The Feasibility of Three Prediction Techniques of the Artificial Neural Network, Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System, and Hybrid Particle Swarm Optimization for Assessing the Safety Factor of Cohesive Slopes
Abstract
1. Introduction
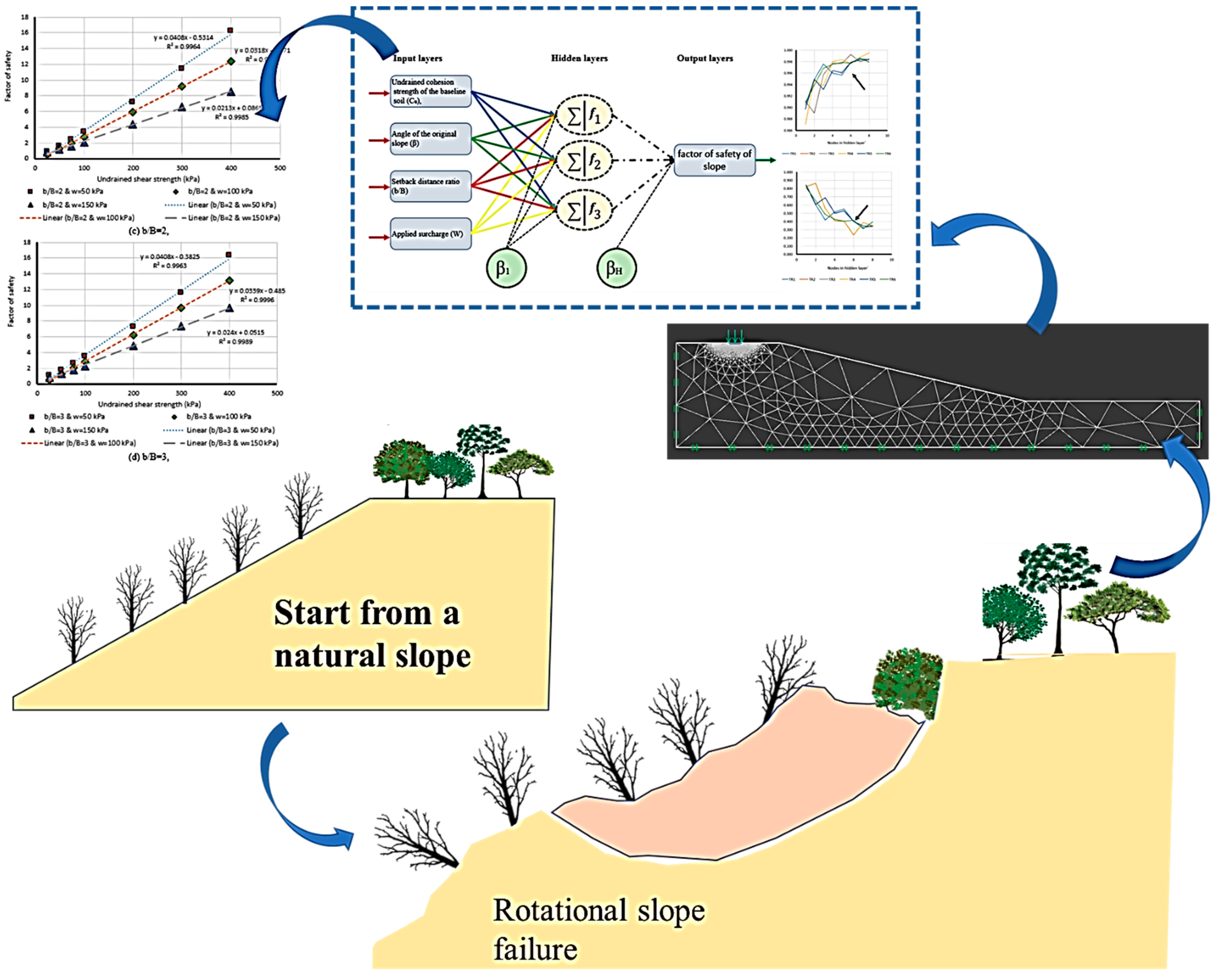
2. Data Collection and Methodology
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Methodology
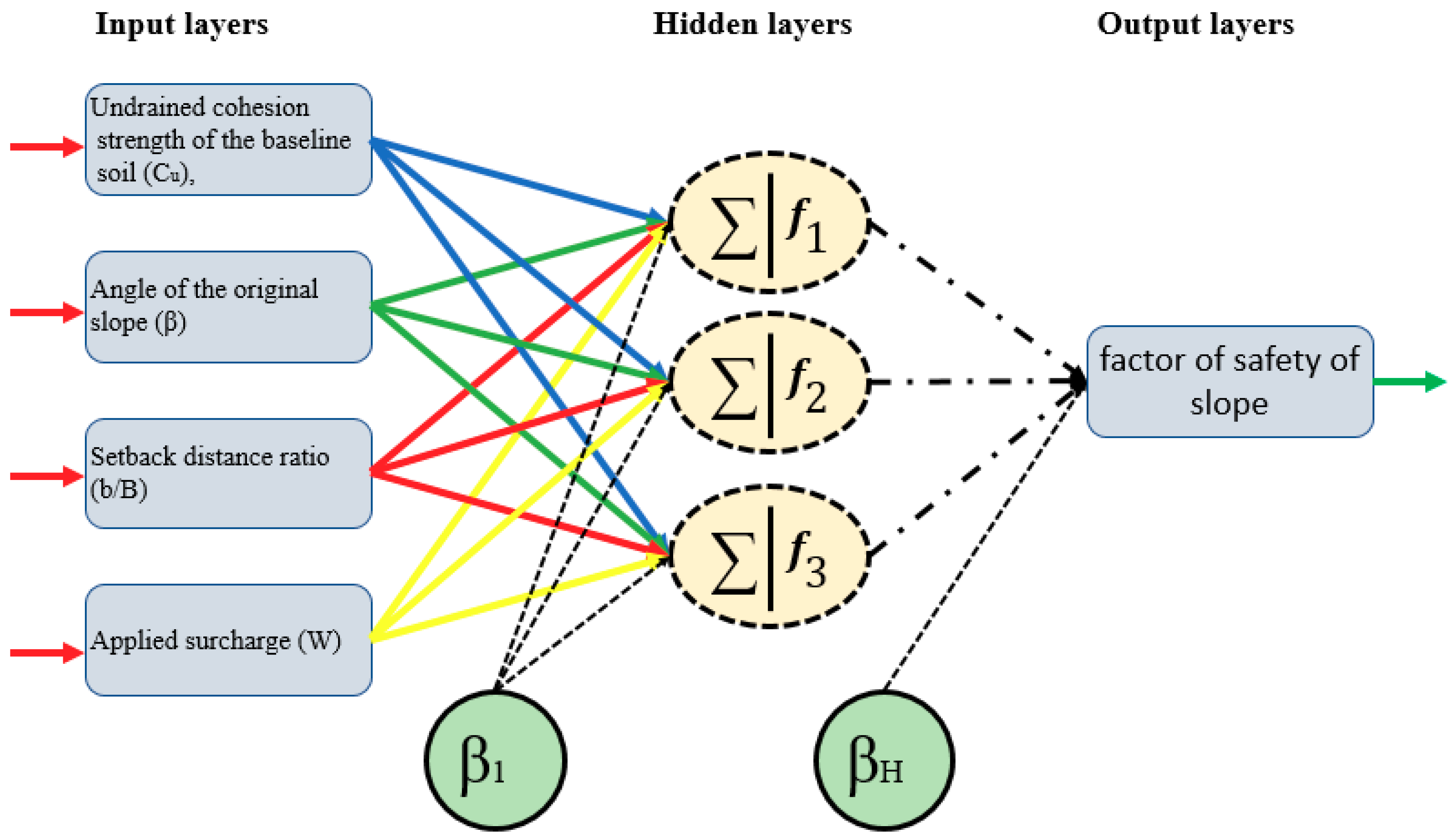
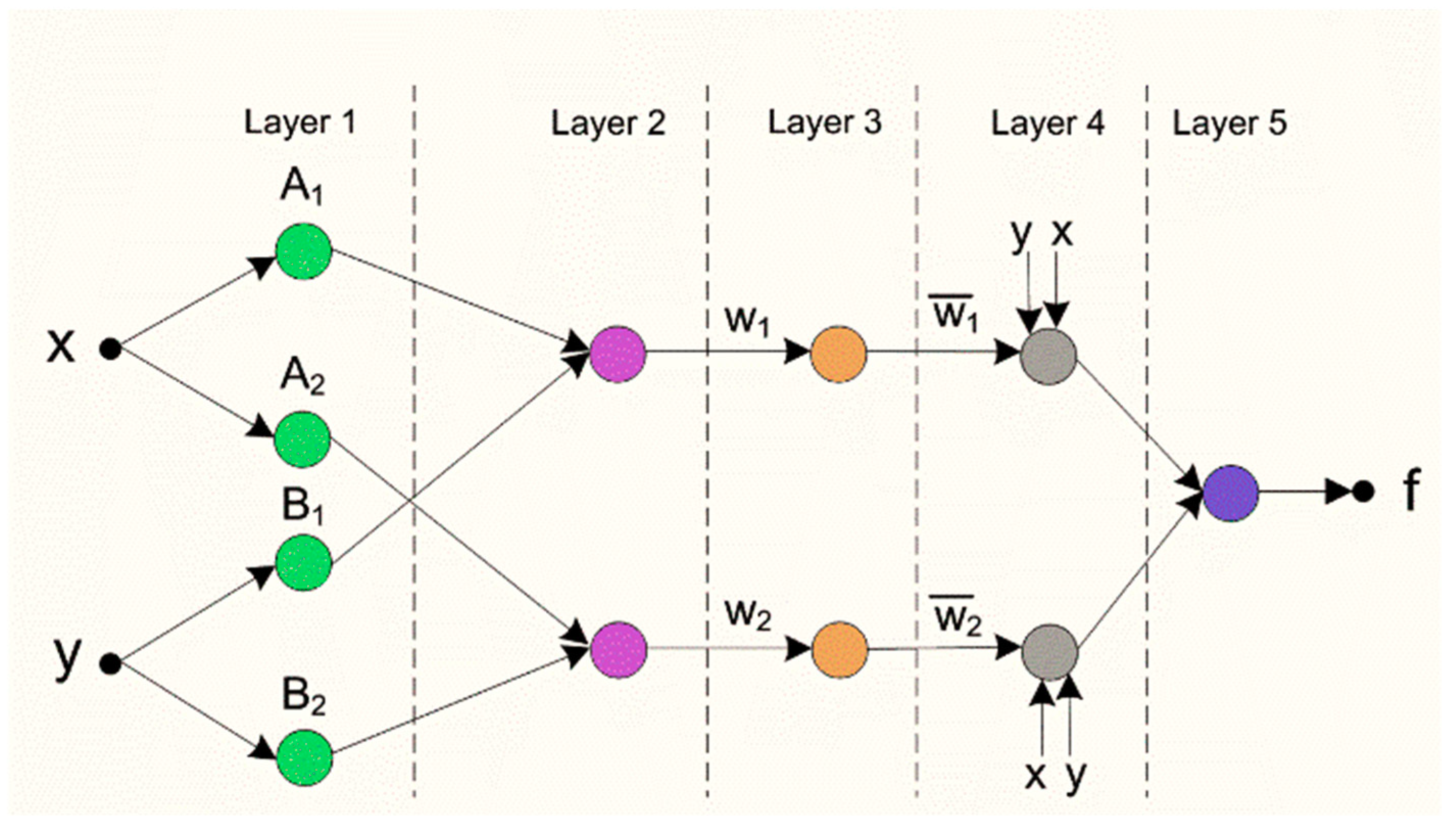
2.2.1. Artificial intelligence Implementation
2.2.2. Model Development for Estimation of a Factor of Safety
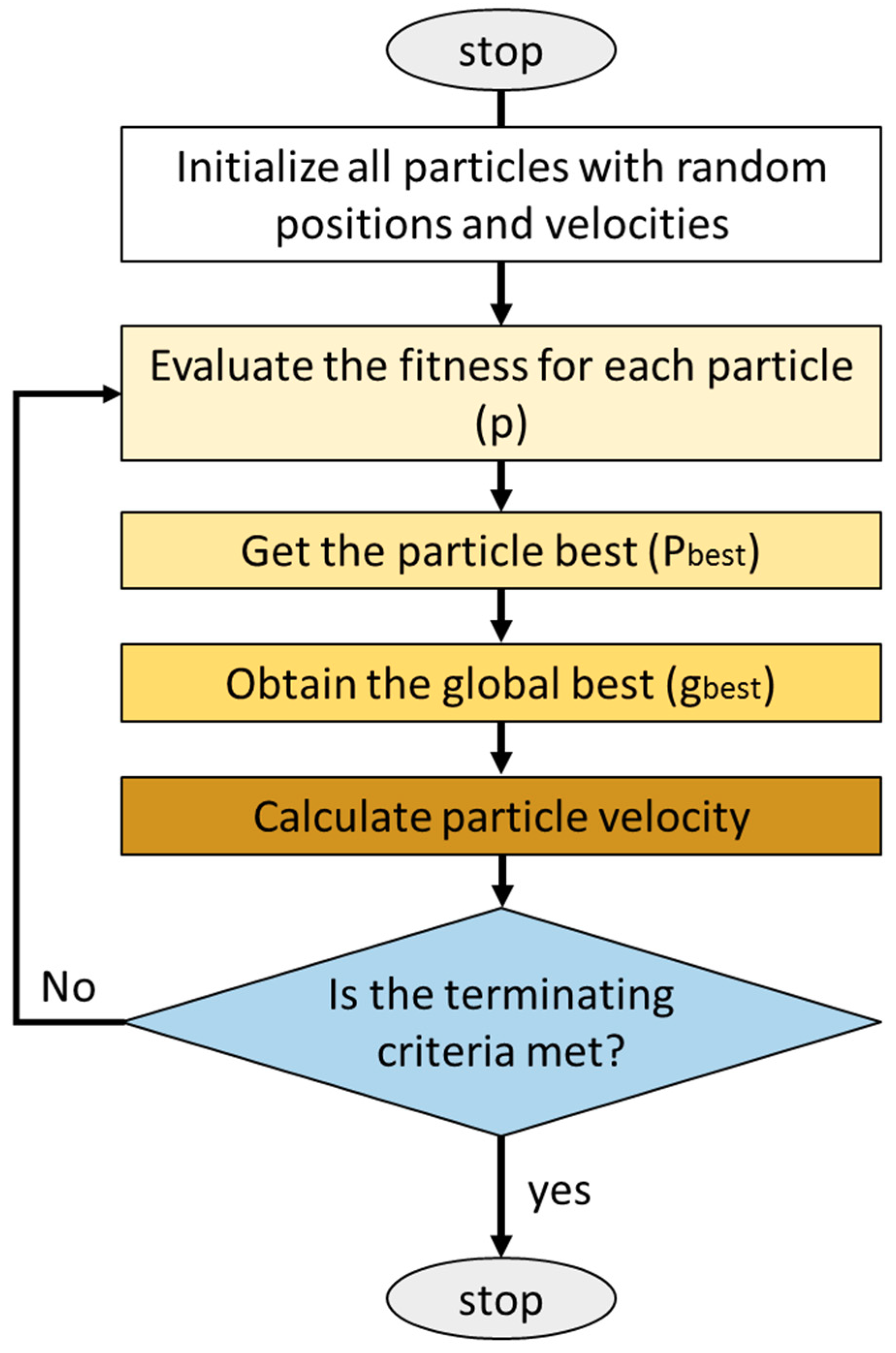
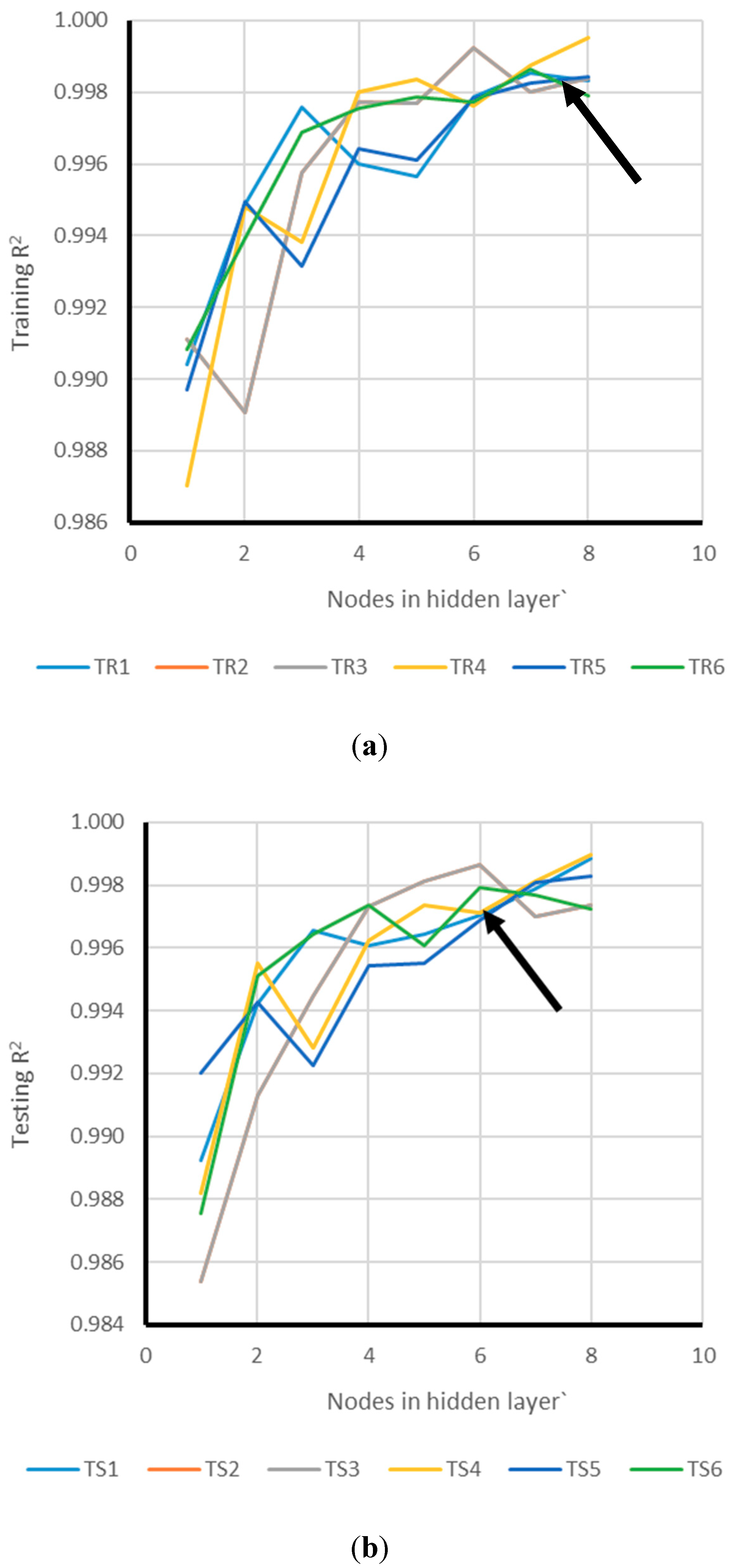
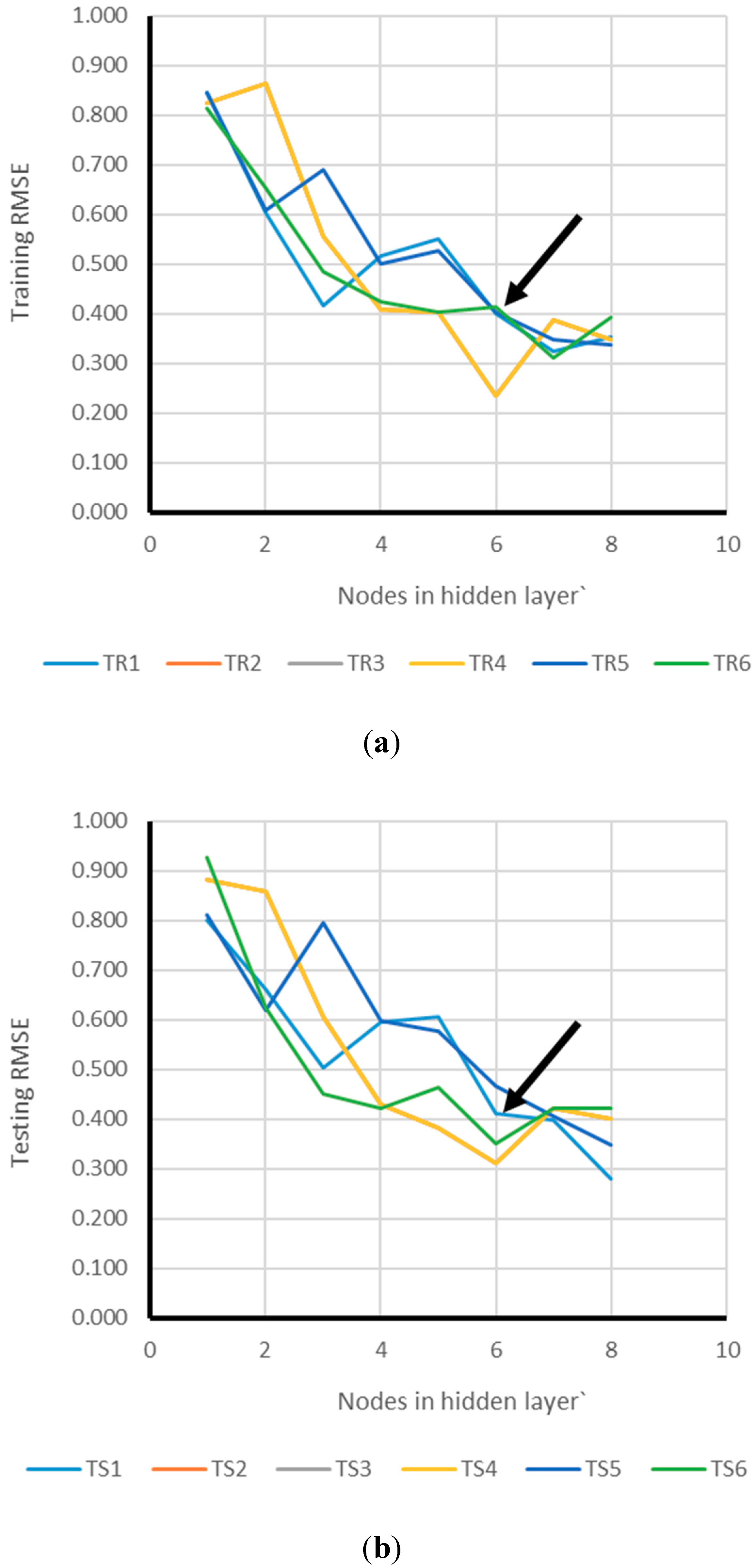
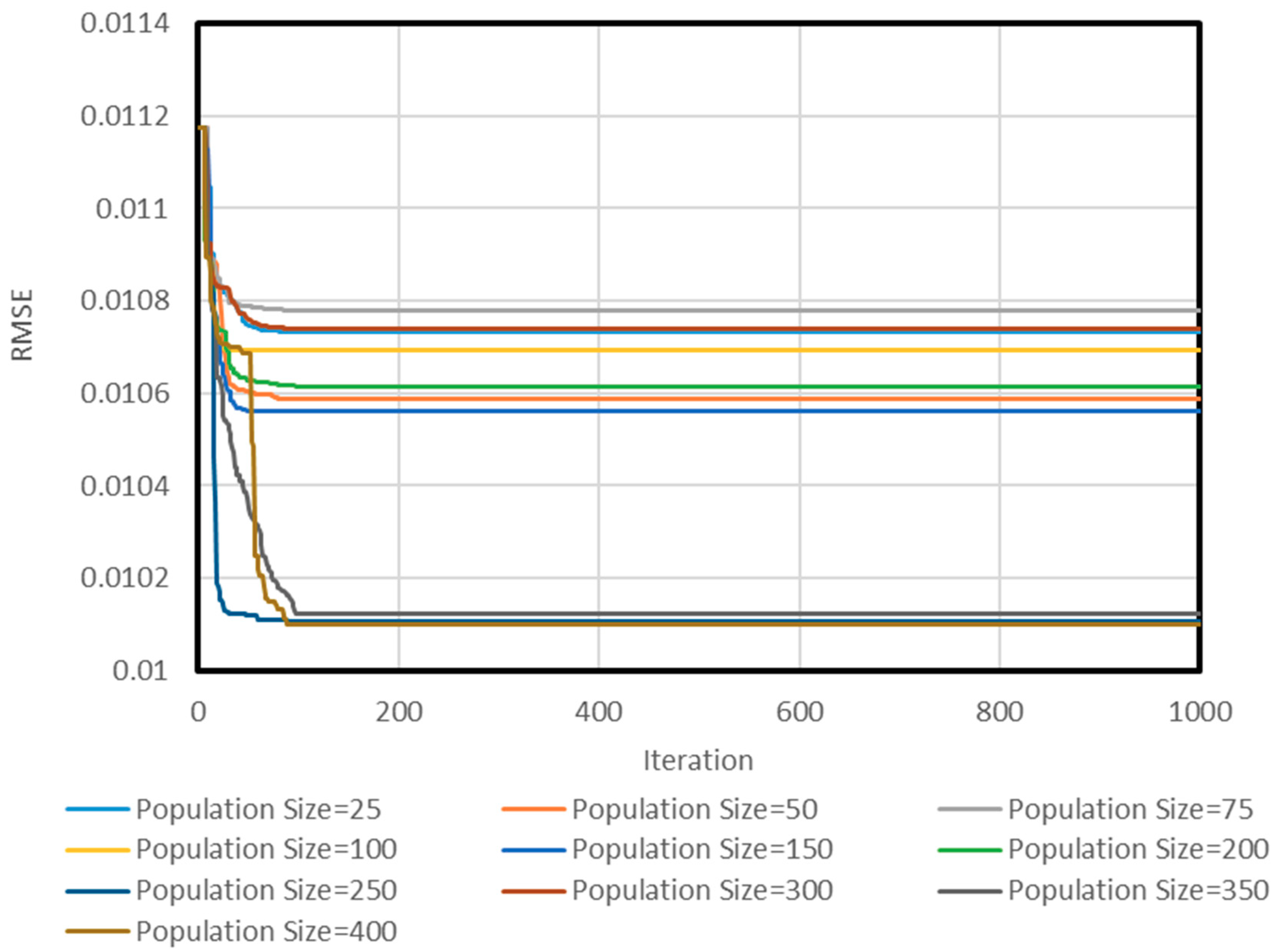
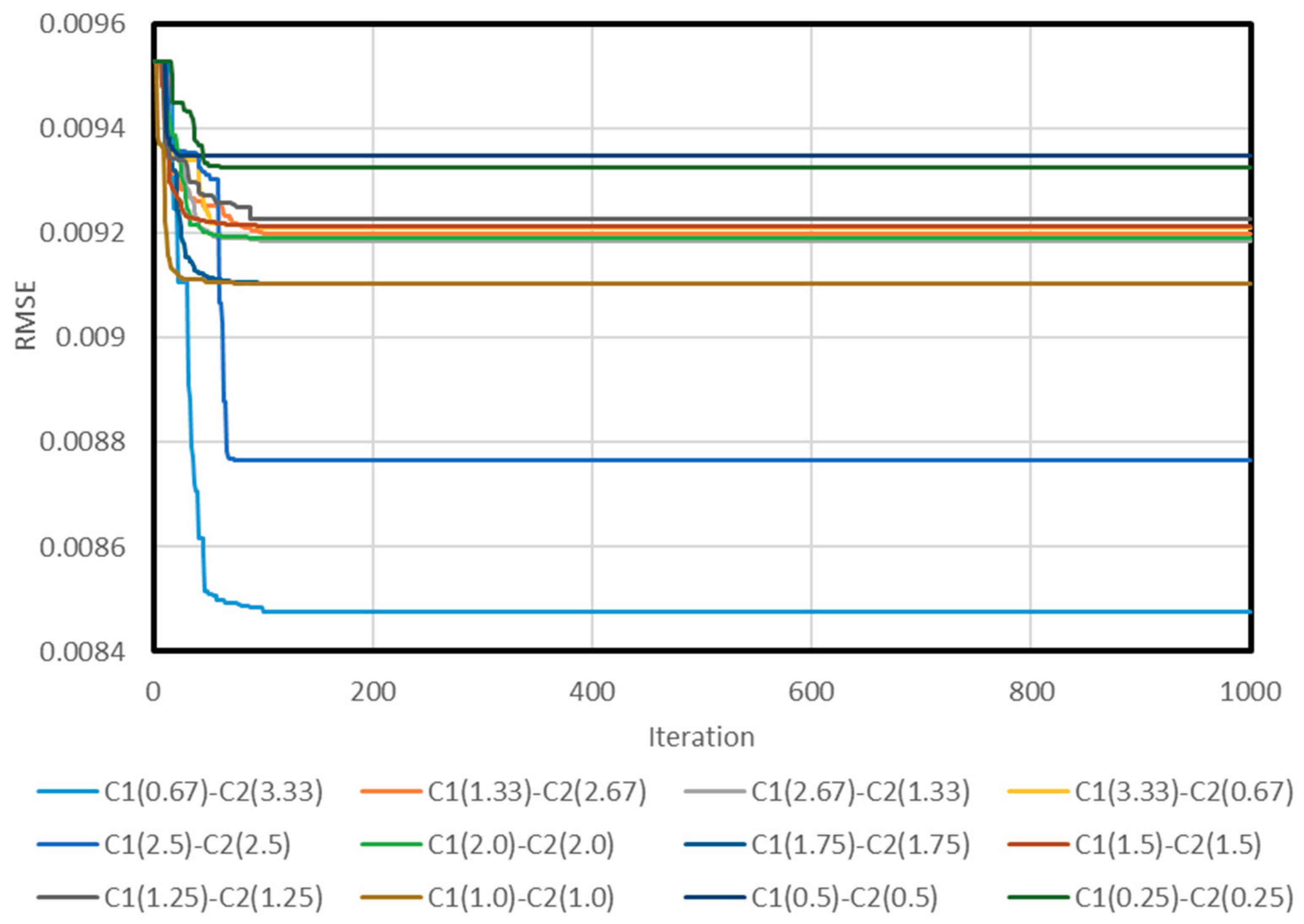
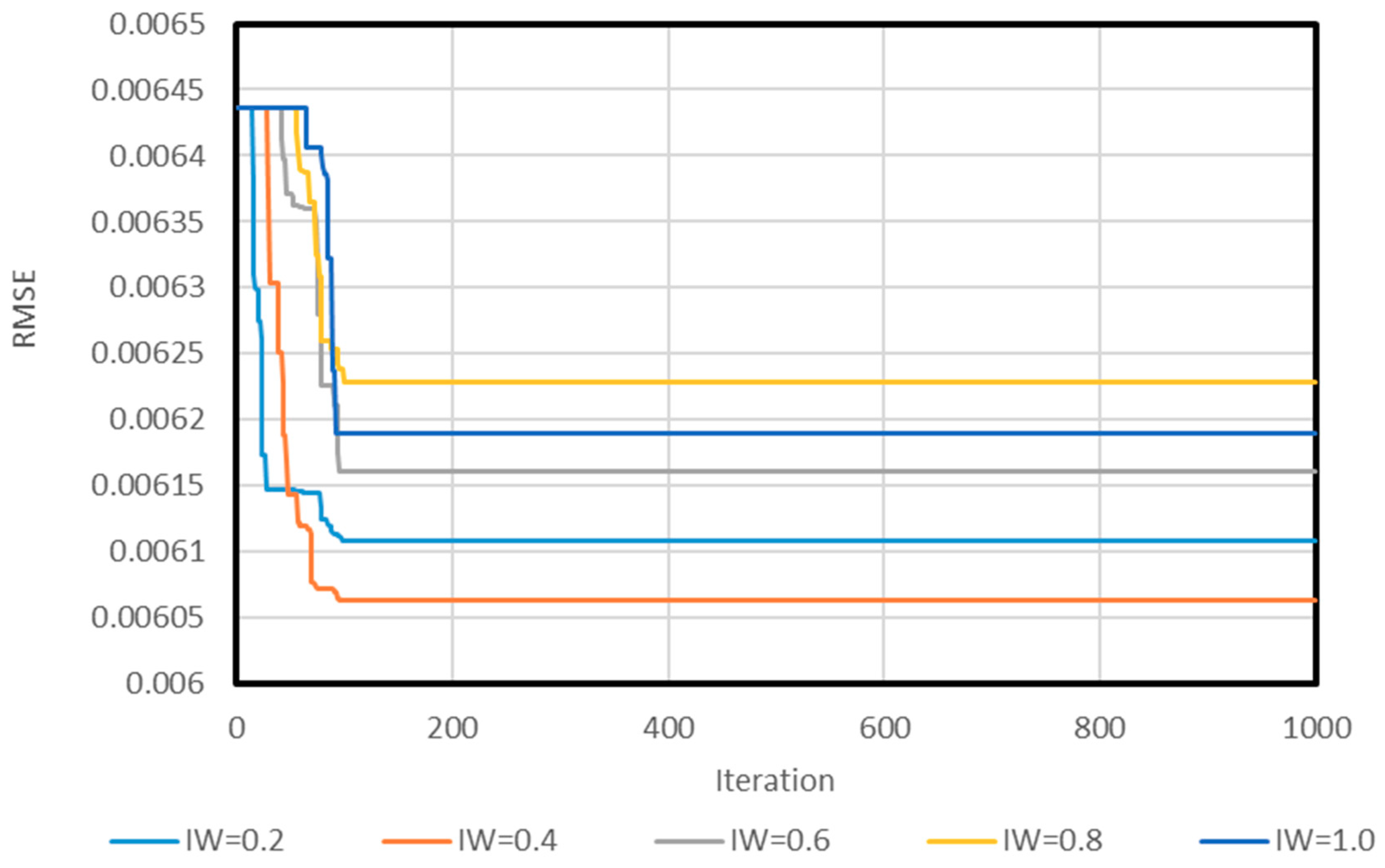
2.2.3. Network Structure Optimization
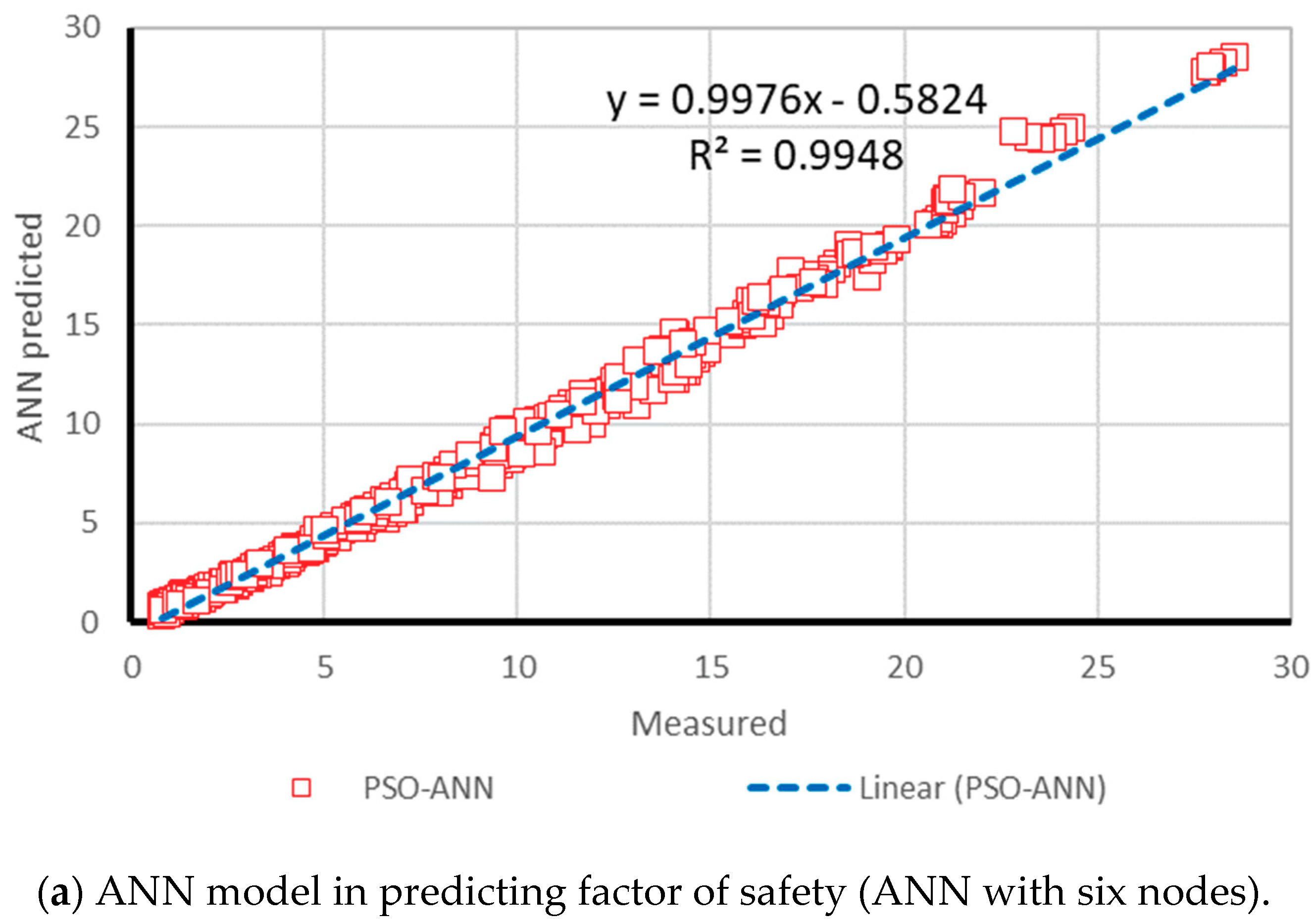
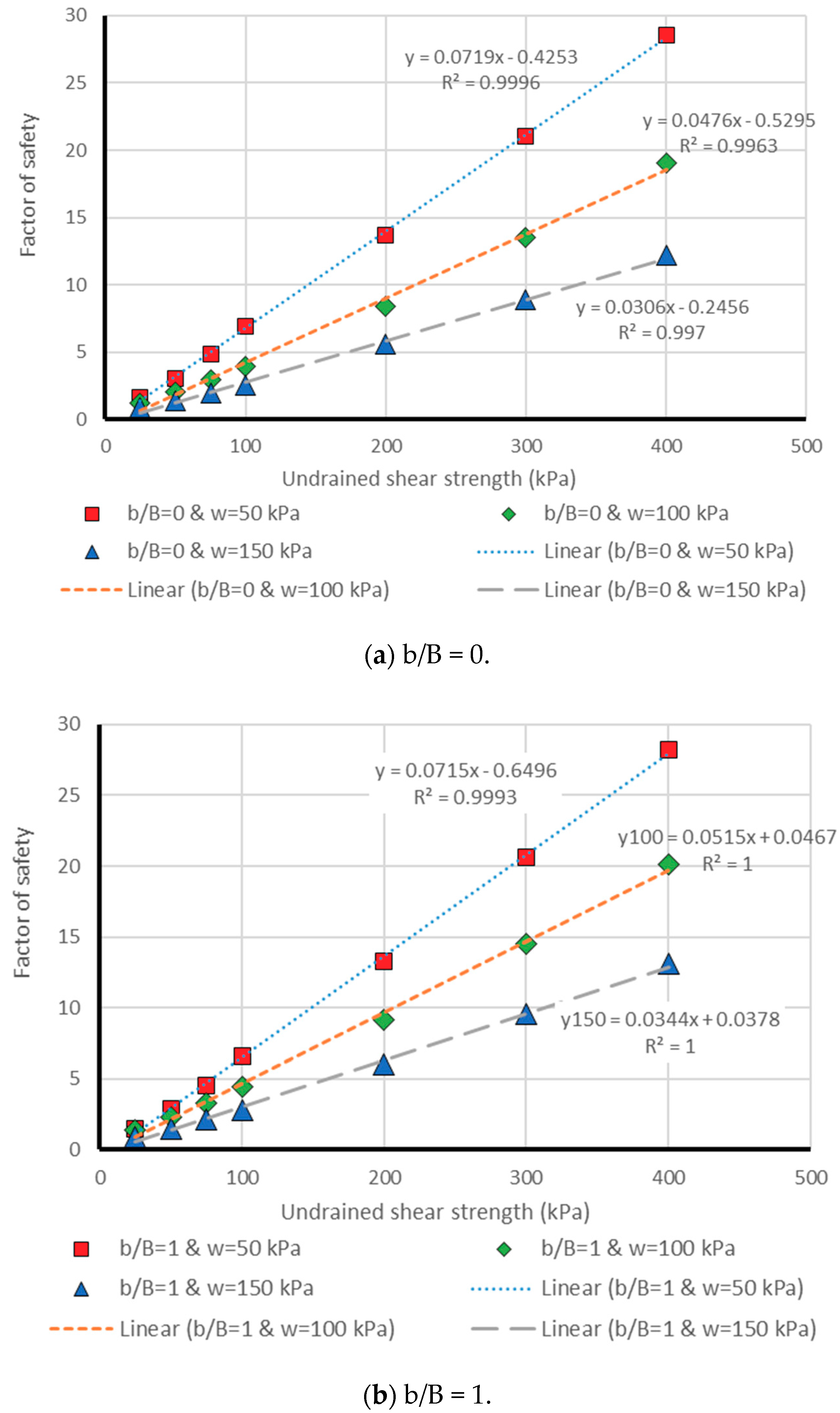
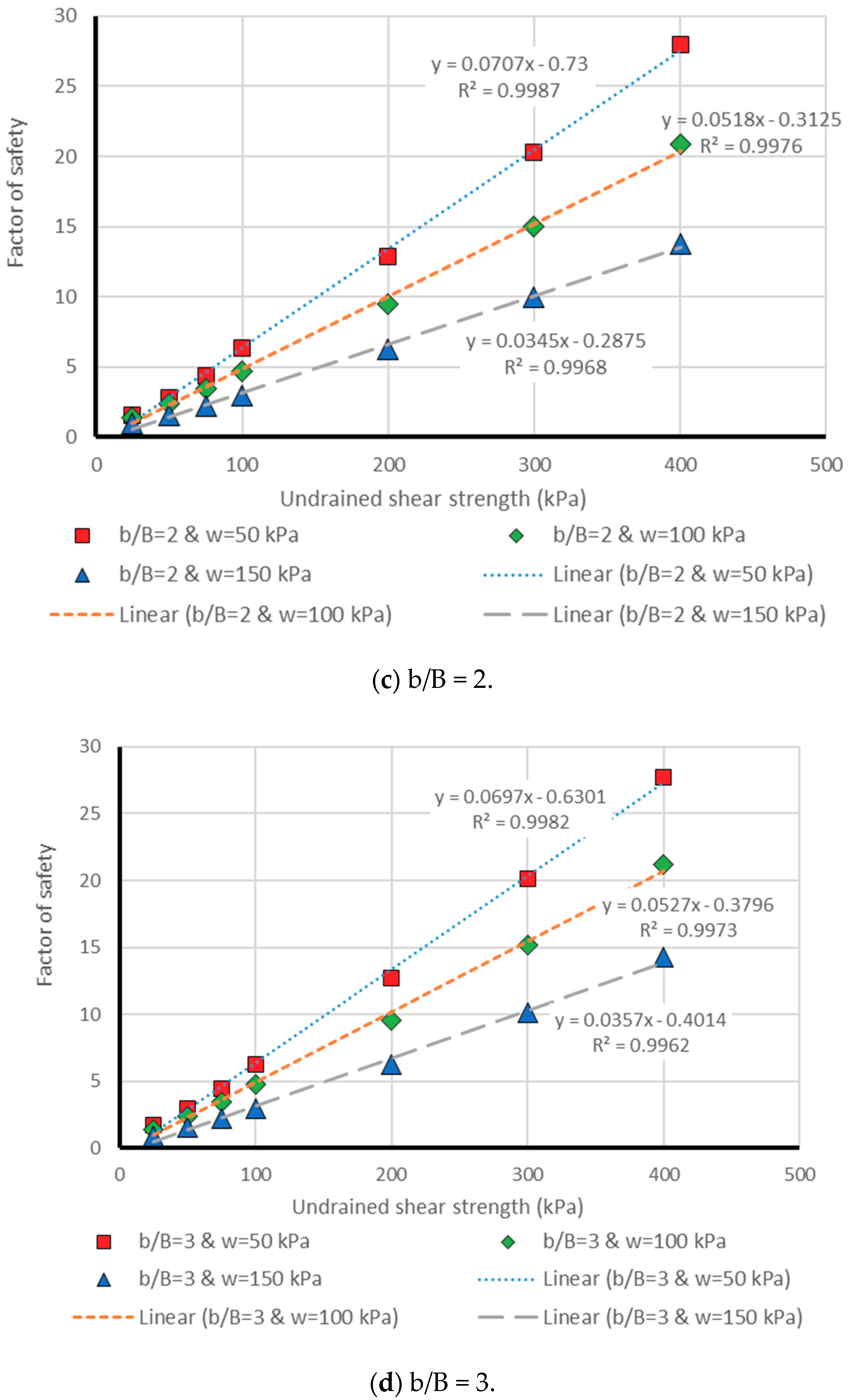
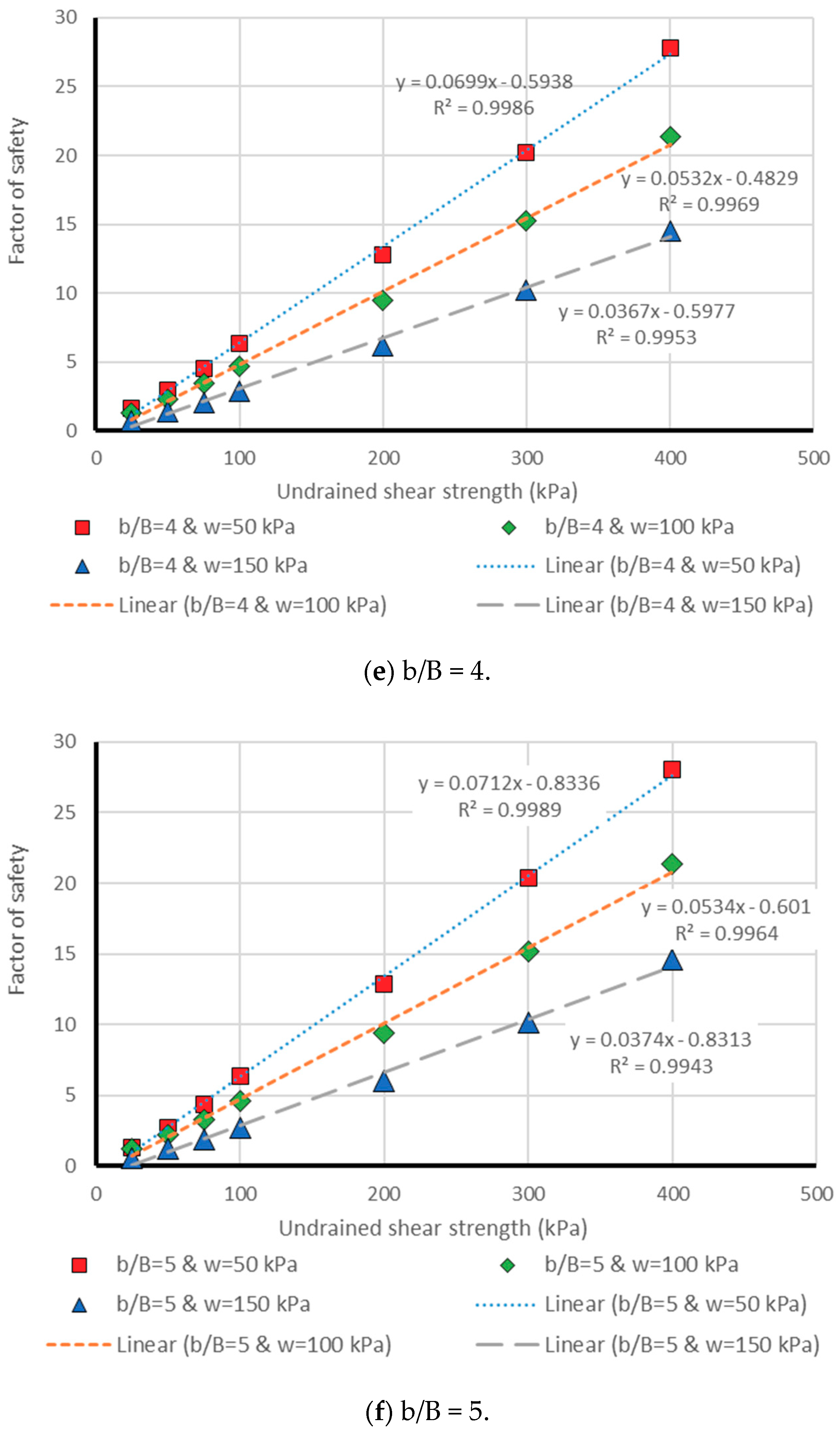
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Neuro PSO-ANN Optimization
3.2. Model Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pei, H.; Zhang, S.; Borana, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yin, J. Slope stability analysis based on real-time displacement measurements. Measurement 2019, 131, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellali, B.; Frikha, W. Constrained particle swarm optimization algorithm applied to slope stability. Int. J. Geomech. 2017, 17, 06017022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binh Thai, P.; Manh Duc, N.; Kien-Trinh Thi, B.; Prakash, I.; Chapi, K.; Dieu Tien, B. A novel artificial intelligence approach based on multi-layer perceptron neural network and biogeography-based optimization for predicting coefficient of consolidation of soil. Catena 2019, 173, 302–311. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, A.M.; Pradhan, B.; Al-Harthi, S.G. Assessment of rock slope stability and structurally controlled failures along Samma escarpment road, Asir Region (Saudi Arabia). Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 6835–6852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binh Thai, P.; Dieu Tien, B.; Prakash, I. Bagging based support vector machines for spatial prediction of landslides. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 146. [Google Scholar]
- Binh Thai, P.; Prakash, I.; Dieu Tien, B. Spatial prediction of landslides using a hybrid machine learning approach based on random subspace and classification and regression trees. Geomorphology 2018, 303, 256–270. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.; Bui, X.-N.; Tran, Q.-H.; Le, T.-Q.; Do, N.-H. Evaluating and predicting blast-induced ground vibration in open-cast mine using ANN: A case study in Vietnam. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayedi, H.; Mosallanezhad, M.; Safuan, A.R.A.; Amizah, W.J.W.; Muazu, M.A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of artificial neural network application in geotechnical engineering: Theory and applications. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayedi, H.; Mosallanezhad, M.; Mehrabi, M.; Safuan, A.R.A.; Biswajeet, P. Modification of landslide susceptibility mapping using optimized PSO-ANN technique. Eng. Comput. 2019, 35, 967–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J. Research of steel plate temperature prediction based on the improved PSO-ANN algorithm for roller hearth normalizing furnace. In Proceedings of the 2010 8th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation (WCICA), Jinan, China, 7–9 July 2010; pp. 2464–2469. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.P.; Ren, S.B.; Guo, Z.C. The tunnel surrounding rock parameters identification method based on PSO-ANN. In Advances in Structural Engineering, Pts 1–3; Zhou, X.J., Ed.; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Durnten-Zurich, Switzerland, 2011; Volume 94–96, pp. 637–640. [Google Scholar]
- Alnaqi, A.A.; Moayedi, H.; Shahsavar, A.; Nguyen, T.K. Prediction of energetic performance of a building integrated photovoltaic/thermal system thorough artificial neural network and hybrid particle swarm optimization models. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 183, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayedi, H.; Hayati, S. Applicability of a CPT-based neural network solution in predicting load-settlement responses of bored pile. Int. J. Geomech. 2018, 18, 06018009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayedi, H.; Huat, B.; Kazemian, S.; Asadi, A. Optimization of shear behavior of reinforcement through the reinforced slope. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 2010, 15, 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Raftari, M.; Kassim, K.A.; Rashid, A.S.A.; Moayedi, H. Settlement of shallow foundations near reinforced slopes. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 2013, 18, 797–808. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, J.J.; Wang, X.S.; Nandy, S. Confined groundwater zone and slope instability in weathered igneous rocks in Hong Kong. Eng. Geol. 2005, 80, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourghasemi, H.R.; Moradi, H.R.; Aghda, S.M.F.; Gokceoglu, C.; Pradhan, B. GIS-based landslide susceptibility mapping with probabilistic likelihood ratio and spatial multi-criteria evaluation models (North of Tehran, Iran). Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 1857–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayedi, H.; Armaghani, D.J. Optimizing an ANN model with ICA for estimating bearing capacity of driven pile in cohesionless soil. Eng. Comput. 2017, 34, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayedi, H.; Mosallanezhad, M.; Nazir, R. Evaluation of maintained load test (MLT) and pile driving analyzer (PDA) in measuring bearing capacity of driven reinforced concrete piles. Soil Mech. Found. Eng. 2017, 54, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krabbenhoft, K.; Lyamin, A.; Krabbenhoft, J. Optum Computational Engineering (OptumG2). Computer Software. 2015. Available online: https://www. optumce.com (accessed on 15 June 2016).
- McCulloch, W.S.; Pitts, W. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull. Math. Biophys. 1943, 5, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebb, D. The Organization of Behavior: A Neurophysiological Approach; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Guirao, J.L.G.; Abdel-Aty, M.; Xi, W. An independent set degree condition for fractional critical deleted graphs. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. S 2019, 12, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Guirao, J.L.G.; Basavanagoud, B.; Wu, J. Partial multi-dividing ontology learning algorithm. Inf. Sci. 2018, 467, 35–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.A.; Ebadi, M.; Shokrollahi, A.; Majidi, S.M.J. Evolving artificial neural network and imperialist competitive algorithm for prediction oil flow rate of the reservoir. Appl. Soft Comput. 2013, 13, 1085–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-C. Artificial neural network. In Interdisciplinary Computing in Java Programming; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 81–100. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Moayedi, H.; Shahsavar, A. The feasibility of genetic programming and ANFIS in prediction energetic performance of a building integrated photovoltaic thermal (BIPVT) system. Sol. Energy 2019, 183, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Wu, H.; Siddiqui, M.K.; Baig, A.Q. Study of biological networks using graph theory. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moayedi, H.; Hayati, S. Artificial intelligence design charts for predicting friction capacity of driven pile in clay. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 31, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-L.; Dun, J.-F. A distributed PSO–SVM hybrid system with feature selection and parameter optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 2008, 8, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsarraf, J.; Moayedi, H.; Rashid, A.S.A.; Muazu, M.A.; Shahsavar, A. Application of PSO–ANN modelling for predicting the exergetic performance of a building integrated photovoltaic/thermal system. Eng. Comput. 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayedi, H.; Raftari, M.; Sharifi, A.; Jusoh, W.A.W.; Rashid, A.S.A. Optimization of ANFIS with GA and PSO estimating α ratio in driven piles. Eng. Comput. 2019, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong-Thao, T.N.; Nhat-Duc, H.; Pradhan, B.; Quang Khanh, N.; Xuan Truong, T.; Quang Minh, N.; Viet Nghia, N.; Samui, P.; Bui, D.T. A novel hybrid swarm optimized multilayer neural network for spatial prediction of flash floods in tropical areas using sentinel-1 SAR imagery and geospatial data. Sensors 2018, 18, 3704. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, J.-S.R.; Sun, C.-T. Neuro-fuzzy modeling and control. Proc. IEEE 1995, 83, 378–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-S.R.; Sun, C.-T.; Mizutani, E. Neuro-Fuzzy and Soft Computing: A Computational Approach to Learning and Machine Intelligence; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, S.R. ANFIS: Adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1993, 23, 665–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Pillai, G.N.; Pal, K.; Jagtap, P. Prediction of ground motion parameters using randomized ANFIS (RANFIS). Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 40, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieu Tien, B.; Khosravi, K.; Li, S.; Shahabi, H.; Panahi, M.; Singh, V.P.; Chapi, K.; Shirzadi, A.; Panahi, S.; Chen, W.; et al. New hybrids of ANFIS with several optimization algorithms for flood susceptibility modeling. Water 2018, 10, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
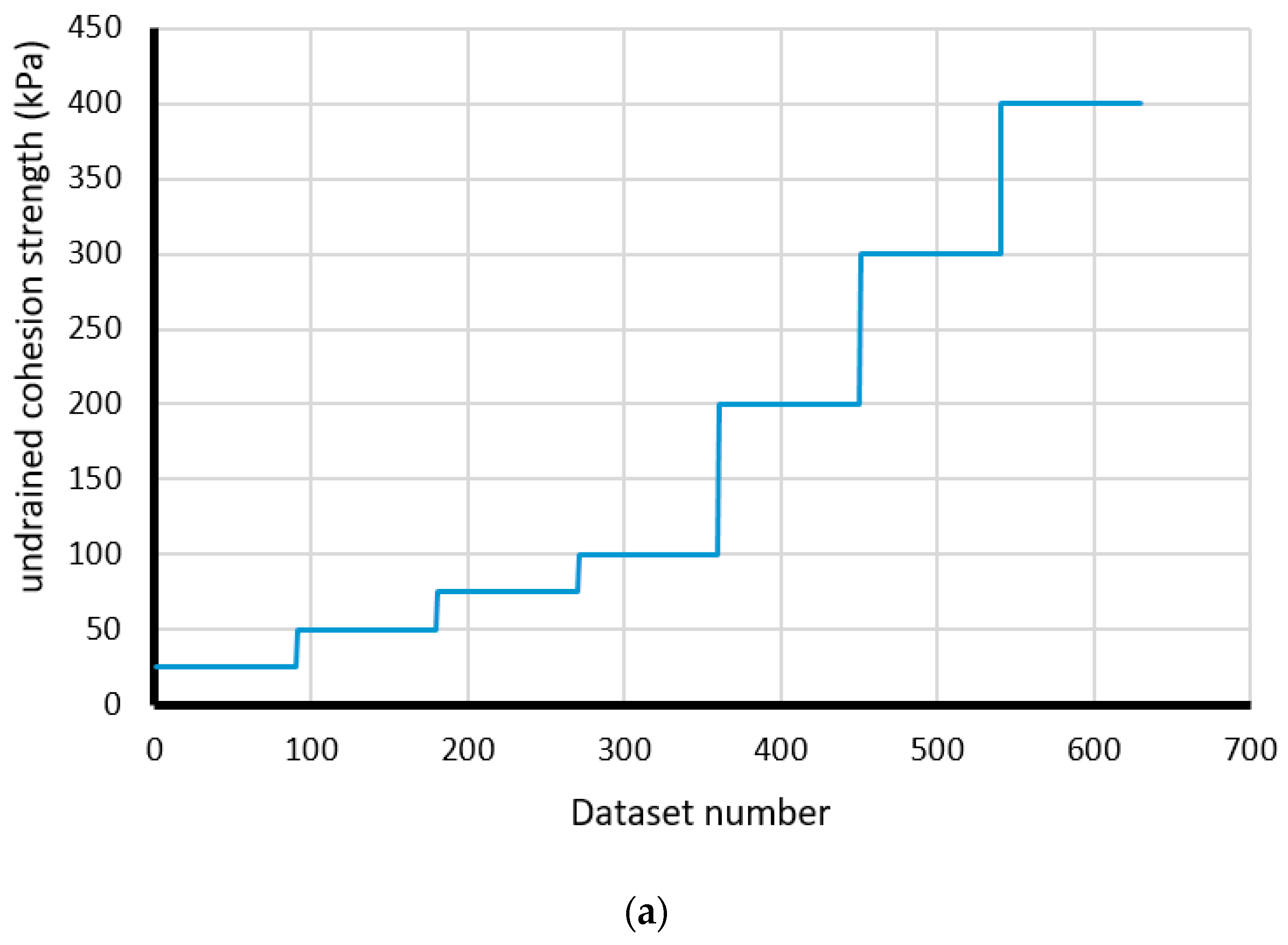
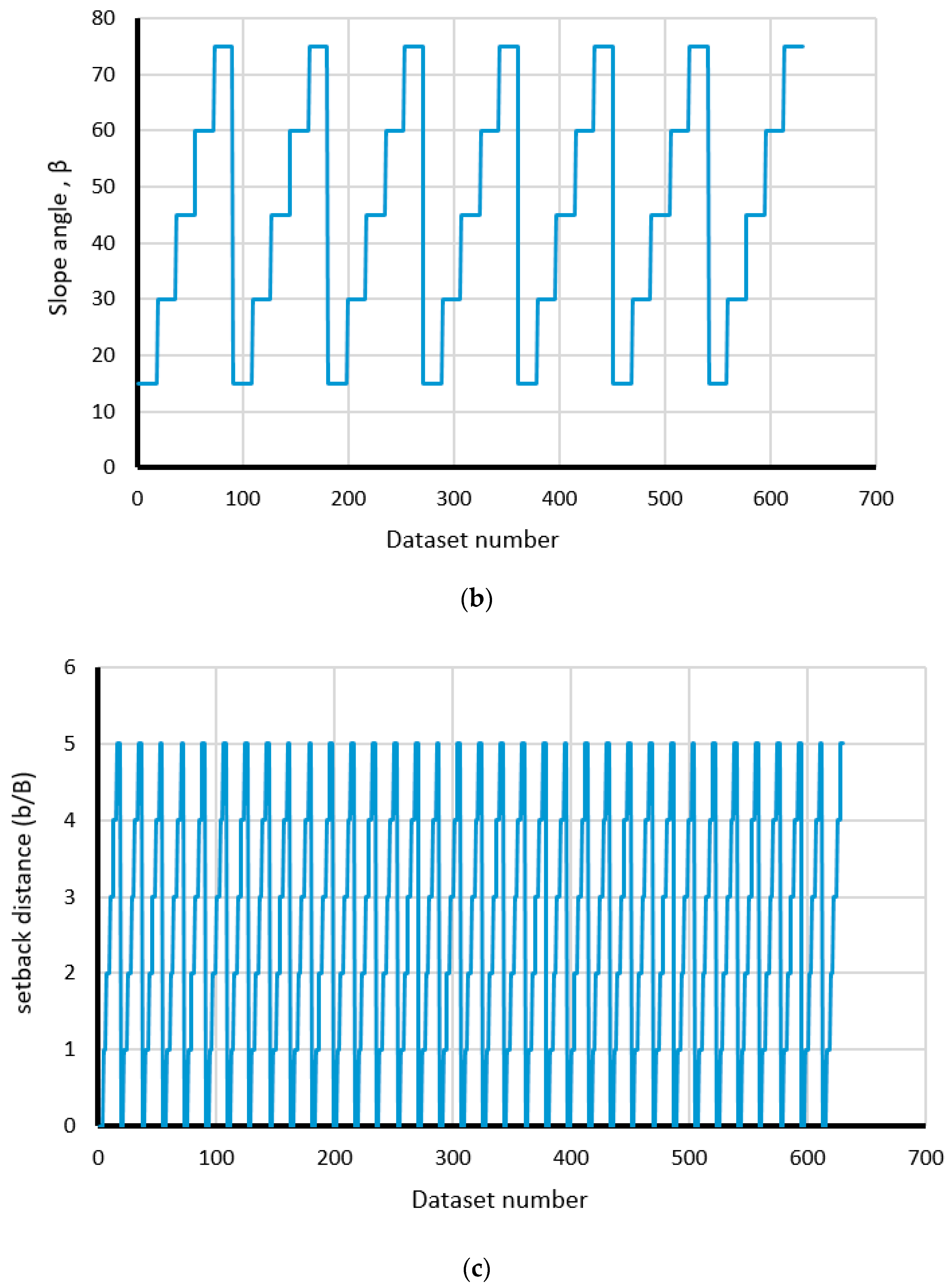
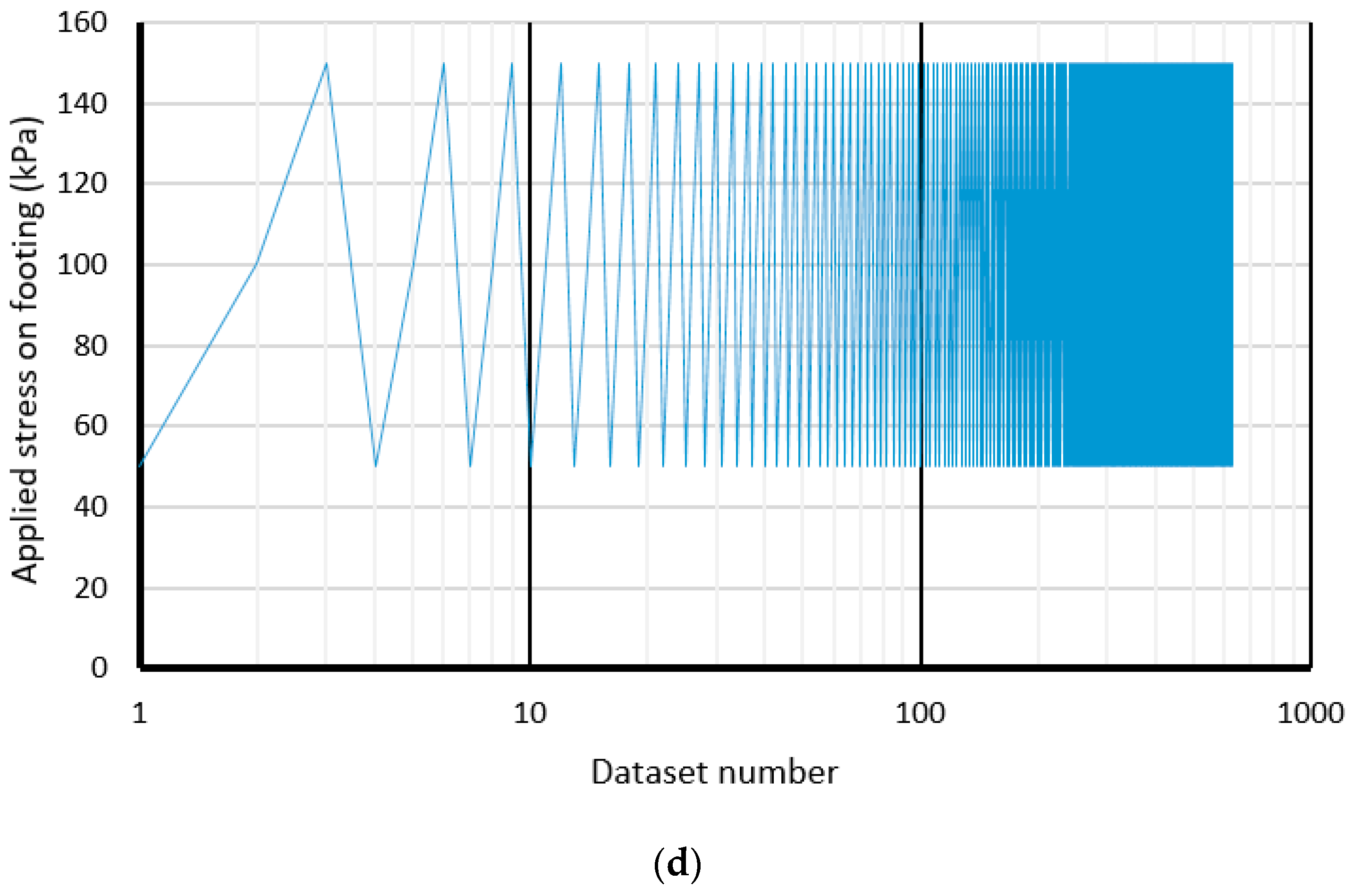


| Model Number | Inputs | Output | Model Number | Inputs | Output | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu (kN/m2) | β (°) | b/B (-) | W (kN/m2) | Safety Factor | Cu (kN/m2) | β (°) | b/B (-) | W (kN/m2) | Safety Factor | ||
| 1 | 25 | 15 | 0 | 50 | 1.872 | 570 | 400 | 30 | 3 | 150 | 14.06 |
| 2 | 25 | 15 | 0 | 100 | 1.196 | 571 | 400 | 30 | 4 | 50 | 23.24 |
| 3 | 25 | 15 | 0 | 150 | 0.8154 | 572 | 400 | 30 | 4 | 100 | 19.63 |
| 4 | 25 | 15 | 1 | 50 | 1.852 | 573 | 400 | 30 | 4 | 150 | 14.11 |
| 5 | 25 | 15 | 1 | 100 | 1.324 | 574 | 400 | 30 | 5 | 50 | 22.82 |
| 6 | 25 | 15 | 1 | 150 | 0.8981 | 575 | 400 | 30 | 5 | 100 | 19.63 |
| 7 | 25 | 15 | 2 | 50 | 1.834 | 576 | 400 | 30 | 5 | 150 | 14.07 |
| 8 | 25 | 15 | 2 | 100 | 1.354 | 577 | 400 | 45 | 0 | 50 | 22 |
| 9 | 25 | 15 | 2 | 150 | 0.9133 | 578 | 400 | 45 | 0 | 100 | 13.76 |
| 10 | 25 | 15 | 3 | 50 | 1.824 | 579 | 400 | 45 | 0 | 150 | 9.387 |
| 11 | 25 | 15 | 3 | 100 | 1.356 | 580 | 400 | 45 | 1 | 50 | 21.32 |
| 12 | 25 | 15 | 3 | 150 | 0.9169 | 581 | 400 | 45 | 1 | 100 | 16.36 |
| 13 | 25 | 15 | 4 | 50 | 1.825 | 582 | 400 | 45 | 1 | 150 | 11.94 |
| 14 | 25 | 15 | 4 | 100 | 1.356 | 583 | 400 | 45 | 2 | 50 | 21.11 |
| 15 | 25 | 15 | 4 | 150 | 0.9171 | 584 | 400 | 45 | 2 | 100 | 16.52 |
| 16 | 25 | 15 | 5 | 50 | 1.832 | 585 | 400 | 45 | 2 | 150 | 13.08 |
| 17 | 25 | 15 | 5 | 100 | 1.357 | 586 | 400 | 45 | 3 | 50 | 21.16 |
| 18 | 25 | 15 | 5 | 150 | 0.9179 | 587 | 400 | 45 | 3 | 100 | 16.85 |
| 19 | 25 | 30 | 0 | 50 | 1.597 | 588 | 400 | 45 | 3 | 150 | 13.49 |
| 20 | 25 | 30 | 0 | 100 | 1.035 | 589 | 400 | 45 | 4 | 50 | 21.47 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moayedi, H.; Tien Bui, D.; Gör, M.; Pradhan, B.; Jaafari, A. The Feasibility of Three Prediction Techniques of the Artificial Neural Network, Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System, and Hybrid Particle Swarm Optimization for Assessing the Safety Factor of Cohesive Slopes. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8090391
Moayedi H, Tien Bui D, Gör M, Pradhan B, Jaafari A. The Feasibility of Three Prediction Techniques of the Artificial Neural Network, Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System, and Hybrid Particle Swarm Optimization for Assessing the Safety Factor of Cohesive Slopes. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2019; 8(9):391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8090391
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoayedi, Hossein, Dieu Tien Bui, Mesut Gör, Biswajeet Pradhan, and Abolfazl Jaafari. 2019. "The Feasibility of Three Prediction Techniques of the Artificial Neural Network, Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System, and Hybrid Particle Swarm Optimization for Assessing the Safety Factor of Cohesive Slopes" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 8, no. 9: 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8090391
APA StyleMoayedi, H., Tien Bui, D., Gör, M., Pradhan, B., & Jaafari, A. (2019). The Feasibility of Three Prediction Techniques of the Artificial Neural Network, Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System, and Hybrid Particle Swarm Optimization for Assessing the Safety Factor of Cohesive Slopes. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 8(9), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8090391








