Evaluation of Urban Street Historical Appearance Integrity Based on Street View Images and Transfer Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Relevant Studies on the Conservation and Evaluation of Historic Urban Landscape
2.2. Relevant Studies on the Use of SVIs in Examining Urban Built Environments
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Conceptual Definition and Research Framework
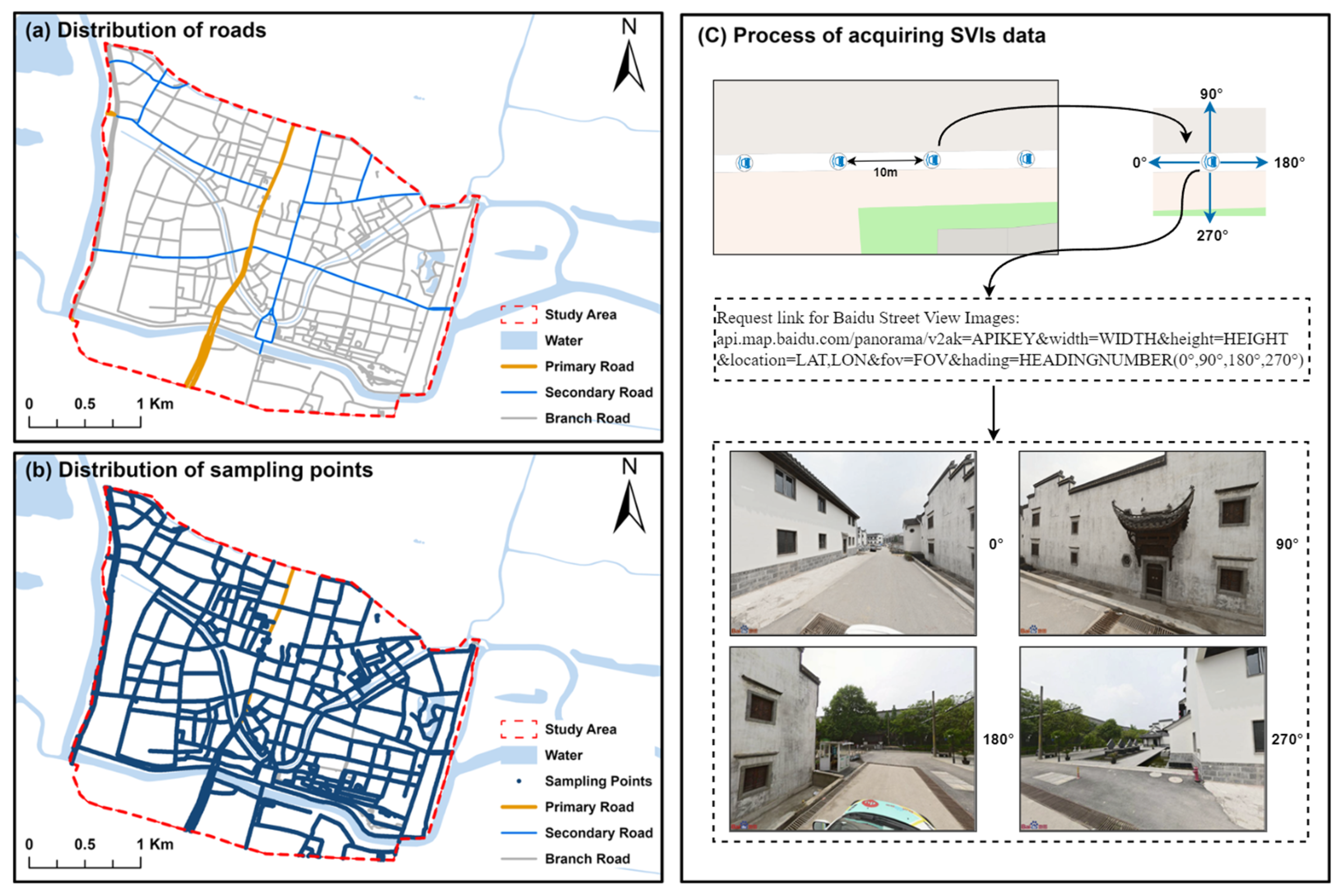
3.2. Study Area
3.3. Data Collection and Preprocessing
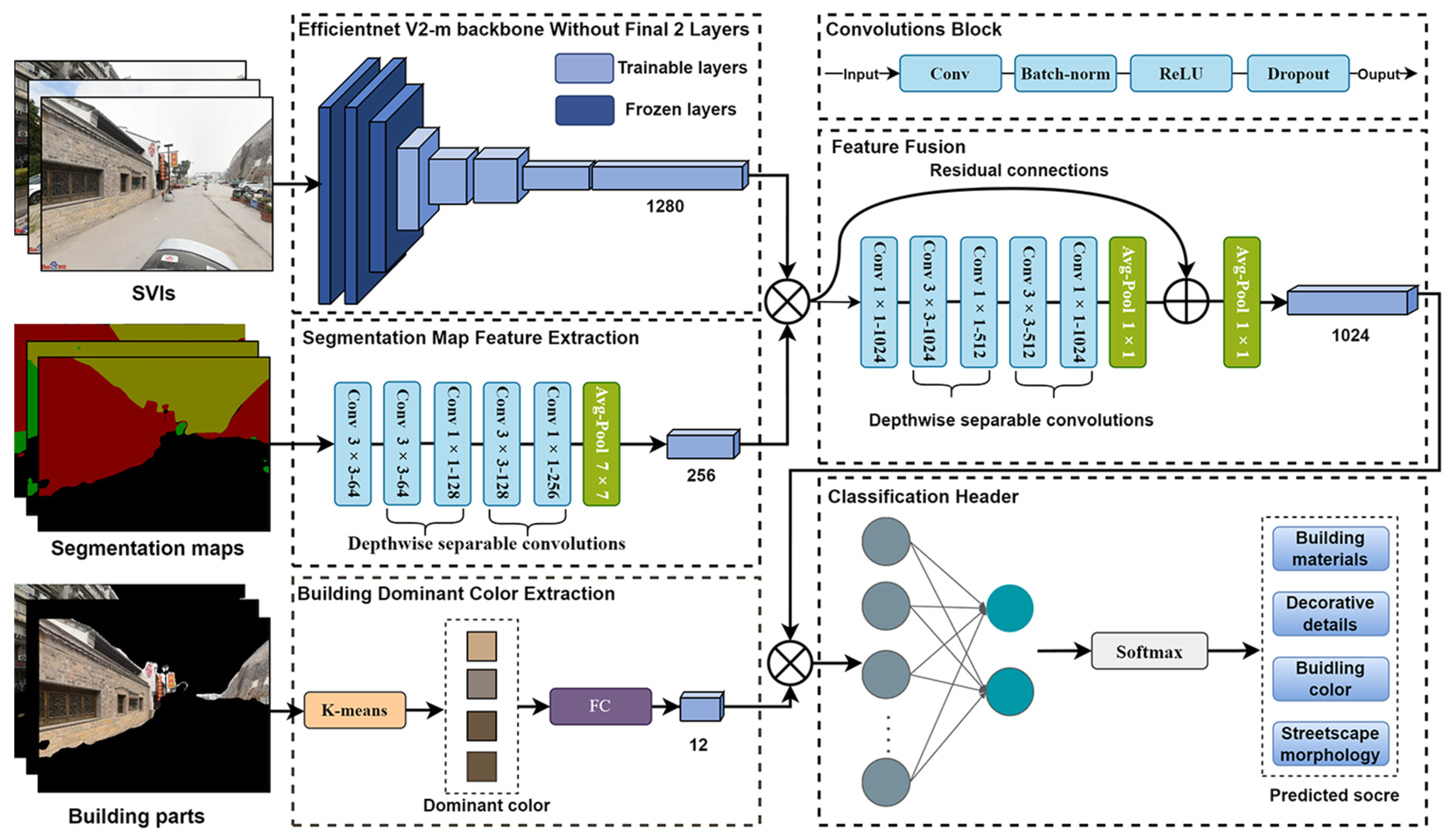
3.4. Semantic Segmentation and Building Dominant Color Extraction
3.5. Expert Judgment and Elo Rating
3.6. Historical Appearance Integrity Evaluation
4. Results
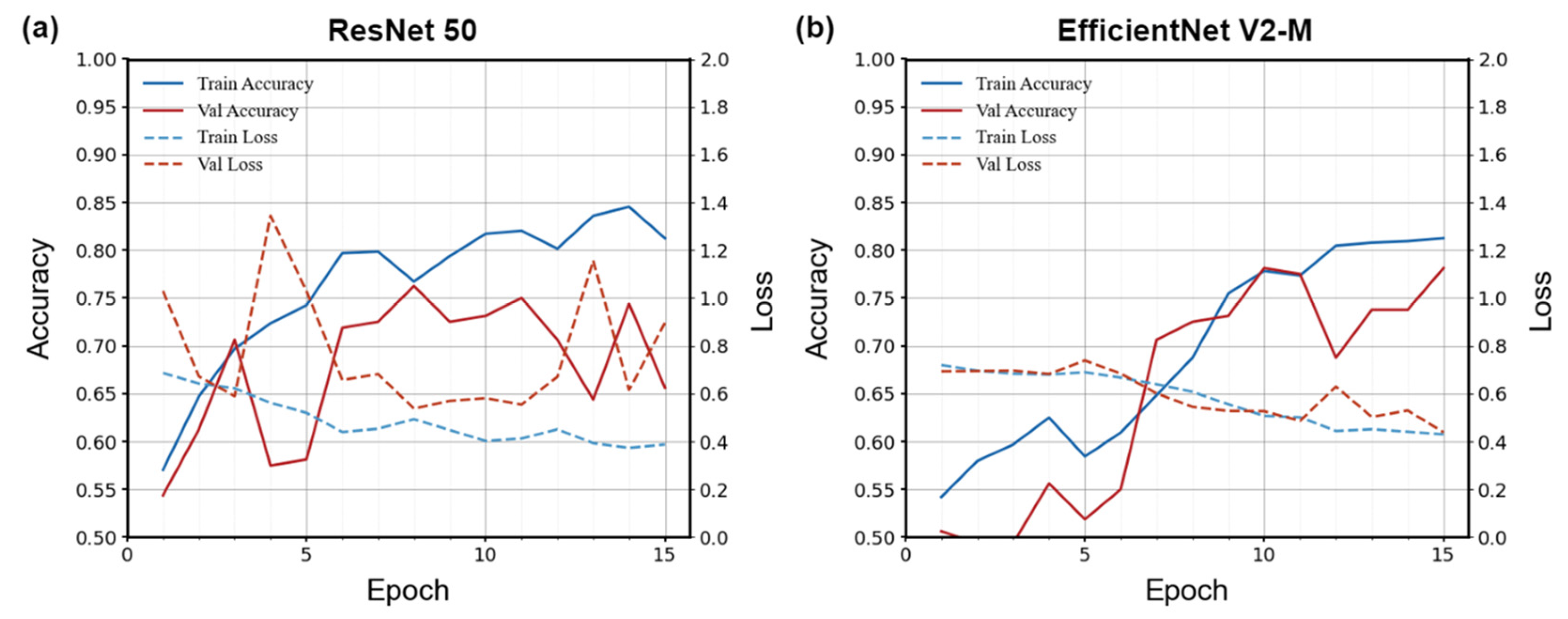
4.1. Results of Semantic Segmentation Model Training and SVIs Filtering
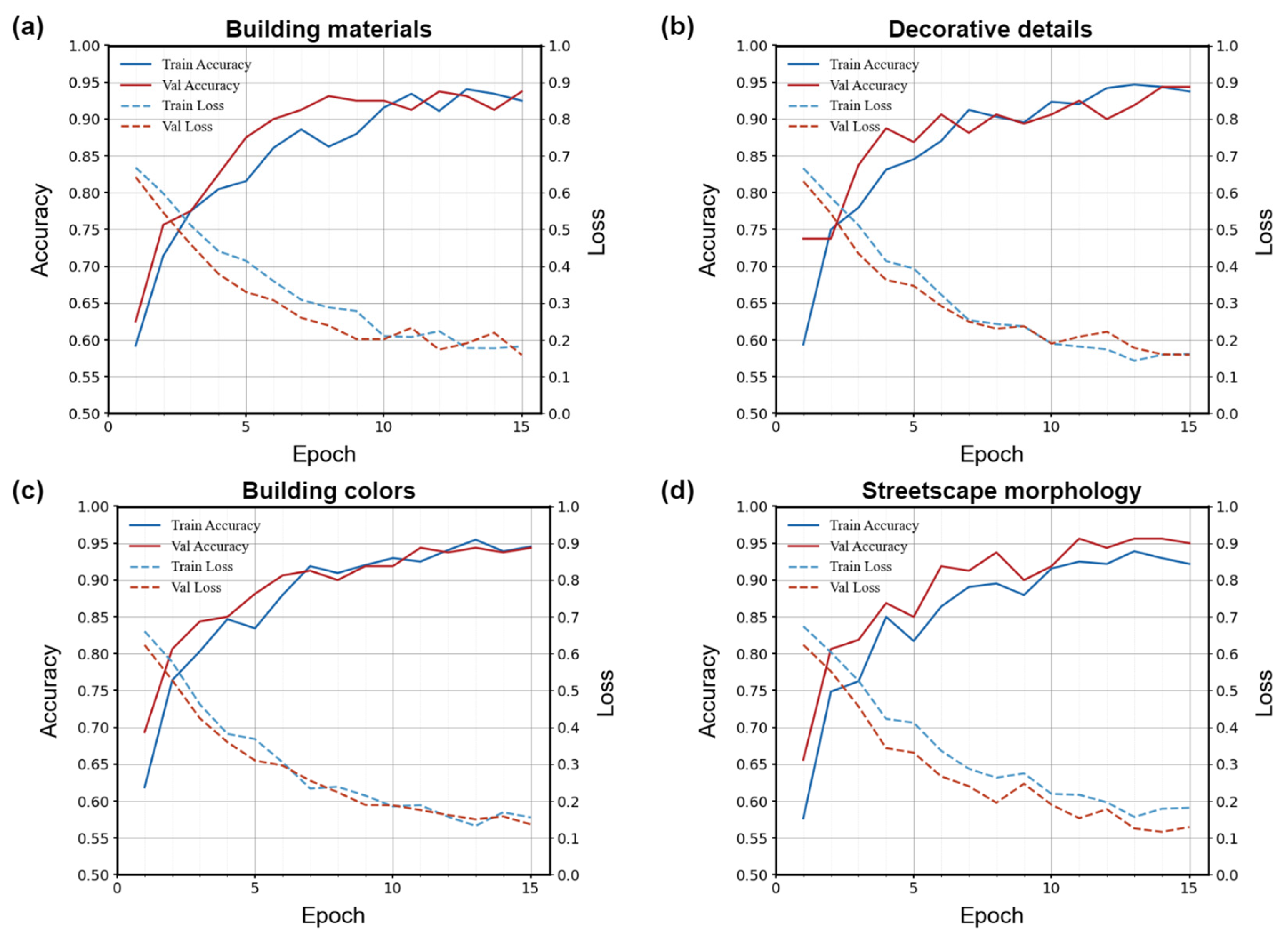
4.2. Results of the HAI Evaluation Model Training
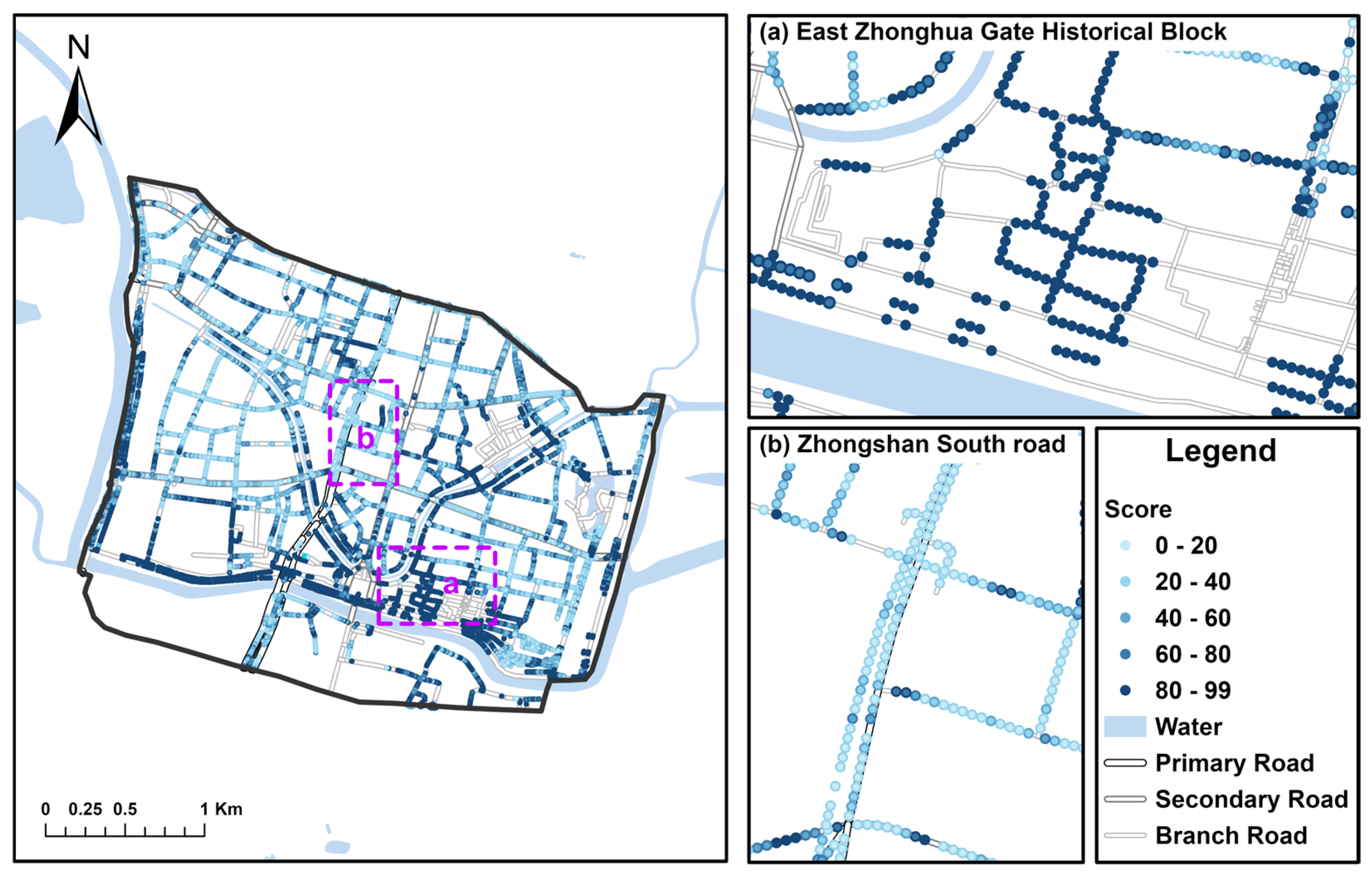
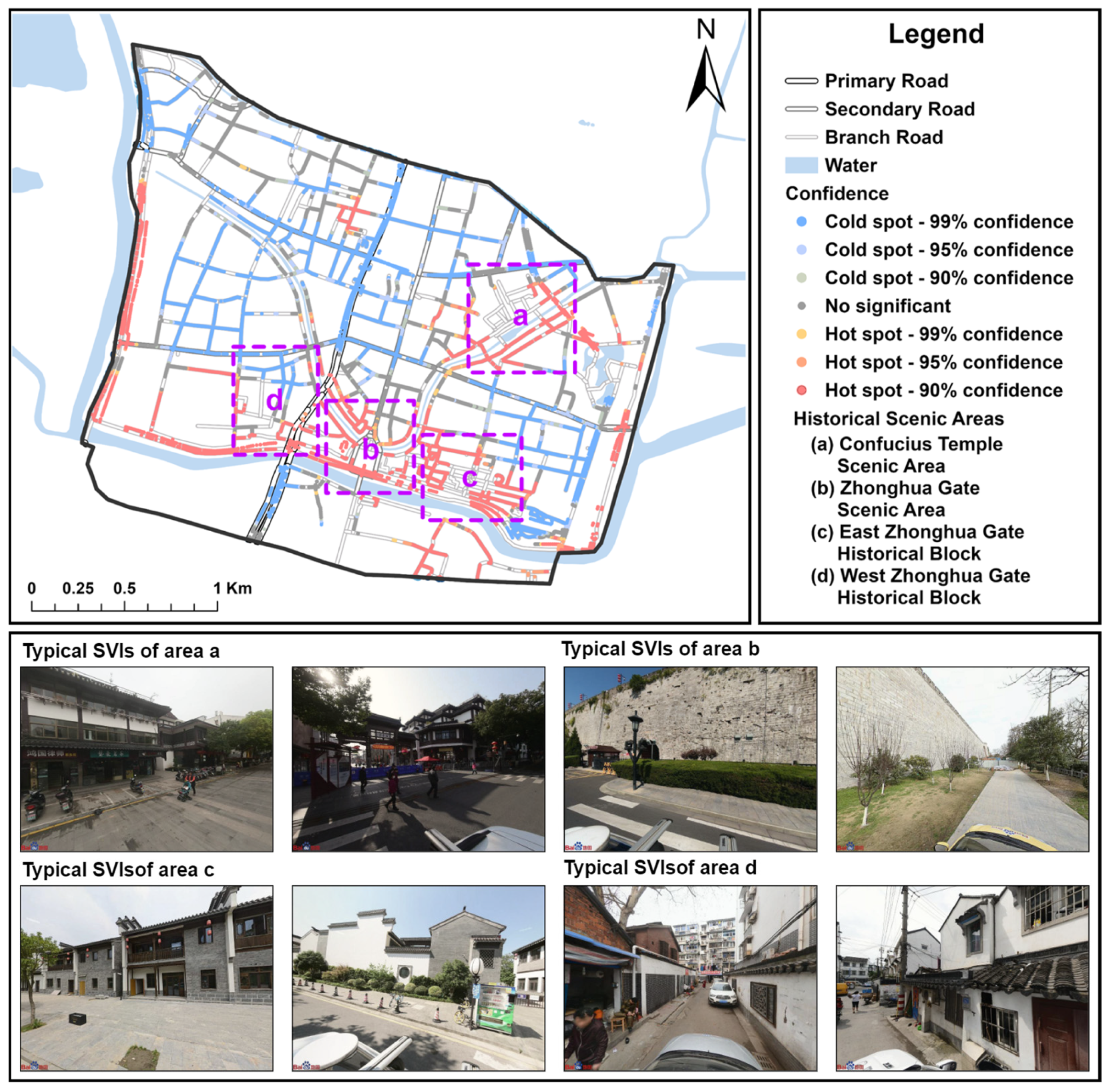
4.3. Spatial Distribution of Historical Appearance Integrity
4.4. Validation of Model Accuracy and the Effect of Overexposure on Model Performance
5. Discussion
5.1. Uncover Deep Features of the Urban Built Environment Using SVIs
5.2. Fine-Grained Evaluation of Historical Appearance at the Street Level
5.3. Limitations and Prospects
5.4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HUL | Historical Urban Landscape |
| HAI | Historical Appearance Integrity |
| AHP | Analytic Hierarchy Process |
| GIS | Geographic Information Systems |
| CNNs | Convolutional Neural Networks |
References
- Been, V.; Ellen, I.G.; Gedal, M.; Glaeser, E.; McCabe, B.J. Preserving History or Restricting Development? The Heterogeneous Effects of Historic Districts on Local Housing Markets in New York City. J. Urban Econ. 2016, 92, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, J.; Lin, Y.; Xiao, L.; Zhou, J. Revitalizing Historic Districts: Identifying Built Environment Predictors for Street Vibrancy Based on Urban Sensor Data. Cities 2021, 117, 103305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Recommendation on the Historic Urban Landscape; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yeoh, B.S.; Huang, S. The Conservation-Redevelopment Dilemma in Singapore. Cities 1996, 13, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özyavuz, M. (Ed.) “Theories, Techniques, Strategies” for Spatial Planners & Designers; Peter Lang D: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2021; ISBN 978-3-631-85438-9. [Google Scholar]
- Shipley, R.; Snyder, M. The Role of Heritage Conservation Districts in Achieving Community Economic Development Goals. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2013, 19, 304–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, X. Spatial Pattern and Micro-Location Rules of Tourism Businesses in Historic Towns: A Case Study of Pingyao, China. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2022, 25, 100721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Miao, C.; Xu, J.; Yu, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation and enhancement of historic district regeneration effectiveness in the context of cultural-tourism integration: A case study of three historic districts in Kaifeng. J. Nat. Resour. 2025, 40, 164. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fan, W.; You, J. Evaluation of Tourism Elements in Historical and Cultural Blocks Using Machine Learning: A Case Study of Taiping Street in Hunan Province. npj Herit. Sci. 2025, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İpekoğlu, B. An Architectural Evaluation Method for Conservation of Traditional Dwellings. Build. Environ. 2006, 41, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.-M.; Tang, Y.-F.; Zeng, Y.-K.; Feng, L.-Y.; Wu, Z.-G. Sustainable Historic Districts: Vitality Analysis and Optimization Based on Space Syntax. Buildings 2025, 15, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Long, H.; Liu, P.; Liu, X. The Protection and its evaluation system of traditional village: A case study of traditional village in Hunan province. Hum. Geogr. 2018, 33, 121–128. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, H.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S. Conservation for Sustainable Development: The Sustainability Evaluation of the Xijie Historic District, Dujiangyan City, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wang, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Gong, C. Visual Comfort Impact Assessment for Walking Spaces of Urban Historic District in China Based on Semantic Segmentation Algorithm. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2025, 114, 107917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Abd Malek, M.I.; Ja’afar, N.H.; Sima, Y.; Han, Z.; Liu, Z. Unveiling the Potential of Space Syntax Approach for Revitalizing Historic Urban Areas: A Case Study of Yushan Historic District, China. Front. Archit. Res. 2023, 12, 1144–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shen, J. Integrating Historic Landscape Characterization for Historic District Assessment through Multi-Source Data: A Case Study from Hangzhou, China. npj Herit. Sci. 2025, 13, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Lei, Z. Cultural Diversity Conservation in Historic Districts via Spatial-Gene Perspectives: The Small Wild Goose Pagoda District, Xi’an. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. The True Nature and the Preservation Principles for the Historic Blocks. Hum. Geogr. 2005, 20, 48–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biljecki, F.; Ito, K. Street View Imagery in Urban Analytics and GIS: A Review. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 215, 104217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Yue, W.; Li, M.; Gao, J. Mapping Human Perception of Urban Landscape from Street-View Images: A Deep-Learning Approach. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 112, 102886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Ye, C.; Wang, Z.; Tang, G.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Y. City-Scale Mapping of Urban Façade Color Using Street-View Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2021, 13, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhong, T.; Liu, M.; Ye, Y. Evaluating Building Color Harmoniousness in a Historic District Intelligently: An Algorithm-Driven Approach Using Street-View Images. Environ. Plan. B Urban. Anal. City Sci. 2023, 50, 1838–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Council on Monuments and Sites (ICOMOS). The Athens Charter for the Restoration of Historic Monuments; Adopted at the First International Congress of Architects and Technicians of Historic Monuments; International Council on Monuments and Sites (ICOMOS): Athens, Greece, 1931. [Google Scholar]
- Azpeitia Santander, A.; Azkarate Garai-Olaun, A.; De La Fuente Arana, A. Historic Urban Landscapes: A Review on Trends and Methodologies in the Urban Context of the 21st Century. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Vienna Memorandum on World Heritage and Contemporary Architecture—Managing the Historic Urban Landscape; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Teng, M.; Yue, H.; Ye, Y. Perceiving the Fine-Scale Urban Poverty Using Street View Images through a Vision-Language Model. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 123, 106267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Dang, A.; Zhang, P.; Yang, Y.; Wu, S. Conversation and Management of Hutong-Historical and Cultural District of Beijing Inner City Supported by GIS. In Proceedings of the 2009 17th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Fairfax, VA, USA, 12–14 August 2009; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Xi, X.; Wang, S. Urban Landscape Planning Based on Ecological Infrastructure: A Case Study of Weihe City, Shandong Province, China. Urban Plan. 2008, 3, 87–92. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhen, X. From Historical Features Protection to Urban Landscape Management- Based on the Historic Urban Landscape Approach. Landsc. Archit. 2017, 6, 14–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Meng, Q.; Li, M.; Yang, D. Enhancing Authenticity in Historic Districts via Soundscape Design. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Han, D.; Yi, Y. Urban Overall Architectural Landscape Planning and Control Methods. Urban Plan. Forum 2022, 5, 81–89. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanghai Municipal Bureau of Planning and Natural Resources. Notice on Issuing the Guidelines for the Conservation of Shanghai’s Historical Urban Features [EB/OL]. Available online: https://ghzyj.sh.gov.cn/zcwj/cxgh/20241212/5216da83ad6142598247d9d6357cfdcb.html (accessed on 22 June 2025).
- Shenzhen Municipal Bureau of Planning and Natural Resources. Notice on Issuing the Measures for the Conservation of Shenzhen Historical Urban Features and Historic Buildings [EB/OL]. Available online: https://www.sz.gov.cn/zfgb/zcjd/content/post_11998589.html (accessed on 22 June 2025).
- Brusaporci, S. (Ed.) Handbook of Research on Emerging Digital Tools for Architectural Surveying, Modeling, and Representation; Advances in Geospatial Technologies; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-4666-8379-2. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, M.; Feng, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Xu, D. Color Authenticity for the Sustainable Development of Historical Areas: A Case Study of Shiquan. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Tian, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Cao, S.-J. Sustaining the Local Color of a Global City. Nat. Cities 2025, 2, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Li, G. Urban Neighbourhood Environment Assessment Based on Street View Image Processing: A Review of Research Trends. Environ. Chall. 2021, 4, 100090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Biljecki, F. Understanding Urban Perception with Visual Data: A Systematic Review. Cities 2024, 152, 105169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.; Garcia, L.M.T.; Goodman, A.; Johnson, R.; Aldred, R.; Murugesan, M.; Brage, S.; Bhalla, K.; Woodcock, J. Estimating City-Level Travel Patterns Using Street Imagery: A Case Study of Using Google Street View in Britain. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Y.; Ye, Y. Measuring Human-Scale Urban Form and Its Performance. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 191, 103612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, M.G.; Hout, M.C.; Kardan, O.; Hunter, M.R.; Yourganov, G.; Henderson, J.M.; Hanayik, T.; Karimi, H.; Jonides, J. The Perception of Naturalness Correlates with Low-Level Visual Features of Environmental Scenes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Salazar-Miranda, A.; Duarte, F.; Vale, L.; Hack, G.; Chen, M.; Liu, Y.; Batty, M.; Ratti, C. Urban Visual Intelligence: Studying Cities with Artificial Intelligence and Street-Level Imagery. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2024, 114, 876–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Zeng, L.; Li, S.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wan, B. Spatial Context-Aware Method for Urban Land Use Classification Using SVIs. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 192, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.-B.; Zhang, F.; Gong, F.-Y.; Ratti, C.; Li, X. Classification and Mapping of Urban Canyon Geometry Using Google Street View Images and Deep Multitask Learning. Build. Environ. 2020, 167, 106424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorian, S.S.; Psyllidis, A.; Bozzon, A. ST-Sem: A Multimodal Method for Points-of-Interest Classification Using Street-Level Imagery. In Web Engineering; Bakaev, M., Frasincar, F., Ko, I.-Y., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 11496, pp. 32–46. ISBN 978-3-030-19273-0. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Lu, Y.; Ao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhao, R.; Wang, R. Global and Local Associations between Urban Greenery and Travel Propensity of Older Adults in Hong Kong. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 63, 102442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Yabuki, N.; Fukuda, T. Development of a System for Assessing the Quality of Urban Street-Level Greenery Using Street View Images and Deep Learning. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 59, 126995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Ki, D.; Osutei, N.; Lee, S.; Hipp, J.R. Beyond Visual Inspection: Capturing Neighborhood Dynamics with Historical Google Street View and Deep Learning-Based Semantic Segmentation. J. Geogr. Syst. 2024, 26, 541–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salesses, P.; Schechtner, K.; Hidalgo, C.A. The Collaborative Image of The City: Mapping the Inequality of Urban Perception. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porzi, L.; Rota Bulò, S.; Lepri, B.; Ricci, E. Predicting and Understanding Urban Perception with Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 23rd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Brisbane, Australia, 13 October 2015; pp. 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ito, K.; Biljecki, F. Assessing the Equity and Evolution of Urban Visual Perceptual Quality with Time Series Street View Imagery. Cities 2024, 145, 104704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Kim, J.; Park, J.; Lee, J. Assessment of Perceived and Physical Walkability Using Street View Images and Deep Learning Technology. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Q.H.; Kwon, N.; Nguyen, T.H.; Kim, B.; Ahn, Y. Sensing Perceived Urban Stress Using Space Syntactical and Urban Building Density Data: A Machine Learning-Based Approach. Build. Environ. 2024, 266, 112054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Huang, C.; Ye, Y. Measuring Street Quality: A Human-Centered Exploration Based on Multi-Sourced Data and Classical Urban Design Theories. Buildings 2024, 14, 3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendran, R.; Jude Hemanth, D. Scene Understanding Using Deep Neural Networks—Objects, Actions, and Events: A Review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Innovative Computing and Communications, Delhi, India, 21–23 February 2020; Khanna, A., Gupta, D., Bhattacharyya, S., Snasel, V., Platos, J., Hassanien, A.E., Eds.; Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing. Springer: Singapore, 2020; Volume 1087, pp. 223–231, ISBN 978-981-15-1285-8. [Google Scholar]
- Afifi, M.; Brown, M.S. Deep White-Balance Editing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Biljecki, F.; Zhao, T.; Liang, X.; Hou, Y. Sensitivity of Measuring the Urban Form and Greenery Using Street-Level Imagery: A Comparative Study of Approaches and Visual Perspectives. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 122, 103385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fukuda, T.; Yabuki, N. Development of a City-Scale Approach for Façade Color Measurement with Building Functional Classification Using Deep Learning and Street View Images. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasar, J.L. Perception, Cognition, and Evaluation of Urban Places. In Public Places and Spaces; Altman, I., Zube, E.H., Eds.; Human Behavior and Environment; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1989; Volume 10, pp. 31–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elo, A.E. The Rating of Chessplayers, Past and Present; Arco Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, A.A.; Sajid Iqbal, M.; Hamza Shahbaz, M. Development of Intelligent Fault-Tolerant Control Systems with Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Transfer Learning Algorithms: A Review. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 121956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNetV2: Smaller models and faster training. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 10096–10106. [Google Scholar]
- Yosinski, J.; Clune, J.; Bengio, Y.; Lipson, H. How Transferable Are Features in Deep Neural Networks? arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.1792. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, C.M.; Wilson, J.S.; Baker, E.A.; Miller, D.K.; Schootman, M. Using Google Street View to Audit the Built Environment: Inter-Rater Reliability Results. Ann. Behav. Med. 2013, 45, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
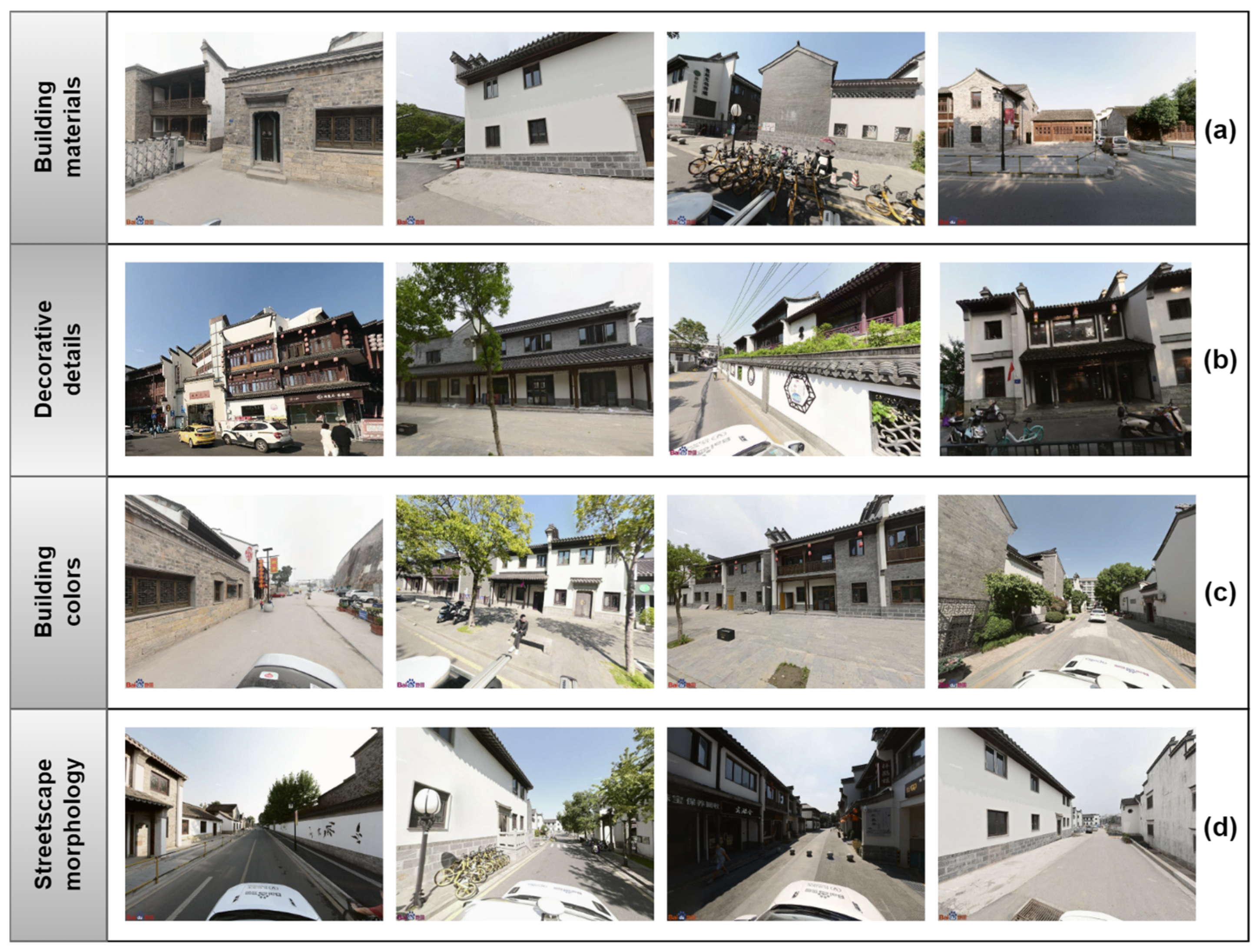




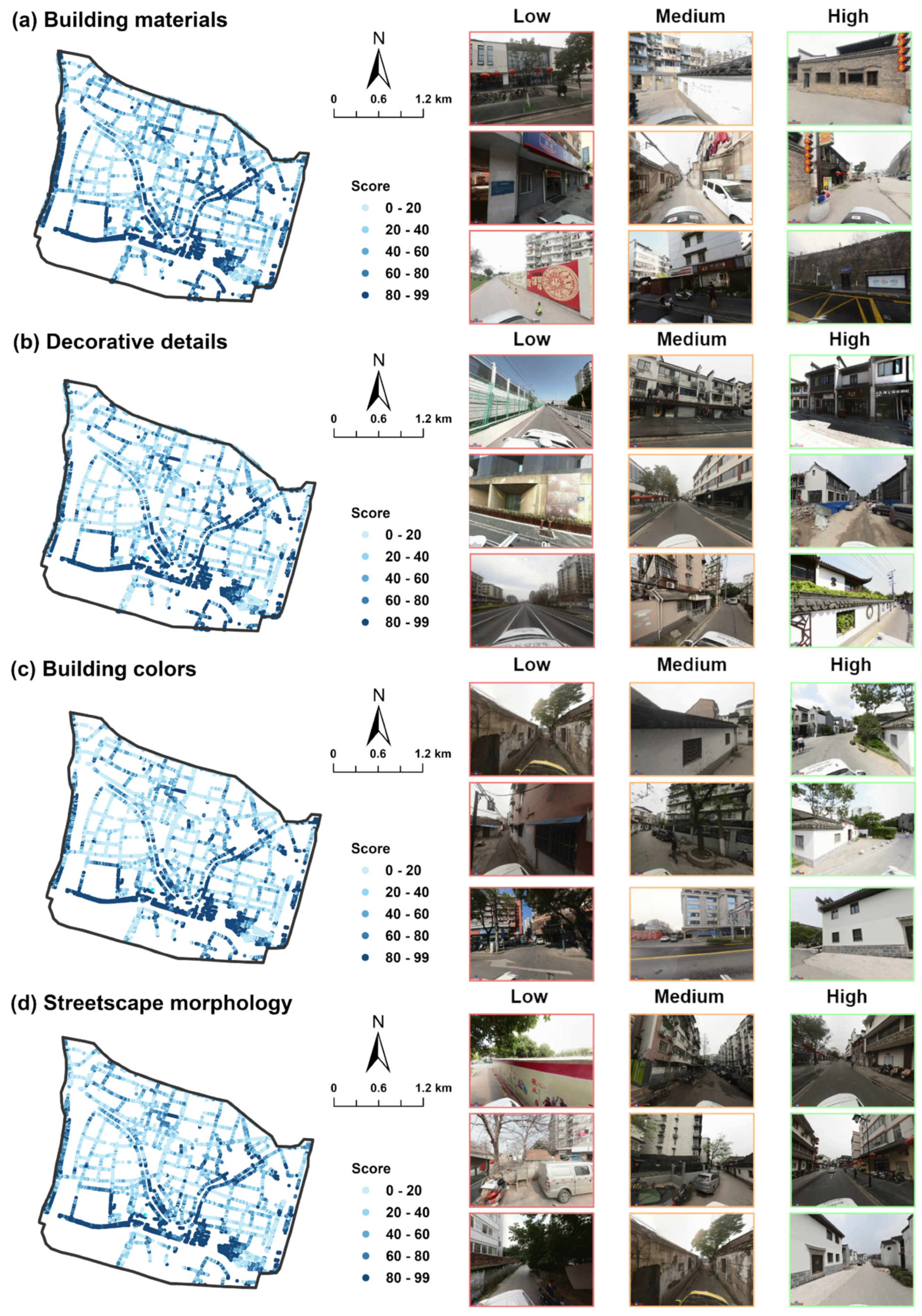
| A | (Building Materials) | (Decorative Details) | (Building Colors) | (Streetscape Morphology) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0.35 | |
| 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0.35 | |
| 1/3 | 1/3 | 1 | 2/3 | 0.12 | |
| 1/2 | 1/2 | 3/2 | 1 | 0.18 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Learning Rate | 0.007 |
| Epochs | 40 |
| Loss Function | Cross-Entropy Loss |
| Backbone Neural Network | MobileNet |
| Batch Size | 8 |
| Optimizer | SGD |
| Semantic Class | Pixel Accuracy | Precision | IoU |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buildings | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.93 |
| Greenery | 0.91 | 0.84 | 0.77 |
| Sky | 0.92 | 0.93 | 0.86 |
| Background | 0.91 | 0.93 | 0.85 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Learning Rate | 0.0001 |
| Epochs | 15 |
| Loss Function | Cross-Entropy Loss |
| Batch Size | 8 |
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Indicator | Class | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Building materials | Negative | 0.91 | 0.96 | 0.94 |
| Positive | 0.96 | 0.91 | 0.94 | |
| Decorative details | Negative | 0.93 | 0.96 | 0.94 |
| Positive | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.94 | |
| Building color | Negative | 0.93 | 0.96 | 0.95 |
| Positive | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.95 | |
| Streetscape morphology | Negative | 0.93 | 0.99 | 0.96 |
| Positive | 0.99 | 0.93 | 0.96 |
| Index | Building Materials | Decorative Details | Building Colors | Streetscape Morphology | Historical Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran’s I | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| z-score | 31.41 | 29.81 | 29.59 | 29.63 | 30.20 |
| p-value | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Road Level | Number of Sampling Points | Average Score | Proportion of Scores Above 50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary | 268 | 23.17 | 9.70% |
| Secondary | 769 | 27.73 | 12.90% |
| Branch | 5148 | 46.93 | 34.87% |
| SVI Quality | Class | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overexposure | Negative | 0.58 | 0.78 | 0.67 |
| Positive | 0.84 | 0.67 | 0.74 | |
| Non-overexposure | Negative | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.91 |
| Positive | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Dai, Y.; Cai, J.; Qian, H.; Peng, Z.; Zhong, T. Evaluation of Urban Street Historical Appearance Integrity Based on Street View Images and Transfer Learning. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2025, 14, 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14070266
Xu J, Dai Y, Cai J, Qian H, Peng Z, Zhong T. Evaluation of Urban Street Historical Appearance Integrity Based on Street View Images and Transfer Learning. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2025; 14(7):266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14070266
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jiarui, Yunxuan Dai, Jiatong Cai, Haoliang Qian, Zimu Peng, and Teng Zhong. 2025. "Evaluation of Urban Street Historical Appearance Integrity Based on Street View Images and Transfer Learning" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 14, no. 7: 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14070266
APA StyleXu, J., Dai, Y., Cai, J., Qian, H., Peng, Z., & Zhong, T. (2025). Evaluation of Urban Street Historical Appearance Integrity Based on Street View Images and Transfer Learning. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 14(7), 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14070266







