Genetic and Molecular Determinants of Lymphatic Malformations: Potential Targets for Therapy
Abstract
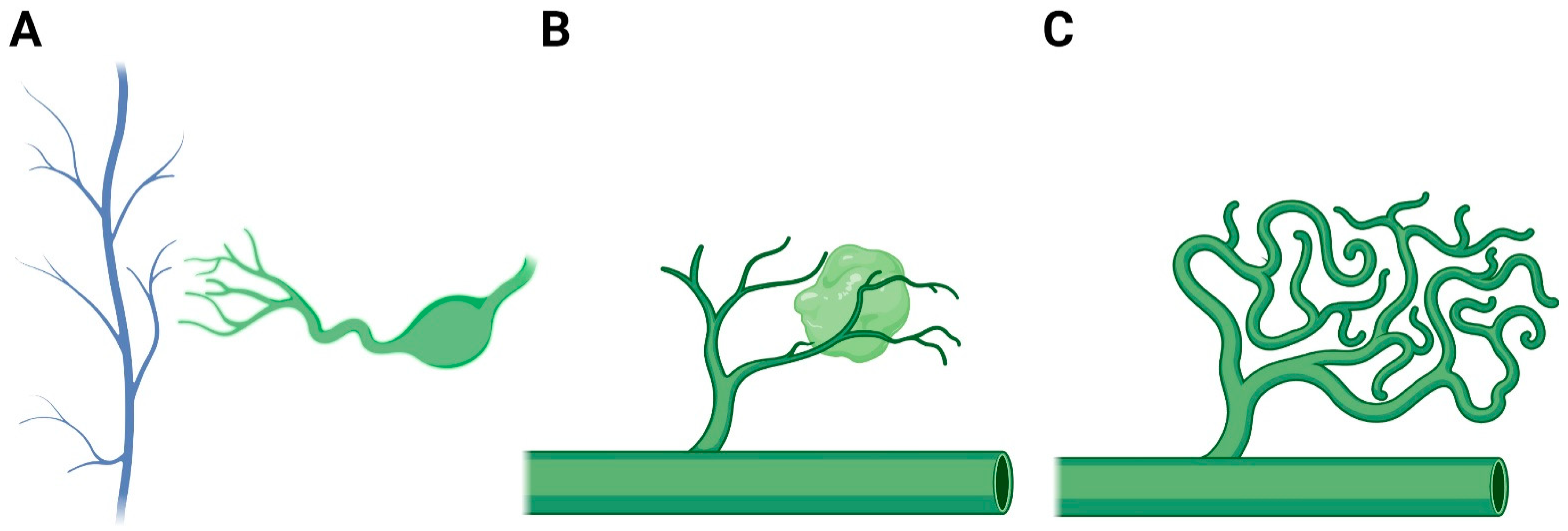
:1. Introduction
2. Lymphatic Development
3. Pathogenesis
3.1. Clinical Syndromes
3.2. Genetic Mutations
3.3. Gene Dysregulation
4. Clinical Implications
4.1. Current Surgical Treatment
4.2. Current Medical Treatment
5. Future Therapies
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fishman, S.J.; Young, A.E. Slow-Flow Vascular Malformations; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-0-19-935714-7. [Google Scholar]
- Dubois, J.; Thomas-Chaussé, F.; Soulez, G. Common (Cystic) Lymphatic Malformations: Current Knowledge and Management. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 22, 100631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulungowski, A.M.; Patel, M. Lymphatic Malformations. Semin. Pediatr. Surg. 2020, 29, 150971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrow, A.C.; Gupta, A.; Patel, M.N.; Adams, D.M. 2014 Revised Classification of Vascular Lesions from the International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies: Radiologic-Pathologic Update. Radiographics 2016, 36, 1494–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elluru, R.G.; Balakrishnan, K.; Padua, H.M. Lymphatic Malformations: Diagnosis and Management. Semin. Pediatr. Surg. 2014, 23, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouillard, P.; Boon, L.; Vikkula, M. Genetics of Lymphatic Anomalies. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semo, J.; Nicenboim, J.; Yaniv, K. Development of the Lymphatic System: New Questions and Paradigms. Development 2016, 143, 924–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewis, F.T. The Development of the Lymphatic System in Rabbits. Am. J. Anat. 1905, 5, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huntington, G.S.; McClure, C.F.W. The Anatomy and Development of the Jugular Lymph Sacs in the Domestic Cat (Felis Domestica). Am. J. Anat. 1910, 10, 177–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ny, A.; Koch, M.; Schneider, M.; Neven, E.; Tong, R.T.; Maity, S.; Fischer, C.; Plaisance, S.; Lambrechts, D.; Héligon, C.; et al. A Genetic Xenopus Laevis Tadpole Model to Study Lymphangiogenesis. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilting, J.; Aref, Y.; Huang, R.; Tomarev, S.I.; Schweigerer, L.; Christ, B.; Valasek, P.; Papoutsi, M. Dual Origin of Avian Lymphatics. Dev. Biol. 2006, 292, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yaniv, K.; Isogai, S.; Castranova, D.; Dye, L.; Hitomi, J.; Weinstein, B.M. Live Imaging of Lymphatic Development in the Zebrafish. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuda, K.S.; Astin, J.W.; Misa, J.P.; Flores, M.V.; Crosier, K.E.; Crosier, P.S. Lyve1 Expression Reveals Novel Lymphatic Vessels and New Mechanisms for Lymphatic Vessel Development in Zebrafish. Development 2012, 139, 2381–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Impel, A.; Zhao, Z.; Hermkens, D.M.A.; Roukens, M.G.; Fischer, J.C.; Peterson-Maduro, J.; Duckers, H.; Ober, E.A.; Ingham, P.W.; Schulte-Merker, S. Divergence of Zebrafish and Mouse Lymphatic Cell Fate Specification Pathways. Development 2014, 141, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srinivasan, R.S.; Dillard, M.E.; Lagutin, O.V.; Lin, F.-J.; Tsai, S.; Tsai, M.-J.; Samokhvalov, I.M.; Oliver, G. Lineage Tracing Demonstrates the Venous Origin of the Mammalian Lymphatic Vasculature. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 2422–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Corral, I.; Ulvmar, M.H.; Stanczuk, L.; Tatin, F.; Kizhatil, K.; John, S.W.M.; Alitalo, K.; Ortega, S.; Makinen, T. Nonvenous Origin of Dermal Lymphatic Vasculature. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klotz, L.; Norman, S.; Vieira, J.M.; Masters, M.; Rohling, M.; Dubé, K.N.; Bollini, S.; Matsuzaki, F.; Carr, C.A.; Riley, P.R. Cardiac Lymphatics Are Heterogeneous in Origin and Respond to Injury. Nature 2015, 522, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stanczuk, L.; Martinez-Corral, I.; Ulvmar, M.H.; Zhang, Y.; Laviña, B.; Fruttiger, M.; Adams, R.H.; Saur, D.; Betsholtz, C.; Ortega, S.; et al. CKit Lineage Hemogenic Endothelium-Derived Cells Contribute to Mesenteric Lymphatic Vessels. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 1708–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koning, J.J.; Konijn, T.; Lakeman, K.A.; O’Toole, T.; Kenswil, K.J.G.; Raaijmakers, M.H.G.P.; Michurina, T.V.; Enikolopov, G.; Mebius, R.E. Nestin-Expressing Precursors Give Rise to Both Endothelial as Well as Nonendothelial Lymph Node Stromal Cells. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 2686–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wigle, J.T.; Oliver, G. Prox1 Function Is Required for the Development of the Murine Lymphatic System. Cell 1999, 98, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Nguyen, V.P.; Petrova, T.V.; Cruz, M.; Alitalo, K.; Dumont, D.J. Embryonic Vascular Endothelial Cells Are Malleable to Reprogramming via Prox1 to a Lymphatic Gene Signature. BMC Dev. Biol. 2010, 10, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srinivasan, R.S.; Geng, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mukatira, S.; Studer, M.; Porto, M.P.R.; Lagutin, O.; Oliver, G. The Nuclear Hormone Receptor Coup-TFII Is Required for the Initiation and Early Maintenance of Prox1 Expression in Lymphatic Endothelial Cells. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- François, M.; Caprini, A.; Hosking, B.; Orsenigo, F.; Wilhelm, D.; Browne, C.; Paavonen, K.; Karnezis, T.; Shayan, R.; Downes, M.; et al. Sox18 Induces Development of the Lymphatic Vasculature in Mice. Nature 2008, 456, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerji, S.; Ni, J.; Wang, S.X.; Clasper, S.; Su, J.; Tammi, R.; Jones, M.; Jackson, D.G. LYVE-1, a New Homologue of the CD44 Glycoprotein, Is a Lymph-Specific Receptor for Hyaluronan. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 144, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiteneder-Geleff, S.; Soleiman, A.; Kowalski, H.; Horvat, R.; Amann, G.; Kriehuber, E.; Diem, K.; Weninger, W.; Tschachler, E.; Alitalo, K.; et al. Angiosarcomas Express Mixed Endothelial Phenotypes of Blood and Lymphatic Capillaries: Podoplanin as a Specific Marker for Lymphatic Endothelium. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 154, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaipainen, A.; Korhonen, J.; Mustonen, T.; van Hinsbergh, V.W.; Fang, G.H.; Dumont, D.; Breitman, M.; Alitalo, K. Expression of the Fms-like Tyrosine Kinase 4 Gene Becomes Restricted to Lymphatic Endothelium during Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 3566–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joukov, V.; Pajusola, K.; Kaipainen, A.; Chilov, D.; Lahtinen, I.; Kukk, E.; Saksela, O.; Kalkkinen, N.; Alitalo, K. A Novel Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor, VEGF-C, Is a Ligand for the Flt4 (VEGFR-3) and KDR (VEGFR-2) Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkinen, T.; Veikkola, T.; Mustjoki, S.; Karpanen, T.; Catimel, B.; Nice, E.C.; Wise, L.; Mercer, A.; Kowalski, H.; Kerjaschki, D.; et al. Isolated Lymphatic Endothelial Cells Transduce Growth, Survival and Migratory Signals via the VEGF-C/D Receptor VEGFR-3. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 4762–4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, F.; Chang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Hong, Y.-K.; Shen, B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, F.; Lu, G.; Tvorogov, D.; Alitalo, K.; et al. Akt/Protein Kinase B Is Required for Lymphatic Network Formation, Remodeling, and Valve Development. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 2124–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Atri, D.; Eichmann, A.; Simons, M. Endothelial ERK Signaling Controls Lymphatic Fate Specification. J. Clin. Invest. 2013, 123, 1202–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yuan, L.; Mak, J.; Pardanaud, L.; Caunt, M.; Kasman, I.; Larrivée, B.; del Toro, R.; Suchting, S.; Medvinsky, A.; et al. Neuropilin-2 Mediates VEGF-C–Induced Lymphatic Sprouting Together with VEGFR3. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 188, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karkkainen, M.J.; Haiko, P.; Sainio, K.; Partanen, J.; Taipale, J.; Petrova, T.V.; Jeltsch, M.; Jackson, D.G.; Talikka, M.; Rauvala, H.; et al. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor C Is Required for Sprouting of the First Lymphatic Vessels from Embryonic Veins. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achen, M.G.; Roufail, S.; Domagala, T.; Catimel, B.; Nice, E.C.; Geleick, D.M.; Murphy, R.; Scott, A.M.; Caesar, C.; Makinen, T.; et al. Monoclonal Antibodies to Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-D Block Its Interactions with Both VEGF Receptor-2 and VEGF Receptor-3. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 2505–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joukov, V.; Sorsa, T.; Kumar, V.; Jeltsch, M.; Claesson-Welsh, L.; Cao, Y.; Saksela, O.; Kalkkinen, N.; Alitalo, K. Proteolytic Processing Regulates Receptor Specificity and Activity of VEGF-C. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 3898–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stacker, S.A.; Stenvers, K.; Caesar, C.; Vitali, A.; Domagala, T.; Nice, E.; Roufail, S.; Simpson, R.J.; Moritz, R.; Karpanen, T.; et al. Biosynthesis of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-D Involves Proteolytic Processing Which Generates Non-Covalent Homodimers. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 32127–32136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baldwin, M.E.; Halford, M.M.; Roufail, S.; Williams, R.A.; Hibbs, M.L.; Grail, D.; Kubo, H.; Stacker, S.A.; Achen, M.G. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor D Is Dispensable for Development of the Lymphatic System. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 2441–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeltsch, M.; Jha, S.K.; Tvorogov, D.; Anisimov, A.; Leppänen, V.-M.; Holopainen, T.; Kivelä, R.; Ortega, S.; Kärpanen, T.; Alitalo, K. CCBE1 Enhances Lymphangiogenesis via A Disintegrin and Metalloprotease With Thrombospondin Motifs-3–Mediated Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-C Activation. Circulation 2014, 129, 1962–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roukens, M.G.; Peterson-Maduro, J.; Padberg, Y.; Jeltsch, M.; Leppänen, V.-M.; Bos, F.L.; Alitalo, K.; Schulte-Merker, S.; Schulte, D. Functional Dissection of the CCBE1 Protein. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1660–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gale, N.W.; Thurston, G.; Hackett, S.F.; Renard, R.; Wang, Q.; McClain, J.; Martin, C.; Witte, C.; Witte, M.H.; Jackson, D.; et al. Angiopoietin-2 Is Required for Postnatal Angiogenesis and Lymphatic Patterning, and Only the Latter Role Is Rescued by Angiopoietin-1. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.S.; Oliver, G. Prox1 Dosage Controls the Number of Lymphatic Endothelial Cell Progenitors and the Formation of the Lymphovenous Valves. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 2187–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiegand, S.; Eivazi, B.; Barth, P.J.; von Rautenfeld, D.B.; Folz, B.J.; Mandic, R.; Werner, J.A. Pathogenesis of Lymphangiomas. Virchows Arch. 2008, 453, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadvinskis, D.P.; Benson, M.T.; Kerr, H.H.; Mancuso, A.A.; Cacciarelli, A.A.; Madrazo, B.L.; Mafee, M.F.; Dalen, K. Congenital Malformations of the Cervicothoracic Lymphatic System: Embryology and Pathogenesis. Radiographics 1992, 12, 1175–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliver, G.; Kipnis, J.; Randolph, G.J.; Harvey, N.L. The Lymphatic Vasculature in the 21st Century: Novel Functional Roles in Homeostasis and Disease. Cell 2020, 182, 270–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baluk, P.; Fuxe, J.; Hashizume, H.; Romano, T.; Lashnits, E.; Butz, S.; Vestweber, D.; Corada, M.; Molendini, C.; Dejana, E.; et al. Functionally Specialized Junctions between Endothelial Cells of Lymphatic Vessels. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 2349–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weingast, G.R.; Hopper, K.D.; Gottesfeld, S.A.; Manco-Johnson, M.L. Congenital Lymphangiectasia with Fetal Cystic Hygroma: Report of Two Cases with Coexistent Down’s Syndrome. J. Clin. Ultrasound 1988, 16, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Putte, S.C.J. Lymphatic Malformation in Human Fetuses. Virchows Arch. A Path. Anat. Histol. 1977, 376, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, H.E.; McGahan, J.P. Intrauterine Fetal Cystic Hygromas: Sonographic Detection. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1981, 136, 799–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Meerhaeghe, T.; Vandenbroucke, F.; Velkeniers, B. Systemic Generalised Lymphangiomatosis: Unknown Aetiology and a Challenge to Treat. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e237331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozeki, M.; Nozawa, A.; Kawamoto, N.; Fujino, A.; Hirakawa, S.; Fukao, T. Potential Biomarkers of Kaposiform Lymphangiomatosis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2019, 66, e27878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croteau, S.E.; Kozakewich, H.P.W.; Perez-Atayde, A.R.; Fishman, S.J.; Alomari, A.I.; Chaudry, G.; Mulliken, J.B.; Trenor, C.C. Kaposiform Lymphangiomatosis: A Distinct Aggressive Lymphatic Anomaly. J. Pediatr. 2014, 164, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruggieri, P.; Montalti, M.; Angelini, A.; Alberghini, M.; Mercuri, M. Gorham–Stout Disease: The Experience of the Rizzoli Institute and Review of the Literature. Skelet. Radiol. 2011, 40, 1391–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Buonuomo, P.S.; Battafarano, G.; Conforti, A.; Mariani, E.; Algeri, M.; Pelle, S.; D’Agostini, M.; Macchiaiolo, M.; De Vito, R.; et al. Dissecting the Mechanisms of Bone Loss in Gorham-Stout Disease. Bone 2020, 130, 115068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurek, K.C.; Luks, V.L.; Ayturk, U.M.; Alomari, A.I.; Fishman, S.J.; Spencer, S.A.; Mulliken, J.B.; Bowen, M.E.; Yamamoto, G.L.; Kozakewich, H.P.W.; et al. Somatic Mosaic Activating Mutations in PIK3CA Cause CLOVES Syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le Cras, T.D.; Goines, J.; Lakes, N.; Pastura, P.; Hammill, A.M.; Adams, D.M.; Boscolo, E. Constitutively Active PIK3CA Mutations Are Expressed by Lymphatic and Vascular Endothelial Cells in Capillary Lymphatic Venous Malformation. Angiogenesis 2020, 23, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luks, V.L.; Kamitaki, N.; Vivero, M.P.; Uller, W.; Rab, R.; Bovée, J.V.M.G.; Rialon, K.L.; Guevara, C.J.; Alomari, A.I.; Greene, A.K.; et al. Lymphatic and Other Vascular Malformative/Overgrowth Disorders Are Caused by Somatic Mutations in PIK3CA. J. Pediatr. 2015, 166, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burrows, P.E.; Gonzalez-Garay, M.L.; Rasmussen, J.C.; Aldrich, M.B.; Guilliod, R.; Maus, E.A.; Fife, C.E.; Kwon, S.; Lapinski, P.E.; King, P.D.; et al. Lymphatic Abnormalities Are Associated with RASA1 Gene Mutations in Mouse and Man. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8621–8626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Gui, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Han, L.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. A Somatic Mutation in PIK3CD Unravels a Novel Candidate Gene for Lymphatic Malformation. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindhurst, M.J.; Sapp, J.C.; Teer, J.K.; Johnston, J.J.; Finn, E.M.; Peters, K.; Turner, J.; Cannons, J.L.; Bick, D.; Blakemore, L.; et al. A Mosaic Activating Mutation in AKT1 Associated with the Proteus Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, D.; Turner, J.T.; Olsen, C.; Biesecker, L.G.; Darling, T.N. Cutaneous Manifestations of Proteus Syndrome: Correlations with General Clinical Severity. Arch. Dermatol. 2004, 140, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlAnzi, T.; Al-Mashharawi, E.; Alhashem, A. Proteus Syndrome Caused by Novel Somatic AKT1 Duplication. Saudi Med. J. 2021, 42, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivanco, I.; Sawyers, C.L. The Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase–AKT Pathway in Human Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangas, J.; Nätynki, M.; Eklund, L. Development of Molecular Therapies for Venous Malformations. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 123, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Corral, I.; Zhang, Y.; Petkova, M.; Ortsäter, H.; Sjöberg, S.; Castillo, S.D.; Brouillard, P.; Libbrecht, L.; Saur, D.; Graupera, M.; et al. Blockade of VEGF-C Signaling Inhibits Lymphatic Malformations Driven by Oncogenic PIK3CA Mutation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Yan, J.; Chen, H.; Ji, Y.; Chen, J.; Cui, J.; Shen, W.; Zou, J. HIF-1α Contributes to Tube Malformation of Human Lymphatic Endothelial Cells by Upregulating VEGFR-3. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boussat, S.; Eddahibi, S.; Coste, A.; Fataccioli, V.; Gouge, M.; Housset, B.; Adnot, S.; Maitre, B. Expression and Regulation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Human Pulmonary Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2000, 279, L371–L378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mizukami, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Zimmer, M.A.; Iliopoulos, O.; Chung, D.C. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1-Independent Regulation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor by Hypoxia in Colon Cancer. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, X.; Yang, D.; Hu, J.; Hao, X.; Gao, J.; Mao, Z. Hypoxia Inducible Factor-Alpha Expression Correlates with Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-C Expression and Lymphangiogenesis/Angiogenesis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Acevedo, H.; Dornhoffer, J.R.; Stone, A.; Dai, Y.; Richter, G.T. Gene Expression Differences in Pediatric Lymphatic Malformations: Size Really Matters. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2018, 16, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinnebusch, A.G. The Scanning Mechanism of Eukaryotic Translation Initiation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2014, 83, 779–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalwani, N.M.; Rockson, S.G. Management of Lymphatic Vascular Malformations: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Vasc. Surg. Venous Lymphat. Disord. 2021, 9, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dighe, M.K.; Peterson, S.E.; Dubinsky, T.J.; Perkins, J.; Cheng, E. EXIT Procedure: Technique and Indications with Prenatal Imaging Parameters for Assessment of Airway Patency. Radiographics 2011, 31, 511–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilla-Velez, J.; Moore, B.P.; Cleves, M.A.; Buckmiller, L.; Richter, G.T. Surgical Resection of Macrocystic Lymphatic Malformations of the Head and Neck: Short and Long-Term Outcomes. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 134, 110013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glade, R.S.; Buckmiller, L.M. CO2 Laser Resurfacing of Intraoral Lymphatic Malformations: A 10-Year Experience. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2009, 73, 1358–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.W.; Kauvanough, K.; Orbach, D.B.; Alomari, A.I.; Mulliken, J.B.; Rahbar, R. Long-Term Outcome of Radiofrequency Ablation for Intraoral Microcystic Lymphatic Malformation. Arch. Otolaryngol.–Head Neck Surg. 2011, 137, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, M.C.; Zimmerman, M.B.; Burke, D.K.; Bauman, N.M.; Sato, Y.; Smith, R.J.H. OK-432 Collaborative Study Group Efficacy and Safety of OK-432 Immunotherapy of Lymphatic Malformations. Laryngoscope 2009, 119, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, P.; Pandey, V.; Bera, R.N.; Sharma, S.P.; Chauhan, N. Bleomycin Sclerotherapy in Lymphangiomas of the Head and Neck Region: A Prospective Study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 50, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, A.M.; Nijs, E.; Ballah, D.; Rabinowitz, D.; Thompson, L.; Rintoul, N.; Hedrick, H.; Jacobs, I.; Low, D. Percutaneous Sclerotherapy in Neonatal and Infant Head and Neck Lymphatic Malformations: A Single Center Experience. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2011, 46, 2083–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.M.; Wieck, M.M.; Grant, C.N.; Dossa, A.; Nowicki, D.; Stanley, P.; Zeinati, C.; Howell, L.K.; Anselmo, D.M. Doxycycline Sclerotherapy Is Superior in the Treatment of Pediatric Lymphatic Malformations. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 27, 1846–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, K.; Menezes, M.D.; Chen, B.S.; Magit, A.E.; Perkins, J.A. Primary Surgery vs Primary Sclerotherapy for Head and Neck Lymphatic Malformations. JAMA Otolaryngol.–Head Neck Surg. 2014, 140, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, S.; Wichmann, G.; Dietz, A. Treatment of Lymphatic Malformations with the MTOR Inhibitor Sirolimus: A Systematic Review. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2018, 16, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freixo, C.; Ferreira, V.; Martins, J.; Almeida, R.; Caldeira, D.; Rosa, M.; Costa, J.; Ferreira, J. Efficacy and Safety of Sirolimus in the Treatment of Vascular Anomalies: A Systematic Review. J. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 71, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, D.M.; Trenor, C.C.; Hammill, A.M.; Vinks, A.A.; Patel, M.N.; Chaudry, G.; Wentzel, M.S.; Mobberley-Schuman, P.S.; Campbell, L.M.; Brookbank, C.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Sirolimus in the Treatment of Complicated Vascular Anomalies. Pediatrics 2016, 137, e20153257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, L.S.; Vautier, M.; Allenbach, Y.; Zahr, N.; Benveniste, O.; Funck-Brentano, C.; Salem, J.-E. Sirolimus and MTOR Inhibitors: A Review of Side Effects and Specific Management in Solid Organ Transplantation. Drug Saf. 2019, 42, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danial, C.; Tichy, A.L.; Tariq, U.; Swetman, G.L.; Khuu, P.; Leung, T.H.; Benjamin, L.; Teng, J.; Vasanawala, S.S.; Lane, A.T. An Open-Label Study to Evaluate Sildenafil for the Treatment of Lymphatic Malformations. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 70, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koshy, J.C.; Eisemann, B.S.; Agrawal, N.; Pimpalwar, S.; Edmonds, J.L. Sildenafil for Microcystic Lymphatic Malformations of the Head and Neck: A Prospective Study. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 79, 980–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozeki, M.; Kanda, K.; Kawamoto, N.; Ohnishi, H.; Fujino, A.; Hirayama, M.; Kato, Z.; Azuma, E.; Fukao, T.; Kondo, N. Propranolol as an Alternative Treatment Option for Pediatric Lymphatic Malformation. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2013, 229, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samuels, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bardelli, A.; Silliman, N.; Ptak, J.; Szabo, S.; Yan, H.; Gazdar, A.; Powell, S.M.; Riggins, G.J.; et al. High Frequency of Mutations of the PIK3CA Gene in Human Cancers. Science 2004, 304, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madsen, R.R.; Knox, R.G.; Pearce, W.; Lopez, S.; Mahler-Araujo, B.; McGranahan, N.; Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Semple, R.K. Oncogenic PIK3CA Promotes Cellular Stemness in an Allele Dose-Dependent Manner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8380–8389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keppler-Noreuil, K.M.; Parker, V.E.R.; Darling, T.N.; Martinez-Agosto, J.A. Somatic Overgrowth Disorders of the PI3K/AKT/MTOR Pathway & Therapeutic Strategies. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2016, 172, 402–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venot, Q.; Blanc, T.; Rabia, S.H.; Berteloot, L.; Ladraa, S.; Duong, J.-P.; Blanc, E.; Johnson, S.C.; Hoguin, C.; Boccara, O.; et al. Targeted Therapy in Patients with PIK3CA-Related Overgrowth Syndrome. Nature 2018, 558, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delestre, F.; Venot, Q.; Bayard, C.; Fraissenon, A.; Ladraa, S.; Hoguin, C.; Chapelle, C.; Yamaguchi, J.; Cassaca, R.; Zerbib, L.; et al. Alpelisib Administration Reduced Lymphatic Malformations in a Mouse Model and in Patients. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabg0809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhani, N.; Tolcher, A.W.; Rasco, D.W.; Patnaik, A.; O’Rourke, T.J.; Schwartz, B.E.; Abbadessa, G.; Kazakin, J.; Savage, R.; Wang, Y.; et al. Results of a Phase Ib Study of ARQ 092 in Combination with Carboplatin (C) plus Paclitaxel (P), or with P in Patients (Pts) with Solid Tumors. JCO 2017, 35, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyman, D.; Bonafede, M.; O’Cearbhaill, R.; Grisham, R.; Zamarin, D.; Tew, W.; Aghajanian, C.; Cadoo, K.; Friedman, C.; Savage, R.E.; et al. Abstract CT035: A Phase Ib Study of Miransertib (ARQ 092) in Combination with Anastrozole in Patients with PIK3CA or AKT1-Mutant ER+ Endometrial or Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, CT035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppler-Noreuil, K.M.; Sapp, J.C.; Lindhurst, M.J.; Darling, T.N.; Burton-Akright, J.; Bagheri, M.; Dombi, E.; Gruber, A.; Jarosinski, P.F.; Martin, S.; et al. Pharmacodynamic Study of Miransertib in Individuals with Proteus Syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 104, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forde, K.; Resta, N.; Ranieri, C.; Rea, D.; Kubassova, O.; Hinton, M.; Andrews, K.A.; Semple, R.; Irvine, A.D.; Dvorakova, V. Clinical Experience with the AKT1 Inhibitor Miransertib in Two Children with PIK3CA-Related Overgrowth Syndrome. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-W.; Galanzha, E.I.; Shashkov, E.V.; Moon, H.-M.; Zharov, V.P. Golden Carbon Nanotubes as Multimodal Photoacoustic and Photothermal High-Contrast Molecular Agents. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.Y.; Loll, E.G.; Hassan, A.-E.S.; Cheng, M.; Wang, A.; Farmer, D.L. Genetic and Molecular Determinants of Lymphatic Malformations: Potential Targets for Therapy. J. Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb10010011
Lee SY, Loll EG, Hassan A-ES, Cheng M, Wang A, Farmer DL. Genetic and Molecular Determinants of Lymphatic Malformations: Potential Targets for Therapy. Journal of Developmental Biology. 2022; 10(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb10010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Su Yeon, Emma Grace Loll, Abd-Elrahman Said Hassan, Mingyu Cheng, Aijun Wang, and Diana Lee Farmer. 2022. "Genetic and Molecular Determinants of Lymphatic Malformations: Potential Targets for Therapy" Journal of Developmental Biology 10, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb10010011
APA StyleLee, S. Y., Loll, E. G., Hassan, A.-E. S., Cheng, M., Wang, A., & Farmer, D. L. (2022). Genetic and Molecular Determinants of Lymphatic Malformations: Potential Targets for Therapy. Journal of Developmental Biology, 10(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb10010011






