Abstract
Since at least half of the world’s population resides and works within coastal land, the coastal zone processes and resource management is of great economic and social importance. One of the fundamental issues for coastal city planners, researchers, managers, and engineers is the coastal city land-use suitability. Land-use suitability is the ability of a given type of land to support a defined use. Rapid urbanization and consequent haphazard growth of cities result in deterioration of infrastructure facilities, loss of agricultural land, water bodies, open spaces, and many micro-climatic changes. Hence, accurate data on coastal city hazards are essential and valuable tools for coastal planning and management, sustainable coastal development, coastal environment conservation, selection of a site for coastal city structures, and coastal resources. In this investigation, the Delphi and Analytical Hierarchy Process (D-AHP) Hybrid model and Geographic Information System (GIS) technique for Coastal Land-Use Assessment (CLUA) are mapped to detect the most suitable and unsuitable areas in the Kuala Terengganu coastal zone. Furthermore, this research offered information not only on the present urban land-use trend and established amenity status in Kuala Terengganu, but also on the suitability of land for the potential establishment of urban facilities for improved urban planning and appropriate decision-making. Using the D-AHP Hybrid model and GIS tool for coastal city management is broadly practical for government, policymakers, and planners to appropriately strategize and plan for the future of coastal cities in Malaysia and other analog coastal cities around the world.
1. Introduction
Land suitability assessment is a land evaluation approach that identifies the key qualitative and quantitative evaluation limiting criteria [1]. Climate, hydrology, topography, vegetation, and soil characteristics are examined in qualitative land suitability assessments, whereas the results are more thorough, and yield is calculated in quantitative assessments [2]. The systematic examination of land and water potential, land-use alternatives, and economic and social circumstances to choose and implement the optimal land-use options is known as land suitability assessment [3].
Coastal city lands have relatively stable or consistent cyclic behavior as part of the Earth’s surface [4]. Coastal city land-use suitability assessment for agriculture, settlement, housing, and industry depends on its elements. However, these elements have been depleted, especially in the last few centuries [5]. Coastal city lands refer to the areas where natural and artificial variations happen most often [6]. Natural changes severely affect coastal city zones because of their locations in the interaction zone of sea and land environments. Furthermore, the use of coastal zones by humans for housing, settlement, transportation, economy, and other purposes throughout history has resulted in artificial variations in these areas [7].
Thus, such areas possess numerous short-term changes which therefore represent tremendous test sets for the various detection methods of coastal data [8]. Consequently, coastal city change monitoring is a vital task for numerous studies [9]. Several challenges exist in the consideration of coastal land-use suitability assessment since the rapid urbanization process had made the coastal zones economically developed and densely populated [10]. Coastal lands could experience greater damage when threatened with hazards, namely global warming, increased settlements sea-level rise, erosion, flood, inundation, heavy run-off and rainfall, and productivity losses which are threatening the quality and availability of food, water, and energy, and are affecting the security and quality of life [11].
The CLUA is a rule-based collection of algorithms that combine soil, climate, and landscape elements to generate a graded appropriateness rating for a vulnerability and hazard criteria to aid in land risk management in coastal city areas [12]. The qualities used to describe each of the variables are based on their shown capacity to influence land loss and erosion, as well as their measurement capability and availability in searchable databases. It is critical to conduct scientific land evaluations to decrease human impact on natural resources and to determine suitable land use [13]. This type of research enables decision-makers to identify the major limiting factors for the vulnerability region and design risk management strategies that will enhance land-use planning. Land-use suitability’s primary goal is to identify the most suitable land or geographical location for a given future land use, as well as to assess the potential of land for alternative land uses, based on a large and complicated collection of specific indications [14].
Vulnerability refers to a person’s vulnerability to damage as a result of exposure to pressures connected with environmental and societal change, as well as a lack of ability to adapt [15]. The concept of vulnerability has been a powerful analytical tool for describing states of susceptibility to harm, powerlessness, and marginality of both environmental and social systems, and for guiding the normative analysis of actions to enhance well-being through reduction of risk [16]. The semi-quantitative vulnerability study took into account three factors: environmental sensitivity, economic, and social structure vulnerability [17].
One of the major adverse effects of climate change is a rise in sea level, and sea-level change causes an important risk for coastal city areas [18]. The average sea-level rise globally in the 21st Century might lead to several physical modifications to the coasts of the world which could threaten coastal infrastructure and populations and endanger several coastal ecosystems [19]. Between 1901 and 2018, the global mean sea level rose by 0.20 m. Between 1901 and 1971, the average rate of sea-level rise was 1.3 mm per year, increasing to 1.9 mm per year between 1971 and 2006, and then to 3.7 mm per year between 2006 and 2018. Since at least 1971, human impact has most certainly been the primary cause of these increases [20]. According to studies on long-term sea-level rise, the rate of the global sea-level increase caused by climate change is +3.32 mm/year [21]. Despite the expected significant scale of the consequences of sea-level rise, emphasized that the application and effectiveness of adaptation remain enormous uncertainties that demand further attention and evaluation. The global rise in sea level is not the sole process that leads to coastal land change, but coastal erosion and land-use change occur due to short-term and long-term events such as wave action, storms, tides, winds, and glaciation cycles [22]. Essentially, diverse processes and factors which occur at different spatial periods, and are involved in triggering coastal land changes [23]. Although the physical effects of the rise in sea level seem obvious, the immediate effect is submergence and greater coastal land flooding [24]. Hence, these could have impacts on water resources, coastal city zone, food supply, public health, etc. which may compel national and international responses to confront climate change [25]. The rainfall and temperature are rising, and they are foretasted respectively −1 to 32% and +0.6 to 3.4 °C in 60 years, whiles, the rise of sea level due to global warming is forecasted roughly 1.30–9.40 mm/year in 100 years in Peninsular Malaysia [26].
Ref. [27] observed that in East Coast of Malaysia, apart from erosion, accretion also happens within the neighborhood of a 25-km stretch of coastline, especially throughout the northeast monsoon season. However, in the coastlines of Kelantan Terengganu, little effort had been made to explain this erosional discrimination feature of the northeast monsoon waves. Kuala Terengganu’s climate is dominated by the northeast monsoon that is prevalent from November to March, and the yearly temperature ranges from 25.6 °C to 27.8 °C [28].
The observed average sea-level rate near the Malaysian coast was estimated between 2.7–7.0 mm/year based on satellite altimetry data from 1993 to 2010. In Peninsular Malaysia, the anticipated sea-level increase for the year 2100 was about 2.50–5.20 mm/year, with the low-lying northeast and west coast portions of the peninsular (Kelantan and Kedah) having the highest value [29]. According to the [30] study, around 3.3% of the 1963 km of coastline is classified as severely vulnerable, with the northern reaches of Kedah’s shoreline and the southern lengths of Terengganu’s beachfront being among these locations. The study revealed a significant increase in the trend of sea-level rise in the past 5 years, compared to 20 years ago. The National Coastal Erosion Study (NCES) found that of a total of 4809 km of the coastal area of Peninsular Malaysia, roughly 1360 km, covering 28% of the coastline currently threatened with the erosion of varying degrees of intensity, threatening the economic values of human activities [31].
The Malaysia coastal land erosion problem arises mainly due to the dynamic process, human activities. Evidence from past studies indicated spatial variations of coastal lands and erosion, and accretion in Terengganu coastal area disclosed the geomorphological changes. Kuala Terengganu is one of the areas that was endangered by serious erosion and land loss, and it became necessary to monitor its coastal land [32]. Conversely, another factor that also causes coastal city erosion and land-use change are human activities such as settlements, industrial development, agriculture, deforestation, and coastal protection in the coastal area within watersheds, river catchments, and offshore [33]. The combination of human activities and natural forces, particularly development in coastal lands usually worsen coastal city erosion [34]. The effects of coastal city erosion are generally because of inadequate foresight in the planning and location of infrastructure or facilities [35]. The continuous location of facilities in coastal areas that are vulnerable to erosion could aggravate the problem of coastal land erosion except for developers appropriately consider the causes and effects of erosion [36]. In the areas that have developed the central threat is on the houses or residential structures as well as the local access roads linking those houses several housing and residential land might be lost if the erosion processes are left uncontrolled. The likelihood of an occurrence of intensity equal to or greater than a category value occurring during a period of exposure is described as a hazard. Subsidence, sea-level rise, erosion are examples of environmental and climatic hazards (H) in the research region [37].
Finally, risk (R) is defined as the likelihood of a loss impacting an element occurring because of a high-intensity event. Risk is calculated as a function of hazard and vulnerability and was assessed using the equation R = (H, V) [38]. The likelihood of a disaster and the financial worth of potential losses or consequences are frequently the only factors considered in risk assessments. These findings are used to determine if preventing certain calamities is economically possible [39]. Risk assessment is an important step in the risk management of land use, and many researchers have provided their valuable work in this field during recent decades [40].
The assessment of coastal land suitability is analogous to the selection of a land-use position and attempts to map a suitability index for the whole research area [41]. It is necessary to choose the most suitable coastal land suitability evaluation algorithm for current and future land-use planning [42]. One of the most significant prerequisites for coastal land-use decisions is the creation of suitability maps [43]. It is important to consider many conditions and requirements related to coastal land and its uses.
Social and economic influences are far more manipulated than bio-physical and environmental factors through human interventions [44]. With many of the cities clustered near the sea, there are long lands in Peninsular Malaysia, and over 90% of the coast is among the easily erodible [45].
Some essential economic sectors in Malaysia are confronted with adverse effects of climate change and such sectors include industries, energy, transport, agriculture, forestry, public health and waste sector as well as water and coastal resources. Therefore, rapid responses via adaptation and mitigation approaches are required to curtail the risks, possible losses as well as maximize the beneficial opportunities. The Malaysia government has taken diverse programs and actions to reduce the effect of climate change in all important sectors [46].
The East Coast Economic Region (ECER) in Malaysia has a widespread and diverse coastal city zone, and as with several coastal areas of the globe, would also be influenced by future human-oriented climate change especially via increased coastal land erosion [47]. In essence, low-lying areas that have large socio-economic activities and populations are in danger of being inundated. For instance, the low-lying Kuala Terengganu area has more susceptibility to coastal erosion throughout the monsoon season especially [48].
This study selects Kuala Terengganu as the study area due to its location which represents an active tourism gateway to the ECER. There are several distinctive tourism attractions especially in the areas of mainland coastal and sustainable island tourism, ecotourism, urban tourism, and its typical cultural and heritage tourism [49]. The ECER Malaysia was established as an economic corridor with the objective of creating the socio-economic transformation of the east coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Thus, ECER covers the states of Terengganu, Kelantan, Pahang as well as the and the districts of Johor and Mersing [50].
Therefore, assessing the weight of each factor influencing the suitability of coastal land is a crucial step in evaluating the suitability of coastal land use for hazard evaluation. Because for the interest groups concerned, each element has its degree of value or weight, it can be difficult to weigh them [51].
Land suitability assessment using a Geographic Information System (GIS) has been widely used in the real world, for example, mapping [52], urban growth [53], managing transportation issues [54], Environmental Impact Analysis [55], risk and disaster management [56], flood risk areas [57], Natural Resources Management [58], Geology [59], Planning and Community Development [60], Irrigation Water Management [61], regional planning and land-use suitability for agricultural activities [62]. GIS tools, according to [63], were proven to be a quick tool for CLUA, especially in partial data settings. The GIS-based Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) is the most widely used approach in various literature to assess land-use suitability for future coastal city sustainable development MCDA [64]. This method uses several approaches for creating decision problems as well as weighing and ranking various choices [65]. To establish the weighting and score of various criteria, researchers employed a variety of methods [66].
Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) is used to help in complex decision-making, particularly in uncertain situations where there exist a limited practicable set of options, and to select the best alternative according to the scores of many characteristics and its multi-attribute decision-making problem [67]. MCDA offers greater-supported methods to compare project alternatives based on decision matrices. It also gives structured approaches to incorporate the opinions of project stakeholders in the ranking of alternatives [68]. One vital merit of MCDA is its ability to bring out the similarities and possible conflict areas among stakeholders in group decision-making that enhance a thorough understanding of the values of others [69]. The Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) is a multi-criteria analysis approach extensively used to aid individual and group decision-making across the world [70]. The AHP remains one of the broadest techniques in the MCDA setting [71]. AHP is frequently used in conjunction with other techniques, with writers estimating the weight of the criterion using AHP. Fuzzy AHP is one of the most widely used methods of MCDA, with many articles devoted to a comparison of classical AHP with fuzzy AHP [72]. The current method of MCDA used specifically for environmental sciences includes the AHP, best-worst method (BWM, level-based weight assessment (LBWA), and full consistency method (FUCOM) [73]. The best-worst method (BWM) is a MCDA approach for weighing a collection of options against a set of decision criteria [74]. The BWM is based on a pairwise comparison of the choice index in a methodical manner [75]. The new level-based weight assessment (LBWA) approach allows experts from many areas to collaborate to define the relationships between indicator and make reasonable decisions [76]. The approach may be used in real-world situations in specialized decision-making support systems, as well as in virtual settings for alternative conflict settlement [77]. The complete consistency method (FUCOM) is a novel methodology for weighing literature criteria [78]. This approach is a semi-objective assessment method that lowers the number of indexes comparisons inside each other and optimizes the criterion weights with a few comparisons using an optimization algorithm [79].
There are many advantages of AHP techniques, namely it is relatively easy to use, can integrate qualitative and subjective factors, tolerates speedy replanning, obtain the greatest judgmental decision estimate from numerous credit analysts, and offers a method to assess the consistency of these judgments [80]. The most fascinating aspect remains its ability to include judgments and personal values reasonably therefore making a complex decision problem to be structured hierarchically [81]. This viewpoint was corroborated by [82] who submitted that AHP is the frequently and extensively applied as well as fastest emergent decision analytic approaches. AHP has been used in numerous complex decisions especially in the field of environment, namely the challenges of management of natural resources [83], Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM) [84], environmental issues [85], social science, and technology [86], economic studies [87], risk management process [88], land-use planning [89], urban planning [90].
The Delphi technique might be used to improve the quality of expert views used in the AHP approach [91]. The Delphi technique has been applied in numerous studies in the fields of environmental studies, project management, and industrial engineering [92]. Therefore, this technique is suitable as a research instrument especially when the knowledge of a phenomenon or problem is incomplete [93].
Since the 1990s, coastal city planners have significantly increased their attention to the incorporation of the MCDA approach with GIS to solve the problems of spatial planning [94]. The ability of GIS to handle spatial facets of risk assessment has improved its’ application in the index-based assessment for prioritization and selection of possible appropriate and inappropriate areas. This is since most of the conditions for CLUA are spatial data [95]. GIS tools were a speedy tool for coastal city land-use suitability, especially incomplete data situations [96]. In support of currently available literature [97], we believe AHP is the most suitable technique that widely used MCDA methods in decision support system processes which includes multiple actors, scenarios, and GIS layers classes [98].
The overall goal of this research is to create risk and land used suitability maps for hazard management in Kuala Terengganu, a coastal city on Peninsular Malaysia’s east coast. We have developed a CLUA model by integrating GIS tools and the D-AHP Hybrid model for coastal city land use. The combination of the GIS technique and the D-AHP model is a powerful approach that used risk assessment and land-use suitability in coastal city areas [99].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Terengganu is a constitutive state of federal Malaysia (Peninsular Malaysia) and is bordered in the northwest by Kelantan, the southwest by Pahang, and the east by the South China Sea. Kuala Terengganu which is located at the mouth of the broad Terengganu River is the largest city in Terengganu state. The eastern part of Kuala Terengganu where faces the South China Sea is characterized by sandy coastal beaches that cover the entire stretch of both parts (Figure 1). The study area is selected along the coastline of Kuala Terengganu which extends from Merang to Rusila for about 68.84 km. In this area, the coastal area was characterized by the northeast monsoon, with semidiurnal tides and an average annual temperature of 25 °C to 27 °C. The shoreline in this area is categorized as a critical region by the local authorities. It is mainly due to the dynamic physical process in the area, sea-level change, and human activities.
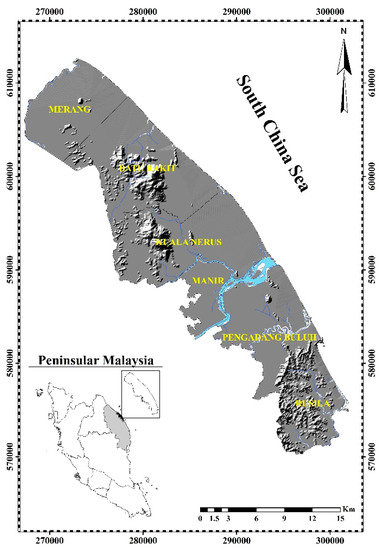
Figure 1.
The geographical location of Kuala Terengganu in Peninsular Malaysia.
2.2. Data Used
The study collects two kinds of data, namely primary and secondary data, for the CLUA framework (Table 1). Thus, the D-AHP model’s primary data were obtained via the Expert Choice Matrix (ECM) and were given to 12 specialists from various agencies or departments in Malaysia (DID, SMART, NAHRIM). Thus, the ECM was run for five-month (for three runs). The study conducts the first run between 14 February 2014 and 17 April 2014, the second run from 22 August 2014 to 20 September 2014, and the final run was conducted between 3 October 2014 and 7 November 2014. The secondary data regarding mapping in GIS were gathered from similar departments or agencies. The GIS secondary spatial data include land-use map (2008), topographic map (2002), and MUKIM map (2010) obtained from JUPEM, Flood map (2008) obtained from DID, Geology map obtained from the Geology Department, Soil map (2008) obtained from Department of Agriculture (DOA) and Population map (2010) obtained from Department of Statistics.

Table 1.
Coastal land-use changes spatial and non-spatial data.
2.3. CLUA Model Framework
The D-AHP Hybrid model’s semi-quantitative architecture has improved system consistency as well as weight computation for layers and classes [100]. The D-AHP method is organized hierarchically at diverse levels with each level containing a finite amount of decision components. The general goal of CLUA is represented by the upper level of the hierarchy whereas one or more intermediate levels symbolize the decision GIS layers and classes. Hence, the lower level comprises all potential options (Zones) as alternatives. Applies the D-AHP model to assess the vulnerability, hazard layers, and classes on coastal city region’s erosion that necessitated semi-quantitative analysis of the coastal region’s information. The semi-quantitative design uses two GIS layers for the measurement of erosion risk, namely vulnerability and hazard layers. Therefore, D-AHP’s first step is to create a hierarchy by shaping the problem into its basic elements. This model ascribes significance weights to the variables with the use of pairwise comparison at every hierarchy level. The class of the risk appraisal process is that the pairwise compression of the layers at a hierarchy level with the objective at the next level. CLUA components are based on their common features and the development of a hierarchical model that has diverse levels [101].
Twelve phases are involved in the CLUA framework.
Phase 1 of the D-AHP Hybrid structure is associated with the configuration of the decision problem into hierarchical coastal land use. Thus, vulnerability and hazard maps in semi-qualitative hierarchy design could involve vulnerability and hazard Index ratios. The AHP semi-quantitative design, vulnerability, and Hazard maps may encompass vulnerability and hazard GIS layers and ratios (Figure 2).
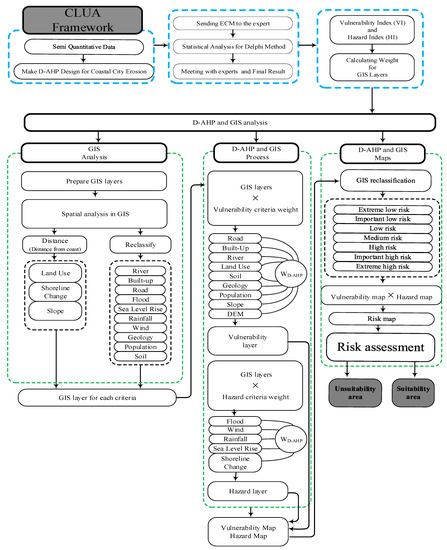
Figure 2.
Risk assessment model framework for Kuala Terengganu Structuring the decision hierarchy comprises the disintegration of the decision problem.
Phase 2 comprises an empirical study under the Delphi method and expert choice matrix to enhance gathered essential layers and classes from a review of the literature and to examine other layers emanating from the opinion of the expert panel.
Phase 3 is associated with the collection of input data by pairwise comparisons of decision components as well as obtaining the judgment scales. Having arranged the problem in a hierarchical technique, the subsequent step is to appraise the relative significance of the emanating and classes to the general goal. The study applies two designs expert choice matrix with the first design being a 5-point expert choice matrix of which the user enables the selection of the best and essential layers from the expert. The second design signifies a 9-point expert choice matrix which is used for the semi-quantitative data layers. By using pairwise relative comparison, the preference between layers and GIS classes with a 9-point rating scale would be asked for deriving weights by the AHP model. The relative significance of every variable is evaluated through the application of Saaty’s nine scales. For the semi-quantification process in AHP, the pairwise comparisons of layers and classes use a scale of unconditional judgments generally known as Saaty’s nine scales, which specifies the degree at which one item prevails over the other regarding the certain feature. This scale changes semi-quantification assessments into statistical values from 1 to 9 which is used for semi-quantitative GIS classes to complete the pairwise comparison matrix [102].
Phase 4 is concerned with the evaluation of the weight consistency of comparisons. This step conducted the calculations to determine the maximum eigenvalue, Consistency Index (CI), Consistency Ratio (CR), and normalized values for every layer and class [103]. The AHP determines the general consistency of judgments through a CR Equation (1). As noted by some studies [104,105], the judgmental matrix consistency can be accomplished through the examination of total CR, the ratio of CI and RI denoted as follows:
where RI signifies the random consistency index of a reciprocal matrix that was randomly created from the 9-point scale, with reciprocals forced [106] (the average CI of 500 randomly filled matrices). A CR below 10% suggests that the matrix could be considered to be possessing an acceptable consistency [107]. Thus, [108] computed the random indices as indicated in Table 2.

Table 2.
Random indices.
The scores that attained a certain level of consistency were accepted as demonstrated by a CI calculated by [109] Equation (2). He proposed a CI that is denoted as follows:
The CR allows determining the number of errors that were generated when offering expert judgments. The calculated CI can be compared with the created paired comparison matrix RI to examine CR (Table 2). The CR indicated whether the judgment weights of the decision-maker were accepted. A value of CR below 0.1 reveals that the errors are relatively small and considered acceptable. This is because human judgments do not necessarily need to be always consistent since some inconsistencies may be introduced due to the nature of the scale used [110].
Phase 5 concerns local weights and consistency of comparisons using expert choice software for the calculation of the D-AHP weight. This step calculates the local weights of the components by using expert choice software.
Phase 6 deals with the aggregation of weights through several levels to obtain the ultimate weights of GIS layer classes. After obtaining the local weights of components of diverse levels as highlighted in the preceding step, they are combined or aggregated to obtain the ultimate weights of the decision options. Thus, the layer class weights known as local priorities are seen as decision components in the decision process second step. The decision-maker must offer these preferences or priorities by pairwise comparisons concerning the weights and scores. The weights () and scores values are stimulated from these comparisons and denoted in a decision table.
Phase 7 of the AHP combines or aggregates all preferences from the decision table with a weighted summation of the kind [111] and creates the local priorities through all layers to determine the global preference or priority [112] Equation (3). The ultimate GIS layer classes weights in semi-quantitative data would be calculated using the formula given as follows:
where represents the global priority of the GIS layer classes, signifies local priority while denotes the weight of the layer classes j. Thus, global priorities attained in this research are ultimately used to normalize through the division of the score of every layer class solely by the layer classes score and choose the optimum classes in each layer.
Phase 8 To produce the vulnerability and hazard map, all shapefile layers are transformed to raster layers and each vulnerability and hazard layer is computed and multiplied with D-AHP weights in Arc Map.
For Phase 9, 10 and 11, a seven-class method was used to categorize the assessment findings of hazard, vulnerability, and risk maps to derive the land-use suitability region from the risk map. When executing the categorization technique, assigning rank to the alternative of the values (1) Extreme low (null); (2) Very low (not subjected areas); (3) low (potential areas); (4) medium (fragile areas); (5) high (critical areas); (6) Very high (degraded areas); (7) Extreme high (No data) are proportionally assigned to give more sensitive vulnerability, hazard, and risk levels in the coastal city region [113,114].
In this research vulnerability, hazard and risk map the classified into seven classes because, according to several Malaysian reports (DID, 1985, and NAHRIM 2010), the Kuala Terengganu coastline area has extreme erosion, the low and high extreme erosion classes are significant in determining the best suited and unsuitable areas. on the other hand, Kuala Terengganu coastline, offers a broad range of tourism attractions, including mainland coastal and sustainable island tourism, ecotourism, urban tourism, traditional culture and historical tourism, and traditional culture and historical tourism. As a result, we need an accurate and significant classification of vulnerability, hazard, and risk in cities and coastal areas, which may help planners and politicians make better decisions.
Phase 9 vulnerability assessment that refers to a susceptible element’s vulnerability to a hazard, such as human populations, physical structures, economic assets, or sensitive environmental components. Most of them have quantitative measurements in place, such as the number of lives lost or the monetary value of serious hazard [115].
The D-AHP weights have been calculated and multiplied with each vulnerability layer, using GIS tools Equation (4).
where (V) represents vulnerability, () signifies vulnerability layer and denotes the weight of the vulnerable layer class.
Phase 10 hazard is a potentially dangerous event that might threaten the lives of people or damage to property or the environment. Severity, length, amount, intensity, and frequency are all factors to consider. A bigger threat is represented by a higher numeric number [116].
The capacity of GIS tools to incorporate the D-AHP weight, which is connected to each hazard layer, has been demonstrated in this section of the research Equation (5).
where (H) signifies hazard, () represents hazard layer and denotes the weight of the hazard layer class.
Phase 11 The possibility of a calamity is referred to as risk. On a small range, it can be measured as a weighted rank [117].
The development of the CLUA followed a combination of the above model’s Equation (6) in the GIS [118]. Thus, the hazard index was multiplied by the vulnerability index in GIS to generate the risk map as indicated s below:
where (R) signifies the risk layer of CLUA, (H) denotes the hazard layer, and (V) symbolizes the vulnerability layer.
The variability of catastrophes is referred to as the hazard potential factor. In general, as catastrophe intensity and frequency rise, so does the severity of the damage and loss. All persons and things potentially threatened by the hazard factors, such as local inhabitants, animals, residences, crops, and so on, are referred to as impacted objects. An area with a higher property density that is exposed to risk factors will have a higher loss potential.
Phase 12 This project calculates and generates a land-use suitability map from a risk map with seven classes in a GIS that depicts the sensitivity and suitability in the coastal city area. The three varieties of low-risk classes on the risk map are suitable area, whereas the three types of high-risk classes are unsuitable areas. There are many null lands and deforestation areas in the coastal city region, particularly in Kuala Terengganu. Therefore, the seven rankings developed for this study are beneficial for determining the optimum land-use suitable location on a small regional scale with considerable coastal erosion. The final risk maps from GIS for the Kuala Terengganu coastal zone used to create two-class maps in suitable and unsuitable for six zones.
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Vulnerability Maps on the Local Scale
The vulnerability assessment for the semi-quantitative model design refers to a region with the specific relative weakness of exposure to natural disasters and their ability to handle them when they occur. Based on the results of the model from experts’ opinion, the study constructed, classified seven coastal vulnerability layers into two domains, namely environmental layers and human activity layers. The environmental layers domain refers to the soil, slope, geology, digital elevation map, river, and land use. In the human activity layers, the population density, built-up, and road network were taken into consideration. Conversely, another factor that also causes shoreline change and coastal city erosion is human activity in the coastal area within watersheds, river catchments, and offshore [116]. The combination of human activities and natural forces, particularly development in the coastal areas usually worsen coastal erosion [117].
The environmental layers classes are weighted due to serious coastal city erosion problems. The computed weights for each environmental layer’s classes will be used in the GIS analysis for an estimate of hazard, vulnerability, and risk area on the local scale Table 3.

Table 3.
Vulnerability GIS Layers class and weights.
Figure 3 shows the final results of the vulnerability analysis for the 3 vulnerability erosion zones of the Kuala Terengganu coastal areas that were selected and choose this area base on literature and some government agency reports. Expert knowledge was used to rank vulnerability parameters for each zone from extremely high (7) to extremely low (1).
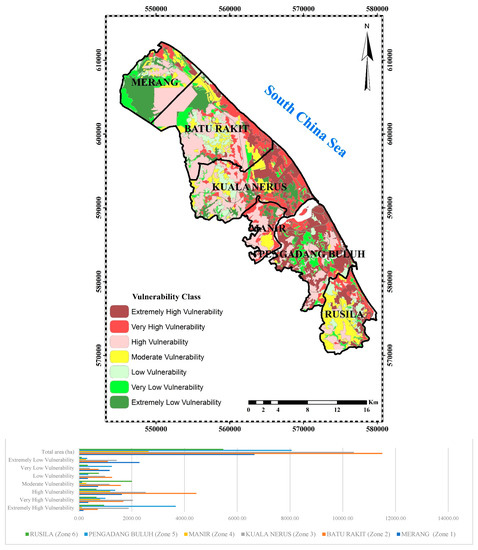
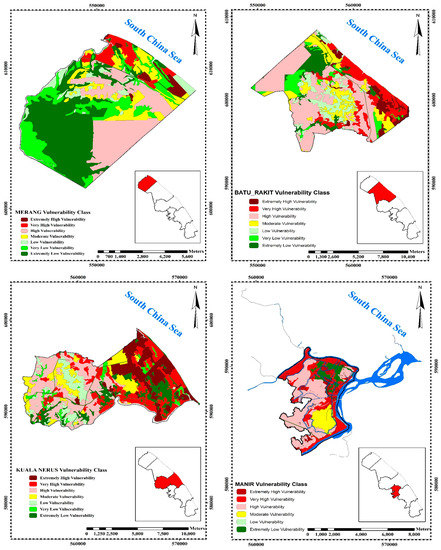
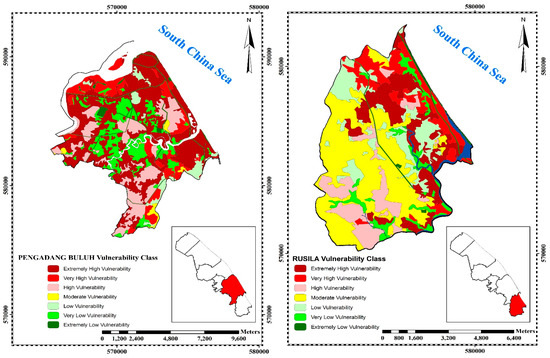
Figure 3.
Final vulnerability map and sensitive zones.
In Batu Rakit (Zone 2) with 11,500 ha, 6.2% (710 ha) of the area is considered to be an extremely highly vulnerable, 14.16% (1678 ha) is seen as very highly vulnerable, 38.7% (4452 ha) is highly vulnerable, 13.7% (1580 ha) represents moderate vulnerable, 10.9% (1254 ha) signifies low vulnerable, 6.4% (739 ha) is considered to be very low vulnerable and 9.5% (1088 ha) represents extremely low vulnerable (Figure 3).
Kuala Nerus (Zone 3) which covers a total area of 10,418 ha has an extremely highly vulnerable area of 1880 ha (18%), a very highly vulnerable area of 2035 ha (19.5%), a highly vulnerable area of 2528 ha (24.3%), moderate vulnerable area of 1157 ha (11.1%), low vulnerable area of 989 ha (9.5%), very low vulnerable area of 404 ha (3.9%) and extremely low vulnerable area of 1426 ha (13.7%).
Pengadang Buluh (Zone 5) covers a total area of 8059 ha and has 45.5% (3667 ha) extremely highly vulnerable area, 12.4% (1003 ha) very highly vulnerable area, 17% (1370 ha) highly vulnerable area, 1.4% (115 ha) moderate vulnerable area, 4.3% (350 ha) low vulnerable area, 15.4% (1242 ha) very low vulnerable area and 3.9% (313 ha) extremely low vulnerable area (Figure 3). Pengadang Buluh (Zone 5) has the highest vulnerability with a vulnerability rate of 74.9% according to the observed data (map and survey) and fieldwork compared to 61.8% and 59.5% vulnerability rate in Kuala Nerus (Zone 3) and Batu Rakit (Zone 2), respectively.
3.2. Analysis of Hazard Maps on a Local Scale
The hazard assessment was done with the D-AHP analysis of the Kuala Terengganu and the GIS map of different classes is presented in Figure 4. The GIS layers and D-AHP weights are illustrated in Table 4.
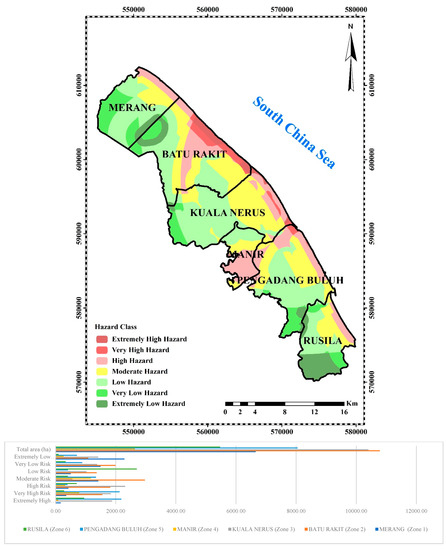
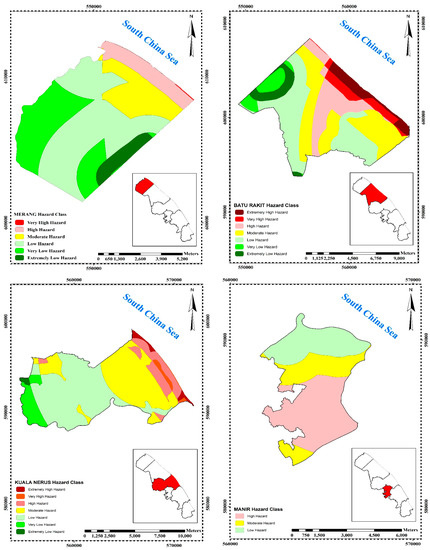
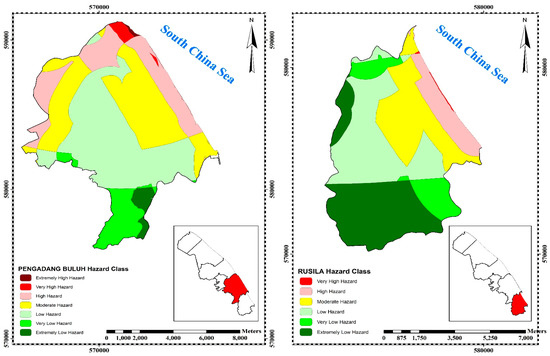
Figure 4.
Final hazard map and sensitive zones.

Table 4.
Hazard GIS layers class and weights.
Figure 4 presents the hazard potential of 3 hazard erosion zones of Kuala Terengganu. The three zones that have the highest rate of hazard, namely Zone 2 (Batu Rakit), Zone 3 (Kuala Nerus), Zone 5 (Pengadang Buluh) and are also presented. In Batu Rakit (Zone 2) with a total area of 11,619 ha, 6.06% (704.56 ha) is an extremely high hazard area, 6.11% (710 ha) is a very high hazard area, 15.99% (1858 ha) is a high hazard area, 28.77% (3342 ha) is moderate hazard area, 31.35% (3642 ha) is low hazard area, 5.61% (652 ha) is very low hazard area and 6.11% (710 ha) is an extremely low hazard area. Kuala Nerus (Zone 3) with a total area of 10,590 ha has 1.6% (173 ha) as an extremely high hazard area, 1.7% (176 ha) as a very high hazard area, 9.9% (1047 ha) as a high hazard area, 34.5% (3655 ha) as moderate hazard area, 44.7% (4732 ha) as low hazard area, 7.1% (748 ha) as very low hazard area and 0.5% (58 ha) as an extremely low hazard. Finally, Pengadang Buluh (Zone 5) which covers a total area of 9023 ha has an extremely high hazard area of 20 ha (0.2%), a very high hazard area of 122 ha (1.3%), a high hazard area of 1591 ha (17.6%), moderate hazard area of 2784 ha (30.9%), low hazard area of 3515 ha (39%), very low hazard area of 773 ha (8.6%) and extremely low hazard area of 219 ha (2.4%) (Figure 4).
The result shows that there is an extreme flood in Zones 3, 2, and 5 as well as a river. Zones 2 and 3 are in low-lying and low elevation in the DEM layer in GIS. There are shoreline changes and coastal erosion in transects 10, 11, 12, and 13 with the rates of 6.44, 5.90, 6.92, and 3.95 m/year, respectively, which are located in Zones 2 and 3. Pengadang Buluh (Zone 5) has the lowest hazard with a rate of 19.2% compared to Zones 3 and 2. This could be due to the construction of some coastal protections, namely brake water and a jetty in this area.
3.3. Coastal City Erosion Risk Assessment Maps on the Local Scale
Figure 5 is the final risk map which demonstrates the risk of coastal disaster damage resulting from the coastal vulnerability and potential hazard maps. From the analysis and overlaying of coastal vulnerability and hazard maps in the GIS environment, the study found that among 3 zones, Batu Rakit (Zone 2), Kuala Nerus (Zone 3), and Pengadang Buluh (Zone 5) are high-risk areas. Among these three zones, Pengadang Buluh (Zone 5) was found to be the highest risk area. About 6.2% (710 ha) of Batu Rakit (Zone 2) is extremely high-risk area, while 13.5% (1553 ha), 15.8% (1817 ha), 25.8% (2969 ha), 11.9% (1366 ha), 17.3% (1993 ha), and 9.4% (1085 ha) are very high risk, high risk, moderate risk, low risk, very low risk and extremely low risk, respectively (Figure 5). Kuala Nerus (Zone 3) has 18.1% (1879 ha) extremely high-risk area, 17.7% (1838 ha) is very high-risk area, 22.2% (2312 ha) is high risk, 5.4% (558 ha) is moderate risk, 9.8% (1024 ha) is low risk, 13.3% (1379 ha) is very low risk and 13.6% (1415 ha) is extremely low risk. Pengadang Buluh (Zone 5) with a total area of 8049 ha has an extremely high-risk area of 2185 ha (27.1%), very high-risk area of 2127 ha (26.4%), high-risk area of 394 ha (4.9%), moderate risk area of 1341 ha (16.7%), low-risk area of 406 ha (5%), very low-risk area of 886 ha (11%) and extremely low-risk area of 709 ha (8.8%) (Figure 5). Overall, Pengadang Buluh (Zone 5) is the highest risk area with a risk rate of 58.5%, followed by Kuala Nerus (Zone 3) with a risk rate of 57.9%, and Batu Rakit (Zone 2) with a risk rate of 35.5%. A change in the vulnerability of the area would also change the rate of risk. This shows that Zone 5 has the highest potential to be significantly affected by the negative impacts of climate change hazards.
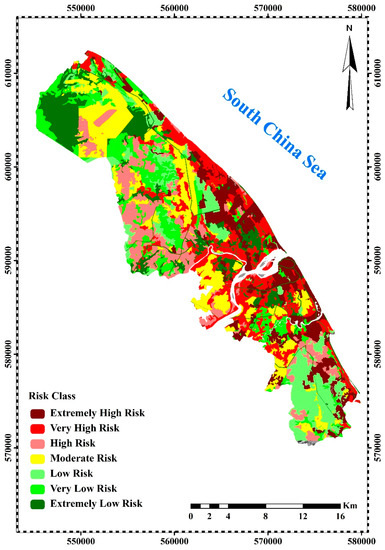
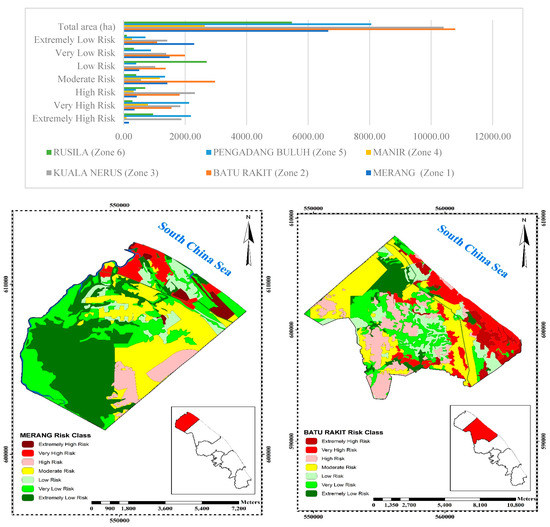
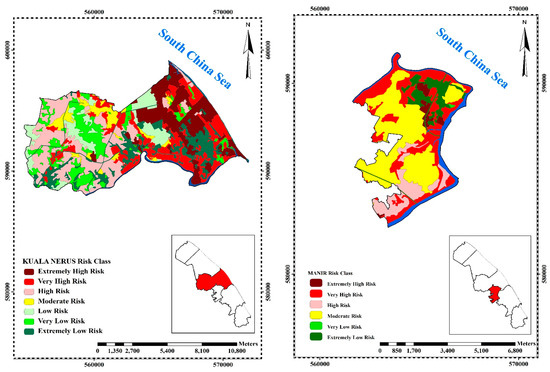
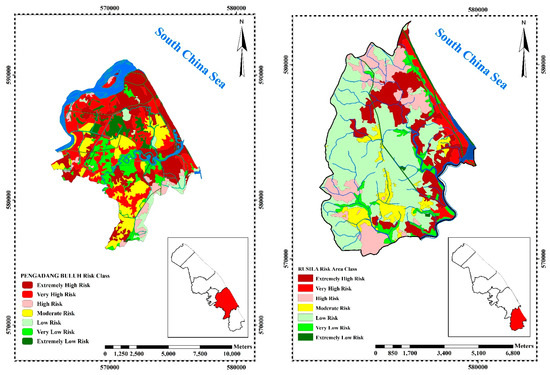
Figure 5.
Final risk map and sensitive zones.
3.4. Assessment of Land-Use Suitability Area
The result of land-use suitability and unsuitability assessment for Kuala Terengganu shows that among three zones (2, 3, and 5), Zone 2 has the most suitable area, followed by Zones 3 and 5. Out of 8524 ha land area in Batu Rakit (Zone 2), about 52.1% (4444 ha) is a suitable area and around 47.9% (4080 ha) is an unsuitable area (Figure 6). Out of 9847 ha total land area in Kuala Nerus (Zone 3), about 38.8% (3818 ha) is considered to be a suitable area 61.2% (6029 ha) is an unsuitable area. Out of 6708 ha of the total land of Pengadang Buluh (Zone 5), only 29.8% (2001 ha) is a suitable area while about 70.2% (4706 ha) is an unsuitable area (Figure 6). It shows that Zone 5 is less suitable for construction, agriculture, and tourism activities compared to other zones. The suitability maps provide the most satisfactory means of conveying the result of the assessment to the user in a summary form. Overall, the northeast and southeast parts of the study area had been categorized as suitable areas, because these regions are less vulnerable to hazard factors such as a river, flood, coastal hazards, and human activity compared to the middle part of the study area. The matching of current land-use type and land suitability classification can support and contribute information for site selection and planning for the government. For example, some of the government agencies, universities, and international airports, as well as build-up areas near the coast, are in highly vulnerable and risk zones. Therefore, before undertaking any plan and development in the coastal area, the suitability or unsuitability of the land for a specific purpose should be taken into consideration. Suitability analysis allows regional planners to make timely and more informed decisions. Furthermore, it determines how the land would be used in the future. Hazards and risks affect the future development of land. Hence, it is important to include hazard and risk information in the land-use planning process, particularly in the areas facing natural hazards.
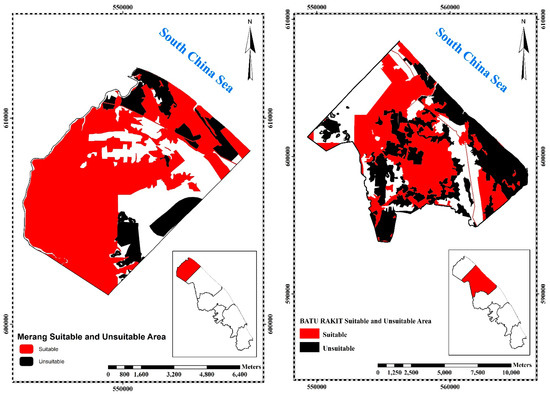
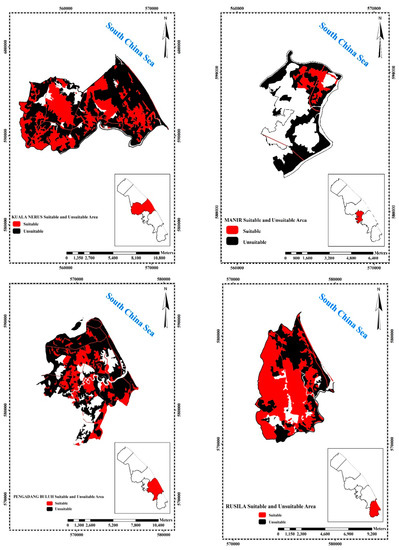
Figure 6.
Suitability and unsuitability land-use maps for coastal city erosion.
4. Discussion
The coastal city erosion vulnerability control and management plan is a continuing plan requiring federal government actions that the nature of this action will change with time but will change gradually through able to be foreseen future. The federal government actions are reactionary, and they must produce management, decisions, structural control works to protect facilities developed over past years. Additionally, they produce guidance to ensure that disastrous erosion risk consequences do not threaten facilities developed in future years.
Classification is an informed judgment on the environmental, socio-economic, and physical impacts of coastal city risk assessment. That judgment depends on the integration of the many technical analyses and the varied technical information comprising. The rate of erosion is the base for determining when and how seriously, a value will be impacted. Values considered are those generally affected by erosion in the Kuala Terengganu coastal area. To achieve these ends, the eroding areas are classified and grouped into three classes (Table 5):

Table 5.
Critical, significant and acceptable erosion areas.
Critical erosion risk areas, the anticipated socio-economic impacts indicate that the social and economic costs of erosion may soon be unacceptable. Possibility studies to more precisely define and quantify those costs and the costs of control so that protection investment decisions can be made for affected facilities are needed for the Kuala Terengganu area. Those decisions have already been made for six areas—Merang, Batu Rakit, Kuala Nerus, Manir, Pengadang Buluh, Rusila in this research. Kuala Nerus and Pengadang Buluh in Kuala Terengganu are recreational resorts near Gong Merbau and Left Bank. K. Ibai. The recreational facility is a sandy beach and is quite well known with excellent name recognition. Resort housing and food stalls support the beach. Erosion has already had a high physical impact; the remaining beach is only 30 or 40 m wide. There are alternate beach areas in the vicinity and recreation could relocate to those without great inconvenience. However, Kuala Nerus and Pengadang Buluh in Kuala Terengganu are the beaches people are accustomed to using, it has established support facilities, and it is well known. These considerations combine to indicate a moderate demographic impact. Similar reasoning gives it a moderate economic impact assessment. Damages have already occurred; the beach has been diminished and a swimming pool has been destroyed. This gives the feasibility study need considerable urgency and places it in priority.
The feasibility study will compare groins, breakwaters, Jetty, and beach restoration singly and in combination, to determine the most appropriate protection plan. Kuala Nerus and Pengadang Buluh (Zone 3 and Zone 5) is a big town that has a big river (Kuala Terengganu River) crossing it. This area is a low-lying and low elevation area in Digital Elevation Map (DEM) layer in GIS. The area with the highest vulnerability was identified and could serve as a guide for adaptive management planning in the future. The Nerus, Sekati, Manir, Kepung, Telemung, Cepuh, Pertang, Tersat, and Berang, Pur, Pauh, Pueh, Dura, and Sala are the primary tributaries of the Kuala Terengganu River basin, with a total catchment area of roughly 5000 km2. These rivers flow through a variety of socioeconomically structured regions, including agriculture, tourism, farming, aquaculture, commercial industries, urban and rural settlements, reserves, and forests. The purpose of studying rivers is to develop a field of knowledge that includes topics such as floods, erosion, sedimentation, water quality, and other studies of streams that are often researched today. In this research river class has the highest weighting of 0.281 and is very sensitive to erosion in the environment layer, whereas the geology class has the lowest loading of 0.028. The land-use class is the most sensitive and significant to erosion in the environment layer, with the greatest weighting of 0.160 after the river class. Land-use activities trigger land erosion rates and create sediment yields due to the reduction of agricultural land during historical events. Land use is a type of synthetic land surface modification that has a significant impact on environmental function and aquatic life. The kind and variables of land use will be used to evaluate the influence of river corrosion and erosion on the catchment grassland and vegetation cover. As a result, Idle Grassland, which has the greatest value of 0.233 in the land-use criterion, is essential to erosion in the Kuala Terengganu coastline area.
The soil class is sensitive and crucial to erosion in the environment layer, with the greatest weighting of 0.094, and the water body (River and coastal area) as a sub-criterion has the highest weighting of 0.299. Soil erosion is one of the factors that contribute to increased total suspended solid concentrations. This is because land erosion is one of the most difficult problems to predict, especially in tropical areas with a lot of rain. If the sediment lifting process cannot be solved, it will cause a slew of issues in the river and coastal area care and management. Furthermore, human activities such as municipal, industrial, aquaculture, and aquaculture led to the occurrence of total suspended solid concentrations. This is evident when the overall suspended solid concentration in the Kuala Terengganu River and coastal area is high.
This circumstance demonstrated the expansion of land-use development such as residential, industrial, and tourism structures surrounding the Kuaka Terengganu River and coastal area, which raises the risk of soil erosion.
Right Bank Kg. Merang, Kg. Seberang Takir, Left Bank of Kuala Marang in Kuala Terengganu are a fishing village. The primary access road to the village has been destroyed by erosion. There is an alternative path, but it passes through the village and is much less convenient than the primary road. The impact on transportation is considered moderate. Threatened houses are temporary type structures of relatively low economic value and road loss forces all traffic to and from the village to detour and experience a delay. The sand beach that once fronted the village has been eliminated by erosion. Because it had the only minor capability for recreation, the physical impact is had the only minor capability for recreation, the physical impact is moderate. The threatened dislocation of so many families and the loss of the primary access road combine to considerably affect and disrupt the established communal life of the village near Kuala Terengganu River and coastal area. Because high demographic impact and moderate economic impact are probable within 3 to 5 years, the need for the feasibility study is urgent.
Acceptable erosion areas distinguished from other eroding areas because no significant social or economic losses from erosion are expected within the next 10 to 15 m years (Table 5). Consequently, feasibility studies are not needed in the foreseeable future. Furthermore, feasibility studies to determine erosion protection needs should not ever be needed because such needs should not be allowed to develop. Unacceptable losses are not expected either because activities in the area are already adequately protected or because the area is undeveloped, not because it is free of erosion. Any development in 3 class areas must properly consider the causes and considers the causes and consequences of erosion and incorporate appropriate control measures (Table 5).
5. Conclusions
D-AHP Hybrid model was used to develop the CLUA analysis. Understanding and determining land-use change causal indicators is critical for developing the coastal city hazard model in the research region. Other significant variables include choosing the best local agency in the country or an international agency in another country, as well as the number and quality of experts needed to build the expert choice matrix and the best MCDA model. The criteria, sub-criteria, and alternatives were chosen based on information gathered from the literature research, different Malaysian publications such as NAHRIM (2010) and DID (2010), and foreign papers such as the Ministry of Environment (2008) and ETC CCA (2011). Others include fieldwork studies and ECM development by specialists from Malaysian government agencies such as DID, SMART, and NAHRIM.
As a result, several theme data layers relating to erosion cause vulnerability and hazard indicators, such as topography, river, slope, soil, geology, land use, road, build-up, population, flood, sea-level residual, shoreline change, wind, and rainfall, must be organized. These indexes are categorized as preparation indexes categories that affected coastal land-use change and erosion and they are considered to be responsible for vulnerability and hazards in the research location. One of the most significant aspects of this study was the selection of the best and most important criteria and sub-criteria using the AHP Hybrid design and Delphi technique to provide a useful outcome.
The understanding and determination of erosion causative layers are crucial for the study area to develop the CLUA model. Although many layers could be important concerning the land-use change occurrence for the specific coastal city region, the same factors may not be important for other regions. These layers are categorized as the preparatory layers categories that affected the land-use change directly or indirectly and they are considered to be responsible for land-use change and erosion occurrence in the study area. One of the most significant aspects of this research was the selection of the best and most important layers and classes using AHP design for coastal erosion and the Delphi technique to achieve a useful result. Combines approach through two components and presents the findings and contributions. These were the design of environmental indicator consisting of semi-quantitative data including hazard and vulnerability index in a GIS environment with a D-AHP Hybrid model and generated new coastal land-use change layers in the GIS environment. To estimate erosion risks, a good erosion model and accurate mapping of erosion-prone areas are needed. The application of D-AHP Hybrid and GIS techniques produce the final maps for important and sensitive zones of the study area. Thus, a risk assessment was performed for the vulnerability of coastal hazards due to environmental and climate change factors. The D-AHP Hybrid model was used to investigate the potential coastal city land-use change and erosion vulnerability and risk. The output of D-AHP was used as an input layer in GIS to map the hazard, vulnerability, and risk in the area. From the final results of GIS maps, we found high and low-risk areas and suitable and unsuitable areas for each of the six zones. We conclude that D-AHP and GIS techniques can improve the decision-making process.
The definition of suitable and unsuitable areas would be very important for the government to recognize which area is facing high risk or low risk for coastal land construction. For example, results show that UMT is one of the vulnerable areas to erosion and the international airport in Kuala Terengganu is at moderate risk because the airport building is in a low-lying and flooding area.
Hence the government could adopt the new policies to protect this area against coastal erosion by constructing jetties and seawalls to protect the inland area against wave action and prevent coastal erosion. The results may help managers to make better decisions and new management, as well as enable the government to plan how to solve the problem in this area. Policymakers can evaluate the sustainability of cities or near the sea, regarding how to identify the best suitable and unsuitable areas for land-use planning.
The results indicate that for land-use change and erosion vulnerability assessment, the river criterion has a highly significant effect, and the geology criterion has less effect for erosion. Conversely, built-up in human activity criterion has a high effect and road criterion has less effect on erosion. Zone 5 has highly vulnerable erosion for the coastal and city area. The shoreline change (coastal hazard) and rainfall (climate change) have a highly significant effect on erosion. Zone 5 is highly vulnerable to shoreline change, and Zones 5 and 6 are highly vulnerable to rainfall. Vulnerability is significantly affected by hazards in the coastal area of Kuala Terengganu. The Northern and Southern regions of Kuala Terengganu coastal area are comparatively less vulnerable to erosion.
Since this research has been conducted using limited coastal city data and maps, therefore, it is clear that it can only give a general view of environmental hazards for the Kuala Terengganu coastal area. However, as one of the first overall coastal management and planning studies in the Kuala Terengganu coastal area, it could indicate ways of conducting future related research. The definition of suitable and unsuitable areas would be very important for the government to recognize which area is facing high risk or low risk for coastal construction.
There are several constraints for integrated environmental geospatial modeling in coastal cities areas such as Kuala Terengganu. They are as follows: One of the main limitations in using MCDA models is the inadequacy of sources of the environmental criteria and sub-criteria for erosion on coastal areas. The limitation of a fundamental database for the environmental and coastal city in the study area. For environmental indexes, we estimated the semi-quantitative measurements from the experts in some Malaysian agencies. For environmental and climate data, requesting data and collected data were one of the main problems. They were collected from different departments and local agencies in Malaysia. Another limitation was the lack of frequently measured shoreline data sources with appropriate accuracy and time intervals as well as coastal engineering data. The short history of reliable shoreline imagery data caused long-term shoreline study to be impossible for this research. It was difficult and, in some cases, impossible to find identifiable and consistently defined shoreline indicators in aerial photographs in specific coastal sites. Since this study has been conducted using limited coastal city data and maps, therefore, it is clear that it can only give a general view of environmental hazards for the Kuala Terengganu coastal area. However, as one of the first overall coastal management and planning studies in the Kuala Terengganu coastal area, it could indicate ways of conducting future related research.
According to the findings of this study, the research indicates the need for future research for the following issues: Results of this study show that integration of MCDA models and GIS can be applied for erosion risk assessment in the Kuala Terengganu coastal area. Our study is the first attempt to use the integration of these methods in a coastal city risk assessment modeling that used different causative factors. Although the models can demonstrate the potential of using these integration methods and provide useful results in the study area, further research and more application of this methodology are required to test the transferability of the models in several criterion and alternatives with similar and different coastal hazard conditions.
For future studies, coastal environmental conservation can aggregate the environmental sustainability and vulnerability, because the hazard and vulnerability such as erosion and flood can affect the conservation and sustainability in coastal city areas. This research can also assist coastal managers, planners, and developers to identify threatened areas using the geospatial model and improve coastal land-use management. The future sustainability of the coastal city systems can then be projected using a time-series data map and satellite images for the identified indicators, the projected sustainability will be more informative. Therefore, decision-making information can be successfully derived and assist government policymaking to establish stronger sustainable development of the coastal zones. Using the spatial data and digital representation of rainfall, land use, topography, soils and other factors by GIS can help to better define the hazard and vulnerability and finally risk of erosion area in the coastal city zone. The use of these maps (suitable and unsuitable maps) enables managers and planners to improve the current policies and management of land use. It should be noted that the erosion criteria of this study should be changed in another study area because these indicators in Kuala Terengganu coastal city may not be applicable for other regions.
Author Contributions
Milad Bagheri; Zelina Zaiton Ibrahim; Shattri Mansor; Latifah Abd Manaf; Methodology, Milad Bagheri; Zelina Zaiton Ibrahim; Shattri Mansor; Latifah Abd Manaf; Software, Milad Bagheri; Zelina Zaiton Ibrahim; Validation, Milad Bagheri; Zelina Zaiton Ibrahim; Formal Analysis, Milad Bagheri; Zelina Zaiton Ibrahim; Latifah Abd Manaf; Investigation, Milad Bagheri; Zelina Zaiton Ibrahim; Shattri Mansor; Latifah Abd Manaf; Resources, Milad Bagheri; Zelina Zaiton Ibrahim; Data Curation, Milad Bagheri; Zelina Zaiton Ibrahim; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, Milad Bagheri; Zelina Zaiton Ibrahim; Writing—Review and Editing, Mohd Fadzil Akhir; Wan Izatul Asma Wan Talaat; Amin Beiranvand Pour; Visualization, Milad Bagheri; Zelina Zaiton Ibrahim; Supervision, Milad Bagheri; Zelina Zaiton Ibrahim; Shattri Mansor; Latifah Abd Manaf; Project Administration, Milad Bagheri; Zelina Zaiton Ibrahim; Shattri Mansor; Latifah Abd Manaf; Funding Acquisition, Milad Bagheri; Zelina Zaiton Ibrahim; Mohd Fadzil Akhir; Wan Izatul Asma Wan Talaat; supervision Amin Beiranvand Pour. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding for this project has been provided by the Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM) RUGS 4 with Project Number (03-04-11-1477RU) and RUGS 6 with Project Number (03-01-12-1664RU) programs.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to all the government agencies of Peninsular Malaysia who helped in this project, as well as the many pilots, which made this project possible. Thanks as well to the NAHRIN, DID, JUPEM, and SMART for providing time. Acknowledgment also goes to the INOS Higher Institution of Centre of Excellence (UMT-LRGS (56041)) and (Vot 66928) for partially supporting the extension of the study through the Long-term Research Grant Scheme on Ocean Climate Change under the Malaysian Ministry of Higher Education.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Rabati, A.P.; Jafarzadeh, A.A.; Shahbazi, F.; Rezapour, S.; Momtaz, H.R. Qualitative and quantitative land-suitability evalua-tion for sunflower and maize in the north-west of Iran. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2012, 58, 1229–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Nabiollahi, K.; Rasoli, L.; Kerry, R.; Scholten, T. Land Suitability Assessment and Agricultural Production Sustainability Using Machine Learning Models. Agronomy 2020, 10, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wrachien, D. Land use planning: A key to sustainable agriculture. In Conservation Agriculture; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 471–483. [Google Scholar]
- Azadi, H.; Barati, A.A.; Mohajeri, F.; Passel, S.V.; Witlox, F. Land-use suitability in Northeast Iran: Application of AHP-GIS hybrid model. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 396. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, P. Tourism Impacts, Planning and Management; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, R.; Crowe, T.P.; Hawkins, S.J. Rocky intertidal communities: Past environmental changes, present status and predictions for the next 25 years. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 168–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łabuz, T.A. Environmental Impacts—Coastal Erosion and Coastline Changes. In North Sea Region Climate Change Assessment; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 381–396. [Google Scholar]
- Mitasova, H.; Overton, M.F.; Recalde, J.J.; Bernstein, D.J.; Freeman, C.W. Raster-Based Analysis of Coastal Terrain Dynamics from Multitemporal Lidar Data. J. Coast. Res. 2009, 252, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolednik, D. Coastal monitoring for change detection using multi-temporal LiDAR data. In Proceedings of the CESCG 2014: The 18th Central European Seminar on Computer Graphics, Smolenice, Slovakia, 25–27 May 2014; pp. 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Chee, S.Y.; Othman, A.G.; Sim, Y.K.; Adam, A.N.M.; Firth, L. Land reclamation and artificial islands: Walking the tightrope between development and conservation. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2017, 12, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. A comprehensive risk analysis of coastal zones in China. Estuarine, Coast. Shelf. Sci. 2014, 140, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawala, S.; Ota, T.; Ahmed, A.U.; Smith, J.; Van Aalst, M. Development and Climate Change in Bangladesh: Focus on Coastal Flooding and the Sundarbans; OECD: Paris, UK, 2003; pp. 1–49. [Google Scholar]
- Bock, M.; Gasser, P.-Y.; Pettapiece, W.W.; Brierley, A.J.; Bootsma, A.; Schut, P.; Neilsen, D.; Smith, C.A.S. The Land Suitability Rating System Is a Spatial Planning Tool to Assess Crop Suitability in Canada. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdelRahman, M.A.; Natarajan, A.; Hegde, R. Assessment of land suitability and capability by integrating remote sens-ing and GIS for agriculture in Chamarajanagar district, Karnataka, India. Egypt. J. Remote. Sens. Space Sci. 2016, 19, 125–141. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Lee, M.W.V.; Wong, Y.H.I.; Tang, Y.T.K.; Aziz, S. GIS Based Multi-Criteria Land Suitability Assessment for Future Urban Development in The Country Park Peripheries of Hong Kong, Lantu North Country Park & Extension. Preprints 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P. Hazards, Disasters, and Risks. In IHDP/Future Earth-Integrated Risk Governance Project Series; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, K.; Hardy, R.D.; Lazrus, H.; Mendez, M.; Orlove, B.; Rivera-Collazo, I.; Winthrop, R. Explaining differential vulnera-bility to climate change: A social science review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2019, 10, e565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paul, S.K. Vulnerability Concepts and its Application in Various Fields: A Review on Geographical Perspective. J. Life Earth Sci. 2014, 8, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, B.; Vafeidis, A.T.; Zimmermann, J.; Nicholls, R.J. Future coastal population growth and exposure to sea-level rise and coastal flooding—A global assessment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118571. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. In Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Core Writing Team; Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; p. 151. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V.P., Zhai, A., Pirani, S.L., Connors, C., Péan, S., Berger, N., Caud, Y., Chen, L., Goldfarb, M.I., Gomis, M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021; 65p. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, R. Rethinking vulnerability and human behaviour in arid and semi-arid regions in northwestern China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimura, N. Sea-level rise caused by climate change and its implications for society. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2013, 89, 281–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McLean, R.F.; Tsyban, A.; Burkett, V.; Codignotto, J.O.; Forbes, D.L.; Mimura, N.; Ittekkot, V. Coastal Zones and Marine Ecosystems; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001; pp. 343–379. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhou, W. Prediction of Floor Water Inrush: The Application of GIS-Based AHP Vulnerable Index Method to Donghuantuo Coal Mine, China. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2011, 44, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Cazenave, A. Sea-Level Rise and Its Impact on Coastal Zones. Science 2010, 328, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, S.R. Migration, social capital and the environment: Considering Migrant Selectivity and Networks in Relation to Coastal Ecosystems. In Population and Environment: Methods of Analysis; Lutz, W., Prskawetz, A., Sanderson, W., Eds.; Population Council: New York, NY, USA, 2002; p. 252. [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth, P.L.; Melet, A.; Marcos, M.; Ray, R.D.; Wöppelmann, G.; Sasaki, Y.N.; Cirano, M.; Hibbert, A.; Huthnance, J.M.; Monserrat, S.; et al. Forcing Factors Affecting Sea Level Changes at the Coast. Surv. Geophys. 2019, 40, 1351–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raj, J.; Yusoff, I.; Abdullah, W.H. Past and present-day coastal changes between Kuala Sungai Besar and Kuala Besar, Kelantan Darul Naim. Bull. Geol. Soc. Malays. 2007, 53, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, P.H.; Akhir, M.F.; Qiao, F. Distinctive characteristics of upwelling along the Peninsular Malaysia’s east coast during 2009/10 and 2015/16 El Niños. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 184, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NAHRIM. The Study of the Impact of Climate Change on Sea Level Rise in Malaysia (Final Report); National Hydraulic Research Institute Malaysia: Seri Kembangan, Selangor, Malaysia, 2010; 172p. [Google Scholar]
- NAHRIM. Proceedings of the National Seminar on Coastal Morphology (COSMO) the Muddy Coast of Malaysia (Final Report), 14 December 2010; Coastal Research Centre, National Hydraulic Research Institute Malaysia (NAHRIM): Seri Kembangan, Selangor, Malaysia, 2010; 220p. [Google Scholar]
- Yanalagaran, R.; Ramli, N.I. Assessment of Coastal Erosion Related to Wind Characteristics in Peninsular Malaysia. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2018, 13, 3677–3690. [Google Scholar]
- Chalabi, A.; Mohd-Lokman, H.; Mohd-Suffian, I.; Karamali, K.; Karthigeyan, V.; Masita, M. Monitoring shoreline change using IKONOS image and aerial photographs: A case study of Kuala Terengganu area, Malaysia. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Commission VII Mid-Term Symposium “Remote Sensing: From Pixels to Processes”, Enschede, The Netherlands, 6 December 2006; pp. 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Z.; Feng, A.; Yin, P.; Xia, D. Coastal Erosion Induced by Human Activities: A Northwest Bohai Sea Case Study. J. Coast. Res. 2009, 253, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, J.; Pettitt, A.N.; Reeves, R.; Berthelsen, K.K. An efficient Markov chain Monte Carlo method for distributions with intractable normalising constants. Biometrika 2006, 93, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ballesteros, C.; Jiménez, J.A.; Valdemoro, H.I.; Bosom, E. Erosion consequences on beach functions along the Maresme coast (NW Mediterranean, Spain). Nat. Hazards 2017, 90, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liew, M.; Xiao, M.; Jones, B.M.; Farquharson, L.M.; Romanovsky, V. Prevention and control measures for coastal erosion in northern high-latitude communities: A systematic review based on Alaskan case studies. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 093002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, S.; Birkmann, J.; Glade, T. Vulnerability assessment in natural hazard and risk analysis: Current approaches and future challenges. Nat. Hazards 2012, 64, 1969–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aven, T. Risk assessment and risk management: Review of recent advances on their foundation. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2016, 253, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.-P.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Tong, Z.-J.; Bao, Y. GIS-based multi-dimensional risk assessment of the grassland fire in northern China. Nat. Hazards 2012, 64, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.; Sulaiman, W.; Vaghefi, N. Land Use Suitability Analysis Using Multi Criteria Decision Analysis Method for Coastal Management and Planning: A Case Study of Malaysia. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 5, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Everest, T.İ.M.U.Ç.İ.N.; Sungur, A.; Özcan, H. Determination of agricultural land suitability with a multiple-criteria deci-sion-making method in Northwestern Turkey. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 18, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Bagheri, M.; Sulaiman, W.N.A.; Vaghefi, N. Application of geographic information system technique and analytical hier-archy process model for land-use suitability analysis on coastal area. J. Coast. Conserv. 2013, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mensah, J. Sustainable development: Meaning, history, principles, pillars, and implications for human action: Literature review. Cogent Soc. Sci. 2019, 5, 1653531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariffin, B.; Helmy, E. Effect of Monsoons on Beach Morphodynamics in the East Coast of Peninsular Malaysia: Examples from Kuala Terengganu Coast. Ph.D. Dissertation, Universiti Malaysia Terengganu, Kuala Terengganu, Malaysia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Eleventh Malaysian Plan. The Economic Planning Unit Prime Minister’s Department, Putrajaya. 2015. Available online: http://rmk11.epu.gov.my/book/eng/Elevent-Malaysia-Plan/RMKe-11%20Book.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Bagheri, M.; Ibrahim, Z.Z.; Bin Mansor, S.; Manaf, L.A.; Badarulzaman, N.; Vaghefi, N. Shoreline change analysis and erosion prediction using historical data of Kuala Terengganu, Malaysia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, J.M.; Radzi, M.A.; Razali, S.M.; Cooke, F.M. Coastal Landscapes of Peninsular Malaysia: The Changes and Implica-tions for Their Resilience and Ecosystem Services. In Landscape Reclamation-Rising from What’s Left; Intech Open: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.H.; Siwar, C. Tourism for Economic Development in East Coast Economic Region (ECER), Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia; Institute for Enviroment and Development, University Kebangsaan Malaysia: Bangi, Malaysia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, Z.A.; Yaacob, M.R.; Ibrahim, M.D. Logistics Development Study of East Coast Region: Early Investigation; University of Malaysia: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Amini, S.; Rohani, A.; Aghkhani, M.H.; Abbaspour-Fard, M.H.; Asgharipour, M.R. Assessment of land suitability and agri-cultural production sustainability using a combined approach (Fuzzy-AHP-GIS): A case study of Mazandaran province, Iran. Inf. Process. Agric. 2020, 7, 384–402. [Google Scholar]
- Sarif, M.O.; Gupta, R.D. Spatiotemporal mapping of Land Use/Land Cover dynamics using Remote Sensing and GIS approach: A case study of Prayagraj City, India (1988–2018). Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahila-Tani, M.; Kytta, M.; Geertman, S. Does mapping improve public participation? Exploring the pros and cons of using public participation GIS in urban planning practices. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 186, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, H.; Fereydoon, V. Transportation planning and choosing the best route after earthquake with emphasis on crisis reduction by GIS. Geography 2019, 9, 745–763. [Google Scholar]
- Barakat, A.; Ouargaf, Z.; Khellouk, R.; El Jazouli, A.; Touhami, F. Land Use/Land Cover Change and Environmental Impact Assessment in Béni-Mellal District (Morocco) Using Remote Sensing and GIS. Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 3, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewski, B. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for Disaster Management; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Komolafe, A.A.; Herath, S.; Avtar, R. Sensitivity of flood damage estimation to spatial resolution. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2015, 11, S370–S381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.S.; Patel, K.; Pendem, S.; Shrivatra, N. Morphometric Analysis and Prioritization of Sub-watersheds for Man-agement of Natural Resources using GIS: A case study of Rajasthan, India. Int. J. Adv. Remote. Sens. GIS 2020, 9, 3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemenkova, P. An empirical study of R applications for data analysis in marine geology. Mar. Sci. Technol. Bull. 2019, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ioki, K.; Din, N.M.; Ludwig, R.; James, D.; Hue, S.W.; Johari, S.A.; Phua, M.H. Supporting forest conservation through commu-nity-based land use planning and participatory GIS–lessons from Crocker Range Park, Malaysian Borneo. J. Nat. Conserv. 2019, 52, 125740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allani, M.; Mezzi, R.; Abdallah, W.; Gharbi, A.; Zouabi, A.; Hedhli, K.; Sahli, A. A contribution to an advisory plan for inte-grated irrigation water management at Nebhana dam system: From research to operational support. Epic. Ser. Eng. 2018, 3, 26-15. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.; Sarkar, D.; Mondal, P.; Goswami, S. GIS and multi-criteria decision-making assessment of sites suitability for agriculture in an anabranching site of sooin river, India. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 7, 571–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, M.J.; Hess, G.R. Planning open spaces for wildlife 2: Modeling and verifying focal species habitat. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2003, 64, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, F.F., Jr.; De Vries, W.T. Establishment of Natural Hazards Mapping Criteria Using Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP). Front. Sustain. 2021, 2, 667105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostić, B.; Šarić, K.; Cvetković, V.; Krstekanic, N.; Pantelić, N.; Bosić, D. A reinterpretation of the geological map of northwestern part of the Lece Volcanic Complex. In Proceedings of the Émile Argand Conference-13th Workshop on Alpine Geological Studies, Zlatibor, Serbia, 7–18 September 2017; p. 55. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jaehnig, E.J.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, B. WebGestalt 2019: Gene set analysis toolkit with revamped UIs and APIs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W199–W205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He-Hua, W.; Jian-Jun, Z.; Xiao-Yan, G.; Ye, C. A Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis Method for Alternative Assessment Results Obeying a Particular Distribution and Application. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, G.; Domínguez-Gómez, J.A.; Aledo, A.; Urgeghe, A.M. Participatory multi-criteria decision analysis for prioritizing impacts in environmental and social impact assessments. Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 2018, 14, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiker, G.A.; Bridges, T.S.; Varghese, A.; Seager, T.P.; Linkov, I. Application of multicriteria decision analysis in environmen-tal decision making. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. Int. J. 2005, 1, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janković, A.; Affairs, D.F.T.M.O.T.A.M.; Popović, M. Methods for assigning weights to decision makers in group AHP decision-making. Decis. Mak. Appl. Manag. Eng. 2019, 2, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadskas, E.K.; Pamučar, D.; Stević, Ž.; Mardani, A. Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Techniques for Improvement Sustainability Engineering Processes. Symmetry 2020, 12, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanković, M.; Gladović, P.; Popović, V. Determining the importance of the criteria of traffic accessibility using fuzzy AHP and rough AHP method. Decis. Mak. Appl. Manag. Eng. 2019, 2, 86–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkayesh, A.E.; Pamucar, D.; Ecer, F.; Chatterjee, P. An integrated BWM-LBWA-CoCoSo framework for evaluation of healthcare sectors in Eastern Europe. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2021, 101052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadjadi, S.J.; Karimi, M. Best-worst multi-criteria decision-making method: A robust approach. Decis. Sci. Lett. 2018, 7, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamučar, D.; Ecer, F.; Cirovic, G.; Arlasheedi, M.A. Application of Improved Best Worst Method (BWM) in Real-World Problems. Mathematics 2020, 8, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žižović, M.; Pamucar, D. New model for determining criteria weights: Level Based Weight Assessment (LBWA) model. Decis. Mak. Appl. Manag. Eng. 2019, 2, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, L.-M.; Tu, K.-J. Establishing Merger Feasibility Simulation Model Based on Multiple-Criteria Decision-Making Method: Case Study of Taiwan’s Property Management Industry. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamučar, D.; Stević, Ž.; Sremac, S. A New Model for Determining Weight Coefficients of Criteria in MCDM Models: Full Consistency Method (FUCOM). Symmetry 2018, 10, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sofuoğlu, M.A. Fuzzy Applications of FUCOM Method in Manufacturing Environment. J. Polytech. 2019, 23, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.; Aumann, I.; Hollander, I.; Damm, K.; Von Der Schulenburg, J.-M.G. Applying the Analytic Hierarchy Process in healthcare research: A systematic literature review and evaluation of reporting. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2015, 15, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ossadnik, W.; Schinke, S.; Kaspar, R.H. Group aggregation techniques for analytic hierarchy process and analytic net-work process: A comparative analysis. Group Decis. Negot. 2016, 25, 421–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bello-Dambatta, A.; Farmani, R.; Javadi, A.; Evans, B. The Analytical Hierarchy Process for contaminated land management. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2009, 23, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Dale, A. JavaAHP: A web-based decision analysis tool for natural resource and environmental management. Environ. Model. Softw. 2001, 16, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orencio, P.M.; Fujii, M. A localized disaster-resilience index to assess coastal communities based on an analytic hierarchy process (AHP). Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2013, 3, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.J.; Braaten, R.; Veitch, S.M.; Lees, B.G.; Sharma, S. Multi-criteria decision analysis in spatial decision support: The AS-SESS analytic hierarchy process and the role of quantitative methods and spatially explicit analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2005, 20, 955–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadeh, A.; Ghaderi, S.F.; Izadbakhsh, H. Integration of DEA and AHP with computer simulation for railway system im-provement and optimization. Appl. Math. Comput. 2008, 195, 775–785. [Google Scholar]
- Bhutta, K.S.; Huq, F. Supplier selection problem: A comparison of the total cost of ownership and analytic hierarchy process approaches. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2002, 7, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, P.; Tabucanon, M.T.; Ogunlana, S. Planning for project control through risk analysis: A petroleum pipeline-laying project. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 1994, 12, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzerra, A.; Cherrared, M.; Chocat, B.; Cherqui, F.; Zekiouk, T. Decision support for sustainable urban drainage system management: A case study of Jijel, Algeria. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 101, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.-M.; Wu, K.-S.; Wang, M.-J. Using the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) and Delphi Analysis to Evaluate Key Factors in the Development of the Taiwan Cruise Tourism Industry. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 36, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skulmoski, G.; Hartman, F.T.; Krahn, J. The Delphi Method for Graduate Research. J. Inf. Technol. Educ. Res. 2007, 6, 001–021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.; Lyytinen, K.; Keil, M.; Cule, P. Identifying Software Project Risks: An International Delphi Study. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2001, 17, 5–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phua, M.-H.; Minowa, M. A GIS-based multi-criteria decision making approach to forest conservation planning at a landscape scale: A case study in the Kinabalu Area, Sabah, Malaysia. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2005, 71, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkan, T.E.; Elsharida, W.M. Combining AHP and ROC with GIS for Airport Site Selection: A Case Study in Libya. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, M.; Thinh, N.X. Evaluation of Land Cover Change and Agricultural Protection Sites: A GIS and Remote Sensing Approach for Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Linkov, I.; Satterstrom, F.K.; Kiker, G.; Batchelor, C.; Bridges, T.; Ferguson, E. From comparative risk assessment to multi-criteria decision analysis and adaptive management: Recent developments and applications. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 1072–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, R.; Devillers, R.; Luther, J.E.; Eddy, B.G. GIS-based multiple-criteria decision analysis. Geography Compass 2011, 5, 412–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.; Azmin, W.N. Application of GIS and AHP technique for land-use suitability analysis on coastal area in terengganu. In World Automation Congress (WAC); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Elsayah, O.S. A Framework for Improvement of Contractor Selection Procedures on Major Construction Project in Libya. Ph.D. Thesis, Edinburgh Napier University, Edinburgh, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vaidya, O.S.; Kumar, S. Analytic hierarchy process: An overview of applications. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2006, 169, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaka, A.; Labib, A. Analytic hierarchy process and expert choice: Benefits and limitations. Or Insight 2009, 22, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saaty, T.L. Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process. Int. J. Serv. Sci. 2008, 1, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zainuddin, N.; Abdul, G.D.S.; Mohd, S.A. Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) in Multi Criteria Decision Making: A Case of Locating the Operations of Low Cost Carrier in Malaysia. In Proceedings of the 2012 WASET, George Town, Malaysia, 6–7 December 2012; pp. 638–650. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. A scaling method for priorities in hierarchical structures. J. Math. Psychol. 1977, 15, 234–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, N.; Ramanathan, R. A review of applications of Analytic Hierarchy Process in operations management. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2012, 138, 215–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafaei, N.; Ribeiro, R.A.; Camarinha-Matos, L.M. Normalization Techniques for Multi-Criteria Decision Making: Analytical Hierarchy Process Case Study. In Proceedings of the 7th Technological Innovation for Cyber-Physical Systems, Singapore, 11–13 April 2016; pp. 261–269. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, I.; Verma, M.K. Application of Analytic Hierarchy Process in Water Resources Planning: A GIS Based Approach in the Identification of Suitable Site for Water Storage. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 5093–5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.J. Shoreline mapping techniques. J. Coast. Res. 2000, 16, 111–124. [Google Scholar]
- Thieler, E.R.; Himmelstoss, E.A.; Zichichi, J.L.; Ergul, A. The Digital Shoreline Analysis System (DSAS) Version 4.0-An ArcGIS extension for calculating shoreline change. In Open-File Report; No. 2008-1278; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sailan, M.I.M.; Hee, Y.Y.; Bedurus, E.A.; Latif, M.T. A Preliminary Study of Water Quality Index in Terengganu River Basin, Malaysia. Sains Malays. 2015, 44, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Wahaba, N.; Kamarudina, M.K.A.; Torimanb, M.E.; Juahira, H.; Saada, M.H.M.; Ataa, F.M.; Harithe, H. Sedimentation and water quality deterioration problems at Terengganu River Basin, Terengganu, Malaysia. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 149, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Razali, A.; Ismail, S.N.S.; Awang, S.; Praveena, S.M.; Abidin, E.Z. Land use change in highland area and its impact on river water quality: A review of case studies in Malaysia. Ecol. Process. 2018, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finizio, A.; Villa, S. Environmental risk assessment for pesticides: A tool for decision making. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2002, 22, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uricchio, V.F.; Giordano, R.; Lopez, N. A fuzzy knowledge-based decision support system for groundwater pollution risk evaluation. J. Environ. Manag. 2004, 73, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noy, I.; Yonson, R. Economic Vulnerability and Resilience to Natural Hazards: A Survey of Concepts and Measurements. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, N.; Huang, H. Assessment of world disaster severity processed by Gaussian blur based on large historical data: Casualties as an evaluating indicator. Nat. Hazards 2018, 92, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauti, N.S.; Daud, M.E.; Kaamin, M.; Sahat, S. GIS spatial modelling for seismic risk assessment based on exposure, resili-ence, and capacity indicators to seismic hazard: A case study of Pahang, Malaysia. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2021, 12, 1948–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).