Beautiful China Construction Evaluation Method Based on POIs: Case Study of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Basic Data
2.2. Index System
2.3. Evaluation Method
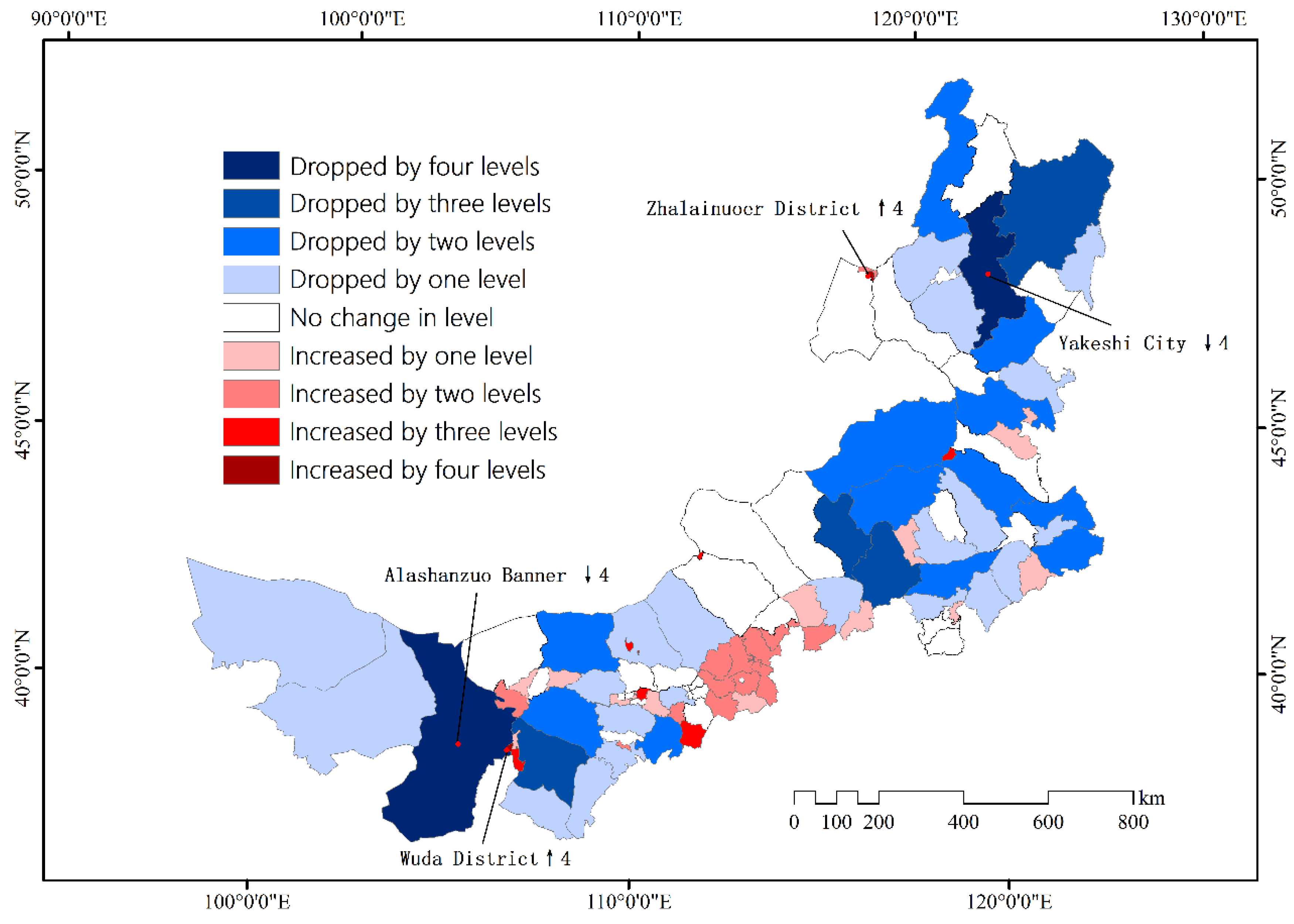
3. Results
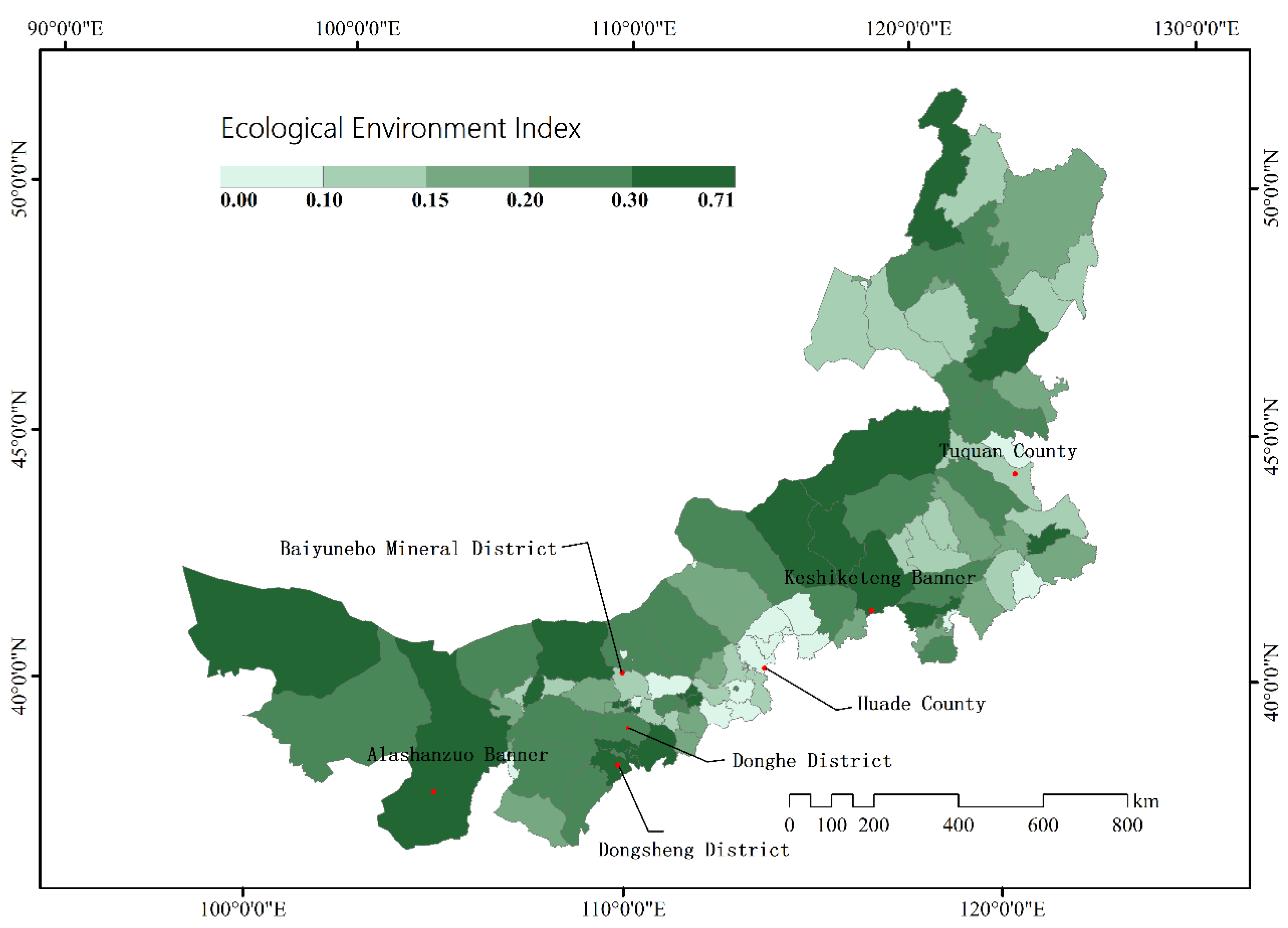
3.1. Ecological Environment
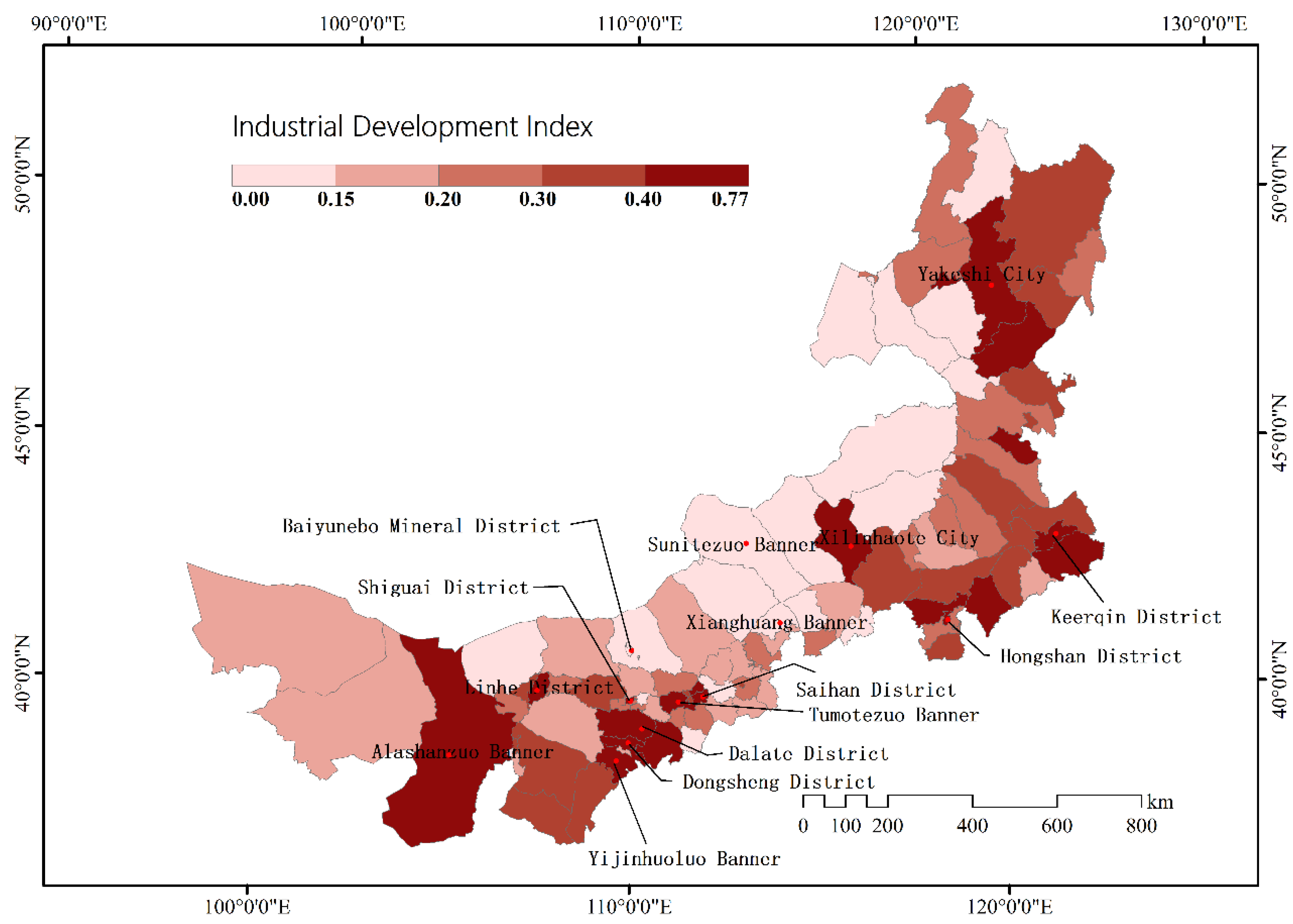
3.2. Industrial Development
3.3. Social Harmony
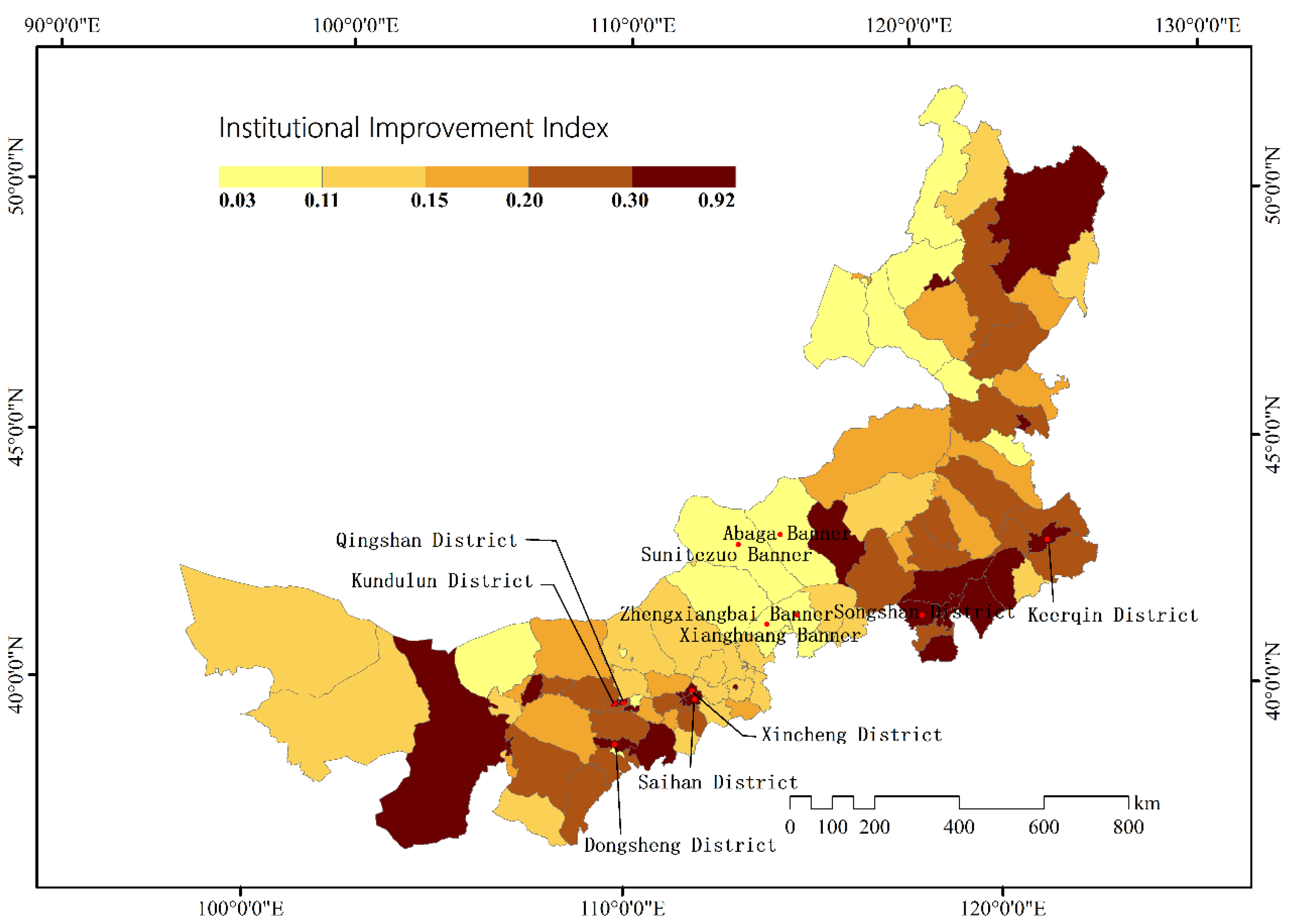
3.4. Institutional Improvement
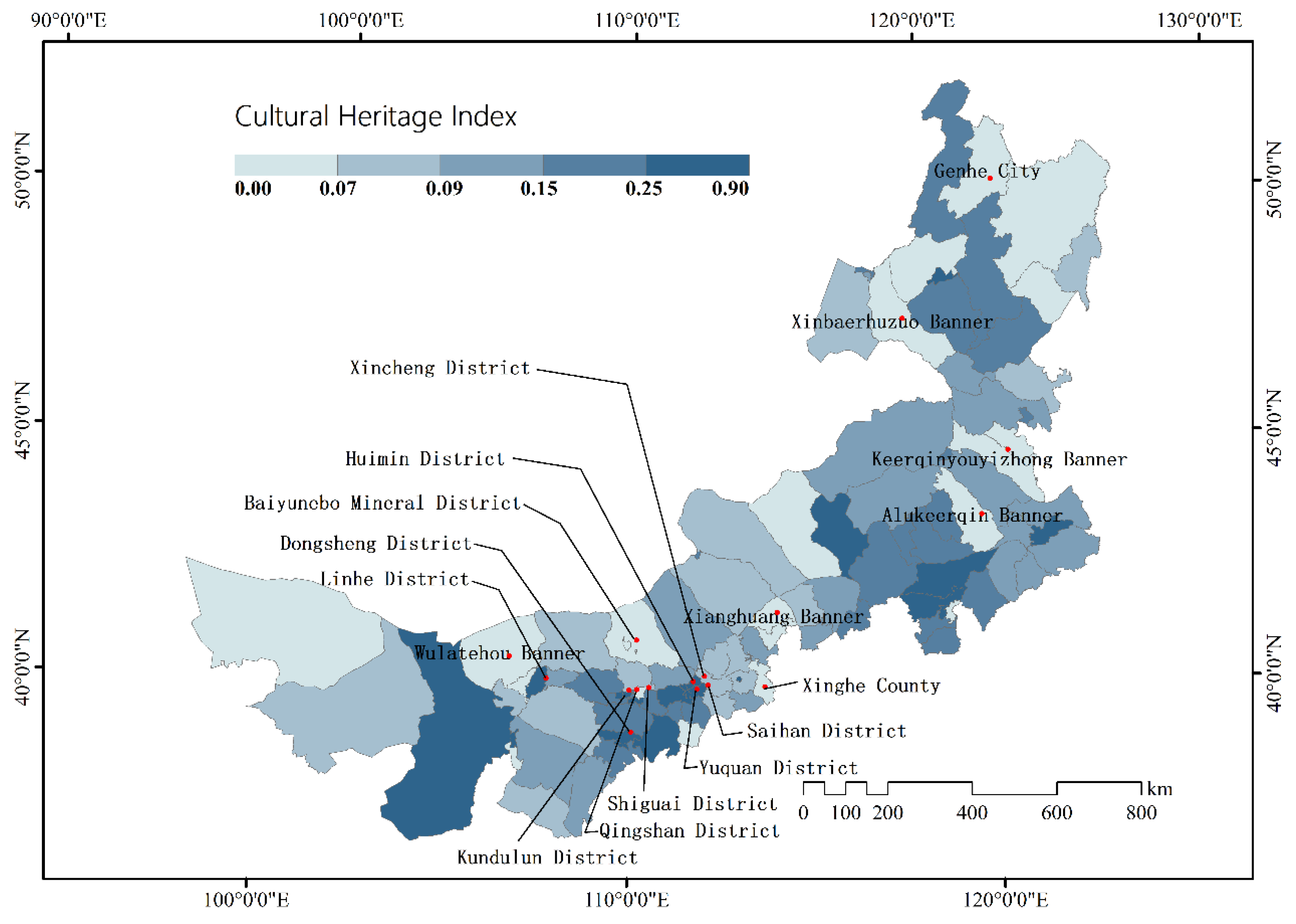
3.5. Cultural Heritage
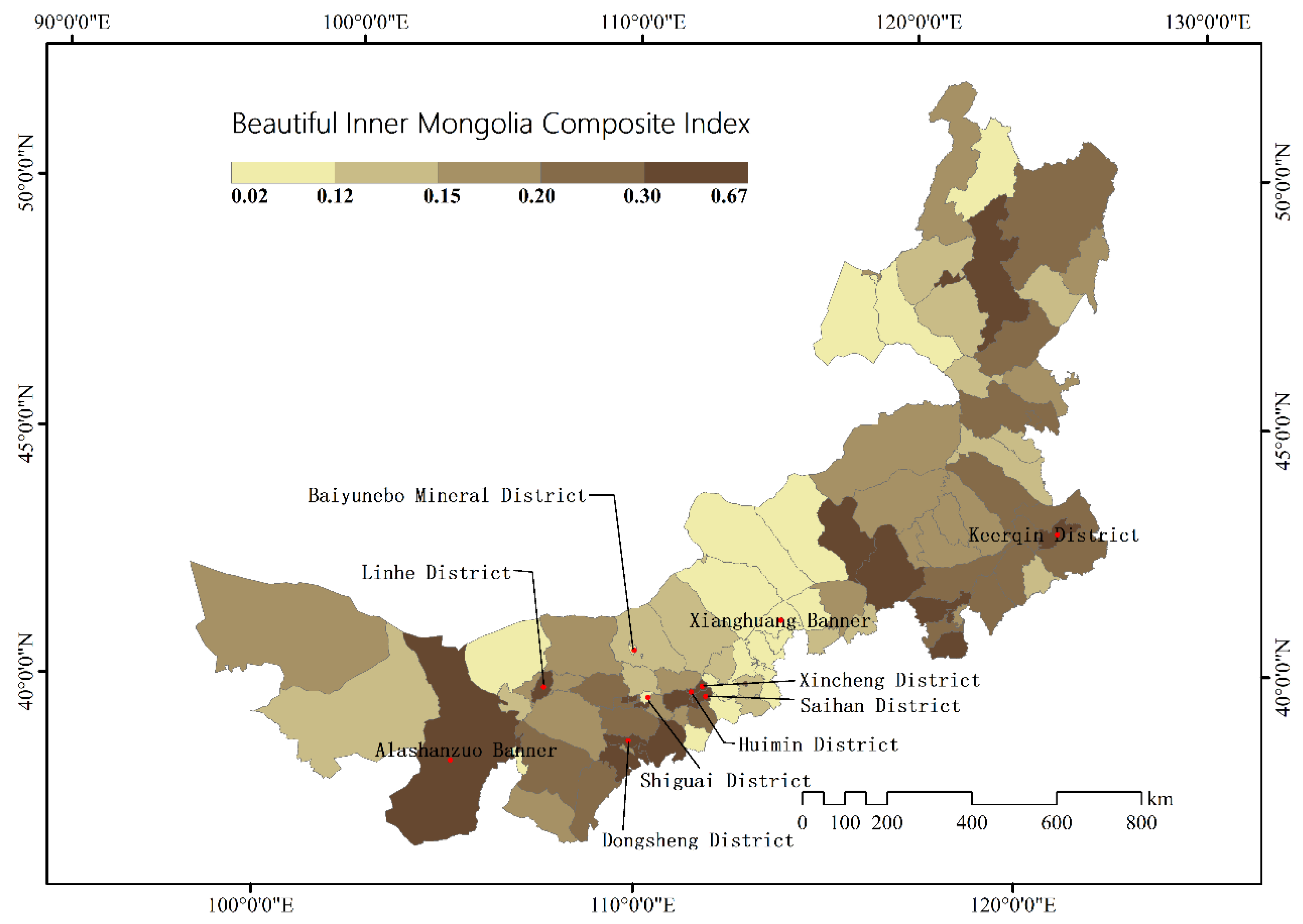
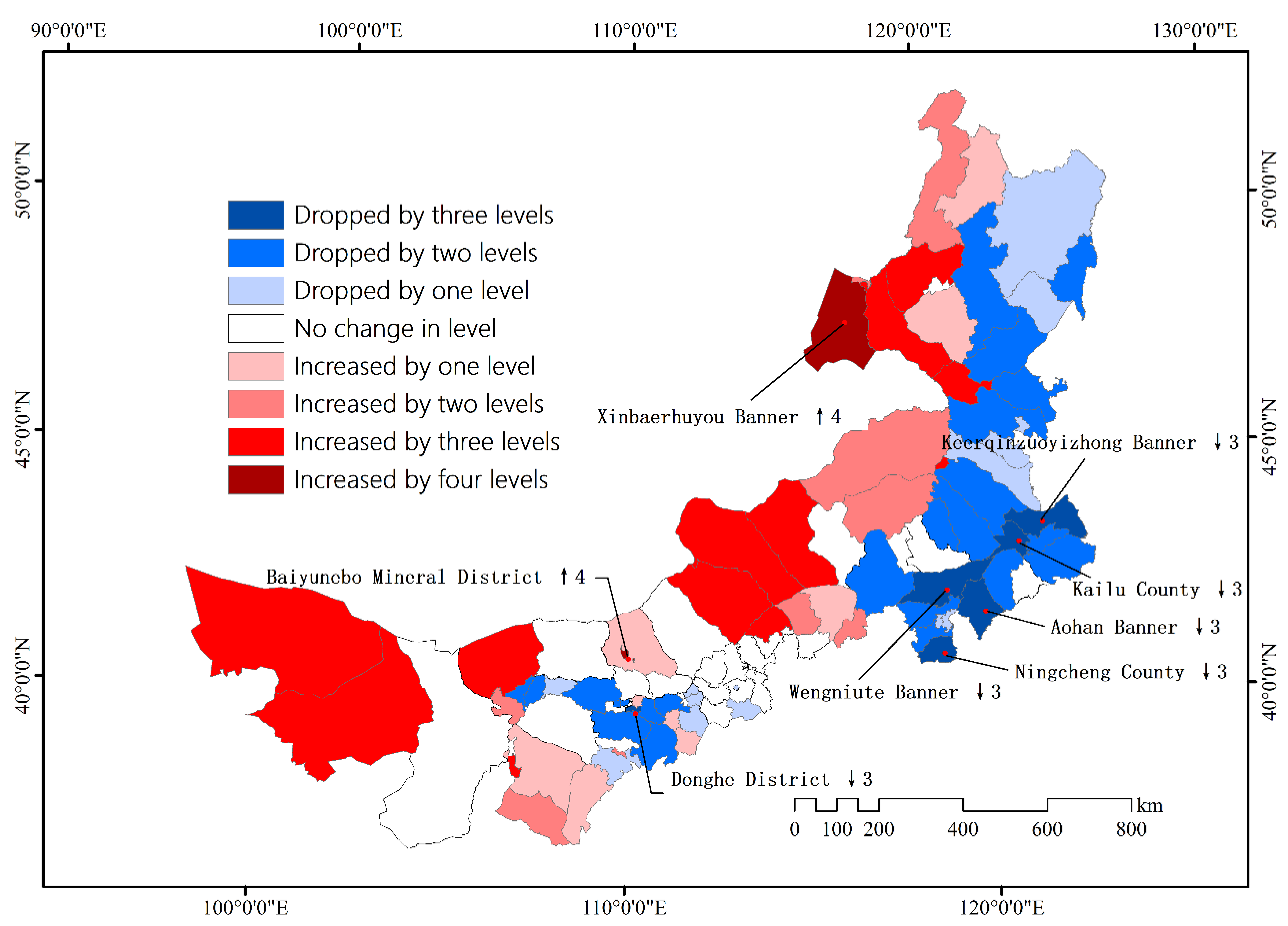
3.6. Comprehensive Evaluation of Beautiful Inner Mongolia
4. Discussion
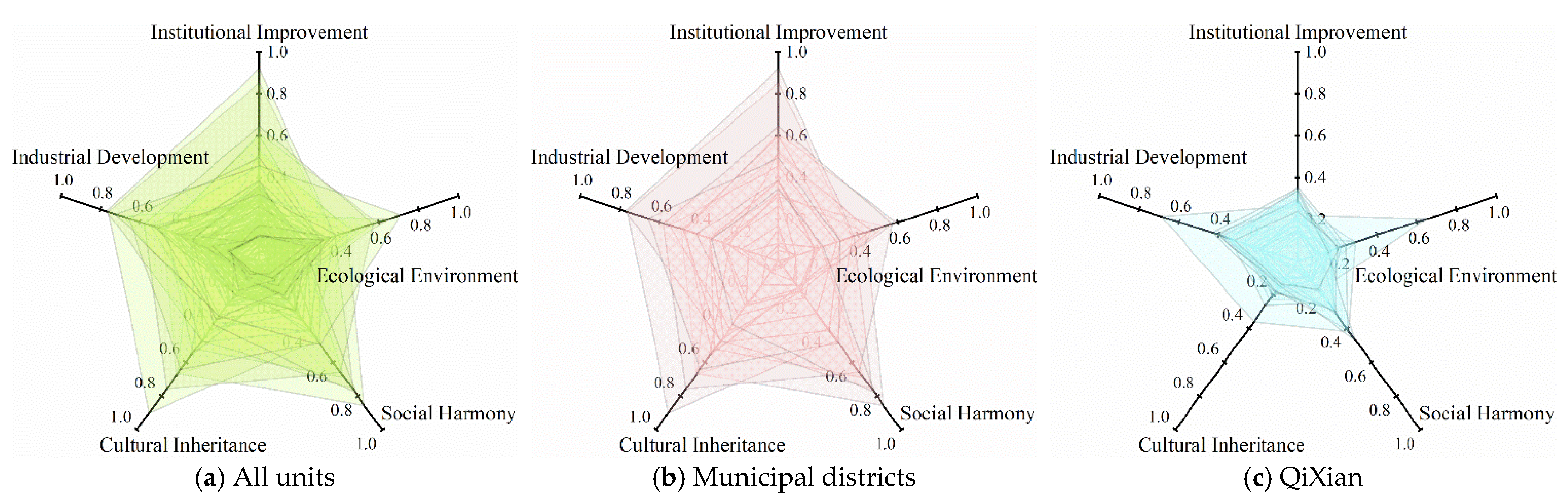
4.1. Differences between Municipal Districts and QiXian
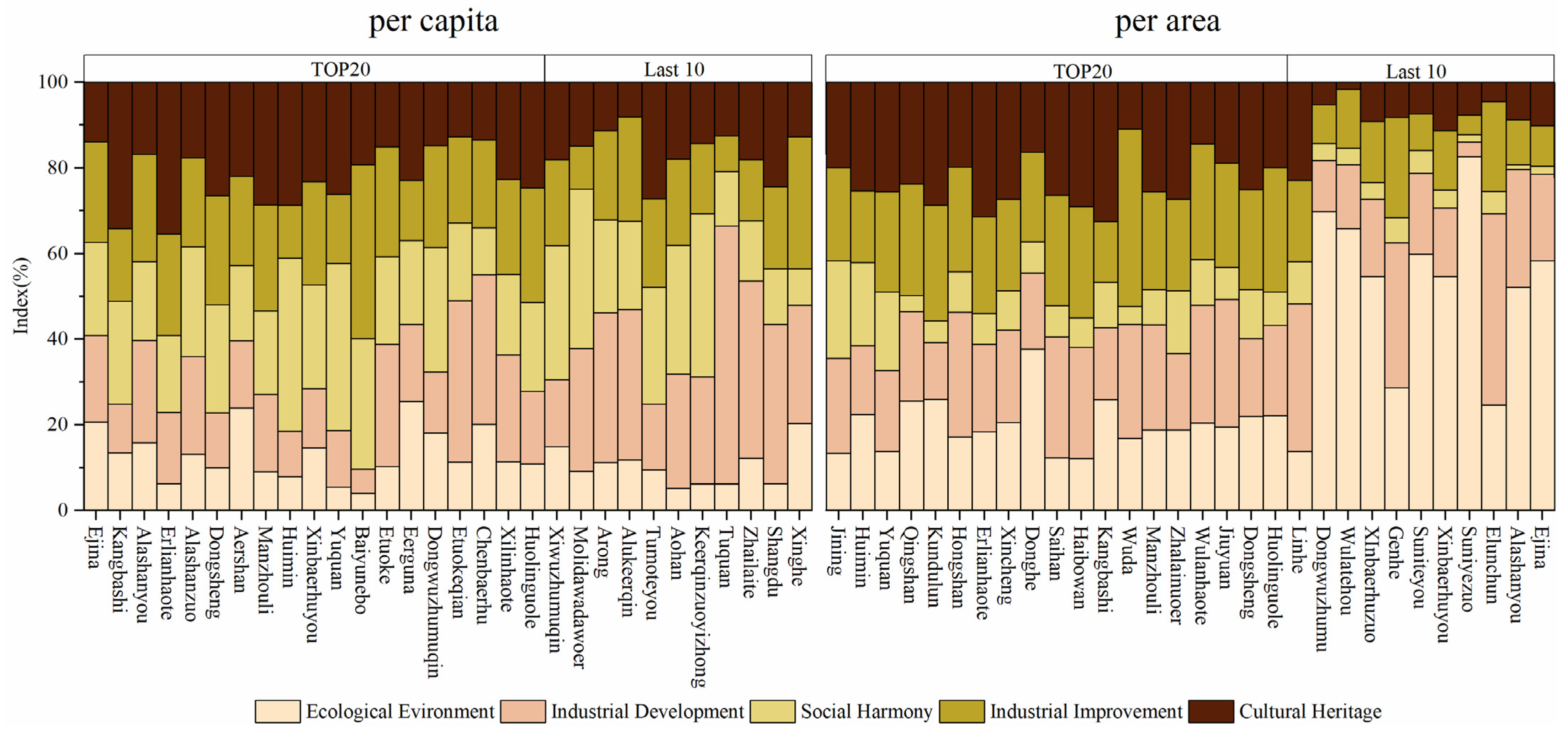
4.2. Differences between Absolute Quantity and Relative Quantity
4.3. Advantages and Uncertainties of Methods Based on POI Data
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xinhua News Agency. Mountains Want Green, People Want Rich—The First Mention of “Beautiful China” in the Report of the 18th National Congress of the Communist Party of China Attracts Attention. Website of the Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China. 8 November 2012. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/jrzg/2012-11/08/content_2260440.htm (accessed on 8 July 2020).
- Fang, C.L.; Wang, Z.B.; Liu, H.M. Exploration of the theoretical basis and evaluation plan for the construction of Beautiful China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 619–632. [Google Scholar]
- National Development and Reform Commission. The National Development and Reform Commission issued the “Green Development Index System” and “Ecological Civilization Construction Assessment Target System”. Website of the Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China. 12 December 2016. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2016-12/23/content_5151575.htm (accessed on 8 July 2020).
- Xinhua News Agency. Promoting Green Development and Building a Beautiful China—An Overview of Comprehensively Deepening the Reform of the Ecological Civilization System Since the Third Plenary Session of the 18th Central Committee. Website of the Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China. 3 January 2019. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2019-01/03/content_5354583.htm (accessed on 8 July 2020).
- National Development and Reform Commission. Notice of the National Development and Reform Commission on Issuing the “Beautiful China Construction Evaluation Index System and Implementation Plan”. Website of the Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China. 28 February 2020. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-03/07/content_5488275.htm (accessed on 8 July 2020).
- Ge, Q.S.; Fang, C.L.; Jiang, D. The mission of geography and the coupling path of man-earth system in the construction of Beautiful China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, L.; Cai, S.W.; Cheng, L. Evaluation of China’s urban construction level from the perspective of “Beautiful China”—Based on a comparative study of provincial capitals and sub-provincial cities. Thinking 2013, 39, 143–148. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Shao, C.F.; Sun, Z.S.; Ju, M.T. Research on Evaluation Index System of “Beautiful Country”. Ecol. Econ. 2014, 30, 392–398. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, Z.L.; Zha, X.C. The construction and application of the evaluation index system of regional ecological civilization construction from the perspective of “Beautiful China”—Taking Shaanxi as an example. Ecol. Econ. 2014, 30, 395–398. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Y.B.; Xie, B.G. “Beautiful China” regional construction evaluation index system design. Stat. Decis. 2015, 5, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.Y.; Zhao, L.K.; Liu, Y.W. Construction and Demonstration of Evaluation Index System of “Beautiful China”. Stat. Decis. 2014, 9, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, B.L.; Chen, Y.L.; Li, X.Q. Application of Coupling Coordination Model in the Construction Evaluation of “Beautiful China”. Econ. Geogr. 2016, 36, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, B.L.; Xiang, Y.B. Construction and Application of Evaluation Index System for the Construction Level of Beautiful China. Econ. Geogr. 2017, 37, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.F.; Wang, Q.Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Ren, W.B. The principle and method of national-scale social and economic data gridding. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2011, 13, 573–578. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, Y.F.; Liu, J.Y.; Liu, Y.; Ren, W.B.; Li, J. Identification of Chinese urban agglomerations based on transportation, population and economy. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2011, 66, 761–770. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Yeh, A.G.; Xie, J.Y.; Ma, C.L.; Li, Q.Q. Measurements of POI-based mixed use and their relationships with neighbourhood vibrancy. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 658–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, K.F.; Chang, Z.J.; Chen, Z.Q.; Wu, J.P.; Yu, B.L. Identifying and evaluating poverty using multisource remote sensing and point of interest (POI) data: A case study of Chongqing, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.W.; Zheng, M.Y. Online Spatial Evaluation of Residential Livability Based on POI Data Mining and LMBP Algorithm. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yan, Q.W.; Bian, Z.F.; Liu, B.L.; Wu, Z.H. A POI and LST Adjusted NTL Urban Index for Urban Built-Up Area Extraction. Sensors 2020, 20, 2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.Y.; Tan, H.L.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.H. Research on Convenience Index of Urban Life Based on POI Data. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1646, 012073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Yin, P.F.; Lee, W.C.; Lee, D.L. Exploiting geographical influence for collaborative point-of-interest recommendation. In Proceedings of the 34th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Beijing, China, 24–28 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Hui, X. Point-of-Interest Recommendation in Location Based Social Networks with Topic and Location Awareness. In Proceedings of the 2013 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining, Austin, TX, USA, 2–4 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie, G.; Janowicz, K.; Adams, B. A weighted multi-attribute method for matching user-generated Points of Interest. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 41, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.F.; Han, Y.Q. Identification of Urban Functional Areas Based on POI Data: A Case Study of the Guangzhou Economic and Technological Development Zone. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.P.; Cao, Y.H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.J.; Wu, W.Z.; Su, F.Z. Research on urban building function classification method based on POI data. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2020, 22, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.Y.; Qing, L.B.; Han, L.M.; Liu, M.; Peng, Y.H.; Shen, L.F. A New Remote Sensing Images and Point-of-Interest Fused (RPF) Model for Sensing Urban Functional Regions. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakillah, M.; Liang, S.; Mobasheri, A.; Arsanjani, J.J.; Zipf, A. Fine-resolution population mapping using OpenStreetMap points-of-interest. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 1940–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.T.; Zhao, N.Z.; Yang, X.C.; Ouyang, Z.T.; Liu, X.P.; Chen, Q.; Hu, K.J.; Yue, W.Z.; Qi, J.G.; Li, Z.S.; et al. Improved population mapping for China using remotely sensed and points-of-interest data within a random forests model. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.C.; Ye, T.T.; Zhao, N.Z.; Chen, Q.; Yue, W.Z.; Qi, J.G.; Zeng, B.; Jia, P. Population Mapping with Multisensor Remote Sensing Images and Point-Of-Interest Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pouke, M.; Goncalves, J.; Ferreira, D.; Kostakos, V. Practical simulation of virtual crowds using points of interest. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2016, 57, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Long, Y. Automated identification and characterization of parcels with OpenStreetMap and points of interest. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2016, 43, 341–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.Y.; Yang, J.; Li, X.C.; Gong, P. Mapping Urban Land Use by Using Landsat Images and Open Social Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, X.P.; Liu, P.H.; Liang, Z.T.; Zhang, J.B.; Mai, K. Sensing spatial distribution of urban land use by integrating points-of-interest and Google Word2Vec model. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 825–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Xing, H.F.; Hou, D.Y.; Xu, H.B.; Liu, J.R. A method of applying interest point data for land surface cover classification. Inf. Sci. Ed. 2019, 44, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Xia, J.J.; Fang, H.; Zuo, H.T.; Jiang, Y. Roadmap towards clean heating in 2035: Case study of inner Mongolia, China. Energy 2019, 189, 116152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.T.; Hu, Y.F.; Han, Y.Q. Spatial Distribution and Dynamic Changes in Research Hotspots for Desertification in China Based on Big Data from CNKI. J. Resour. Ecol. 2019, 10, 612,692–703. [Google Scholar]
- Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Statistics Bureau. Inner Mongolia Statistical Yearbook-2019. 2019. Available online: http://tj.nmg.gov.cn/Files/tjnj/2019/indexch.htm (accessed on 25 December 2020).
- National Basic Geographic Information Center. 1:1 Million National Basic Geographic Database. 2017. Available online: https://www.webmap.cn/commres.do?method=result100W (accessed on 29 December 2019).
- Ministry of Civil Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. 2019. Available online: http://www.mca.gov.cn/ (accessed on 25 December 2020).
- Thomas, L.S. How to make a decision: The analytic hierarchy process. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1990, 48, 9–26. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.M.; Deng, X.; Zeng, H.J.; Chen, J.Y.; Zhao, J.F. Analysis of Analytic Hierarchy Process Weight Calculation Method and Its Application Research. Math. Pract. Theory 2012, 42, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.W.; Li, X.S. Measurement and comparison of regional integration of urban agglomerations in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2013, 22, 996–1003. [Google Scholar]

| Goals (First-Level Indicators) | Dimensions (Second-Level Indicators) | Code | POI Types (Third-Level Indicators) | Typical Surface Objects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beautiful China | Ecological Environment | 110100–110105 | Park squares | Park plazas, parks, zoos, botanical gardens, aquariums, city squares |
| 110000, 110201–110203, 110208–110209 | Scenic spots | Tourist attractions, world heritage sites, national attractions, provincial attractions, beaches, viewing attractions | ||
| 190202–190205 | Natural landscape | Islands, mountains, rivers, lakes | ||
| 080500–080505 | Leisure venues | Other leisure facilities, playgrounds, fishing parks, picking gardens, campsites, water sports centers | ||
| 080400–080402 | Vacation and recuperation places | Resorts, resorts, sanatoriums | ||
| Industrial Development | 170400–170408 | Agricultural, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishing bases (AFAF) | Fish farms, farms, forest farms, pastures, poultry breeding bases, vegetable bases, fruit bases, flower nursery bases and other AFAF bases | |
| 170300 | Factories | Factories | ||
| 170200–170209 | Companies | Companies, advertising decoration, construction companies, pharmaceutical companies, machinery and electronics, metallurgical chemicals, network technology, commercial trade, telecommunications companies, mining companies | ||
| 120100 | Industrial Parks | Industrial parks | ||
| 190301–190311 | Road facilities | Roads, intersections, roundabouts, highway entrances and exits, overpasses, bridges, urban express entrances and exits, tunnels, railways | ||
| Social Harmony | 200000 | Public facilities | Public facilities, newsstands, public telephones, public toilets, restrooms, disabled/accessible toilets, baby changing rooms/nursing rooms/mother and child rooms, emergency shelters | |
| 090000–090400 | Healthcare services | Medical and healthcare service places, general hospitals, tertiary A hospitals, health centers, specialist hospitals, plastic surgery, dental hospitals, eye hospitals, ENT hospitals, chest hospitals, orthopedic hospitals, tumor hospitals, brain hospitals, gynecological hospitals, psychiatric hospitals, infectious disease hospitals, clinics, emergency centers | ||
| 060100–060103, 060400–060415 | Large shopping malls and supermarkets | Shopping malls, shopping malls, general shopping malls, duty-free shops, supermarkets, Carrefour, Wal-Mart, China Resources, Beijing Hualian, Lotte Mart, Watson | ||
| 060200 | People’s shops/convenience stores | People’s shops/convenience stores | ||
| 150100–150700 | Transportation hub | Airports, railway stations, ports, long-distance bus stations, subway stations, light rail stations, bus stations | ||
| Institutional Improvement | 130104–130106 | Government agencies | District/county governments and institutions, township-level governments and institutions, governments and institutions below the township level | |
| 130501–130503, 130506 | Public prosecution law agencies | Public security police, procuratorates, courts, social security agencies | ||
| 130700–130703 | Industrial and commercial tax agencies | Industrial and commercial departments, state tax authorities, land tax authorities | ||
| 160400–160408, 160100–160121 | Financial insurance services | Insurance companies, People’s Insurance Company of China, China Life Insurance Company, Ping An Insurance Company of China, China Pacific Insurance, Xinhua Life Insurance Company, Huatai Property Insurance Co., Ltd., Taikang Life Insurance Company, Bank, People’s Bank of China, China Development Bank, China Export-Import Bank, Bank of China, Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, China Construction Bank, Agricultural Bank of China, Bank of Communications, China Merchants Bank, Hua Xia Bank, China CITIC Bank, China Minsheng Bank, China Everbright Bank, Shanghai Pudong Development Bank, Ping An Bank, Industrial Bank, Rural commercial bank | ||
| 130404–130408 | Social groups | Disabled Persons’ Federation, Red Cross, Consumer Association, Industry Association, Charity | ||
| Cultural Heritage | 140100, 140500, 140800 | Public cultural space | Museums, libraries, cultural palaces | |
| 110204–110207 | Religious cultural landscape | Memorials, temples, churches, Muslim temples | ||
| 061205, 080600–080603, 141000 | Literary and artistic landscape | Bookstores, theater-related, cinemas, concert halls, theaters, literary and artistic groups | ||
| 141201–141203 | Schools | Institutions of higher learning, middle schools, primary schools | ||
| 141100–141105 | Media agencies | Media organizations, TV stations, radio stations, newspapers, magazines, publishing houses |
| First-Level Indicators | Second-Level Indicators | Third-Level Indicators | Weights | Gross |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beautiful Inner Mongolia Index | Ecological Environment Index | Park plazas | 0.0537 | 0.2 |
| Scenic spots | 0.0977 | |||
| Natural landscape | 0.0102 | |||
| Leisure venues | 0.0192 | |||
| Resort and recuperate | 0.0192 | |||
| Industrial Development Index | AFAF bases | 0.0687 | 0.2 | |
| Factories | 0.0258 | |||
| Companies | 0.0258 | |||
| Industrial parks | 0.0110 | |||
| Road facilities | 0.0687 | |||
| Social Harmony Index | Public facilities | 0.0152 | 0.2 | |
| Healthcare services | 0.0291 | |||
| Large shopping malls and supermarkets | 0.0773 | |||
| People’s shops/convenience stores | 0.0698 | |||
| Transportation hubs | 0.0086 | |||
| Institutional Improvement Index | Government agencies | 0.0600 | 0.2 | |
| Public prosecution law agencies | 0.0100 | |||
| Industrial and commercial tax agencies | 0.0600 | |||
| Financial insurance services | 0.0600 | |||
| Social group related | 0.0100 | |||
| Cultural Heritage Index | Public cultural space | 0.0825 | 0.2 | |
| Religious cultural landscape | 0.0068 | |||
| Literary and artistic landscape | 0.0825 | |||
| Schools | 0.0214 | |||
| Media agencies | 0.0068 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Y.; Hu, Y. Beautiful China Construction Evaluation Method Based on POIs: Case Study of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10080508
Liang Y, Hu Y. Beautiful China Construction Evaluation Method Based on POIs: Case Study of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2021; 10(8):508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10080508
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Yuting, and Yunfeng Hu. 2021. "Beautiful China Construction Evaluation Method Based on POIs: Case Study of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 10, no. 8: 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10080508
APA StyleLiang, Y., & Hu, Y. (2021). Beautiful China Construction Evaluation Method Based on POIs: Case Study of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 10(8), 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10080508







