Comprehensive Analysis of BR Receptor Expression under Hormone Treatment in the Rubber Tree (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of BRI1 and BAK1 Genes in Rubber Tree
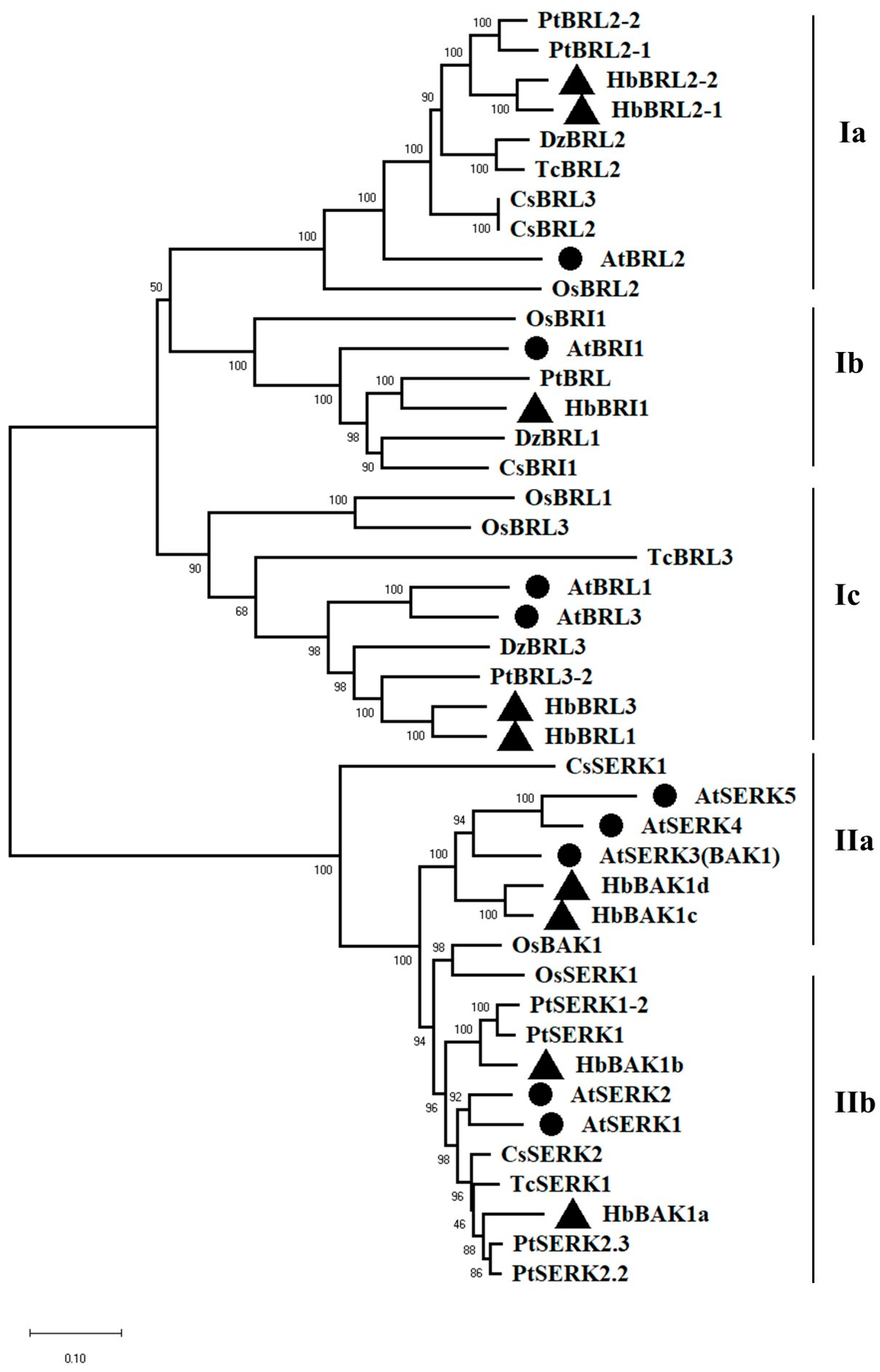
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of BRI1 and BAK1 Members
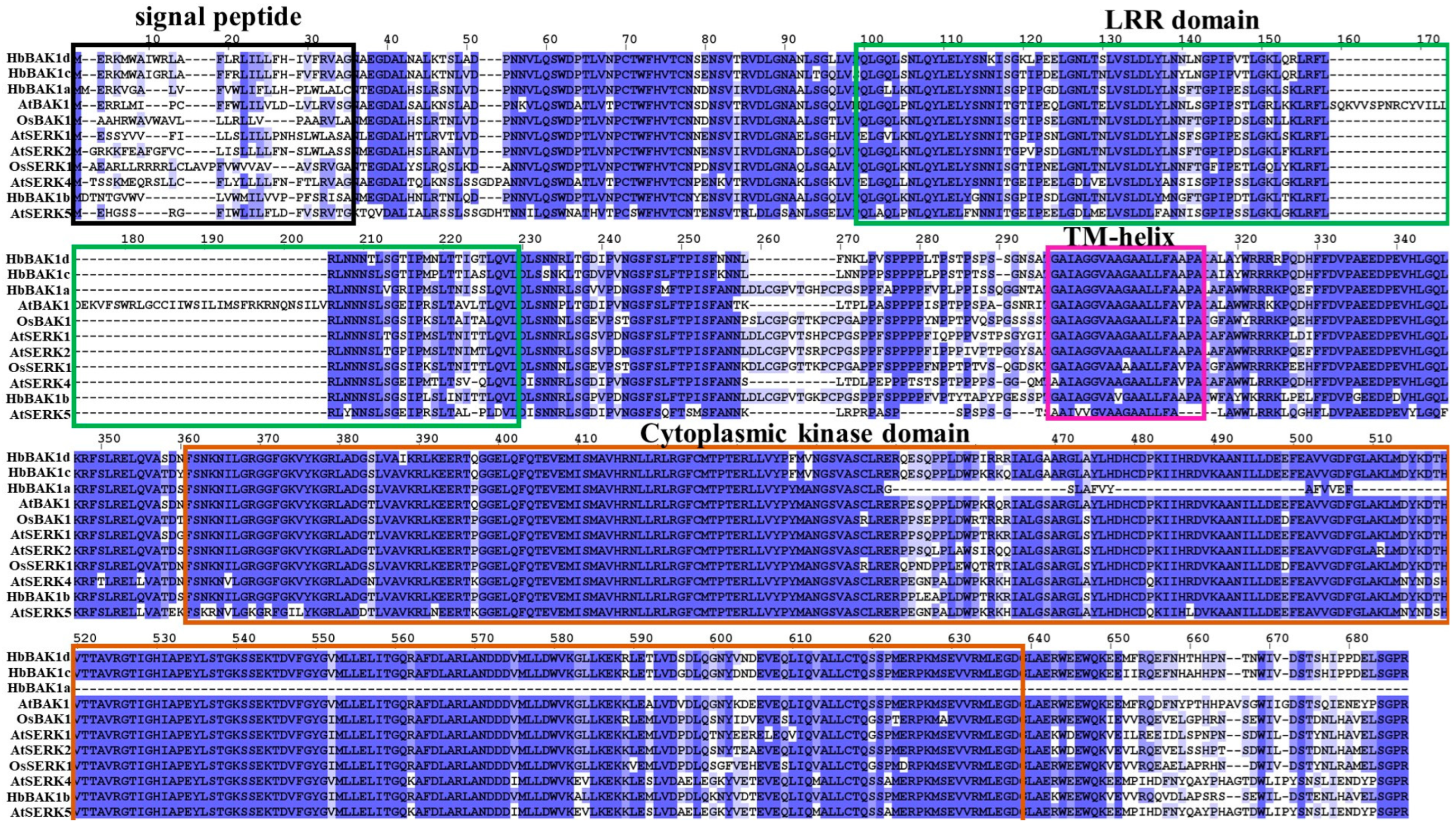
2.3. Sequence Characteristics of HbBRI1 and HbBAK1 Members
2.4. Structural Domain and Cis-Elements in HbBRI1 and HbBAK1
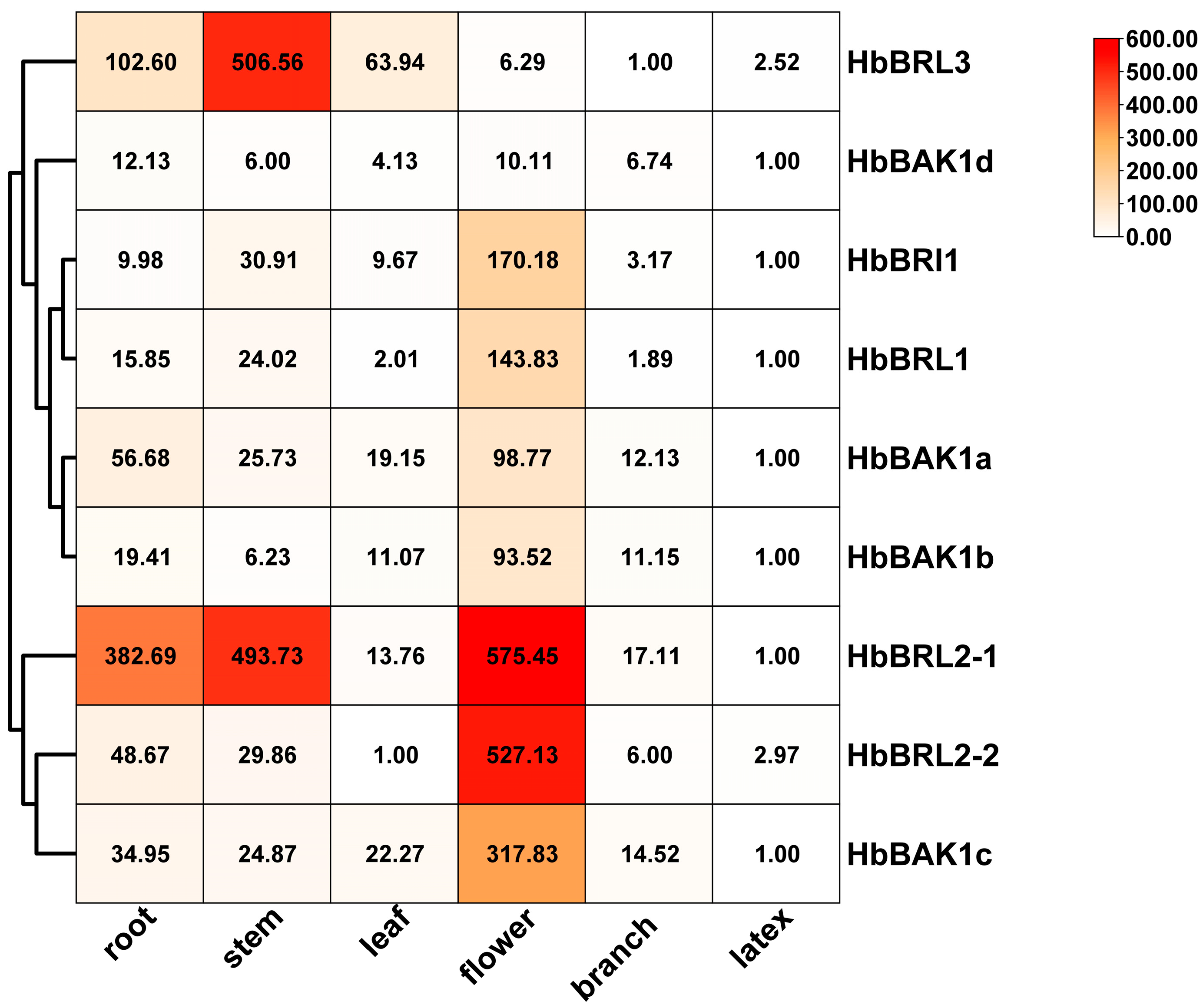
2.5. Expression Analysis of HbBRI1 and HbBAK1 Genes in Different Tissues
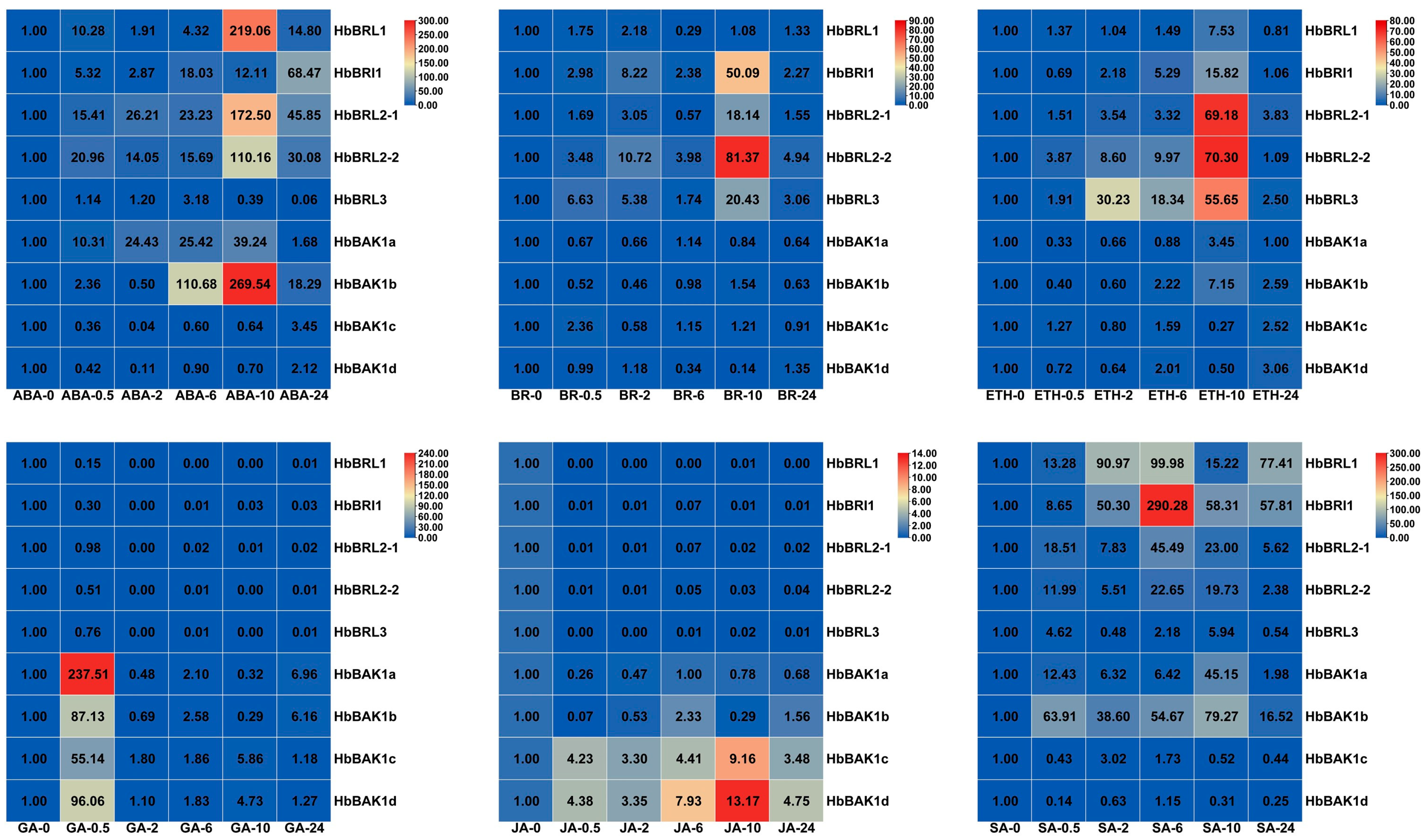
2.6. Expression Profile of HbBRI1 and HbBAK1 Response to Hormone Stress
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Retrieving BRI1 and BAK1 Genes from the Rubber Tree
4.2. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis of the HbBRI1 and HbBAK1 Genes
4.3. Gene Structure and Protein Motif Analysis of BRI1 Family in the Rubber Tree
4.4. Conserved Domain and Cis-Element Analysis
4.5. Plant Materials, Treatment and qRT-PCR Assay
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grove, M.; Spencer, G.; Rohwedder, W.; Mandava, N.; Worley, J.; Warthen, J.; Steffens, G.; Anderson, F.; Cook, J. Brassinolide, a plant growth-promoting steroid isolated from brassica napus pollen. Nature 1976, 281, 216–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clouse, S.; Sasse, J. Brassinosteroids, essential regulators of plant growth and development. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 49, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaubhadel, S.; Browning, K.S.; Gallie, D.R.; Krishna, P. Brassinosteroid functions to protect the translational machinery and heat-shock protein synthesis following thermal stress. Plant J. 2002, 29, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, C.; Lu, Y.; Jin, J.; Wang, X. The mechanisms of brassinosteroids’ action: From signal transduction to plant development. Mol. Plant 2011, 4, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.C.; Zhang, R. Relationship of a putative receptor protein kinase from maize to the s-locus glycoproteins of brassica. Nature 1990, 345, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.; Sun, J.; Oh, D.H.; Zielinski, R.E.; Clouse, S.D.; Huber, S.C. Enhancing Arabidopsis leaf growth by engineering the brassinosteroid insensitive1 receptor kinase. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chory, J. A putative leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase involved in brassinosteroid signal transduction. Cell 1997, 90, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, J.; Han, Z.; Kim, T.; Wang, J.; Cheng, W.; Chang, J.; Shi, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, M.; Wang, Z.; et al. Structural insight into brassinosteroid perception by BRI1. Nature 2011, 474, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Seto, H.; Fujioka, S.; Yoshida, S.; Chory, J. BRI1 is a critical component of a plasma-membrane receptor for plant steroids. Nature 2001, 410, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gou, X.; Yuan, T.; Lin, H.; Asami, T.; Yoshida, S.; Russell, S.D.; Li, J. BAK1 and BKK1 regulate brassinosteroid-dependent growth and brassinosteroid-independent cell-death pathways. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, D.A.; Yi, Y.B.; Yu, C.; Vafeados, D.; Mora-Garcia, S.; Cheng, J.C.; Nam, K.H.; Li, J.; Chory, J. BRI1 and BRI3 are novel brassinosteroid receptors that function in vascular differentiation in Arabidopsis. Developemnt 2004, 131, 5341–5351. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, A.; Wang, H.; Walker, J.C.; Li, J. BRI1, a leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein kinase, is functionally redundant with bri1 in regulating Arabidopsis brassinosteroid signaling. Plant J. 2004, 40, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrichsen, D.M.; Joazeiro, C.A.P.; Li, J.; Hunter, T.; Chory, J. Brassinosteroid-insensitive-1 is a ubiquitously expressed leucine-rich repeat receptor serine/threonine kinase. Plant Physiol. 2000, 123, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Fujioka, S.; Choe, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Yuan, H.; Feldmann, K.A.; Tax, F.E. Brassinosteroid-insensitive dwarf mutants of Arabidopsis accumulate brassinosteroids. Plant Physiol. 1999, 121, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hothorn, M.; Belkhadir, Y.; Dreux, M.; Dabi, T.; Noel, J.P.; Wilson, I.A.; Chory, J. Structural basis of steroid hormone perception by the receptor kinase BRI1. Nature 2011, 474, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russinova, E.; Borst, J.W.; Kwaaitaal, M.; Cano-Delgado, A.; Yin, Y.; Chory, J.; de Vries, S.C. Heterodimerization and endocytosis of Arabidopsis brassinosteroid receptors BRI1 and AtSERK3 (BAK1). Plant Cell 2004, 16, 3216–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.X.; Gendron, J.M.; Sun, Y.; Gampala, S.S.; Gendron, N.; Sun, C.Q.; Wang, Z.Y. BZR1 is a transcriptional repressor with dual roles in brassinosteroid homeostasis and growth responses. Science 2005, 307, 1634–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vert, G.; Chory, J. Downstream nuclear events in brassinosteroid signalling. Nature 2006, 441, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.Y.; Zhang, L.Y.; Gampala, S.S.; Zhu, S.W.; Song, W.Y.; Chong, K.; Wang, Z.Y. Functions of OsBZR1 and 14-3-3 proteins in brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13839–13844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Huang, S.; Wang, S.; Cheng, D.; Liu, J.; Lv, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, X. Enhancing brassinosteroid signaling via overexpression of tomato (solanum lycopersicum) slbri1 improves major agronomic traits. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, G.; Park, J.I.; Jung, H.J.; Ahmed, N.U.; Kayum, M.A.; Kang, J.G.; Nou, I.S. Molecular characterization of BZR transcription factor family and abiotic stress induced expression profiling in brassica rapa. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2015, 92, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Y.; Dai, C.; Lee, M.M.; Kwak, J.M.; Nam, K.H. BRI1-associated receptor kinase 1 regulates guard cell aba signaling mediated by open stomata 1 in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Fujioka, S.; Sunohara, H.; Kamiya, N.; Hong, Z.; Inukai, Y.; Miura, K.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; et al. The role of OsBRI1 and its homologous genes, OsBRI1 and OsBRI3, in rice. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.S.; Kumar, G.B.; Khan, M.; Doohan, F.M. Brassinosteroid enhances resistance to fusarium diseases of barley. Phytopathology 2013, 103, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clouse, S.D. Brassinosteroid signal transduction: From receptor kinase activation to transcriptional networks regulating plant development. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, V.; Vielle-Calzada, J.P.; Hartog, M.V.; Schmidt, E.D.; Boutilier, K.; Grossniklaus, U.; de Vries, S.C. The Arabidopsis somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase 1 gene is expressed in developing ovules and embryos and enhances embryogenic competence in culture. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Takaya, K.; Kurata, N. Expression of SERK family receptor-like protein kinase genes in rice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1730, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Jin, H.; Tzfira, T.; Li, J. Multiple mechanism-mediated retention of a defective brassinosteroid receptor in the endoplasmic reticulum of Arabidopsis(w). Plant Cell 2008, 20, 3418–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, R.; Huang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Burlingame, A.L.; et al. OsBRI1 activates BR signaling by preventing binding between the TPR and kinase domains of OsBSK3 via phosphorylation. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 1149–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceserani, T.; Trofka, A.; Gandotra, N.; Nelson, T. VH1/BRL2 receptor-like kinase interacts with vascular-specific adaptor proteins VIT and VIK to influence leaf venation. Plant J. 2009, 57, 1000–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wen, J.; Lease, K.A.; Doke, J.T.; Tax, F.E.; Walker, J.C. BAK1, an Arabidopsis LRR receptor-like protein kinase, interacts with BRI1 and modulates brassinosteroid signaling. Cell 2002, 110, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, C.; Boutrot, F.; Segonzac, C.; Schwessinger, B.; Gimenez-Ibanez, S.; Chinchilla, D.; Rathjen, J.P.; de Vries, S.C.; Zipfel, C. Brassinosteroids inhibit pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered immune signaling independent of the receptor kinase BAK1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Xiong, L.; Yang, Y. Rice SERK1 gene positively regulates somatic embryogenesis of cultured cell and host defense response against fungal infection. Planta 2005, 222, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, T.; Cano-Delgado, A.; Seto, H.; Hiranuma, S.; Fujioka, S.; Yoshida, S.; Chory, J. Binding of brassinosteroids to the extracellular domain of plant receptor kinase BRI1. Nature 2005, 433, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Zhou, J.M. Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases, central players in plant receptor kinase-mediated signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2018, 69, 267–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Yan, K.; Han, J.T.; Tao, L.; Lv, M.H.; Shi, T.; He, Y.X.; Wierzba, M.; Tax, F.E.; Li, J. Scanning for new BRI1 mutations via tilling analysis. Plant Physiol. 2017, 174, 1881–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Goshe, M.B.; Soderblom, E.J.; Phinney, B.S.; Kuchar, J.A.; Li, J.; Asami, T.; Yoshida, S.; Huber, S.C.; Clouse, S.D. Identification and functional analysis of in vivo phosphorylation sites of the Arabidopsis brassinosteroid-insensitive1 receptor kinase. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 1685–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.H.; Bleecker, A.B. Plant receptor-like kinase gene family, diversity, function, and signaling. Sci STKE 2001, 113, re22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Kong, L.; Zou, M.; Lu, G.; Cao, J.; Yu, X. Identification, expression, and comparative genomic analysis of the IPT and CKX gene families in chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. Pekinensis). BMC Genomics 2013, 14, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clouse, S.D.; Zurek, D.M.; McMorris, T.C.; Baker, M.E. Effect of brassinolide on gene expression in elongating soybean epicotyls. Plant Physiol 1992, 100, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.H.; Clouse, S.D. Brassinolide affects the rate of cell division in isolated leaf protoplasts of petunia hybrida. Plant Cell Rep. 1998, 17, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Gupta, A.; Laxmi, A. Glucose control of root growth direction in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 2981–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Gupta, A.; Laxmi, A. Glucose and phytohormone interplay in controlling root directional growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal. Behav. 2014, 9, e29219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Shang, X.; Oh, E.; Fan, M.; Bai, Y.; Rodolfo, Z.; Sun, T.; Wang, Z. Brassinosteroid, gibberellin and phytochrome impinge on a common transcription module in Arabidopsis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Nagpal, P.; Vitart, V.; McMorris, T.C.; Chory, J. A role for brassinosteroids in light-dependent development of Arabidopsis. Science 1996, 272, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carsten, M.; Christian, B.; Janina, L.; Ursula, U.; Elmar, W.W.; Thomas, A. A novel stress-inducible 12-oxophytodienoate reductase from Arabidopsis thaliana provides a potential link between brassinosteroid-action and jasmonic-acid synthesis. J. Plant Physiol. 2000, 157, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Han, C.; Peng, W.; Peng, Z.; Xiong, X.; Zhu, Q.; Gao, B.; Xie, D.; Ren, C. Brassinosteroid negatively regulates jasmonate inhibition of root growth in arabidopsis. Plant Signal. Behav. 2010, 5, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Han, C.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, K.; Huang, H.; Ren, C. Brassinosteroid enhances jasmonate-induced anthocyanin accumulation in Arabidopsis seedlings. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2011, 53, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidel, L.; Ana, I.C. Emerging roles of vascular brassinosteroid receptors of the BRI1-like family. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2019, 51, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Sun, J.; Bai, J.; Han, Y.; Fan, F.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Han, Z.; Lu, D. Identification of critical cysteine sites in brassinosteroid-insensitive 1 and novel signaling regulators using a transient expression system. New Phytol. 2019, 222, 1405–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mao, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, N.; Chen, X. Brassinolide inhibits flavonoid biosynthesis and red-flesh coloration via the mdbeh2.2-mdmyb60 complex in apple. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 6382–6399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chono, M.; Honda, I.; Zeniya, H.; Yoneyama, K.; Saisho, D.; Takeda, K.; Takatsuto, S.; Hoshino, T.; Watanabe, Y. A semidwarf phenotype of barley uzu results from a nucleotide substitution in the gene encoding a putative brassinosteroid receptor. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koka, C.V.; Cerny, R.E.; Gardner, R.G.; Noguchi, T.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Clouse, S.D. A putative role for the tomato genes dumpy and CURL-3 in brassinosteroid biosynthesis and response. Plant Physiol. 2000, 122, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinchilla, D.; Zipfel, C.; Robatzek, S.; Kemmerling, B.; Nurnberger, T.; Jones, J.D.; Felix, G.; Boller, T. A flagellin-induced complex of the receptor FLS2 and BAK1 initiates plant defence. Nature 2007, 448, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Yang, Y.; Gao, C.; Ma, J.; Shah, K.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, C.; Xing, L.; Han, M.; Na, A.; et al. Transcriptome analysisi reveals new insight into MdBAK1-mediated plant growth in malus domestica. J. Agric Food Chem. 2019, 35, 9757–9771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Ma, J.; Song, C.; An, N.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, C.; Qi, S.; Han, M. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling analysis of brassinolide signal transduction genes regulating apple tree architecture. Acta Physiol. Plant 2017, 39, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Luan, L.Y.; Zhang, Z.W.; Huo, S.S.; Gao, X.; Fang, Y.L.; Xi, Z.M. Phenolic profiles and antioxidant properties of young wines made from yan73 (Vitis vinifera L.) and cabernet sauvignon (Vitis vinifera L.) Grapes treated by 24-epibrassinolide. Molecules 2014, 19, 10189–10207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, P.; Ma, X.; Lin, W.; Chen, S.; Mishev, K.; Lu, D.; Kumar, R.; Vanhoutte, I.; et al. Regulation of Arabidopsis brassinosteroid receptor BRI1 endocytosis and degradation by plant U-box PUB12/PUB13-mediated ubiquitination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusotoit-Coucaud, A.; Brunel, N.; Kongsawadworakul, P.; Viboonjun, U.; Lacointe, A.; Julien, J.L.; Chrestin, H.; Sakr, S. Sucrose importation into laticifers of Hevea brasiliensis, in relation to ethylene stimulation of latex production. Ann. Bot. 2009, 104, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symons, G.M.; Davies, C.; Shavrukov, Y.; Dry, I.B.; Reid, J.B.; Thomas, M.R. Grapes on steroids. Brassinosteroids are involved in grape berry ripening. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Yang, H.; Dai, L.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L. F Genome-wide identification and response stress expression analysis of the BES1 family in rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis muell. Arg.). Peer J. 2022, 10, e13189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene Name | Locus | Strand | CDS (bp) | Amino Acid (aa) | Molecular Weight | PI | GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HbBRI1 | scaffold0387 | + | 3688 | 1228 | 134,151.21 | 6.19 | −0.076 |
| HbBRL1 | scaffold0057 | − | 3679 | 1225 | 133,394.55 | 6.18 | −0.041 |
| HbBRL2-1 | scaffold0406 | − | 3409 | 1135 | 124,018.58 | 5.94 | −0.003 |
| HbBRL2-2 | scaffold0740 | − | 3406 | 1134 | 123,651.87 | 5.82 | −0.002 |
| HbBRL3 | scaffold1656 | − | 3667 | 1221 | 132,827.64 | 5.48 | −0.013 |
| HbBAK1a | scaffold0043 | + | 1206 | 402 | 43,793.59 | 8.15 | 0.117 |
| HbBAK1b | scaffold0283 | − | 1872 | 624 | 69,033.25 | 5.41 | −0.135 |
| HbBAK1c | scaffold0441 | − | 1845 | 615 | 68,225.60 | 5.76 | −0.218 |
| HbBAK1d | scaffold0577 | − | 1848 | 616 | 68,547.43 | 6.01 | −0.199 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, B.; Dai, L.; Yang, H.; Zhao, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, L. Comprehensive Analysis of BR Receptor Expression under Hormone Treatment in the Rubber Tree (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.). Plants 2023, 12, 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12061280
Guo B, Dai L, Yang H, Zhao X, Liu M, Wang L. Comprehensive Analysis of BR Receptor Expression under Hormone Treatment in the Rubber Tree (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.). Plants. 2023; 12(6):1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12061280
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Bingbing, Longjun Dai, Hong Yang, Xizhu Zhao, Mingyang Liu, and Lifeng Wang. 2023. "Comprehensive Analysis of BR Receptor Expression under Hormone Treatment in the Rubber Tree (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.)" Plants 12, no. 6: 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12061280
APA StyleGuo, B., Dai, L., Yang, H., Zhao, X., Liu, M., & Wang, L. (2023). Comprehensive Analysis of BR Receptor Expression under Hormone Treatment in the Rubber Tree (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.). Plants, 12(6), 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12061280







