Progressive Amalgamation of Building Clusters for Map Generalization Based on Scaling Subgroups
Abstract
:1. Introduction
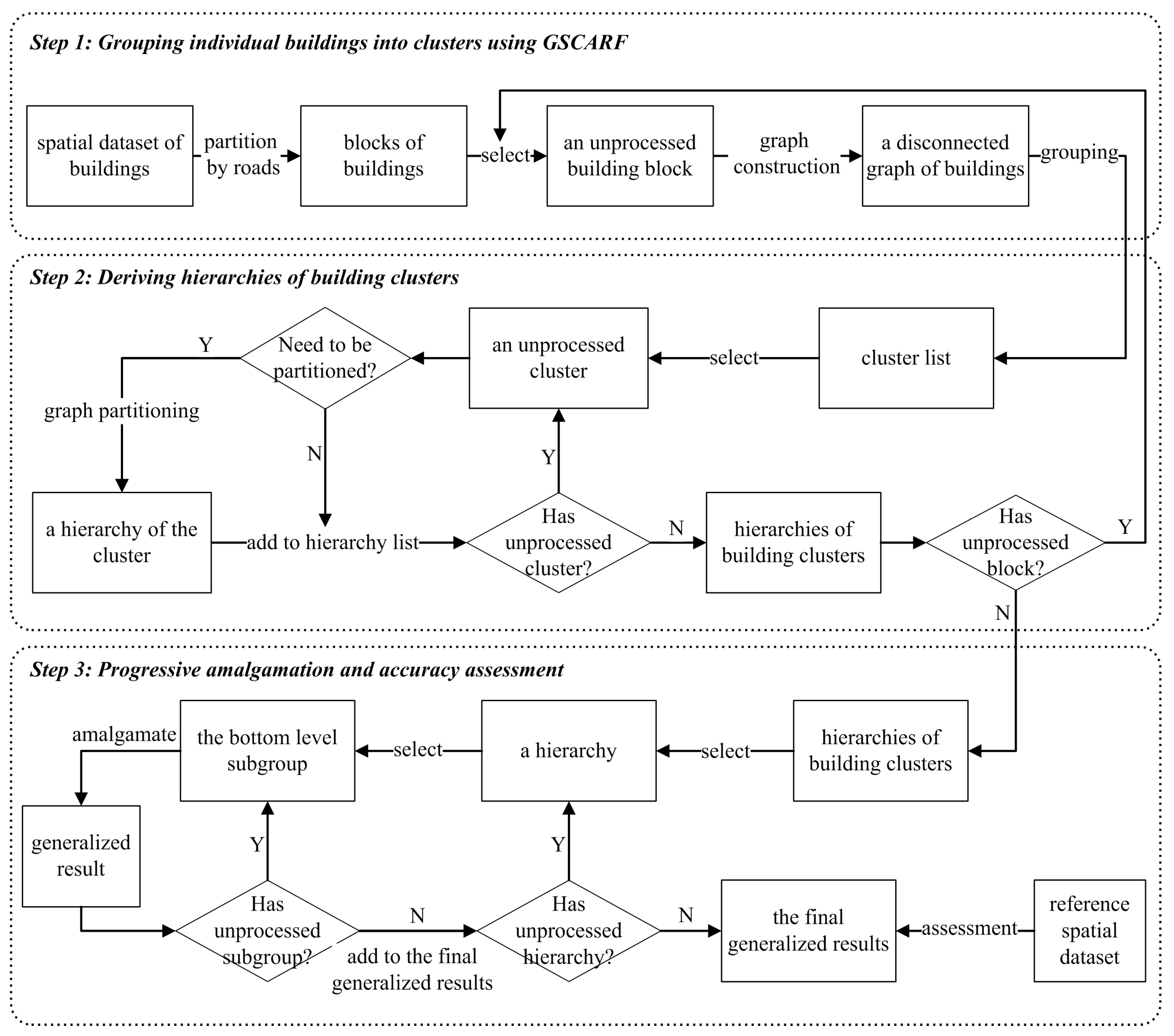
2. Methodology
2.1. Grouping Individual Buildings into Clusters
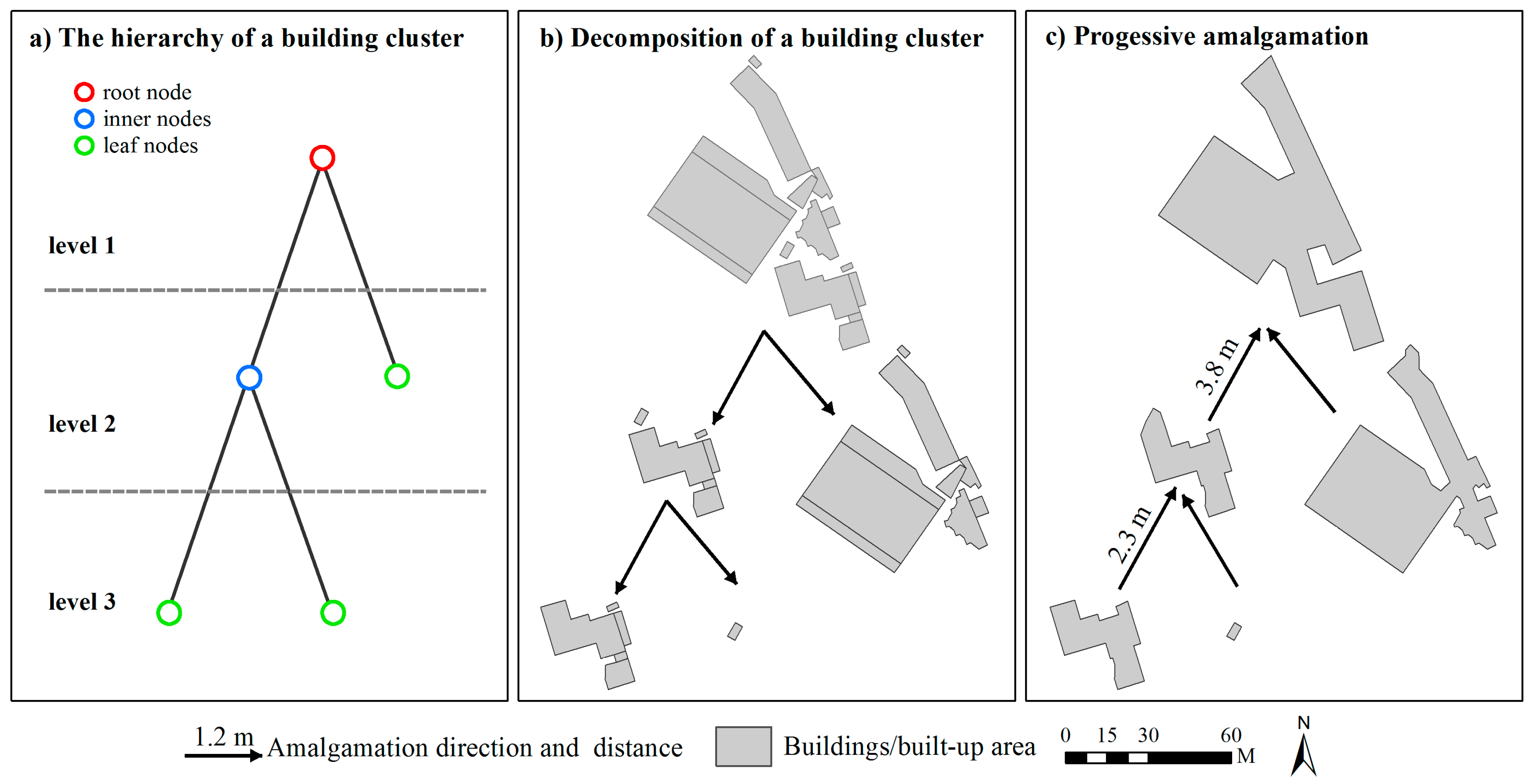
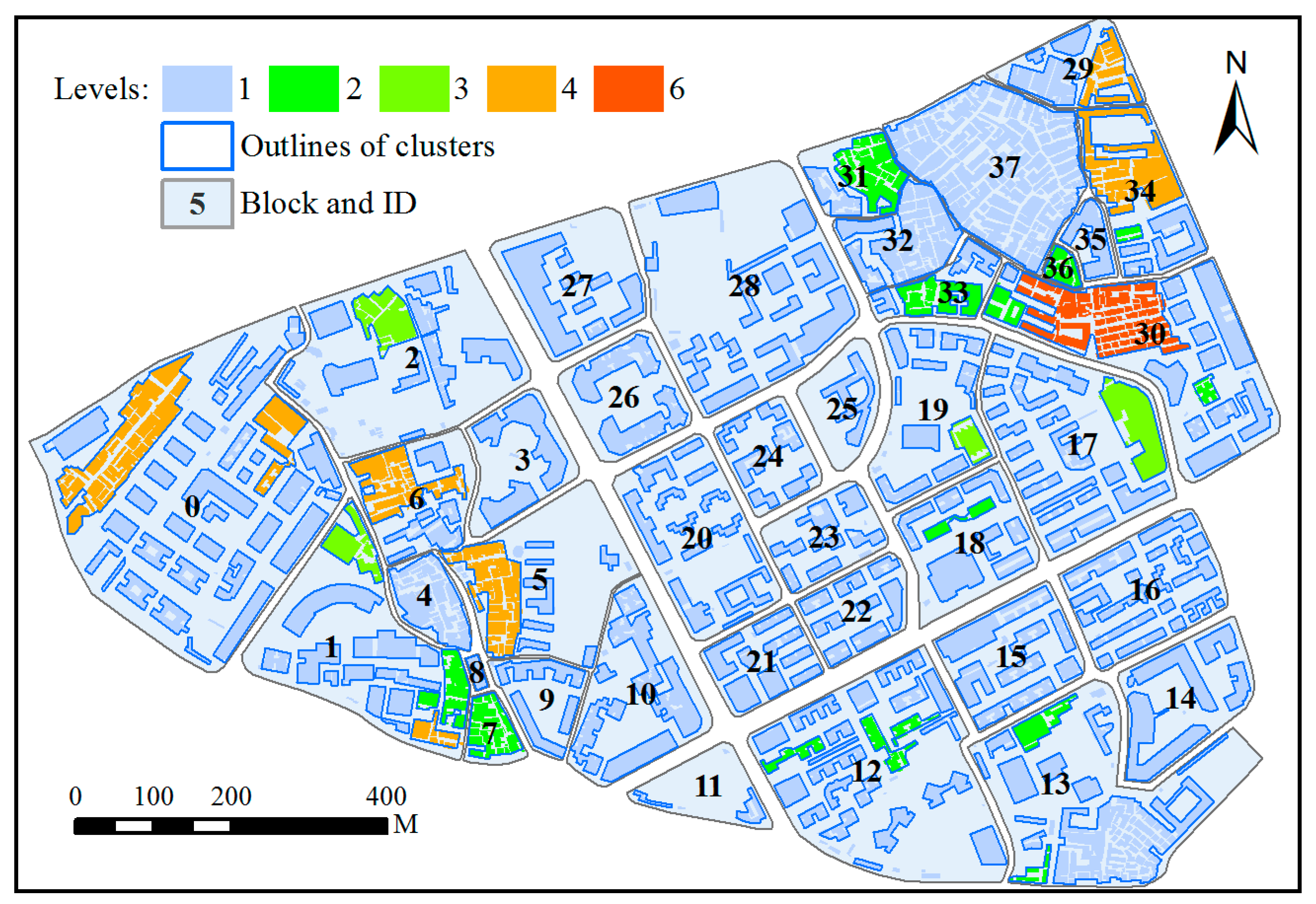
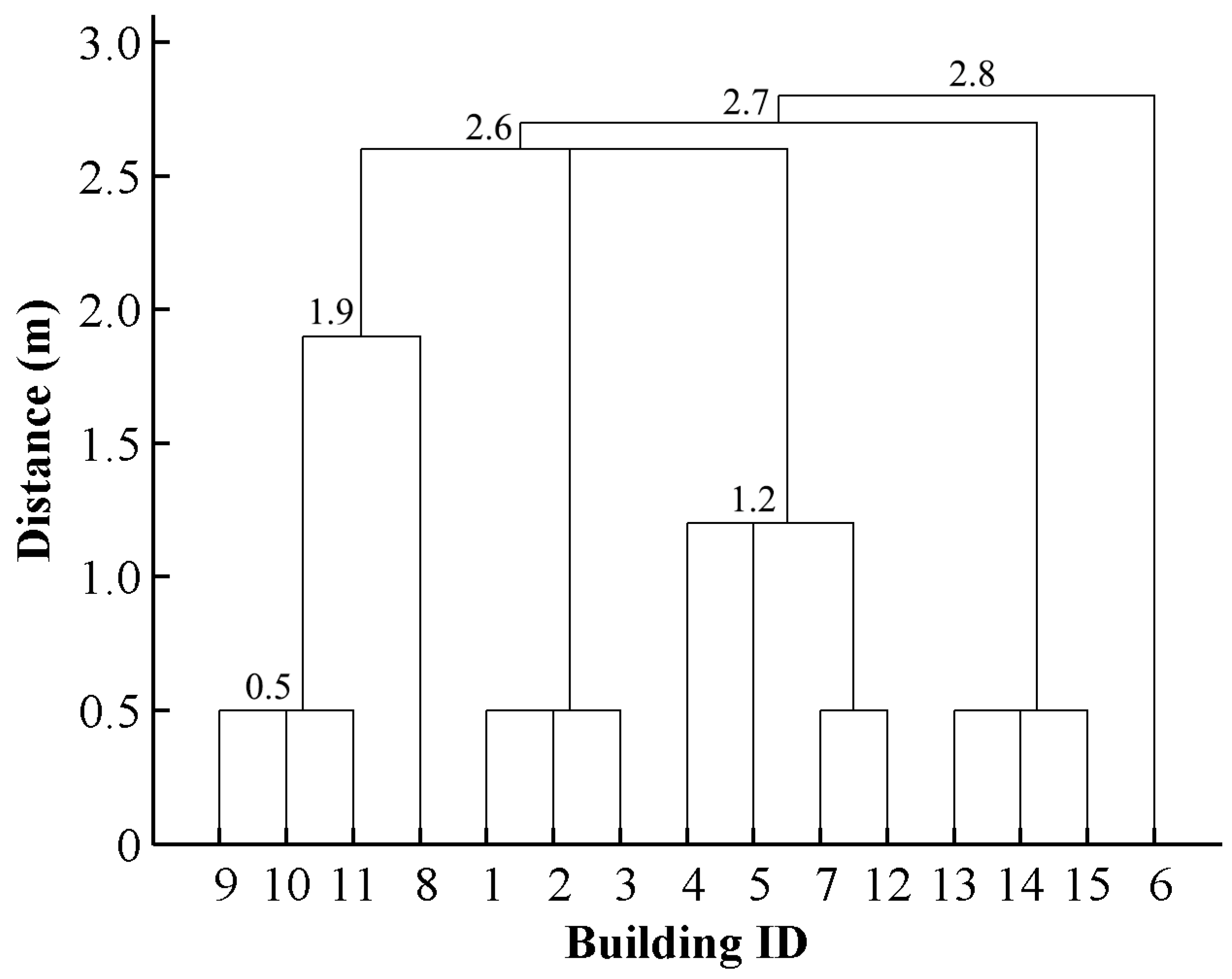
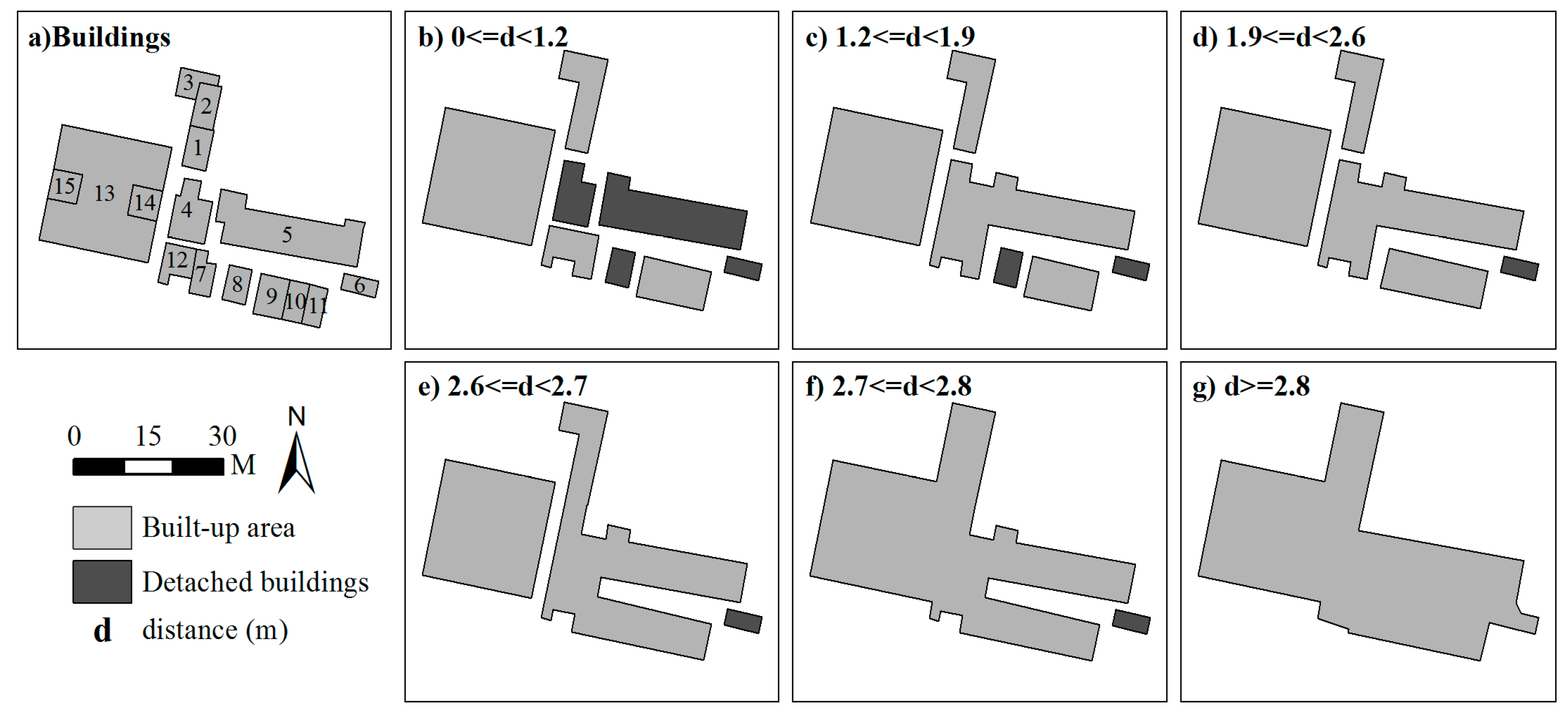
2.2. Deriving Hierarchies by Segmenting Building Clusters
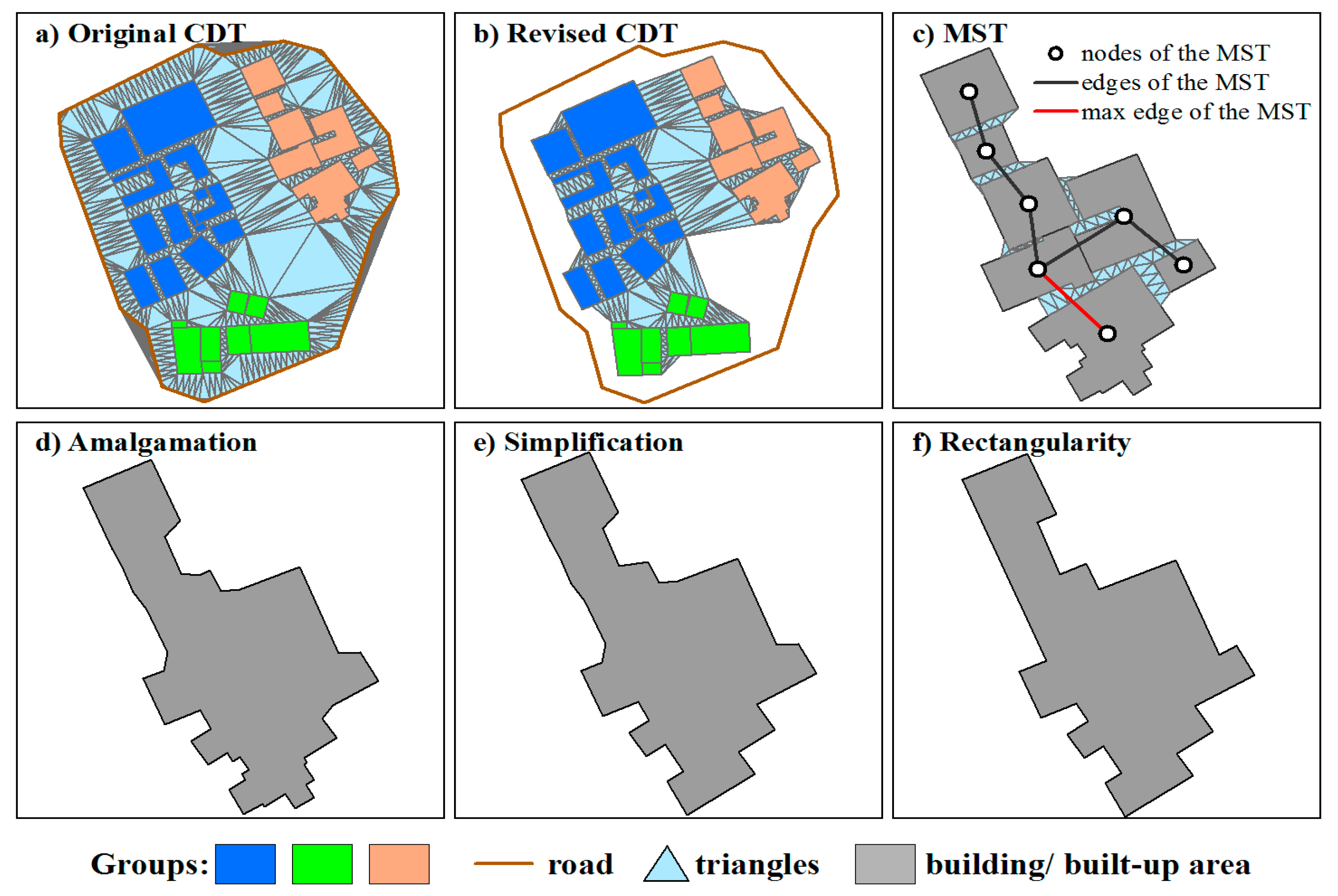
2.3. Progressive Amalgamation Based on Hierarchies of Building Groups
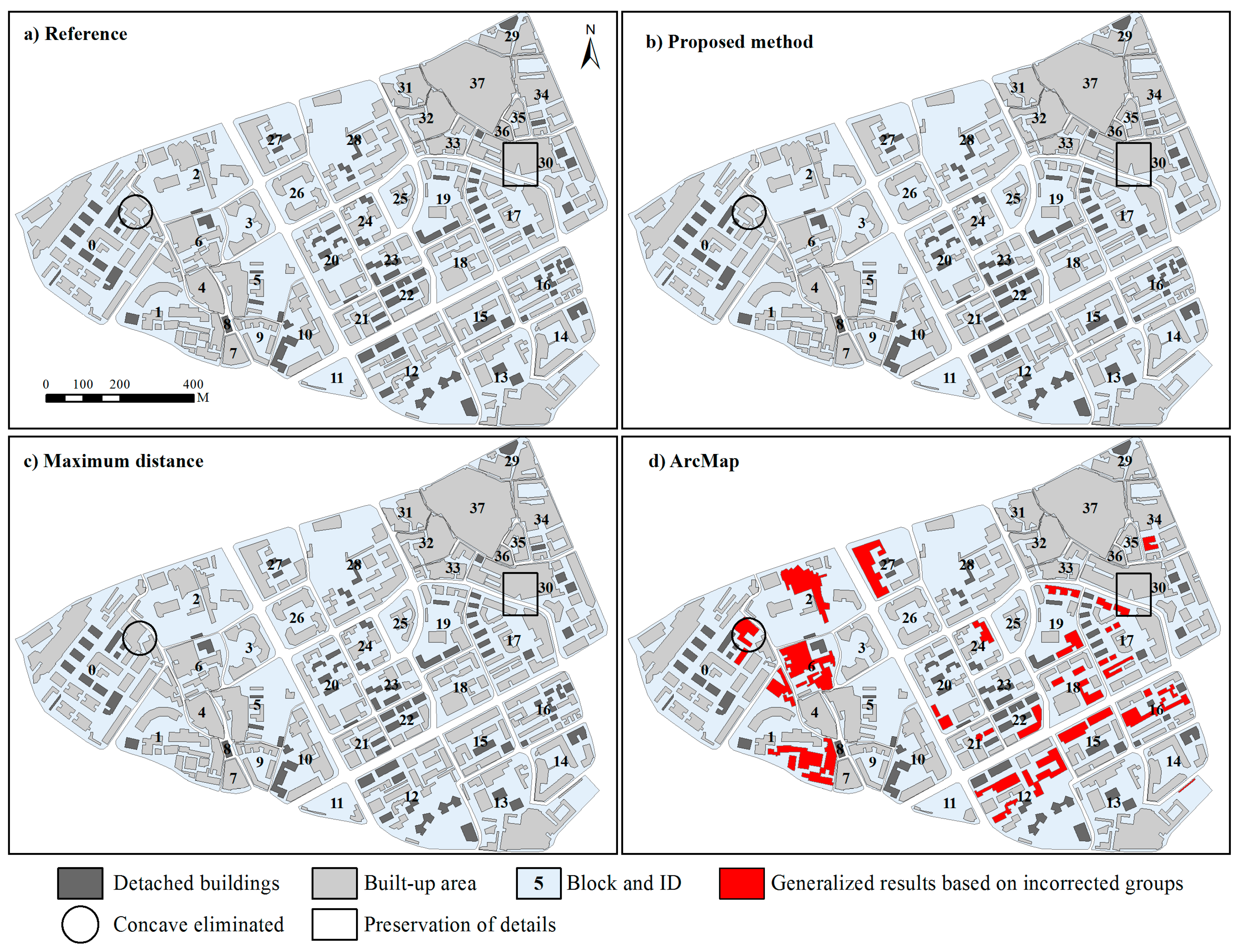
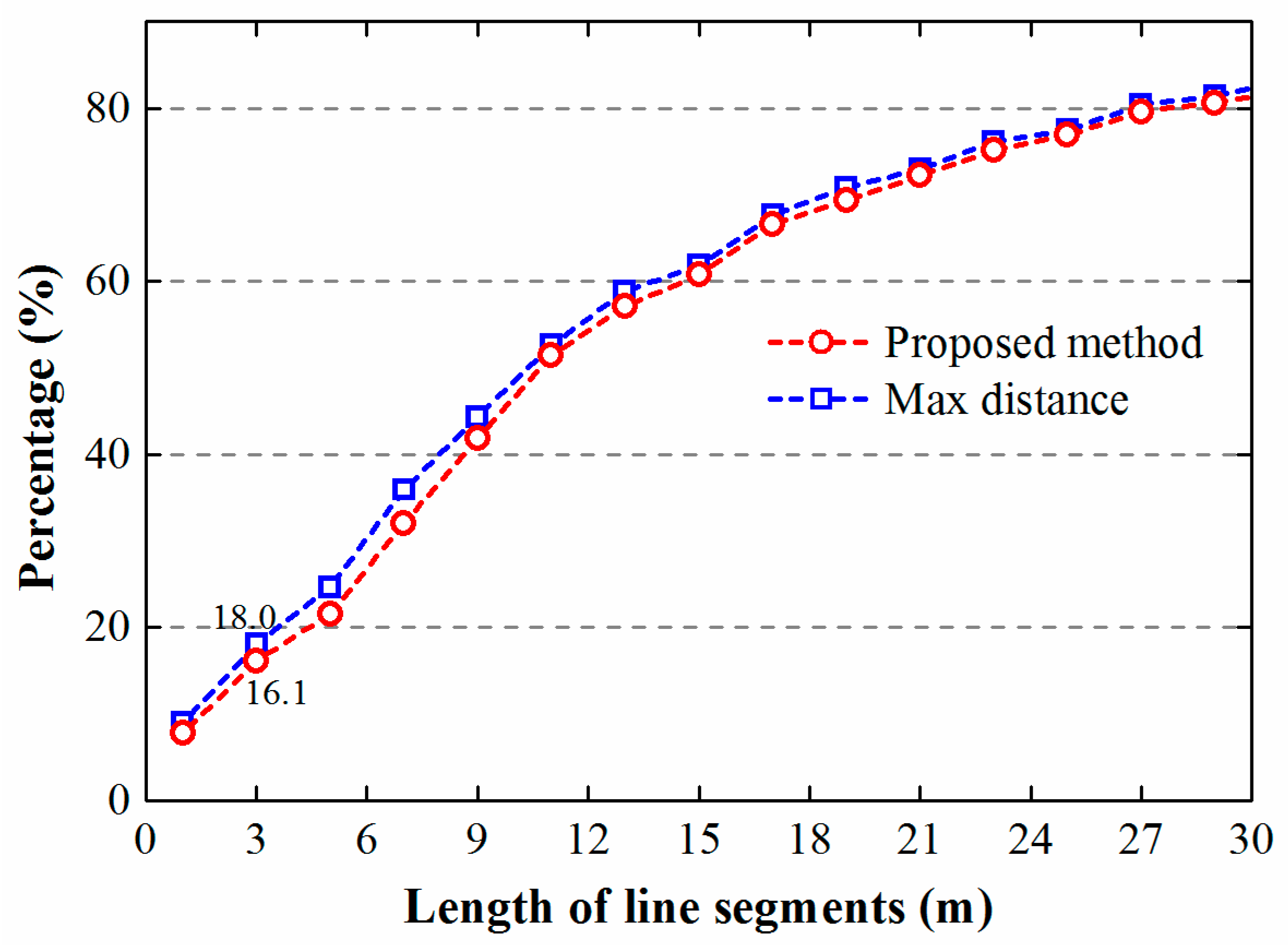
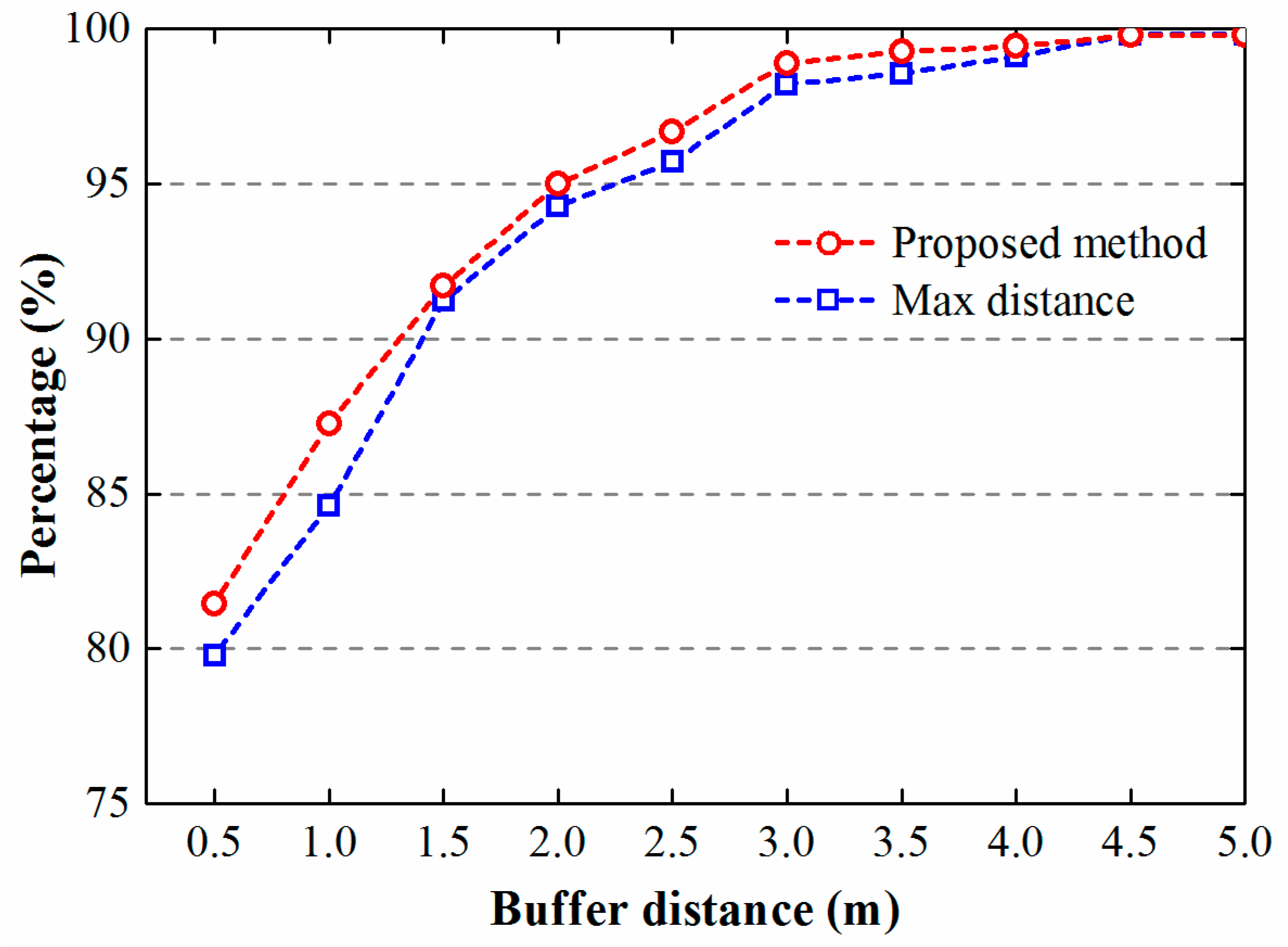
2.4. Method Comparisons and Assessment
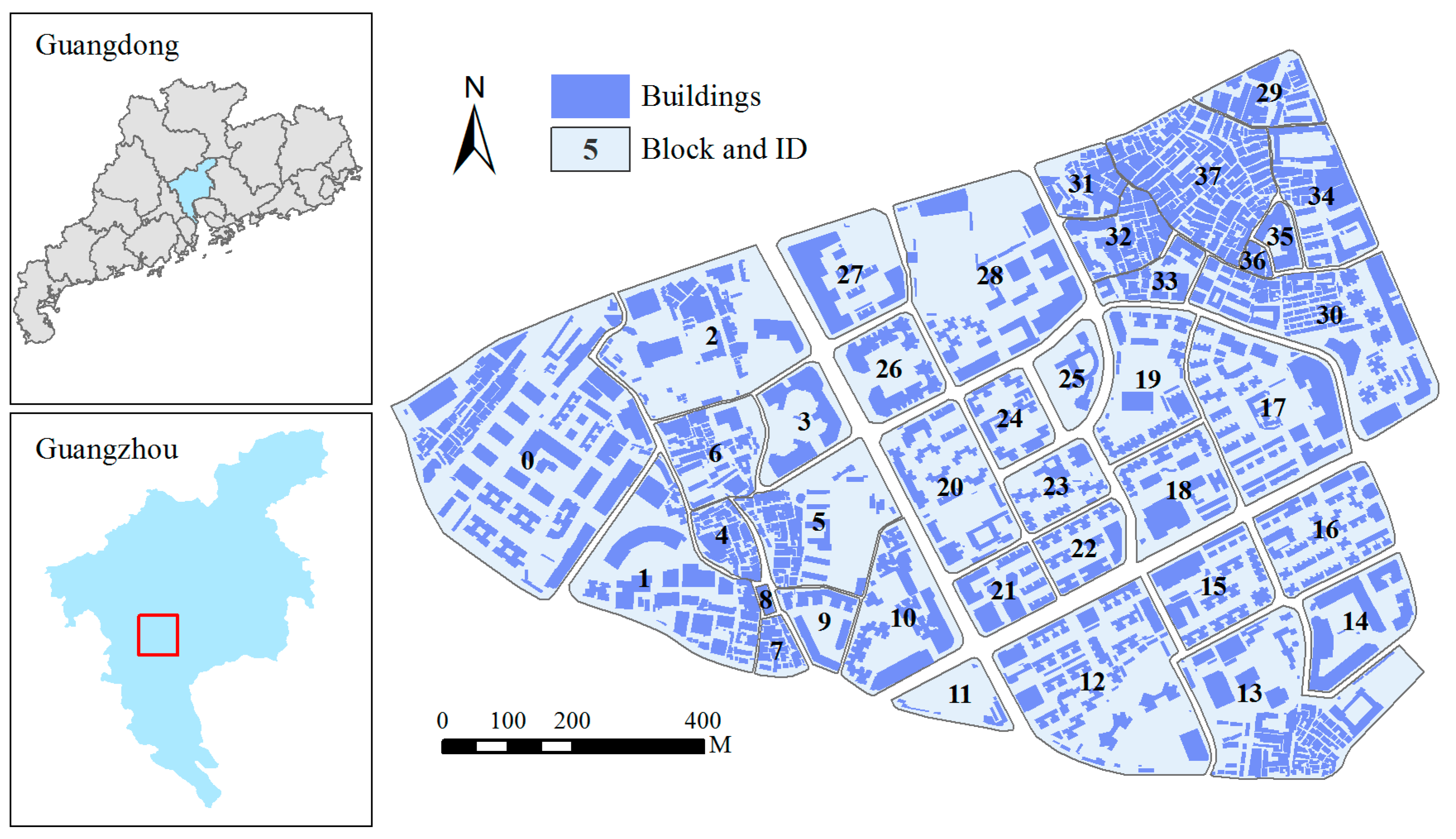
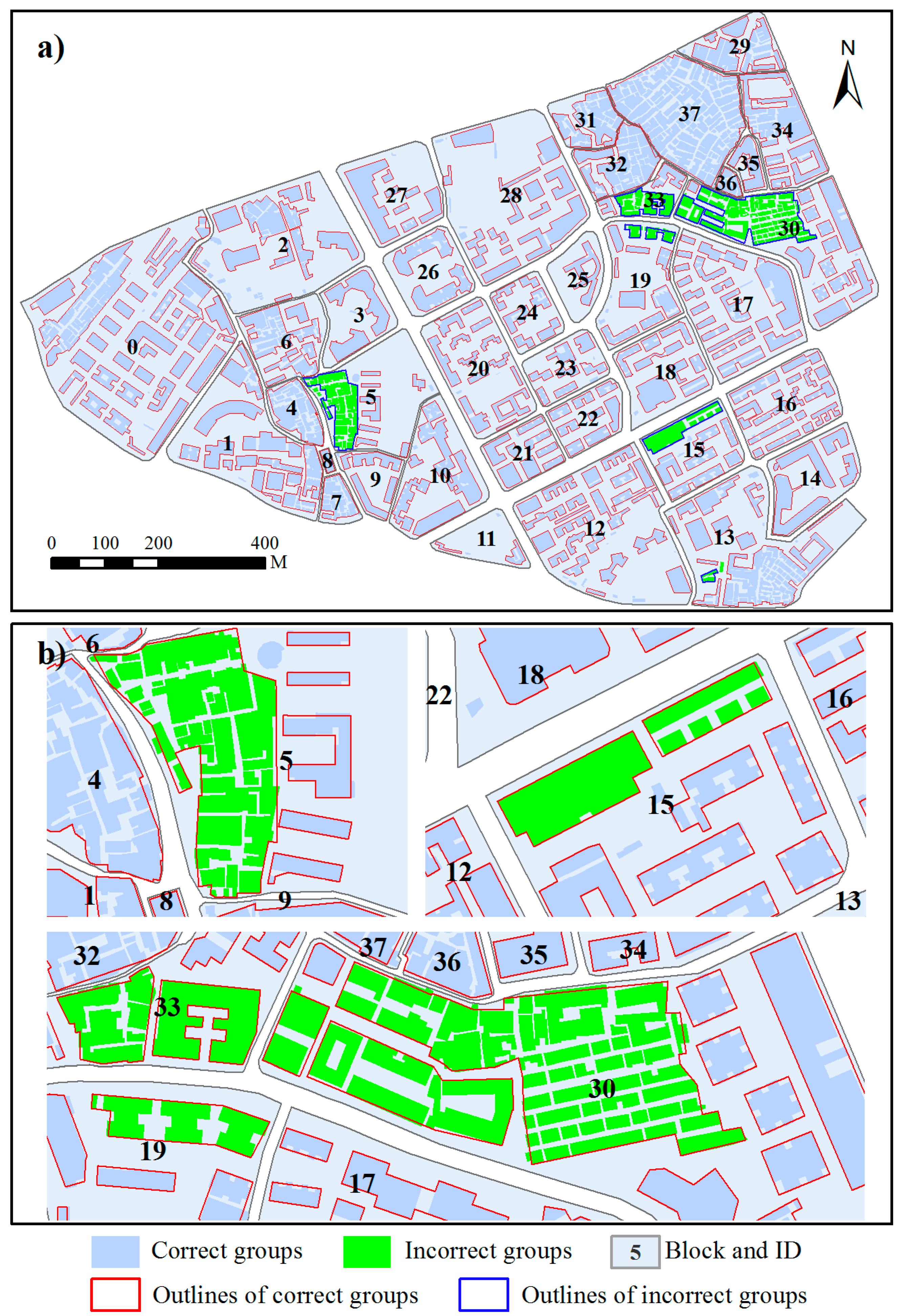
3. Test Data
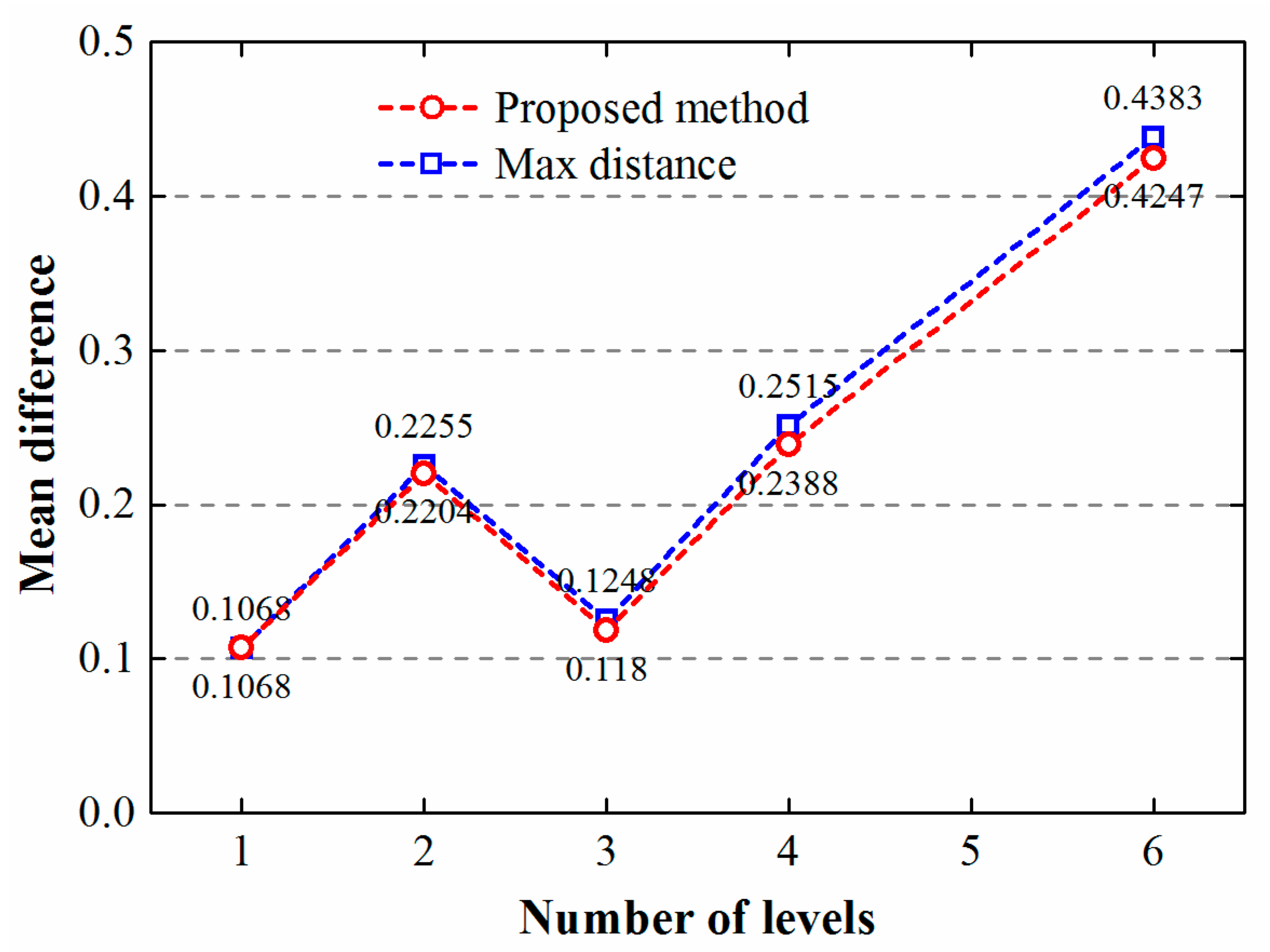
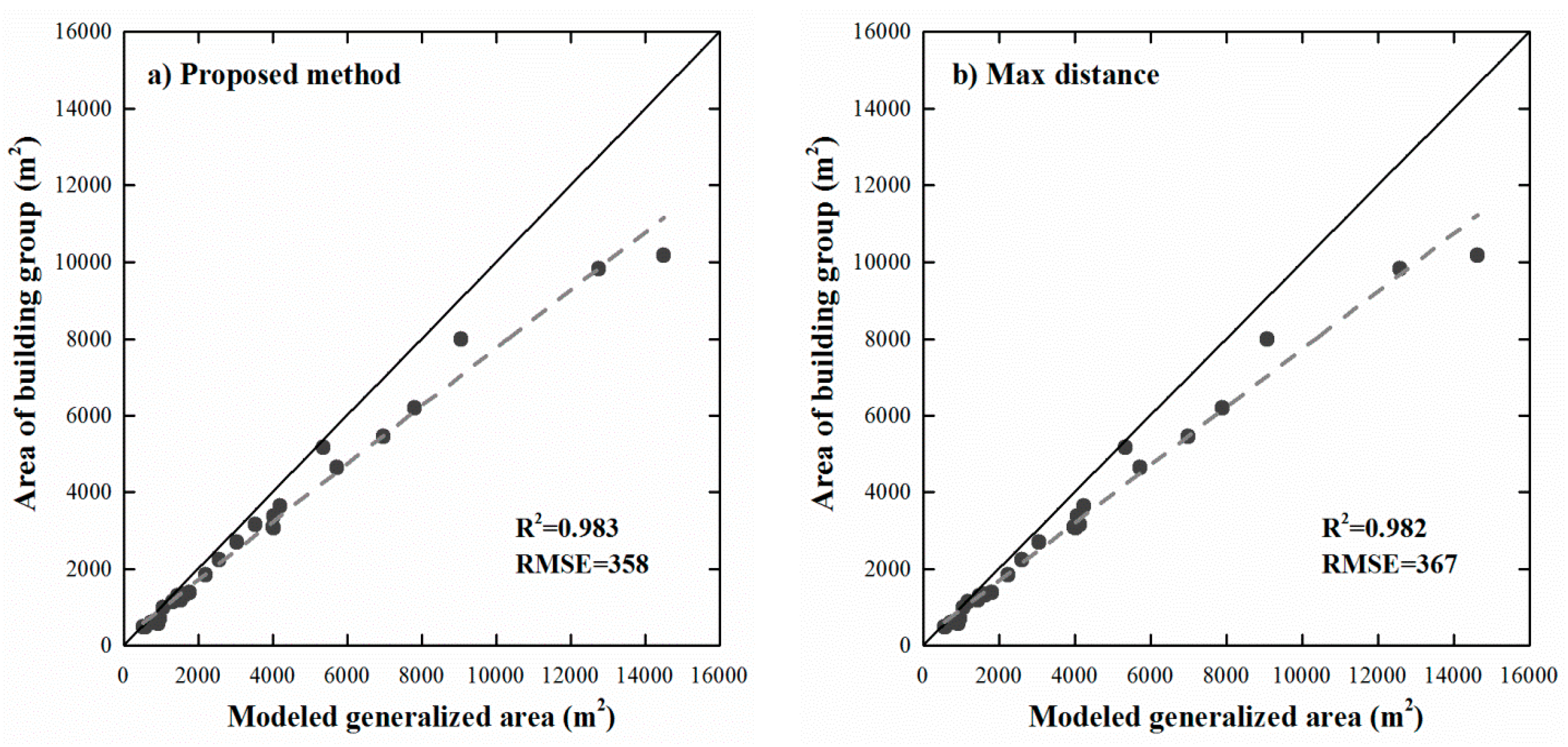
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McMaster, R.B.; Shea, K.S. Generalization in Digital Cartography; Association of American Geographers: Washington, DC, USA, 1992; pp. 17–69. [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness, W.; Burghardt, D.; Cécile, D. Map generalisation: Fundamental to the modelling and understanding of geographic space. In Abstracting Geographic Information in a Data Rich World; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, T.; Huang, J.; Xin, Q. Propagating updates of residential areas in multi-representation databases using constrained Delaunay triangulations. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2016, 5, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ai, T.; Stoter, J.; Zhao, X. Data matching of building polygons at multiple map scales improved by contextual information and relaxation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 92, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brassel, K.E.; Weibel, R. A review and conceptual framework of automated map generalization. Int. J. Geogr. Inform. Sci. 1988, 2, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarjakoski, L.T. Conceptual models of generalisation and multiple representation. In Generalisation of Geographic Information: Cartographic Modelling and Applications; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 11–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ware, J.M.; Jones, C.B.; Bundy, G.L. A triangulated spatial model for cartographic generalisation of areal objects. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Spatial Information Theory, Semmering, Austria, 21–23 September 1995; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1995; pp. 173–192. [Google Scholar]
- Allouche, M.K.; Moulin, B. Amalgamation in cartographic generalization using Kohonen’s feature nets. Int. J. Geogr. Inform. Sci. 2005, 19, 899–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guercke, R.; Götzelmann, T.; Brenner, C.; Sester, M. Aggregation of LoD 1 building models as an optimization problem. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, T.; Zhang, X. The Aggregation of urban building clusters based on the skeleton partitioning of gap space. In The European Information Society; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 153–170. [Google Scholar]
- Regnauld, N. Algorithms for the amalgamation of topographic data. In Proceedings of the 21st International Cartographic Conference, Durban, South Africa, 10–16 August 2003; pp. 222–234. [Google Scholar]
- Regnauld, N. Contextual building typification in automated map generalization. Algorithmica 2001, 30, 312–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, K.H. A hierarchical graph-clustering approach to find groups of objects. In Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Progress in Automated Map Generalization, Paris, France, 28–30 April 2003; Citeseer: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Ai, T.; Stoter, J.; Kraak, M.; Molenaar, M. Building pattern recognition in topographic data: Examples on collinear and curvilinear alignments. GeoInformatica 2013, 17, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Luo, L.; Cao, K.; Shu, M. Extracting building patterns with multilevel graph partition and building grouping. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 122, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, T.; Guo, R. Polygon cluster pattern mining based on Gestalt principles. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2007, 36, 302–308. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Zhang, X.; Xin, Q. Recognition of building group patterns in topographic maps based on graph partitioning and random forest. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 136, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schylberg, L. Cartographic amalgamation of area objects. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1993, 29, 135. [Google Scholar]
- Su, B.; Li, Z.; Lodwick, G.; Muller, J.C. Algebraic models for the aggregation of area features based upon morphological operators. Int. J. Geogr. Inform. Sci. 1997, 11, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cámara, M.; López, F. Mathematical morphology applied to raster generalization of urban city block maps. Cartographica 2000, 1, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Liu, Q.; Li, X. Local perception-based intelligent building outline aggregation approach with back propagation neural network. Neural Process Lett. 2015, 41, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, P.; Mooney, P.; Bertolotto, M. Spatial relations using high level concepts. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2012, 1, 333–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regnauld, N.; Revell, P. Automatic amalgamation of buildings for producing ordnance survey 1:50000 scale maps. Cartogr. J. 2007, 44, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Li, C.; Yin, Y. Classification and filtering of constrained Delaunay triangulation for automated building aggregation. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2016, 45, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D. Geographic and cartographic contexts in generalization. In Proceedings of the ICA Workshop on Generalisation and Multiple Representation, Leicester, UK, 20–21 August 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Basaraner, M.; Selcuk, M. A structure recognition technique in contextual generalisation of buildings and built-up areas. Cartogr. J. 2008, 45, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetinkaya, S.; Basaraner, M.; Burghardt, D. Proximity-based grouping of buildings in urban blocks: A comparison of four algorithms. Geocarto Int. 2015, 30, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, K.H. Grid typification. In Progress in Spatial Data Handling; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 633–642. [Google Scholar]
- Zahn, C.T. Graph-theoretical methods for detecting and describing gestalt clusters. IEEE Trans. Comput. 1971, 100, 68–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.B.; Bundy, G.L.; Ware, M.J. Map generalization with a triangulated data structure. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 1995, 22, 317–331. [Google Scholar]
- Bader, M.; Barrault, M.; Weibel, R. Building displacement over a ductile truss. Int. J. Geogr. Inform. Sci. 2005, 19, 915–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Systems Research Institute (ESRI). ArcGIS for Desktop. Available online: http://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/latest/tools/cartography-toolbox/aggregate-polygons.htm (accessed on 9 February 2018).
- Zhang, X.; Stoter, J.; Ai, T.; Kraak, M.; Molenaar, M. Automated evaluation of building alignments in generalized maps. Int. J. Geogr. Inform. Sci. 2013, 27, 1550–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China (SAC). Cartographic Symbols for National Fundamental Scale Maps-Part 2: Specifications for Cartographic Symbols 1:5000 & 1:10000 Topographic Maps; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Geográfico Português (IGP). Cartografia e Ortofotocartografia à Escala 1:10,000; Normas Técnicas de Produção e Reprodução; Instituto Geográfico Português: Lisboa, Portugal, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Burghardt, D.; Schmid, S. Constraint-Based Evaluation of Automated and Manual Generalised Topographic Maps; Cartography in Central and Eastern Europe; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 147–162. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Ai, T.; Liu, P.; Yang, M. Continuous scale transformations of linear features using simulated annealing-based morphing. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šuba, R.; Meijers, M.; Oosterom, P. Continuous road network generalization throughout all scales. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2016, 5, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Method | No. of Objects | Min Distance (m) | Area (m2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Mean | RMSE * | |||
| Proposed method | 280 | 2.03 | 212.67 | 37,439.73 | 1597.88 | 44.47 |
| Max distance | 280 | 2.03 | 212.67 | 37,439.73 | 1600.79 | 135.26 |
| ArcMap | 260 | 0.36 | 193.31 | 37,320.84 | 1726.28 | — |
| Reference | 280 | 1.98 | 208.05 | 37,738.60 | 1589.37 | — |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J. Progressive Amalgamation of Building Clusters for Map Generalization Based on Scaling Subgroups. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi7030116
He X, Zhang X, Yang J. Progressive Amalgamation of Building Clusters for Map Generalization Based on Scaling Subgroups. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2018; 7(3):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi7030116
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Xianjin, Xinchang Zhang, and Jie Yang. 2018. "Progressive Amalgamation of Building Clusters for Map Generalization Based on Scaling Subgroups" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 7, no. 3: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi7030116
APA StyleHe, X., Zhang, X., & Yang, J. (2018). Progressive Amalgamation of Building Clusters for Map Generalization Based on Scaling Subgroups. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 7(3), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi7030116





