Exogenous Calcium Induces Different Hydraulic Strategies in Response to Osmotic Stress in Maize Seedlings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
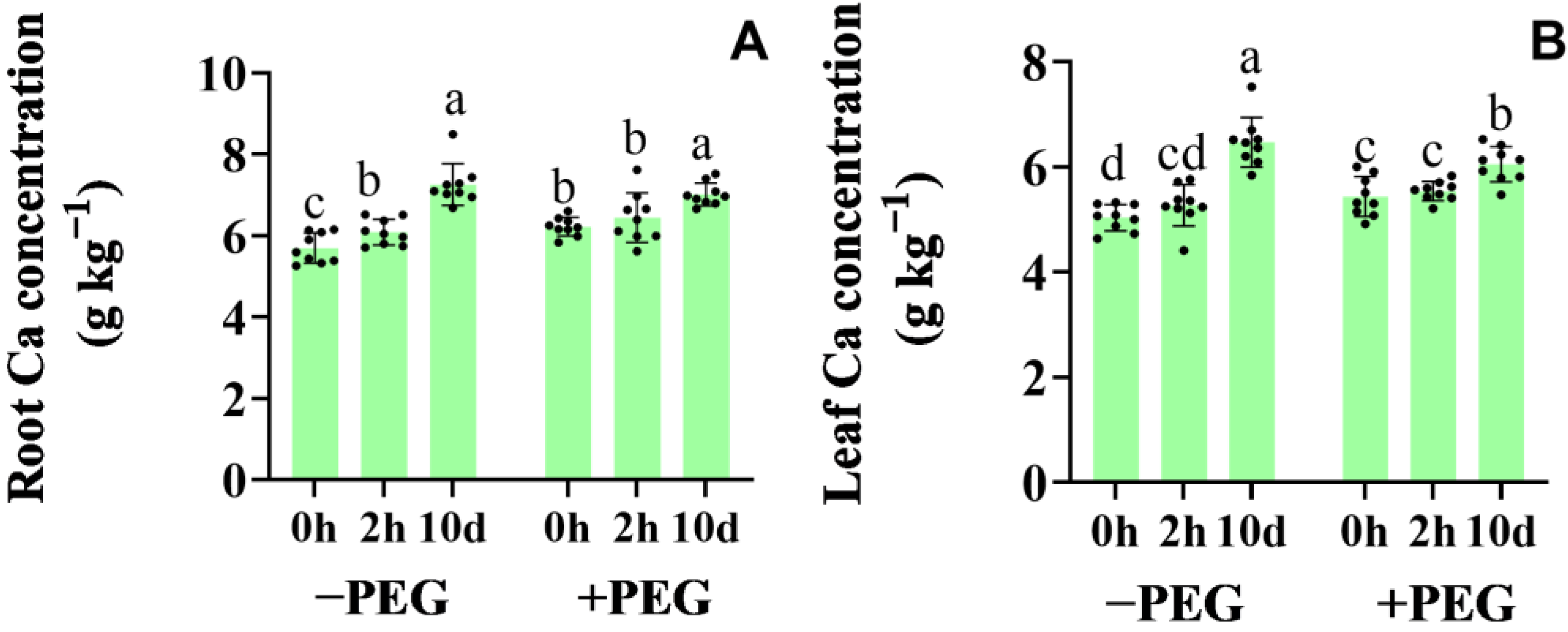
2.1. Calcium Contents
2.2. Effect of Calcium on the Photosynthetic Rate, Stomatal Conductance, and Transpiration Rate
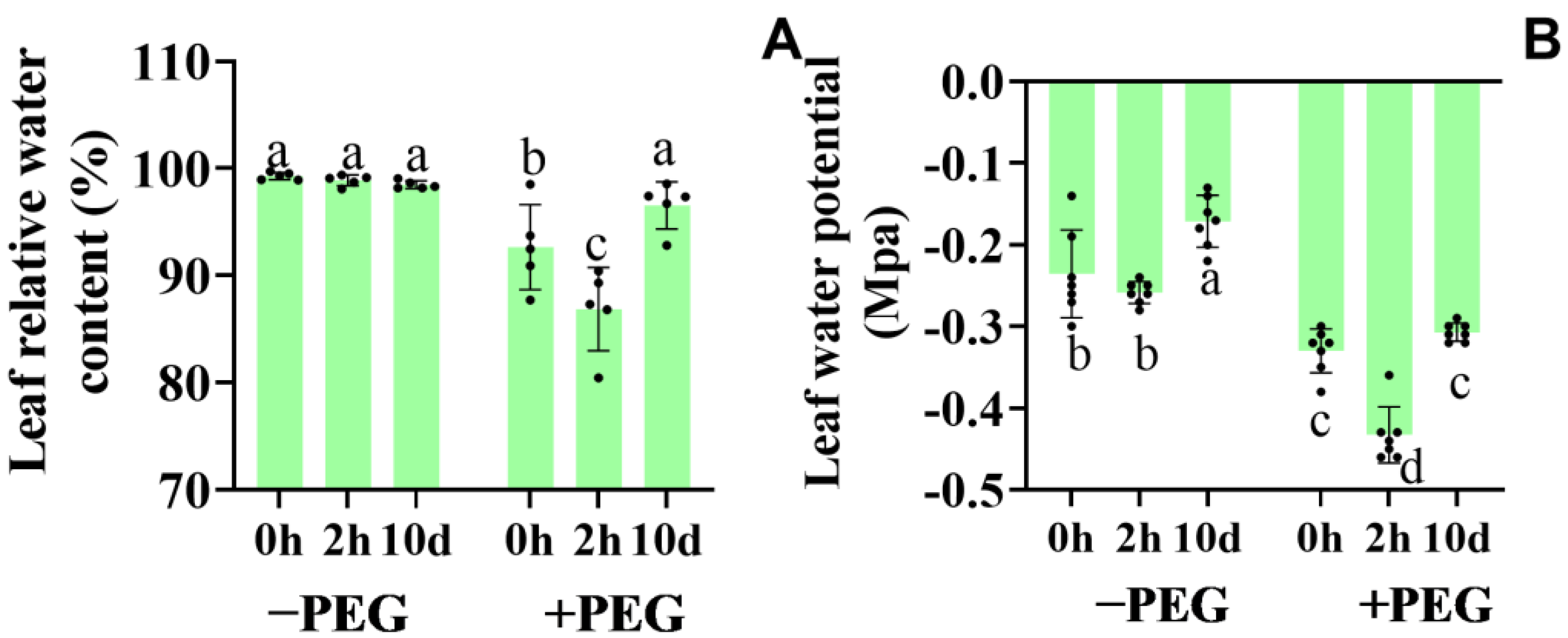
2.3. Effect of Calcium on the Leaf Relative Water Content and Leaf Water Potential
2.4. Effect of Calcium on the Root Water Uptake and Transport under Osmotic Stress
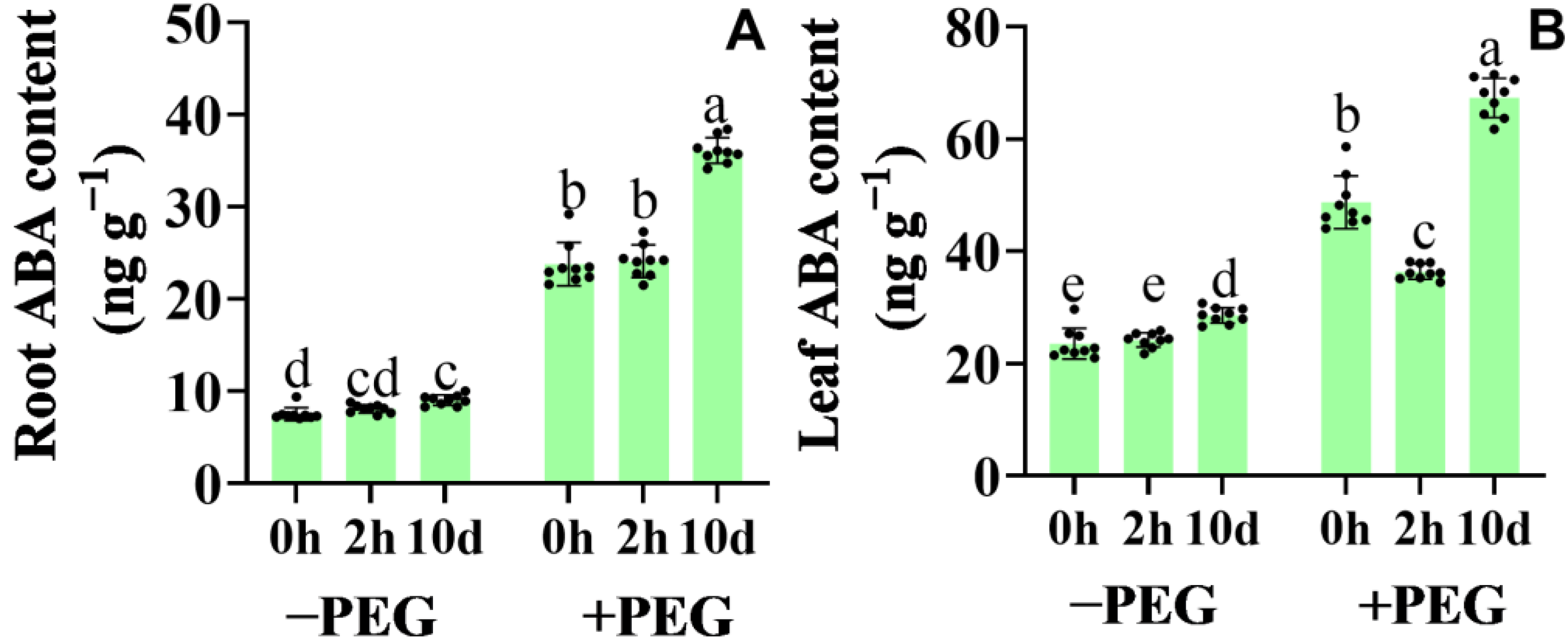
2.5. Calcium−Induced ABA Accumulation and Gene Expression of the Core ABA Signaling
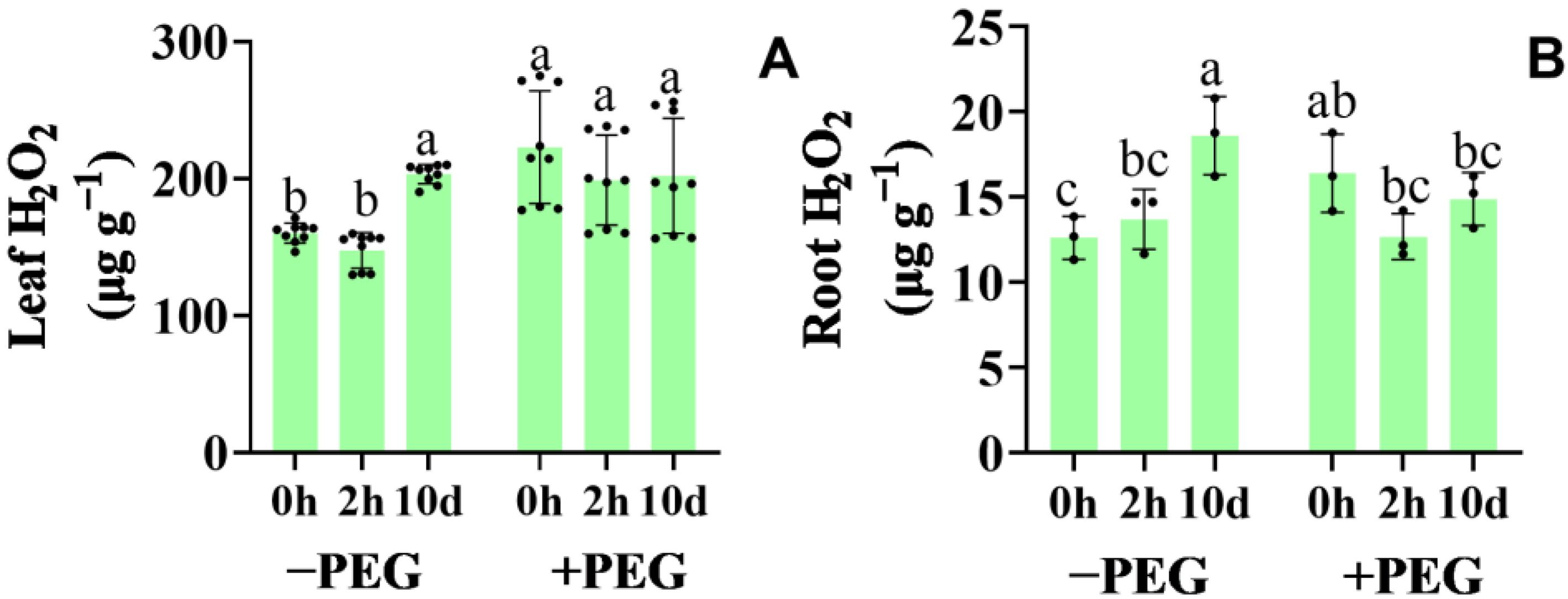
2.6. Effect of Calcium on the Hydrogen Peroxide Synthesis and Antioxidant Defense Systems
2.7. Effect of Calcium on the PIPs Expression during the Osmotic Stress Conditions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Experimental Design
4.2. Ca Concentration
4.3. Photosynthetic Rate, Stomatal Conductance, and Transpiration Rate
4.4. Leaf Relative Water Content and Water Potential
4.5. Root Hydraulic Conductivity (Lpr)
4.6. Osmotic Potential of Root Xylem Sap
4.7. Hydraulic Conductivity of Root Cortical Cells (Lpc)
4.8. Hydrogen Peroxide Content
4.9. Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
4.10. RNA Purification and Expression Analysis
4.11. ABA Content
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aldon, D.; Mbengue, M.; Mazars, C.; Galaud, J.P. Calcium Signalling in Plant Biotic Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Seo, P.J. Ca2+ talyzing Initial Responses to Environmental Stresses. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 26, 849–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAinsh, M.R.; Pittman, J.K. Shaping the calcium signature. New Phytol. 2009, 181, 275–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudla, J.; Becker, D.; Grill, E.; Hedrich, R.; Hippler, M.; Kummer, U.; Parniske, M.; Romeis, T.; Schumacher, K. Advances and current challenges in calcium signaling. New Phytol. 2018, 218, 414–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Schumaker, K.S.; Zhu, J.K. Cell signaling during cold, drought, and salt stress. Plant Cell 2002, 14 (Suppl. S1), S165–S183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudla, J.; Batistic, O.; Hashimoto, K. Calcium signals: The lead currency of plant information processing. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 541–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.; Li, Q.; Jiang, W.; Chen, G.; Xue, D.; Deng, F.; Zeng, F.; Chen, Z.H. Molecular Evolution of Calcium Signaling and Transport in Plant Adaptation to Abiotic Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.J.; Chu, S.P.; Schumacher, K.; Shimazaki, C.T.; Vafeados, D.; Kemper, A.; Hawke, S.D.; Tallman, G.; Tsien, R.Y.; Harper, J.F.; et al. Alteration of stimulus−specific guard cell calcium oscillations and stomatal closing in Arabidopsis det3 mutant. Science 2000, 289, 2338–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, J.F. Dissecting calcium oscillators in plant cells. Trends Plant Sci. 2001, 6, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Yang, H.; Xue, Y.; Kong, D.; Ye, R.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Theprungsirikul, L.; Shrift, T.; Krichilsky, B.; et al. OSCA1 mediates osmotic−stress−evoked Ca2+ increases vital for osmosensing in Arabidopsis. Nature 2014, 514, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Wallrad, L.; Almutairi, B.O.; Kudla, J. Ca2+ signaling in plant responses to abiotic stresses. J Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollist, H.; Zandalinas, S.I.; Sengupta, S.; Nuhkat, M.; Kangasjärvi, J.; Mittler, R. Rapid Responses to Abiotic Stress: Priming the Landscape for the Signal Transduction Network. Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 24, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.; Xiong, L.; Shi, H.; Yang, S.; Herrera−Estrella, L.R.; Xu, G.; Chao, D.Y.; Li, J.; Wang, P.Y.; Qin, F.; et al. Plant abiotic stress response and nutrient use efficiency. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 635–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Cao, J.; He, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, X.; Yang, Y. Molecular Mechanism for the Regulation of ABA Homeostasis During Plant Development and Stress Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, F.; Suzuki, T.; Osakabe, Y.; Betsuyaku, S.; Kondo, Y.; Dohmae, N.; Fukuda, H.; Yamaguchi−Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. A small peptide modulates stomatal control via abscisic acid in long−distance signalling. Nature 2018, 556, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.K. Abiotic Stress Signaling and Responses in Plants. Cell 2016, 167, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Chinnusamy, V.; Rodrigues, A.; Rubio, S.; Antoni, R.; Park, S.Y.; Cutler, S.R.; Sheen, J.; Rodriguez, P.L.; Zhu, J.K. In vitro reconstitution of an abscisic acid signalling pathway. Nature 2009, 462, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Verslues, P.E.; Zhu, J.K. Arabidopsis decuple mutant reveals the importance of SnRK2 kinases in osmotic stress responses in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postiglione, A.E.; Muday, G.K. The Role of ROS Homeostasis in ABA−Induced Guard Cell Signaling. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz de Carvalho, M.H. Drought stress and reactive oxygen species: Production, scavenging and signaling. Plant Signal. Behav. 2008, 3, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierla, M.; Waszczak, C.; Vahisalu, T.; Kangasjärvi, J. Reactive Oxygen Species in the Regulation of Stomatal Movements. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 1569–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Parihar, P.; Singh, S.; Mishra, R.K.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. Reactive oxygen species signaling and stomatal movement: Current updates and future perspectives. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gechev, T.; Petrov, V. Reactive Oxygen Species and Abiotic Stress in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Song, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Niu, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W. Signaling Transduction of ABA, ROS, and Ca(2+) in Plant Stomatal Closure in Response to Drought. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suku, S.; Knipfer, T.; Fricke, W. Do root hydraulic properties change during the early vegetative stage of plant development in barley (Hordeum vulgare)? Ann. Bot. 2014, 113, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez−Vilalta, J.; Garcia−Forner, N. Water potential regulation, stomatal behaviour and hydraulic transport under drought: Deconstructing the iso/anisohydric concept. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 962–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steudle, E. The Cohesion−Tension Mechanism and the Acquisition of Water by Plant Roots. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 2001, 52, 847–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachez, C.; Besserer, A.; Chevalier, A.S.; Chaumont, F. Insights into plant plasma membrane aquaporin trafficking. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H.; Zheng, H.L. Mechanisms for calcium sensing receptor−regulated stomatal closure in response to the extracellular calcium signal. Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H.; Yi, X.Q.; Han, A.D.; Liu, T.W.; Chen, J.; Wu, F.H.; Dong, X.J.; He, J.X.; Pei, Z.M.; Zheng, H.L. Calcium−sensing receptor regulates stomatal closure through hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide in response to extracellular calcium in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooyers, N.J. The evolution of drought escape and avoidance in natural herbaceous populations. Plant Sci. 2015, 234, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rane, J.; Singh, A.K.; Tiwari, M.; Prasad, P.V.; Jagadish, S.V. Effective Use of Water in Crop Plants in Dryland Agriculture: Implications of Reactive Oxygen Species and Antioxidative System. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 778270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachez, C.; Veselov, D.; Ye, Q.; Reinhardt, H.; Knipfer, T.; Fricke, W.; Chaumont, F. Short−term control of maize cell and root water permeability through plasma membrane aquaporin isoforms. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Y. The root cortex cell hydraulic conductivity is enhanced with increasing chromosome ploidy in wheat. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 68, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Wang, S.; Eltayeb, A.E.; Uddin, M.I.; Yamamoto, Y.; Tsuji, W.; Takeuchi, Y.; Tanaka, K. Overexpression of dehydroascorbate reductase, but not monodehydroascorbate reductase, confers tolerance to aluminum stress in transgenic tobacco. Planta 2010, 231, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Treatment | −PEG | +PEG | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h Calcium | 2 h Calcium | 10 d Calcium | 0 h Calcium | 2 h Calcium | 10 d Calcium | |
| Lpr | 18.27 ± 1.28 b | 19.94 ± 057 a | 18.76 ± 0.88 b | 13.25 ± 0.43 d | 16.24 ± 0.51 c | 11.4 ± 0.73 e |
| Turgor | 0.52 ± 0.022 a | 0.53 ± 0.020 a | 0.54 ± 0.018 a | 0.33 ± 0.009 b | 0.35 ± 0.008 b | 0.36 ± 0.009 b |
| ε | 0.65 ± 0.022 a | 0.70 ± 0.018 a | 0.55 ± 0.018 b | 1.29 ± 0.077 c | 1.23 ± 0.043 cd | 1.08 ± 0.026 d |
| T1/2 | 2.41 ± 0.031 c | 2.53 ± 0.093 c | 2.23 ± 0.052 d | 3.93 ± 0.058 a | 3.9 ± 0.15 a | 3.16 ± 0.17 b |
| Lpc | 22.56 ± 1.28 c | 23.7 ± 0.57 b | 25.98 ± 0.88 a | 9.68 ± 0.43 f | 9.34 ± 0.51 e | 15.28 ± 0.74 d |
| Treatment | −PEG | +PEG | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h Calcium | 2 h Calcium | 10 d Calcium | 0 h Calcium | 2 h Calcium | 10 d Calcium | ||
| ZmNCED | 1.00 ± 0.08 c | 1.10 ± 0.11 c | 1.51 ± 0.14 c | 3.47 ± 0.07 a | 2.18 ± 0.08 b | 3.68 ± 0.11 a | |
| Leaf | ZmABA3 | 1.00 ± 0.27 c | 0.92 ± 0.10 c | 1.60 ± 0.12 c | 3.09 ± 0.12 b | 1.82 ± 0.07 c | 6.03 ± 0.44 a |
| ZmAO2 | 1.00 ± 0.20 c | 0.55 ± 0.073 c | 0.68 ± 0.045 c | 3.27 ± 0.12 b | 1.21 ± 0.066 c | 5.99 ± 0.12 a | |
| ZmNCED | 1.00 ± 0.019 e | 0.99 ± 0.008 e | 1.54 ± 0.031 d | 2.17 ± 0.026 c | 2.37 ± 0.031 b | 3.12 ± 0.040 a | |
| Root | ZmABA3 | 1.00 ± 0.007 d | 0.78 ± 0.042 e | 1.38 ± 0.020 c | 1.55 ± 0.032 b | 1.33 ± 0.038 c | 3.10 ± 0.053 a |
| ZmAO2 | 1.00 ± 0.002 d | 1.00 ± 0.017 d | 1.00 ± 0.003 d | 2.35 ± 0.056 b | 2.13 ± 0.029 c | 3.35 ± 0.029 a | |
| Treatment | −PEG | +PEG | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h Calcium | 2 h Calcium | 10 d Calcium | 0 h Calcium | 2 h Calcium | 10 d Calcium | ||
| CAT | 38.89 ± 0.43 cd | 37.64 ± 1.08 d | 40.21 ± 0.89 c | 42.58 ± 0.79 b | 43.96 ± 0.95 b | 51.65 ± 0.66 a | |
| Leaf | SOD | 41.63 ± 0.69 d | 44.78 ± 0.96 c | 62.13 ± 2.01 a | 40.74 ± 1.76 e | 35.81 ± 2.28 f | 55.78 ± 0.81 b |
| APX | 0.34 ± 0.004 e | 0.35 ± 0.003 de | 0.42 ± 0.009 c | 0.37 ± 0.013 d | 0.47 ± 0.006 b | 0.53 ± 0.007 a | |
| GR | 19.34 ± 0.41 d | 20.65 ± 0.36 c | 22.44 ± 0.63 b | 24.29 ± 0.43 a | 20.31 ± 0.35 cd | 21.57 ± 0.52 bc | |
| CAT | 5.33 ± 0.146 d | 6.78 ± 0.068 c | 6.84 ± 0.127 c | 7.65 ± 0.245 b | 8.07 ± 0.173 b | 11.12 ± 0.166 a | |
| Root | SOD | 33.00 ± 0.59 d | 32.23 ± 0.63 d | 36.13 ± 0.68 b | 35.21 ± 0.57 bc | 34.18 ± 0.36 cd | 38.95 ± 0.53 a |
| APX | 0.29 ± 0.008 f | 0.48 ± 0.008 e | 0.64 ± 0.017 d | 0.82 ± 0.014 c | 1.03 ± 0.021 b | 1.13 ± 0.027 a | |
| GR | 8.78 ± 0.13 d | 9.36 ± 0.39 cd | 10.12 ± 0.50 bc | 9.23 ± 0.22 d | 10.34 ± 0.23 b | 11.33 ± 0.24 a | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Yan, M.; Liang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S. Exogenous Calcium Induces Different Hydraulic Strategies in Response to Osmotic Stress in Maize Seedlings. Plants 2023, 12, 1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12101999
Li D, Yan M, Liang H, Li Z, Zhang S. Exogenous Calcium Induces Different Hydraulic Strategies in Response to Osmotic Stress in Maize Seedlings. Plants. 2023; 12(10):1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12101999
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dongyang, Minfei Yan, Haofeng Liang, Zhe Li, and Suiqi Zhang. 2023. "Exogenous Calcium Induces Different Hydraulic Strategies in Response to Osmotic Stress in Maize Seedlings" Plants 12, no. 10: 1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12101999
APA StyleLi, D., Yan, M., Liang, H., Li, Z., & Zhang, S. (2023). Exogenous Calcium Induces Different Hydraulic Strategies in Response to Osmotic Stress in Maize Seedlings. Plants, 12(10), 1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12101999





