Bridging Humanitarian Mapping and the Sustainable Development Goals
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. From Agenda 2030 to SDGs
- Tier I: Indicator is conceptually clear, has an internationally established methodology and standards are available, and data are regularly produced by countries for at least 50 per cent of countries and of the population in every region where the indicator is relevant.
- Tier II: Indicator is conceptually clear, has an internationally established methodology, and standards are available, but data are not regularly produced by countries. [10].
1.2. Geospatial Information for the Quality of Each Indicator
- Contributing directly to the proposed framework, not only in terms of sources of information to increase data availability and spatial disaggregation but also in terms of methods and analysis to produce indicators resulting from the integration of geospatial and statistical information;
- Promoting common accepted standards and frameworks to guarantee comparability;
- Encouraging innovation and modernization [15].
1.3. From Citizen Science to Humanitarian Mapping
1.4. Humanitarian Mapping as One of the Pillars in the SDG Data Framework
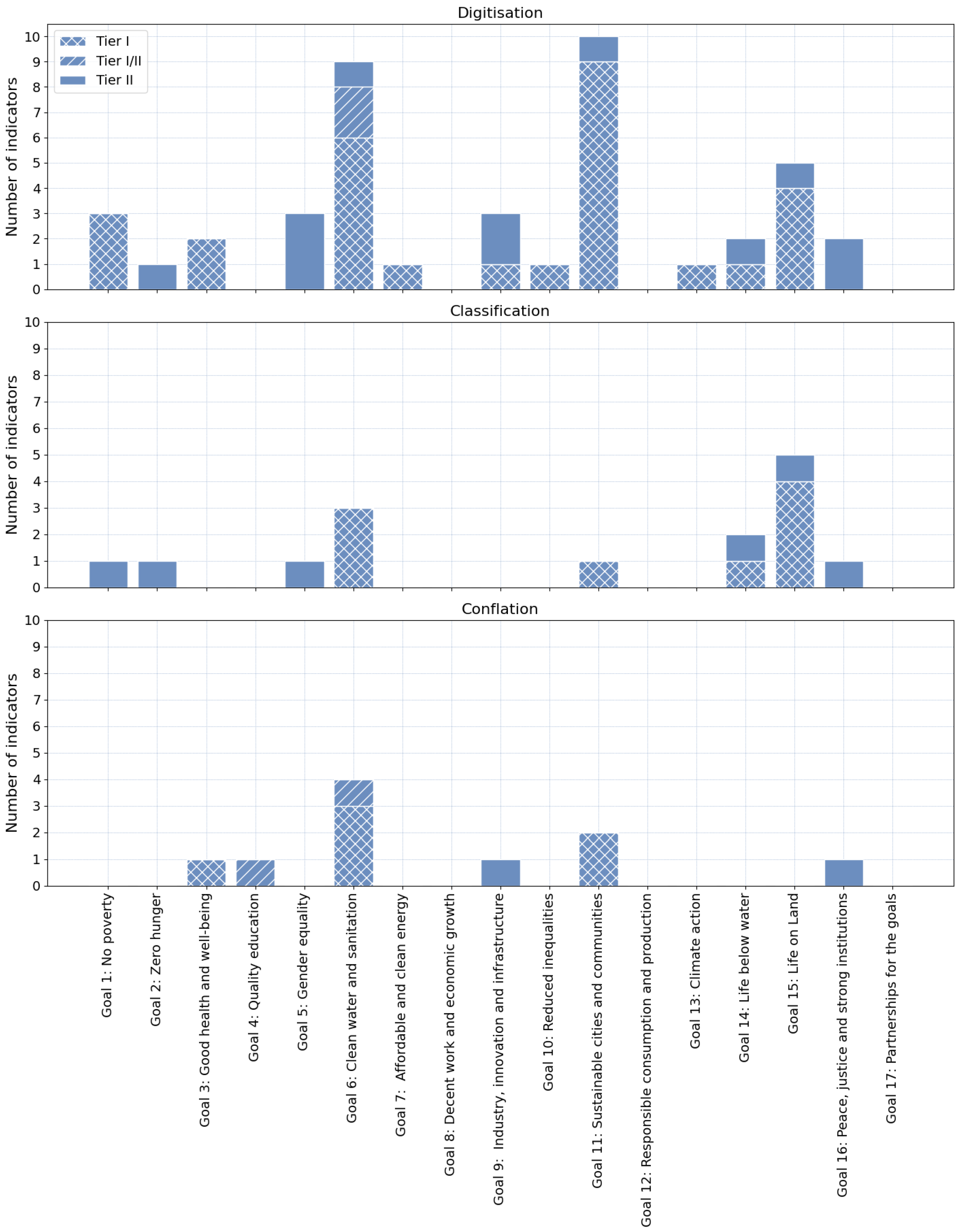
- Classification: The process of assigning predefined attributes (values/categories) to existing geographical information.
- Digitization: The process of creating new digital geographic objects based on existing geographic information.
- Conflation: The process of integrating existing geographic information representing the same real-world object into a consistent digital representation [43].
- HOT-TM is a platform develop by the Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team (HOT) for OSM digitization, dedicated mostly to HM purposes [44]. HOT-TM splits the mapping area into a grid of smaller squared areas, called tasks. Each mapper is assigned a task and collaborates with the other members of the team without worrying about conflicts.
- MapSwipe is a web and mobile application in which a user classifies a certain area by looking at satellite images [45]. Similarly to HOT-TM, MapSwipe assigns tasks to the mapper, represented as 3 × 3 squares, in both the cases of mobile and web browsers. Users are instructed to examine the basemap and report the presence of mapping objects by tapping each square on the screen.
- Ushahidi, founded in 2008, is a powerful toolbox for gathering monitoring data at a fast pace in the web environment [46]. The organizers create deployments on specific themes, then users can contribute by reporting emails, text, and multimedia through posts. Unlike HOT-TM and MapSwipe, each deployment is open-ended, organizers can expand the project without creating its replica, and there is no need to eliminate duplication theoretically.
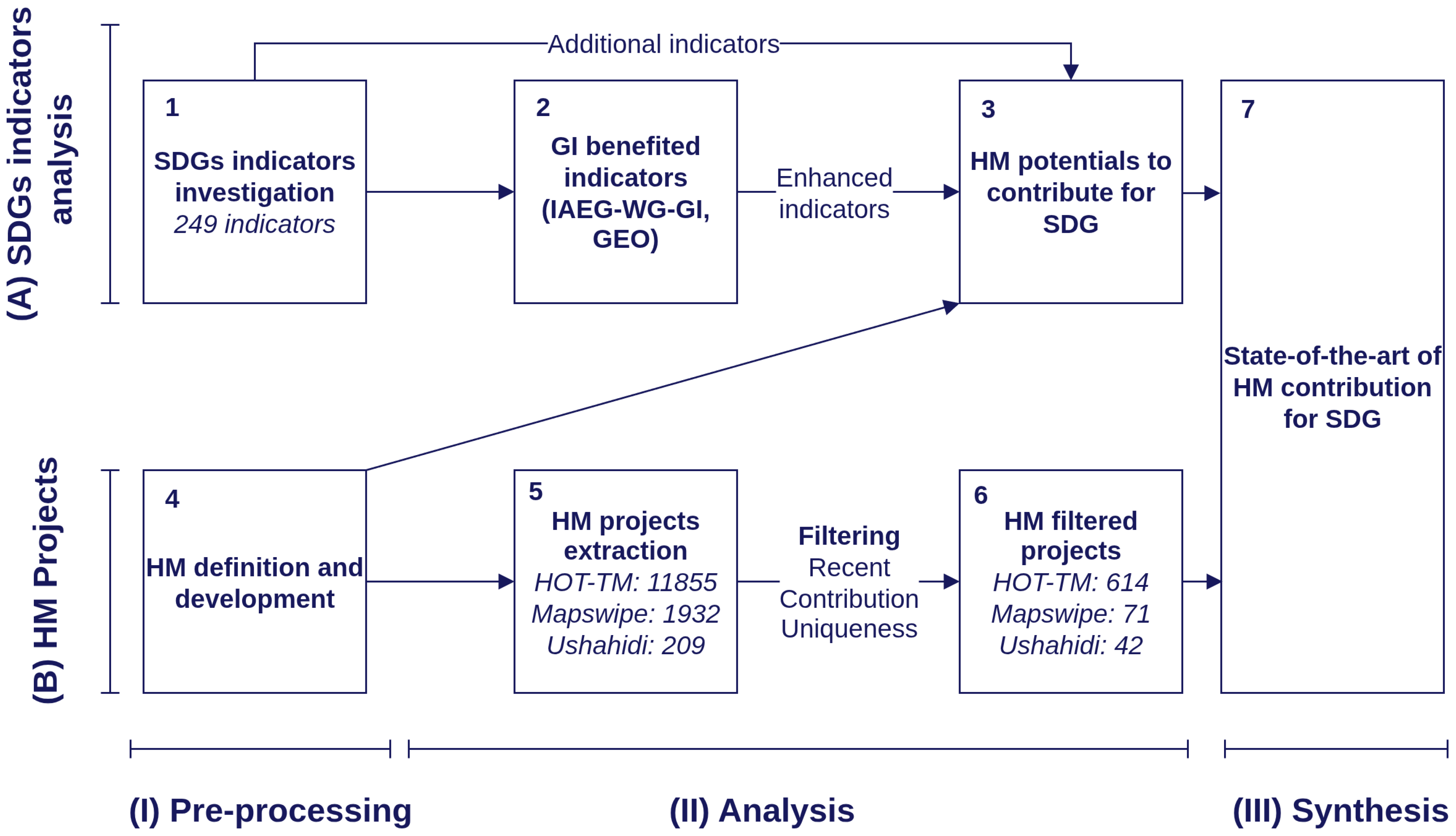
2. Materials and Methods
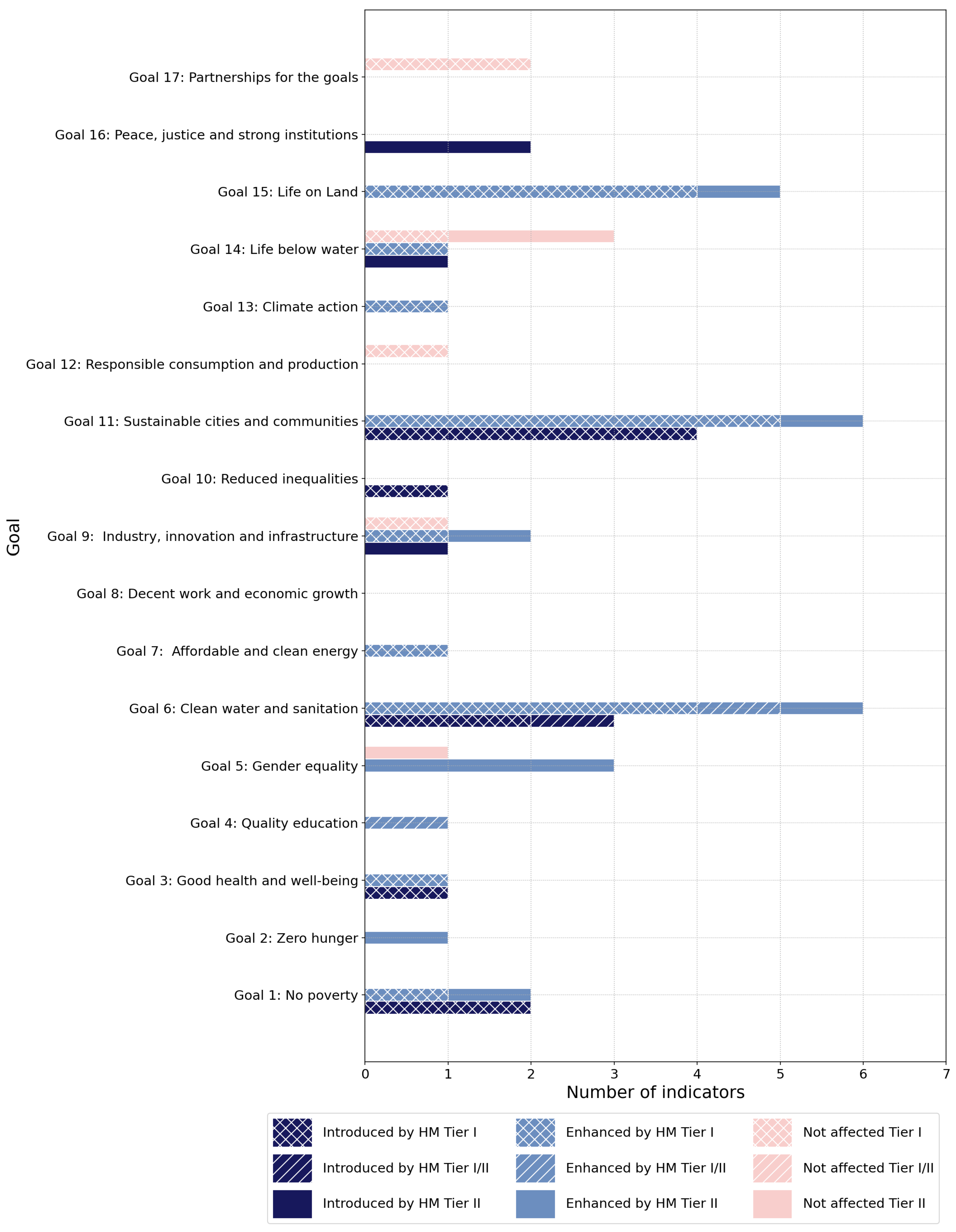
- Introduced indicators (HM-I) are indicators that were not included in the IAEG-SDG-WG-GI and GEO lists, but are included in this study.
- Enhanced indicators (HM-E) are indicators that are mentioned in the IAEG-SDG-WG-GI and GEO lists, and have the potential to be improved by HM.
- Non-affected indicators are unrelated indicators.
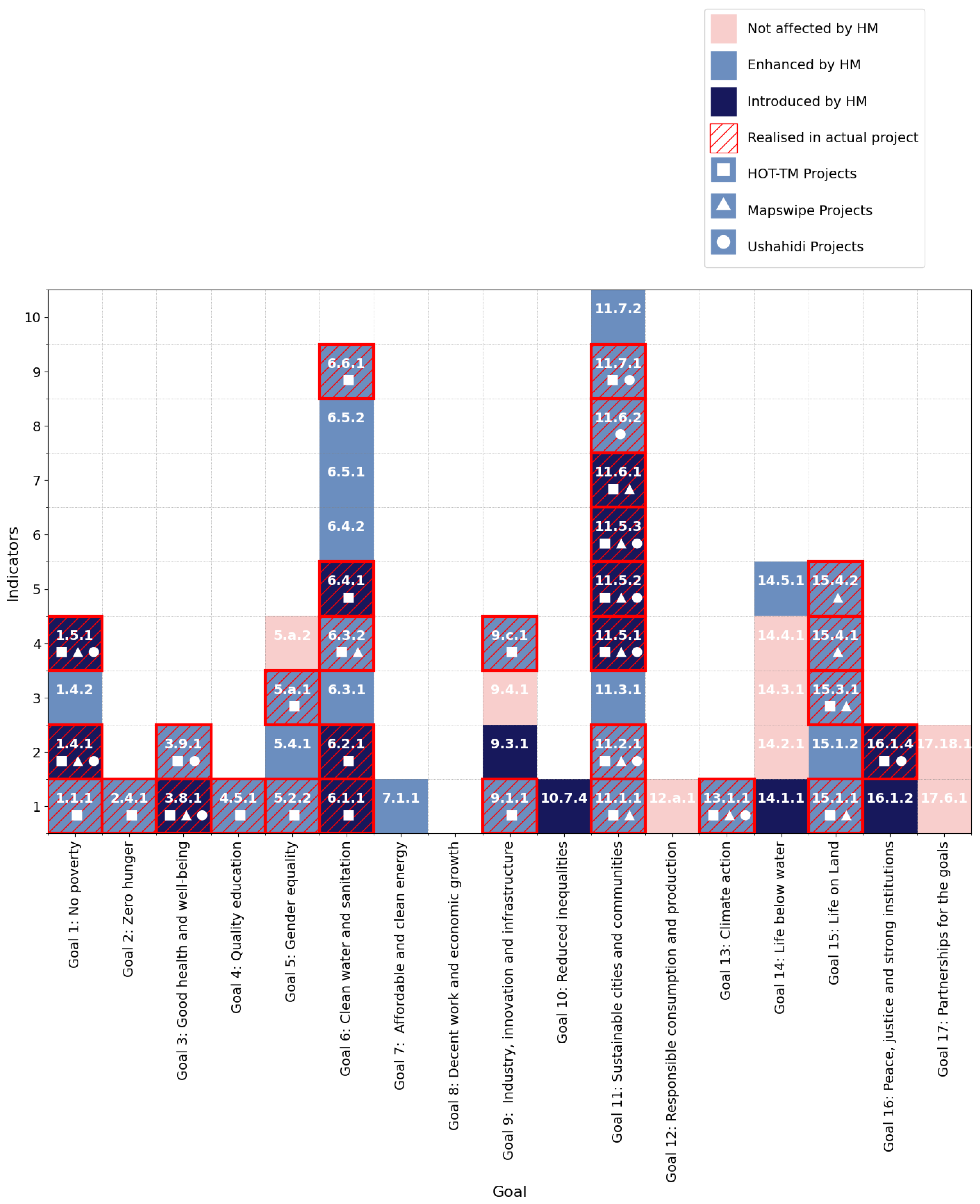
3. Results
3.1. SDG Indicator Analysis
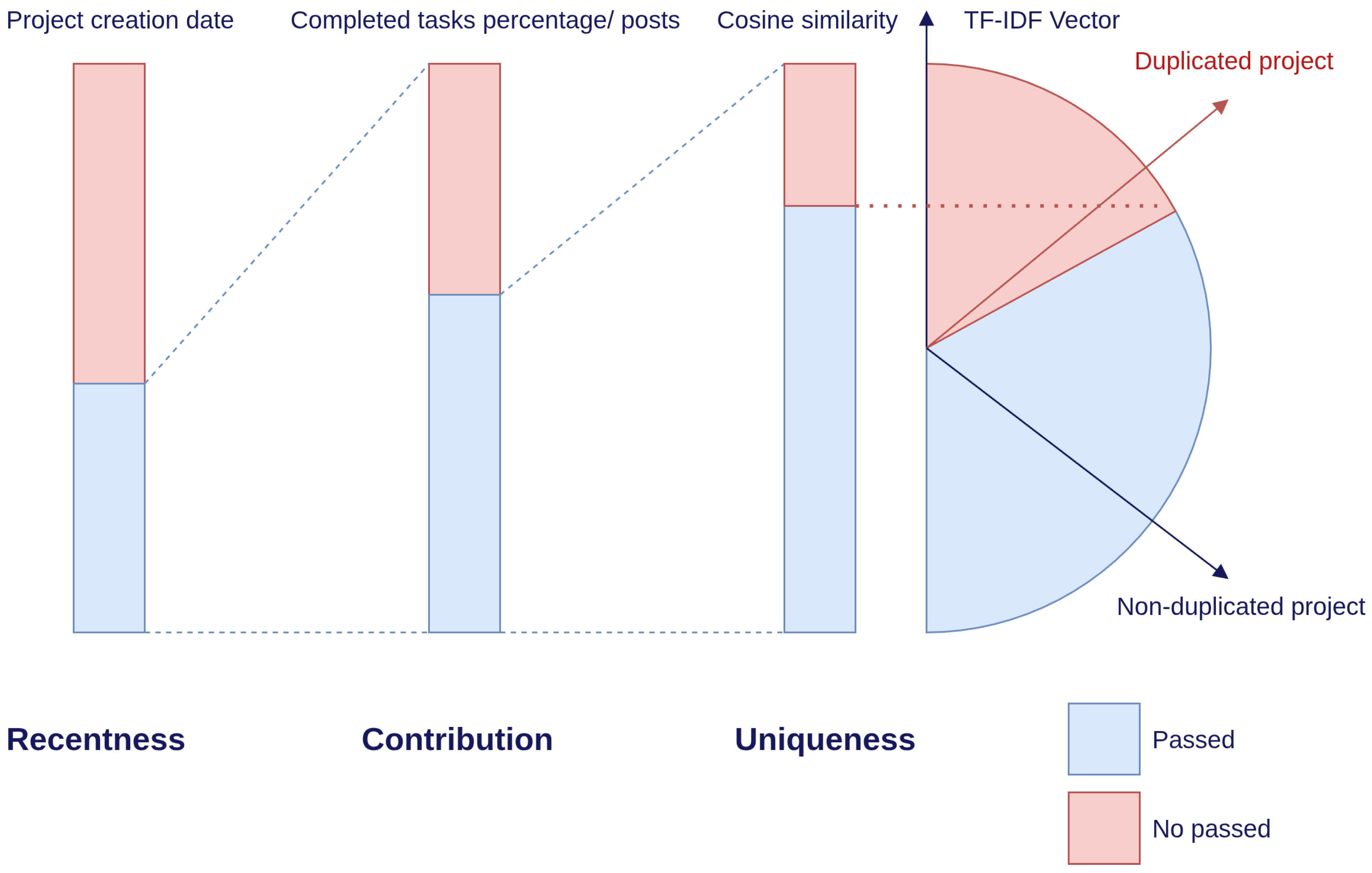
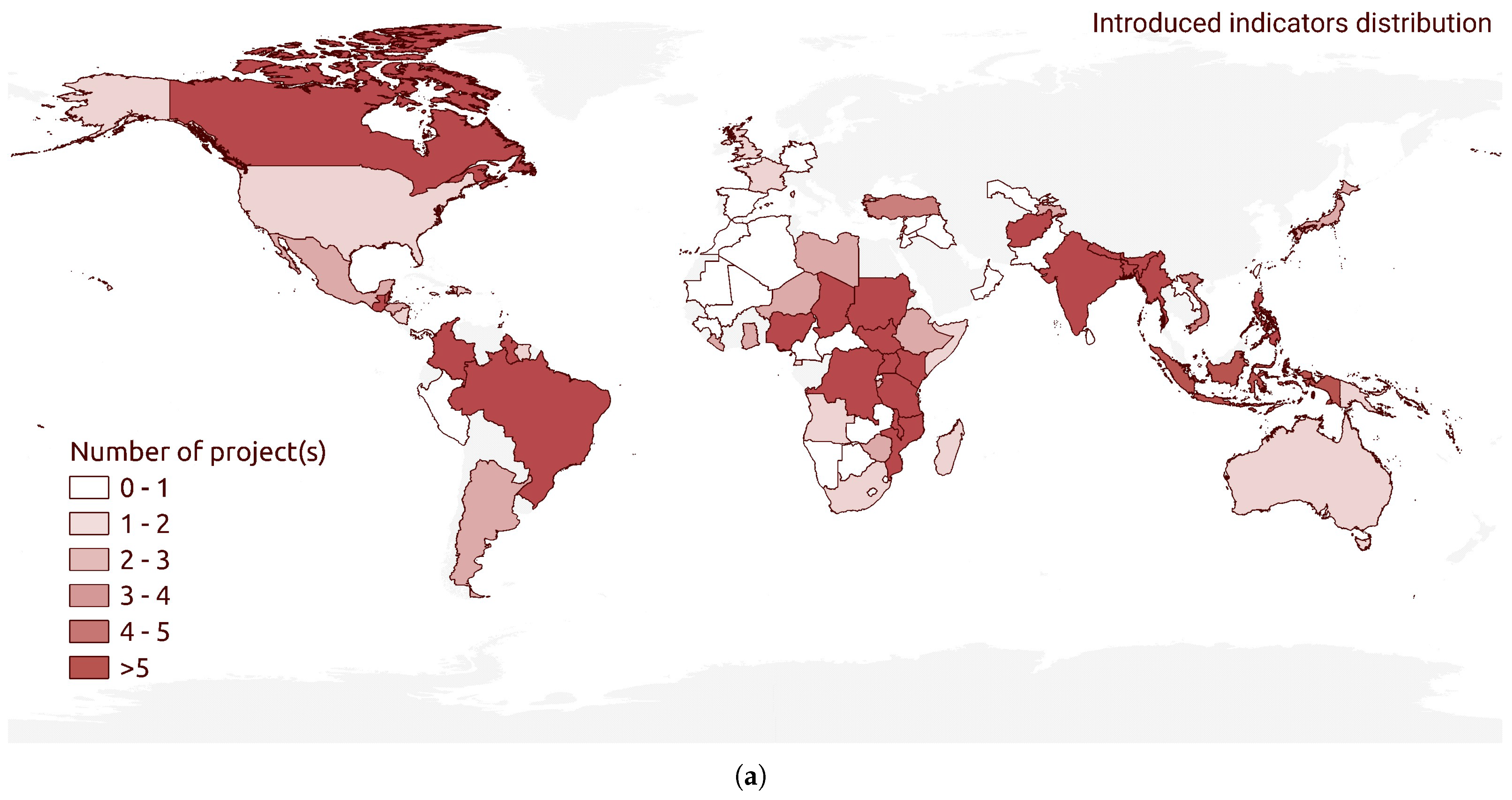
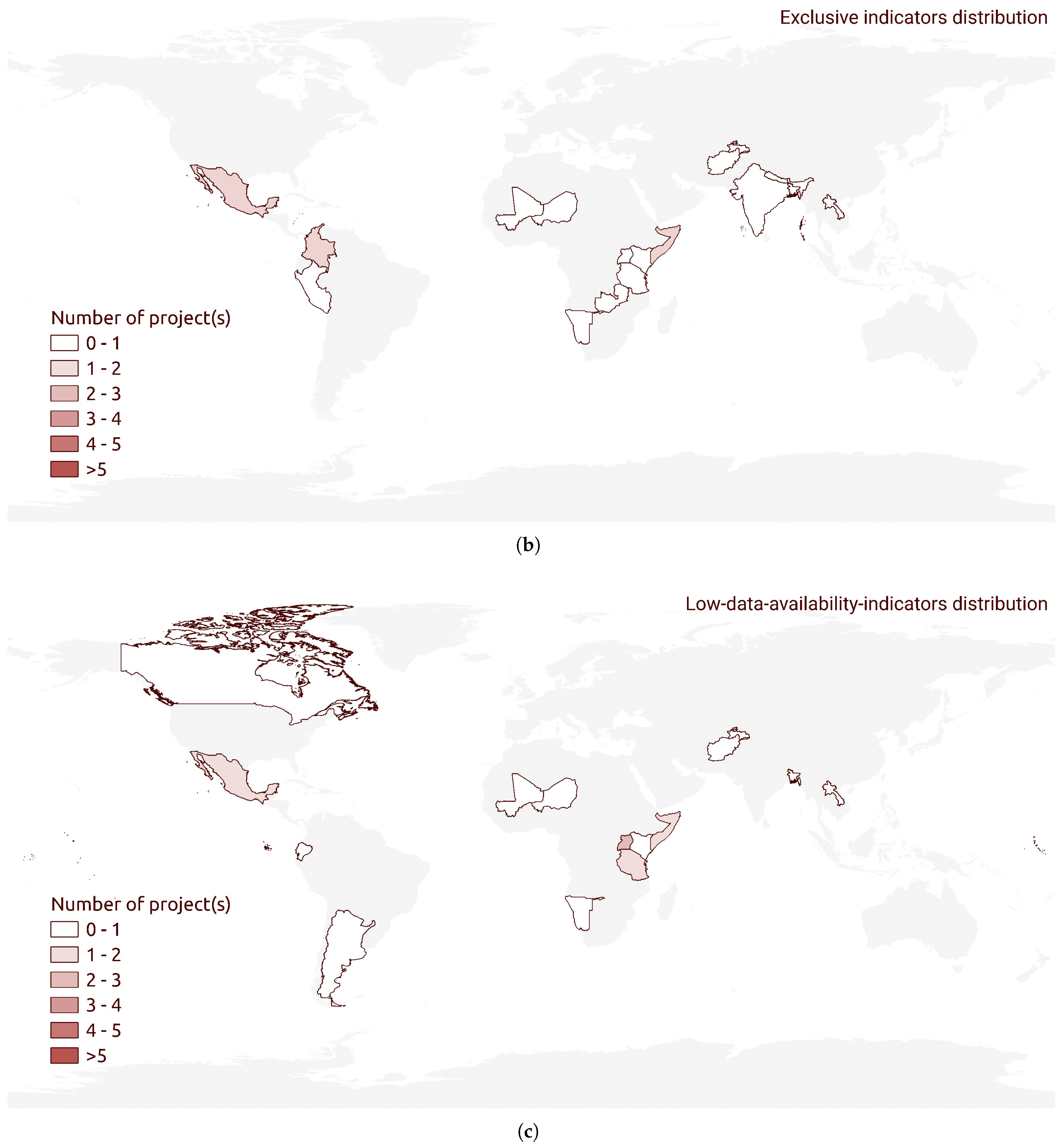
3.2. Humanitarian Mapping Project Data Resource Distribution
3.3. HM Contribution to SDG
4. Discussion and Conclusions
4.1. Trends and Gaps
4.2. Limitations
4.3. Contribution
4.4. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| CS | Citizen science |
| DA | Data availability |
| DRR | Disaster risk response |
| GI | Geospatial information |
| GEO | Group on Earth Observations |
| HM | Humanitarian mapping |
| HM-I | Indicators introduced by humanitarian mapping |
| HM-E | Indicators enhanced by humanitarian mapping |
| HOT | Humanitarian Openstreetmap Team |
| HOT-TM | Humanitarian Openstreetmap Team Tasking Manager |
| IGO | Intergovernmental Organization |
| IAEG-SDG | Inter-agency and Expert Group on SDG Indicators |
| IAEG-SDGs-WG-GI | Inter-Agency Expert Group on Sustainable Development Goals Indicators Working Group on Geospatial Information |
| MDGs | Millennium Development Goals |
| NGO | Non-governmental organization |
| OSM | OpenStreetMap |
| SD | Sustainable development |
| SDGs | Sustainable Development Goals |
| TF-IDF | Term frequency-inverse document frequency |
| UN | United Nations |
| VGI | Volunteered geographic information |
Appendix A. The SDG Indicator Analysis
| Goal | Indicator | Indicator Description | Data Availability | IAEG- SDGs- WG- GI | GEO | HM-I | HM-E | Mapping Types | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.1.1 | 1.1.1 Proportion of the population living below the international poverty line by sex, age, employment status and geographic location (urban/rural) | Tier I | X | X | Digitisation | Mapping buildings to support demographic distribution data | ||
| 1 | 1.4.1 | 1.4.1 Proportion of population living in households with access to basic services | Tier I | X | Digitisation | Mapping buildings and public facilities; support data disaggregation by geographic location | |||
| 1.4.2 | 1.4.2 Proportion of total adult population with secure tenure rights to land, (a) with legally recognized documentation, and (b) who perceive their rights to land as secure, by sex and type of tenure | Tier II | X | X | Classification | Mapping landuse; support data disaggregation by geographic location | |||
| 1.5.1 | 1.5.1 Number of deaths, missing persons and directly affected persons attributed to disasters per 100,000 population | Tier I | X | Digitisation | Mapping damaged buildings; support data disaggregation by geographic location | ||||
| 2 | 2.4.1 | 2.4.1 Proportion of agricultural area under productive and sustainable agriculture | Tier II | X | X | Classification, Digitisation | Mapping landcover (agriculture area); support data disaggregation by geographic location | ||
| 3 | 3.8.1 | 3.8.1 Coverage of essential health services | Tier I | X | Digitisation | Mapping distribution of essential health services; support data disaggregation by geographic location | |||
| 3.9.1 | 3.9.1 Mortality rate attributed to household and ambient air pollution | Tier I | X | Digitisation, Conflation | Building mapping (building and ambient air quality mapping) | ||||
| 4 | 4.5.1 | 4.5.1 Parity indices (female/male, rural/urban, bottom/top wealth quintile and others such as disability status, indigenous peoples and conflict-affected, as data become available) for all education indicators on this list that can be disaggregated | Tier I/II | X | X | Conflation | Support calculating location dimension of Parity Index | ||
| 5 | 5.2.2 | 5.2.2 Proportion of women and girls aged 15 years and older subjected to sexual violence by persons other than an intimate partner in the previous 12 months, by age and place of occurrence | Tier II | X | X | Digitisation | Mapping place of occurence;support data disaggregation by geographic location | ||
| 5.4.1 | 5.4.1 Proportion of time spent on unpaid domestic and care work, by sex, age and location | Tier II | X | X | Digitisation | Support data disaggregation by geographic location | |||
| 5.a.1 | 5.a.1 (a) Proportion of total agricultural population with ownership or secure rights over agricultural land, by sex; and (b) share of women among owners or rights-bearers of agricultural land, by type of tenure | Tier II | X | X | Classification, Digitisation | Mapping landcover (agriculture area); support data disaggregation by geographic location | |||
| 5.a.2 | 5.a.2 Proportion of countries where the legal framework (including customary law) guarantees women’s equal rights to land ownership and/or control | Tier II | X | ||||||
| 6 | 6.1.1 | 6.1.1 Proportion of population using safely managed drinking water services | Tier I | X | Digitisation | Mapping location of drinking water sources; support data disaggregation by geographic location | |||
| 6.2.1 | 6.2.1 Proportion of population using (a) safely managed sanitation services and (b) a hand-washing facility with soap and water | Tier I/II | X | Digitisation | Support data disaggregation by geographic location | ||||
| 6.3.1 | 6.3.1 Proportion of domestic and industrial wastewater flows safely treated | Tier I/II | X | X | Digitisation, Conflation | Mapping wastewater sources; | |||
| 6.3.2 | 6.3.2 Proportion of bodies of water with good ambient water quality | Tier I | X | X | Classification, Digitisation, Conflation | Mapping water (including basin, stream, water surface, pollution points); support data disaggregation by geographic location | |||
| 6.4.1 | 6.4.1 Change in water-use efficiency over time | Tier I | X | Digitisation | support data disaggregation by geographic location | ||||
| 6.4.2 | 6.4.2 Level of water stress: freshwater withdrawal as a proportion of available freshwater resources | Tier I | X | X | Digitisation | Support data disaggregation by geographic location | |||
| 6.5.1 | 6.5.1 Degree of integrated water resources management | Tier I | X | X | Digitisation | Support data disaggregation by geographic location | |||
| 6.5.2 | 6.5.2 Proportion of transboundary basin area with an operational arrangement for water cooperation | Tier I | X | X | Digitisation, Classification, Conflation | Mapping water (including basin, stream, water surface, pollution points); support data disaggregation by geographic location | |||
| 6.6.1 | 6.6.1 Change in the extent of water-related ecosystems over time | Tier I | X | X | Classification, Digitisation, Conflation | Mapping water (including basin, stream, water surface, pollution points); support data disaggregation by geographic location | |||
| 7 | 7.1.1 | 7.1.1 Proportion of population with access to electricity | Tier I | X | X | Digitisation | Support data disaggregation by geographic location | ||
| 9 | 9.1.1 | 9.1.1 Proportion of the rural population who live within 2 km of an all-season road | Tier II | X | X | Digitisation, Conflation | Mapping buildings and all-season roands; support data disaggregation by geographic location | ||
| 9.3.1 | 9.3.1 Proportion of small-scale industries in total industry value added | Tier II | X | Digitisation | Mapping small-scale industries distribution | ||||
| 9.4.1 | 9.4.1 CO2 emission per unit of value added | Tier I | X | ||||||
| 9.c.1 | 9.c.1 Proportion of population covered by a mobile network, by technology | Tier I | X | X | Digitisation | Mapping living area of the population who is covered by a mobile network, broken down by technology | |||
| 10 | 10.7.4 | 10.7.4 Proportion of the population who are refugees, by country of origin | Tier I | X | Digitisation | Support data disaggregation by geographic location | |||
| 11 | 11.1.1 | 11.1.1 Proportion of urban population living in slums, informal settlements or inadequate housing | Tier I | X | X | Digitisation | Mapping buildings; support data disaggregation by geographic location | ||
| 11.2.1 | 11.2.1 Proportion of population that has convenient access to public transport, by sex, age and persons with disabilities | Tier I | X | X | Digitisation | Mapping public transport accessibility (Point of interest); support data disaggregation by geographic location | |||
| 11.3.1 | 11.3.1 Ratio of land consumption rate to population growth rate | Tier I | X | X | Digitisation, Conflation | Mapping urbnized area, urbanized area change, built-up area; support data disaggregation by geographic location | |||
| 11.5.1 | 11.5.1 Number of deaths, missing persons and directly affected persons attributed to disasters per 100,000 population | Tier I | X | Digitisation | Mapping damaged buildings; support data disaggregation by geographic location | ||||
| 11.5.2 | 11.5.2 Direct economic loss attributed to disasters in relation to global gross domestic product (GDP) | Tier I | X | Digitisation | Mapping damaged buildings; support data disaggregation by geographic location | ||||
| 11.5.3 | 11.5.3 (a) Damage to critical infrastructure and (b) number of disruptions to basic services, attributed to disasters | Tier I | X | Digitisation | Mapping damaged buildings and critical infrastructure; support data disaggregation by geographic location | ||||
| 11.6.1 | 11.6.1 Proportion of municipal solid waste collected and managed in controlled facilities out of total municipal waste generated, by cities | Tier I | X | Digitisation | Mapping municipal solid waste collected and managed in controlled facilities mapping; support data disaggregation by geographic location | ||||
| 11.6.2 | 11.6.2 Annual mean levels of fine particulate matter (e.g. PM2.5 and PM10) in cities (population weighted) | Tier I | X | Digitisation, Classification, Conflation | Air quality mapping | ||||
| 11.7.1 | 11.7.1 Average share of the built-up area of cities that is open space for public use for all, by sex, age and persons with disabilities | Tier I | X | X | Digitisation | Mapping buildings, roads, public spaces; support data disaggregation by geographic location | |||
| 11.7.2 | 11.7.2 Proportion of persons victim of non-sexual or sexual harassment, by sex, age, disability status and place of occurrence, in the previous 12 months | Tier II | X | X | Digitisation | Mapping place of occurence; support data disaggregation by geographic location | |||
| 12 | 12.a.1 | 12.a.1 Installed renewable energy-generating capacity in developing and developed countries (in watts per capita) | Tier I | X | |||||
| 13 | 13.1.1 | 13.1.1 Number of deaths, missing persons and directly affected persons attributed to disasters per 100,000 population | Tier I | X | X | Digitisation | Mapping damaged buildings; support data disaggregation by geographic location | ||
| 14 | 14.1.1 | 14.1.1 (a) Index of coastal eutrophication; and (b) plastic debris density | Tier II | X | Digitisation, Classification | Support geospatial analysis | |||
| 14.2.1 | 14.2.1 Number of countries using ecosystem-based approaches to managing marine areas | Tier II | X | ||||||
| 14.3.1 | 14.3.1 Average marine acidity (pH) measured at agreed suite of representative sampling stations | Tier II | X | ||||||
| 14.4.1 | 14.4.1 Proportion of fish stocks within biologically sustainable levels | Tier I | X | ||||||
| 14.5.1 | 14.5.1 Coverage of protected areas in relation to marine areas | Tier I | X | X | Digitisation, Classification | Mapping protected area | |||
| 15 | 15.1.1 | 15.1.1 Forest area as a proportion of total land area | Tier I | X | X | Digitisation, Classification | Mapping Forest Area | ||
| 15.1.2 | 15.1.2 Proportion of important sites for terrestrial and freshwater biodiversity that are covered by protected areas, by ecosystem type | Tier I | X | X | Digitisation, Classification | Mapping protected area | |||
| 15.3.1 | 15.3.1 Proportion of land that is degraded over total land area | Tier I | X | X | Classification, Digitisation | Mapping degraded land area | |||
| 15.4.1 | 15.4.1 Coverage by protected areas of important sites for mountain biodiversity | Tier I | X | X | Digitisation, Classification | Mapping protected area | |||
| 15.4.2 | 15.4.2 (a) Mountain Green Cover Index and (b) proportion of degraded mountain land | Tier I | X | X | Digitisation, Classification | Mapping Mountain Area, Landcover and degraded land area | |||
| 16 | 16.1.2 | 16.1.2 Conflict-related deaths per 100,000 population, by sex, age and cause | Tier II | X | Digitisation | Mapping place of death | |||
| 16.1.4 | 16.1.4 Proportion of population that feel safe walking alone around the area they live after dark | Tier II | X | Classification, Digitisation, Conflation | Mapping neightborhood | ||||
| 17 | 17.6.1 | 17.6.1 Fixed broadband subscriptions per 100 inhabitants, by speed | Tier I | X | |||||
| 17.18.1 | 17.18.1 Statistical capacity indicators | Tier I | X |
References
- UN. Secretary-General; World Commission on Environment and Development. Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development: Note/by the Secretary-General; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 1987; Available online: https://digitallibrary.un.org/record/139811?v=pdf (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Brundtland, G.H. Our common future. In Earth and Us; Tolba, M.K., Biswas, A.K., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK; Boston, MA, USA, 1991; pp. 29–31. Available online: https://digitallibrary.un.org/record/247793?ln=en (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Mensah, J. Sustainable development: Meaning, history, principles, pillars, and implications for human action: Literature review. Cogent Soc. Sci. 2019, 5, 1653531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggerio, C.A. Sustainability and sustainable development: A review of principles and definitions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations. About Us. Publisher: United Nations. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/about-us (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- UN. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Technical Report. 2015. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/sites/default/files/publications/21252030%20Agenda%20for%20Sustainable%20Development%20web.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Scott, G.; Rajabifard, A. Sustainable development and geospatial information: A strategic framework for integrating a global policy agenda into national geospatial capabilities. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, 20, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentier, C.L.; Braun, H. Agenda 2030 for Sustainable Development: A powerful global framework. J. Int. Counc. Small Bus. 2020, 1, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.P.; Xu, K. Task and Progress of IAEG-SDGS: WGGI in Monitoring SDGS Through a ‘Geographic Location’ Lens. In Proceedings of the ISPRS TC III Mid-term Symposium “Developments, Technologies and Applications in Remote Sensing” (Volume XLII-3), Beijing, China, 7–10 May 2018; Copernicus GmbH: Göttingen, Germany, 2018; Volume XLII-3, pp. 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEG-SDGs. Tier Classification for Global SDG Indicators. Technical Report. 2025. Available online: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/iaeg-sdgs/tier-classification/ (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- United Nations ESCAP. Geospatial Information and the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Technical Report. Available online: https://repository.unescap.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/13280a24-305b-44f5-899d-b7d65173a4b8/content (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- United Nations ESCWA. Integration of Geospatial Information with Statistical Information in Support of the SDG Indicators. 2021. Available online: https://www.unescwa.org/sites/default/files/pubs/pdf/integration-geospatial-information-statistical-sdg-indicators-english_2.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Inter-agency and Expert Group on the Sustainable Development Goals (United Nations). The SDGs Geospatial Roadmap (English); UN-GGIM: New York, NY, USA, 2022; Available online: https://ecosoc.un.org/en/node/19594 (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Brovelli, M.A.; Codrina, M.I.; Coetzee, S. Openness and Community Geospatial Science for Monitoring SDGs—An Example From Tanzania. In Sustainable Development Goals Connectivity Dilemma; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; Available online: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/oa-edit/10.1201/9780429290626/sustainable-development-goals-connectivity-dilemma-abbas-rajabifard?refId=7602ecb9-37e7-4de2-926f-241a555ceb9e&context=ubx (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- UN GGIM: Europe Working Group B, Cetl, V. The Territorial Dimension in SDG Indicators: Geospatial Data Analysis and Its Integration with Statistical Data; Instituto Nacional de Estatística: Lisbon, Portugal, 2019. Available online: https://un-ggim-europe.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/UN_GGIM_08_05_2019-The-territorial-dimension-in-SDG-indicators-Final.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Herfort, B.; Lautenbach, S.; Porto De Albuquerque, J.; Anderson, J.; Zipf, A. The evolution of humanitarian mapping within the OpenStreetMap community. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lämmerhirt, D.; Gray, J.; Venturini, T.; Meunier, A. Advancing Sustainability Together? Citizen-Generated Data and the Sustainable Development Goals; SSRN Electronic Journal: Rochester, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraisl, D.; Campbell, J.; See, L.; Wehn, U.; Wardlaw, J.; Gold, M.; Moorthy, I.; Arias, R.; Piera, J.; Oliver, J.L.; et al. Mapping citizen science contributions to the UN sustainable development goals. Sustain. Sci. 2020, 15, 1735–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, S.; Pateman, R. How Could Citizen Science Support the Sustainable Development Goals? Stockholm Environment Institute: Stockholm, Sweden, 2017; Available online: https://www.sei.org/mediamanager/documents/Publications/SEI-2017-PB-citizen-science-sdgs.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Oxford English Dictionary. Citizen Science, n. Meanings, Etymology and More|Oxford English Dictionary. Available online: https://www.oed.com/dictionary/citizen-science_n (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Haklay, M.M.; Dörler, D.; Heigl, F.; Manzoni, M.; Hecker, S.; Vohland, K. What Is Citizen Science? The Challenges of Definition. In The Science of Citizen Science; Vohland, K., Land-Zandstra, A., Ceccaroni, L., Lemmens, R., Perelló, J., Ponti, M., Samson, R., Wagenknecht, K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodchild, M.F. Citizens as sensors: The world of volunteered geography. GeoJournal 2007, 69, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodchild, M.; Glennon, J. Crowdsourcing geographic information for disaster response: A research frontier. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2010, 3, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulnerman, A.G.; Senel, M.; Gokduman, O.D. Comparing two crowdsourcing platforms: Assessing their potential for mapping Antarctica. Earth Sci. Inform. 2024, 17, 4655–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senaratne, H.; Mobasheri, A.; Ali, A.L.; Capineri, C.; Haklay, M.M. A review of volunteered geographic information quality assessment methods. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 139–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, L.; Mooney, P.; Foody, G.; Bastin, L.; Comber, A.; Estima, J.; Fritz, S.; Kerle, N.; Jiang, B.; Laakso, M.; et al. Crowdsourcing, Citizen Science or Volunteered Geographic Information? The Current State of Crowdsourced Geographic Information. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2016, 5, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degrossi, L.C.; Porto de Albuquerque, J.; Dos Santos Rocha, R.; Zipf, A. A taxonomy of quality assessment methods for volunteered and crowdsourced geographic information. Trans. GIS 2018, 22, 542–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandusescu, A.; Sieber, R.E.; Jochems, S. Confronting the hype: The use of crisis mapping for community development. Converg. Int. J. Res. into New Media Technol. 2016, 22, 616–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, F. #Help: Digital Humanitarianism and the Remaking of International Order; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Cinnamon, J. Humanitarian Mapping. In International Encyclopedia of Human Geography, 2nd ed.; Kobayashi, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štampach, R.; Herman, L.; Trojan, J.; Tajovská, K.; Řezník, T. Humanitarian Mapping as a Contribution to Achieving Sustainable Development Goals: Research into the Motivation of Volunteers and the Ideal Setting of Mapathons. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taft-Morales, M. Haiti Earthquake: Crisis and Response; Congressional Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. Available online: https://sgp.fas.org/crs/row/R41023.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Meier, P. Digital Humanitarians: How Big Data Is Changing the Face of Humanitarian Response; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Available online: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/mono/10.1201/b18023/digital-humanitarians-patrick-meier (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Kankanamge, N.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Goonetilleke, A.; Kamruzzaman, M. Can volunteer crowdsourcing reduce disaster risk? A systematic review of the literature. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 35, 101097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís, P.; McCusker, B.; Menkiti, N.; Cowan, N.; Blevins, C. Engaging global youth in participatory spatial data creation for the UN sustainable development goals: The case of open mapping for malaria prevention. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 98, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilashi, M.; Boon, O.K.; Tan, G.; Lin, B.; Abumalloh, R. Critical Data Challenges in Measuring the Performance of Sustainable Development Goals: Solutions and the Role of Big-Data Analytics. Harv. Data Sci. Rev. 2023, 5, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Guo, L.; Thebault-Spieker, J. Productivity or Equity? Tradeoffs in Volunteer Microtasking in Humanitarian OpenStreetMap. Proc. ACM-Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2024, 8, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction. Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2022: Our World at Risk: Transforming Governance for a Resilient Future; Technical Report; United Nations: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; Available online: https://www.undrr.org/gar/gar2022-our-world-risk-gar#container-downloads (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Aitsi-Selmi, A. Reflections on a science and technology agenda for 21st century disaster risk reduction: Based on the scientific content of the 2016 UNISDR science and technology conference on the implementation of the sendai framework for disaster risk reduction 2015–2020. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2016, 7, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspari, F.; Stucchi, L.; Bratic, G.; Jovanovic, D.; Ponti, C.; Biagi, L.G.A.; Brovelli, M.A. Innovation in Teaching: The Polimappers Collaborative and Humanitarian Mapping Course at Politecnico Di Milano. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, 46, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís, P.; Rajagopalan, S.; Villa, L.; Mohiuddin, M.B.; Boateng, E.; Wavamunno Nakacwa, S.; Peña Valencia, M.F. Digital humanitarians for the Sustainable Development Goals: YouthMappers as a hybrid movement. J. Geogr. High. Educ. 2022, 46, 80–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, T.; Kateregga, G.; Machmud, H.; Redhead, C.; Mwanja, I. Youth and Humanitarian Action: Open Mapping Partnerships for Disaster Response and the SDGs. In Open Mapping Towards Sustainable Development Goals; Solís, P., Zeballos, M., Eds.; Sustainable Development Goals Series; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, J.P.d.; Herfort, B.; Eckle, M. The Tasks of the Crowd: A Typology of Tasks in Geographic Information Crowdsourcing and a Case Study in Humanitarian Mapping. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HOT. HOT Tasking Manager. Available online: https://tasks.hotosm.org (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- MapSwipe. Available online: https://mapswipe.org/en/ (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Ushahidi. About Ushahidi. Available online: https://www.ushahidi.com/about/our-story/ (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Ittoo, A.; Nguyen, L.M.; van den Bosch, A. Text analytics in industry: Challenges, desiderata and trends. Comput. Ind. 2016, 78, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Kamber, M.; Pei, J. (Eds.) 2—Getting to Know Your Data. In Data Mining, 3rd ed.; The Morgan Kaufmann Series in Data Management Systems; Morgan Kaufmann: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 39–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remote Mapping in Malawi: Supporting Field Operations. Available online: https://www.missingmaps.org/blog/2023/06/02/Malawi-MSF-Cholera-Cyclone-Response/ (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- USAID TerresEauVie Activity. 2019. Available online: https://winrock.org/projects/terreseauvie-rise-ii/ (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Schott, M.; Lautenbach, S.; Größchen, L.; Zipf, A. Openstreetmap Element Vectorisation—A Tool For High Resolution Data Insights And Its Usability in the Land-Use and Land-Cover Domain. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022; XLVIII-4-W1-2022, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monitoring Forest Change—El Carmen (1)|MapSwipe. Available online: https://mapswipe.org/en/projects/-NhbfISzxa2V8cpZSRap/ (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Ruzindana, E.; Gaspari, F.; Ntakobangize, E.; Ponti, C.; Biraghi, C.A.; Kilsedar, C.E.; Tadi, M.; Muindi, Z.; Agenga, P.; Mugeha, L. Open Data Addressing Challenges Associated with Informal Settlements in the Global South. In Open Mapping Towards Sustainable Development Goals; Solís, P., Zeballos, M., Eds.; Sustainable Development Goals Series; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Wilson, B.; Sarraf, S.; Jana, A. Open data for informal settlements: Toward a user’s guide for urban managers and planners. J. Urban Manag. 2015, 4, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| HOT-TM | MapSwipe | Ushahidi | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Web browser | Web browser, mobile application | Web browser |
| Data sources | Satellite | Satellite | Mixed (email, news, other sources) |
| Project type | Digitization | Classification | Conflation |
| Project geographic border | Predefined | Predefined | Non-defined |
| Project management | Project | Project | Deployment |
| Task unit | Task | Task | Post |
| Task number | Limited | Limited | Unlimited |
| Data contribution | OSM | Proper server | Proper server |
| Platform | Introduced Indicators (a) | Exclusive Indicators (b) | Low-Data-Availability Indicators (c) | Total Number of Unique Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOT-TM | 11 | 11 | 8 | 27 |
| MapSwipe | 7 | 2 | 1 | 12 |
| Ushahidi | 7 | 1 | 1 | 15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, Q.H.; Brovelli, M.A.; Albertella, A.; Furuhashi, T.; Montani, M. Bridging Humanitarian Mapping and the Sustainable Development Goals. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2025, 14, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14080307
Nguyen QH, Brovelli MA, Albertella A, Furuhashi T, Montani M. Bridging Humanitarian Mapping and the Sustainable Development Goals. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2025; 14(8):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14080307
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Quang Huy, Maria Antonia Brovelli, Alberta Albertella, Taichi Furuhashi, and Michael Montani. 2025. "Bridging Humanitarian Mapping and the Sustainable Development Goals" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 14, no. 8: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14080307
APA StyleNguyen, Q. H., Brovelli, M. A., Albertella, A., Furuhashi, T., & Montani, M. (2025). Bridging Humanitarian Mapping and the Sustainable Development Goals. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 14(8), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14080307







