End-to-End Vector Simplification for Building Contours via a Sequence Generation Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
- End-to-end vector simplification: TPSM is introduced, which is capable of directly handling vector data and generating simplified vector coordinate sequences, thereby enabling end-to-end learning for building simplification.
- Enhanced shape feature extraction: The multihead attention mechanism is analyzed and improved upon by integrating position encoding directly into the attention mechanism. This allows the TPSM to more effectively capture the shape features inherent in the vector sequence coordinates.
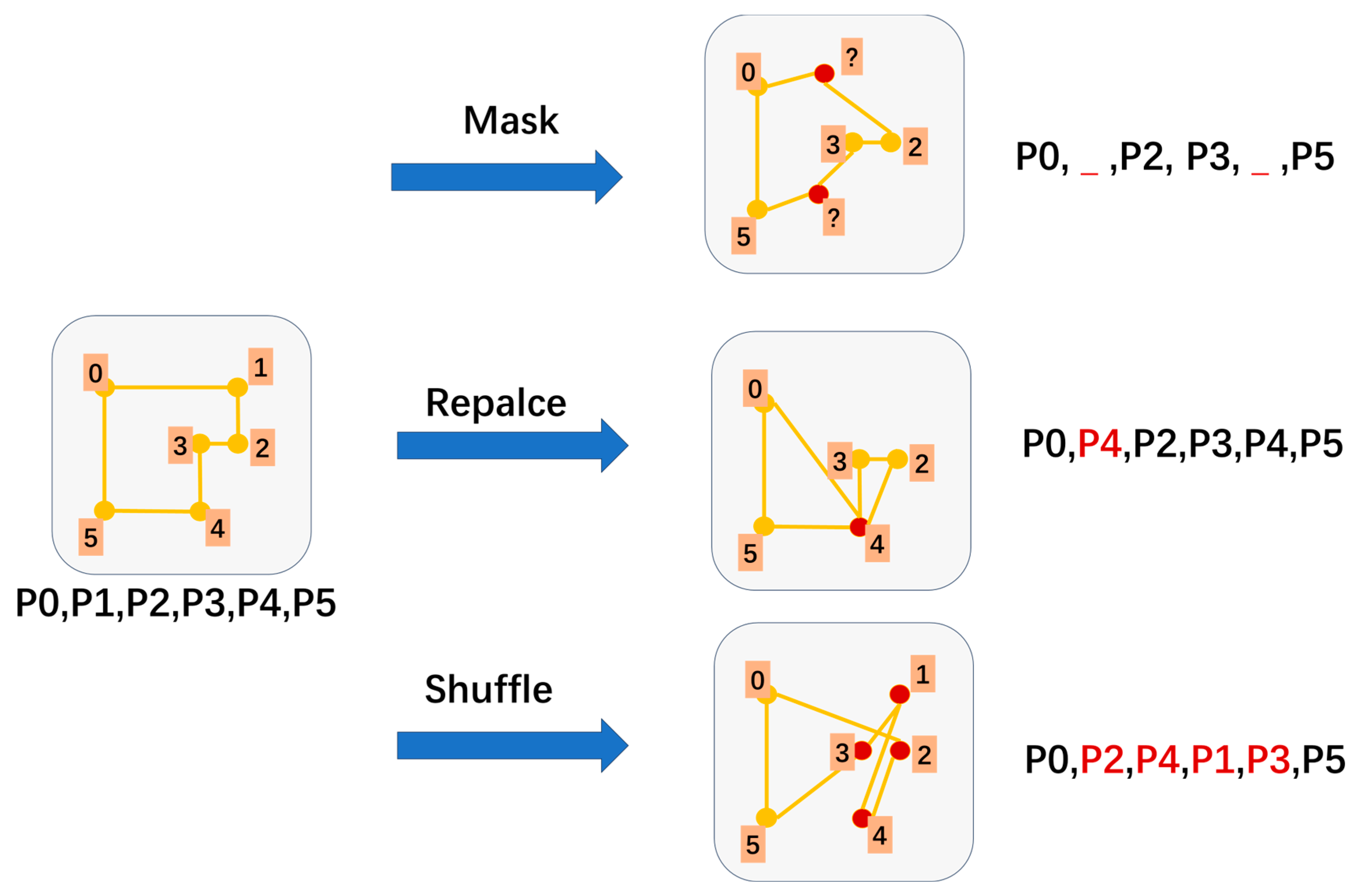
- Self-supervised reconstruction task: A self-supervised reconstruction task is proposed, wherein the model is trained to reconstruct the original building outline from noise-injected vector sequences. This facilitates the learning of implicit geometric relationships, reduces reliance on labeled data, and enhances training efficiency and model generalization.
- Comprehensive evaluation: Experiments were conducted with comparative testing and evaluations using several metrics. The results demonstrate TPSM’s superiority in preserving the key characteristics of building outlines.
2. Materials and Methods
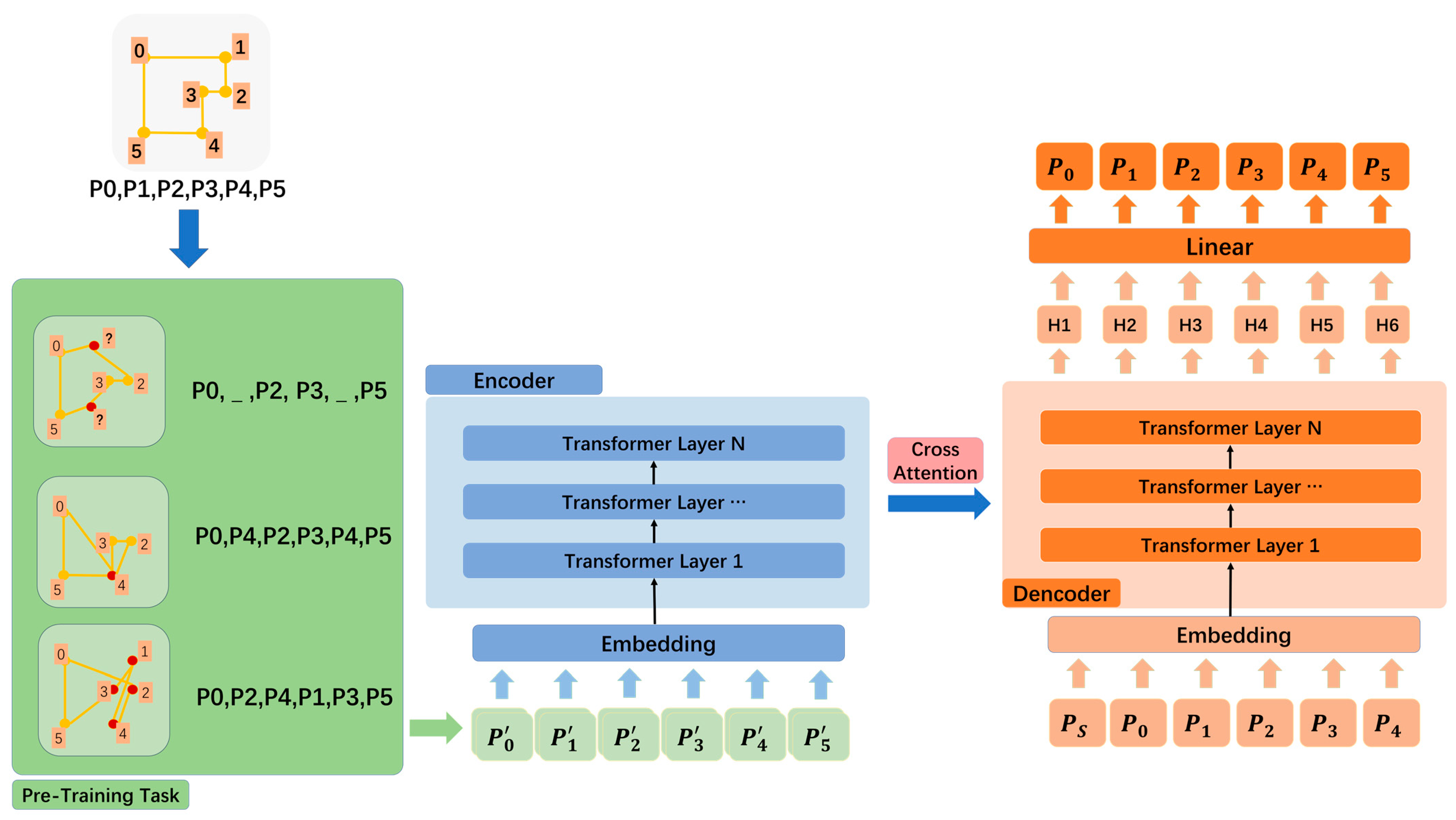
2.1. Model Architecture
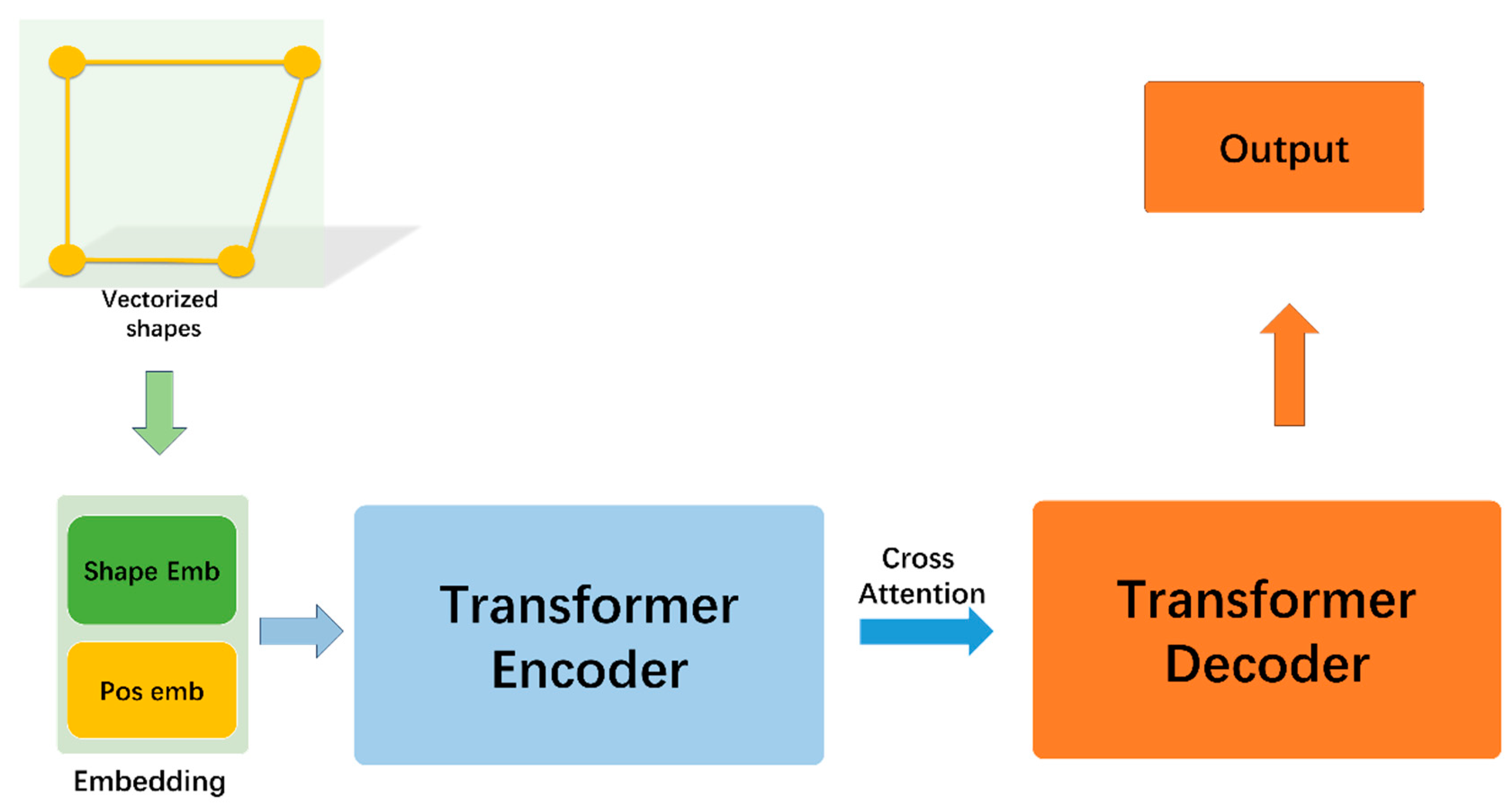
2.1.1. Input Representation
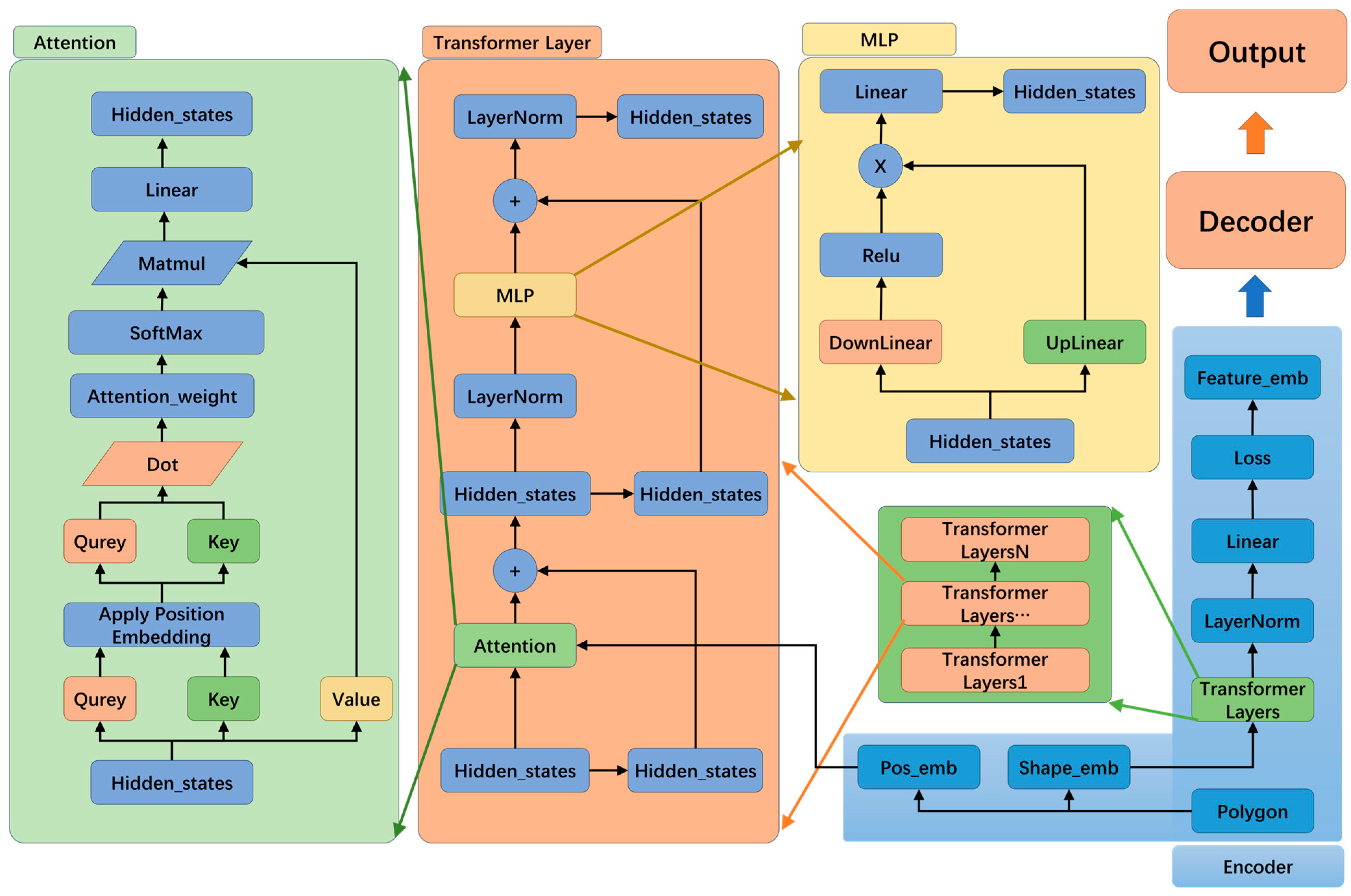
2.1.2. Encoder
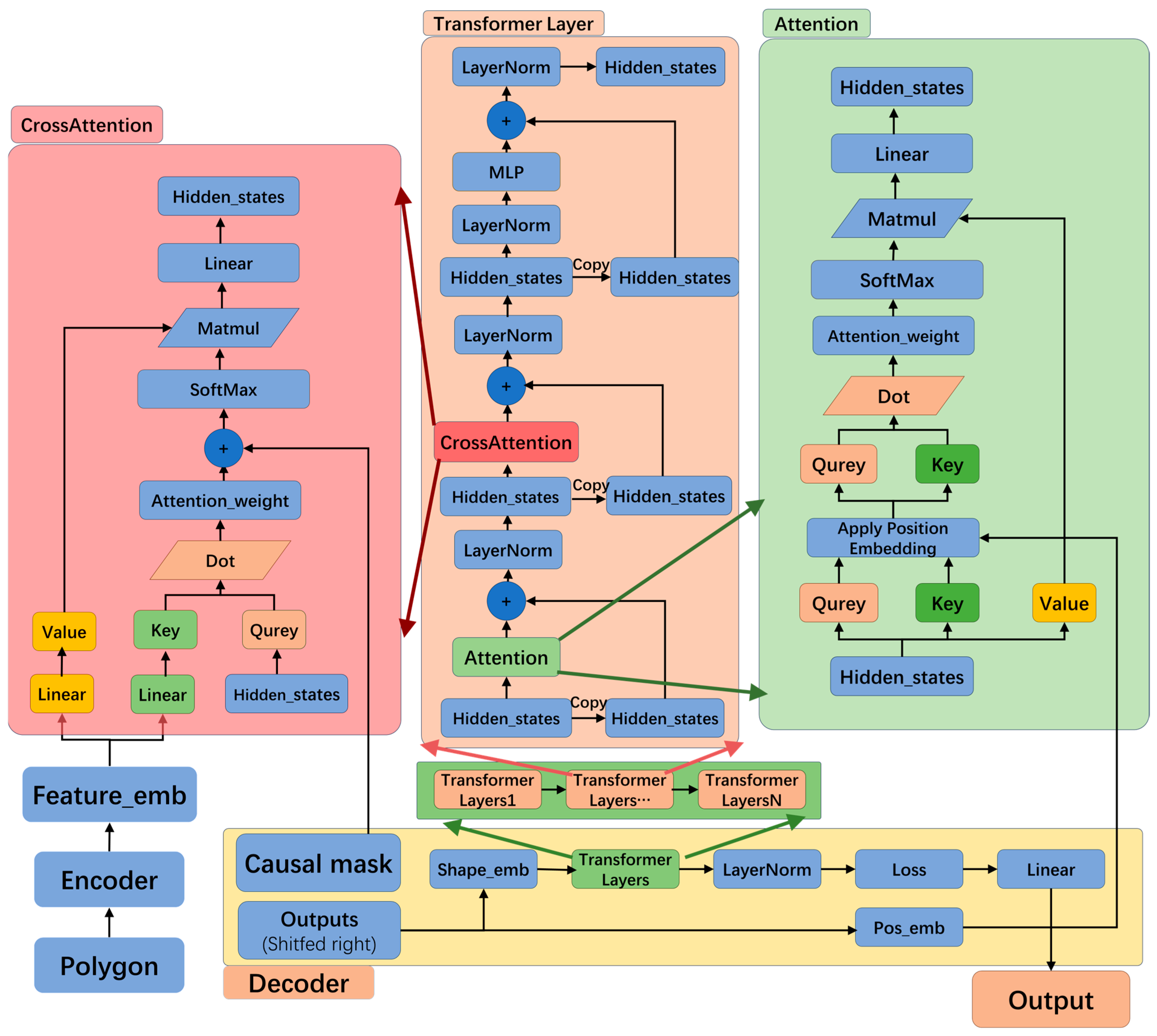
2.1.3. Decoder
2.2. Self-Supervised Reconstruction Task
2.3. End-to-End Building Simplification
2.4. Hyperparameter Tuning
- −
- Encoder/decoder layers: {2, 4, 6}.
- −
- Attention heads: {8, 12}.
- −
- Hidden layer dimensions: {256, 512, 768}.
3. Results
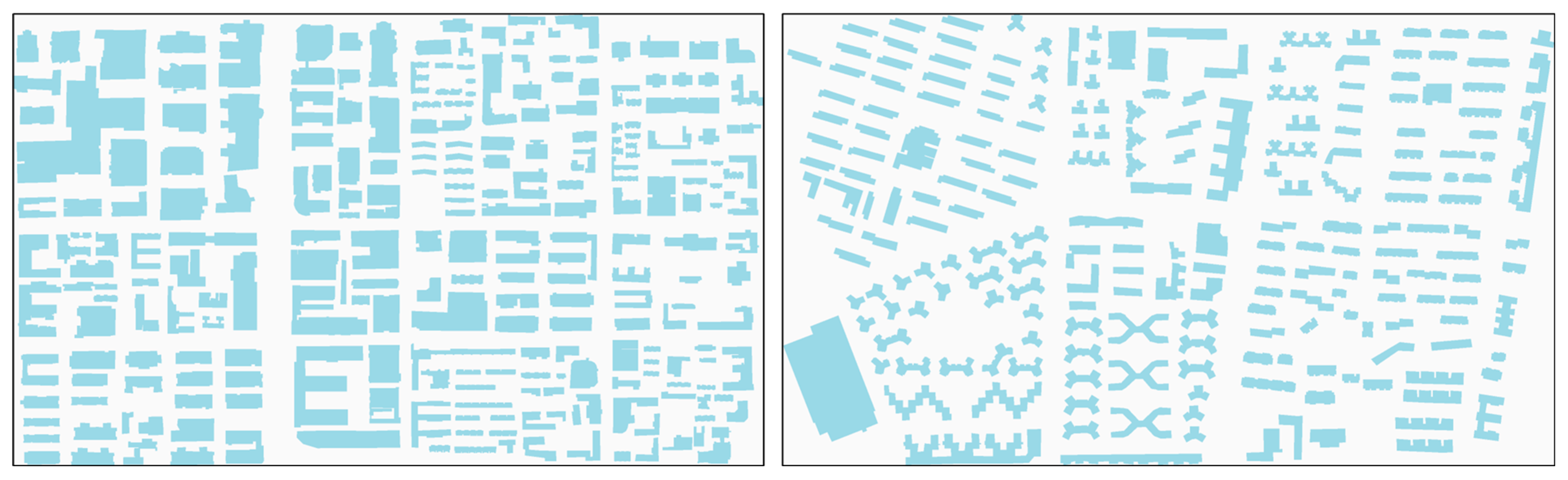
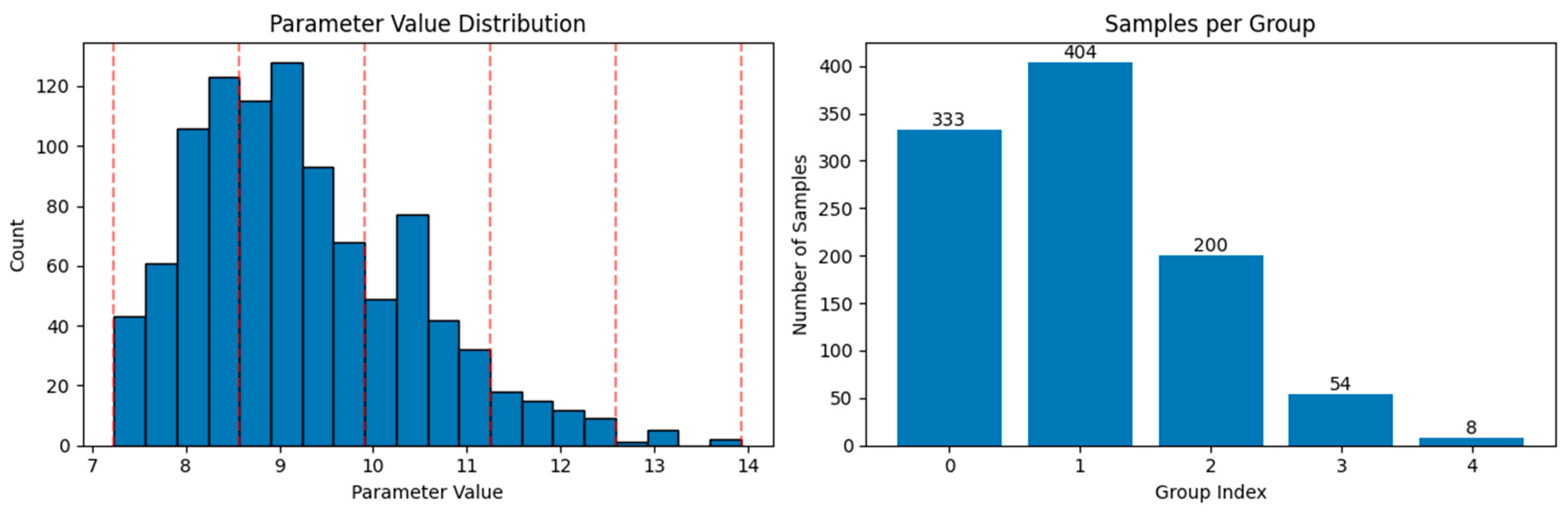
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Model Parameter Settings
3.3. Evaluation Metrics
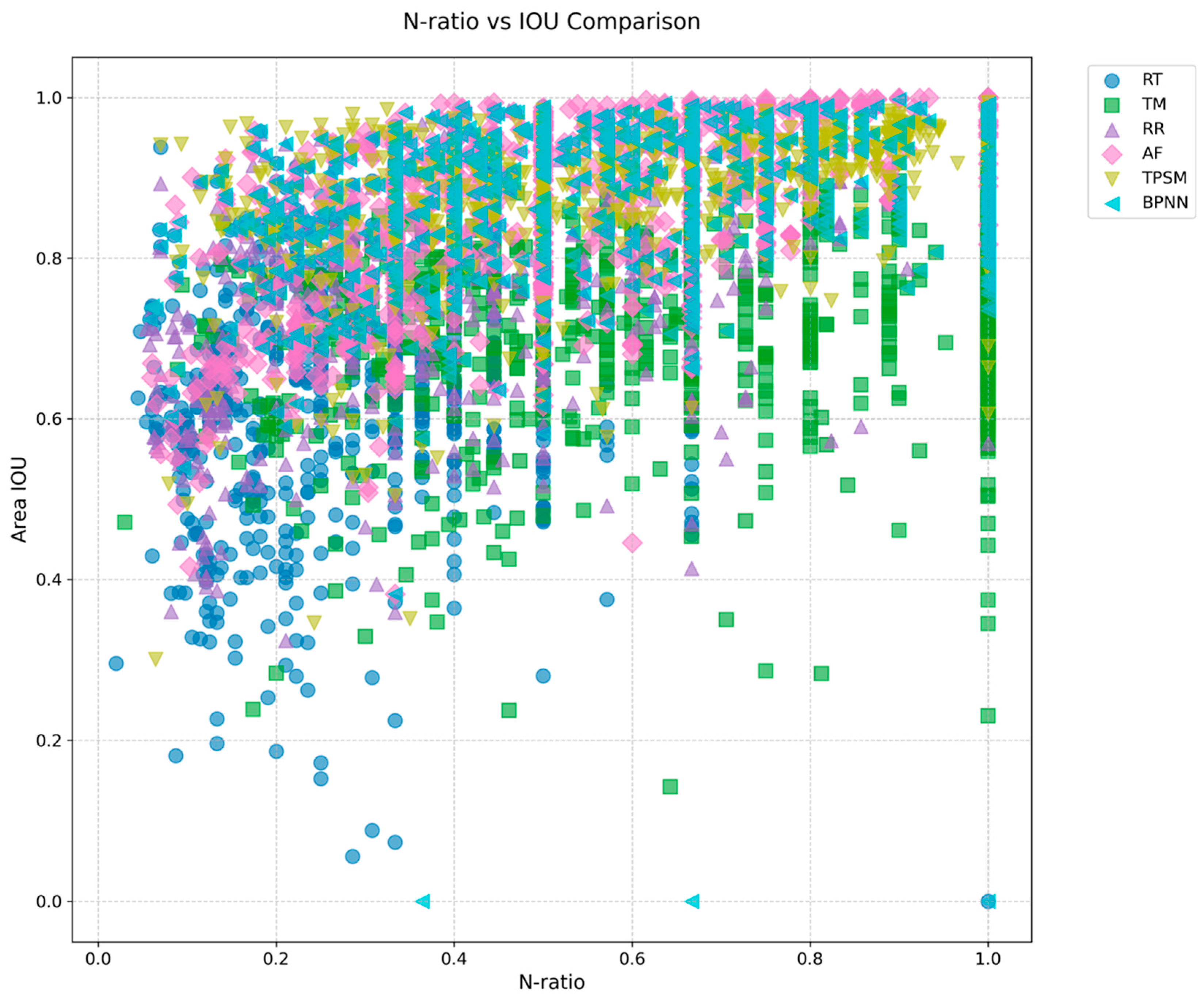
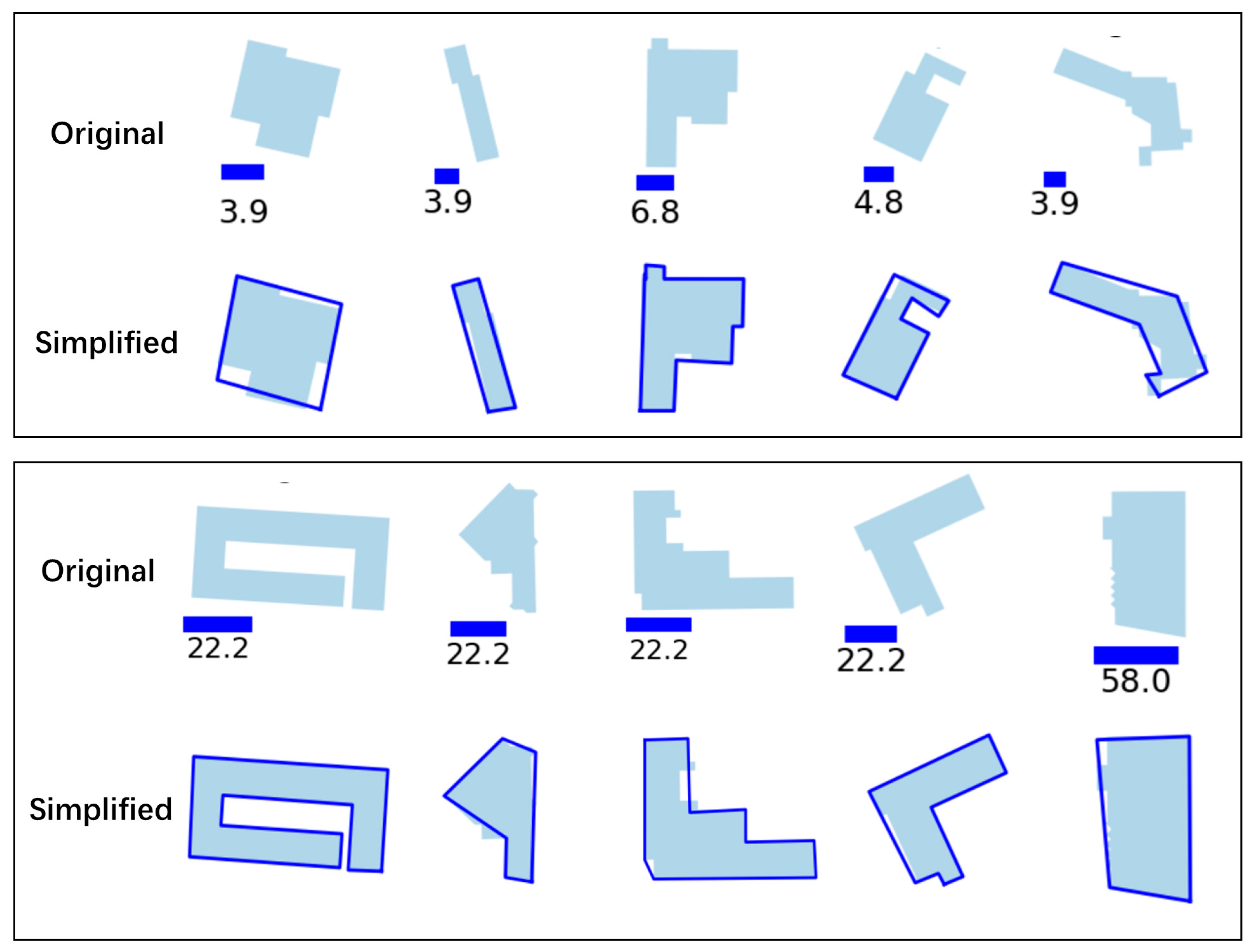
3.4. Experiments and Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Ablation Studies
4.2. Comparison and Analysis
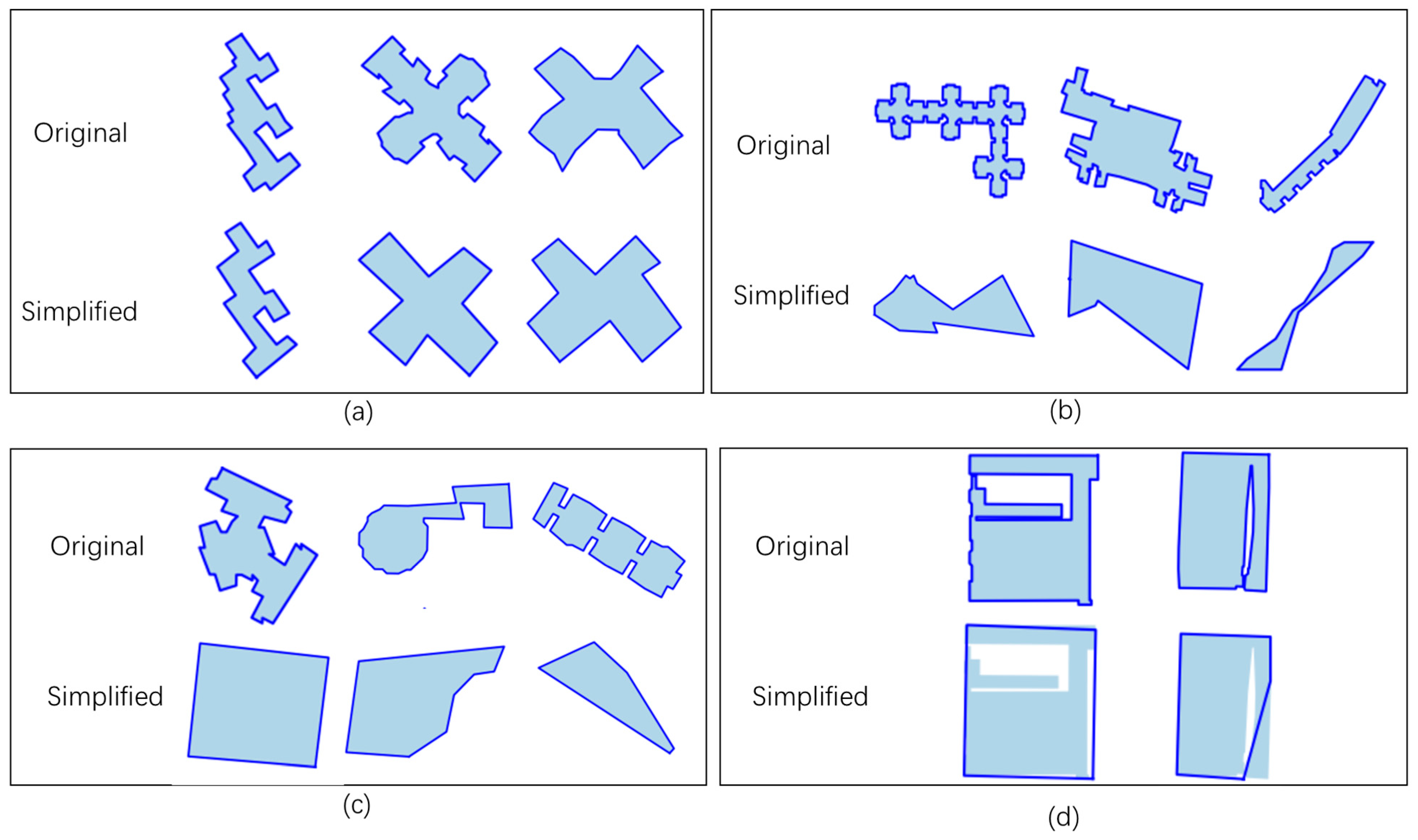
4.3. Simplification of Buildings with Different Complexities
4.4. Cross-Regional Generalization Evaluation
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Touya, G. Multi-criteria geographic analysis for automated cartographic generalization. Cartogr. J. 2022, 59, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiniger, S.; Weibel, R. Relations among map objects in cartographic generalization. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2007, 34, 175–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Persello, C.; Stein, A. Building outline delineation: From aerial images to polygons with an improved end-to-end learning framework. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2021, 175, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Yuan, T.; Yan, X.; Ai, T.; Jiang, C. A hybrid approach to building simplification with an evaluator from a backpropagation neural network. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2022, 36, 280–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yang, M. A deep learning approach for polyline and building simplification based on graph autoencoder with flexible constraints. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2024, 51, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Xu, S.; Li, Z. Polyline simplification using a region proposal network integrating raster and vector features. GISci. Remote Sens. 2023, 60, 2275427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtial, A.; Touya, G.; Zhang, X. Constraint-based evaluation of map images generalized by deep learning. J. Geovisualization Spat. Anal. 2022, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, D.H.; Peucker, T.K. Algorithms for the reduction of the number of points required to represent a digitized line or its caricature. Cartographica 1973, 10, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Openshaw, S. Algorithms for automated line generalization based on a natural principle of objective generalization. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1992, 6, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvalingam, M.; Whyatt, J.D. Line generalisation by repeated elimination of points. Cartogr. J. 1993, 30, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainsford, D.; Mackaness, W. Template matching in support of generalisation of rural buildings. In Proceedings of the Advances in Spatial Data Handling; Richardson, D.E., van Oosterom, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Ai, T.; Zhang, X. Template matching and simplification method for building features based on shape cognition. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2017, 6, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, Q.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wei, Z. Contextual building selection based on a genetic algorithm in map generalization. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2017, 6, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qingsheng, G.; Jianhua, M. The method of graphic simplification of area feature boundary with right angles. Geo Spat. Inf. Sci. 2000, 3, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenshua, X. Simplification of building polygon based on adjacent four-point method. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2013, 42, 929–936. [Google Scholar]
- Sester, M. Optimization approaches for generalization and data abstraction. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2005, 19, 871–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, T. Automated building simplification using a recursive approach. In Cartography in Central and Eastern Europe: CEE 2009; Gartner, G., Ortag, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 121–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haunert, J.-H.; Wolff, A. Optimal and topologically safe simplification of building footprints. In Proceedings of the 18th SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, San Jose, CA, USA, 2–5 November 2010; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Qian, H.; He, H.; Xie, L.; Luo, D. A Line Simplification method based on support vector machine. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2020, 45, 744–752, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Ai, T.; Yang, M.; Yin, H. A graph convolutional neural network for classification of building patterns using spatial vector data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2019, 150, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, Y. Building simplification using backpropagation neural networks: A combination of cartographers’ expertise and raster-based local perception. GIScience Remote Sens. 2013, 50, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sester, M.; Feng, Y.; Thiemann, F. Building generalization using deep learning. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, XLII-4, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Thiemann, F.; Sester, M. Learning cartographic building generalization with deep convolutional neural networks. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2019, 8, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtial, A.; El Ayedi, A.; Touya, G.; Zhang, X. Exploring the potential of deep learning segmentation for mountain roads generalisation. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2020, 9, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtial, A.; Touya, G.; Zhang, X. Deriving map images of generalised mountain roads with generative adversarial networks. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2023, 37, 499–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Wu, F.; Xing, R.; Gong, X.; Yu, L. Segmentation and sampling method for complex polyline generalization based on a generative adversarial network. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 4158–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Chen, Y. Data-driven polyline simplification using a stacked autoencoder-based deep neural network. Trans. GIS 2022, 26, 2302–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.; Liu, Y.; Goyal, N.; Ghazvininejad, M.; Mohamed, A.; Levy, O.; Stoyanov, V.; Zettlemoyer, L. BART: Denoising sequence-to-sequence pre-training for natural language generation, translation, and comprehension. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5–10 July 2020; Jurafsky, D., Chai, J., Schluter, N., Tetreault, J., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 7871–7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, F.M. Recurrent neural networks (RNN). In Recurrent Neural Networks: From Simple to Gated Architectures; Salem, F.M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 43–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, C.; Ballesteros, M.; Ling, W.; Matthews, A.; Smith, N.A. Transition-Based Dependency Parsing with Stack Long Short-Term Memory. In Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), Beijing, China, 26–31 July 2015; Zong, C., Strube, M., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lee, D. Building simplification based on pattern recognition and shape analysis. In Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Spatial Data Handling, Beijing, China, 10–12 August 2000; pp. 58–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Fu, C.; Weibel, R. Move and remove: Multi-task learning for building simplification in vector maps with a graph convolutional neural network. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 202, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
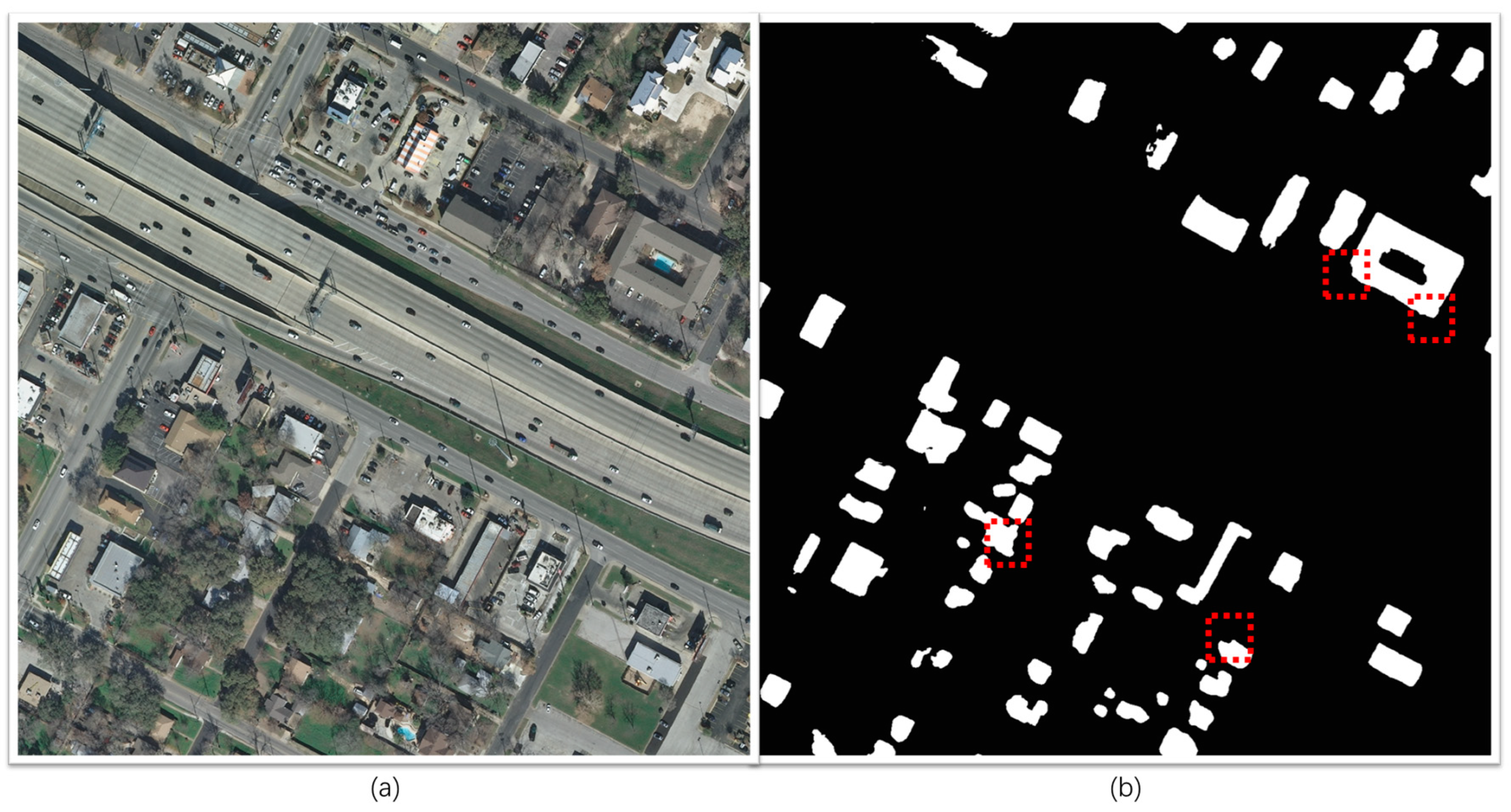







| METRIC | AC | IoU | PC | HD | N-Ratio | SRP | C-IoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEAN | 0.955 | 0.901 | 1.026 | 0.314 | 0.637 | 0.152 | 0.735 |
| MEDIASN | 0.982 | 0.925 | 0.988 | 0.206 | 0.667 | 0.124 | 0.779 |
| STD. DEV. | 0.081 | 0.086 | 0.459 | 0.391 | 0.23 | 0.181 | 0.211 |
| Model Variant | AC | IoU | PC | HD | N-Ratio | SRP | C-IoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPSM (Full) | 0.955 | 0.901 | 1.026 | 0.314 | 0.637 | 0.152 | 0.735 |
| TPSM (APE) | 0.921 | 0.855 | 0.932 | 0.496 | 0.731 | 0.358 | 0.588 |
| TPSM (No SSR) | 0.641 | 0.455 | 0.91 | 1.296 | 0.374 | 0.658 | 0.283 |
| TPSM (2 Encoder/Decoder) | 0.555 | 0.352 | 0.826 | 2.314 | 0.785 | 0.772 | 0.135 |
| TPSM (4 Encoder/Decoder) | 0.895 | 0.791 | 1.131 | 0.514 | 0.779 | 0.302 | 0.535 |
| Scale | Measure | Our Approach | BPNN | RT | TM | AF | RR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:25 k | HD | 0.3132 | 0.3108 | 0.7370 | 0.5973 | 0.3685 | 0.4190 |
| AC | 0.9551 | 0.9883 | 0.9990 | 0.9666 | 0.9696 | 0.9405 | |
| PC | 0.9641 | 0.9467 | 0.7853 | 0.9810 | 0.8997 | 0.8738 | |
| IoU | 0.9012 | 0.8752 | 0.6981 | 0.7298 | 0.8684 | 0.8019 | |
| N-Ratio | 0.637 | 0.556 | 0.3 | 0.679 | 0.48 | 0.425 | |
| SRP | 0.152 | 0.041 | 0 | 0.034 | 0.133 | 0 | |
| C-IoU | 0.735 | 0.654 | 0.376 | 0.572 | 0.609 | 0.525 |
| Comparison | Test Statistic | p-Value | Effect Size | Mean (TPSM) | Mean (Other) | Std (TPSM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| vs. BPNN | 8.7315 | <0.001 | 0.3908 | 0.7354 | 0.6538 | 0.211 |
| vs. AF | 13.3684 | <0.001 | 0.5983 | 0.7354 | 0.6086 | 0.211 |
| vs. RT | 40.293 | <0.001 | 1.8033 | 0.7354 | 0.3758 | 0.211 |
| vs. RR | 21.214 | <0.001 | 0.9495 | 0.7354 | 0.525 | 0.211 |
| vs. TM | 18.3082 | <0.001 | 0.8194 | 0.7354 | 0.5721 | 0.211 |
| METRIC | AC | IoU | PC | HD | N-Ratio | SRP | C-IoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEAN | 0.98 | 0.947 | 0.988 | 0.306 | 0.716 | 0.098 | 0.782 |
| MEDIASN | 0.973 | 0.958 | 0.998 | 0.138 | 0.732 | 0.101 | 0.812 |
| STD. DEV. | 0.04 | 0.056 | 0.109 | 0.22 | 0.227 | 0.172 | 0.151 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, L.; Xu, J.; Jiang, L.; Qian, H. End-to-End Vector Simplification for Building Contours via a Sequence Generation Model. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2025, 14, 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14030124
Cui L, Xu J, Jiang L, Qian H. End-to-End Vector Simplification for Building Contours via a Sequence Generation Model. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2025; 14(3):124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14030124
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Longfei, Junkui Xu, Lin Jiang, and Haizhong Qian. 2025. "End-to-End Vector Simplification for Building Contours via a Sequence Generation Model" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 14, no. 3: 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14030124
APA StyleCui, L., Xu, J., Jiang, L., & Qian, H. (2025). End-to-End Vector Simplification for Building Contours via a Sequence Generation Model. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 14(3), 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14030124






