Comparative Analysis on Two Schemes for Synthesizing the High Temporal Landsat-like NDVI Dataset Based on the STARFM Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area

3. Data and Preprocessing
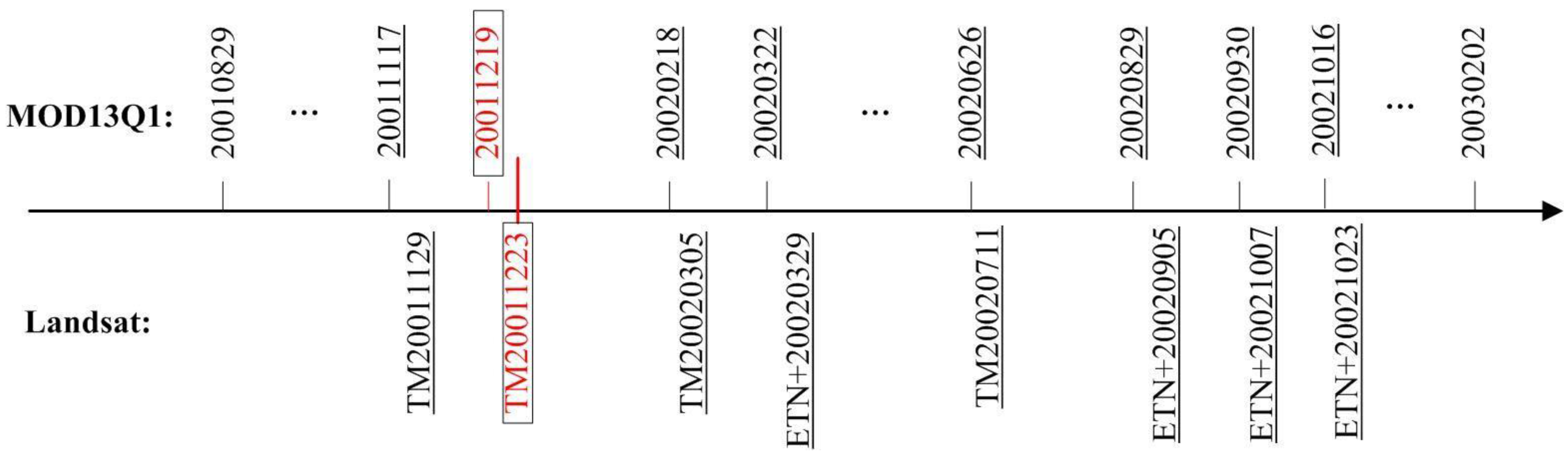
4. Methods
4.1. The STARFM Algorithm
4.2. Two Comparable Schemes
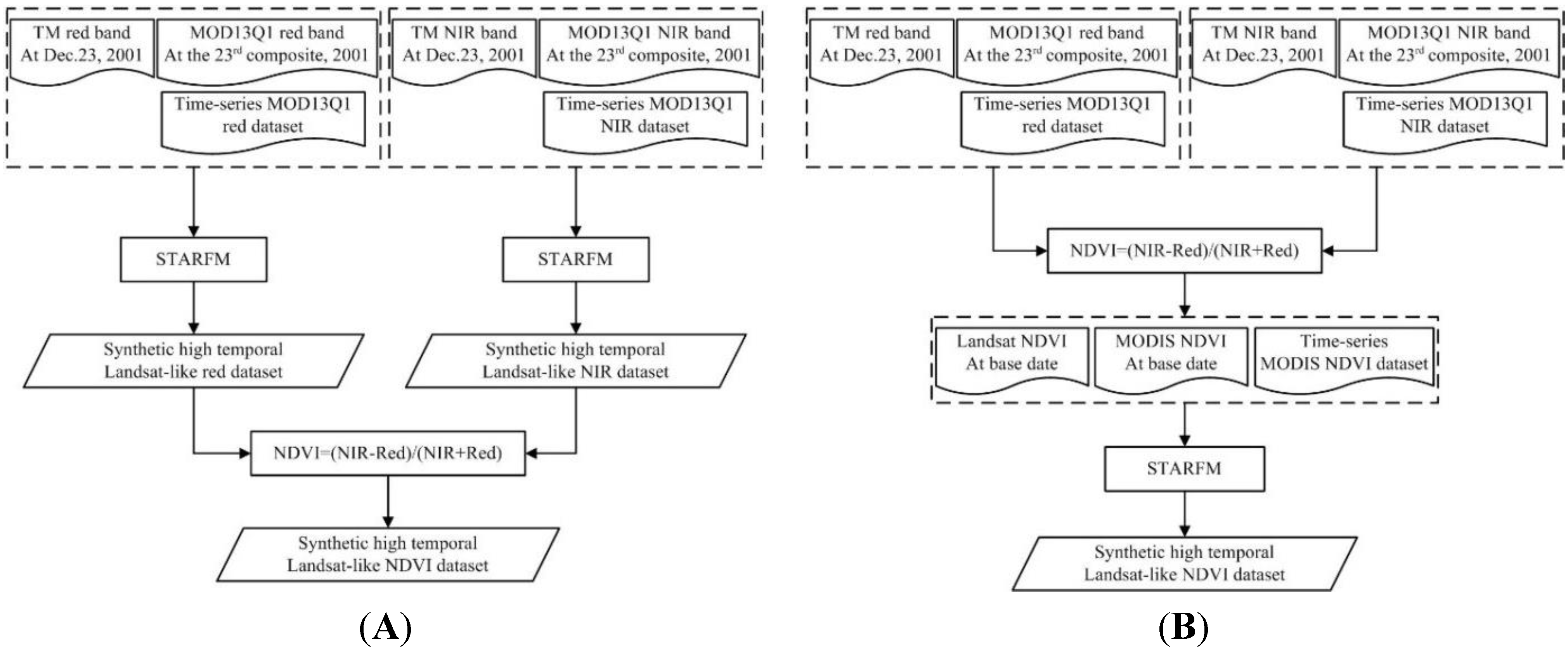
4.3. Parameter Settings
4.4. Comparison and Evaluation Protocol
4.4.1. Prediction Accuracy Evaluation
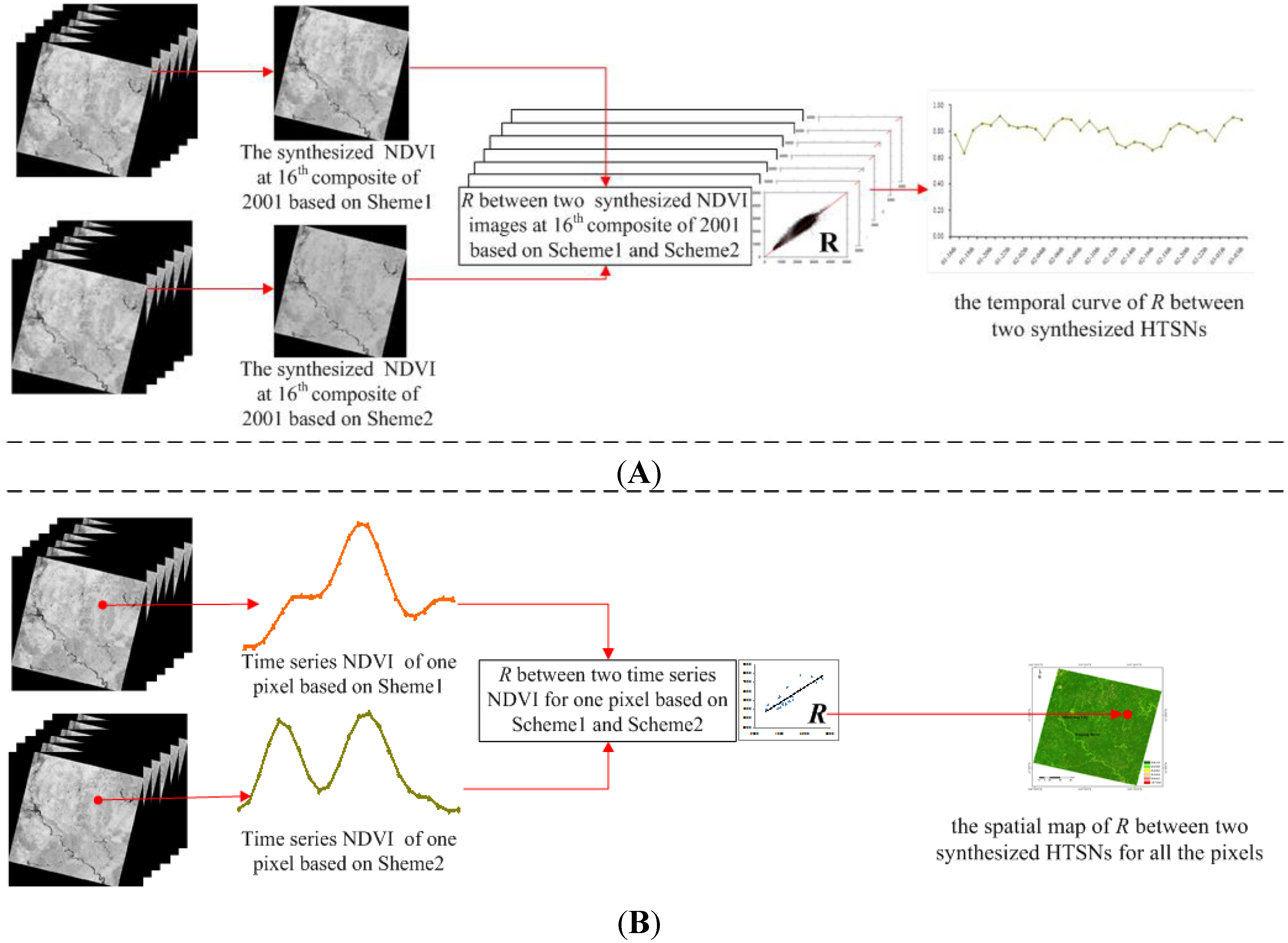
4.4.2. Consistence Comparisons
4.4.3. Application Comparisons
5. Results and Analysis
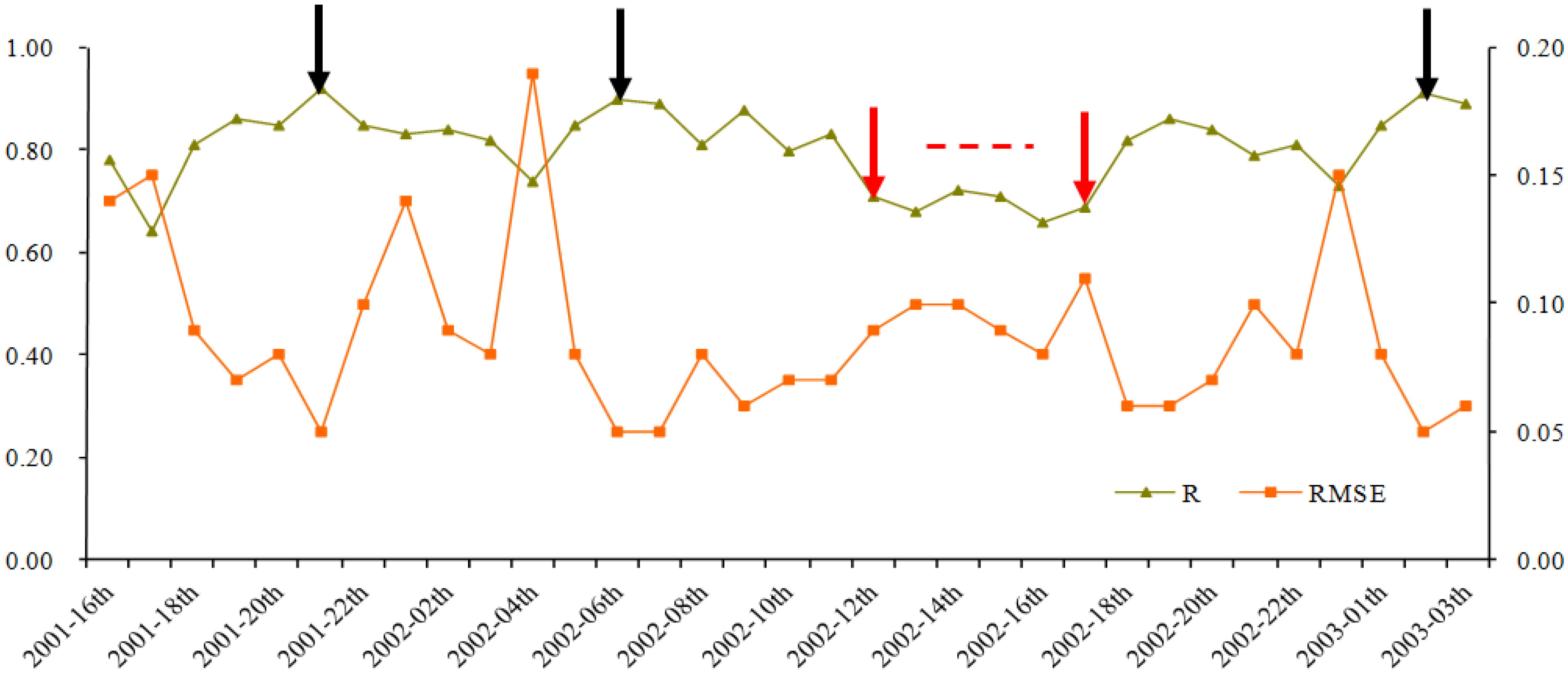
5.1. Prediction Accuracy Comparisons
5.2. Consistence Comparisons
5.2.1. Temporal Consistence
| Acquisition Dates (MM-DD-YYYY) | R2 | RMSE | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scheme 1 | Scheme 2 | Scheme 1 | Scheme 2 | |||||
| Red | NIR | NDVI | NDVI | Red | NIR | NDVI | NDVI | |
| 11-29-2001 | 0.42 | 0.72 | 0.42 | 0.46 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.09 |
| 03-05-2002 | 0.01 | 0.42 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.29 | 0.30 |
| 03-29-2002 | 0.64 | 0.67 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.10 |
| 07-11-2002 | 0.32 | 0.45 | 0.30 | 0.36 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.11 |
| 09-05-2002 | 0.45 | 0.42 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.11 |
| 10-07-2002 | 0.45 | 0.29 | 0.23 | 0.27 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.12 |
| 10-23-2002 | 0.56 | 0.36 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.13 |
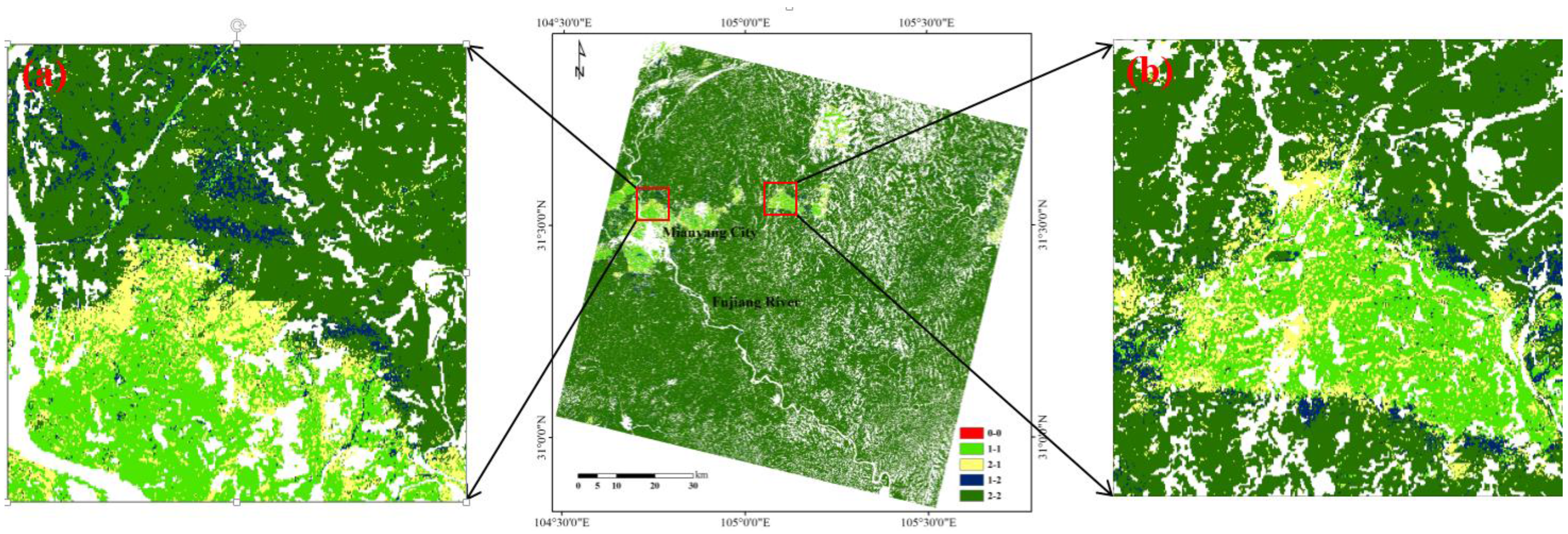
5.2.2. Spatial Consistence
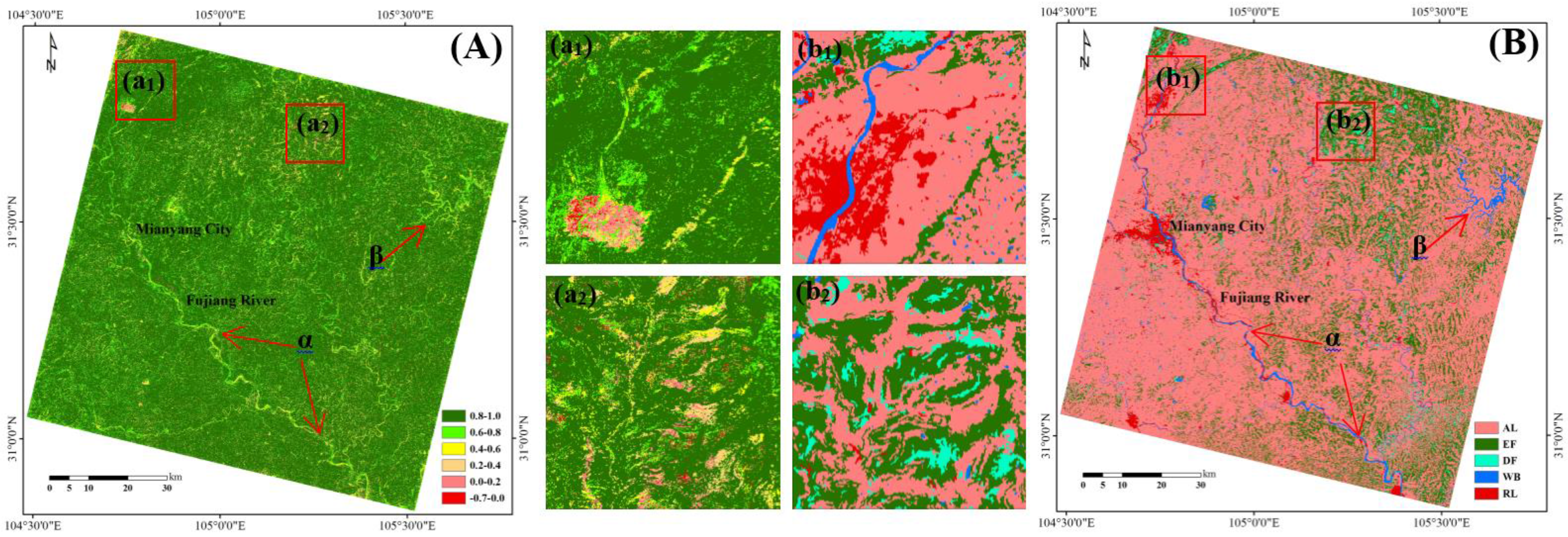
5.3. Application Comparisons
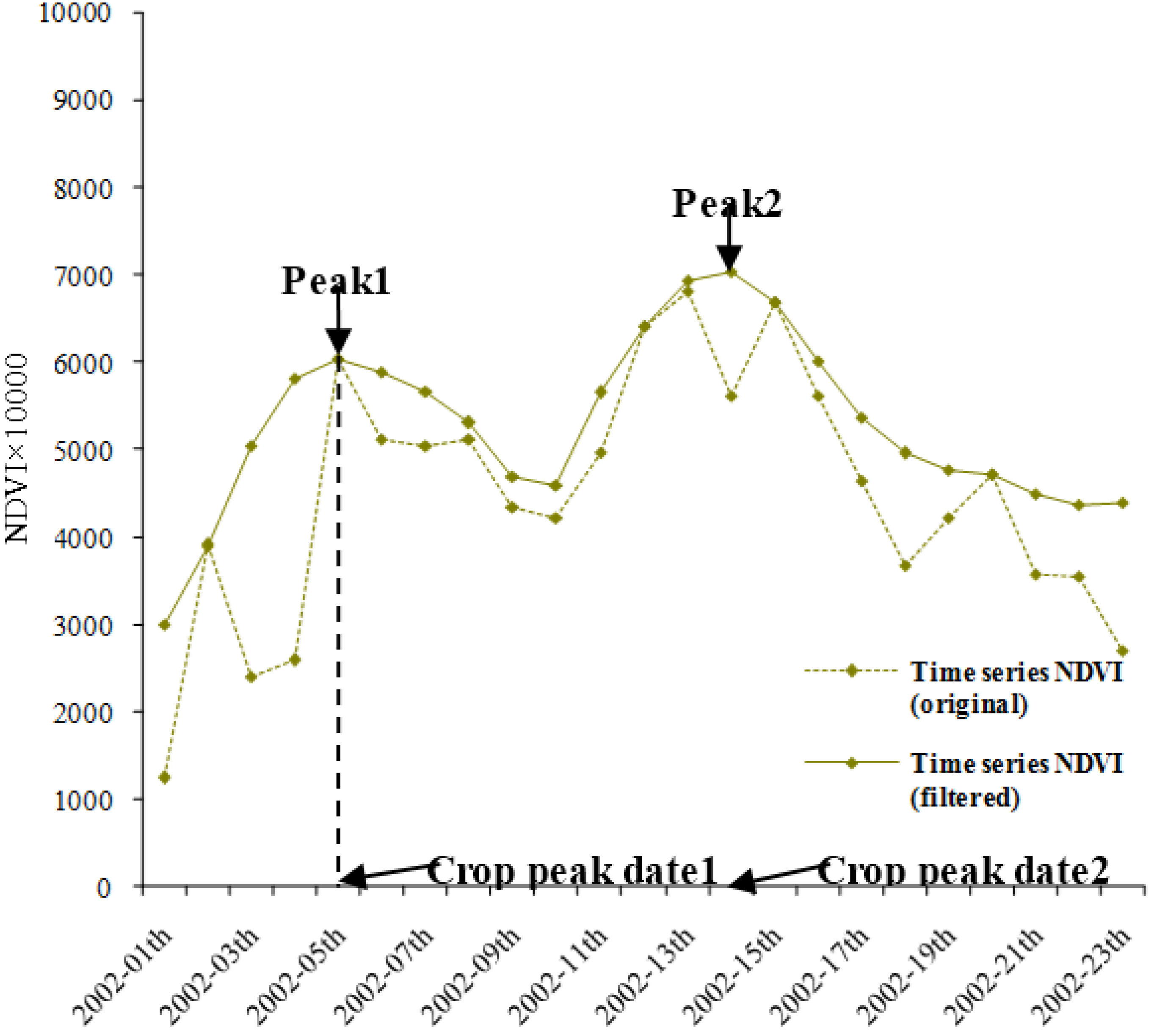
5.3.1. Cropping Intensity
| Cropping System | Cropping Intensity | Crop Peak Date | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coincidence | Total a | Coincidence Rate b | Coincidence | Total a | Coincidence Rate b | |
| No-till | 230 | 1118 | 20.57% | - | - | - |
| Single crop | 283,618 | 499,273 | 56.81% | 176,034 | 499,273 | 35.26% |
| Double crops | 7,933,397 | 8,253,983 | 96.12% | 11,890,458c | 16,507,966 c | 72.03% |
| All | 8,217,245 | 8,754,374 | 93.86% | 12,066,492 | 17,007,239 | 70.95% |
5.3.2. Crop Peak Date
6. Discussions
6.1. Parameter Settings
6.2. Prediction Accuracy
6.3. Applications
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marfai, M.A.; Almohammad, H.; Dey, S.; Susanto, B.; King, L. Coastal dynamic and shoreline mapping: Multi-sources spatial data analysis in Semarang Indonesia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 142, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilker, T.; Wulder, M.A.; Coops, N.C.; Linke, J.; McDermid, G.; Masek, J.G.; Gao, F.; White, J.C. A new data fusion model for high spatial-and temporal-resolution mapping of forest disturbance based on Landsat and MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1613–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, E.; Shimabukuro, Y.E.; Pereira, G.; Vijaykumar, N.L. A multi-resolution multi-temporal technique for detecting and mapping deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon rainforest. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 1943–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, A.; Jin, H.; Bian, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, G.; Qin, Z.; Huang, C. An enhanced spatial and temporal data fusion model for fusing Landsat and MODIS surface reflectance to generate high temporal Landsat-like data. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 5346–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maselli, F. Definition of spatially variable spectral endmembers by locally calibrated multivariate regression analyses. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 75, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busetto, L.; Meroni, M.; Colombo, R. Combining medium and coarse spatial resolution satellite data to improve the estimation of sub-pixel NDVI time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A. A simple model for the temporal variations of NDVI at regional scale over agricultural countries. Validation with ground radiometric measurements. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 1421–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdiles, H.; Grondona, M. NOAA-AVHRR NDVI decomposition and subpixel classification using linear mixing in the Argentinean Pampa. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 1303–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Masek, J.; Schwaller, M.; Hall, F. On the blending of the Landsat and MODIS surface reflectance: Predicting daily Landsat surface reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar]
- Zurita-Milla, R.; Kaiser, G.; Clevers, J.; Schneider, W.; Schaepman, M. Downscaling time series of MERIS full resolution data to monitor vegetation seasonal dynamics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1874–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, J.D.; Powell, S.L.; Lawrence, R.L.; Hilker, T. Improved classification of conservation tillage adoption using high temporal and synthetic satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.; De Beurs, K.; Wynne, R.; Gao, F. Evaluation of Landsat and MODIS data fusion products for analysis of dryland forest phenology. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Udelhoven, T.; Gill, T.; Röder, A. Long term data fusion for a dense time series analysis with MODIS and Landsat imagery in an Australian Savanna. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2012, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Emelyanova, I.V.; McVicar, T.R.; Van Niel, T.G.; Li, L.T.; Van Dijk, A.I. Assessing the accuracy of blending Landsat? MODIS surface reflectances in two landscapes with contrasting spatial and temporal dynamics: A framework for algorithm selection. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 133, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilker, T.; Wulder, M.A.; Coops, N.C.; Seitz, N.; White, J.C.; Gao, F.; Masek, J.G.; Stenhouse, G. Generation of dense time series synthetic Landsat data through data blending with MODIS using a spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1988–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.; Phinn, S.; Gill, T. Preparing Landsat Image Time Series (LITS) for monitoring changes in vegetation phenology in Queensland, Australia. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 1856–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Wu, B.; Du, X.; Niu, L.; Zhuang, F. Method to construct high sptial and temporal resolution NDVI dataset-STAVFM. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 15, 44–59. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Huete, A. From AVHRR-NDVI to MODIS-EVI: Advances in vegetation index research. Acta Eco. Sin. 2003, 23, 979–987. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, A.; Li, Y. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics and variation tendency of Precipitation in Mianyang. Plate Mt. Meteor. Res. 2009, 29, 63–69. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- The National Bureau of Statistics Survey Team in Mianyang City. The Bureau of Statistics of Mianyang City. In Statistical Yearbook of Mianyang City; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2011; pp. 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Jönsson, P.; Tamura, M.; Gu, Z.; Matsushita, B.; Eklundh, L. A simple method for reconstructing a high-quality NDVI time-series data set based on the Savitzky–Golay filter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 91, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS Global Visualization Viewer. Available online: http://glovis.usgs.gov (accessed on 13 August 2015).
- Masek, J.G.; Vermote, E.F.; Saleous, N.E.; Wolfe, R.; Hall, F.G.; Huemmrich, K.F.; Gao, F.; Kutler, J.; Lim, T.-K. A Landsat surface reflectance dataset for North America, 1990–2000. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Lei, G.; Zhang, Z.; Bian, J.; Deng, W. China land cover monitoring in mountainous regions. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Quebec, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014.
- Feng, M.; Huang, C.; Channan, S.; Vermote, E.F.; Masek, J.G.; Townshend, J.R. Quality assessment of Landsat surface reflectance products using MODIS data. Comput. Geosci. 2012, 38, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galford, G.L.; Mustard, J.F.; Melillo, J.; Gendrin, A.; Cerri, C.C.; Cerri, C.E.P. Wavelet analysis of MODIS time series to detect expansion and intensification of row-crop agriculture in Brazil. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Yokozawa, M.; Toritani, H.; Shibayama, M.; Ishitsuka, N.; Ohno, H. A crop phenology detection method using time-series MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Huang, J.; Jin, H. Monitoring the sequential cropping index of Arable land in Zhejiang Province of China using MODIS-NDVI. Agri. Sci. China 2007, 6, 208–213. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, J.; Li, A.; Song, M.; Ma, L.; Jiang, J. Reconstruction of NDVI time-series datasets of MODIS based on Savitzky-Golay filter. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 14, 725–741. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Wu, B. A methodology for retrieving cropping index from NDVI profile. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 8, 628–636. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.H.; Zhu, W.Q.; Cui, X.F. A Shape-matching Cropping Index (CI) mapping method to determine agricultural cropland intensities in China using MODIS time-series data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2012, 78, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y.; Ai, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. A spatial and temporal reflectance fusion model considering sensor observation differences. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 4367–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wang, J.; Song, H.; Fu, D.; Wong, K. Generating high spatiotemporal resolution land surface temperature for urban heat island monitoring. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Fu, P.; Gao, F. Generating daily land surface temperature at Landsat resolution by fusing Landsat and MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D. Evaluation of long-term NDVI time series derived from Landsat data through blending with MODIS data. Atmósfera 2012, 25, 43–63. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, J.J.; deBeurs, K.M.; Wynne, R.H. Dryland vegetation phenology across an elevation gradient in Arizona, USA, investigated with fused MODIS and Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 144, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Wang, Y.; Fensholt, R.; Wang, K.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Y. Mapping and evaluation of NDVI trends from synthetic time series obtained by blending Landsat and MODIS data around a coalfield on the Loess Plateau. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4255–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Ju, J.; Lewis, P.; Schaaf, C.; Gao, F.; Hansen, M.; Lindquist, E. Multi-temporal MODIS-Landsat data fusion for relative radiometric normalization, gap filling, and prediction of Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3112–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Mondal, P.; DeFries, R.S.; Small, C.; Galford, G.L. Mapping cropping intensity of smallholder farms: A comparison of methods using multiple sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, A.; Zhang, W.; Lei, G.; Bian, J. Comparative Analysis on Two Schemes for Synthesizing the High Temporal Landsat-like NDVI Dataset Based on the STARFM Algorithm. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2015, 4, 1423-1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi4031423
Li A, Zhang W, Lei G, Bian J. Comparative Analysis on Two Schemes for Synthesizing the High Temporal Landsat-like NDVI Dataset Based on the STARFM Algorithm. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2015; 4(3):1423-1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi4031423
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ainong, Wei Zhang, Guangbin Lei, and Jinhu Bian. 2015. "Comparative Analysis on Two Schemes for Synthesizing the High Temporal Landsat-like NDVI Dataset Based on the STARFM Algorithm" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 4, no. 3: 1423-1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi4031423
APA StyleLi, A., Zhang, W., Lei, G., & Bian, J. (2015). Comparative Analysis on Two Schemes for Synthesizing the High Temporal Landsat-like NDVI Dataset Based on the STARFM Algorithm. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 4(3), 1423-1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi4031423






