A Novel QTL for Resistance to Phytophthora Crown Rot in Squash
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material, DNA Extraction and SNP Genotyping
2.2. Inoculation and Phenotyping
2.3. Linkage Map Construction and QTL Analysis
2.4. Marker Test and Candidate Gene Identification
3. Results
3.1. Phenotypic Analysis
3.2. SNP Analysis and Map Construction
3.3. QTL Detection, Candidate Genes and Marker Validation
4. Discussion
4.1. Phenotypic Analysis
4.2. Linkage Mapping and QTL Detection
4.3. Marker Validation and Candidate Genes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lamour, K.H.; Stam, R.; Jupe, J.; Huteima, E. The oomycete broad-host-range pathogen Phytophthora capsici. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babadoost, M. Oomycete Diseases of Cucurbits: History, Significance, and Management. In Horticultural Reviews; Jules, J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 279–314. [Google Scholar]
- Hausbeck, M.K.; Lamour, K.H. Phytophthora capsici on Vegetable Crops: Research Progress and Management Challenges. Plant Dis. 2004, 88, 1292–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ristaino, J.B. Population Densities of Phytophthora capsici in Field Soils in Relation to Drip Irrigation, Rainfall, and Disease Incidence. Plant Dis. 1992, 76, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploetz, R.; Heine, G.; Haynes, J.; Watson, M. An investigation of biological attributes that may contribute to the importance of Phytophthora capsici as a vegetable pathogen in Florida. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2002, 140, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamour, K.H.; Hausbeck, M.K. Mefenoxam Insensitivity and the Sexual Stage of Phytophthora capsici in Michigan Cucurbit Fields. Phytopathology 2000, 90, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- French-Monar, R.D.; Jones, J.B.; Roberts, P.D. Characterization of Phytophthora capsici Associated with Roots of Weeds on Florida Vegetable Farms. Plant Dis. 2006, 90, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Babadoost, M.; Pavon, C. Survival of Oospores of Phytophthora capsici in Soil. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 1478–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meyer, M.D.; Hausbeck, M.K. Using cultural practices and cultivar resistance to manage Phytophthora crown rot on summer squash. HortScience 2012, 47, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogel, G.; LaPlant, K.E.; Mazourek, M.; Gore, M.A.; Smart, C.D. A combined BSA-Seq and linkage mapping approach identifies genomic regions associated with Phytophthora root and crown rot resistance in squash. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 1015–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, H.S. History of the Cultivar-Groups of Cucurbita pepo. In Horticultural Reviews; Janick, J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Oxford, UK, 2001; pp. 71–170. [Google Scholar]
- Paris, H.S. Summer squash: History, diversity, and distribution. Horttechnology 1996, 6, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krasnow, C.S.; Hammerschmidt, R.; Hausbeck, M.K. Characteristics of resistance to Phytophthora Root and Crown rot in Cucurbita pepo. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padley, L.D.; Kabelka, E.A.; Roberts, P.D.; French, R. Evaluation of Cucurbita pepo accessions for Crown rot resistance to isolates of Phytophthora capsici. HortScience 2008, 43, 1996–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michael, V.N.; Fu, Y.; Meru, G. Inheritance of Resistance to Phytophthora Crown Rot in Cucurbita pepo. HortScience 2019, 54, 1156–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanca, J.; Cañizares, J.; Roig, C.; Ziarsolo, P.; Nuez, F.; Picó, B. Transcriptome characterization and high throughput SSRs and SNPs discovery in Cucurbita pepo (Cucurbitaceae). BMC Genomics 2011, 12, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, L.; Stift, G.; Kofler, R.; Pachner, M.; Lelley, T. Microsatellites for the genus Cucurbita and an SSR-based genetic linkage map of Cucurbita pepo L. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 117, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Esteras, C.; Gomez, P.; Monforte, A.J.; Blanca, J.; Vicente-Dolera, N.; Roig, C.; Nuez, F.; Pico, B. High-throughput SNP genotyping in Cucurbita pepo for map construction and quantitative trait loci mapping. BMC Genomics 2012, 13, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montero-Pau, J.; Blanca, J.; Bombarely, A.; Ziarsolo, P.; Esteras, C.; Martí-Gómez, C.; Ferriol, M.; Gómez, P.; Jamilena, M.; Mueller, L.; et al. De novo assembly of the zucchini genome reveals a whole-genome duplication associated with the origin of the Cucurbita genus. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mackay, T.F.C. The Genetic Architecture of Quantitative Traits. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2001, 35, 303–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lander, E.S.; Botstein, D. Mapping mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 1989, 121, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, E.; Kruglyak, L. Genetic dissection of complex traits: Guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results. Nat. Genet. 1995, 11, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.H.; Fernando, R.L.; Dekkers, J.C.M. Power and precision of alternate methods for linkage disequilibrium mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 2007, 175, 1975–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, R.N.; Myers, J.R. A Genetic Map of Squash (Cucurbita sp.) with Randomly Amplified Polymorphic DNA Markers and Morphological Markers. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2002, 127, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zraidi, A.; Stift, G.; Pachner, M.; Shojaeiyan, A.; Gong, L.; Lelley, T. A consensus map for Cucurbita pepo. Mol. Breed. 2007, 20, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Pau, J.; Blanca, J.; Esteras, C.; Martínez-Pérez, E.M.; Gómez, P.; Monforte, A.J.; Cañizares, J.; Picó, B. An SNP-based saturated genetic map and QTL analysis of fruit-related traits in Zucchini using Genotyping-by-sequencing. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramos, A.; Fu, Y.; Michael, V.; Meru, G. QTL-seq for identification of loci associated with resistance to Phytophthora crown rot in squash. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garrison, E.; Marth, G. Haplotype-based variant detection from short-read sequencing. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1207.3907. [Google Scholar]
- Padley, L.D.; Kabelka, E.A.; Roberts, P.D. Inheritance of Resistance to Crown Rot Caused by Phytophthora capsici in Cucurbita. HortScience 2009, 44, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaner, G.; Finney, R.E. The effect of nitrogen fertilization on the expression of slow-mildewing resistance in Knox wheat. Phytopathology 1977, 67, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Margarido, G.R.A.; Souza, A.P.; Garcia, A.A.F. OneMap: Software for genetic mapping in outcrossing species. Hereditas 2007, 144, 78–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R-Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: http://www.r-project.org (accessed on 20 March 2021).
- Kosambi, D.D. The Estimation of Map Distances from Recombination Values. Ann. Eugen. 1943, 12, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollinari, M.; Margarido, G.R.A.; Vencovsky, R.; Garcia, A.A.F. Evaluation of algorithms used to order markers on genetic maps. Heredity 2009, 103, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Broman, K.W.; Gatti, D.M.; Simecek, P.; Furlotte, N.A.; Prins, P.; Sen, Ś.; Yandell, B.S.; Churchill, G.A. R/qtl2: Software for Mapping Quantitative Trait Loci with High-Dimensional Data and Multiparent Populations. Genetics 2019, 211, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Churchill, G.A.; Doerge, R.W. Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 1994, 138, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorrips, R.E. MapChart: Software for the Graphical Presentation of Linkage Maps and QTLs. J. Hered. 2002, 93, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Semagn, K.; Babu, R.; Hearne, S.; Olsen, M. Single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping using Kompetitive Allele Specific PCR (KASP): Overview of the technology and its application in crop improvement. Mol. Breed. 2014, 33, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.K.; Al-Koofee, D.A.F. BatchPrimer3: A free web application for allele specific (SBE and allele flanking) primer design for SNPs genotyping in molecular diagnostics: A bioinformatics study. Gene Rep. 2019, 17, 100524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meru, G.; McGregor, C.E. A Genetic Locus Associated with Resistance to Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. niveum Race 2 in Citrullus lanatus-type Watermelon. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2016, 141, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- deVicente, M.C.; Tanksley, S.D. QTL analysis of transgressive segregation in an interspecific tomato cross. Genetics 1993, 134, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieseberg, L.H.; Archer, M.A.; Wayne, R.K. Transgressive segregation, adaptation and speciation. Heredity 1999, 83, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Duan, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, W.; Huang, S.; Sui, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C. A High-Density EST-SSR-Based Genetic Map and QTL Analysis of Dwarf Trait in Cucurbita pepo L. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vales, M.I.; Schön, C.C.; Capettini, F.; Chen, X.M.; Corey, A.E.; Mather, D.E.; Mundt, C.C.; Richardson, K.L.; Sandoval-Islas, J.S.; Utz, H.F.; et al. Effect of population size on the estimation of QTL: A test using resistance to barley stripe rust. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 111, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meru, G.; McGregor, C. Genetic Mapping of Seed Traits Correlated with Seed Oil Percentage in Watermelon. HortScience 2013, 48, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, H.; Abe, A.; Yoshida, K.; Kosugi, S.; Natsume, S.; Mitsuoka, C.; Uemura, A.; Utsushi, H.; Tamiru, M.; Takuno, S.; et al. QTL-seq: Rapid mapping of quantitative trait loci in rice by whole genome resequencing of DNA from two bulked populations. Plant J. 2013, 74, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Halterman, D. Analysis of proteins differentially accumulated during potato late blight resistance mediated by the RB resistance gene. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2009, 74, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Dong, L.; Gao, T.; Liu, T.; Li, N.; Wang, L.; Chang, X.; Wu, J.; Xu, P.; Zhang, S. The bHLH transcription factor GmPIB1 facilitates resistance to Phytophthora sojae in Glycine max. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 2527–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ai, G.; Shen, D.; Chai, C.; Jia, Y.; Liu, W.; Dou, D. Bioinformatical analysis and prediction of Nicotiana benthamiana bHLH transcription factors in Phytophthora parasitica resistance. Genomics 2019, 111, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Lamothe, R.; Tsitsigiannis, D.I.; Ludwig, A.A.; Panicot, M.; Shirasu, K.; Jones, J.D.G. The U-Box Protein CMPG1 Is Required for Efficient Activation of Defense Mechanisms Triggered by Multiple Resistance Genes in Tobacco and Tomato. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 1067–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volpi, C.; Janni, M.; Lionetti, V.; Bellincampi, D.; Favaron, F.; D’Ovidio, R. The Ectopic Expression of a Pectin Methyl Esterase Inhibitor Increases Pectin Methyl Esterification and Limits Fungal Diseases in Wheat. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2011, 24, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Zhong, C.; Tan, M.; Song, Y.; Qi, X.; Xu, Q.; Chen, X. Identification of MicroRNAs and Their Targets That Respond to Powdery Mildew Infection in Cucumber by Small RNA and Degradome Sequencing. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, V.; Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Wei, C.; Changqing, X.; Zhang, X. Comparative Analysis, Characterization and Evolutionary Study of Dirigent Gene Family in Cucurbitaceae and Expression of Novel Dirigent Peptide against Powdery Mildew Stress. Genes 2021, 12, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Tuo, D.; Shen, W.; Yan, P.; Li, X.; Zhou, P. NIa-Pro of Papaya ringspot virus interacts with Carica papaya eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit G (CpeIF3G). Virus Genes 2015, 50, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Han, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Li, C.; Xie, Q.; Chong, K.; Xu, Y. The E3 Ligase AtRDUF1 Positively Regulates Salt Stress Responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enkerli, K.; Mims, C.W.; Hahn, M.G. Ultrastructure of compatible and incompatible interactions of soybean roots infected with the plant pathogenic oomycete Phytophthora sojae. Can. J. Bot. 1997, 75, 1493–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, A.R.; Smart, C.D. Interactions of Phytophthora capsici with Resistant and Susceptible Pepper Roots and Stems. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Chromosome | Number of Genotyped SNPs | Number of Mapped SNPs | Length of Linkage Group (cM) | Average Number of SNPs per cM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cp4.1LG00 | 3 | 2 | 0.37 | 0.2 |
| Cp4.1LG01 | 45 | 19 | 243.89 | 12.8 |
| Cp4.1LG02 | 30 | 11 | 89.73 | 8.2 |
| Cp4.1LG03 | 36 | 22 | 237.40 | 10.8 |
| Cp4.1LG04 | 24 | 12 | 107.93 | 9.0 |
| Cp4.1LG05 | 32 | 17 | 111.61 | 6.6 |
| Cp4.1LG06 | 25 | 13 | 84.08 | 6.5 |
| Cp4.1LG07 | 18 | 12 | 84.52 | 7.0 |
| Cp4.1LG08 | 31 | 16 | 121.01 | 7.6 |
| Cp4.1LG09 | 28 | 8 | 120.54 | 15.1 |
| Cp4.1LG10 | 29 | 19 | 109.62 | 5.8 |
| Cp4.1LG11 | 32 | 7 | 90.74 | 13.0 |
| Cp4.1LG12 | 36 | 17 | 133.56 | 7.9 |
| Cp4.1LG13 | 25 | 14 | 98.99 | 7.1 |
| Cp4.1LG14 | 14 | 6 | 87.81 | 14.6 |
| Cp4.1LG15 | 19 | 12 | 68.61 | 5.7 |
| Cp4.1LG16 | 24 | 6 | 55.86 | 9.3 |
| Cp4.1LG17 | 6 | 2 | 0.75 | 0.4 |
| Cp4.1LG18 | 23 | 9 | 55.21 | 6.1 |
| Cp4.1LG19 | 24 | 10 | 102.36 | 10.2 |
| Cp4.1LG20 | 19 | 10 | 64.34 | 6.4 |
| Total | 523 | 244 | 2068.96 | Mean = 8.1 |
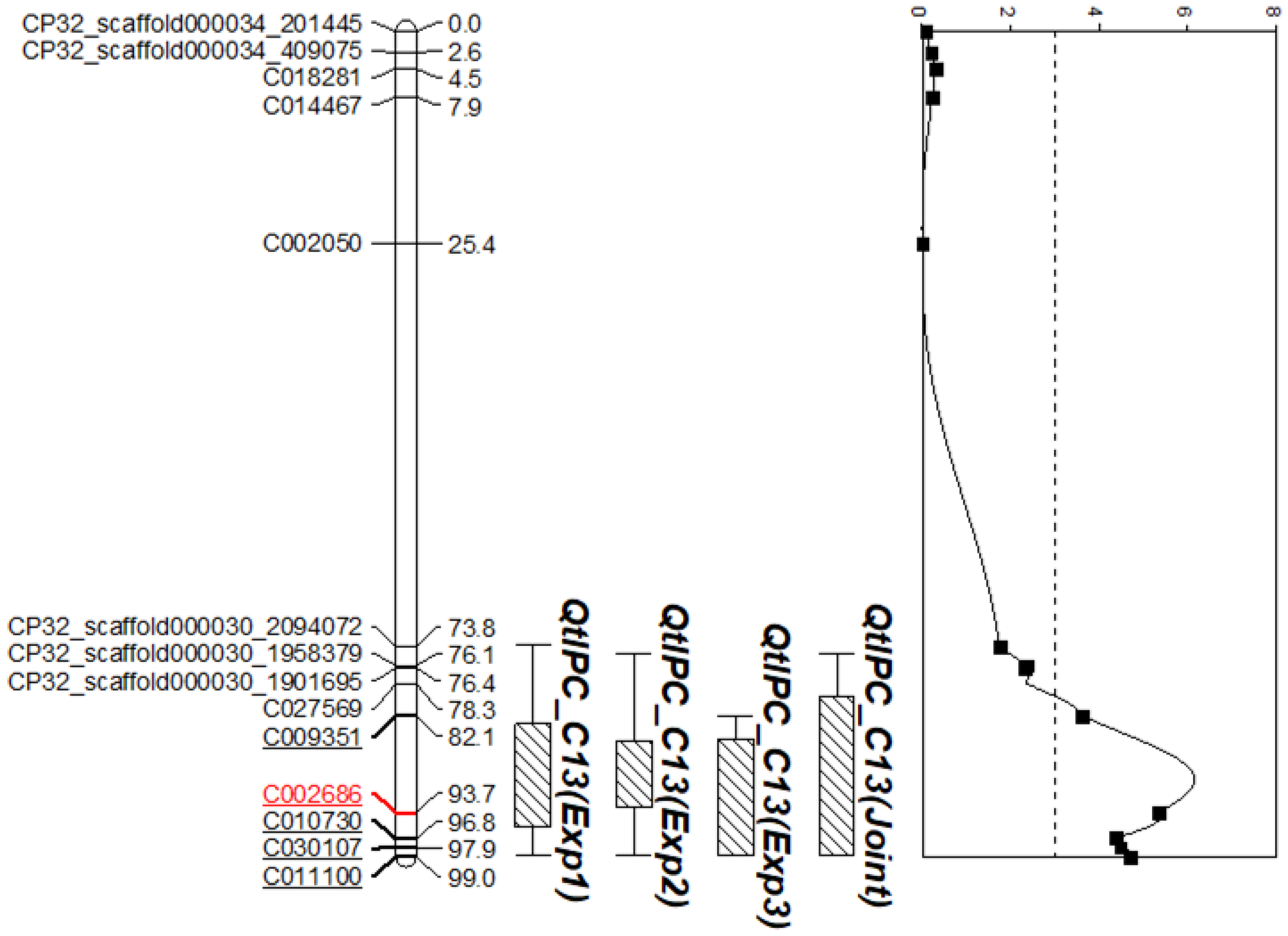
| Screen | Position (cM) | R2 | LOD | Peak SNP | Additive Effect | Dominance Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment 1 | 89.3 | 17.92 | 3.66 | C002686 | 4.14 | 1.75 |
| Experiment 2 | 97.9 | 18.47 | 3.14 | C002686 | 3.14 | 2.84 |
| Experiment 3 | 90.5 | 21.47 | 4.04 | C002686 | 3.81 | 2.78 |
| Joint Analysis | 89.7 | 20.79 | 5.92 | C002686 | 3.88 | 2.41 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Michael, V.N.; Fu, Y.; Shrestha, S.; Meru, G. A Novel QTL for Resistance to Phytophthora Crown Rot in Squash. Plants 2021, 10, 2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102115
Michael VN, Fu Y, Shrestha S, Meru G. A Novel QTL for Resistance to Phytophthora Crown Rot in Squash. Plants. 2021; 10(10):2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102115
Chicago/Turabian StyleMichael, Vincent Njung’e, Yuqing Fu, Swati Shrestha, and Geoffrey Meru. 2021. "A Novel QTL for Resistance to Phytophthora Crown Rot in Squash" Plants 10, no. 10: 2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102115
APA StyleMichael, V. N., Fu, Y., Shrestha, S., & Meru, G. (2021). A Novel QTL for Resistance to Phytophthora Crown Rot in Squash. Plants, 10(10), 2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102115






