Automatic Positioning of Street Objects Based on Self-Adaptive Constrained Line of Bearing from Street-View Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
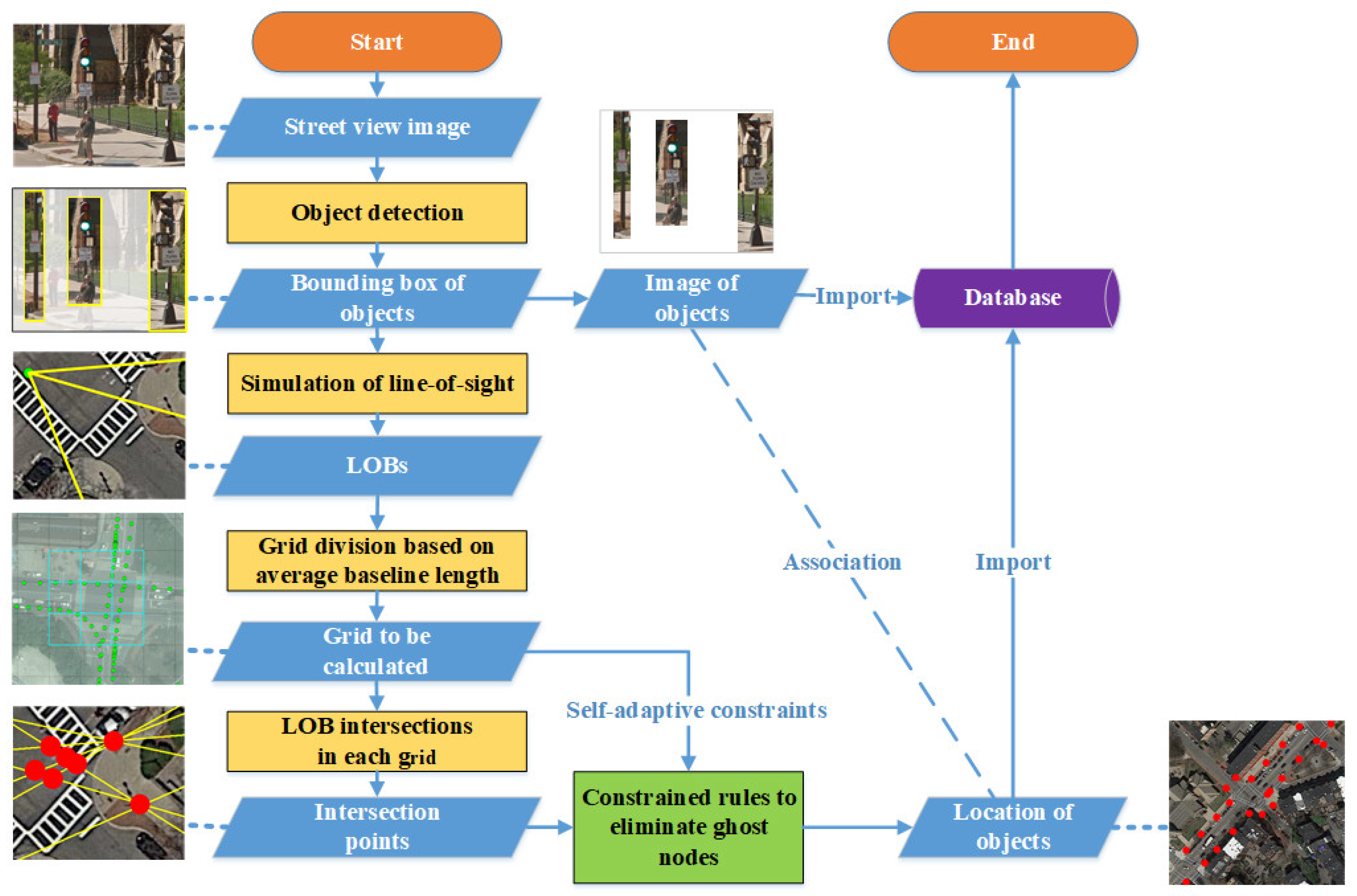
2. Methodology
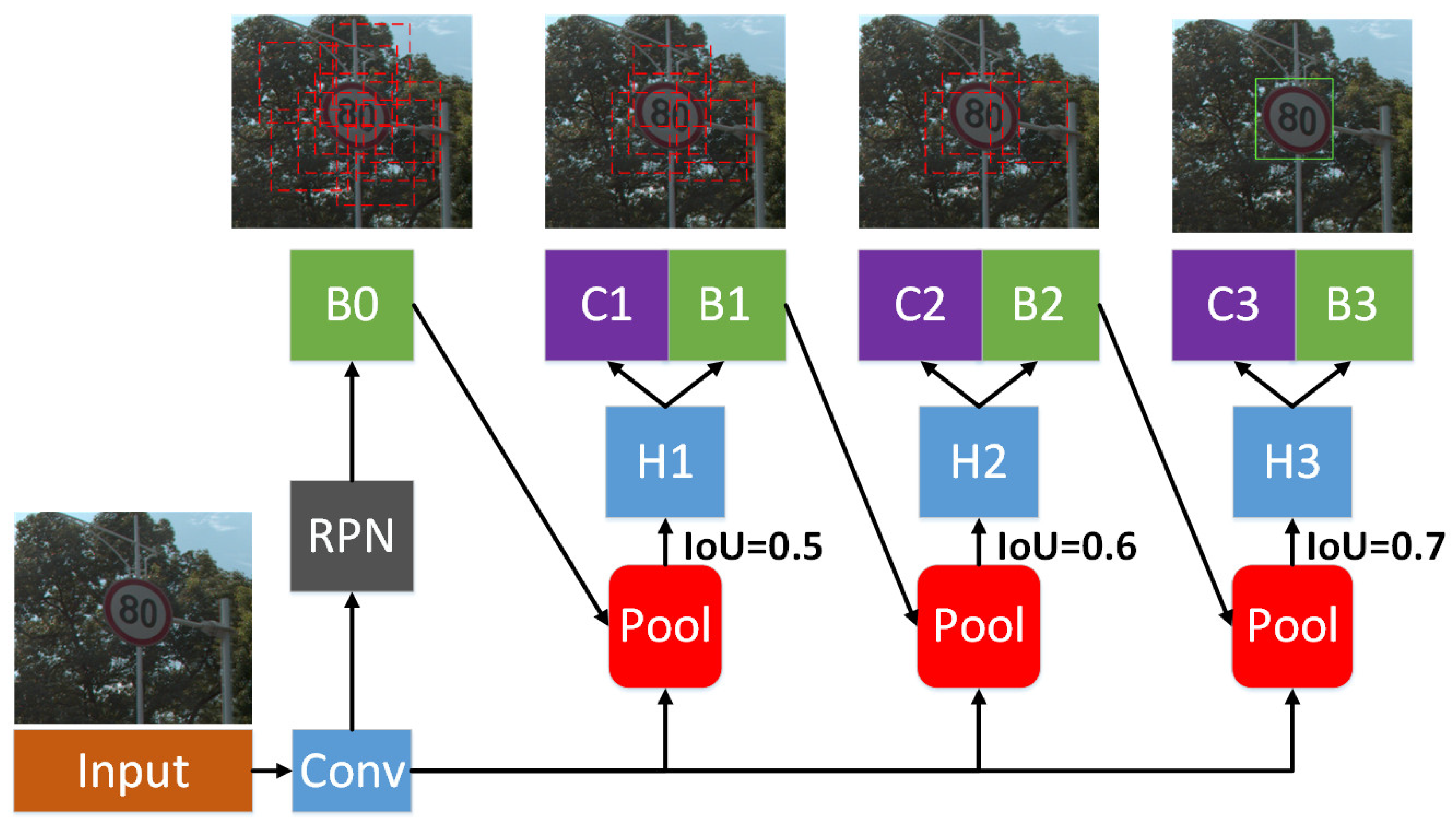
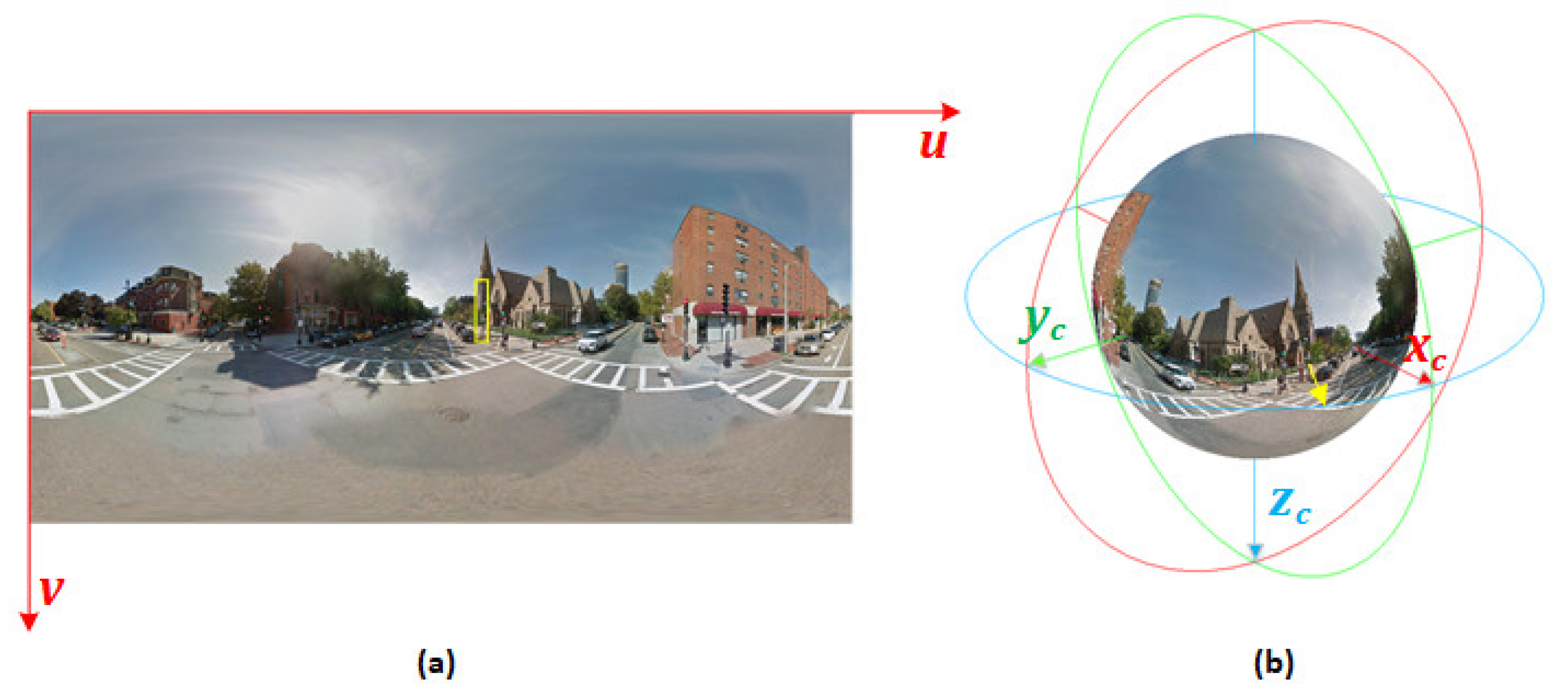
2.1. LOB Mapping Based on Object-Detection Results
2.2. Geographic Positioning Based on Self-Adaptive Constrained LOB
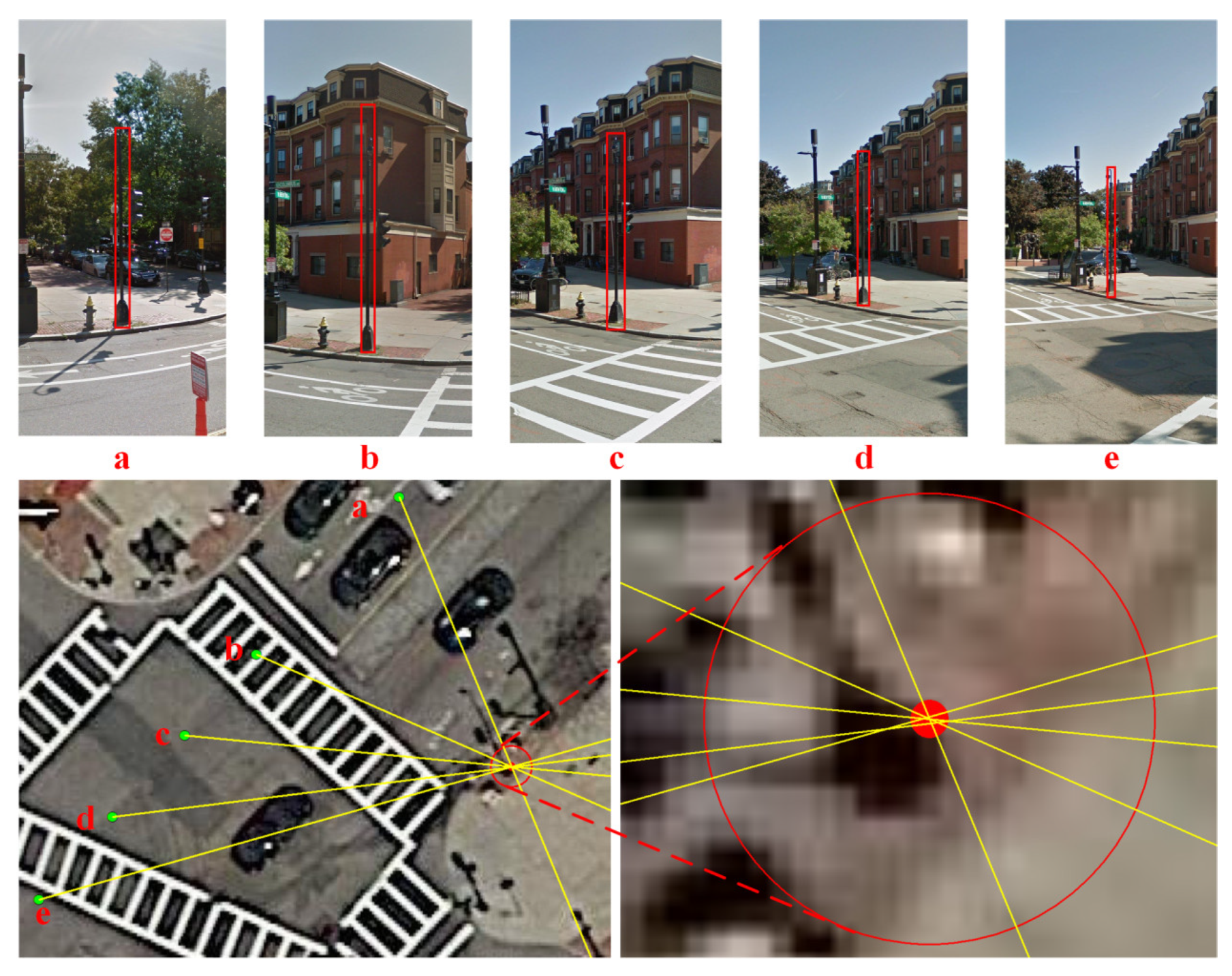
2.2.1. LOB Measurement
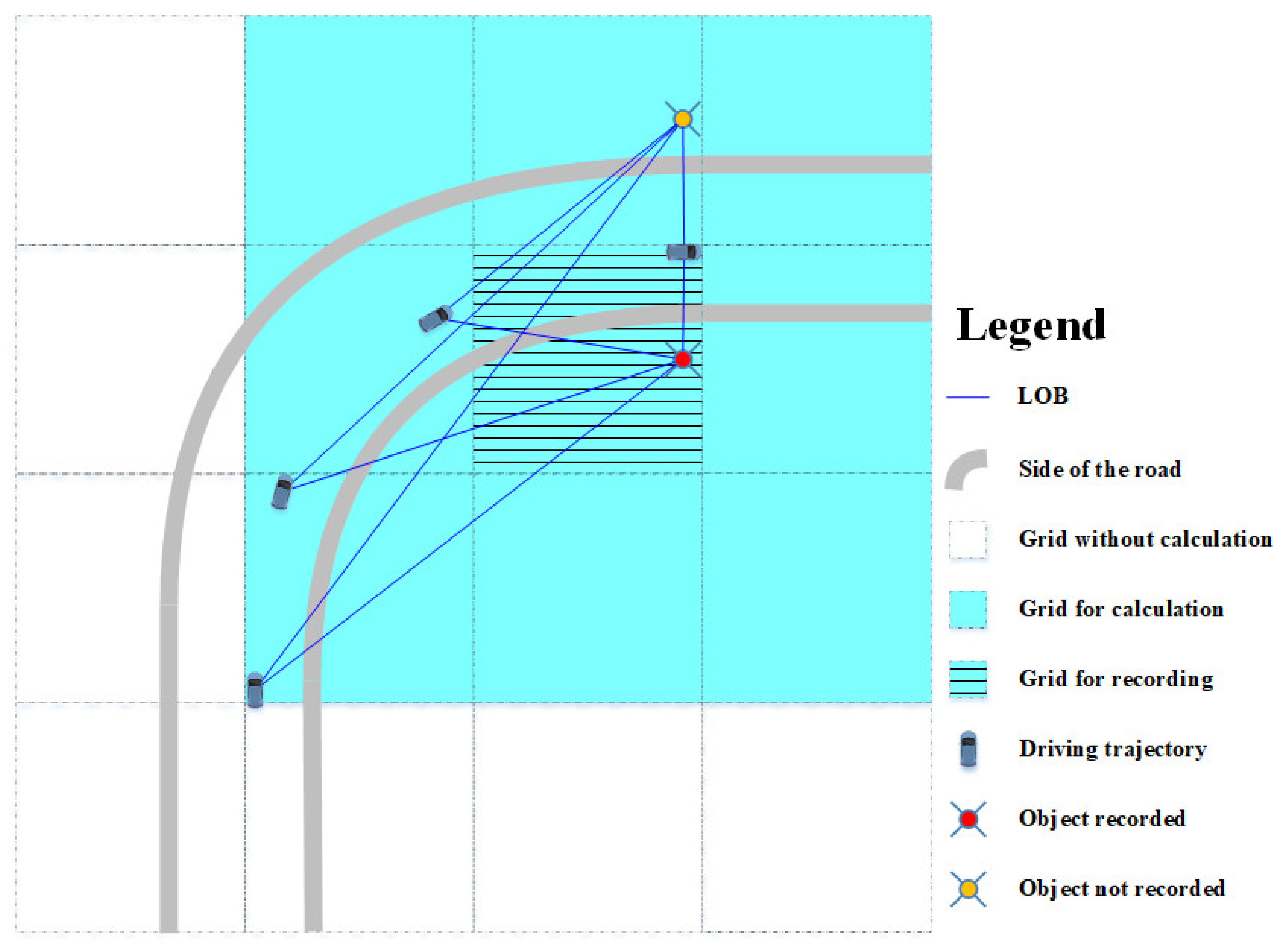
2.2.2. Division of Grid
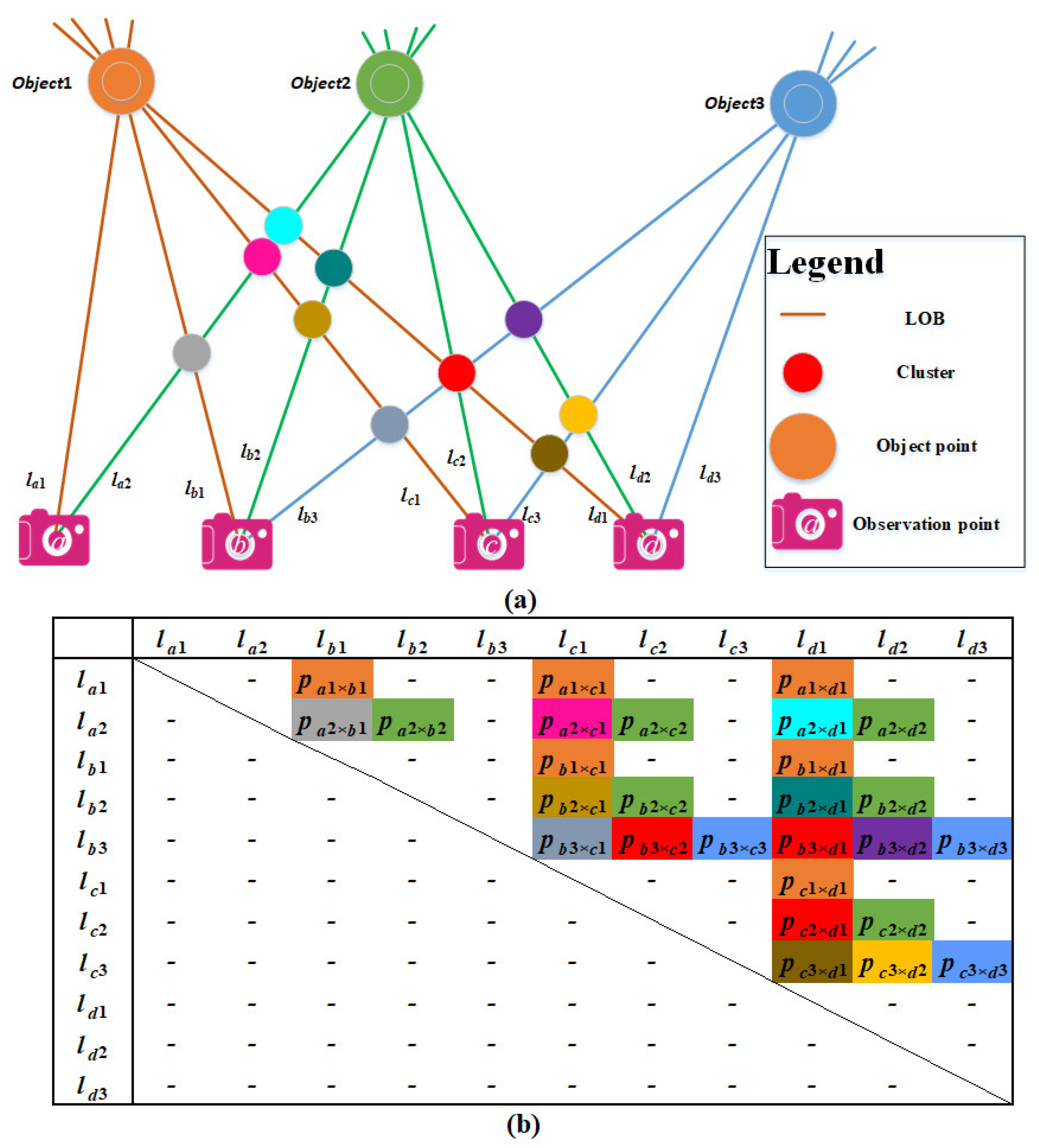
2.2.3. Relationship Matrix Construction
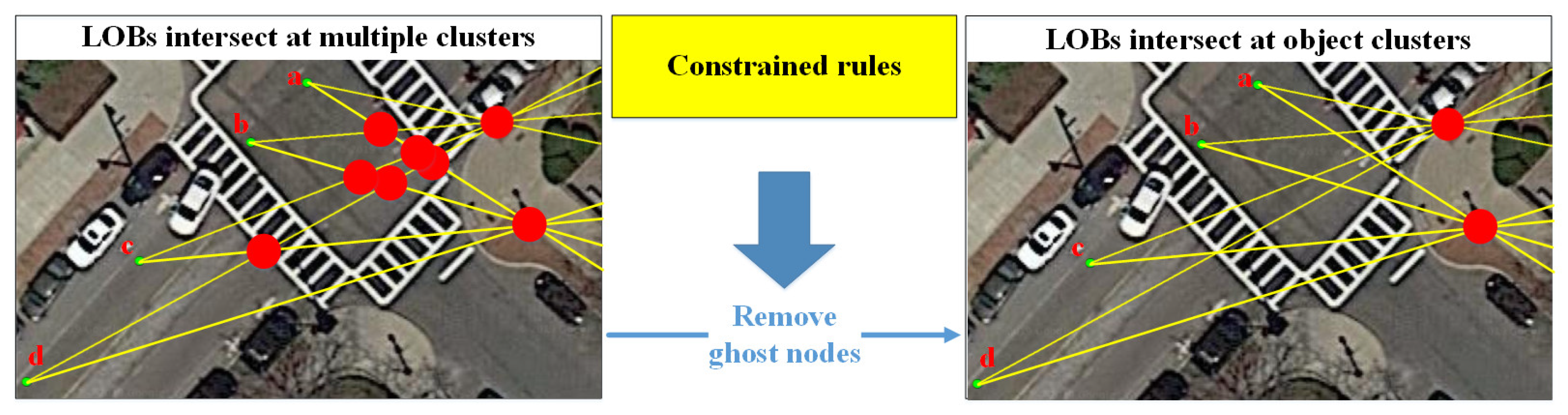
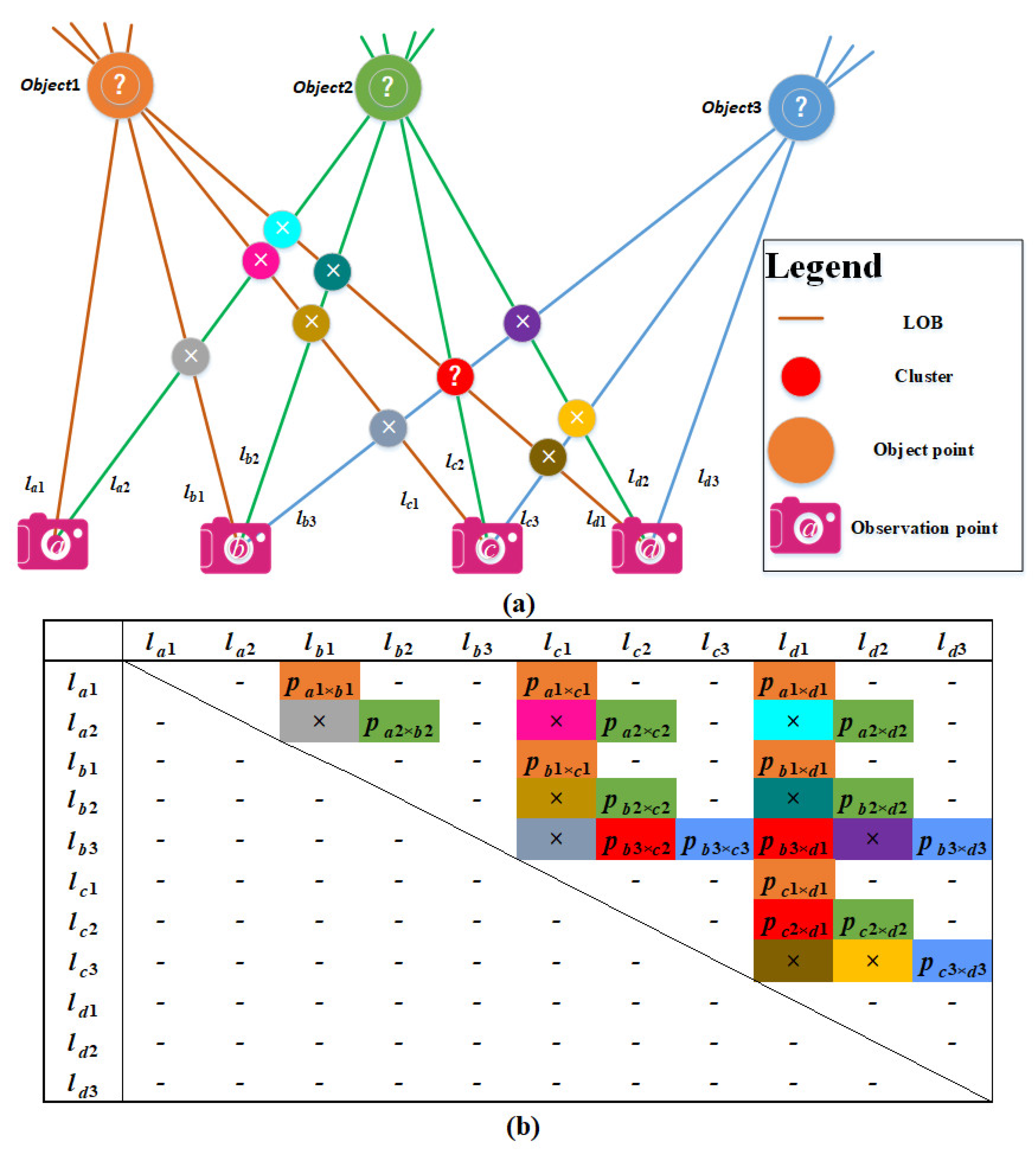
2.2.4. Elimination of Ghost Nodes Based on Constrained Rules
- 1.
- Constrained rules based on the minimum number of intersections in the cluster
- 2.
- Constrained rules based on the uniqueness of LOB association
3. Experimental Results and Discussions
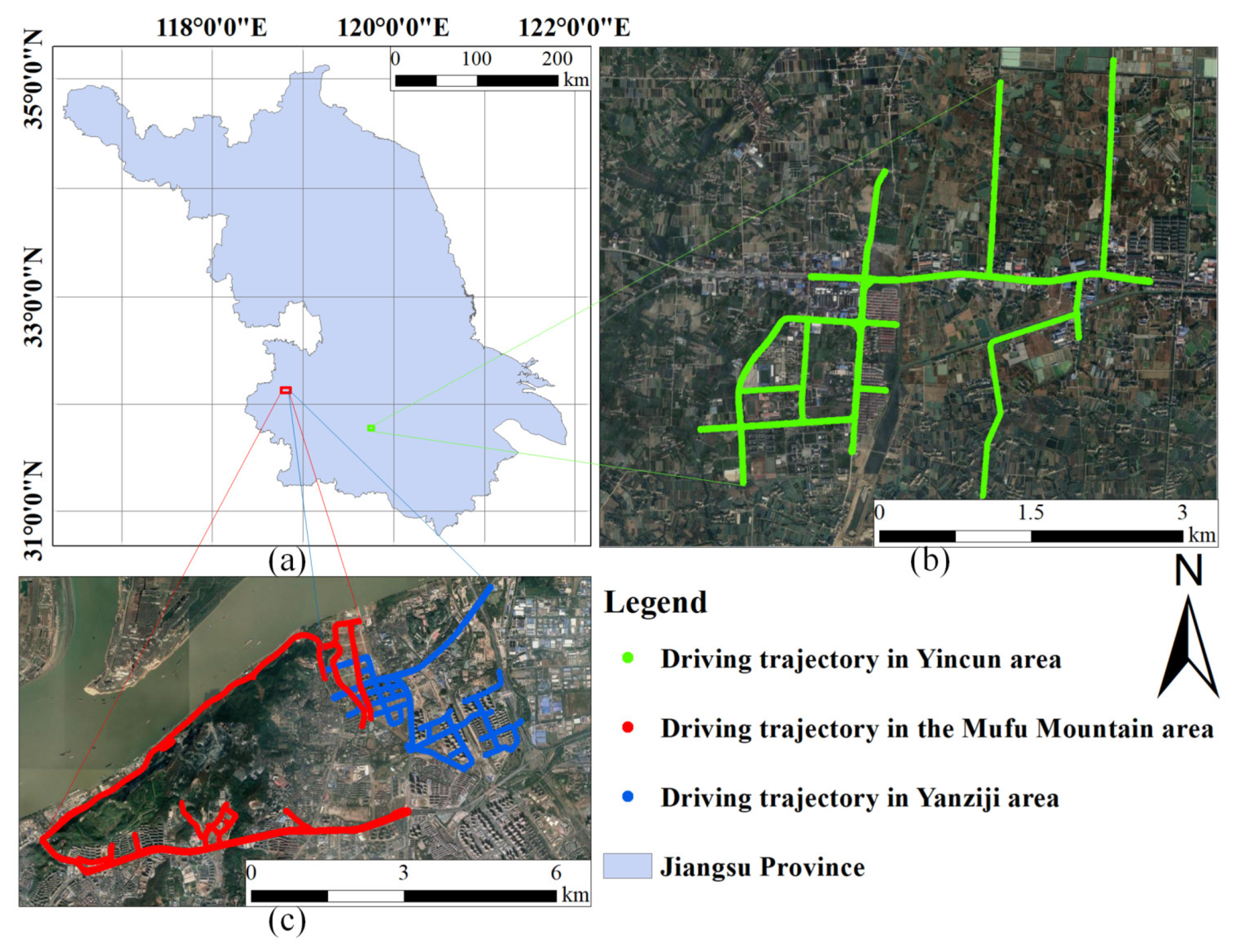
3.1. Data Collection and Selection of Research Area
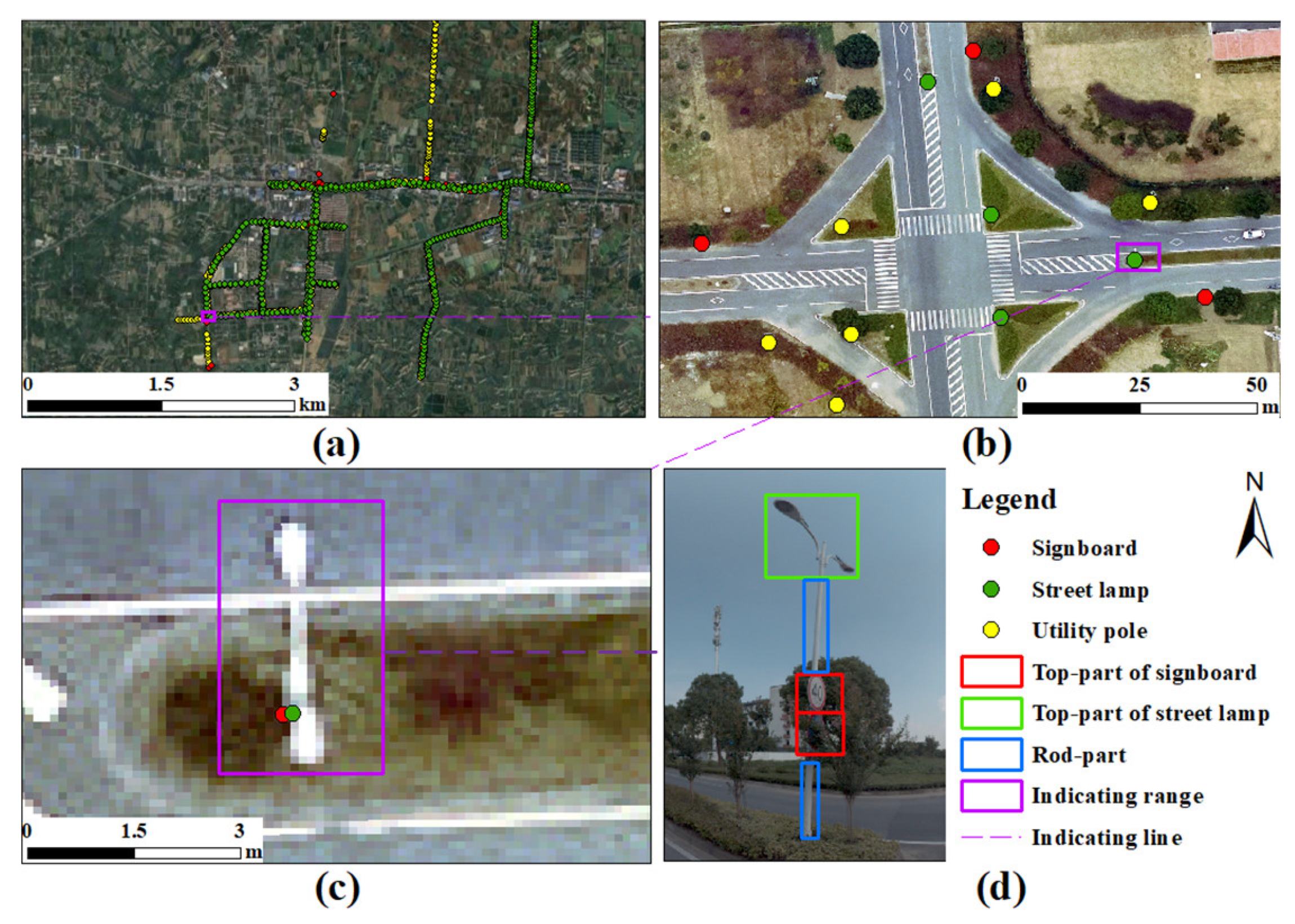
3.2. Object Detection and LOB Mapping
3.3. Geographic Positioning Based on Self-Adaptive Constrained LOB
3.4. Comparative Analysis and Discussions with Existing Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Escalera, A.D.L.; Armingol, J.M.; Mata, M. Traffic sign recognition and analysis for intelligent vehicles. Image Vis. Comput. 2003, 21, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, C.Z.; Kidono, K.; Meguro, J.; Kojima, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Naito, T. A low-cost solution for automatic lane-level map generation using conventional in-car sensors. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 17, 2355–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadmanesh, M.; Cross, C.; Mashhadi, A.H.; Rashidi, A.; Wempen, J. Highway Asset and Pavement Condition Management using Mobile Photogrammetry. Transp. Res. Record. 2021, 2675, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafiso, S.; Di Graziano, A.; Pappalardo, G. Safety Inspection and Management Tools for Low-Volume Road Network. Transp. Res. Record. 2015, 2472, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ding, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, C.; Su, Y. A multinomial logit model: Safety risk analysis of interchange area based on aggregate driving behavior data. J. Saf. Res. 2022, 80, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.G.; Han, D.Y.; Yu, K.Y.; Kim, Y.; Rhee, S.M. Efficient extraction of road information for car navigation applications using road pavement markings obtained from aerial images. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2006, 33, 1320–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, M.; Easa, S.M. Extracting streetlight poles from orthophotos: Methodology and case study in Ontario, Canada. J. Surv. Eng. 2007, 133, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.H.; Sohn, H.G.; Song, Y.S. Road infrastructure data acquisition using a vehicle-based mobile mapping system. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2010, 21, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente, I.; González-Jorge, H.; Martínez-Sánchez, J.; Arias, P. Review of mobile mapping and surveying technologies. Measurement 2013, 46, 2127–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, J.D.; Branson, S.; Hall, D.; Schindler, K.; Perona, P. Cataloging public objects using aerial and street-level images—Urban trees. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Tang, X.; Xie, J.; Gao, X.; Zhao, W.; Mo, F.; Zhang, G. Deep-learning and depth-map based approach for detection and 3D localization of small traffic signs. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 2096–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Yan, Y.; Shen, C.; Wang, H. Real-time high-performance semantic image segmentation of urban street scenes. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 3258–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Xiao, G. Real-time chinese traffic warning signs recognition based on cascade and CNN. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2020, 18, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofte, R.; Van Gool, L. Multi-view manhole detection, recognition, and 3D localisation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV Workshops), Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bayoudh, K.; Hamdaoui, F.; Mtibaa, A. Transfer learning based hybrid 2D-3D CNN for traffic sign recognition and semantic road detection applied in advanced driver assistance systems. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 124–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, V.J.D.; Chang, C.-T. Feature position on Google street view panoramas. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2012, 4, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nassar, A.S.; Lang, N.; Lefèvre, S.; Wegner, J.D. Learning geometric soft constraints for multi-view instance matching across street-level panoramas. In Proceedings of the 2019 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE), Vannes, France, 22–24 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa, M.; Aizawa, K. Identification of Buildings In Street Images Using Map Information. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, Taiwan, China, 22–25 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Yang, T.; Chen, C. Revisiting Street-to-Aerial View Image Geo-localization and Orientation Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nassar, A.S.; D’Aronco, S.; Lefèvre, S.; Wegner, J.D. GeoGraph: Graph-based multi-view object detection with geometric cues End-to-End. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Krylov, V.A.; Kenny, E.; Dahyot, R. Automatic discovery and geotagging of objects from street view imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hebbalaguppe, R.; Garg, G.; Hassan, E.; Ghosh, H.; Verma, A. Telecom inventory management via object recognition and localisation on Google street view images. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Santa Rosa, CA, USA, 24–31 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pattipati, K.R.; Deb, S.; Bar-Shalom, Y.; Washburn, R.B. A new relaxation algorithm and passive sensor data association. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1992, 37, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, A.N.; Pathirana, P.N. Localization of emitters via the intersection of bearing lines: A ghost elimination approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2007, 56, 3106–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, J.D.; Silva, C.R.C.M.D.; Buehrer, R.M. Multiple-source localization using line-of-bearing measurements: Approaches to the data association problem. In Proceedings of the MILCOM 2008—2008 IEEE Military Communications Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 16–19 November 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, L.; Chen, W. Correction of Mobile Positioning and Direction via CNNs Based on Street View Images. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Taiwan (ICCE-TW), Taichung, Taiwan, China, 19–21 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hazelhoff, L.; Creusen, I.; de With, P.H. System for semi-automated surveying of street-lighting poles from street-level panoramic images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Steamboat Springs, CO, USA, 24–26 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hazelhoff, L.; Creusen, I.; de With, P.H. Robust detection, classification and positioning of traffic signs from street-level panoramic images for inventory purposes. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Workshop on the Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Breckenridge, CO, USA, 9–11 January 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lumnitz, S.; Devisscher, T.; Mayaud, J.R.; Radic, V.; Coops, N.C.; Griess, V.C. Mapping trees along urban street networks with deep learning and street-level imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 175, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Witharana, C.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Parent, J. Using deep learning to identify utility poles with crossarms and estimate their locations from google street view images. Sensors 2018, 18, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.; Asim, W.; Ulhaq, A.; Ghazi, B.; Robinson, R.W. Health assessment of eucalyptus trees using siamese network from Google street and ground truth images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soheilian, B.; Paparoditis, N.; Vallet, B. Detection and 3D reconstruction of traffic signs from multiple view color images. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 77, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofte, R.; Zimmermann, K.; Van Gool, L. Multi-view traffic sign detection, recognition, and 3D localisation. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2014, 25, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Vasconcelos, N. Cascade R-CNN: Delving into high quality object detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, N.; Roncella, R. Accuracy Assessment of 3d Models Generated from Google Street View Imagery. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-2/W9, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, V.J.D.; Chang, C.T. Three-dimensional positioning from Google street view panoramas. IET Image Process. 2013, 7, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alpha 3D Vehicle-mounted Laser Scanning Measurement System. Available online: http://www.huace.cn/product/product_show1/431 (accessed on 19 February 2022).


| k-Effective Viewing Distance (m) | Threshold of Cluster Distance (m) | Time Consumption (s) | Estimated Number of Poles | Recall Rate | Precision Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2–40.81 | 0.1 | 6.36 | 1509 | 0.88 | 0.97 |
| 0.2 | 5.66 | 1393 | 0.92 | 0.97 | |
| 0.3 | 5.18 | 1374 | 0.92 | 0.97 | |
| 0.4 | 5.14 | 1357 | 0.91 | 0.97 | |
| 0.5 | 4.99 | 1344 | 0.9 | 0.97 | |
| 0.6 | 5.05 | 1342 | 0.9 | 0.96 | |
| 0.7 | 5.58 | 1321 | 0.89 | 0.96 | |
| 0.8 | 5.25 | 1328 | 0.89 | 0.96 | |
| 0.9 | 5.65 | 1319 | 0.88 | 0.96 | |
| 1 | 5.36 | 1316 | 0.88 | 0.95 | |
| 3–61.22 | 0.1 | 5.79 | 1608 | 0.92 | 0.97 |
| 0.2 | 5.57 | 1420 | 0.93 | 0.97 | |
| 0.3 | 6.08 | 1400 | 0.93 | 0.97 | |
| 0.4 | 5.31 | 1388 | 0.93 | 0.96 | |
| 0.5 | 5.22 | 1367 | 0.92 | 0.96 | |
| 0.6 | 5.18 | 1369 | 0.91 | 0.96 | |
| 0.7 | 5.12 | 1343 | 0.9 | 0.96 | |
| 0.8 | 5.09 | 1350 | 0.9 | 0.95 | |
| 0.9 | 5.47 | 1346 | 0.89 | 0.95 | |
| 1 | 5.19 | 1337 | 0.89 | 0.95 | |
| 4–81.63 | 0.1 | 8.51 | 1617 | 0.92 | 0.96 |
| 0.2 | 8.03 | 1422 | 0.93 | 0.96 | |
| 0.3 | 8.05 | 1401 | 0.93 | 0.96 | |
| 0.4 | 7.50 | 1393 | 0.93 | 0.96 | |
| 0.5 | 7.55 | 1364 | 0.91 | 0.96 | |
| 0.6 | 7.39 | 1373 | 0.91 | 0.95 | |
| 0.7 | 7.19 | 1356 | 0.9 | 0.95 | |
| 0.8 | 7.38 | 1365 | 0.9 | 0.94 | |
| 0.9 | 6.95 | 1360 | 0.89 | 0.94 | |
| 1 | 6.76 | 1346 | 0.89 | 0.94 | |
| 5–102.04 | 0.1 | 13.01 | 1618 | 0.91 | 0.96 |
| 0.2 | 11.86 | 1424 | 0.93 | 0.96 | |
| 0.3 | 11.43 | 1402 | 0.93 | 0.96 | |
| 0.4 | 11.28 | 1384 | 0.92 | 0.96 | |
| 0.5 | 11.18 | 1360 | 0.91 | 0.96 | |
| 0.6 | 10.74 | 1355 | 0.9 | 0.96 | |
| 0.7 | 10.44 | 1345 | 0.9 | 0.95 | |
| 0.8 | 10.04 | 1356 | 0.89 | 0.94 | |
| 0.9 | 9.95 | 1354 | 0.88 | 0.93 | |
| 1 | 9.74 | 1359 | 0.88 | 0.92 |
| Number of Views | Threshold of Angle (°) | Threshold of Distance to Center of Selected Road (m) | Time Consumption (s) | Estimated Number of Poles | Recall Rate | Precision Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 1 | 10 | 5.20 | 1318 | 0.83 | 0.9 |
| 15 | 5.20 | 1442 | 0.9 | 0.89 | ||
| 20 | 5.28 | 1465 | 0.91 | 0.88 | ||
| 2 | 10 | 5.82 | 1452 | 0.85 | 0.84 | |
| 15 | 5.79 | 1604 | 0.92 | 0.83 | ||
| 20 | 5.57 | 1637 | 0.92 | 0.81 | ||
| 3 | 10 | 5.68 | 1579 | 0.85 | 0.78 | |
| 15 | 5.85 | 1760 | 0.92 | 0.76 | ||
| 20 | 7.19 | 1808 | 0.93 | 0.75 | ||
| 4 | 1 | 10 | 6.65 | 1358 | 0.83 | 0.87 |
| 15 | 7.27 | 1498 | 0.9 | 0.86 | ||
| 20 | 7.15 | 1538 | 0.91 | 0.84 | ||
| 2 | 10 | 6.82 | 1522 | 0.85 | 0.81 | |
| 15 | 7.84 | 1699 | 0.92 | 0.78 | ||
| 20 | 7.34 | 1755 | 0.93 | 0.76 | ||
| 3 | 10 | 7.33 | 1696 | 0.85 | 0.74 | |
| 15 | 8.36 | 1917 | 0.93 | 0.71 | ||
| 20 | 8.61 | 1994 | 0.93 | 0.69 | ||
| 5 | 1 | 10 | 6.86 | 1387 | 0.84 | 0.86 |
| 15 | 8.08 | 1547 | 0.91 | 0.84 | ||
| 20 | 8.03 | 1593 | 0.91 | 0.82 | ||
| 2 | 10 | 8.27 | 1575 | 0.85 | 0.79 | |
| 15 | 9.78 | 1788 | 0.92 | 0.75 | ||
| 20 | 9.62 | 1862 | 0.93 | 0.72 | ||
| 3 | 10 | 9.30 | 1773 | 0.86 | 0.71 | |
| 15 | 10.83 | 2051 | 0.93 | 0.67 | ||
| 20 | 11.53 | 2161 | 0.93 | 0.64 | ||
| 6 | 1 | 10 | 8.35 | 1416 | 0.84 | 0.85 |
| 15 | 9.56 | 1590 | 0.91 | 0.82 | ||
| 20 | 9.50 | 1651 | 0.91 | 0.79 | ||
| 2 | 10 | 9.87 | 1625 | 0.85 | 0.76 | |
| 15 | 11.16 | 1872 | 0.92 | 0.72 | ||
| 20 | 11.69 | 1981 | 0.93 | 0.68 | ||
| 3 | 10 | 11.03 | 1844 | 0.86 | 0.69 | |
| 15 | 13.78 | 2182 | 0.93 | 0.63 | ||
| 20 | 14.29 | 2342 | 0.94 | 0.59 | ||
| 7 | 1 | 10 | 8.94 | 1447 | 0.84 | 0.83 |
| 15 | 10.33 | 1649 | 0.91 | 0.79 | ||
| 20 | 11.45 | 1738 | 0.91 | 0.75 | ||
| 2 | 10 | 11.59 | 1670 | 0.85 | 0.74 | |
| 15 | 14.13 | 1964 | 0.92 | 0.68 | ||
| 20 | 15.01 | 2131 | 0.93 | 0.63 | ||
| 3 | 10 | 13.89 | 1914 | 0.86 | 0.66 | |
| 15 | 17.95 | 2321 | 0.93 | 0.59 | ||
| 20 | 20.04 | 2564 | 0.94 | 0.54 | ||
| 8 | 1 | 10 | 10.70 | 1467 | 0.84 | 0.82 |
| 15 | 12.41 | 1709 | 0.91 | 0.76 | ||
| 20 | 13.46 | 1838 | 0.91 | 0.71 | ||
| 2 | 10 | 13.14 | 1704 | 0.85 | 0.73 | |
| 15 | 17.11 | 2064 | 0.92 | 0.65 | ||
| 20 | 18.54 | 2290 | 0.93 | 0.59 | ||
| 3 | 10 | 15.86 | 1966 | 0.86 | 0.64 | |
| 15 | 22.78 | 2465 | 0.93 | 0.56 | ||
| 20 | 24.29 | 2804 | 0.94 | 0.49 | ||
| 9 | 1 | 10 | 11.65 | 1487 | 0.84 | 0.81 |
| 15 | 14.55 | 1761 | 0.91 | 0.74 | ||
| 20 | 16.09 | 1919 | 0.91 | 0.68 | ||
| 2 | 10 | 15.05 | 1736 | 0.85 | 0.71 | |
| 15 | 20.37 | 2150 | 0.92 | 0.62 | ||
| 20 | 22.99 | 2422 | 0.93 | 0.56 | ||
| 3 | 10 | 19.08 | 2016 | 0.86 | 0.63 | |
| 15 | 26.94 | 2608 | 0.93 | 0.53 | ||
| 20 | 31.65 | 3026 | 0.94 | 0.46 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Lu, X.; Lin, B.; Zhou, L.; Lv, G. Automatic Positioning of Street Objects Based on Self-Adaptive Constrained Line of Bearing from Street-View Images. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11040253
Li G, Lu X, Lin B, Zhou L, Lv G. Automatic Positioning of Street Objects Based on Self-Adaptive Constrained Line of Bearing from Street-View Images. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2022; 11(4):253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11040253
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guannan, Xiu Lu, Bingxian Lin, Liangchen Zhou, and Guonian Lv. 2022. "Automatic Positioning of Street Objects Based on Self-Adaptive Constrained Line of Bearing from Street-View Images" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 11, no. 4: 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11040253
APA StyleLi, G., Lu, X., Lin, B., Zhou, L., & Lv, G. (2022). Automatic Positioning of Street Objects Based on Self-Adaptive Constrained Line of Bearing from Street-View Images. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 11(4), 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11040253





