An Urban Heat Island Study of the Colombo Metropolitan Area, Sri Lanka, Based on Landsat Data (1997–2017)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
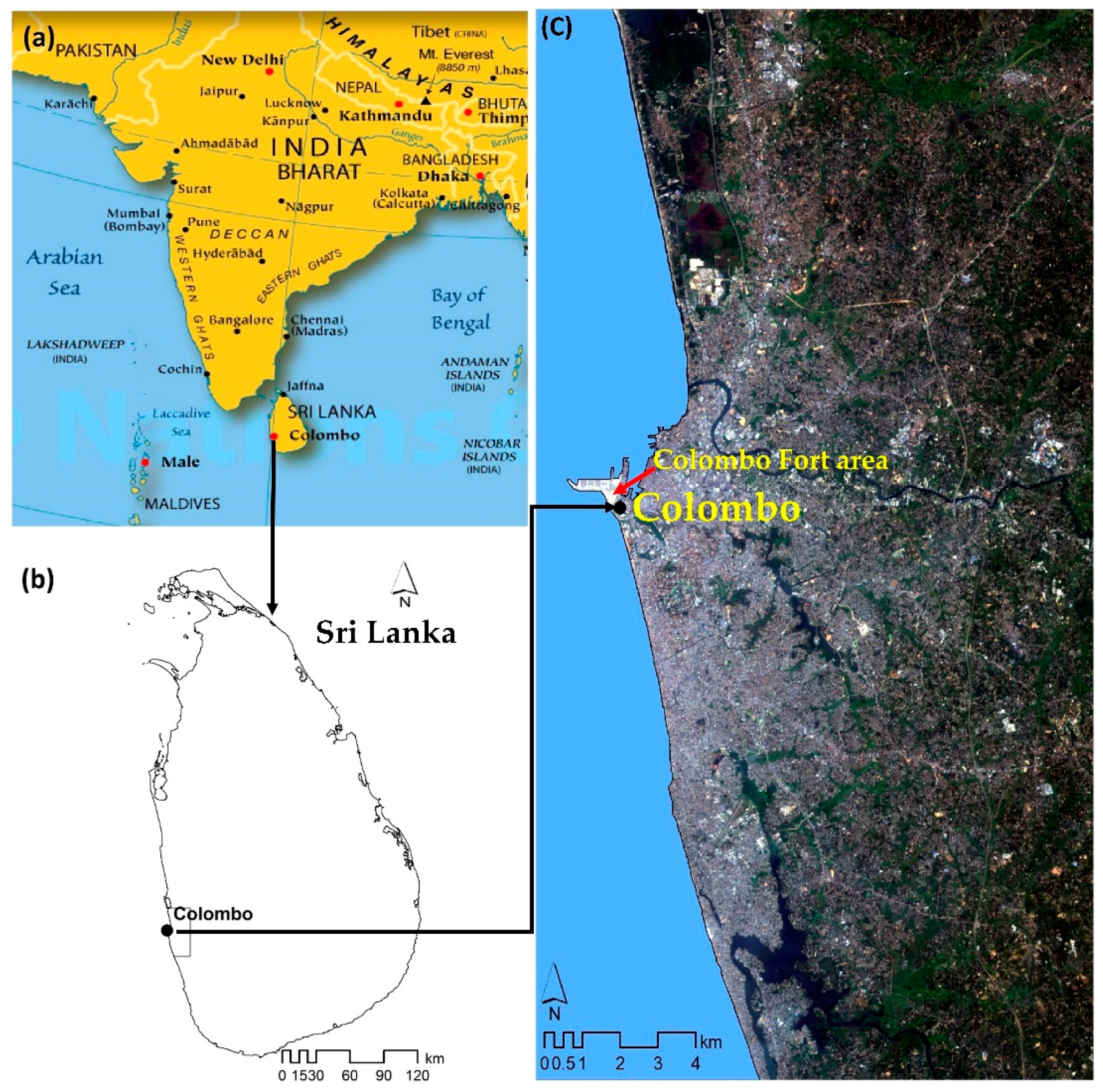
2.1. Study Area: Colombo Metropolitan Area (CMA), Sri Lanka
2.2. Data Descriptions and Pre-Processing
2.3. Land Surface Temperature (LST) Retrieval
2.4. Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and Normalized Difference Built-Up Index (NDBI)
2.5. Environmental Criticality Index (ECI)
2.6. Urban-Rural Gradient Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
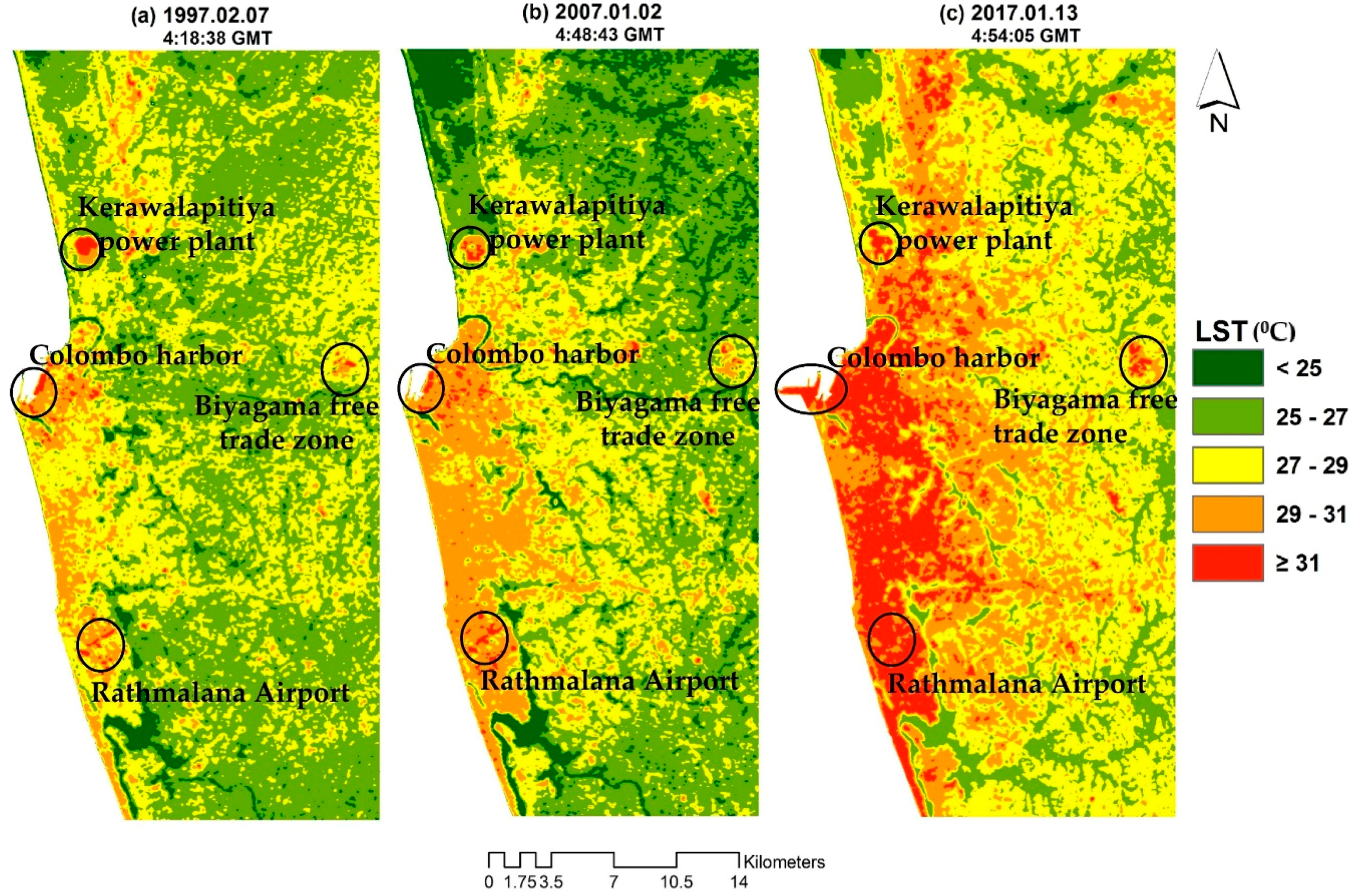
3.1. LST in 1997, 2007 and 2017
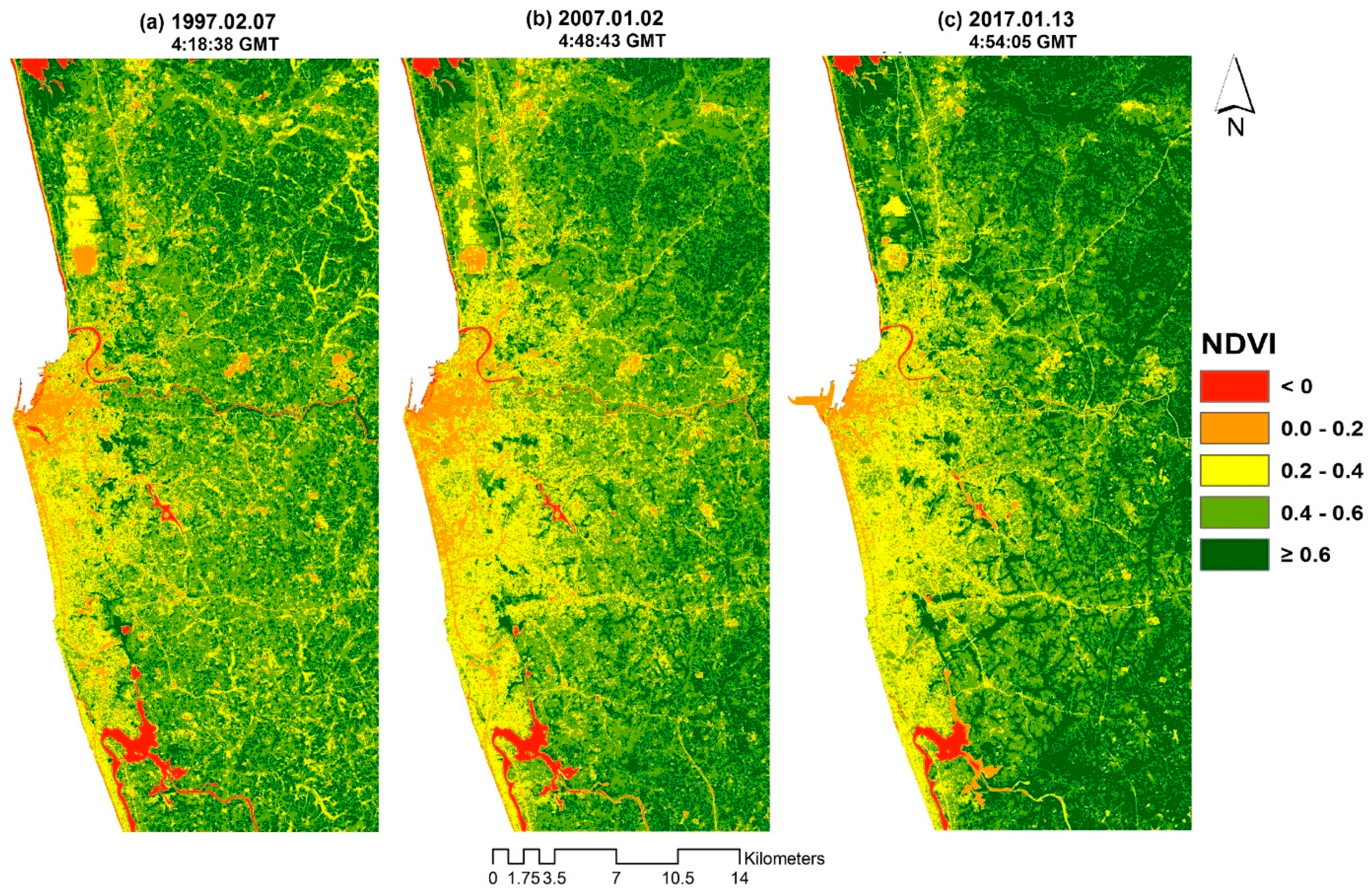
3.2. NDVI in 1997, 2007 and 2017
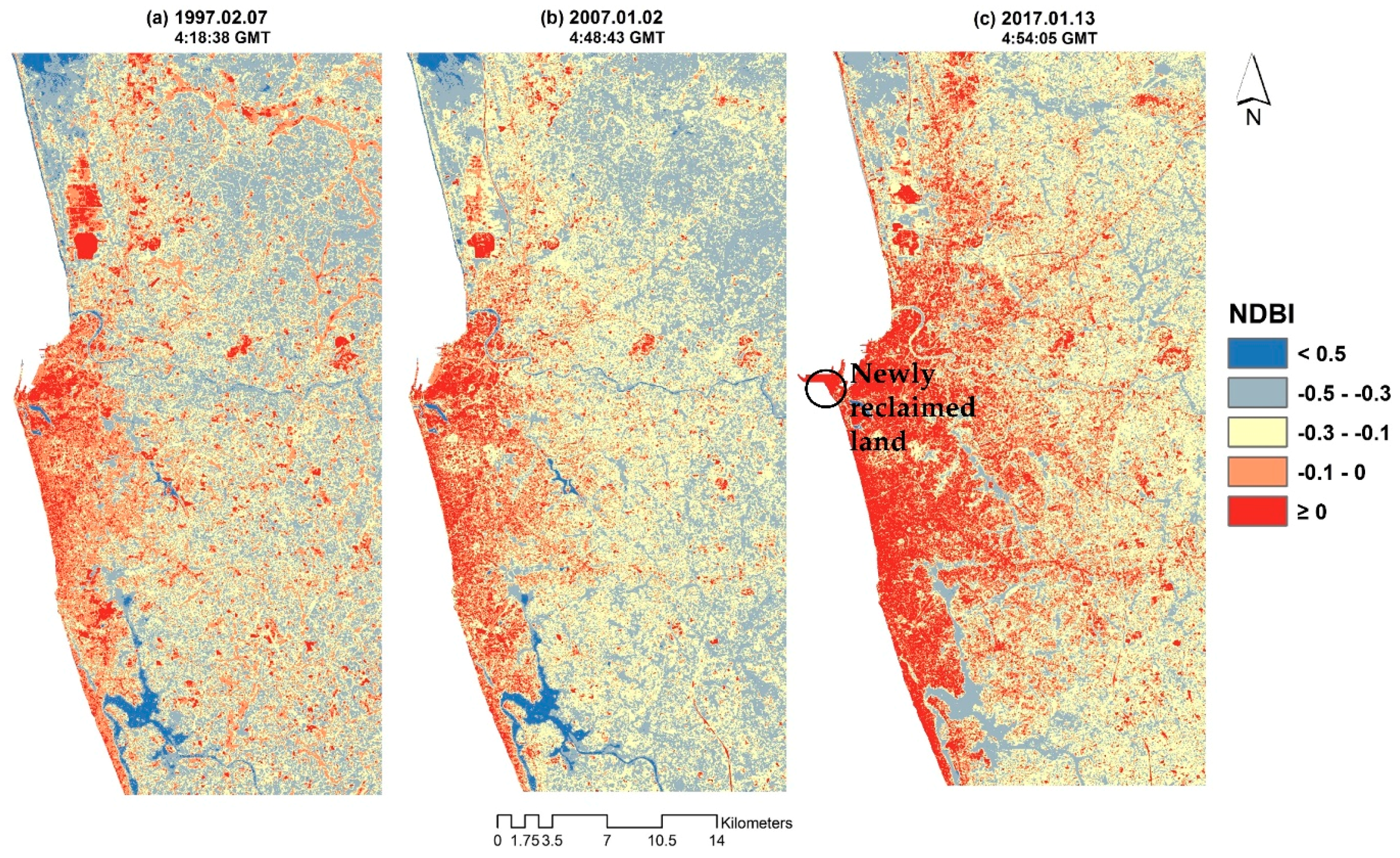
3.3. NDBI in 1997, 2007 and 2017
3.4. ECI in 1997, 2007 and 2017
3.5. Urban–Rural Gradient Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. The Urbanization of the CMA
4.2. The Formation of SUHI and Its Implications for Sustainable Landscape and Urban Planning in the CMA
4.3. Limitations of the Study and Future Research
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2014 Revision: Highlights; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Estoque, R.C.; Murayama, Y. Measuring sustainability based upon various perspectives: A case study of a hill station in Southeast Asia. Ambio 2014, 43, 943–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senanayake, I.P.; Welivitiya, W.D. D.P.; Nadeeka, P.M. Remote sensing based analysis of urban heat islands with vegetation cover in Colombo city, Sri Lanka using Landsat-7 ETM+ data. Urban Clim. 2013, 5, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estoque, R.C.; Murayama, Y.; Myint, S.W. Effects of landscape composition and pattern on land surface temperature: An urban heat island study in the megacities of Southeast Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 577, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, L. The Climate of London; W. Phillips: London, UK, 1818. [Google Scholar]
- Kikon, N.; Singh, P.; Singh, S.K.; Vyas, A. Assessment of urban heat islands (UHI) of Noida City, India using multi-temporal satellite data. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2016, 22, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency). Reducing Urban Heat Islands: Compendium of Strategies Urban Heat Island Basics; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Rizwan, A.M.; Dennis, L.Y.C.; Liu, C. A review on the generation, determination and mitigation of Urban Heat Island. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogan, J.; Ziemer, M.; Martin, D.; Ratick, S.; Cuba, N.; DeLauer, V. The impact of tree cover loss on land surface temperature: A case study of central Massachusetts using Landsat Thematic Mapper thermal data. Appl. Geogr. 2013, 45, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Shekhar, S. Statistical analysis of land surface temperature-vegetation indexes relationship through thermal remote sensing. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 121, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dousset, B.; Gourmelon, F. Satellite multi-sensor data analysis of urban surface temperatures and landcover. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2003, 58, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aniello, C.; Morgan, K.; Busbey, A.; Newland, L. Mapping micro-urban heat islands using LANDSAT TM and a GIS. Comput. Geosci. 1995, 21, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathopoulou, M.; Cartalis, C. Daytime urban heat islands from Landsat ETM+ and Corine land cover data: An application to major cities in Greece. Sol. Energy 2007, 81, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Lu, D.; Schubring, J. Estimation of land surface temperature-vegetation abundance relationship for urban heat island studies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 89, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L.; Zhao, H.M.; Li, P.X.; Yin, Z.Y. Remote sensing image-based analysis of the relationship between urban heat island and land use/cover changes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 104, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. Thermal infrared remote sensing for urban climate and environmental studies: Methods, applications, and trends. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2009, 64, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Song, C.; Cao, L.; Zhu, F.; Meng, X.; Wu, J. Impacts of landscape structure on surface urban heat islands: A case study of Shanghai, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3249–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.; Kainz, W. Monitoring patterns of urban heat islands of the fast-growing Shanghai metropolis, China: Using time-series of Landsat TM/ETM+ data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 19, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokaie, M.; Zarkesh, M.K.; Arasteh, P.D.; Hosseini, A. Assessment of urban heat island based on the relationship between land surface temperature and land use/land cover in Tehran. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2016, 23, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Estoque, R.C.; Murayama, Y. An urban heat island study in Nanchang City, China based on land surface temperature and social-ecological variables. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 32, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, E. Seasonal and spatial variation of surface urban heat island intensity in a small urban agglomerate in Brazil. Climate 2016, 4, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.; Uchihama, D.; Ochi, S.; Yasuoka, Y. Assessment with satellite data of the urban heat island effects in Asian mega cities. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2006, 8, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Y. Urban heat island analysis using the landsat TM data and ASTER Data: A case study in Hong Kong. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 1535–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Gao, J.; Ni, S. Use of normalized difference built-up index in automatically mapping urban areas from TM imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Odeh, I.O.A.; Han, C. Bi-temporal characterization of land surface temperature in relation to impervious surface area, NDVI and NDBI, using a sub-pixel image analysis. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2009, 11, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Bauer, M.E. Comparison of impervious surface area and normalized difference vegetation index as indicators of surface urban heat island effects in Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, W.; Zhang, H. Remote sensing evaluation of urban heat island and its spatial pattern of the Shanghai metropolitan area, China. Ecol. Complex. 2009, 6, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Li, W.; Schienke, E.W.; Wang, X. Spatial pattern of impervious surfaces and their impacts on land surface temperature in Beijing, China. J. Environ. Sci. (China) 2007, 19, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subasinghe, S.; Estoque, R.C.; Murayama, Y. Spatiotemporal analysis of urban growth using GIS and remote sensing: A case study of the Colombo Metropolitan Area, Sri Lanka. Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2016, 5, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, R.; Fernando, H.J.S. Urban heat islands in humid and arid climates: Role of urban form and thermal properties in Colombo, Sri Lanka and Phoenix, USA. Clim. Res. 2007, 34, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, R.; Johansson, E. Influence of urban morphology and sea breeze on hot humid microclimate: The case of Colombo, Sri Lanka. Clim. Res. 2006, 30, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, R. Thermal comfort implications of urbanization in a warm-humid city: The Colombo Metropolitan Region (CMR), Sri Lanka. Build. Environ. 2005, 40, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, D.; Pitawala, A.; Gunatilake, J. Heavy metals in road deposited sediments and road dusts of Colombo Capital, Sri Lanka. J. Nat. Sci. Found. Sri Lanka 2016, 44, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsat, T.; User, S.D.; Project, L.; Office, S.; Space, G.; Landsat, U. Landsat 7 Science Data Users Handbook. Available online: https://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/Landsat7_Handbook.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2017).
- USGS Landsat 8 (L8) Data Users Handbook. Version 1.0; June 2015. Available online: https://landsat.usgs.gov/sites/default/files/documents/Landsat8DataUsersHandbook.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2017).
- Chander, G.; Markham, B.L.; Helder, D.L. Summary of current radiometric calibration coefficients for Landsat MSS, TM, ETM+, and EO-1 ALI sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Paolini, L. Land surface temperature retrieval from Landsat TM 5. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, O.; Ekercin, S.; Dadaser-Celik, F. Use of Landsat land surface temperature and vegetation indices for monitoring drought in the Salt Lake Basin Area, Turkey. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Weng, Q. Enhancing temporal resolution of satellite imagery for public health studies: A case study of West Nile Virus outbreak in Los Angeles in 2007. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Du, Z.; Ling, F.; Zhou, D.; Wang, H.; Gui, Y.; Sun, B.; Zhang, X. A comparison of land surface water mapping using the normalized difference water index from TM, ETM+ and ALI. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 5530–5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevanatha and Colombo Municipal Council (CMC). Poverty Profile City of Colombo: Urban Poverty Reduction Through Community Empowerment, Colombo. Available online: http://www.ucl.ac.uk/dpu-projects/drivers_urb_change/urb_society/pdf_liveli_vulnera/Sevanatha_Poverty_Profile1.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2017).
- Department of Census and Statistics. Census of Population and Housing 2012; Department of Census and Statistics: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2012.
- City of Colombo. Available online: http://colombo.mc.gov.lk/colombo.php (accessed on 15 February 2017).
- Census of Population and Housing 2012. Available online: http://www.statistics.gov.lk/pophousat/cph2011/index.php?fileName=Activities/TentativelistofPublications (accessed on 27 May 2017).
- The World Bank, World Development Indicators: GDP (Current US$). Available online: http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.CD?locations=LK (accessed on 17 April 2017).
- The World Bank. Colombo: The Heartbeat of Sri Lanka. 2013. Available online: http://www.worldbank.org/en/news/feature/2013/03/21/colombo-heartbeat-sri-lanka (accessed on 17 April 2017).
- Zimmerman, T. The New Silk Roads: China, the U.S., and the Future of Central Asia. 2015. Available online: http://cic.nyu.edu/sites/default/files/zimmerman_new_silk_road_final_2.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2017).

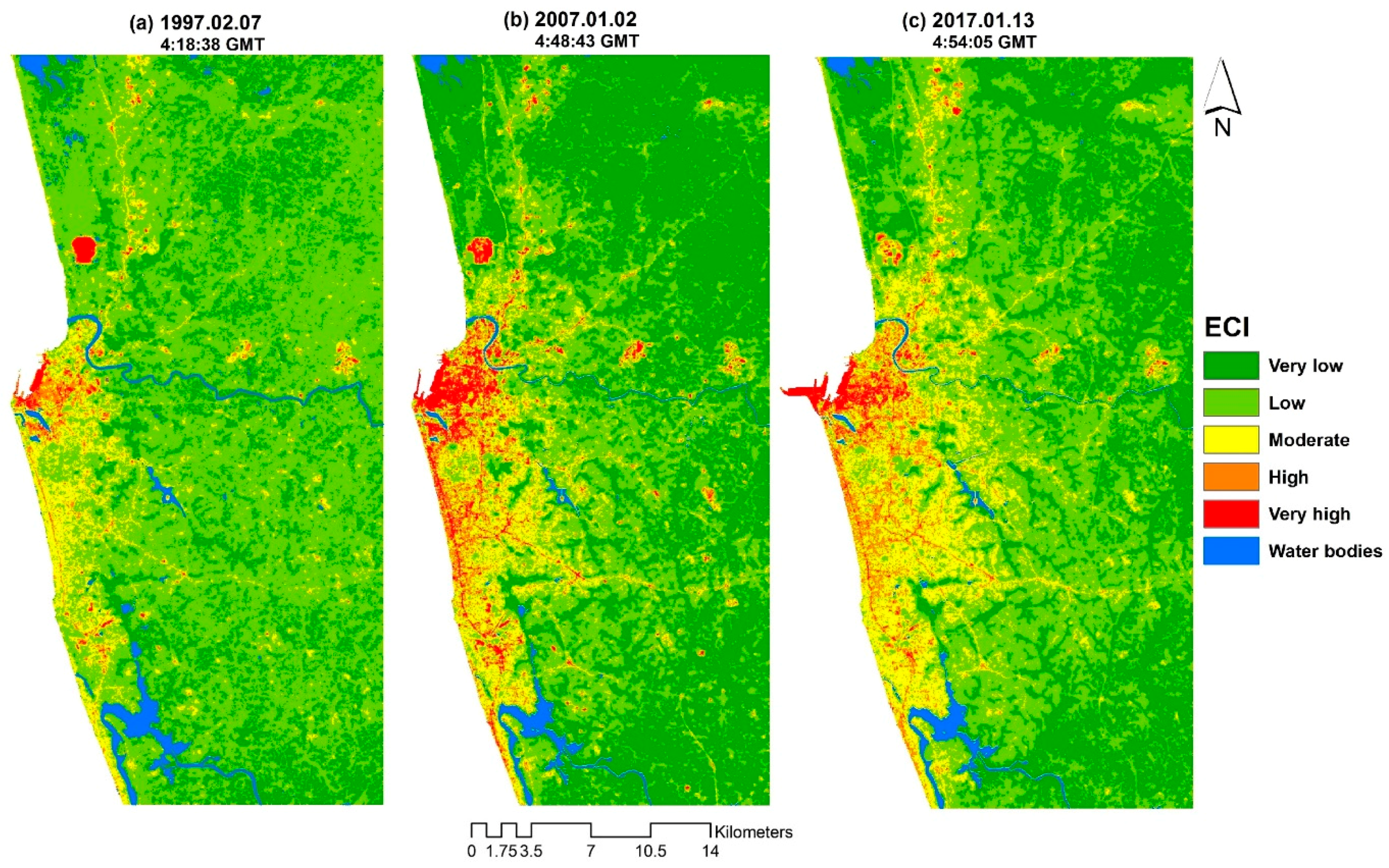
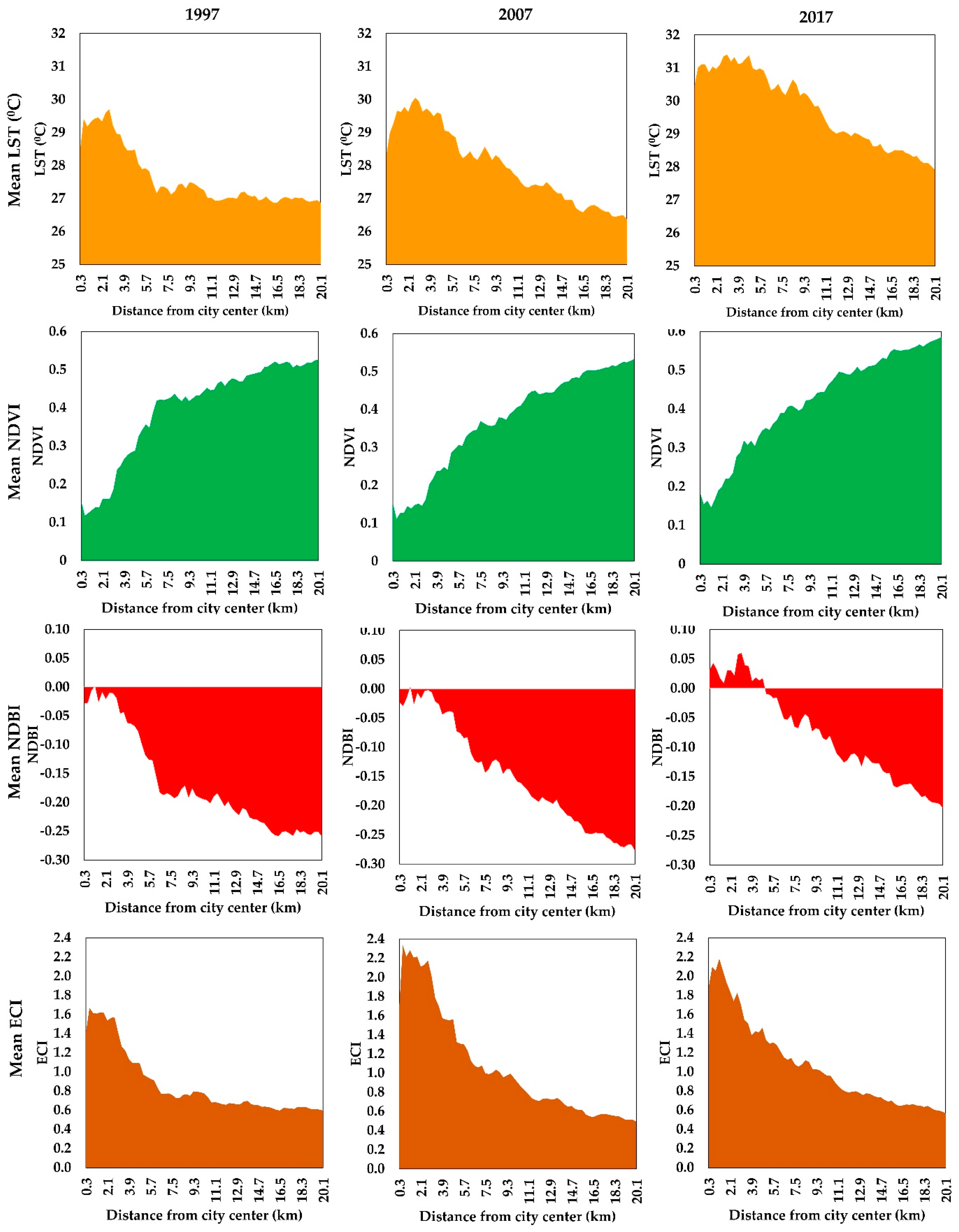
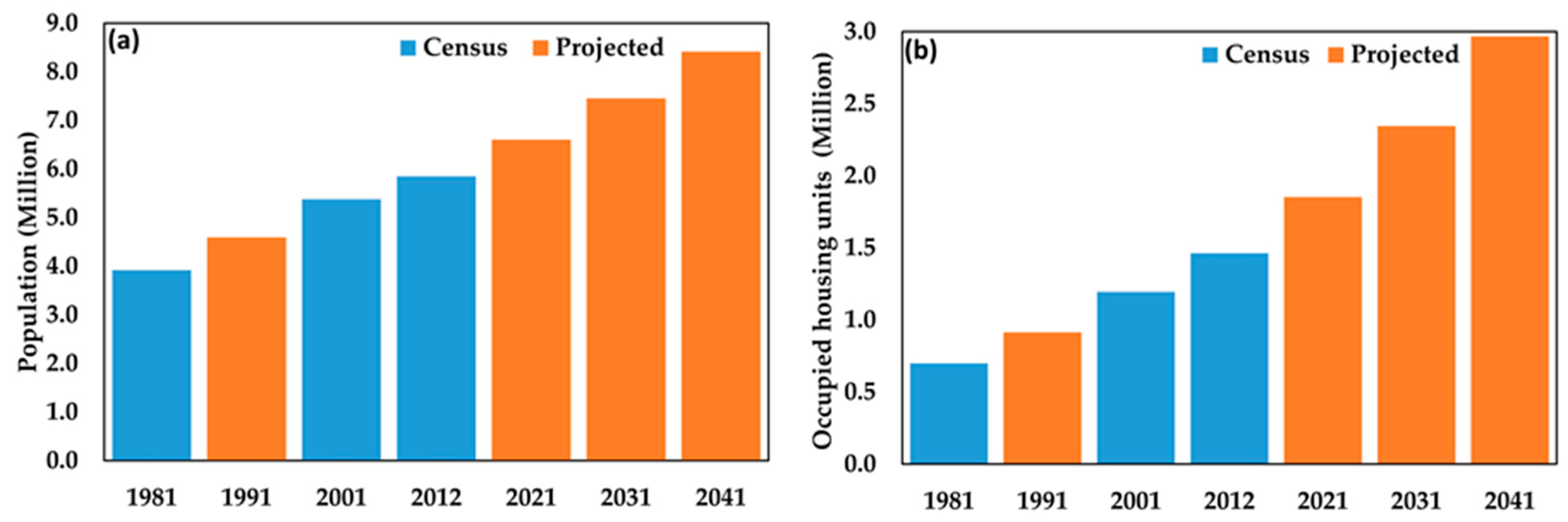

| Sensor | Scene ID | Acquisition Date | Time (GMT) | Season |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat-5 TM | LT51410551997038BKT01 | 7 February 1997 | 04:18:38 | Dry |
| Landsat-5 TM | LT51410552007002BKT00 | 2 January 2007 | 04:48:43 | Dry |
| Landsat-8 OLI/TIRS | LC81410552017013LGN00 | 13 January 2017 | 04:54:05 | Dry |
| Date | Time (GMT) | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 February 1997 | 04:18:38 | 21.06 | 34.86 | 26.98 | 1.12 |
| 2 January 2007 | 04:48:43 | 21.10 | 34.02 | 26.96 | 1.57 |
| 13 January 2017 | 04:54:05 | 22.31 | 35.94 | 28.62 | 1.71 |
| Date | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 February 1997 | −0.75 | 0.84 | 0.47 | 0.17 |
| 2 January 2007 | −0.36 | 0.77 | 0.47 | 0.16 |
| 13 January 2017 | −0.25 | 0.81 | 0.52 | 0.16 |
| Date | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 February 1997 | −1.00 | 0.46 | −0.23 | 0.14 |
| 2 January 2007 | −1.00 | 0.51 | −0.23 | 0.14 |
| 13 January 2017 | −0.67 | 0.66 | −0.15 | 0.14 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ranagalage, M.; Estoque, R.C.; Murayama, Y. An Urban Heat Island Study of the Colombo Metropolitan Area, Sri Lanka, Based on Landsat Data (1997–2017). ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi6070189
Ranagalage M, Estoque RC, Murayama Y. An Urban Heat Island Study of the Colombo Metropolitan Area, Sri Lanka, Based on Landsat Data (1997–2017). ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2017; 6(7):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi6070189
Chicago/Turabian StyleRanagalage, Manjula, Ronald C. Estoque, and Yuji Murayama. 2017. "An Urban Heat Island Study of the Colombo Metropolitan Area, Sri Lanka, Based on Landsat Data (1997–2017)" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 6, no. 7: 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi6070189
APA StyleRanagalage, M., Estoque, R. C., & Murayama, Y. (2017). An Urban Heat Island Study of the Colombo Metropolitan Area, Sri Lanka, Based on Landsat Data (1997–2017). ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 6(7), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi6070189







