FracL: A Tool for Characterizing the Fractality of Landscape Gradients from a New Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The New Definition of Fractal
3. Overview of Metrics under the Latest Definition of Fractal
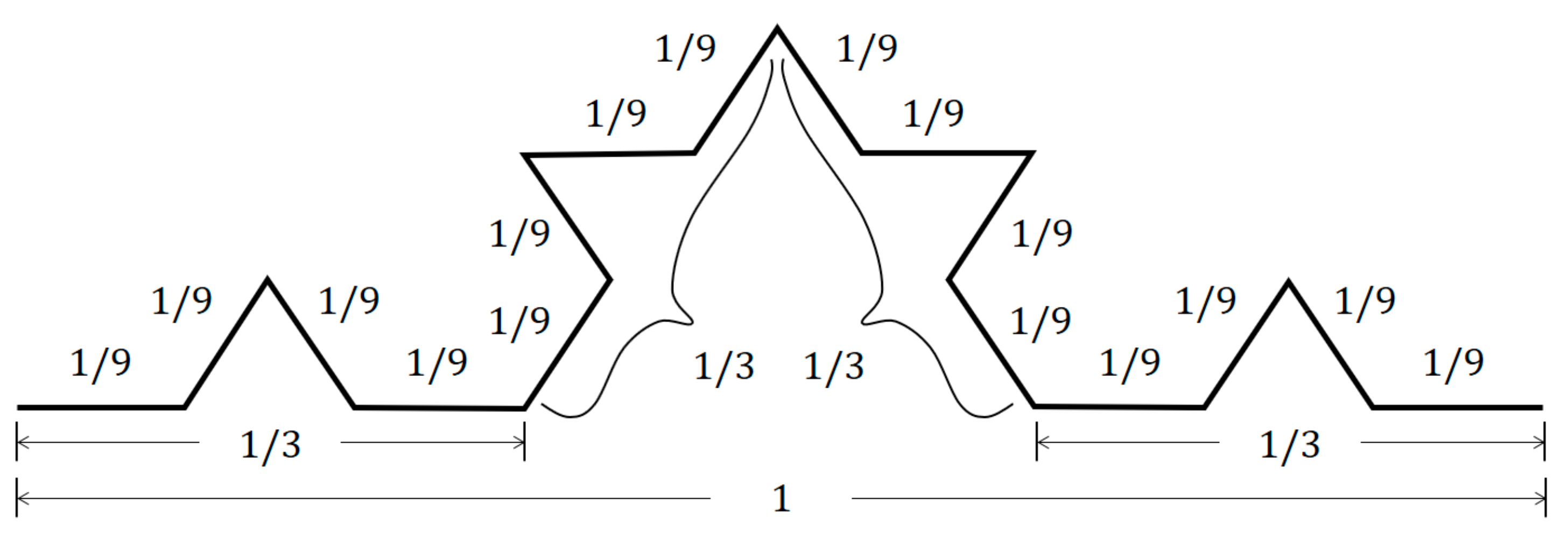
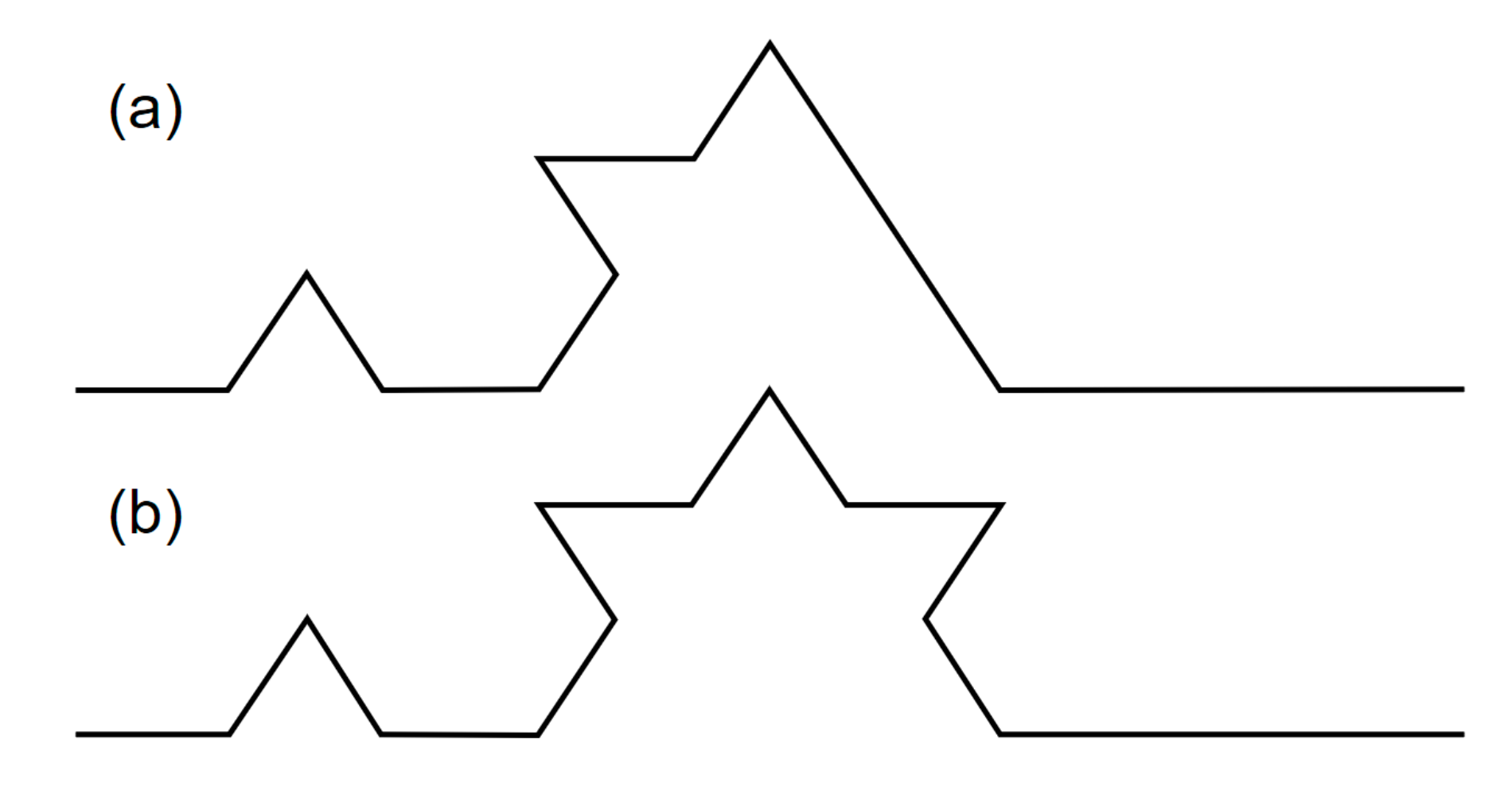
3.1. Ht-Index
3.2. CRG Index
3.3. RA Index
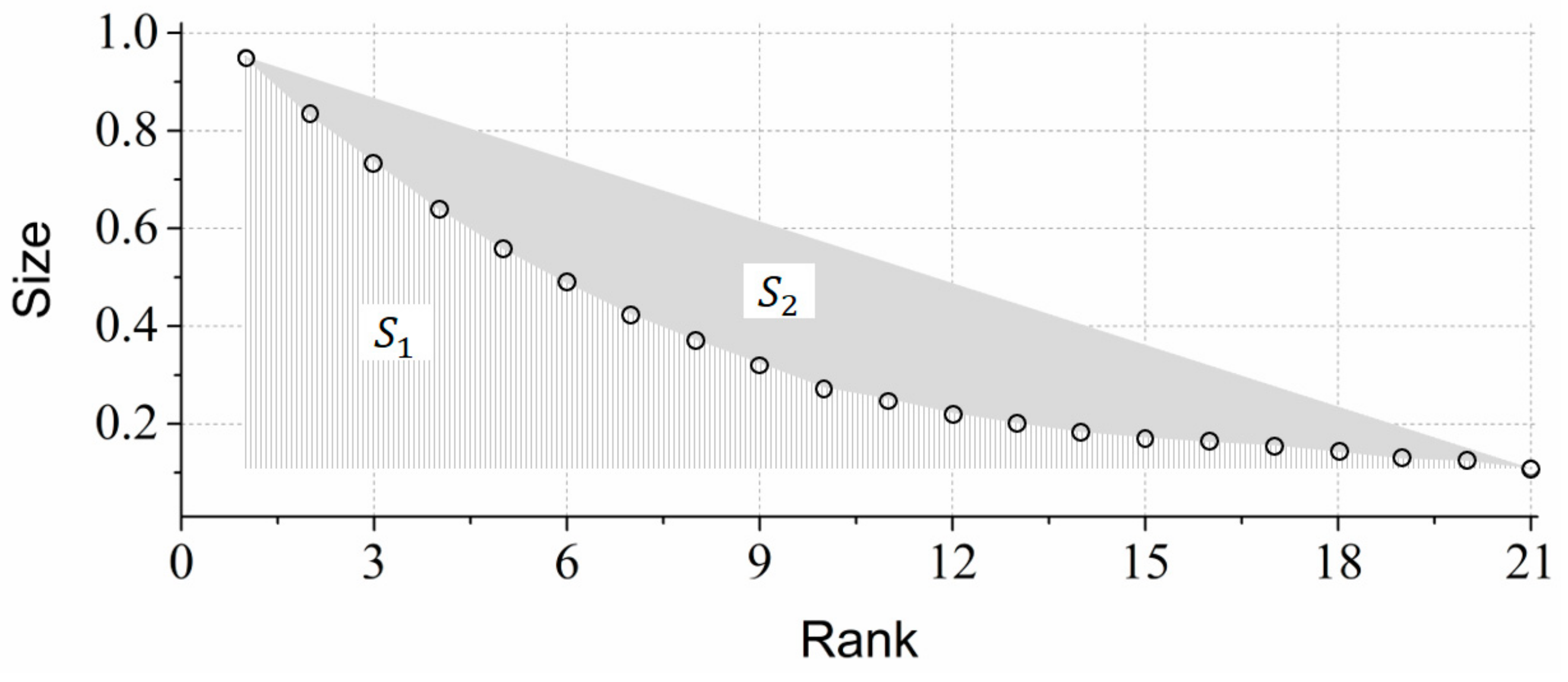
3.4. Unified Metrics
- “I know there are far more small things than large ones, but how small (or large)?”
- “I know there are far more small things than large ones, but how many more?”
3.5. Fht-Index
4. Development of a Software Tool: FracL
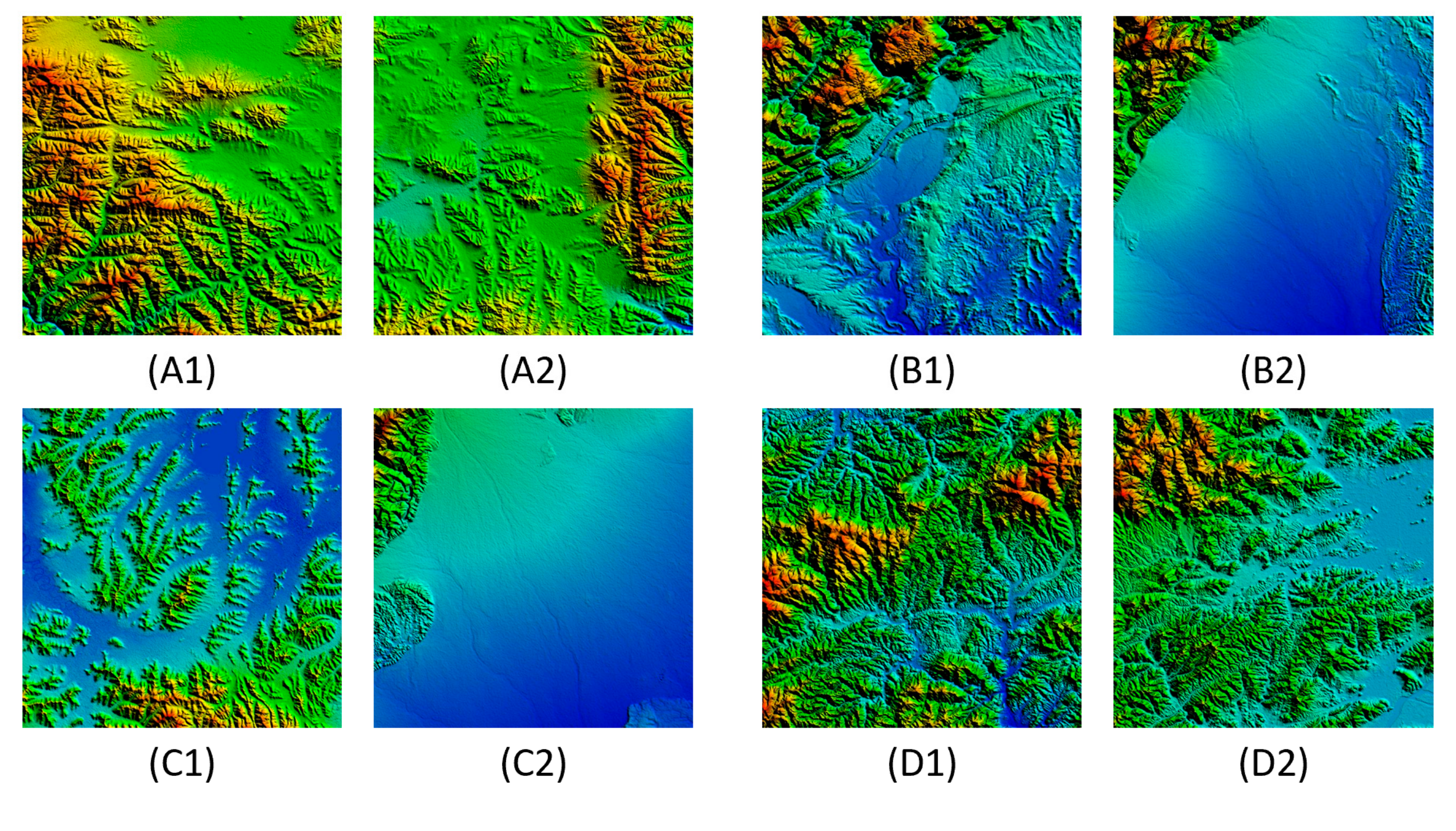
5. Case Study and Analysis
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnot, C.; Fisher, P.F.; Wadsworth, R.; Wellens, J. Landscape metrics with ecotones: Pattern under uncertainty. Landsc. Ecol. 2004, 19, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, A.E.; Wang, L. Modeling landscape structure response across a gradient of land cover intensity. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, R.T.T. Land Mosaics: The Ecology of Landscapes and Regions; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.A. The gradient concept of landscape structure. In Issues and Perspectives in Landscape Ecology; Wiens, J.A., Moss, M.R., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; pp. 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, S.A.; Evans, J.S.; McGarigal, K. Landscape ecology: Past, present, and future. In Spatial Complexity, Informatics, and Wildlife Conservation; Cushman, S.A., Huettmann, F., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2010; pp. 65–82. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, J.S.; Cushman, S.A. Gradient modeling of conifer species using random forests. Landsc. Ecol. 2009, 24, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.A.; Eduard, E. FRAGSTATS v4: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Categorical and Continuous Maps. Available online: http://www.umass.edu/landeco/research/fragstats/fragstats.html (accessed on 17 January 2019).
- Costanza, J.K.; Riitters, K.; Vogt, P.; Wickham, J. Describing and analyzing landscape patterns: Where are we now, and where are we going? Landsc. Ecol. 2019, 34, 2049–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, E.J. How has the state-of-the-art for quantification of landscape pattern advanced in the twenty-first century? Landsc. Ecol. 2019, 34, 2065–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarigal, K.; Tagil, S.; Cushman, S.A. Surface metrics: An alternative to patch metrics for the quantification of landscape structure. Landsc. Ecol. 2009, 24, 433–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedron, P.J.; Frazier, A.E.; Ovando-Montejo, G.A.; Wang, J. Surface metrics for landscape ecology: A comparison of landscape models across ecoregions and scales. Landsc. Ecol. 2018, 33, 1489–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, A.E. Surface metrics: Scaling relationships and downscaling behavior. Landsc. Ecol. 2016, 31, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.C. Bioxgeo/geodiv: Methods for Calculating Gradient Surface Metrics. Available online: https://rdrr.io/github/bioXgeo/geodiv/ (accessed on 9 September 2019).
- Koch, H. Sur une courbe continue sans tangente, obtenue par une construction géométrique élémentaire [On a continuous curve without tangents constructible from elementary geometry]. Arkiv för Matematik 1904, 1, 681–704. [Google Scholar]
- Sierpinski, W. Sur une courbe cantorienne qui contient une image biunivoque et continue de toute courbe donnée [On a cantorian curve which contains a continuous one-to-one image of every given curve]. Comptes Rendus 1916, 162, 629–632. [Google Scholar]
- Menger, K. Allgemeine Räume und Cartesische Räume., I. Proc. Amst. 1927, 29, 476–482. [Google Scholar]
- Mandelbrot, B.B. Fractals: Form, Chance, and Dimension; Freeman: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Mandelbrot, B.B. How long is the coast of Britain? Statistical self-similarity and fractional dimension. Science 1967, 156, 636–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Yin, J.J. Ht-index for quantifying the fractal or scaling structure of geographic features. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2014, 104, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranken, I.; Baudry, J.; Aubinet, M.; Visser, M.; Bogaert, J. A review on the use of entropy in landscape ecology: Heterogeneity, unpredictability, scale dependence and their links with thermodynamics. Landsc. Ecol. 2015, 30, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrott, L.; Proulx, R.; Thibert-Plante, X. Three-dimensional metrics for the analysis of spatiotemporal data in ecology. Ecol. Inform. 2008, 3, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B. Head/tail breaks: A new classification scheme for data with a heavy-tailed distribution. Prof. Geogr. 2013, 65, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Jiang, B. A smooth curve as a fractal under the third definition. Cartogr. Int. J. Geogr. Inform. Geovis. 2018, 53, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac Carron, P.; Kaski, K.; Dunbar, R. Calling Dunbar’s numbers. Soc. Netw. 2016, 47, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Shen, Y.; Jin, X.B. Mapping block-level urban areas for all Chinese cities. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2016, 106, 96–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krummel, J.; Gardner, R.; Sugihara, G.; O’neill, R.; Coleman, P. Landscape patterns in a disturbed environment. Oikos 1987, 48, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, B.T. Measuring the fractal geometry of landscapes. Appl. Math. Comput. 1988, 27, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nams, V.O. The VFractal: A new estimator for fractal dimension of animal movement paths. Landsc. Ecol. 1996, 11, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Ma, K.M.; Anand, M.; Fu, B.J. Multifractal pattern and process during a recent period of forest expansion in a temperate mountainous region of China. Ecol. Inform. 2011, 6, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhao, H.R.; Xie, X.X. Unified metrics for characterizing the fractal nature of geographic features. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2017, 107, 1315–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B. Computing the image of the city. In Planning Support Tools: Policy Analysis, Implementation and Evaluation (Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Informatics and Urban and Regional Planning INPUT2012); Campagna, M., Montis, A.D., Isola, F., Lai, S., Pira, C., Zoppi, C., Eds.; FrancoAngeli: Milan, Italy, 2012; pp. 111–121. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, A.C.; Demšar, U.; Moore, A.B.; Buckley, A.; Jiang, B.; Field, K.; Kraak, M.-J.; Camboim, S.P.; Sluter, C.R. Geospatial big data and cartography: Research challenges and opportunities for making maps that matter. Int. J. Cartogr. 2017, 3, 32–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainuri, Z.G.; Owino, J.O. Spatial variability of soil aggregate stability in a disturbed river watershed. Eur. J. Econ. Bus. Stud. 2017, 9, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, Y.G. Urban chaos and replacement dynamics in nature and society. Phys. A Stat.Mech. Appl. 2014, 413, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, H.; Lan, T.; Cao, W.W.; Wu, X. Exploring the hierarchical structure in road network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Earth Observing and Applications, Guilin, Guangxi, China, 9 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.; Sandberg, M.; Jiang, B. A socio-geographic perspective on human activities in social media. Geogr. Anal. 2017, 49, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNutt, S.R.; Roman, D.C. Volcanic seismicity. In The Encyclopedia of Volcanoes, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 1011–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Sage, L.J. Second light: The biggest stars. J. R. Astron. Soc. Can. 2005, 99, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.G. Effects of changing scale on landscape pattern analysis: Scaling relations. Landsc. Ecol. 2004, 19, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, R.; He, J.; Li, W.L.; Lu, J.Y.; Long, W.; Gao, P.C.; Cai, G.L.; Tang, M. Scaling relation of earthquake seismic data. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2018, 492, 2092–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Z.L. Fractality and self-similarity in the structure of road networks. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2012, 102, 350–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Li, Z.L.; Zhang, H. Urban allometric scaling beneath structural fractality of road networks. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2019, 109, 943–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.Y. Fractal or Scaling Analysis of Natural Cities Extracted from Open Geographic Data Sources. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Gävle, Gävle, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.J.; Zhao, H.R.; Jiang, S.L. A Zipf’s law-based method for mapping urban areas using NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Zhai, W.X.; Shen, Y.; Ye, X.Y. Understanding uneven urban expansion with natural cities using open data. Landsc. Urban Plann. 2017, 177, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xie, M.H.; Tian, K.; Xie, X.X. Classification of PM2. 5 for natural cities based on co-Kriging and head/tail break algorithms. J. Tsinghua Univ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 57, 555–560. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Lv, Z.H.; Zheng, Z.G.; Zhong, C.; Hijazi, I.H.; Cheng, S.D. Assessment of lively street network based on geographic information system and space syntax. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 17801–17819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, R.V.; Johnson, A.R.; King, A.W. A hierarchical framework for the analysis of scale. Landsc. Ecol. 1989, 3, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, R.V.; Deangelis, D.L.; Waide, J.B.; Allen, T.F.; Allen, G.E. A Hierarchical Concept of Ecosystems; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.C.; Liu, Z.; Xie, M.H.; Tian, K.; Liu, G. CRG index: A more sensitive ht-index for enabling dynamic views of geographic features. Prof. Geogr. 2016, 68, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.C.; Liu, Z.; Tian, K.; Liu, G. Characterizing traffic conditions from the perspective of spatial-temporal heterogeneity. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inform. 2016, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Ma, D. How complex is a fractal? Head/tail breaks and fractional hierarchy. J. Geovis. Spatial Anal. 2018, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, J.M.F.; Santos, L.J.C.; Oka-Fiori, C. Spatial correlation analysis between topographic parameters for defining the geomorphometric diversity index: Application in the environmental protection area of the Serra da Esperança (state of Paraná, Brazil). Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.C.; Li, Z.L. Computation of the Boltzmann entropy of a landscape: A review and a generalization. Landsc. Ecol. 2019, 34, 2183–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, S.A. Calculation of configurational entropy in complex landscapes. Entropy 2018, 20, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollinger, S.V.; Aber, J.D.; Federer, A. Estimating regional forest productivity and water yield using an ecosystem model linked to a GIS. Landsc. Ecol. 1998, 13, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, M.L.; Bradley, C.M.; Kiffner, C.; Morrison, T.A.; Lee, D.E. A multi-method approach to delineate and validate migratory corridors. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 1705–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.C.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.L. A hierarchy-based solution to calculate the configurational entropy of landscape gradients. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 1133–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neel, M.C.; McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.A. Behavior of class-level landscape metrics across gradients of class aggregation and area. Landsc. Ecol. 2004, 19, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, S.A.; McGarigal, K.; Neel, M.C. Parsimony in landscape metrics: Strength, universality, and consistency. Ecol. Indic. 2008, 8, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Ren, Z. Geographic space as a living structure for predicting human activities using big data. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2019, 33, 764–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, C. The Nature of Order: An Essay on the Art of Building and The Nature of the Universe; The Center for Environmental Structure: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B. A recursive definition of goodness of space for bridging the concepts of space and place for sustainability. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
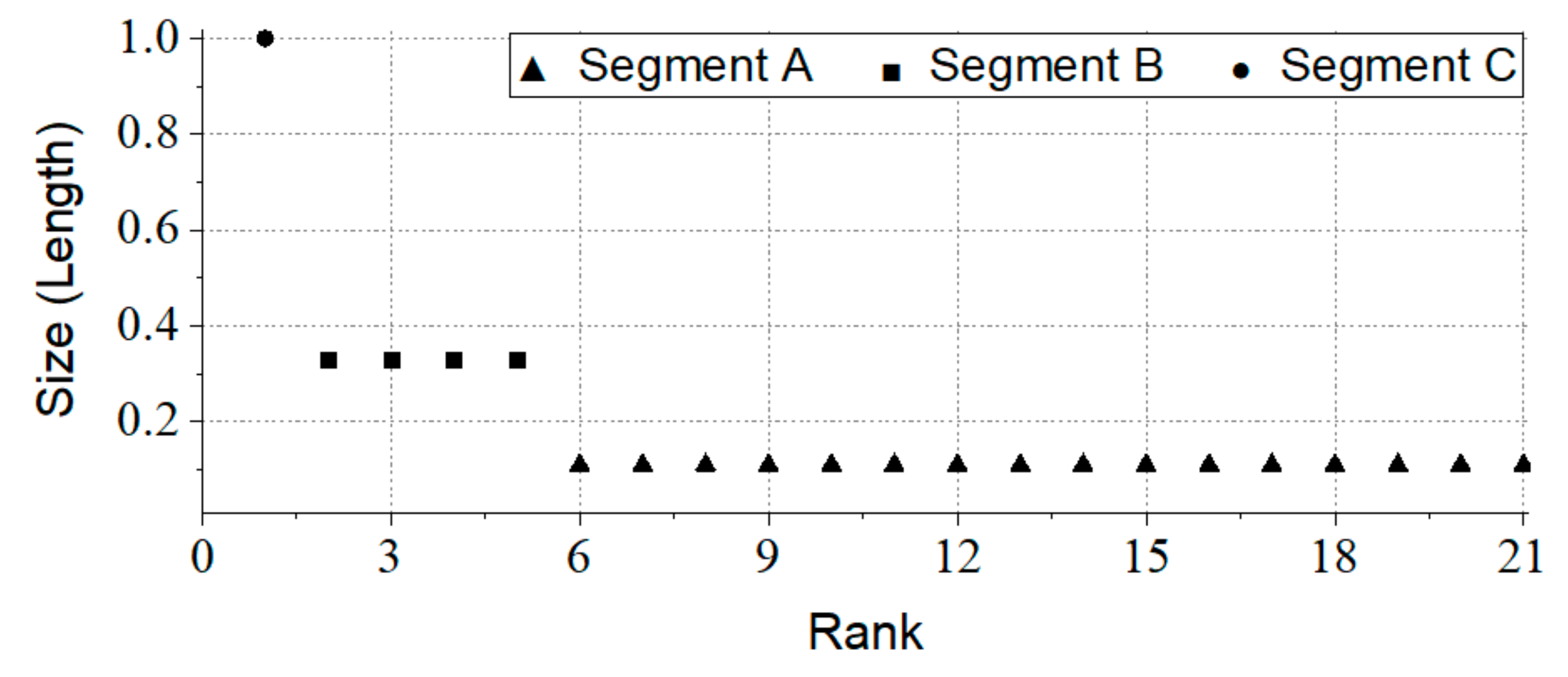
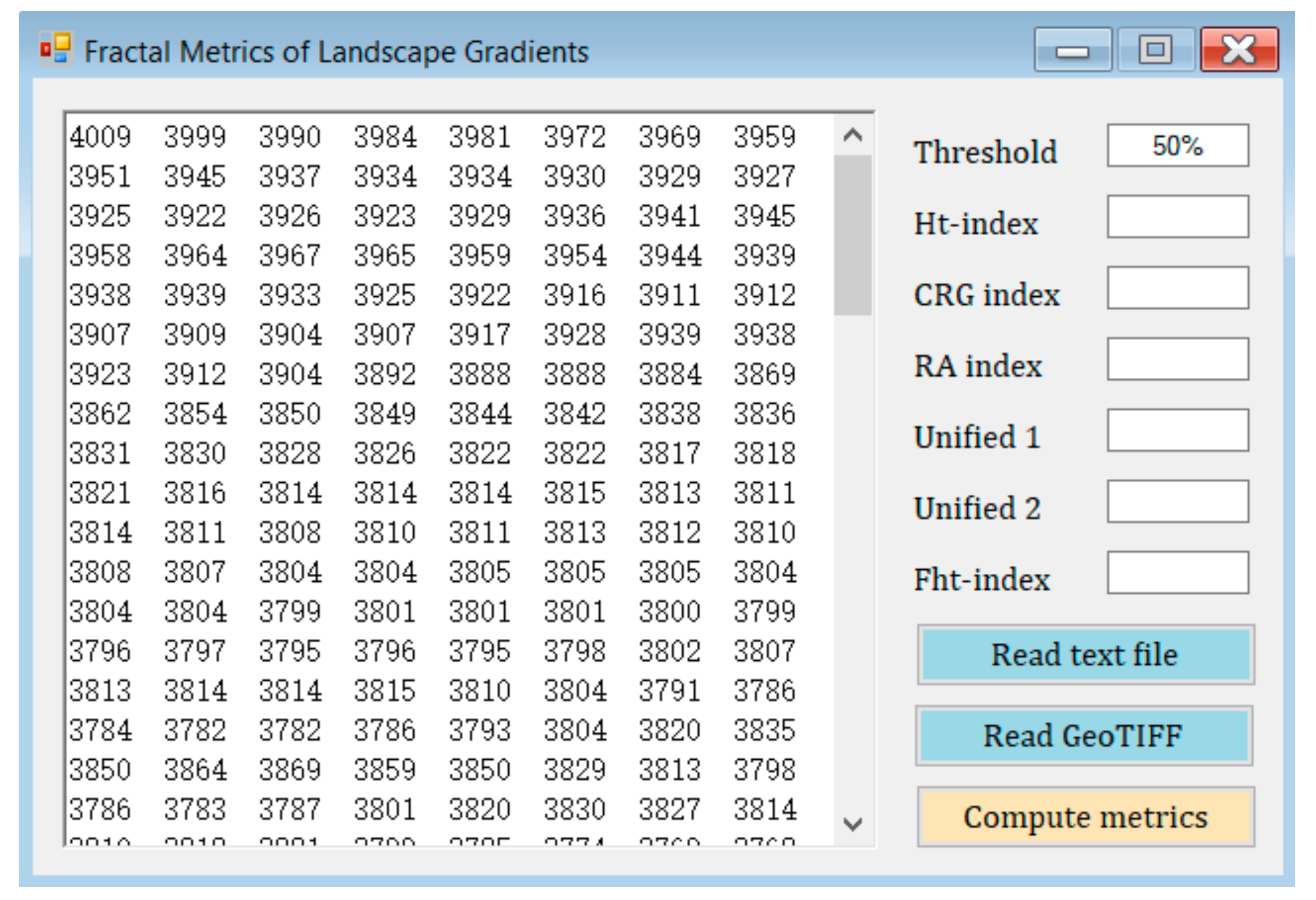
| Numbers | Ht-Index | |
|---|---|---|
| Whole | 4 | |
| Sub-whole 1 | 3 | |
| Sub-whole 2 | 2 |
| Numbers | Ht-Index | Fht-Index | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Whole | 3 | 3.0 | |
| Data set 1 | 3 | 2.8 | |
| Data set 2 | 3 | 2.6 | |
| Data set 3 | 3 | 2.4 | |
| Data set 4 | 3 | 2.2 | |
| Largest sub-whole | 2 | 2.0 |
| DEM | Size | Minimum | Maximum | Difference 1 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 600 600 | 3247 | 4473 | 1226 | 3765 |
| A2 | 600 600 | 3394 | 4380 | 986 | 3717 |
| B1 | 600 600 | 449 | 2327 | 1878 | 724 |
| B2 | 600 600 | 453 | 2498 | 2045 | 634 |
| C1 | 600 600 | 3428 | 4042 | 614 | 3511 |
| C2 | 600 600 | 460 | 2405 | 1945 | 593 |
| D1 | 600 600 | 35 | 1589 | 1554 | 413 |
| D2 | 600 600 | −74 | 1460 | 1534 | 210 |
| DEM | Ht-Index | CRG Index | RA Index | UM1 | UM2 | Fht-Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 13 | 11.1690 | 0.8449 | 13.0397 | 13.5477 | N/A |
| A2 | 14 | 12.1620 | 0.6553 | 14.0415 | 14.6221 | N/A |
| B1 | 15 | 14.3706 | 0.2933 | 15.4017 | 15.7626 | N/A |
| B2 | 11 | 10.5855 | 0.1773 | 11.4036 | 11.8253 | N/A |
| C1 | 12 | 10.1361 | 0.2713 | 12.0249 | 12.6566 | N/A |
| C2 | 13 | 12.5595 | 0.1376 | 13.1656 | 13.6623 | N/A |
| D1 | 15 | 14.5958 | 0.4866 | 15.4144 | 15.6224 | N/A |
| D2 | 13 | 13.4606 | 0.3714 | 13.5256 | 13.6558 | N/A |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, P.; Cushman, S.A.; Liu, G.; Ye, S.; Shen, S.; Cheng, C. FracL: A Tool for Characterizing the Fractality of Landscape Gradients from a New Perspective. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8100466
Gao P, Cushman SA, Liu G, Ye S, Shen S, Cheng C. FracL: A Tool for Characterizing the Fractality of Landscape Gradients from a New Perspective. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2019; 8(10):466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8100466
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Peichao, Samuel A. Cushman, Gang Liu, Sijing Ye, Shi Shen, and Changxiu Cheng. 2019. "FracL: A Tool for Characterizing the Fractality of Landscape Gradients from a New Perspective" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 8, no. 10: 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8100466
APA StyleGao, P., Cushman, S. A., Liu, G., Ye, S., Shen, S., & Cheng, C. (2019). FracL: A Tool for Characterizing the Fractality of Landscape Gradients from a New Perspective. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 8(10), 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8100466








