A Lighting Consistency Technique for Outdoor Augmented Reality Systems Based on Multi-Source Geo-Information
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. AR Lighting Estimation Technology
2.2. Multi-Source Geographic Information Data
3. Methods
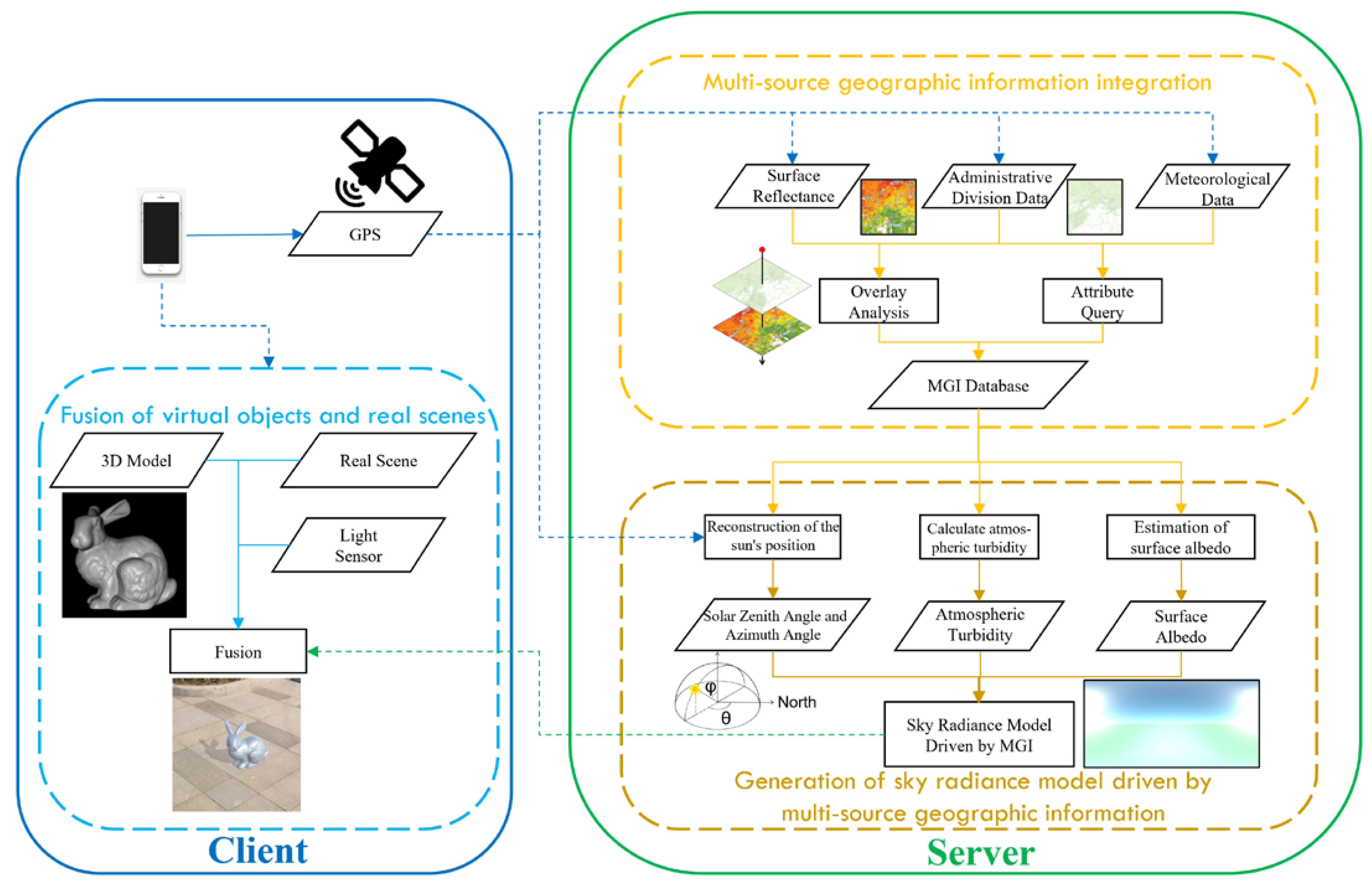
3.1. Overview
3.2. Integration of Multi-Source Geographic Information Based on Multi-Modal Data
- GPS data
- Administrative division data
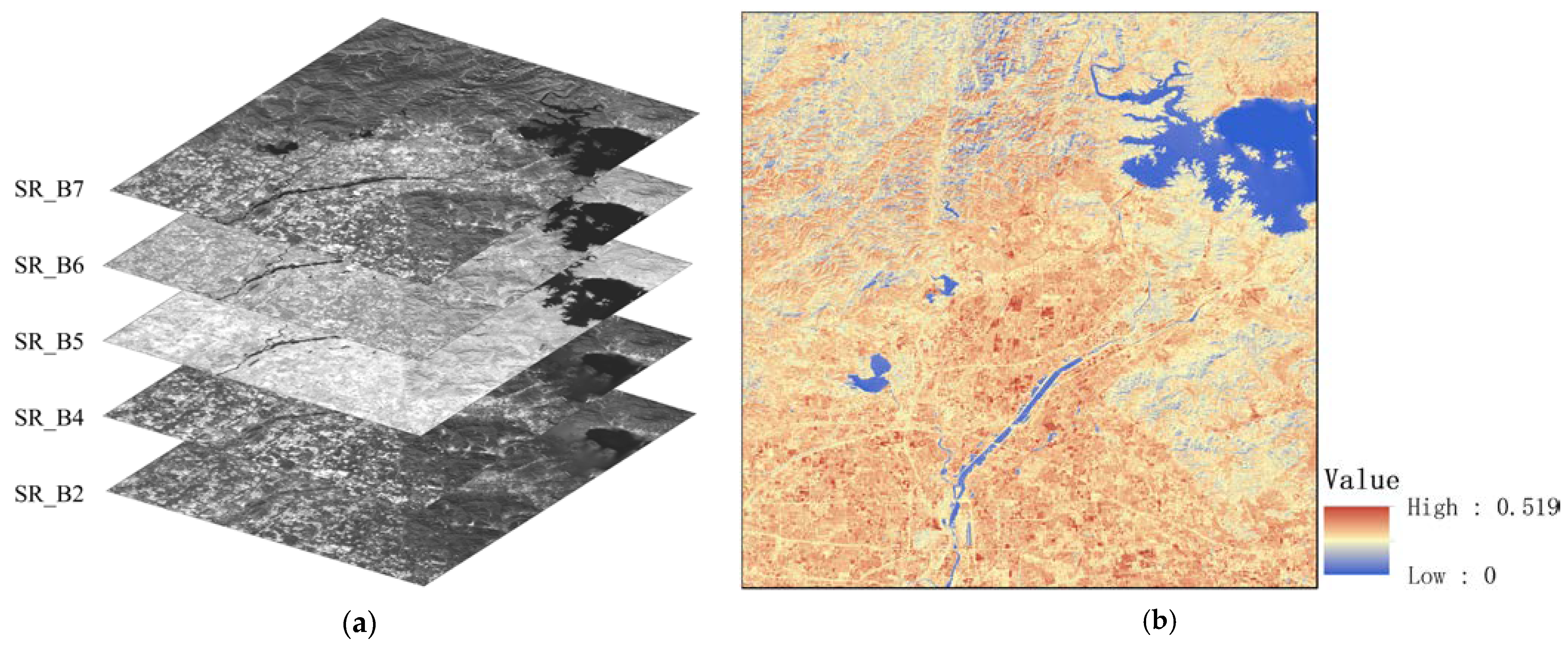
- Surface reflectance data
- Meteorological data
3.3. Generation of a Sky Radiance Model Driven Using Multi-Source Geographic Information
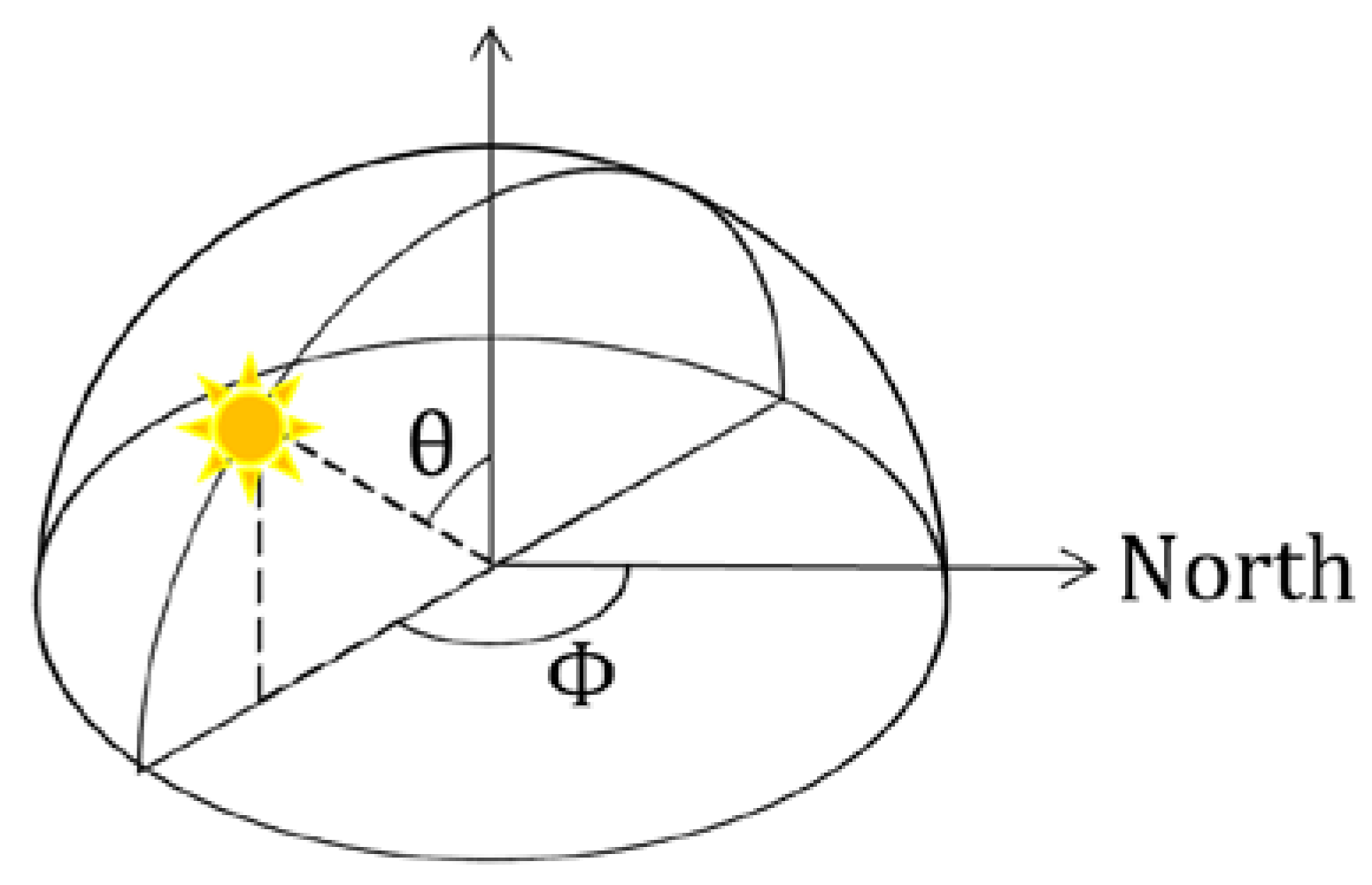
3.3.1. Reconstruction of the Sun’s Position
3.3.2. Atmospheric Turbidity Calculation
3.3.3. Surface Albedo Estimation
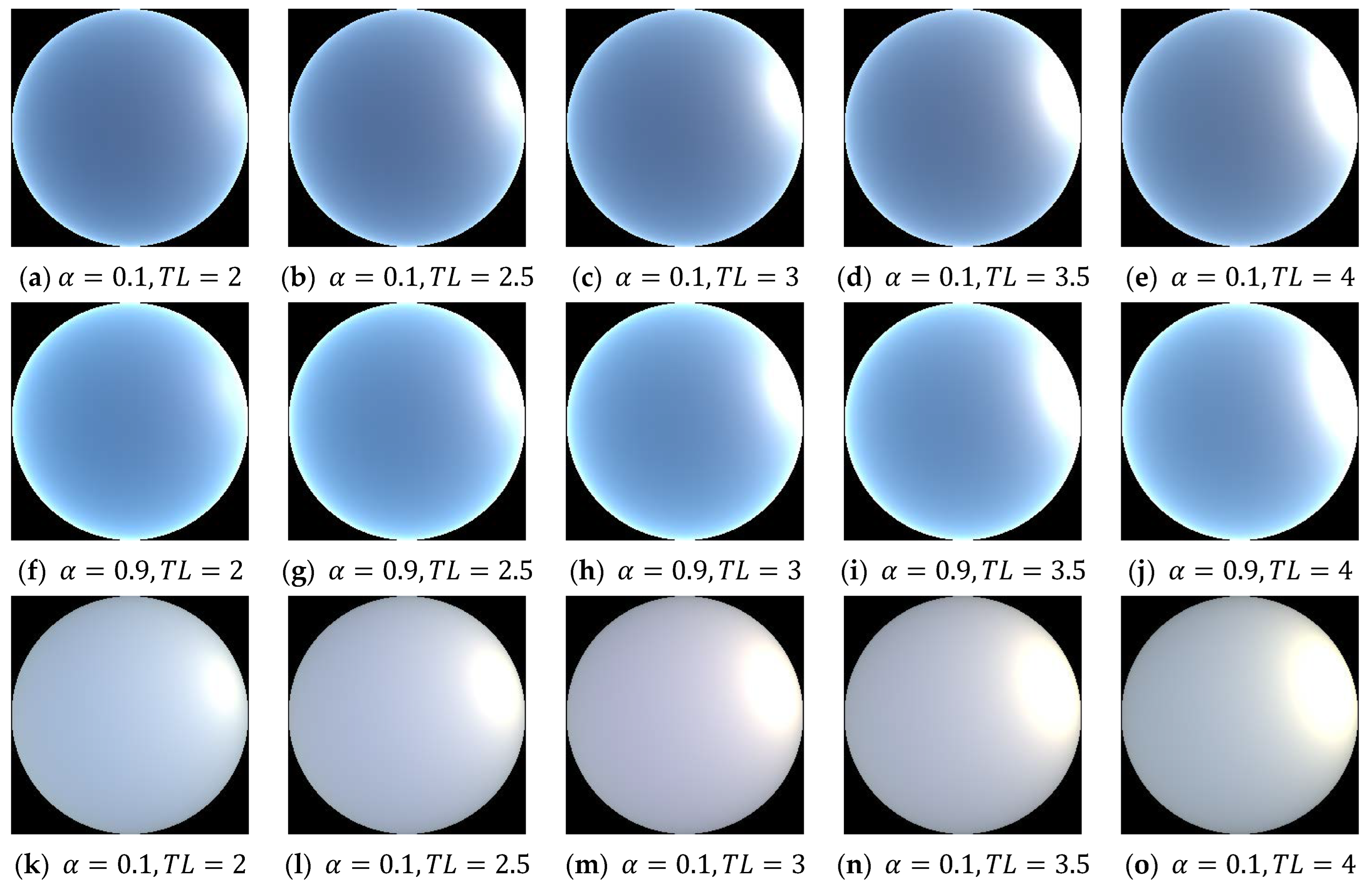
3.3.4. Sky Radiance Model Generation
3.4. Fusion of Real Outdoor Scenes with Virtual 3D Objects
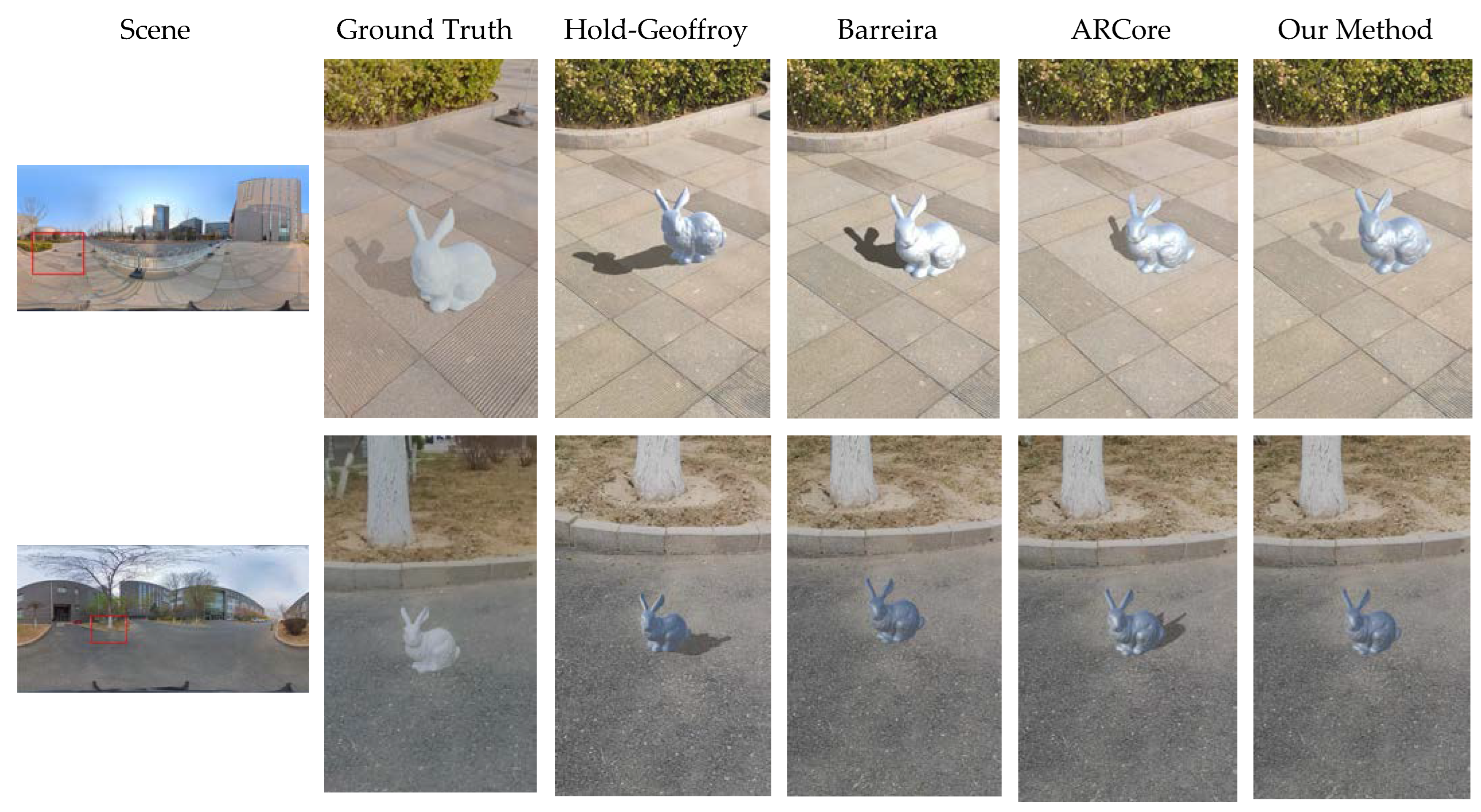
4. Results
4.1. Experiments Setup
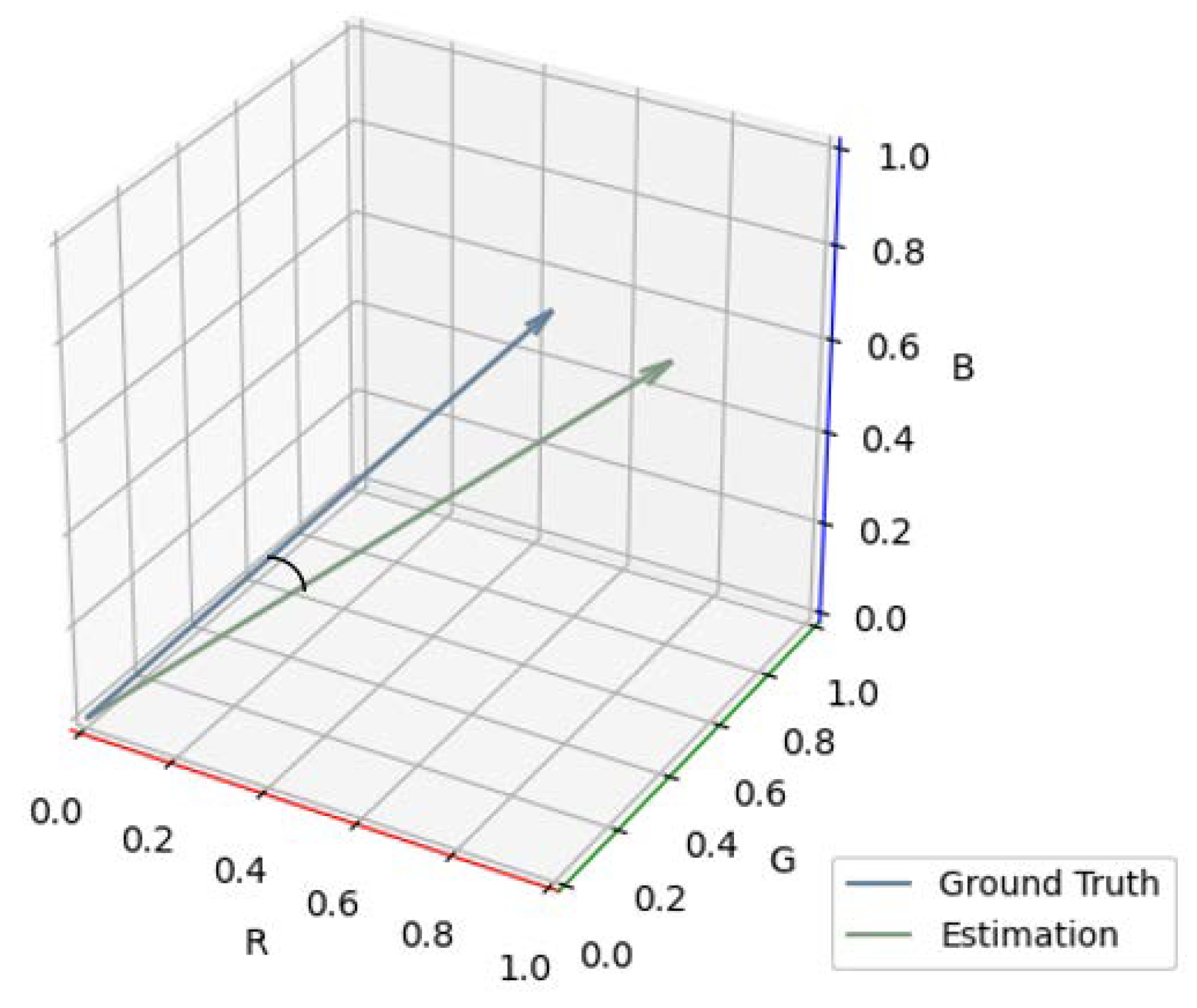
4.2. Evaluation Method and Metric
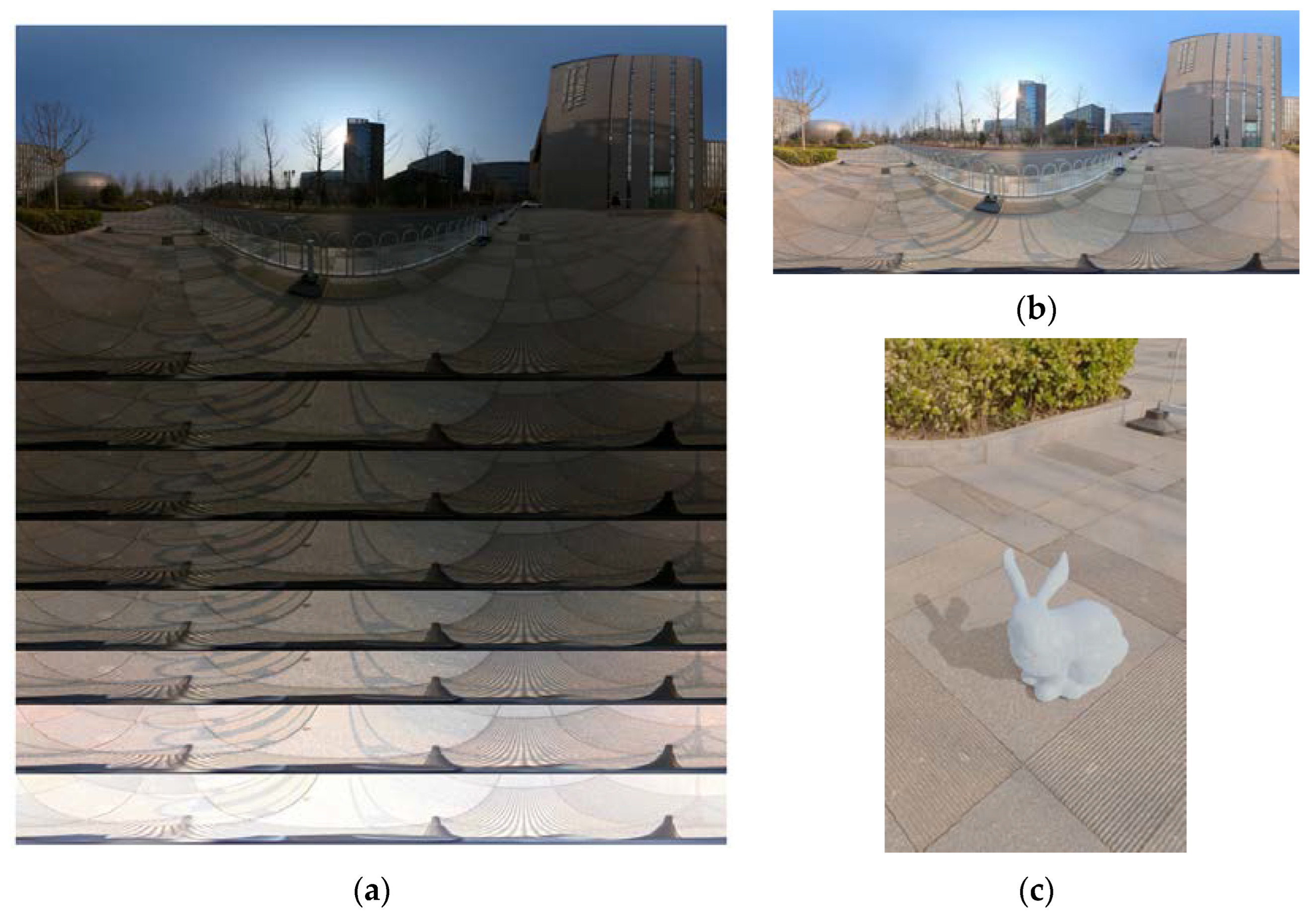
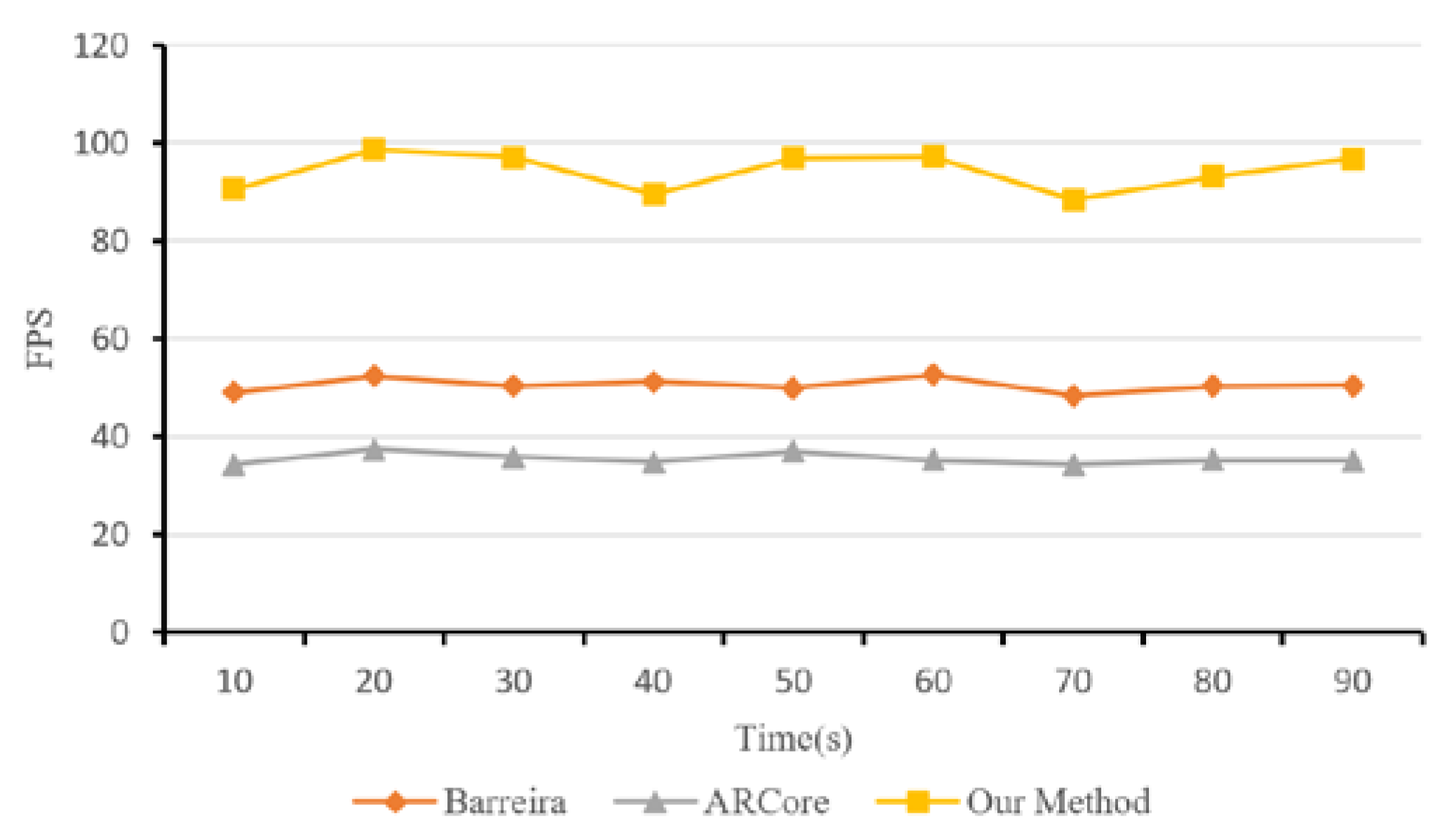
4.3. Experimental Process and Results
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Azuma, R.T. A survey of augmented reality. Presence Teleoper. Virtual Environ. 1997, 6, 355–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guangyun, W.; Zhiping, Z. Realizing Illumination Consistency in Augmented Reality Based on Shadow Detection. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2022, 59, 350–355. [Google Scholar]
- Hagbi, N.; Bergig, O.Y.; Elsana, J.A. Systems and Methods for Tracking Natural Planar Shapes for Augmented Reality Applications. U.S. Patent No. 8,644,551, 15 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; Cheng, C. Application of scene recognition technology based on fast ER and surf algorithm in augmented reality. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Smart and Sustainable City (ICSSC 2017), Shanghai, China, 5–6 June 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, J.; Schöps, T.; Cremers, D. LSD-SLAM: Large-scale direct monocular SLAM. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Proceedings, Part II 13. 2014; pp. 834–849. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Xie, Y.; Gu, S.; Chen, X. A SLAM-based mobile augmented reality tracking registration algorithm. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 2054005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesi, G.; Eichhorn, C.; Plecher, D.A.; Itoh, Y.; Klinker, G. EnvSLAM: Combining SLAM Systems and Neural Networks to Improve the Environment Fusion in AR Applications. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S. An improved augmented-reality framework for differential rendering beyond the Lambertian-world assumption. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2020, 27, 4374–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, Z. DSNet: Deep shadow network for illumination estimation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (VR), Lisboa, Portugal, 27 March–1 April 2021; pp. 179–187. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, M. Multi-sensor data fusion based on fuzzy integral in AR system. In Proceedings of the Advances in Artificial Reality and Tele-Existence: 16th International Conference on Artificial Reality and Telexistence, ICAT 2006, Hangzhou, China, 29 November–1 December 2006; Proceedings. 2006; pp. 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Panagopoulos, A.; Samaras, D.; Paragios, N. Robust shadow and illumination estimation using a mixture model. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 651–658. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Long, C.; Zhang, H.; Yu, H.; Dong, X.; Xiao, C. Arshadowgan: Shadow generative adversarial network for augmented reality in single light scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 8139–8148. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.D.; Lee, K.H. Real time light source estimation using a fish-eye lens with nd filters. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Symposium on Ubiquitous Virtual Reality, Gwangju, Republic of Korea, 10–13 July 2008; pp. 41–42. [Google Scholar]
- Pardel, P.W.; Wojciechowski, K. Three cameras method of light sources extraction in Augmented Reality. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Graphics: International Conference, ICCVG 2010, Warsaw, Poland, 20–22 September 2010; Proceedings, Part II. 2010; pp. 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Gruber, L.; Richter-Trummer, T.; Schmalstieg, D. Real-time photometric registration from arbitrary geometry. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), Altanta, GA, USA, 5–8 November 2012; pp. 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Kawamura, H.; Kojima, A. The hand as a shading probe. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2013 Posters; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Karsch, K.; Hedau, V.; Forsyth, D.; Hoiem, D. Rendering synthetic objects into legacy photographs. ACM Trans. Graph. 2011, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalonde, J.-F.; Efros, A.A.; Narasimhan, S.G. Estimating the natural illumination conditions from a single outdoor image. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2012, 98, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jin, X.; Wang, K. Lighting virtual objects in a single image via coarse scene understanding. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2014, 57, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hold-Geoffroy, Y.; Sunkavalli, K.; Hadap, S.; Gambaretto, E.; Lalonde, J.-F. Deep outdoor illumination estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7312–7321. [Google Scholar]
- Longley, P.A.; Goodchild, M.F.; Maguire, D.J.; Rhind, D.W. Geographic Information Systems and Science; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Jiddi, S.; Robert, P.; Marchand, E. Reflectance and Illumination Estimation for Realistic Augmentations of Real Scenes. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR-Adjunct), Merida, Mexico, 19–23 September 2016; pp. 244–249. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, P.P.; Mildenhall, B.; Tancik, M.; Barron, J.T.; Tucker, R.; Snavely, N. Lighthouse: Predicting Lighting Volumes for Spatially-Coherent Illumination. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 8077–8086. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Jin, X.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; Sun, H. Outdoor illumination estimation via all convolutional neural networks. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 90, 106987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Philion, J.; Fidler, S.; Kautz, J. Learning Indoor Inverse Rendering with 3D Spatially-Varying Lighting. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, BC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 12518–12527. [Google Scholar]
- Jeansoulin, R. Multi-source geo-information fusion in transition: A summer 2019 snapshot. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreira, J.; Bessa, M.; Barbosa, L.; Magalhães, L. A context-aware method for authentically simulating outdoors shadows for mobile augmented reality. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2017, 24, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preetham, A.J.; Shirley, P.; Smits, B. A practical analytic model for daylight. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 8–13 August 1999; pp. 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Hosek, L.; Wilkie, A. An analytic model for full spectral sky-dome radiance. ACM Trans. Graph. 2012, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rabbany, A. Introduction to GPS: The Global Positioning System; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Reda, I.; Andreas, A. Solar position algorithm for solar radiation applications. Sol. Energy 2004, 76, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linke, F. Transmission-koeffizient und trubungsfaktor. Beitr. Phys. Atomos. 1992, 10, 91–103. [Google Scholar]
- Kasten, F. The Linke turbidity factor based on improved values of the integral Rayleigh optical thickness. Sol. Energy 1996, 56, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasten, F. A new table and approximation formula for the relative optial air mass. Arch. Für Meteorol. Geophys. Und Bioklimatol. Ser. B 1965, 14, 206–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molineaux, B.t.; Ineichen, P.; O’Neill, N. Equivalence of pyrheliometric and monochromatic aerosol optical depths at a single key wavelength. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 7008–7018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behar, O.; Sbarbaro, D.; Marzo, A.; Moran, L. A simplified methodology to estimate solar irradiance and atmospheric turbidity from ambient temperature and relative humidity. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 116, 109310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S. Narrowband to broadband conversions of land surface albedo I: Algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 76, 213–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, R.; Hulstrom, R. A Simplified Clear Sky Model for Direct and Diffuse Insolation on Horizontal Surfaces; No. SERI/TR-642-761; Solar Energy Research Institute: Golden, CO, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- LeGendre, C.; Ma, W.-C.; Fyffe, G.; Flynn, J.; Charbonnel, L.; Busch, J.; Debevec, P. Deeplight: Learning illumination for unconstrained mobile mixed reality. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5918–5928. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, F.; Zhang, C.; Yu, Y.; Chang, Y.; Lu, S.; Ma, F.; Xie, X. Emlight: Lighting estimation via spherical distribution approximation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, 2–9 February 2021; pp. 3287–3295. [Google Scholar]
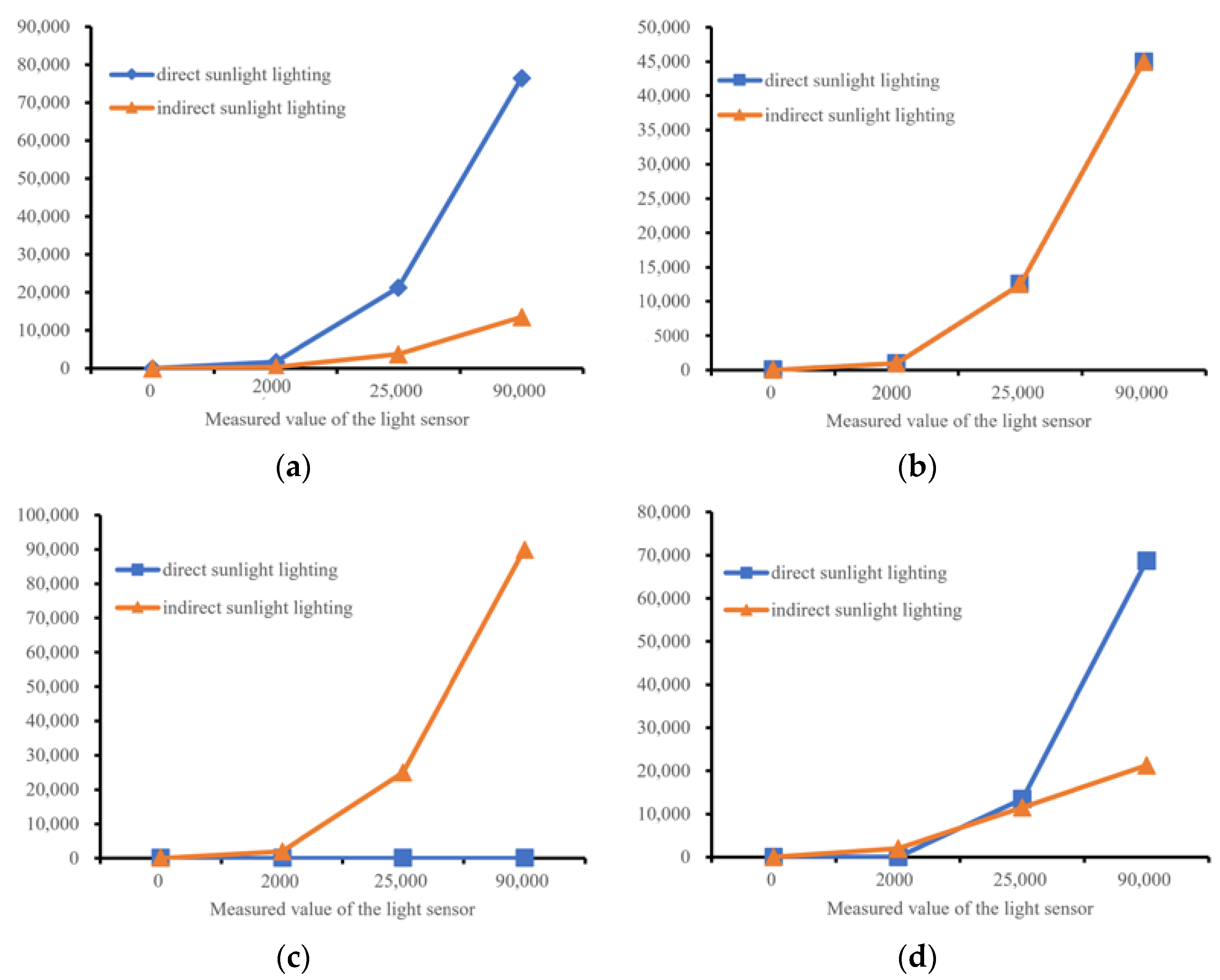

| Lighting Estimation Technology | Advantage | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Based on marker information | Able to accurately estimate lighting information. | Markers or objects need to be set up in advance in the scene. |
| Based on auxiliary equipment | No markers or prior information are needed to be prepared in advance. Lighting information can be estimated in real-time. | Specialized equipment is required to collect information, which makes it difficult to use on mobile devices. |
| Based on image analysis | Lighting estimation can be achieved solely using images without the need for additional specialized equipment. | High image quality is required, and a large amount of computation is needed, which makes it difficult to meet the real-time requirements of AR systems. |
| Data Name | Data Type | Data Source |
|---|---|---|
| GPS data | Text | Mobile device |
| Administrative division data | Vector | GADM (Database of Global Administrative Areas) |
| Surface reflectance data | Raster | Google Earth Engine |
| Meteorological data | Text | China National Meteorological Center |
| ISO | Shutter | ISO | Shutter | ISO | Shutter | ISO | Shutter | ISO | Shutter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 1/8000 | 100 | 1/3200 | 100 | 1/1250 | 100 | 1/500 | 100 | 1/200 |
| 1/6400 | 1/2500 | 1/1000 | 1/400 | 1/160 | |||||
| 1/5000 | 1/2000 | 1/800 | 1/320 | 1/120 | |||||
| 1/4000 | 1/1600 | 1/640 | 1/240 | 1/100 |
| Hold-Geoffroy et al. | Barreira et al. | ARCore | Our Method | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 11.1855 | 13.52 | 10.6263 | 10.6547 |
| AE | 0.5208 | 0.5826 | 0.4285 | 0.4927 |
| SAE | 23.8 | 7.3 | 20.3 | 5.2 |
| FPS | — | 50.52 | 35.48 | 94.26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, K.; Liu, S.; Sun, W.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, Y. A Lighting Consistency Technique for Outdoor Augmented Reality Systems Based on Multi-Source Geo-Information. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12080324
Zhu K, Liu S, Sun W, Yuan Y, Wu Y. A Lighting Consistency Technique for Outdoor Augmented Reality Systems Based on Multi-Source Geo-Information. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2023; 12(8):324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12080324
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Kunpeng, Shuo Liu, Weichao Sun, Yixin Yuan, and Yuang Wu. 2023. "A Lighting Consistency Technique for Outdoor Augmented Reality Systems Based on Multi-Source Geo-Information" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 12, no. 8: 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12080324
APA StyleZhu, K., Liu, S., Sun, W., Yuan, Y., & Wu, Y. (2023). A Lighting Consistency Technique for Outdoor Augmented Reality Systems Based on Multi-Source Geo-Information. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 12(8), 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12080324





