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; p. 823. [Google Scholar]
- Onet, A.; Teusdea, A.; Boja, N.; Domuta, C.; Onet, C. Effects of common oak Quercus robur L. defoliation on the soil properties of an oak forest in Western plain of Romania. Ann. For. Res. 2016, 59, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Component | Value |
|---|---|
| Cellular content | 70.89 ± 0.04 |
| Neutral detergent fiber (NDF) | 29.11 ± 0.02 |
| Acid detergent fiber (ADF) | 18.04 ± 0.43 |
| Lignin | 6.64 ± 0.01 |
| Cellulose | 11.39 ± 0.43 |
| Hemicellulose | 11.07 ± 0.45 |
| Carbon | 29.92 ± 0.13 |
| Nitrogen | 3.12 ± 0.04 |
| C/N ratio | 9.59 ± 0.08 |
| Lignin/N ratio | 1.94 ± 0.00 |
| Parameter | k (day−1) | t½ (days) |
|---|---|---|
| Dry weight loss * | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 4.84 ± 1.5 |
| Nitrogen release ** | 0.024 ± 0.01 | 31.74 ± 8.09 |
| Analysis | SP | SE |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.56 ± 0.00 | 5.67 ± 0.00 |
| Electrical conductivity (dS m−1) | 3.78 ± 0.01 | 1.94 ± 0.00 |
| Organic matter (%) | 71.26 ± 0.02 | 0.14 ± 0.01 |
| Protein (%) | 14.72 ± 0.01 | 0.026 ± 0.00 |
| Ash (%) | 28.74 ± 0.02 | nd |
| Macronutrients (%) | ||
| C | 29.92 ± 0.13 | 0.059 ± 0.00 |
| N | 3.12 ± 0.04 | 0.005 ± 0.00 |
| P | 0.09 ± 0.02 | 0.006 ± 0.00 |
| K | 3.98 ± 0.00 | 0.053 ± 0.00 |
| Ca | 0.49 ± 0.00 | 0.019 ± 0.00 |
| Mg | 1.83 ± 0.01 | 0.029 ± 0.00 |
| Micronutrients (mg kg−1) | ||
| Na | 2560 ± 1.52 | 361 ± 1.50 |
| Cu | 12.70 ± 0.05 | 1.60 ± 0.01 |
| Mn | 4.80 ± 0.02 | <1 ± 0.00 |
| Fe | 142 ± 0.57 | 12 ± 0.57 |
| Zn | 27 ± 0.12 | 27 ± 0.57 |
| Property | Control | SP | SE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bulk density (g cm−3) | 0.57 ± 0.001 b | 0.50 ± 0.017 c | 0.61 ± 0.005 a |
| Particle density (g cm−3) | 1.82 ± 0.005 a | 1.82 ± 0.004 a | 1.79 ± 0.007 b |
| Total pore space (%) | 68.95 ± 0.389 b | 72.36 ± 1.017 a | 66.32 ± 0.374 c |
| pH | 8.73 ± 0.015 b | 7.83 ± 0.01 c | 8.82 ± 0.006 a |
| Electrical conductivity (dS m−1) | 0.21 ± 0.015 c | 1.21 ± 0.006 a | 0.33 ± 0.01 b |
| Organic matter (%) | 16.84 ± 0.6 b | 16.13 ± 0.38 c | 20.42 ± 0.548 a |
| Organic carbon (%) | 9.77 ± 0.348 b | 9.36 ± 0.221 b | 11.84 ± 0.318 a |
| Ash (%) | 83.158 ± 0.6 b | 83.872 ± 0.38 a | 79.586 ± 0.548 c |
| Availed minerals (mg kg−1) | |||
| P | 46.82 ± 0.388 c | 68.27 ± 0.484 a | 48.43 ± 0.755 b |
| K | 901.67 ± 0.306 c | 1663.80 ± 1.058 a | 1006.5 ± 0.624 b |
| Na | 757.00 ± 1.00 c | 1426.33 ± 1.155 a | 937.33 ± 1.528 b |
| Ca | 4815.67 ± 0.57 c | 5186.67 ± 1.528 a | 4990.33 ± 1.53 b |
| Mg | 1697.33 ± 0.58 c | 2892.33 ± 1.16 a | 2234.00 ± 1.00 b |
| Cu | 0.55 ± 0.012 b | 0.73 ± 0.015 a | 0.51 ± 0.015 c |
| Mn | 4.63 ± 0.01 b | 4.22 ± 0.006 c | 5.26 ± 0.071 a |
| Fe | 13.91 ± 0.107 b | 13.80 ± 0.015 c | 14.94 ± 0.071 a |
| Zn | 3.05 ± 0.064 a | 2.09 ± 0.02 b | 1.73 ± 0.036 c |
| Total Microorganisms (CFU × 103 g−1) | Control | SP | SE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | 217.50 ± 12.62 b | 239.36 ± 43.07 b | 445.49 ± 6.51 a |
| Fungi | 110.27 ± 9.72 c | 456.00 ± 49.15 b | 769.98 ± 73.65 a |
| Fungi/Bacteria ratio | 0.51 ± 0.09 c | 1.92 ± 0.13 a | 1.73 ± 0.16 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Espinosa-Antón, A.A.; Zamora-Natera, J.F.; Zarazúa-Villaseñor, P.; Santacruz-Ruvalcaba, F.; Sánchez-Hernández, C.V.; Águila Alcántara, E.; Torres-Morán, M.I.; Velasco-Ramírez, A.P.; Hernández-Herrera, R.M. Application of Seaweed Generates Changes in the Substrate and Stimulates the Growth of Tomato Plants. Plants 2023, 12, 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12071520
Espinosa-Antón AA, Zamora-Natera JF, Zarazúa-Villaseñor P, Santacruz-Ruvalcaba F, Sánchez-Hernández CV, Águila Alcántara E, Torres-Morán MI, Velasco-Ramírez AP, Hernández-Herrera RM. Application of Seaweed Generates Changes in the Substrate and Stimulates the Growth of Tomato Plants. Plants. 2023; 12(7):1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12071520
Chicago/Turabian StyleEspinosa-Antón, Adrian Alejandro, Juan Francisco Zamora-Natera, Patricia Zarazúa-Villaseñor, Fernando Santacruz-Ruvalcaba, Carla Vanessa Sánchez-Hernández, Edith Águila Alcántara, Martha Isabel Torres-Morán, Ana Paulina Velasco-Ramírez, and Rosalba Mireya Hernández-Herrera. 2023. "Application of Seaweed Generates Changes in the Substrate and Stimulates the Growth of Tomato Plants" Plants 12, no. 7: 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12071520
APA StyleEspinosa-Antón, A. A., Zamora-Natera, J. F., Zarazúa-Villaseñor, P., Santacruz-Ruvalcaba, F., Sánchez-Hernández, C. V., Águila Alcántara, E., Torres-Morán, M. I., Velasco-Ramírez, A. P., & Hernández-Herrera, R. M. (2023). Application of Seaweed Generates Changes in the Substrate and Stimulates the Growth of Tomato Plants. Plants, 12(7), 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12071520