Genomic Analysis Highlights Putative Defective Susceptibility Genes in Tomato Germplasm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Homozygous SNPs/Indels
2.2. Heterozygous SNPs/Indels
2.3. sgRNA Design
2.4. Disease Assay
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Mining on S-Genes
3.2. SNP/Indel Data
3.3. SNP Annotation
3.4. Single Guide RNA (sgRNA) Design on Target Genes
3.5. Disease Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fry, W. Phytophthora Infestans: The Plant (and R Gene) Destroyer. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2008, 9, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schie, C.C.N.V.; Takken, F.L.W. Susceptibility Genes 101: How To Be A Good Host. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2014, 52, 551–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, S.S.-E.-A.; Mukhtar, M.S.; Mansoor, S. Genome Editing: Targeting Susceptibility Genes for Plant Disease Resistance. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckardt, N.A. Plant Disease Susceptibility Genes? Plant Cell 2002, 14, 1983–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pavan, S.; Jacobsen, E.; Visser, R.G.F.; Bai, Y. Loss Of Susceptibility As a Novel Breeding Strategy for Durable and Broad-Spectrum Resistance. Mol. Breed. 2009, 25, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piffanelli, P.; Zhou, F.; Casais, C.; Orme, J.; Jarosch, B.; Schaffrath, U.; Collins, N.C.; Panstruga, R.; Schulze-Lefert, P. The Barley Mlo Modulator of Defense and Cell Death Is Responsive to Biotic and Abiotic Stress Stimuli. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pépin, N.; Hebert, F.O.; Joly, D.L. Genome-Wide Characterization of the Mlo Gene Family in Cannabis Sativa Reveals Two Genes As Strong Candidates for Powdery Mildew Susceptibility. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 729261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo-Garcia, J.; Kusch, S.; Panstruga, R. Magical Mystery Tour: Mlo Proteins in Plant Immunity and Beyond. New Phytol. 2014, 204, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunarti, S.; Kissoudis, C.; Van Der Hoek, Y.; Van Der Schoot, H.; Visser, R.G.; Van Der Linden, C.G.; Van De Wiel, C.; Bai, Y. Drought Stress Interacts with Powdery Mildew Infection in Tomato. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 845379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiano, M.; Pavan, S.; Catalano, D.; Zheng, Z.; Bracuto, V.; Lotti, C.; Visser, R.G.F.; Ricciardi, L.; Bai, Y. Identification of Candidate Mlo Powdery Mildew Susceptibility Genes in Cultivated Solanaceae and Functional Characterization of Tobacco Ntmlo1. Transgenic Res. 2015, 24, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pessina, S.; Pavan, S.; Catalano, D.; Gallotta, A.; Visser, R.G.; Bai, Y.; Malnoy, M.; Schouten, H.J. Characterization of the Mlo Gene Family in Rosaceae and Gene Expression Analysis in Malus Domestica. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Z.; Appiano, M.; Van Tuinen, A.; Meijer-Dekens, F.; Schipper, D.; Gao, D.; Huibers, R.; Visser, R.G.; Bai, Y.; Wolters, A.-M.A. Discovery and Characterization of A Novel Tomato Mlo Mutant from an Ems Mutagenized Micro-Tom Population. Genes 2021, 12, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Shan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Gao, C.; Qiu, J.-L. Simultaneous Editing of Three Homoeoalleles in Hexaploid Bread Wheat Confers Heritable Resistance to Powdery Mildew. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 947–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huibers, R.P.; Loonen, A.E.H.M.; Gao, D.; Van Den Ackerveken, G.; Visser, R.G.F.; Bai, Y. Powdery Mildew Resistance in Tomato by Impairment of Slpmr4 and Sldmr1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, E67467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Maioli, A.; Yan, Z.; Bai, Y.; Valentino, D.; Milani, A.M.; Pompili, V.; Comino, C.; Lanteri, S.; Moglia, A.; et al. Crispr/Cas9-Based Knock-Out of the Pmr4 Gene Reduces Susceptibility to Late Blight in Two Tomato Cultivars. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santillán Martínez, M.I.; Bracuto, V.; Koseoglou, E.; Appiano, M.; Jacobsen, E.; Visser, R.G.F.; Wolters, A.-M.A.; Bai, Y. Crispr/Cas9-Targeted Mutagenesis of the Tomato Susceptibility Gene Pmr4 for Resistance against Powdery Mildew. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Wolters, A.-M.A.; Vossen, J.H.; Rouwet, M.E.; Loonen, A.E.H.M.; Jacobsen, E.; Visser, R.G.F.; Bai, Y. Silencing of Six Susceptibility Genes Results in Potato Late Blight Resistance. Transgenic Res. 2016, 25, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vogel, J.P.; Raab, T.K.; Somerville, C.R.; Somerville, S.C. Mutations in Pmr5 Result in Powdery Mildew Resistance and Altered Cell Wall Composition. Plant J. 2004, 40, 968–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, J.P.; Raab, T.K.; Schiff, C.; Somerville, S.C. Pmr6, A Pectate Lyase–Like Gene Required for Powdery Mildew Susceptibility in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 2095–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiniquy, D.; Underwood, W.; Corwin, J.; Ryan, A.; Szemenyei, H.; Lim, C.C.; Stonebloom, S.H.; Birdseye, D.S.; Vogel, J.; Kliebenstein, D.; et al. Pmr5, an Acetylation Protein at the Intersection of Pectin Biosynthesis and Defense against Fungal Pathogens. Plant J. 2019, 100, 1022–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Claus, L.A.; Leslie, M.E.; Tao, K.; Wu, Z.; Liu, J.; Yu, X.; Li, B.; Zhou, J.; Savatin, D.V. Ligand-Induced Monoubiquitination of Bik1 Regulates Plant Immunity. Nature 2020, 581, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Bi, K.; He, Z.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Xie, J.; Jiang, D. Arabidopsis Mutant Bik1 Exhibits Strong Resistance to Plasmodiophora Brassicae. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, J.; Finlayson, S.A.; Salzman, R.A.; Shan, L.; Zhu-Salzman, K. Botrytis-Induced Kinase1 Modulates Arabidopsis Resistance to Green Peach Aphids via Phytoalexin Deficient4. Plant Physiol. 2014, 165, 1657–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahn, I.P. Disturbance of the Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Signalling Pathway is Responsible for the Resistance of Arabidopsis Dnd1 against Pectobacterium Carotovorum Infection. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2007, 8, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Wolters, A.-M.A.; Loonen, A.E.H.M.; Huibers, R.P.; Van Der Vlugt, R.; Goverse, A.; Jacobsen, E.; Visser, R.G.F.; Bai, Y. Down-Regulation of Arabidopsis Dnd1 Orthologs in Potato and Tomato Leads to Broad-Spectrum Resistance to Late Blight and Powdery Mildew. Transgenic Res. 2016, 25, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brewer, H.C.; Hawkins, N.D.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E. Mutations in the Arabidopsis Homoserine Kinase Gene Dmr1 Confer Enhanced Resistance to Fusarium culmorum and F. graminearum. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navet, N.; Tian, M. Efficient Targeted Mutagenesis in Allotetraploid Sweet Basil By Crispr/Cas9. Plant Direct 2020, 4, E00233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, A.J.; Laval, V.; Geri, C.; Laird, J.; Tomos, A.D.; Hooks, M.A.; Milner, J.J. Components of Arabidopsis Defense-and Ethylene-Signaling Pathways Regulate Susceptibility to Cauliflower Mosaic virus by Restricting Long-Distance Movement. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2007, 20, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clarke, J.D.; Aarts, N.; Feys, B.J.; Dong, X.; Parker, J.E. Constitutive Disease Resistance Requires Eds1 in the Arabidopsis Mutants Cpr1 and Cpr6 and is Partially Eds1-Dependent in Cpr5. Plant J. 2001, 26, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Zhao, C.; Wu, G.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, D. Sr1, A Calmodulin-Binding Transcription Factor, Modulates Plant Defense and Ethylene-Induced Senescence by Directly Regulating Ndr1 and Ein3. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 1847–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouko, M.O.; Sambade, A.; Brandner, K.; Niehl, A.; Pena, E.; Ahad, A.; Heinlein, M.; Nick, P. Tobacco Mutants with Reduced Microtubule Dynamics are Less Susceptible to Tmv. Plant J. 2010, 62, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Guo, R.; Gan, S.; Liu, C.-J.; Zhang, K. S5h/Dmr6 Encodes A Salicylic Acid 5-Hydroxylase that Fine-Tunes Salicylic Acid Homeostasis. Plant Physiol. 2017, 175, 1082–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeilmaker, T.; Ludwig, N.; Elberse, J.; Seidl, M.; Berke, L.; Van Doorn, A.; Schuurink, R.; Snel, B.; Van den Ackerveken, G. DOWNY MILDEW RESISTANT 6 and DMR6-LIKE OXYGENASE1 are partially redundant but distinct suppressors ofimmunity in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2015, 81, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomazella, D.P.D.T.; Seong, K.; Mackelprang, R.; Dahlbeck, D.; Geng, Y.; Gill, U.S.; Qi, T.; Pham, J.; Giuseppe, P.; Lee, C.Y. Loss of Function of A Dmr6 Ortholog in Tomato Confers Broad-Spectrum Disease Resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, E2026152118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO); Mullins, E.; Bresson, J.L.; Dalmay, T.; Dewhurst, I.C.; Epstein, M.M.; Firbank, L.G.; Guerche, P.; Hejatko, J.; Moreno, F.J.; et al. Criteria for Risk Assessment of Plants Produced by Targeted Mutagenesis, Cisgenesis and Intragenesis. Efsa J. 2022, 20, E07618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO); Mullins, E.; Bresson, J.L.; Dalmay, T.; Dewhurst, I.C.; Epstein, M.M.; Firbank, L.G.; Guerche, P.; Hejatko, J.; Moreno, F.J. Updated Scientific Opinion on Plants Developed through Cisgenesis and Intragenesis. Efsa J. 2022, 20, E07621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO). Scientific Opinion Addressing the Safety Assessment of Plants Developed through Cisgenesis and Intragenesis. Efsa J. 2012, 10, 2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, T.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Yu, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lun, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, X. Genomic Analyses Provide Insights into the History of Tomato Breeding. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessina, S.; Palmieri, L.; Bianco, L.; Gassmann, J.; Van De Weg, E.; Visser, R.G.; Magnago, P.; Schouten, H.J.; Bai, Y.; Riccardo Velasco, R. Frequency of A Natural Truncated Allele of Mdmlo19 in the Germplasm of Malus domestica. Mol. Breed. 2017, 37, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tegtmeier, R.; Pompili, V.; Singh, J.; Micheletti, D.; Silva, K.J.P.; Malnoy, M.; Khan, A. Candidate Gene Mapping Identifies Genomic Variations in the Fire Blight Susceptibility Genes Hipm and Dipm across the Malus germplasm. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirrello, C.; Zeilmaker, T.; Bianco, L.; Giacomelli, L.; Moser, C.; Vezzulli, S. Mining Grapevine Downy Mildew Susceptibility Genes: A Resource for Genomics-Based Breeding and Tailored Gene Editing. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenser, T.; Theißen, G. Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Convergent Crop Domestication. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acquadro, A.; Barchi, L.; Gramazio, P.; Portis, E.; Vilanova, S.; Comino, C.; Plazas, M.; Prohens, J.; Lanteri, S. Coding Snps Analysis Highlights Genetic Relationships and Evolution Pattern in Eggplant Complexes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, E0180774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prajapati, A.; Nain, V. Screening of Crispr/Cas9 Grna for Mimicking Powdery Mildew Resistant Mlo Ol-2 Mutant. Bioinformation 2021, 17, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Wu, S.; He, P.; Shan, L. Phosphorylation of Receptor-like Cytoplasmic Kinases by Bacterial Flagellin. Plant Signal. Behav. 2010, 5, 598–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Wei, X.; Yan, L.; Liu, D.; Ma, Y.; Guo, Y.; Peng, C.; Zhou, H.; Yang, C.; Lou, Z. Identification and Functional Analysis of Phosphorylation Residues of the Arabidopsis Botrytis-Induced Kinase1. Protein Cell 2013, 4, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cingolani, P.; Platts, A.; Wang, L.L.; Coon, M.; Nguyen, T.; Wang, L.; Land, S.J.; Lu, X.; Ruden, D.M. A Program for Annotating and Predicting the Effects of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms, Snpeff: Snps in the Genome of Drosophila Melanogaster Strain W1118; Iso-2; Iso-3. Fly 2012, 6, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Bao, Z.; Li, H.; Lyu, Y.; Zan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Fang, Y.; Wu, K.; et al. Graph pangenome captures missing heritability and empowers tomato breeding. Nature 2022, 606, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

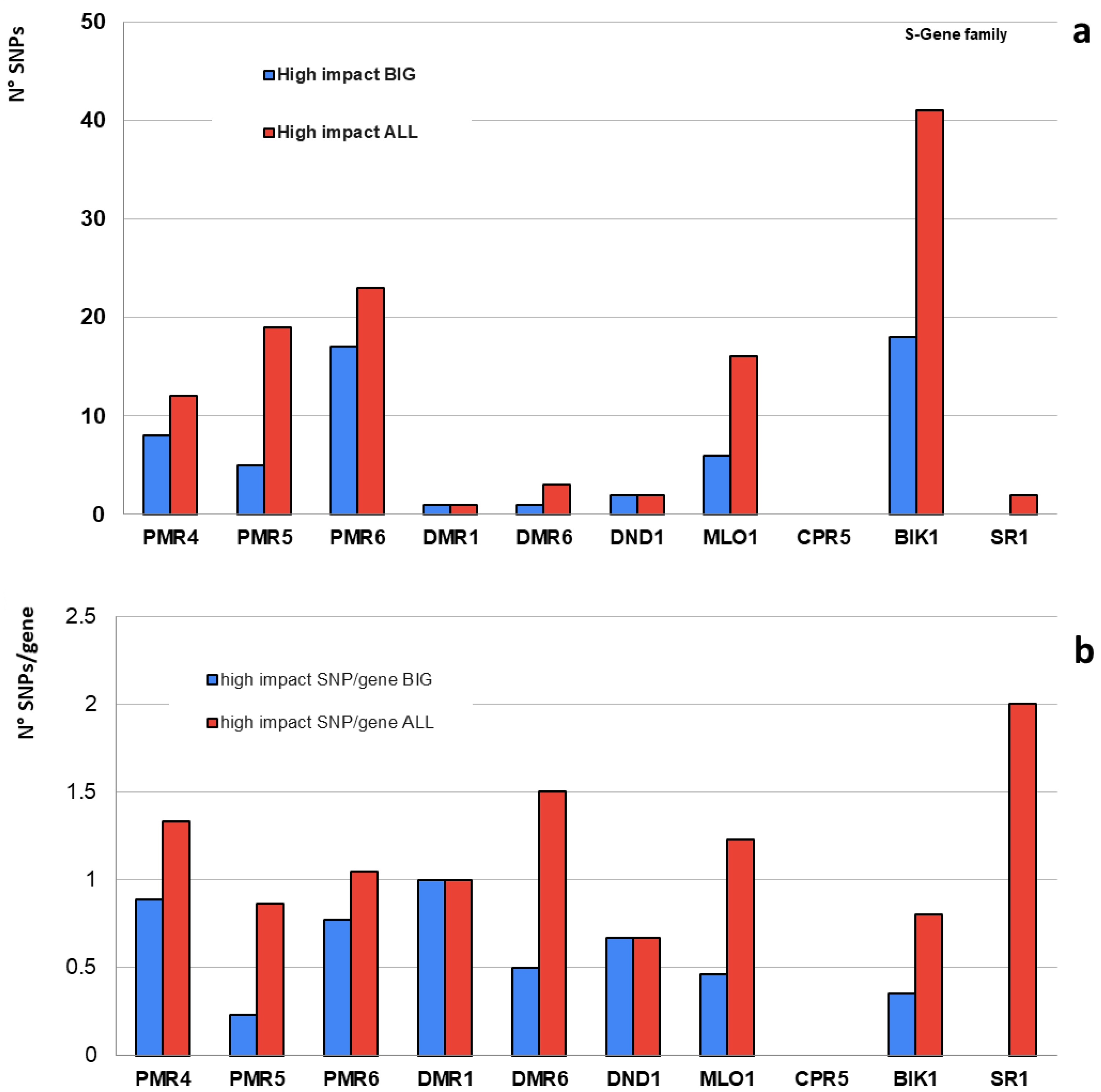

| S-Gene Family | Tomato Ortholog | Genes | High Impact | High Impact (SNP/Gene) | Moderate Impact | Low Impact | N° Variants (Total) | Total SNP/Gene | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIG | ALL | BIG | ALL | BIG | ALL | BIG | ALL | BIG | ALL | BIG | ALL | |||
| PMR4 | Solyc07g053980 | 9 | 8 | 12 | 0.9 | 1.3 | 95 | 199 | 166 | 288 | 2473 | 4033 | 274.8 | 448.1 |
| PMR5 | Solyc06g082070 | 22 | 5 | 19 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 172 | 274 | 151 | 257 | 3341 | 5267 | 151.9 | 239.4 |
| PMR6 | Solyc11g008140 | 22 | 17 | 23 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 104 | 188 | 120 | 187 | 8065 | 12,989 | 366.6 | 590.4 |
| DMR1 | Solyc04g008760 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 12 | 147 | 215 | 147.0 | 215.0 |
| DMR6 | Solyc03g080190 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 7 | 19 | 7 | 19 | 434 | 775 | 217.0 | 387.5 |
| DND1 | Solyc02g088560 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 16 | 38 | 18 | 46 | 410 | 806 | 136.7 | 268.7 |
| MLO1 | Solyc04g049090 | 13 | 6 | 16 | 0.5 | 1.2 | 67 | 120 | 60 | 121 | 5309 | 7787 | 408.4 | 599.0 |
| CPR5 | Solyc04g054170 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 9 | 653 | 873 | 653.0 | 873.0 |
| BIK1 | Solyc10g084770 | 51 | 18 | 41 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 237 | 452 | 272 | 500 | 12,789 | 21,376 | 250.8 | 419.1 |
| SR1 | Solyc01g105230 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0.0 | 2.0 | 9 | 24 | 4 | 15 | 89 | 257 | 89.0 | 257.0 |
| Total | - | 125 | 58 | 119 | - | - | 715 | 1326 | 810 | 1454 | 33,710 | 54,378 | - | - |
| Average | - | 13 | 6 | 12 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 72 | 133 | 81 | 145 | 3371 | 5438 | 269.5 | 429.7 |
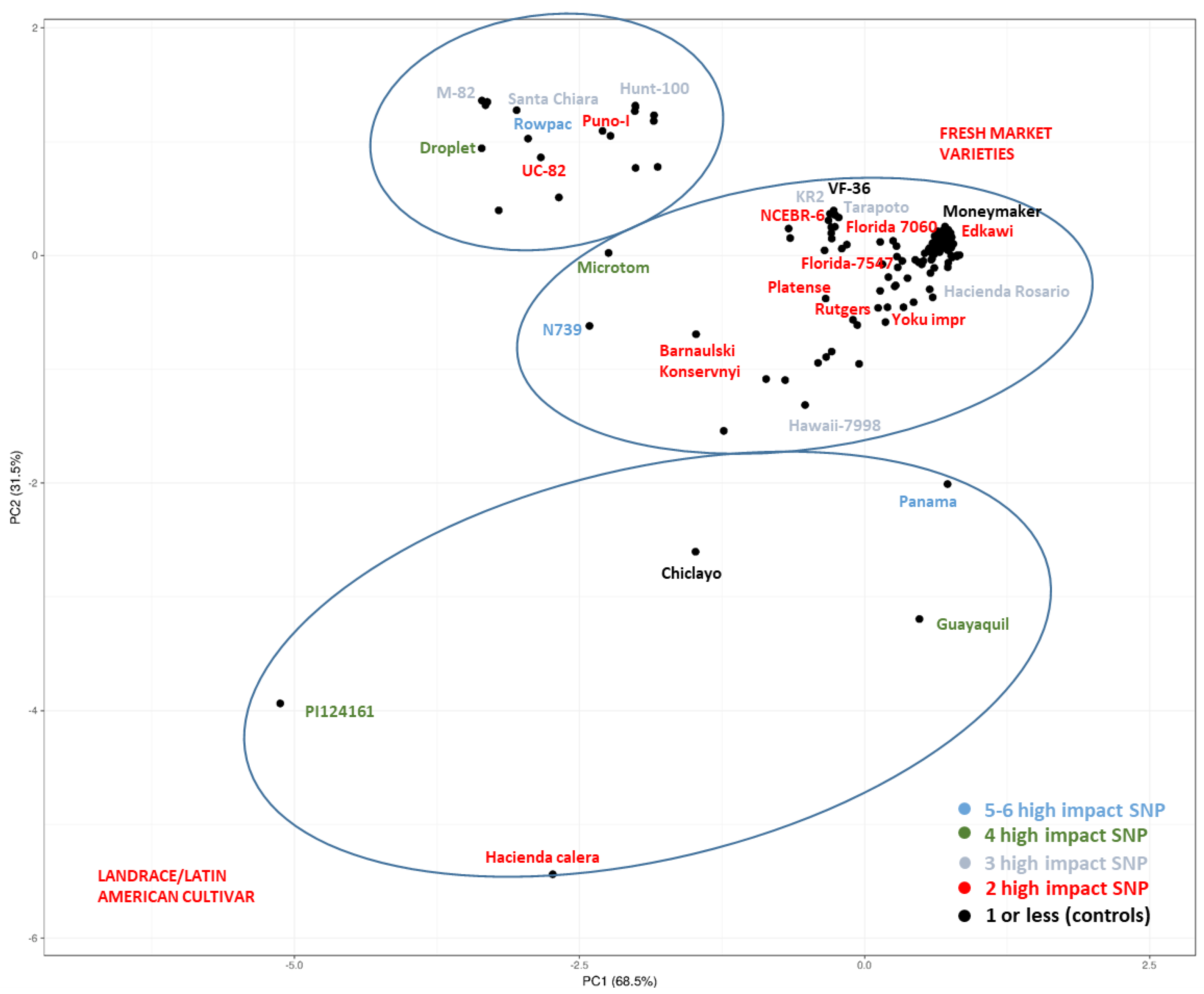
| High-Impact SNPs | High-Impact SNPs in S-Genes | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype | Name | TGRC/PI-CGN/EA | Categories | Total | Hom. | Heteroz. | Total | Hom. | Heteroz. |
| TS-214 | Panama | -/-/- | Landrace | 620 | 569 | 51 | 7 | 6 | 1 |
| TS-074 | N 739 | -/-/- | Fresh market | 647 | 587 | 60 | 5 | 5 | 0 |
| TS-186 | Rowpac | LA3214/-/- | Modern processing | 445 | 423 | 22 | 5 | 5 | 0 |
| TS-007 | Micro-Tom | LA3911/-/- | Modern fresh market | 901 | 724 | 177 | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| TS-224 | Guayaquil | LA0410/PI 258474/- | Landrace/Latin American cultivar | 779 | 767 | 12 | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| TS-296 | Droplet | -/-/- | - | 719 | 668 | 51 | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| TS-409 | - | -/PI124161/- | Landrace | 1526 | 1263 | 263 | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| TS-003 | M-82 | LA3475/-/- | Modern processing | 515 | 424 | 91 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| TS-004 | Hawaii 7998 | LA3856/-/- | Inbreed line | 692 | 606 | 86 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| TS-011 | KR2 | -/-/- | Modern fresh market | 565 | 392 | 173 | 5 | 3 | 2 |
| TS-135 | Hacienda Rosario | LA0466/PI 258469/- | Landrace/Latin American cultivar | 334 | 301 | 33 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| TS-150 | Tarapoto | LA2285/-/- | Landrace/Latin American cultivar | 352 | 326 | 26 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| TS-190 | Santa Chiara | -/-/- | Cultivar | 437 | 366 | 71 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| TS-277 | Hunt100 | LA3144/-/- | Modern processing | 266 | 236 | 30 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| TS-005 | Edkawi | LA2711/-/- | Vintage fresh market | 191 | 116 | 75 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| TS-012 | yoku improvement | -/-/- | Modern fresh market | 505 | 400 | 105 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| TS-078 | - | -/-/EA02895 | Processing tomato | 300 | 273 | 27 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| TS-089 | - | -/-/EA01185 | Processing tomato | 457 | 371 | 86 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| TS-090 | - | -/-/EA02753 | Cocktail tomato | 368 | 286 | 82 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| TS-108 | Puno I | -/-/EA01989 | Processing tomato | 334 | 312 | 22 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| TS-121 | NC EBR-6 | LA3846/-/- | Modern fresh market | 267 | 225 | 42 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| TS-122 | Rutgers | LA1090/-/- | Vintage fresh market | 70 | 58 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| TS-127 | Hacienda Calera | LA0113/-/- | Landrace/Latin American cultivar | 1589 | 886 | 703 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| TS-143 | Florida 7547 | LA4025/-/- | Modern fresh market | 182 | 163 | 19 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| TS-147 | - | -/-/- | - | 482 | 404 | 78 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| TS-171 | UC-82 | LA1706/-/- | Modern processing | 334 | 305 | 29 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| TS-204 | Florida 7060 | LA3840/-/- | Modern fresh market | 247 | 202 | 45 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| TS-220 | Barnaulski Konservnyi | -/-/- | Cultivar | 535 | 455 | 80 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| TS-225 | - | -/PI330336/EA05747 | Processing tomato | 172 | 108 | 64 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| TS-226 | Microtom | -/-/- | Cultivar | 436 | 400 | 36 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| TS-228 | M-82 | -/-/- | Cultivar | 398 | 369 | 29 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| TS-234 | - | -/-/EA01371 | Processing tomato | 234 | 219 | 15 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| TS-237 | Platense | LA3243/-/- | Vintage fresh market | 190 | 145 | 45 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| TS-245 | - | -/-/EA03126 | Processing tomato | 314 | 248 | 66 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| TS-276 | - | -/-/EA03650 | Cocktail/processing tomato | 160 | 124 | 36 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| TS-292 | - | -/-/EA06902 | Processing tomato | 298 | 278 | 20 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| TS-002 | Moneymaker | LA2706/-/- | Vintage fresh market | 207 | 151 | 56 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| TS-008 | E-6203 | LA4024/-/- | Modern processing | 380 | 302 | 78 | 4 | 1 | 3 |
| TS-009 | Ailsa Craig | LA2838A/-/- | Vintage fresh market | 182 | 128 | 54 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| TS-041 | - | -/-/EA02435 | Cocktail tomato | 262 | 218 | 44 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-043 | Moneymaker | -/-/EA00840 | Fresh market | 166 | 130 | 36 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-045 | - | -/PI303718/EA05578 | Processing tomato | 198 | 176 | 22 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-047 | - | -/-/EA01960 | Processing tomato | 144 | 125 | 19 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-049 | Earliana | LA3238/-/- | Vintage processing | 149 | 139 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-051 | - | -/-/- | - | 127 | 100 | 27 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-052 | 05-4126 (97-49-2) | -/-/- | Cultivar | 328 | 281 | 47 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| TS-055 | - | -/-/EA00448 | - | 176 | 117 | 59 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-058 | - | -/-/EA03577 | Processing tomato | 131 | 119 | 12 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-059 | - | -/-/EA02898 | Processing tomato | 690 | 516 | 174 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-068 | Chiclayo | LA0395/-/- | Latin American cultivar | 1640 | 185 | 1455 | 9 | 1 | 8 |
| TS-069 | Huachinango | LA1459/-/- | Latin American cultivar | 247 | 231 | 16 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-073 | Quarantino | -/-/- | - | 126 | 105 | 21 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-076 | - | -/-/EA01230 | Processing tomato | 156 | 129 | 27 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-081 | - | -/-/EA02761 | Processing tomato | 182 | 155 | 27 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-085 | - | -/-/- | - | 474 | 237 | 237 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| TS-086 | - | -/-/EA01684 | - | 139 | 118 | 21 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-095 | Moneymaker | -/-/- | Fresh market | 176 | 147 | 29 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| TS-100 | - | -/-/EA03456 | Processing | 134 | 117 | 17 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-112 | - | -/-/EA03083 | Processing tomato | 175 | 148 | 27 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-115 | - | -/-/EA03426 | Processing tomato | 243 | 222 | 21 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-117 | Scatolone di bolsena | -/-/- | Landrace | 214 | 104 | 110 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-125 | - | -/-/EA00422 | Processing tomato | 241 | 137 | 104 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| TS-128 | Pearson | LA0012/-/- | Vintage processing | 245 | 214 | 31 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-132 | Primabel | LA3903/-/- | Vintage fresh market | 136 | 116 | 20 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-133 | Peto95-43 | LA3528/-/- | Modern processing | 307 | 264 | 43 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-137 | Spagnoletta | -/-/- | Landrace | 305 | 136 | 169 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-142 | Roma | -/-/- | Vintage cultivar | 136 | 122 | 14 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| TS-151 | T-5 | LA2399/-/- | Modern fresh market | 625 | 529 | 96 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| TS-152 | Santa Cruz B | LA1021/-/- | Landrace/Latin American cultivar | 177 | 160 | 17 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-155 | Condine Red | LA0533/-/- | Vintage fresh market, monogenic | 130 | 119 | 11 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-157 | - | -/-/EA03648 | Processing tomato | 121 | 104 | 17 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-160 | - | -/-/EA03533 | Processing tomato | 221 | 185 | 36 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-163 | Marmande | LA1504/-/- | Vintage fresh market | 129 | 114 | 15 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-166 | Piura | LA0404/-/- | Landrace/Latin American cultivar | 178 | 163 | 15 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| TS-167 | Tegucigalpa | LA0147/-/- | Landrace/Latin American cultivar | 158 | 135 | 23 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-168 | - | -/-/- | Landrace | 337 | 256 | 81 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-174 | - | -/-/EA00304 | Processing tomato | 212 | 191 | 21 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-176 | - | -/-/EA02669 | Processing tomato | 197 | 190 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-177 | - | -/-/EA01155 | Processing tomato | 127 | 108 | 19 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-180 | - | -/-/EA02728 | Processing tomato | 116 | 82 | 34 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-183 | - | -/-/EA02764 | Processing tomato | 154 | 133 | 21 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-184 | Tarapoto | LA2283/-/- | - | 338 | 225 | 113 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| TS-193 | Pantano dArdea | -/-/- | Landrace | 170 | 121 | 49 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-194 | - | -/-/- | - | 167 | 143 | 24 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-197 | Libanese | -/-/- | Landrace | 165 | 122 | 43 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-198 | - | -/-/EA00512 | - | 153 | 129 | 24 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-200 | Hot set | LA3320/-/- | Cultivar | 187 | 135 | 52 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-203 | Bell pepper-like | -/-/- | Landrace | 177 | 110 | 67 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-206 | Prince Borghese | LA0089/-/- | Vintage fresh market | 26 | 22 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-211 | NC 84173 | LA4354/-/- | Modern fresh market | 425 | 366 | 59 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-215 | Vrbikanske Nizke | -/-/- | Cultivar | 183 | 126 | 57 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| TS-235 | - | -/-/EA00892 | Processing tomato | 46 | 44 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-239 | NC EBR-5 | LA3845/-/- | Modern fresh market | 126 | 109 | 17 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| TS-242 | Ayacucho | LA0134C/-/- | Latin American cultivar | 530 | 332 | 198 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-251 | - | -/PI647249/EA04001 | - | 150 | 128 | 22 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-256 | - | LA2260/0/EA00744 | Latin American cultivar | 477 | 415 | 62 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-261 | - | LA1511/-/EA01444 | Wild species | 246 | 145 | 101 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| TS-263 | Rio Grande | LA3343/-/- | Processing tomato | 213 | 183 | 30 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-264 | King Humbert #1 | LA0025/-/- | Vintage fresh market | 134 | 119 | 15 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-268 | - | -/-/EA01915 | Cultivar | 147 | 130 | 17 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-274 | - | -/-/EA03613 | Cocktail/processing tomato | 266 | 241 | 25 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-278 | Early Santa Clara | LA0517/-/- | Vintage processing | 207 | 187 | 20 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TS-400 | - | -/-/- | Inbred line | 453 | 398 | 55 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Variety | Code | Type | DS (0–3) | Std. Error | n | p-Value | Reduction (%) | Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VF-36 | TS-1 | control | 3.00 | 0 | 20 | - | - | a |
| Money Maker | TS-2 | assayed | 2.96 | 0.03 | 28 | 0.326189 | 1.2% | a |
| Droplet | TS-296 | assayed | 2.87 | 0.09 | 15 | 0.164318 | 4.4% | a |
| M-82 | TS-003 | assayed | 2.42 | 0.14 | 33 | 0.000367 | 19.2% | b |
| Puno-I | TS-108 | assayed | 2.67 | 0.11 | 21 | 0.004900 | 11.1% | b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Maioli, A.; Lanteri, S.; Moglia, A.; Bai, Y.; Acquadro, A. Genomic Analysis Highlights Putative Defective Susceptibility Genes in Tomato Germplasm. Plants 2023, 12, 2289. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122289
Li R, Maioli A, Lanteri S, Moglia A, Bai Y, Acquadro A. Genomic Analysis Highlights Putative Defective Susceptibility Genes in Tomato Germplasm. Plants. 2023; 12(12):2289. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122289
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ruiling, Alex Maioli, Sergio Lanteri, Andrea Moglia, Yuling Bai, and Alberto Acquadro. 2023. "Genomic Analysis Highlights Putative Defective Susceptibility Genes in Tomato Germplasm" Plants 12, no. 12: 2289. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122289
APA StyleLi, R., Maioli, A., Lanteri, S., Moglia, A., Bai, Y., & Acquadro, A. (2023). Genomic Analysis Highlights Putative Defective Susceptibility Genes in Tomato Germplasm. Plants, 12(12), 2289. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122289







