Genetic Diversity and Environmental Influence on Yield and Yield-Related Traits of Adzuki Bean (Vigna angularis L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Phenotypic Analysis of Traits in Different Environments
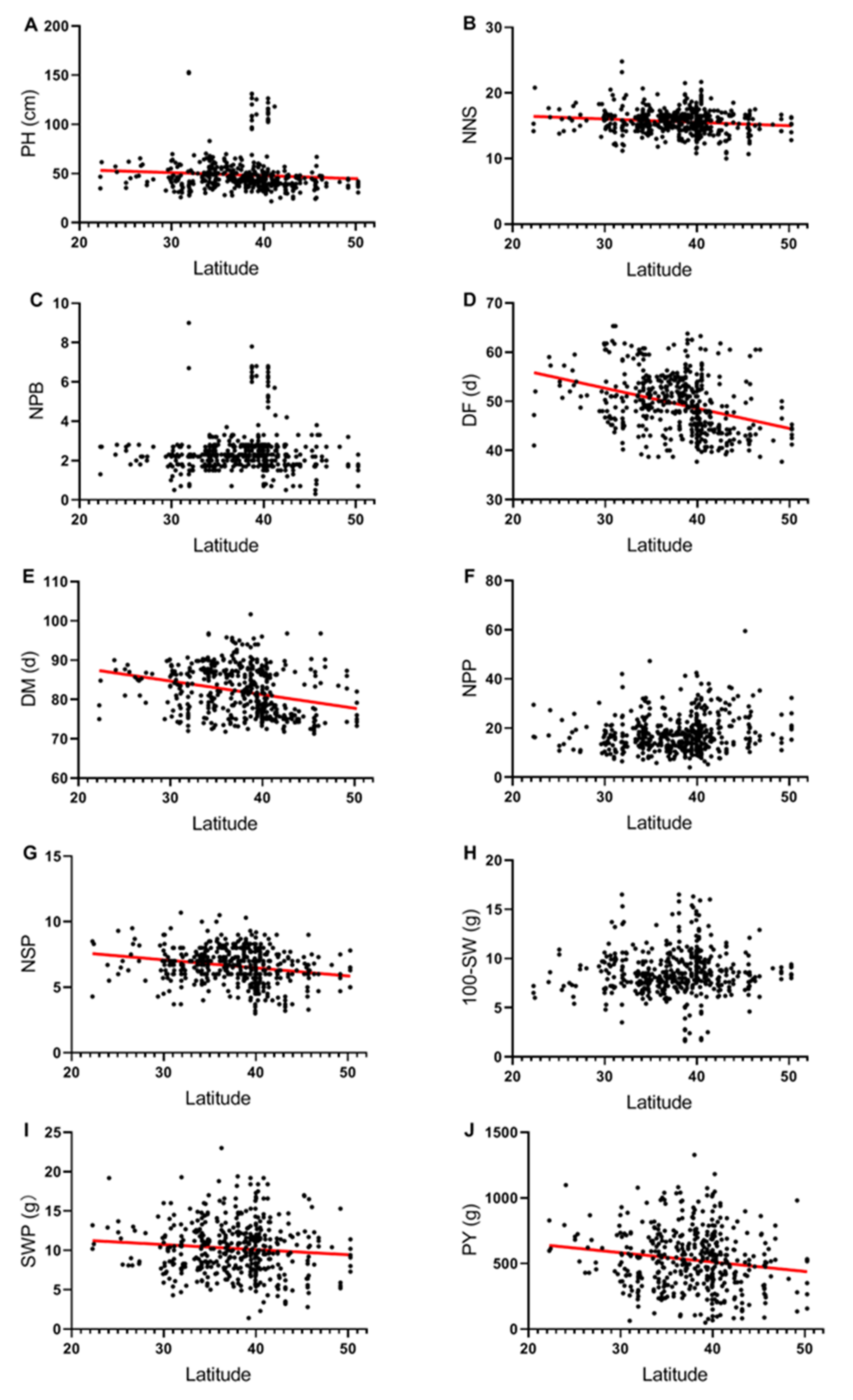
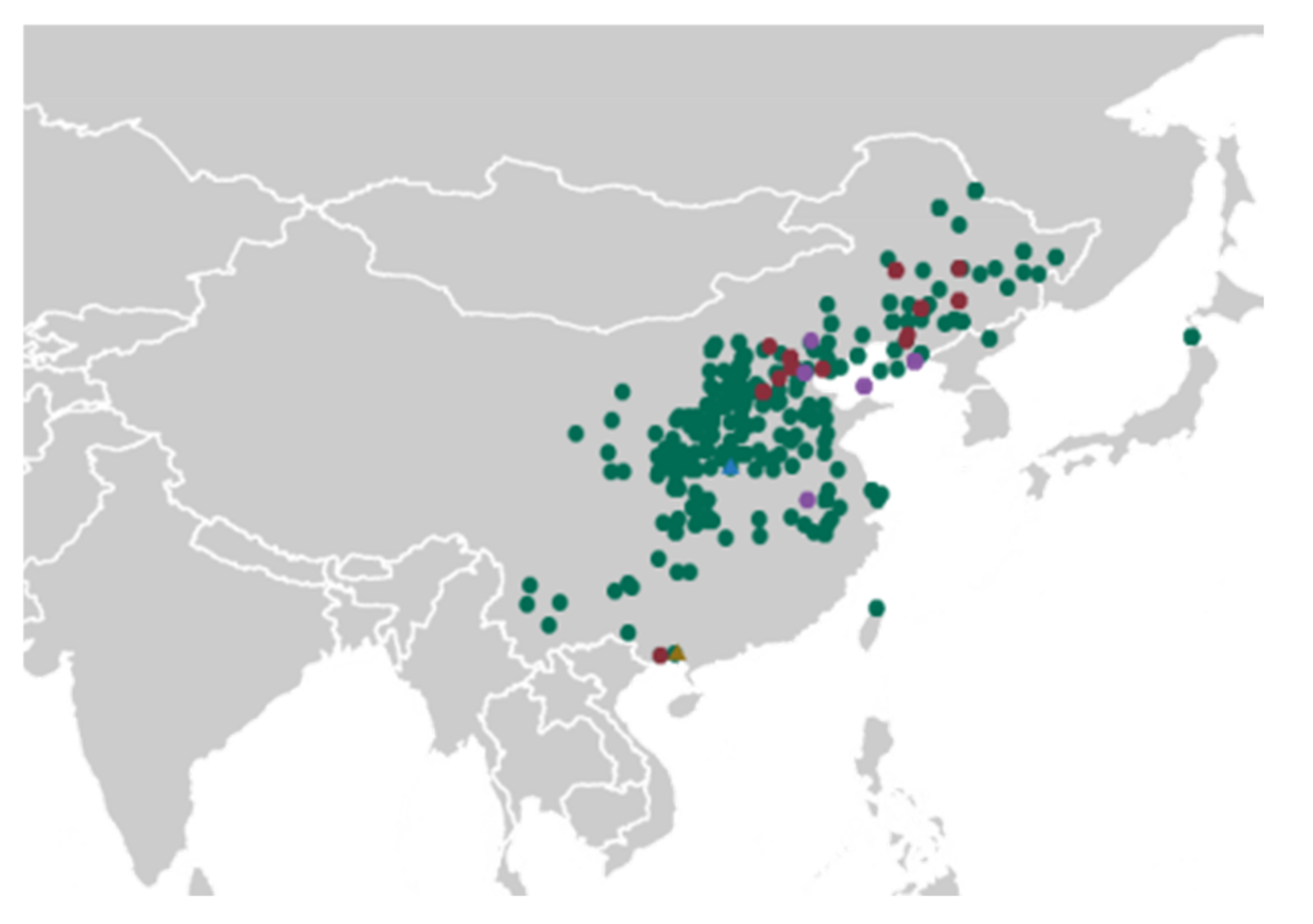
2.2. Relationships between Latitude of Collection Site and Phenotypic Traits
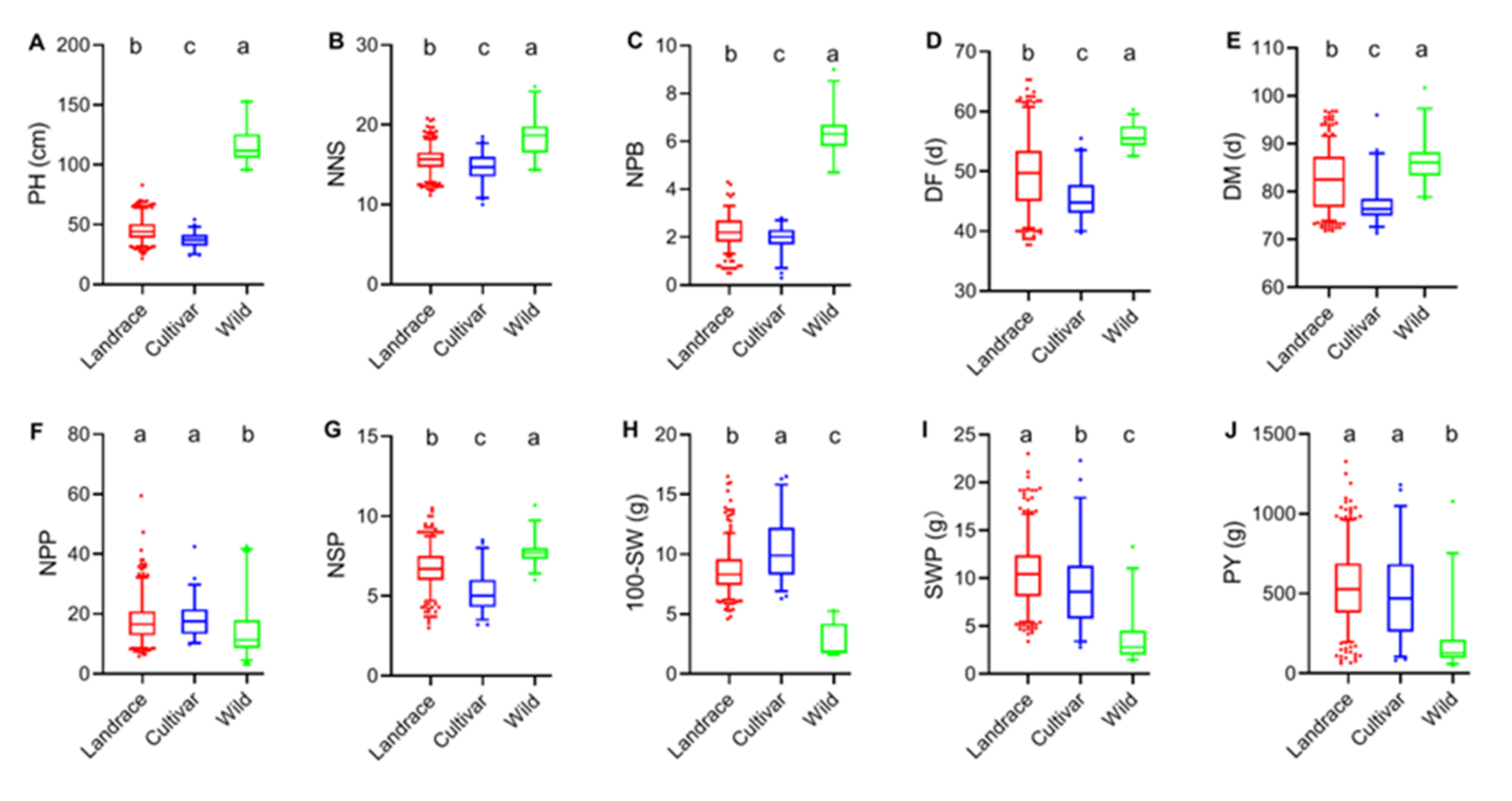
2.3. Phenotypic Analysis of Traits of Different Germplasm Types
2.4. Analysis of Genetic Components
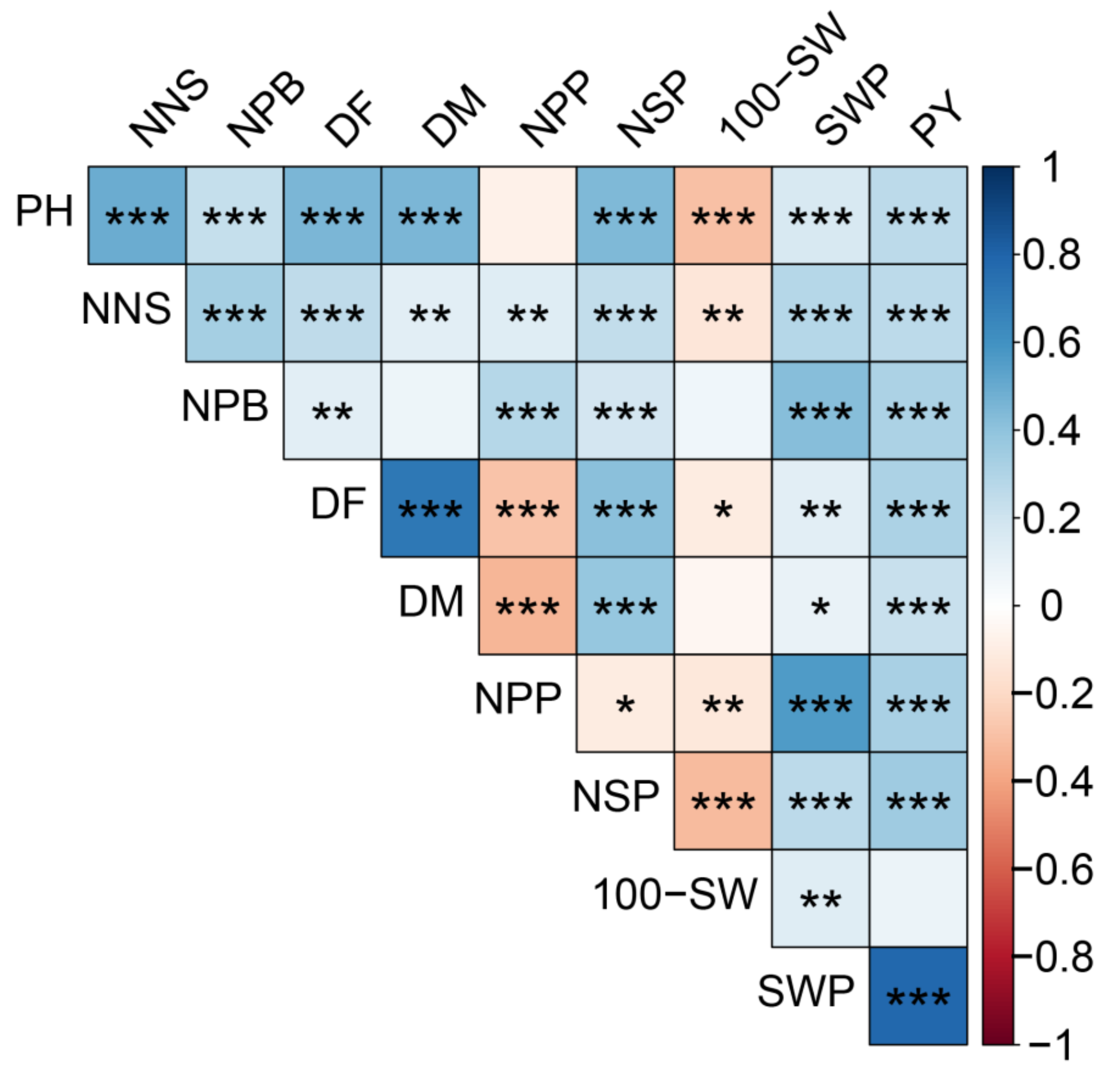
2.5. Correlation Analysis of the Traits
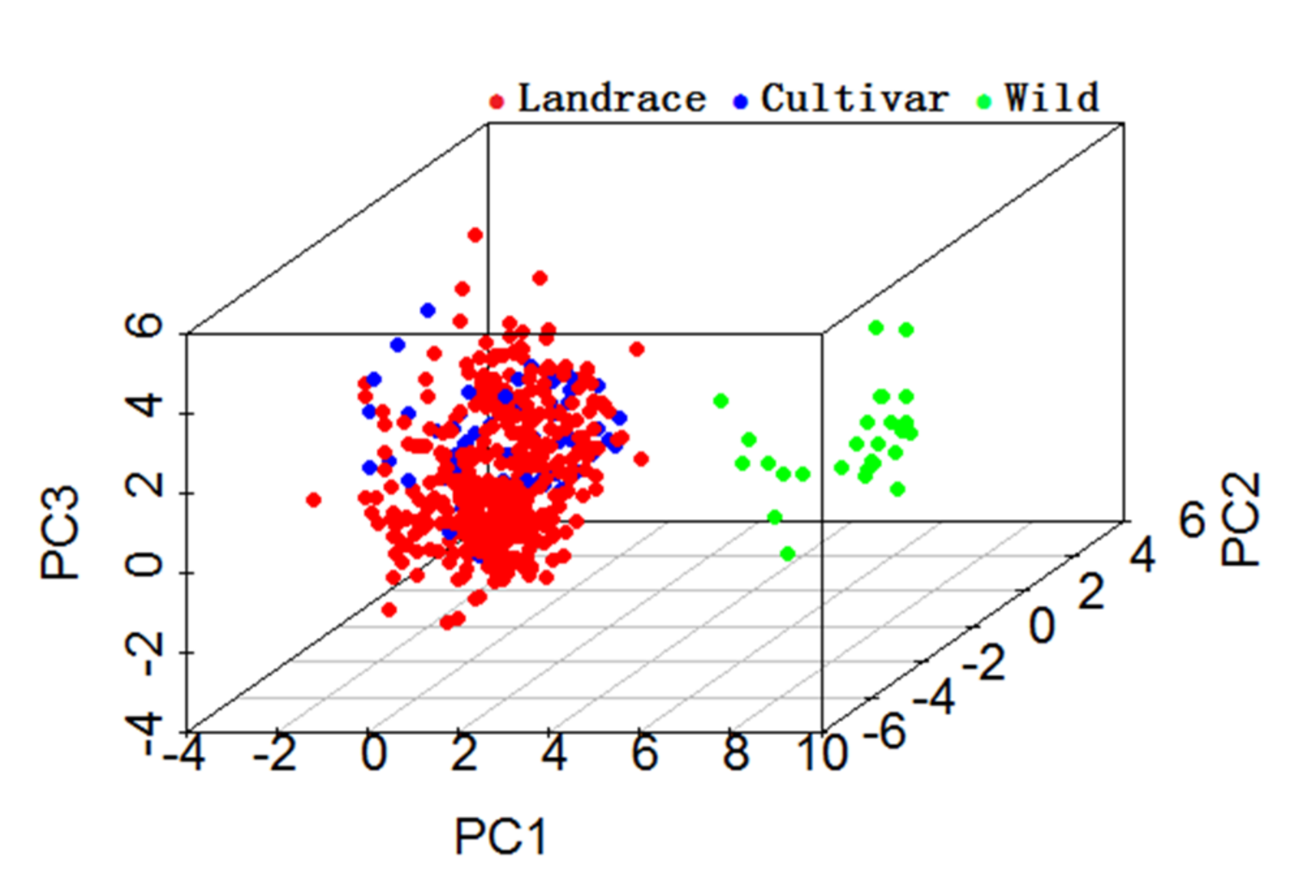
2.6. Principal Component Analysis of Traits
2.7. Cluster Analysis of Traits
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Experiment Location and Trial Design
4.3. Data Collection
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, H.L.; Liu, L.P.; Wang, L.X.; Wang, S.H.; Wang, M.L.; Cheng, X.Z. Development of SSR markers and assessment of genetic diversity of adzuki bean in the Chinese germplasm collection. Mol. Breed. 2015, 35, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J.; Satyawan, D.; Shim, S.; Lee, T.; Lee, J.; Hwang, W.J.; Kim, S.K.; Lestari, P.; Laosatit, K.; Kim, K.H.; et al. Draft genome sequence of adzuki bean, Vigna angularis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Bestel, S.; Shi, J.M.; Song, Y.H.; Chen, X.C. Paleolithic human exploitation of plant foods during the last glacial maximum in North China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5380–5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, K.; Tian, Z.X.; Chen, C.H.; Luo, L.H.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Z.; Yu, L.L.; Li, Y.S.; Sun, Y.D.; Li, W.Y.; et al. Genome sequencing of adzuki bean (Vigna angularis) provides insight into high starch and low fat accumulation and domestication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 13213–13218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Isemura, T.; Tomooka, N.; Kaga, A.; Vaughan, D.A. Comparison of the pattern of crop domestication between two asian beans, azuki bean (Vigna angularis) and rice bean (V. umbellata). Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 2011, 45, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, L.W.; Zhao, P.; Huang, X.Q.; Zhao, B.; Li, Y.S.; Yang, K.; Wan, P. Genetic analysis of seed coat colour in adzuki bean (Vigna angularis L.). Plant Genet. Resour. C. 2021, 19, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano-Okada, T.; Ito, A.; Koide, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Han, K.H.; Shimada, K.; Sasaki, K.; Ohba, K.; Sibayama, S.; Fukushima, M. Anti-obesity role of adzuki bean extract containing polyphenols: In vivo and in vitro effects. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 2644–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukai, Y.; Sato, S. Polyphenol-containing azuki bean (Vigna angularis) extract attenuates blood pressure elevation and modulates nitric oxide synthase and caveolin-1 expressions in rats with hypertension. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2009, 19, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, Y.; Sato, S. Polyphenol-containing azuki bean (Vigna angularis) seed coats attenuate vascular oxidative stress and inflammation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2011, 22, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londo, J.P.; Chiang, Y.C.; Hung, K.H.; Chiang, T.Y.; Schaal, B.A. Phylogeography of Asian wild rice, Oryza rufipogon, reveals multiple independent domestications of cultivated rice, Oryza sativa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9578–9583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaga, A.; Isemura, T.; Tomooka, N.; Vaughan, D.A. The genetics of domestication of the azuki bean (Vigna angularis). Genetics 2008, 178, 1013–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pusadee, T.; Jamjod, S.; Chiang, Y.C.; Rerkasem, B.; Schaal, B.A. Genetic structure and isolation by distance in a landrace of Thai rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13880–13885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Egea-Gilabert, C.; Pagnotta, M.A.; Tripodi, P. Genotype x environment interactions in crop breeding. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, V.; Ljubicic, N.; Kostic, M.; Radulovic, M.; Blagojevic, D.; Ugrenovic, V.; Popovic, D.; Ivosevic, B. Genotype x environment interaction for wheat yield traits suitable for selection in different seed priming conditions. Plants 2020, 9, 1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, H.W.; Jiang, X.W.; Wei, J.W.; Xie, J.L.; Chen, S.P.; Peng, H.C.; Bu, J.Z. A study on genotype x environment interactions for the multiple traits of maize hybrids in China. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 4889–4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.C.; Guo, W.Y.; Liang, J.; Xiao, H.Y.; Hao, X.Y.; Hou, A.F.; Zong, X.X.; Leng, T.R.; Wang, Y.J.; Wang, Q.Y.; et al. Effects of multiple N, P, and K fertilizer combinations on adzuki bean (Vigna angularis) yield in a semi-arid region of northeastern China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, X.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.; Wan, Z.; Li, L.; Sun, L.; Liu, L.; Jiao, C.; Liu, C.; et al. iTRAQ based protein profile analysis revealed key proteins involved in regulation of drought-tolerance during seed germination in adzuki bean. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.X.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Ren, S.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Y.C. Short-day photoperiod effects on plant growth, flower bud differentiation, and yield formation in adzuki bean (Vigna angularis). Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2016, 18, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Horiuchi, Y.; Ogura, R.; Sakai, H.; Sato, H.; Kato, K. Identification and molecular mapping of Flowering Date1 (FD1), a major photoperiod insensitivity gene in the adzuki bean (Vigna angularis). Plant Breed. 2016, 135, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Wang, E.; Li, C.; Zhou, H.; Cai, M.; Cao, C.; Jiang, Y. Comprehensive evaluation of 17 qualities of 84 types of rice based on principal component analysis. Foods 2021, 10, 2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrbic, B.; Durisic-Mladenovic, N.; Cvejanov, J. Principal component analysis of trace elements in Serbian wheat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2171–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.K.; Singh, V.B.; Kumar, R.; Baranwal, D.K.; Ray, P.K. Assessment of genetic diversity based on cluster and principal component analyses for yield and its contributing characters in bitter gourd. Indian J. Hortic. 2014, 71, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Basak, S.; Ramesh, A.M.; Kesari, V.; Parida, A.; Mitra, S.; Rangan, L. Genetic diversity and relationship of Hedychium from northeast India as dissected using PCA analysis and hierarchical clustering. Meta Gene 2014, 2, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boghara, M.C.; Dhaduk, H.L.; Kumar, S.; Parekh, M.J.; Patel, N.J.; Sharma, R. Genetic divergence, path analysis and molecular diversity analysis in cluster bean (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba L. Taub.). Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 89, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, S.; Shah, A.H.; Khan, I.A.; Jan, S.A.; Zubair, M.; Ali, N.; Khan, U. Assessment of genetic diversity in hexaploid wheat of northern areas of Pakistan (Gilgit Baltistan) using morphological marker. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2019, 22, 283–289. [Google Scholar]
- Hegde, V.S.; Kumar, J. Identification of agronomic traits to enhance biomass and grain yield of chickpea under rainfed short-duration environment. Legume Res. 2015, 38, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.J.; Jiang, Y.; Liao, Z.Q.; Xie, W.B.; Zhang, X.M.; Lan, H.; Hu, E.L.; Xu, J.; Feng, X.J.; Wu, F.K.; et al. Evaluation of the contribution of teosinte to the improvement of agronomic, grain quality and yield traits in maize (Zea mays). Plant Breed. 2020, 139, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, S.; Schumann, E.; Pillen, K.; Weber, W.E. Genetic and environmental effects on the occurrence of speltoids in winter wheat cultivars. Plant Breed. 2014, 133, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, V.; Kadar, I.; Andric, L.; Zdunic, Z.; Iljkic, D.; Varga, I.; Jovic, J. Environmental and genetic effects on cadmium accumulation capacity and yield of maize. Czech J. Genet. Plant 2019, 55, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mwiinga, B.; Sibiya, J.; Kondwakwenda, A.; Musvosvi, C.; Chigeza, G. Genotype x environment interaction analysis of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill) grain yield across production environments in Southern Africa. Field Crop Res. 2020, 256, 107922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.H.; Wu, J.G.; Fan, L.J.; Zhu, J.; Wu, P. Developmental genetic analysis of brown rice weight under different environmental conditions in indica rice. Acta Bot. Sin. 2001, 43, 603–609. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H. Florigen trafficking integrates photoperiod and temperature signals in Arabidopsis. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2020, 62, 1385–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adjah, K.L.; Abe, A.; Adetimirin, V.O.; Asante, M.D. Genetic variability, heritability and correlations for milling and grain appearance qualities in some accessions of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2020, 26, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljarrah, M.; Oatway, L.; Albers, S.; Bergen, C. Variability, heritability and genetic advance in some agronomic and forage quality characters of spring triticale in western Canada. Commun. Agric. Appl. Biol. Sci. 2014, 79, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuswantoro, H. The role of heritability and genetic variability in estimated selection response of soybean lines on Tidal Swamp land. Pertanika J. Trop. Agric. 2017, 40, 319–328. [Google Scholar]
- Nechifor, B.; Filimon, R.; Szilagyi, L. Genetic variability, heritability and expected genetic advance as indices for yield and yield components selection in common bean (Phaseolus Vulgaris L.). Sci. Pap. Ser. A Agron. 2011, 54, 332–337. [Google Scholar]
- Gusmao, M.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Flower, K.; Nesbitt, H.; Veneklaas, E.J. Water deficit during the reproductive period of grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) reduced grain yield but maintained seed size. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2012, 198, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicer, B.T. The effect of seed size on yield and yield components of chickpea and lentil. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 1482–1487. [Google Scholar]
- Krajewski, P.; Bocianowski, J.; Gawlowska, M.; Kaczmarek, Z.; Pniewski, T.; Swiecicki, W.; Wolko, B. QTL for yield compo-nents and protein content: A multienvironment study of two pea (Pisum sativum L.) populations. Euphytica 2012, 183, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timmerman-Vaughan, G.M.; Mills, A.; Whitfield, C.; Frew, T.; Butler, R.; Murray, S.; Lakeman, M.; McCallum, J.; Russell, A.; Wilson, D. Linkage mapping of QTL for seed yield, yield components, and developmental traits in pea. Crop Sci. 2005, 45, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambin, B.L.; Borras, L. Resource distribution and the trade-off between seed number and seed weight: A comparison across crop species. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2010, 156, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, K.C.; Malav, P.K.; Gore, P.G.; Tripathi, K.; Rathi, R.S.; Tiwari, U.L.; Ahlawat, S.P. A note on distribution and potential of Japanese wild adzuki bean [Vigna angularis var. nipponensis (Ohwi) Ohwi and H. Ohashi] in India. Genet. Resour. Crop Eviron. 2021, 68, 2157–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, N.; Shimada, H.; Fujita, S. Screening of cultivated and wild adzuki bean for resistance to race 3 of Cadophora gregata f. sp. adzukicola, cause of brown stem rot. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2009, 75, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Q.S.; Yu, L.J.; Yao, W.H.; Zhang, Y.D.; Wang, L.L.; Chen, X.H.; Deng, J.X.; Kang, M.S.; Fan, X.M. Correlation and combining ability analysis of physiological traits and some agronomic traits in maize. Maydica 2014, 59, 176–184. [Google Scholar]
- Crevelari, J.A.; Duraes, N.N.L.; Bendia, L.C.R.; Vettorazzi, J.C.F.; Entringer, G.C.; Ferreira, J.A.; Pereira, M.G. Correlations between agronomic traits and path analysis for silage production in maize hybrids. Bragantia 2018, 77, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukmono, A.; Ardiansyah. Identification of rice field using Multi-Temporal NDVI and PCA method on Landsat 8 (Case Study: Demak, Central Java). IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 54, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, M.; Chauhan, D.K. Studies of genetic diversity and cluster analysis in Rice. Int. J. Agric. Stat. Sci. 2012, 8, 293–297. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, I.; We, G.J.; Kim, D.E.; Cho, Y.S.; Yoon, M.R.; Shin, M.; Ko, S. Classification of rice cultivars based on cluster analysis of hydration and pasting properties of their starches. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 48, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olanrewaju, O.S.; Oyatomi, O.; Babalola, O.O.; Abberton, M. Genetic diversity and environmental influence on growth and yield parameters of bambara groundnut. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 796352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. The mathematical theory of communication (Reprinted). MD Comput. 1997, 14, 306–317. [Google Scholar]
- Baye, T. Genotypic and phenotypic variability in Vernonia galamensis germplasm collected from eastern Ethiopia. J. Agric. Sci. 2002, 139, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, N.; Mut, Z.; Ozcan, H. Estimation of broad-sense heritability for grain yield and some agronomic and quality traits of bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Food Agric. Environ. 2010, 8, 419–421. [Google Scholar]
- Ridzuan, R.; Rafii, M.Y.; Yusoff, M.M.; Ismail, S.I.; Miah, G.; Usman, M. Genetic diversity analysis of selected Capsicum annuum genotypes based on morphophysiological, yield characteristics and their biochemical properties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assefa, K.; Ketema, S.; Tefera, H.; Nguyen, H.T.; Blum, A.; Ayele, M.; Bai, G.; Simane, B.; Kefyalew, T. Diversity among germplasm lines of the Ethiopian cereal tef [Eragrostis tef (Zucc.) Trotter]. Euphytica 1999, 106, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadish, S.V.K.; Septiningsih, E.M.; Kohli, A.; Thomson, M.J.; Ye, C.; Redona, E.; Kumar, A.; Gregorio, G.B.; Wassmann, R.; Ismail, A.M.; et al. Genetic advances in adapting rice to a rapidly changing climate. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2012, 198, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, S.; Meyer, M.; Gregg, C.; Gerber, S. s-CorrPlot: An interactive scatterplot for exploring correlation. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2016, 25, 445–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavent, M.; Kuentz-Simonet, V.; Labenne, A.; Saracco, J. ClustGeo: An R package for hierarchical clustering with spatial constraints. Comput. Stat. 2018, 33, 1799–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Traits | Min | Max | Mean ± SD | CV (%) | SHDI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanning | Nanyang | Nanning | Nanyang | Nanning | Nanyang | Nanning | Nanyang | Nanning | Nanyang | |
| PH | 13.5 | 30.0 | 130.5 | 193.9 | 27.7 ± 10.8 b | 69.3 ± 29.3 a | 39.0 | 42.2 | 1.5 | 1.3 |
| NNS | 6.7 | 12.0 | 22.0 | 27.7 | 11.6 ± 1.8 b | 19.7 ± 2.4 a | 15.6 | 12.3 | 1.9 | 1.9 |
| NPB | 0 | 0.3 | 9.0 | 10.3 | 1.3 ± 0.8 b | 3.5 ± 1.6 a | 59.7 | 56.2 | 0.8 | 1.7 |
| DF | 33.7 | 39.7 | 62.3 | 86.3 | 42.3 ± 4.6 b | 56.7 ± 10.4 a | 10.9 | 18.3 | 1.3 | 2.0 |
| DM | 63.3 | 74.0 | 98.0 | 106.0 | 73.9 ± 6.5 b | 90.1 ± 10.0 a | 8.7 | 11.1 | 1.3 | 1.8 |
| NPP | 2.3 | 2.0 | 80.3 | 109.7 | 15.2 ± 9.0 b | 20.2 ± 12.8 a | 59.3 | 63.6 | 1.8 | 1.8 |
| NSP | 1.7 | 2.0 | 10.7 | 11.0 | 6.6 ± 1.4 | 6.6 ± 1.4 | 21.2 | 20.6 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| 100-SW | 1.5 | 1.7 | 18.5 | 15.5 | 8.5 ± 2.9 | 8.5 ± 2.4 | 34.7 | 28.1 | 1.6 | 1.8 |
| SWP | 1.4 | 1.3 | 33.3 | 35.4 | 8.0 ± 4.4 b | 11.9 ± 6.0 a | 54.6 | 50.4 | 1.8 | 1.9 |
| PY | 14.7 | 51.3 | 1799.6 | 2312.6 | 403.6 ± 297.2 b | 620.5 ± 359.2 a | 73.6 | 57.9 | 1.9 | 1.9 |
| Source of Variation | df | PH | NNS | NPB | DF | DM | NPP | NSP | 100-SW | SWP | PY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blocks | 2 | 306.85 *** | 422.44 *** | 38.00 *** | 59.63 *** | 12.67 *** | 377.65 *** | 0.00 | 0.77 *** | 539.12 *** | 17,837.36 *** |
| Genotypes (G) | 1 | 1,234,467.94 *** | 47,116.40 *** | 3317.76 *** | 147,787.2 * | 187,718.21 | 17,608.09 | 1.82 *** | 0.03 *** | 10458.68 | 33,519,238.06 ** |
| Environments (E) | 474 | 2214.93 *** | 20.38 *** | 7.72 *** | 208.92 *** | 224.31 *** | 320.58 *** | 10.93 | 36.06 | 88.16 *** | 362,497.51 *** |
| G x E | 474 | 704.12 *** | 7.02 *** | 2.09 *** | 178.92 *** | 200.42 *** | 417.62 *** | 0.54 *** | 6.87 *** | 77.14 *** | 289,615.57 *** |
| Error | 1898 | 2.44 | 0.11 | 0.16 | 0.85 | 2.19 | 1.55 | 0.42 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 4.32 |
| Traits | Mean | Vg | Vp | GCV (%) | PCV (%) | RD (%) | h2B (%) | GA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH | 48.5 | 251.8 | 486.7 | 33.1 | 46.0 | 28.1 | 51.7 | 49.1 |
| NNS | 15.6 | 2.2 | 4.4 | 9.6 | 13.5 | 29.0 | 50.4 | 14.0 |
| NPB | 2.4 | 1.0 | 1.6 | 58.7 | 73.5 | 20.1 | 63.9 | 96.7 |
| DF | 49.5 | 3.5 | 66.1 | 3.8 | 16.4 | 76.8 | 5.4 | 1.8 |
| DM | 82.0 | 3.4 | 78.1 | 2.3 | 10.8 | 79.1 | 4.4 | 1.0 |
| NPP | 17.7 | 16.0 | 126.0 | 23.8 | 66.9 | 64.4 | 12.7 | 17.5 |
| NSP | 6.6 | 1.4 | 1.8 | 17.8 | 20.2 | 11.8 | 77.8 | 32.3 |
| 100-SW | 8.5 | 4.9 | 7.2 | 26.1 | 31.7 | 17.5 | 68.0 | 44.3 |
| SWP | 10.0 | 2.0 | 27.5 | 15.4 | 57.6 | 73.3 | 7.2 | 8.5 |
| PY | 512.1 | 48,667.7 | 434,715.4 | 21.7 | 65.0 | 66.5 | 11.2 | 15.0 |
| Traits | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PH | −0.47 | −0.12 | 0.05 |
| NNS | −0.29 | −0.21 | 0.23 |
| NPB | −0.41 | −0.06 | 0.19 |
| DF | −0.21 | −0.44 | −0.23 |
| DM | −0.15 | −0.45 | −0.31 |
| NPP | 0.07 | −0.03 | 0.63 |
| NSP | −0.18 | −0.23 | −0.33 |
| 100-SW | 0.40 | −0.02 | −0.41 |
| SWP | 0.24 | −0.33 | 0.43 |
| PY | 0.20 | −0.32 | 0.30 |
| Eigen values | 3.75 | 2.94 | 1.99 |
| Contribution rate (%) | 31.26 | 24.49 | 16.56 |
| Accumulative contribution rate (%) | 31.26 | 55.75 | 72.31 |
| I | II | III | IV | V | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of members | 143 | 170 | 64 | 74 | 24 |
| PH | 41.7 ± 12.0 | 48.9 ± 12.2 | 43.5 ± 7.2 | 40.0 ± 6.9 | 114.8 ± 12.5 |
| NNS | 15.1 ± 1.8 | 15.9 ± 1.6 | 15.7 ± 1.4 | 15.0 ± 2.0 | 18.3 ± 2.3 |
| NPB | 1.4 ± 0.8 | 1.6 ± 0.6 | 1.8 ± 0.6 | 1.5 ± 0.6 | 5.7 ± 1.0 |
| DF | 47.1 ± 5.6 | 51.8 ± 5.7 | 47.8 ± 5.3 | 49.2 ± 4.3 | 55.8 ± 2.0 |
| DM | 79.9 ± 6.3 | 84.0 ± 5.7 | 80.1 ± 5.8 | 82.8 ± 5.4 | 86.1 ± 4.6 |
| NPP | 15.0 ± 5.1 | 16.7 ± 6.25 | 25.6 ± 8.6 | 14.0 ± 6.3 | 13.0 ± 9.5 |
| NSP | 5.8 ±1.1 | 7.5 ± 0.9 | 6.2 ± 1.1 | 6.0 ± 1.3 | 7.6 ± 0.5 |
| 100-SW | 8.0 ± 1.3 | 8.0 ± 1.4 | 9.7 ± 1.5 | 11.8 ± 2.2 | 2.5 ± 1.2 |
| SWP | 7.3 ± 2.6 | 10.0 ± 2.8 | 13.7 ± 3.2 | 9.0 ± 3.3 | 2.2 ± 1.5 |
| PY | 717.8 ±320.2 | 1214.4 ± 397.7 | 1451.2 ± 527.1 | 998.9 ± 371.6 | 256.2 ± 110.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, L.; Luo, G.; Zhu, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Cheng, X.; Chen, H. Genetic Diversity and Environmental Influence on Yield and Yield-Related Traits of Adzuki Bean (Vigna angularis L.). Plants 2022, 11, 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11091132
Hu L, Luo G, Zhu X, Wang S, Wang L, Cheng X, Chen H. Genetic Diversity and Environmental Influence on Yield and Yield-Related Traits of Adzuki Bean (Vigna angularis L.). Plants. 2022; 11(9):1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11091132
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Liangliang, Gaoling Luo, Xu Zhu, Suhua Wang, Lixia Wang, Xuzhen Cheng, and Honglin Chen. 2022. "Genetic Diversity and Environmental Influence on Yield and Yield-Related Traits of Adzuki Bean (Vigna angularis L.)" Plants 11, no. 9: 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11091132
APA StyleHu, L., Luo, G., Zhu, X., Wang, S., Wang, L., Cheng, X., & Chen, H. (2022). Genetic Diversity and Environmental Influence on Yield and Yield-Related Traits of Adzuki Bean (Vigna angularis L.). Plants, 11(9), 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11091132







