Adaptive Construction of the Virtual Debris Flow Disaster Environments Driven by Multilevel Visualization Task
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
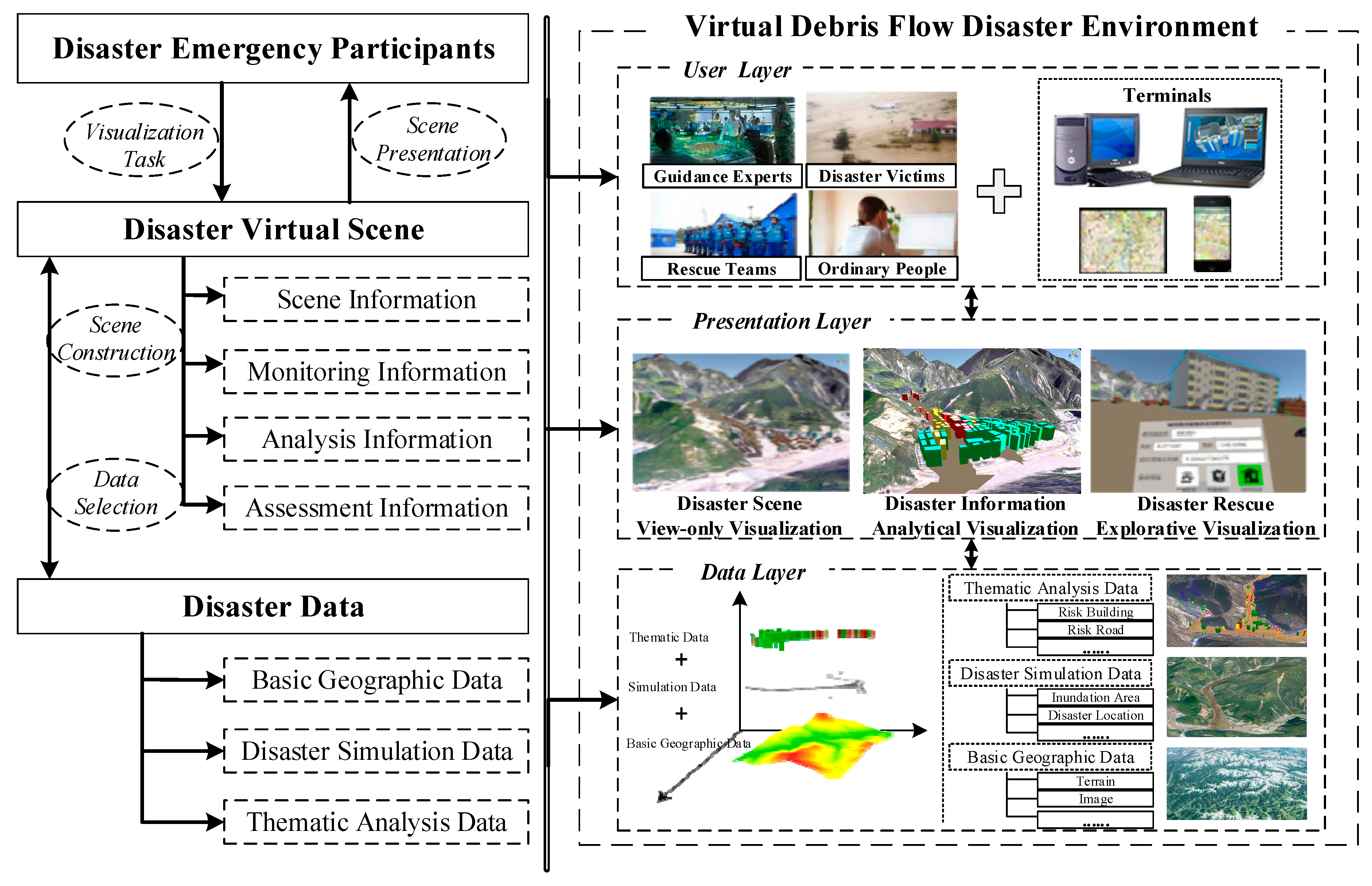
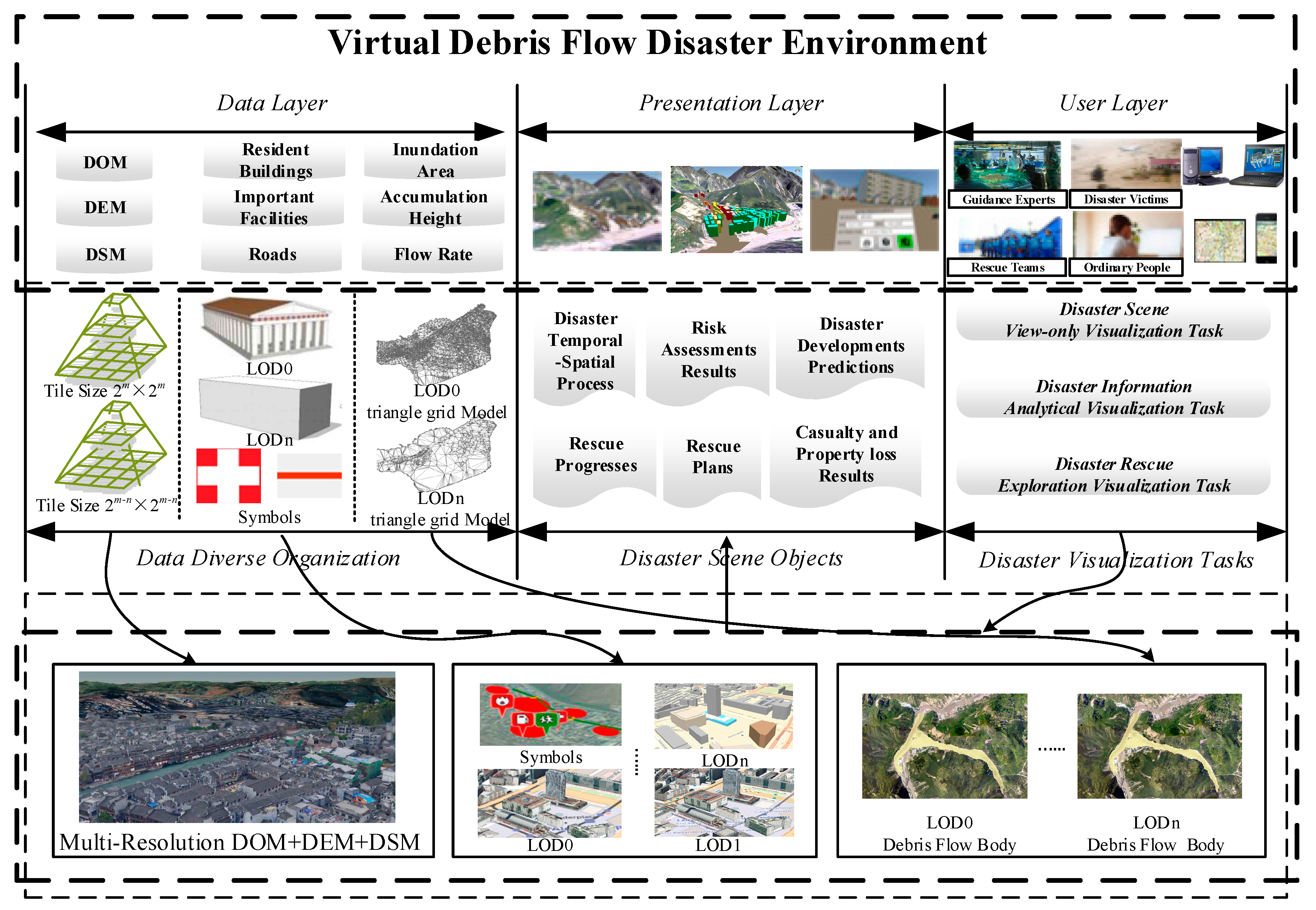
2.1. Framework of Virtual Debris Flow Disaster Environment
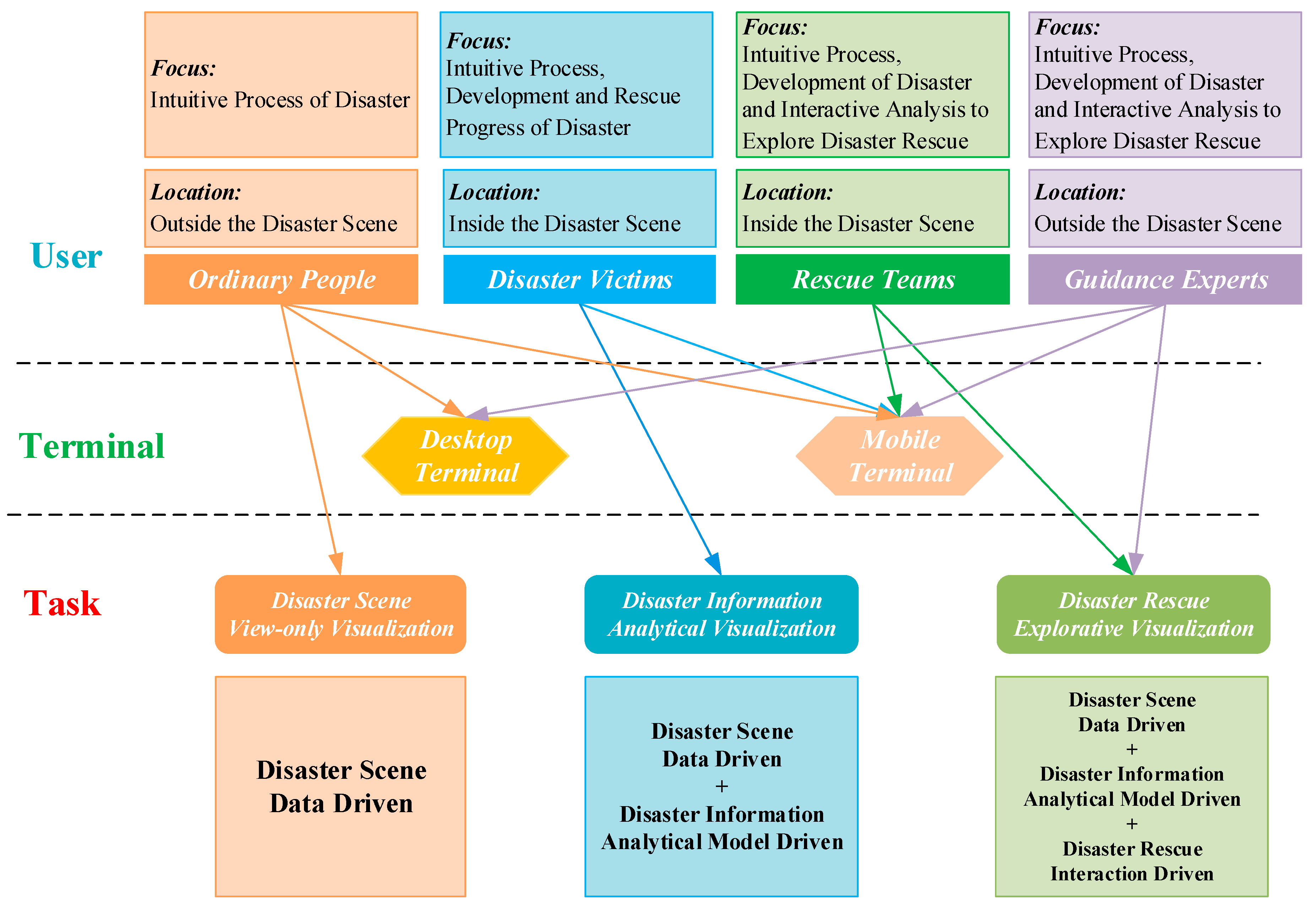
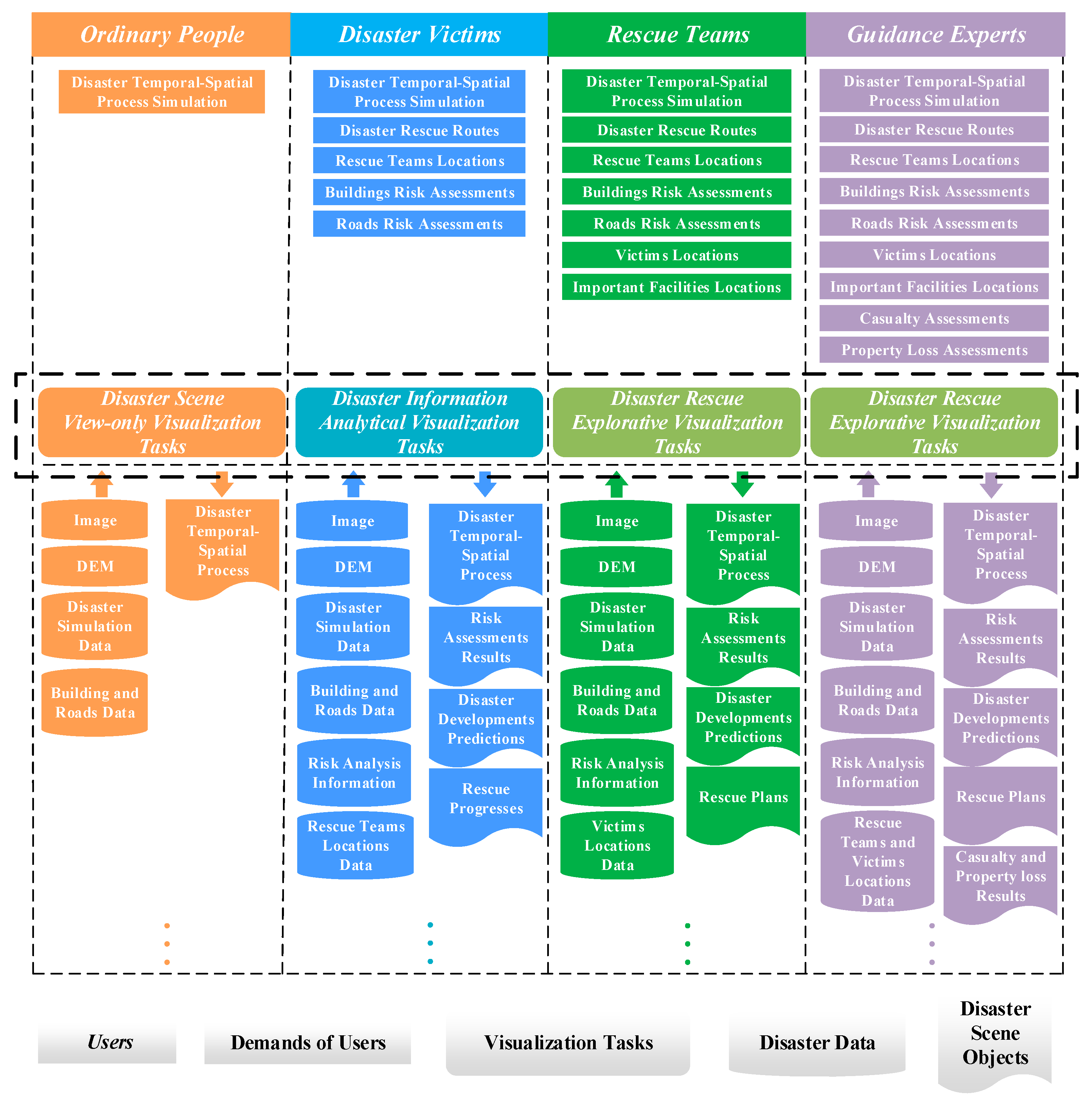
2.2. Multilevel Visualization Task Model for Disaster Emergency Response
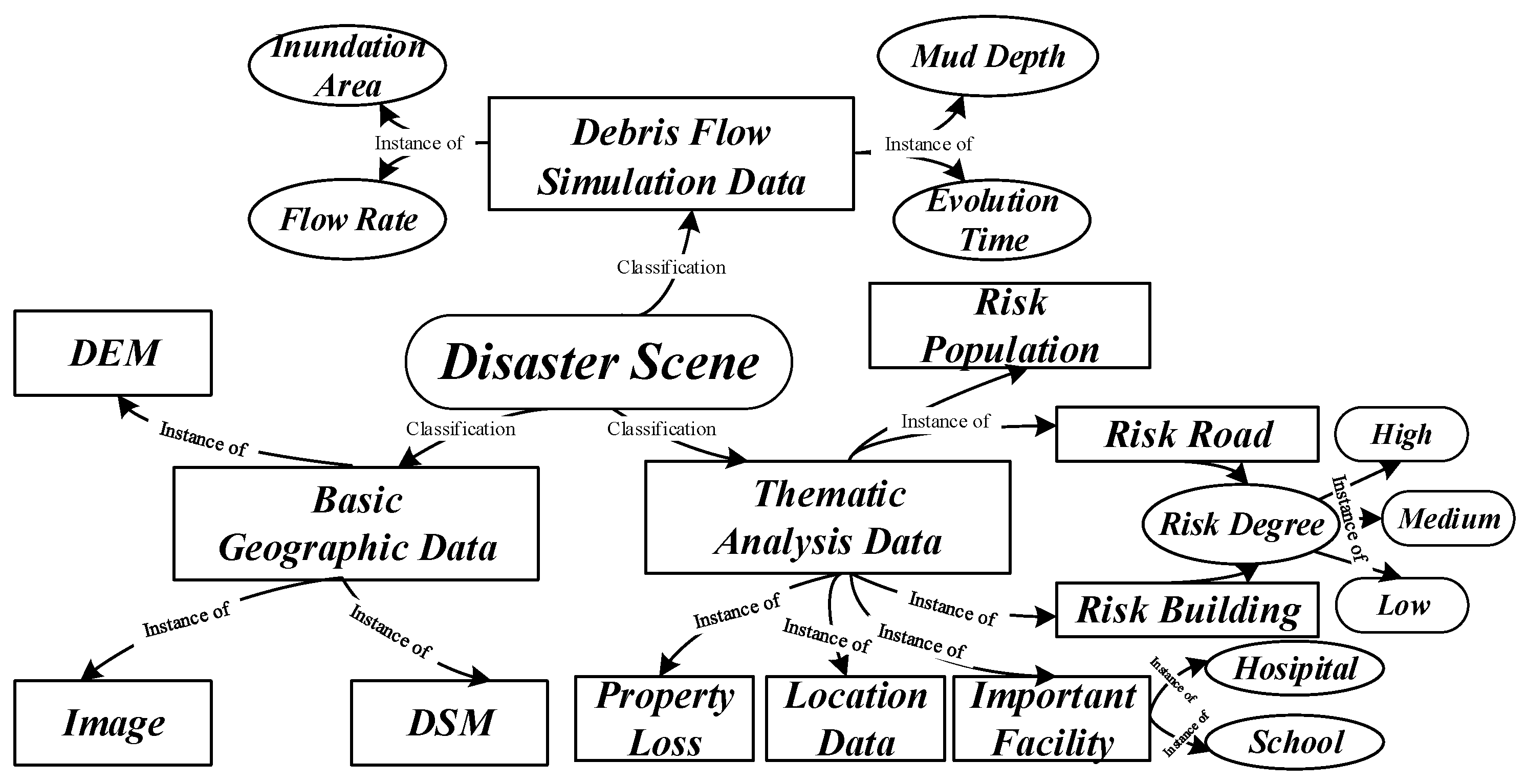
2.3. On-demand Construction of the Virtual Debris Flow Disaster Environments
2.4. Optimized Organization of Debris Flow Disaster Scenes
3. System Implementation and Experimental Analysis
3.1. Case Area and Data Processing
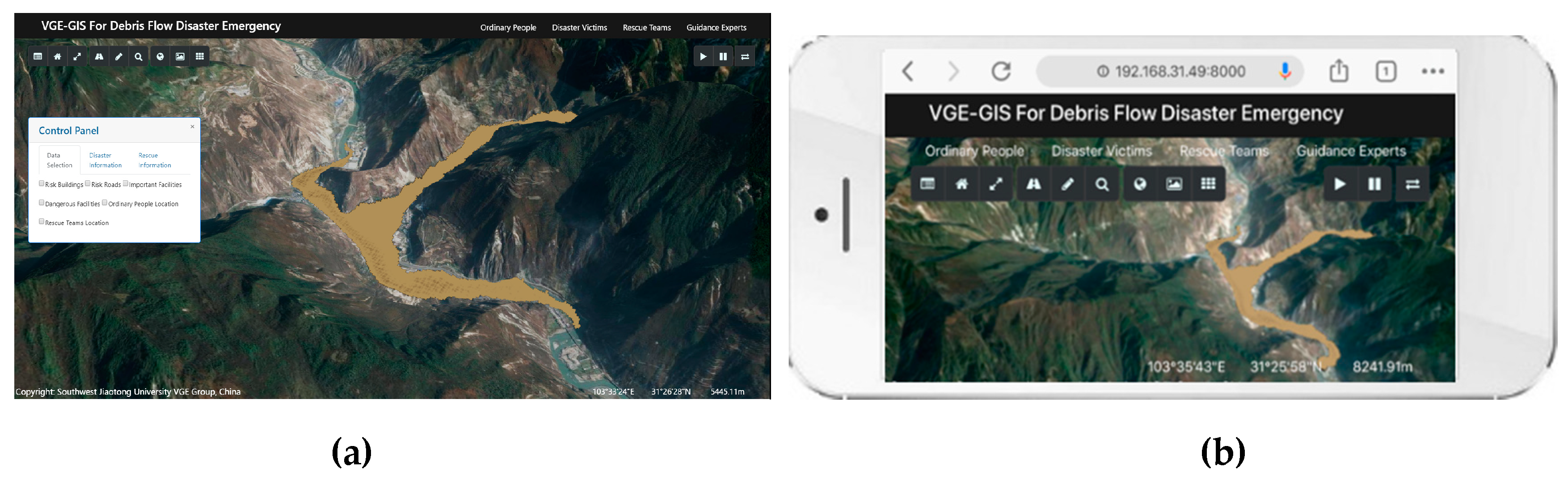
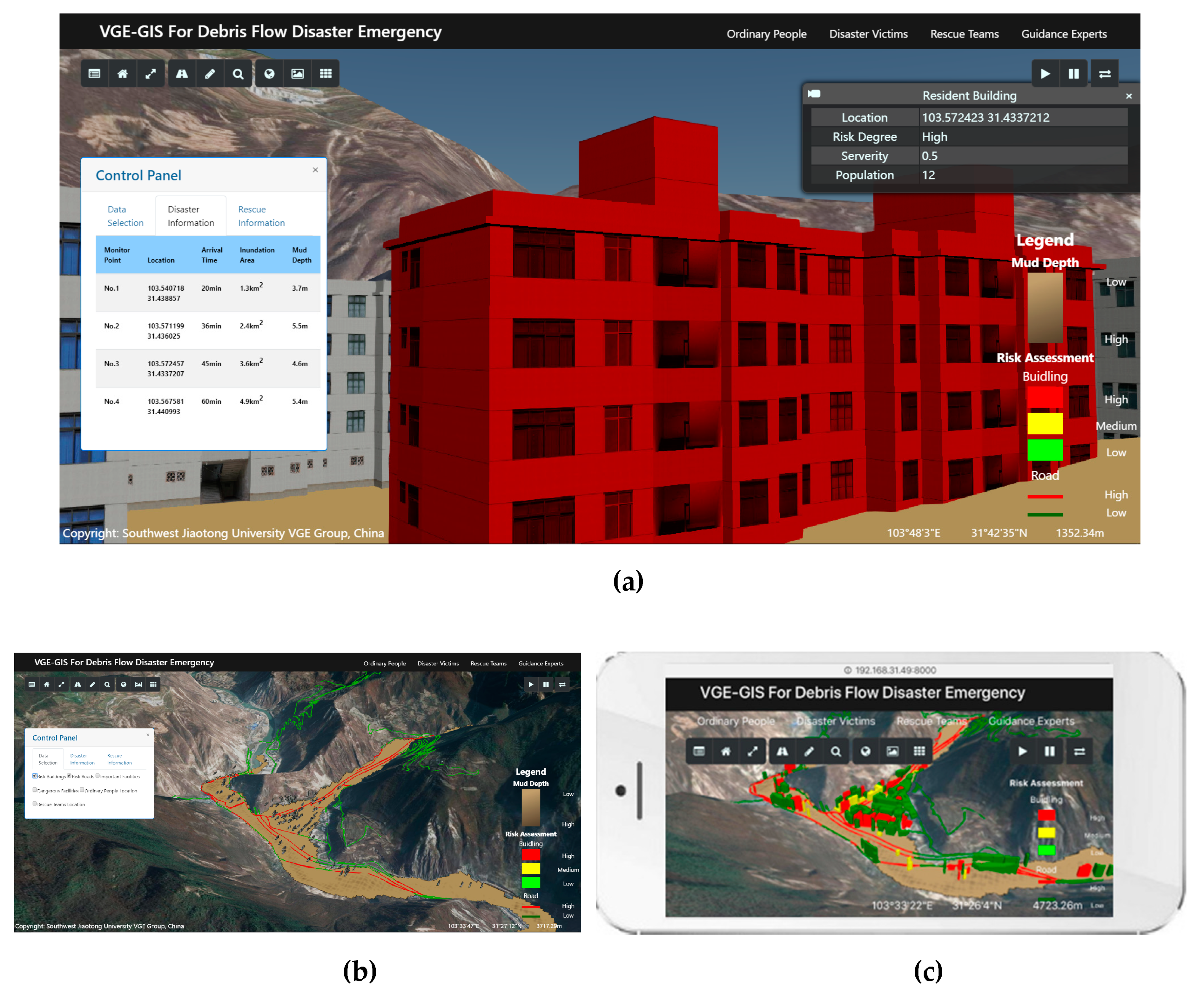
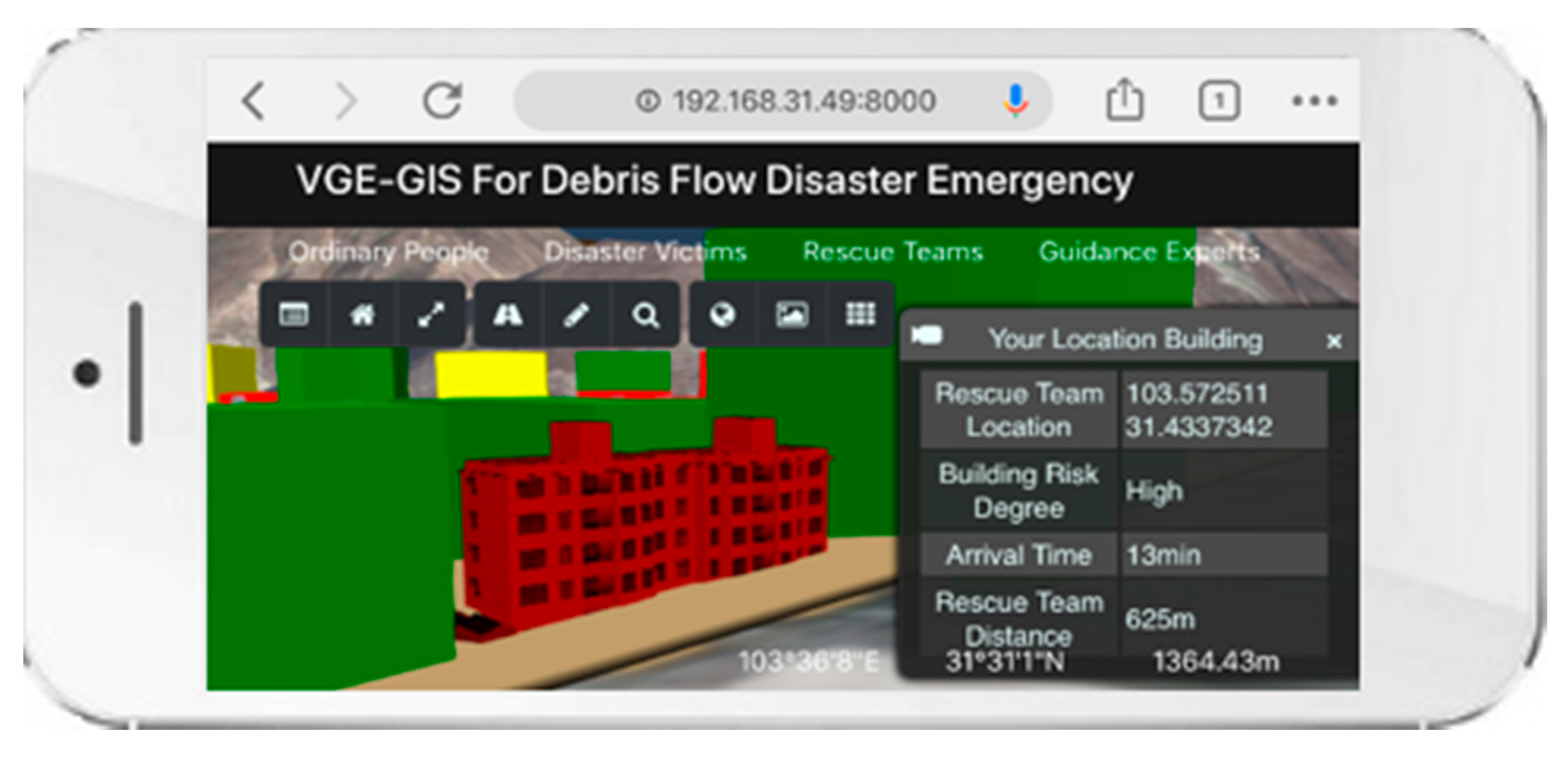
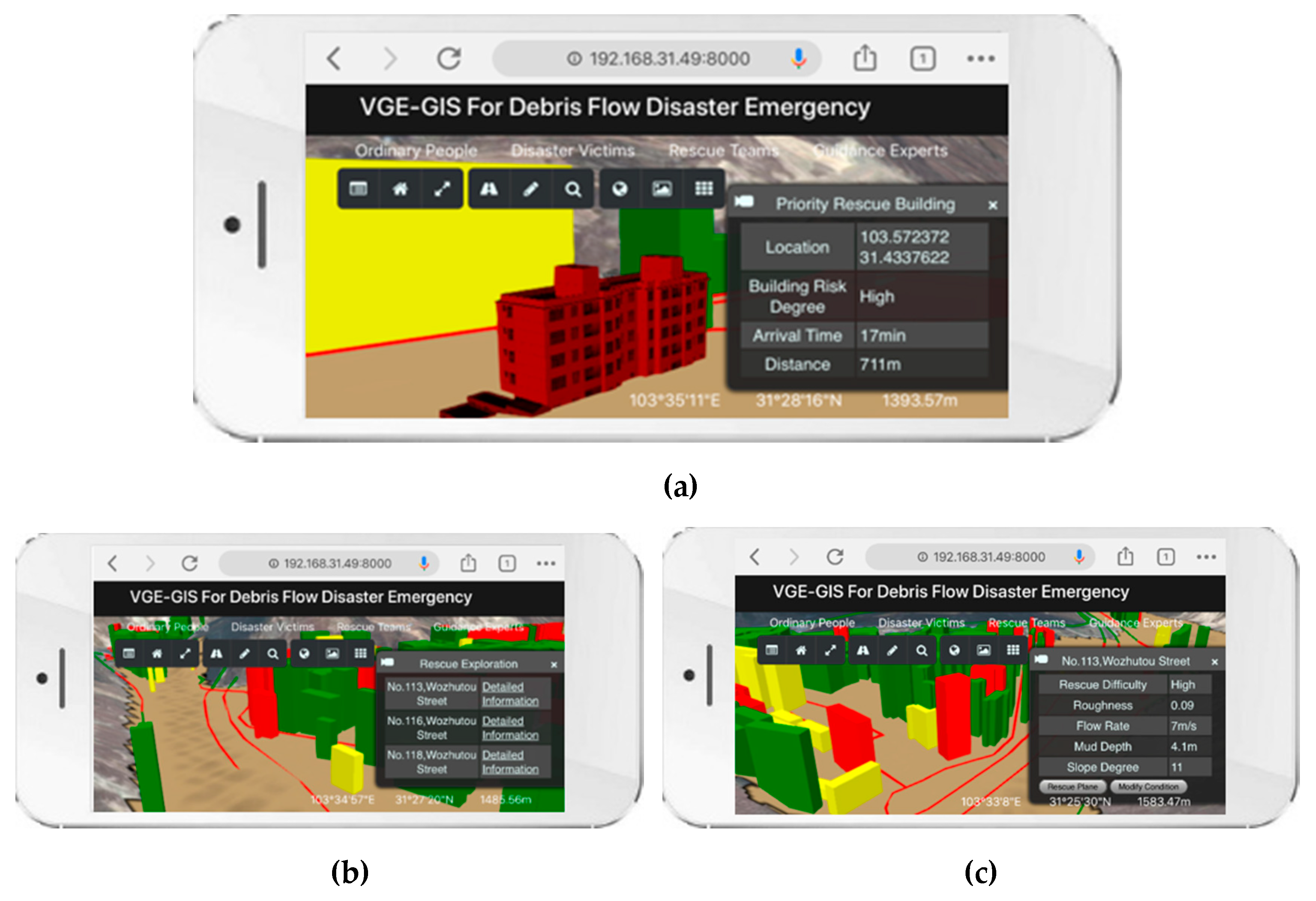
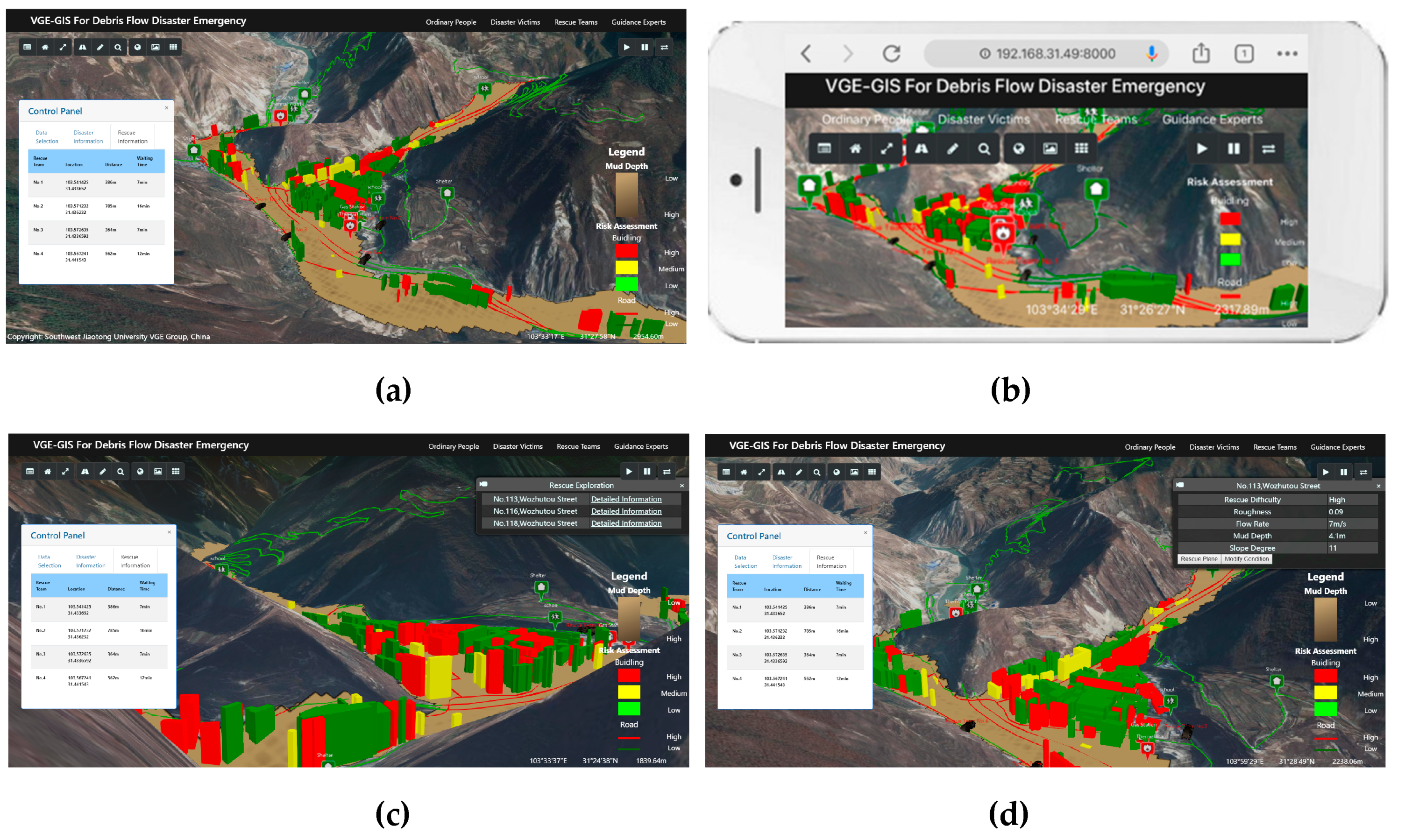
3.2. Prototype System Implementation
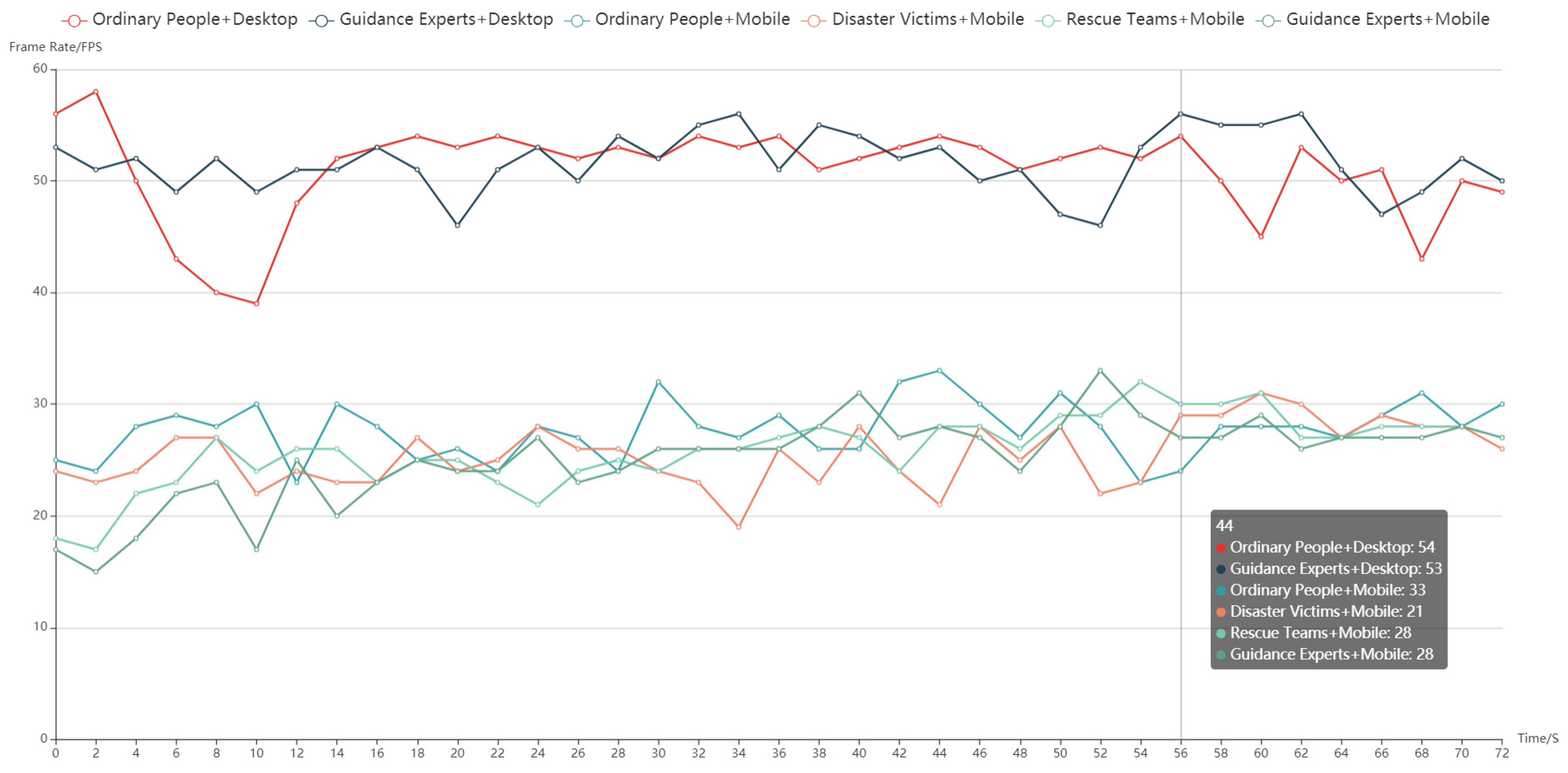
3.3. Experimental Analysis
4. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, Y.D.; Wu, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, M.; Wen, Q. Research progress of disaster remote sensing in China. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 20, 523–535. [Google Scholar]
- Kryvasheyeu, Y.; Chen, H.; Obradovich, N.; Moro, E.; Van Hentenryck, P.; Fowler, J.; Cebrian, M. Rapid assessment of disaster damage using social media activity. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1500779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.C. Seriously study and implement the spirit of General Secretary Xi Jinping’s important speech, comprehensively improve the ability of disaster prevention, mitigation and relief. Disaster Reduct. China 2016, 17, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, J.Q.; Cui, P.; Ge, Y.G.; He, Y.P.; Liu, Y.H.; Guo, X.J. Probability assessment of river blocking by debris flow associated with the Wenchuan earthquake. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 3465–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P. Progress and prospects in research on mountain hazards in China. Prog. Geogr. 2014, 33, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, W.C.; Weng, W.G.; Wu, G.; Meng, Q.F.; Yang, L.X. Basic scientific problems of national security management. Bull. Natl. Nat. Sci. Found. China 2015, 29, 436–443. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.D. Disaster prevention and reduction from “+Internet” to “Internet +”. Disaster Reduct. China 2016, 5, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Bainbridge, W.S. The scientific research potential of virtual worlds. Science 2007, 31, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denolle, M.A.; Dunham, E.M.; Prieto, G.A.; Beroza, G.C. Strong ground motion prediction using virtual earthquakes. Science 2014, 343, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Gong, J.H. Exploring virtual geographic environments. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2001, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Gong, J.H. On virtual geographic environments. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2002, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Chen, M.; Hu, M.Y. Research progress and prospect of virtual geographic environments (VGEs). J. Geomat. Sci. Technol. 2013, 30, 361–368. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, M. The being and non-being generate each other, and the virtual and the real are mutually interactive—The progress of virtual geographic environments (VGE) studies in last 20 years. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2018, 47, 1027–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Lü, G.N. Geographic analysis-oriented virtual geographic environment: Framework, structure and functions. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Lin, H.; Kolditz, O.; Chen, C. Developing dynamic virtual geographic environments (VGEs) for geographic research. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 6975–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Chen, M.; Lü, G.N.; Zhu, Q.; Gong, J.H.; You, X.; Wen, Y.N.; Xu, B.L.; Hu, M.Y. Virtual geographic environments (VGEs): A new generation of geographic analysis tool. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2013, 126, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, C.X.; Chen, M.; Zheng, X.Q. On virtual geographic environments for geographic knowledge representation and sharing. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 20, 1290–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, G.Q.; Wen, Y.N.; Li, Y.T.; Yue, S.S.; Song, Z.Y. Construction of collaborative mapping engine for dynamic disaster and emergency response response. Nat. Hazards 2018, 90, 217–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, P.; Lung, W.S.; Guo, L.; Li, M. A GIS-based generic real-time risk assessment framework and decision tools for chemical spills in the river basin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 227, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steichen, B.; Carenini, G.; Conati, C. User-adaptive information visualization—Using eye gaze data to infer visualization tasks and user cognitive abilities. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, Santa Monica, CA, USA, 19–22 March 2013; pp. 317–328. [Google Scholar]
- Gotz, D.; Wen, Z. Behavior-driven visualization recommendation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, Sanibel Island, FL, USA, 8–11 February 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Steichen, B.; Conati, C.; Carenini, G. Inferring visualization task properties, user performance, and user cognitive abilities from eye gaze data. ACM Trans. Interact. Intell. Syst. 2014, 4, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Qi, H.; Hu, Y.; Cao, Y.G. A distributed virtual geographic environment service system for risk assessment of dam-break. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery, Chongqing, China, 29–31 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.F.; Yin, L.Z.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X. A collaborative virtual geographic environment for emergency response dam-break simulation and risk analysis. J. Spat. Sci. 2016, 61, 133–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yin, L.Z.; Wang, J.H.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.J. Dam-break flood routing simulation and scale effect analysis based on virtual geographic environment. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.Z.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.F. Visual analysis and simulation of dam-break flood spatiotemporal process in a network environment. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 7133–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.L.; Zhu, Q.; Lin, H. An integrated virtual geographic environmental simulation framework: A case study of flood disaster simulation. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, 17, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.W.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, Q.; Qi, H.; Yin, L.Z.; Zhang, X.; Feng, B.; He, H.G.; Yang, W.J.; Chen, L.Y. Optimization of simulation and visualization analysis of dam-failure flood disaster for diverse computing systems. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 1891–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beni, L.H.; Mostafavi, M.A.; Pouliot, J. Geomatics Solutions for Disaster Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, P.D.; Roo, A.P.J. A simple raster-based model for flood inundation simulation. J. Hydrol. 2000, 236, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.Z.; Zhu, J.; Li, Y.; Zeng, C.; Zhu, Q.; Qi, H.; Liu, M.; Li, W.; Cao, Z.; Yang, W.; et al. A virtual geographic environment for debris flow risk analysis in residential areas. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.Z. Real-Time Visual Simulation and Analysis Method for Rapid Risk Assessment of Debris Flow Disasters. Ph.D. Thesis, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Chen, B.; Huang, F.R.; Fang, Y. Using collaborative virtual geographic environment for fire disaster simulation and virtual fire training. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Geoinformatics, Hong Kong, China, 15–17 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jongman, B.; Hochrainer-Stigler, S.; Feyen, L.; Aerts, J.C.J.H.; Mechler, R.; Botzen, W.J.W.; Bouwer, L.M.; Pflug, G.; Rojas, R.; Ward, P.J. Increasing stress on disaster-risk finance due to large floods. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenguer, M.; Sempere-Torres, D.; Hürlimann, M. Debris-flow forecasting at regional scale by combining susceptibility mapping and radar rainfall. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 587–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielen, J.; Bartholmes, J.; Ramos, M.H.; Roo, A. The European flood alert system—Part 1: Concept and development. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avagyan, A.; Manandyan, H.; Arakelyan, A.; Piloyan, A. Toward a disaster risk assessment and mapping in the virtual geographic environment of Armenia. Nat. Hazards 2018, 92, 283–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.C.; Jung, H.; Kim, S.; Chung, K. Slope based intelligent 3D disaster simulation using physics engine. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2016, 86, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.Q.; Reischenbacher, T.; Zirf, A. Map Based Mobile Services; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Fu, X. The review of visual analysis methods of multi-modal spatio-temporal big data. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2017, 46, 1672–1677. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.W.; Zhu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Feng, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.X.; Fu, X.; Zhang, P.C.; Yang, W.J.; Ning, X.W.; et al. The multi-level visualization task model for multi-modal spatio-temporal data. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2018, 47, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.Y. A Smart Aggregation Method of Spatial-Temporal Data for Natural Disaster Emergency Response Tasks. Ph.D. Thesis, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Zhu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Liu, M.W.; He, H.G.; Yang, W.J.; Zhang, P.C.; Cao, Z.Y. Lightweight web visualization of massive dsm data. J. Geomat. Sci. Technol. 2017, 34, 649–653. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, W.L.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhu, Q.; Qi, H.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Z.Y.; Yang, W.J.; Zhang, P.C. Construction and optimization of three-dimensional disaster scenes within mobile virtual reality. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Chen, X.W.; Ding, Y.L.; Liu, M.W.; He, H.G.; Yang, W.J.; Chen, L.Y.; Cao, Z.Y. Organization and scheduling method of 3d urban scene data driven by visual perception. J. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. 2017, 52, 869–876. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, Q.; Li, W.L.; Zhang, J.X.; Liu, M.W.; Li, Y.; Feng, B. Optimized organization and adaptive visualization of complicated mountain disaster 3D scenes for diverse terminals. ISPRS Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 42, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.L.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.H.; Cao, Y.G.; Hu, Y.; Fu, L.; Huang, P.C.; Xie, Y.K.; Yin, L.Z.; Xu, B. A fusion visualization method for disaster information based on self-explanatory symbols and photorealistic scene cooperation. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data Category | Data Organization | Scheduling Method |
|---|---|---|
| Basic geographic data | Hierarchy scene pyramid | Raising/lowering the maximum tile level |
| 3D buildings data | Multilevel LOD models | Scheduling more detailed/simplified LOD models or symbols |
| Roads data | Road centerlines | Scheduling all/main road centerlines |
| Debris flow body data | Multilevel LOD debris flow body | Scheduling more detailed/simplified LOD debris flow bodies |
| Category | Content |
|---|---|
| Basic geographic data | DOM/DEM |
| disaster simulation data | Inundation area/mud depth/flow rate/evolution time/debris flow body model |
| Thematic analysis data | Residents building models/roads/important facilities/dangerous facilities/population/risk assessment/property loss/personnel location |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, W.; Zhu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Fu, L.; Zhang, J.; Huang, P.; Xie, Y.; Yin, L. Adaptive Construction of the Virtual Debris Flow Disaster Environments Driven by Multilevel Visualization Task. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8050209
Zhang Y, Zhu J, Li W, Zhu Q, Hu Y, Fu L, Zhang J, Huang P, Xie Y, Yin L. Adaptive Construction of the Virtual Debris Flow Disaster Environments Driven by Multilevel Visualization Task. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2019; 8(5):209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8050209
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yunhao, Jun Zhu, Weilian Li, Qing Zhu, Ya Hu, Lin Fu, Junxiao Zhang, Pengcheng Huang, Yakun Xie, and Lingzhi Yin. 2019. "Adaptive Construction of the Virtual Debris Flow Disaster Environments Driven by Multilevel Visualization Task" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 8, no. 5: 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8050209
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhu, J., Li, W., Zhu, Q., Hu, Y., Fu, L., Zhang, J., Huang, P., Xie, Y., & Yin, L. (2019). Adaptive Construction of the Virtual Debris Flow Disaster Environments Driven by Multilevel Visualization Task. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 8(5), 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8050209





