Yearly and Daily Relationship Assessment between Air Pollution and Early-Stage COVID-19 Incidence: Evidence from 231 Countries and Regions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data
- Study area
- Air pollution data
- Meteorological data
- COVID-19 confirmed cases
2.2. Measures of Variables
- Yearly changes of air pollution
- Daily air pollution
- Confirmed cases of COVID-19
2.3. Statistical Models
3. Results
3.1. Yearly Relationship Analysis
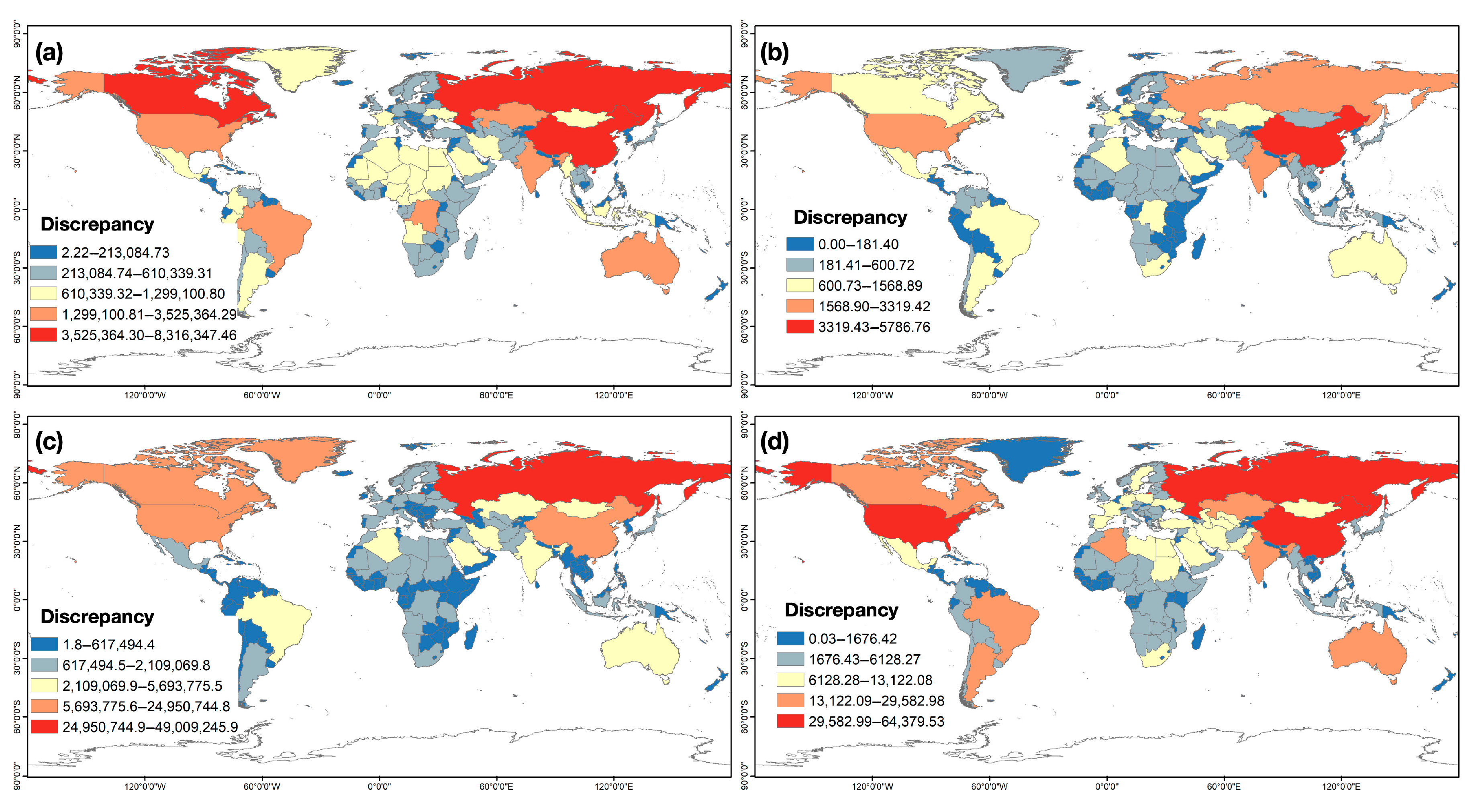
3.1.1. Yearly Air Pollution Discrepancies
3.1.2. Relationship Analysis
3.2. Daily Relationship Analysis
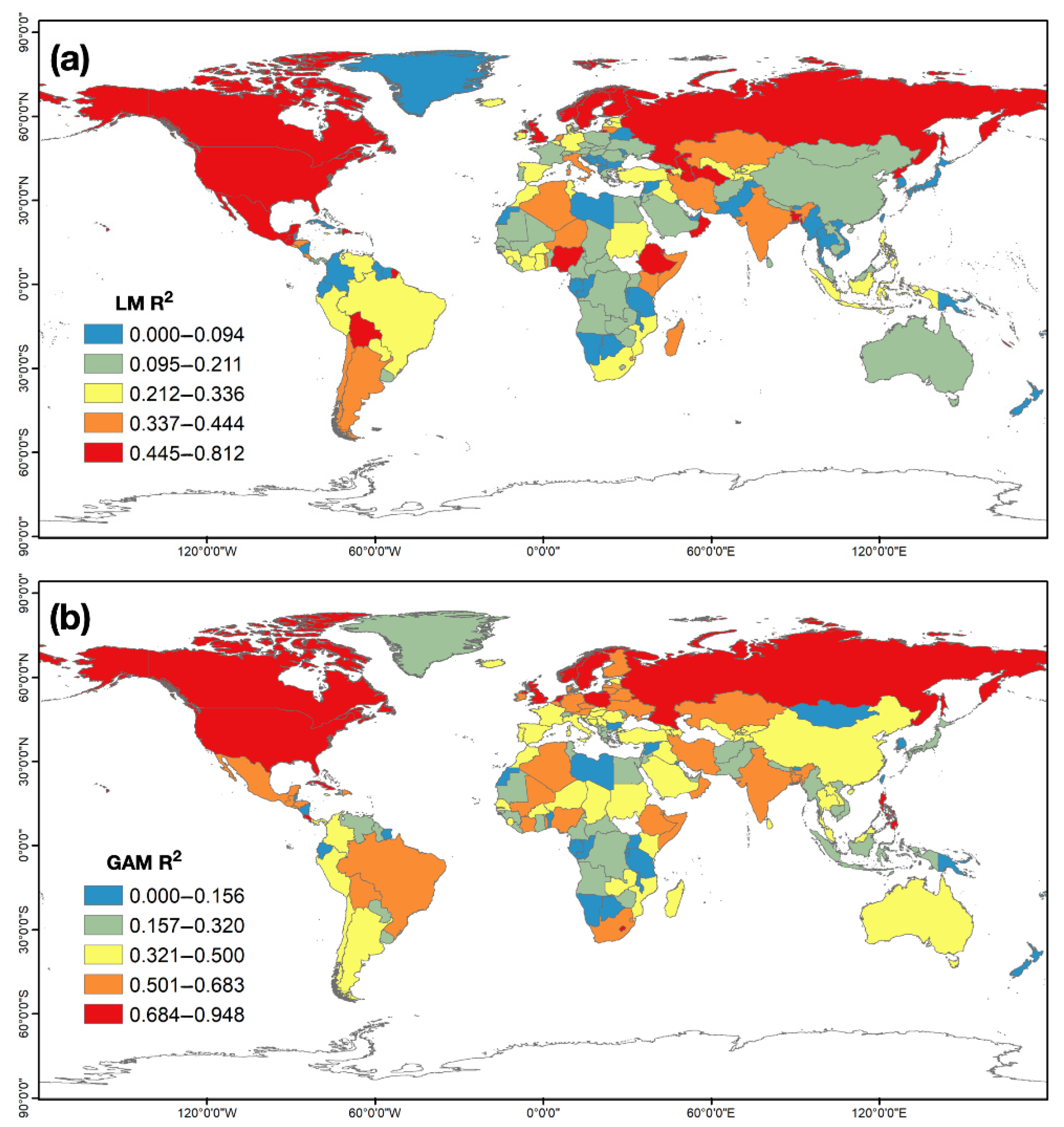
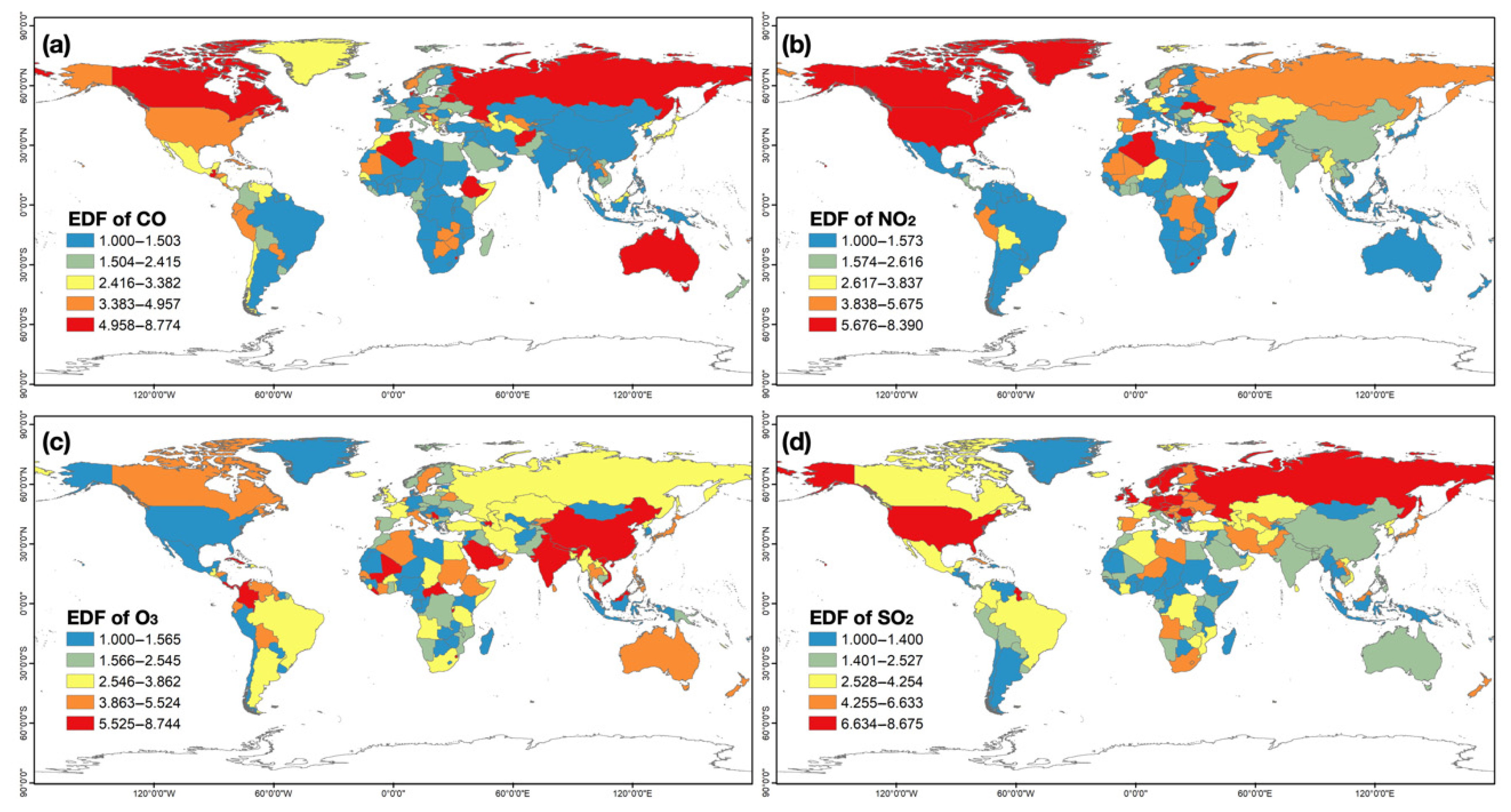
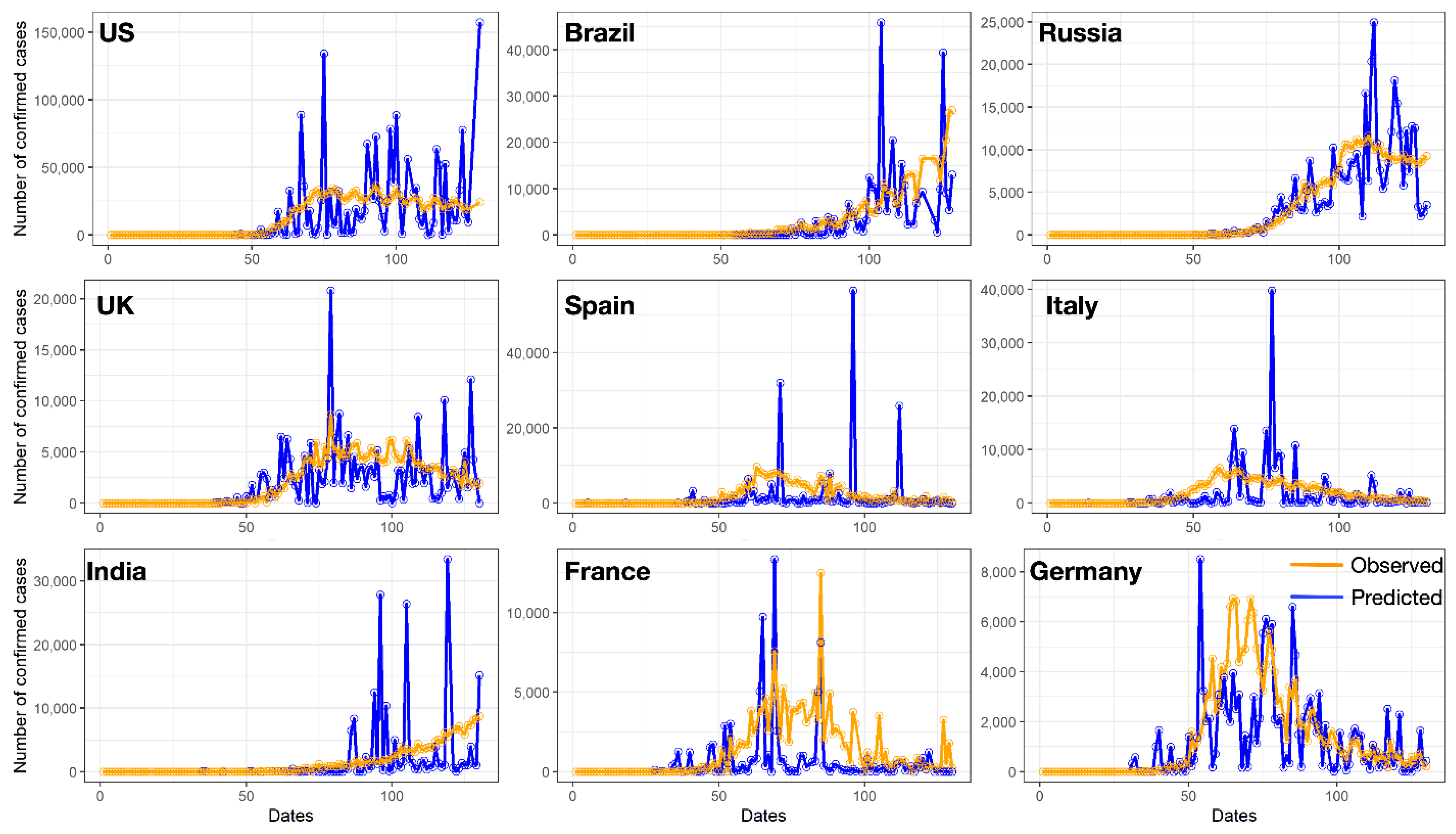
3.2.1. Model Evaluation
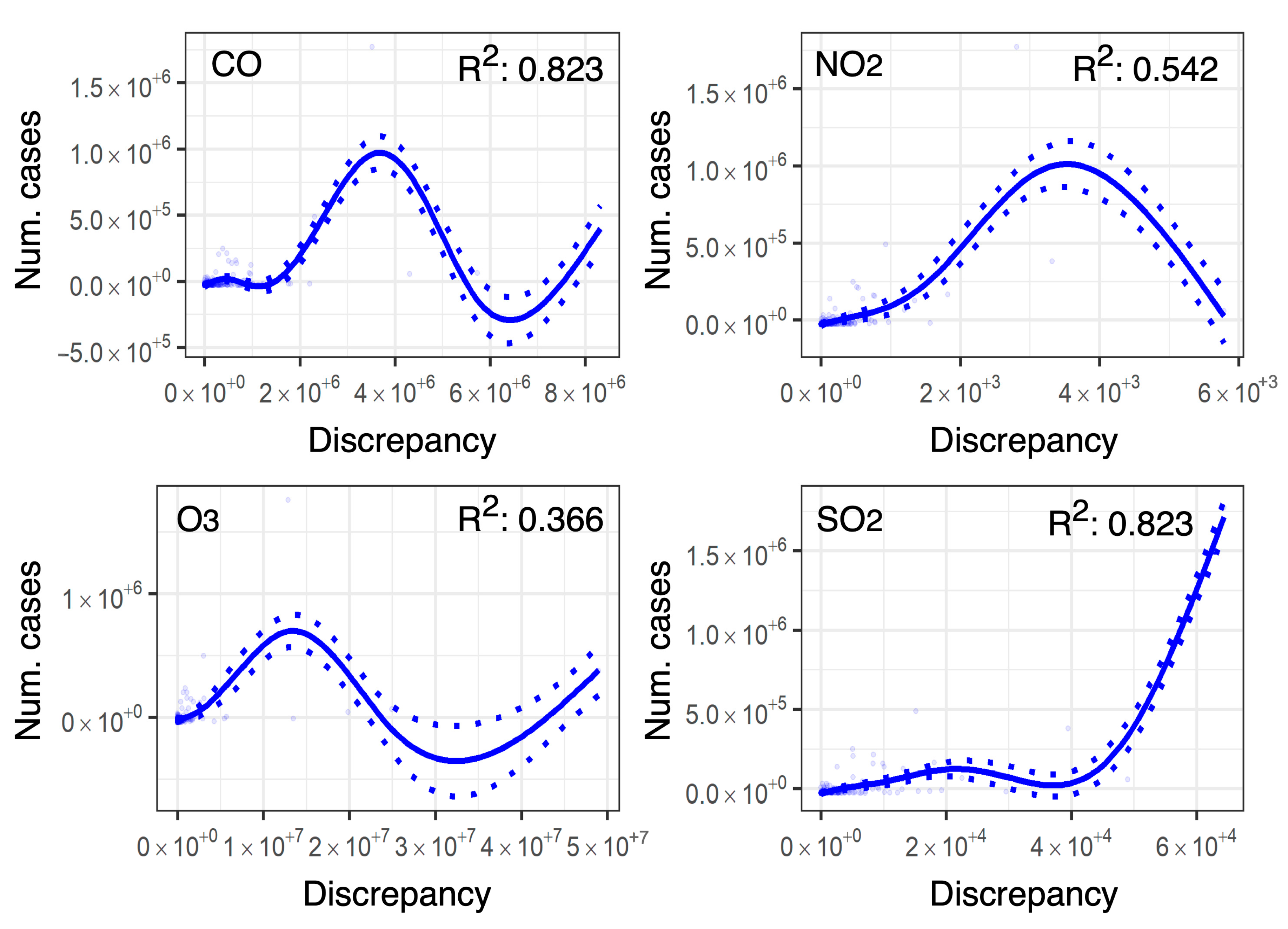
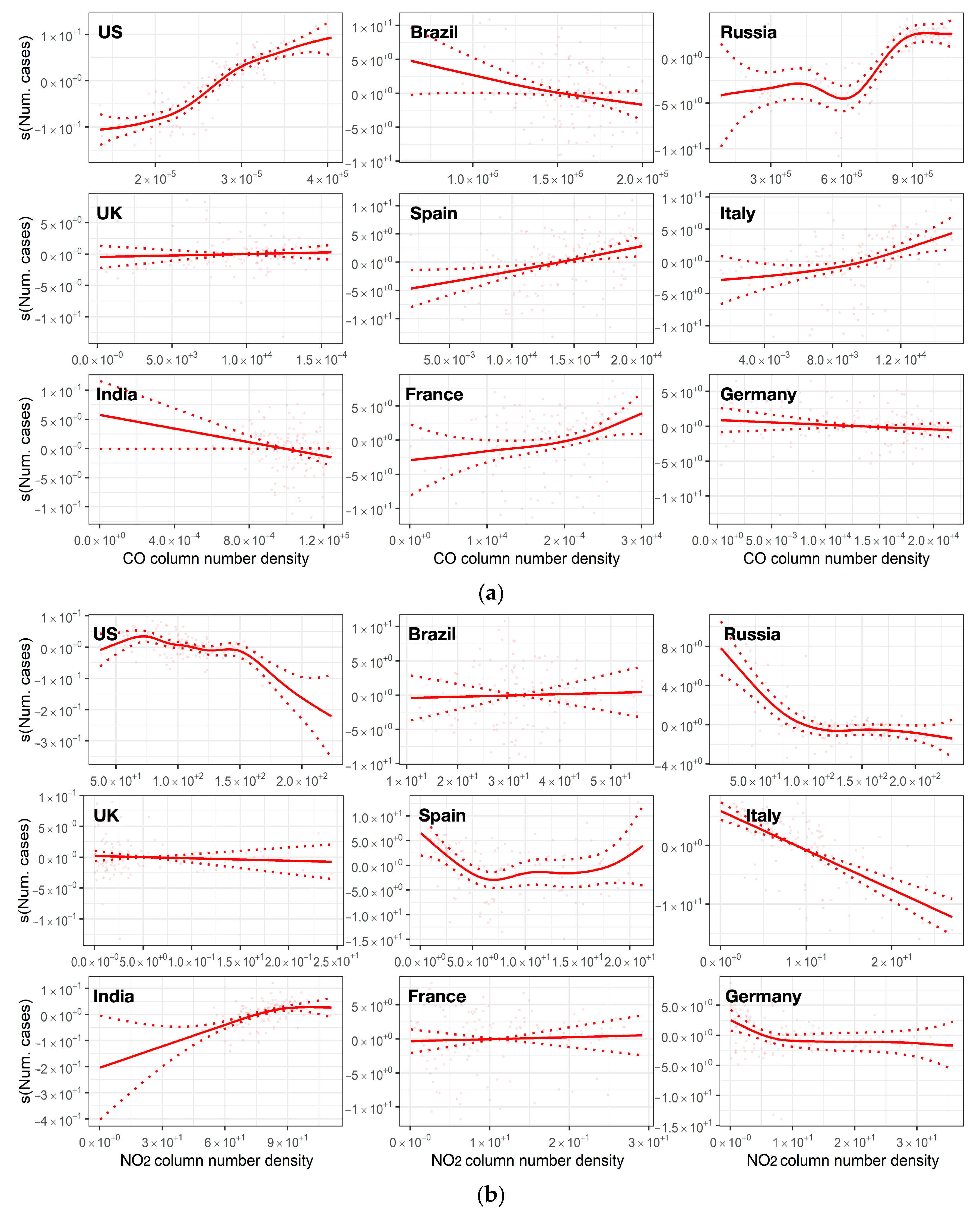
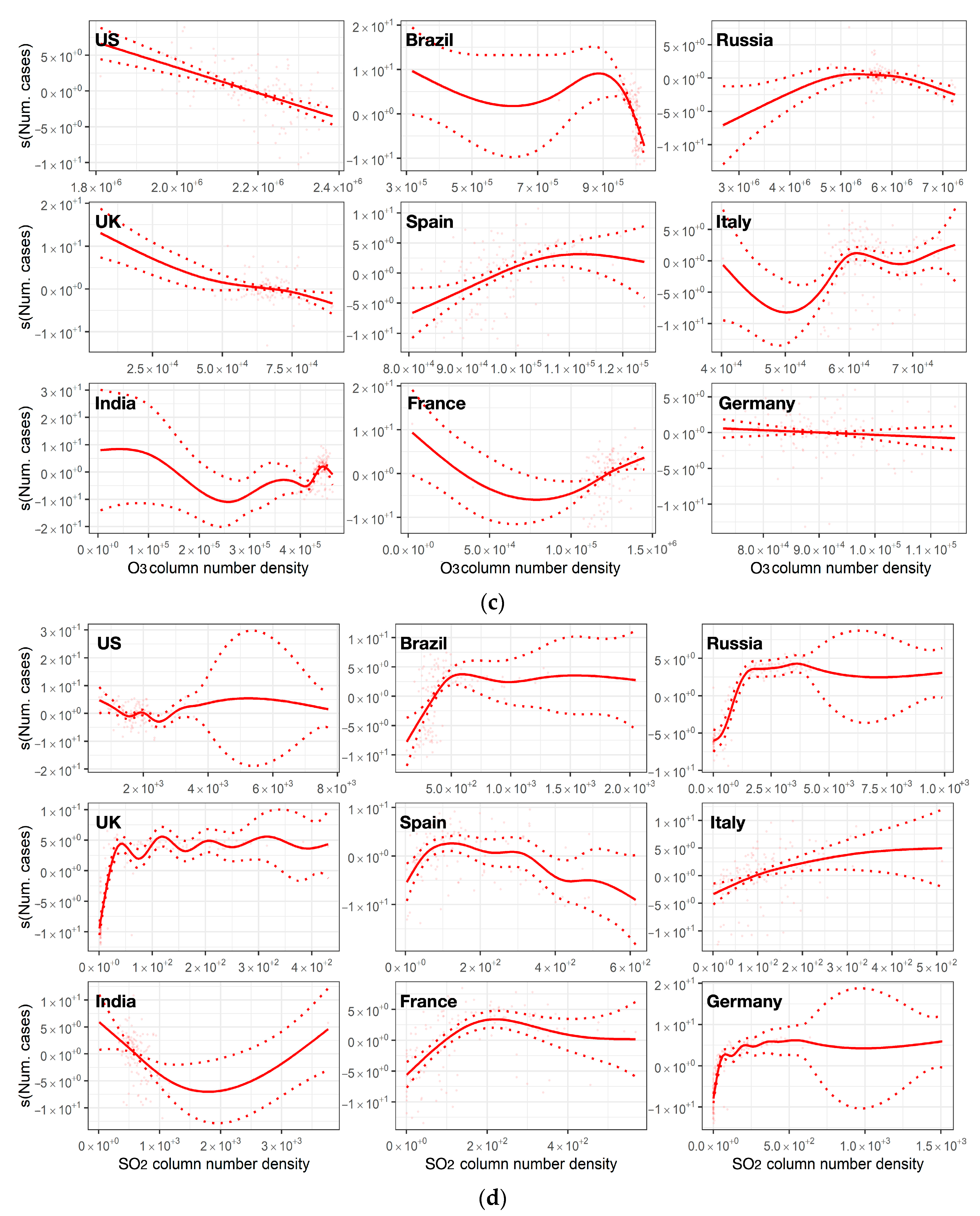
3.2.2. Relationship Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Linking Air Pollution Trends and New Confirmed Cases
4.2. Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gorbalenya, A.E.; Baker, S.C.; Baric, R.S.; Groot, R.J.D.; Ziebuhr, J. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: Classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Pei, S.; Chen, B.; Song, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, W.; Shaman, J. Substantial undocumented infection facilitates the rapid dissemination of novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2). Science 2020, 368, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.; Pullano, G.; Pinotti, F.; Valdano, E.; Poletto, C.; Boëlle, P.-Y.; D’Ortenzio, E.; Yazdanpanah, Y.; Eholie, S.P.; Altmann, M. Preparedness and vulnerability of African countries against importations of COVID-19: A modelling study. Lancet 2020, 395, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Horby, P.W.; Hayden, F.G.; Gao, G.F. A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet 2020, 395, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Situation Report, 82; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.; Kupferschmidt, K. Strategies shift as coronavirus pandemic looms. Science 2020, 367, 962–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepe, E.; Bajardi, P.; Gauvin, L.; Privitera, F.; Lake, B.; Cattuto, C.; Tizzoni, M. COVID-19 outbreak response: A first assessment of mobility changes in Italy following national lockdown. MedRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Peto, J.; Alwan, N.A.; Godfrey, K.M.; Burgess, R.A.; Hunter, D.J.; Riboli, E.; Romer, P.; Buchan, I.; Colbourn, T.; Costelloe, C. Universal weekly testing as the UK COVID-19 lockdown exit strategy. Lancet 2020, 395, 1420–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, H.; Khosrawipour, V.; Kocbach, P.; Mikolajczyk, A.; Schubert, J.; Bania, J.; Khosrawipour, T. The positive impact of lockdown in Wuhan on containing the COVID-19 outbreak in China. J. Travel Med. 2020, 27, taaa037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diffenbaugh, N.S.; Field, C.B.; Appel, E.A.; Azevedo, I.L.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Burke, M.; Burney, J.A.; Ciais, P.; Davis, S.J.; Fiore, A.M. The COVID-19 lockdowns: A window into the Earth System. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Zhang, M.; Gao, J.; Zhang, H.; Kota, S.H. Effect of restricted emissions during COVID-19 on air quality in India. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Klimont, Z.; Smith, S.J.; Van Dingenen, R.; Dentener, F.; Bouwman, L.; Riahi, K.; Amann, M.; Bodirsky, B.L.; Van Vuuren, D.P. Future air pollution in the Shared Socio-economic Pathways. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2017, 42, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, F.; Hubacek, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Feng, K.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, B.; Bi, J. Unequal exchange of air pollution and economic benefits embodied in China’s exports. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3888–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunekreef, B.; Holgate, S.T. Air pollution and health. Lancet 2002, 360, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampa, M.; Castanas, E. Human health effects of air pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Q.; Huang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, A.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Shi, L.; Li, R. Air quality changes during the COVID-19 lockdown over the Yangtze River Delta Region: An insight into the impact of human activity pattern changes on air pollution variation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Wang, M.; Huang, C.; Kinney, P.L.; Anastas, P.T. Air pollution reduction and mortality benefit during the COVID-19 outbreak in China. Lancet Planet. Health 2020, 4, e210–e212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Pan, Y.; Tanaka, T. The short-term impacts of COVID-19 lockdown on urban air pollution in China. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, Z.S.; Aunan, K.; Chowdhury, S.; Lelieveld, J. COVID-19 lockdowns cause global air pollution declines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 18984–18990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xie, J.; Huang, F.; Cao, L. Association between short-term exposure to air pollution and COVID-19 infection: Evidence from China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Nethery, R.C.; Sabath, B.M.; Braun, D.; Dominici, F. Exposure to air pollution and COVID-19 mortality in the United States. MedRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veefkind, J.; Aben, I.; McMullan, K.; Förster, H.; De Vries, J.; Otter, G.; Claas, J.; Eskes, H.; De Haan, J.; Kleipool, Q. TROPOMI on the ESA Sentinel-5 Precursor: A GMES mission for global observations of the atmospheric composition for climate, air quality and ozone layer applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoelst, T.; Compernolle, S.; Pinardi, G.; Lambert, J.-C.; Eskes, H.J.; Eichmann, K.-U.; Fjæraa, A.M.; Granville, J.; Niemeijer, S.; Cede, A. Ground-based validation of the Copernicus Sentinel-5p TROPOMI NO 2 measurements with the NDACC ZSL-DOAS, MAX-DOAS and Pandonia global networks. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2021, 14, 481–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoelst, T.; Compernolle, S.; Granville, J.; Keppens, A.; Pinardi, G.; Lambert, J.-C.; Eichmann, K.-U.; Eskes, H.; Niemeijer, S.; Fjæraa, A.M. Quality assessment of two years of Sentinel-5p TROPOMI NO2 data. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, 4–8 May 2020; p. 15036. [Google Scholar]
- Hubert, D.; Keppen, A.; Verhoelst, T.; Granville, J.; Lambert, J.-C.; Heue, K.-P.; Pedergnana, M.; Loyola, D.; Eichmann, K.-U.; Weber, M. Ground-based Assessment of the First Year of Sentinel-5p Tropospheric Ozone Data. In Proceedings of the Living Planet Symposium 2019, Milan, Italy, 13–17 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, G.; Welch, G. An introduction to the kalman filter. Proc. Siggraph Course 2001, 8, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, E.; Du, H.; Gardner, L. An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, D.J.; Clifford, J. Using dynamic time warping to find patterns in time series. In Proceedings of the KDD Workshop, Seattle, WA, USA, 31 July–1 August 1994; pp. 359–370. [Google Scholar]
- Petitjean, F.; Ketterlin, A.; Gançarski, P. A global averaging method for dynamic time warping, with applications to clustering. Pattern Recognit. 2011, 44, 678–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratanamahatana, C.A.; Keogh, E. Making time-series classification more accurate using learned constraints. In Proceedings of the 2004 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining, Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, 22–24 April 2004; pp. 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Grüss, A.; Yemane, D.; Fairweather, T. Exploring the spatial distribution patterns of South African Cape hakes using generalised additive models. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2016, 38, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagarese, S.R.; Frisk, M.G.; Cerrato, R.M.; Sosebee, K.A.; Musick, J.A.; Rago, P.J. Application of generalized additive models to examine ontogenetic and seasonal distributions of spiny dogfish (Squalus acanthias) in the Northeast (US) shelf large marine ecosystem. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 71, 847–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.N. Generalized Additive Models: An Introduction with R; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zuur, A.; Ieno, E.N.; Walker, N.; Saveliev, A.A.; Smith, G.M. Mixed Effects Models and Extensions in Ecology with R; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sarfraz, M.; Shehzad, K.; Farid, A. Gauging the air quality of New York: A non-linear Nexus between COVID-19 and nitrogen dioxide emission. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2020, 13, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucsela, E.; Perring, A.; Cohen, R.; Boersma, K.; Celarier, E.; Gleason, J.; Wenig, M.; Bertram, T.; Wooldridge, P.; Dirksen, R. Comparison of tropospheric NO2 from in situ aircraft measurements with near-real-time and standard product data from OMI. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, R.; Chen, H.; Szyszkowicz, M.; Fann, N.; Hubbell, B.; Pope, C.A.; Apte, J.S.; Brauer, M.; Cohen, A.; Weichenthal, S. Global estimates of mortality associated with long-term exposure to outdoor fine particulate matter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 9592–9597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiri, M.; Jahangiri, M.; Najafgholipour, M. The sensitivity and specificity analyses of ambient temperature and population size on the transmission rate of the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) in different provinces of Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, A.L.F.; Zanobetti, A.; Schwartz, J. The lag structure between particulate air pollution and respiratory and cardiovascular deaths in 10 US cities. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2001, 43, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, J.D.; Ebisu, K. Changes in US air pollution during the COVID-19 pandemic. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, H.; London, S.J.; Chen, H.; Song, G.; Chen, G.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, B. Diurnal temperature range and daily mortality in Shanghai, China. Environ. Res. 2007, 103, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heesterbeek, H.; Anderson, R.M.; Andreasen, V.; Bansal, S.; De Angelis, D.; Dye, C.; Eames, K.T.; Edmunds, W.J.; Frost, S.D.; Funk, S. Modeling infectious disease dynamics in the complex landscape of global health. Science 2015, 347, aaa4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daley, D.J.; Vere-Jones, D. An Introduction to the Theory of Point Processes: Volume II: General Theory and Structure; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, K.; Wong, S.-S.; Liang, W.; Zanin, M.; Liu, P.; Cao, X.; Gao, Z.; Mai, Z. Modified SEIR and AI prediction of the epidemics trend of COVID-19 in China under public health interventions. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Wang, J.; Cai, J.; Yao, S.; Chan, P.K.S.; Tam, T.H.-W.; Hong, Y.-Y.; Ruktanonchai, C.W.; Carioli, A.; Floyd, J.R. Integrated vaccination and physical distancing interventions to prevent future COVID-19 waves in Chinese cities. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubaugh, N.D.; Hanage, W.P.; Rasmussen, A.L. Making sense of mutation: What D614G means for the COVID-19 pandemic remains unclear. Cell 2020, 182, 794–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, S.; Leung, A.W.; Xu, C. COVID-19 mutation in the United Kingdom. Microbes Infect. Dis. 2021, 2, 187–188. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, Y.; Wong, M.S.; Xing, H.; Kwan, M.-P.; Zhu, R. Yearly and Daily Relationship Assessment between Air Pollution and Early-Stage COVID-19 Incidence: Evidence from 231 Countries and Regions. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10060401
Meng Y, Wong MS, Xing H, Kwan M-P, Zhu R. Yearly and Daily Relationship Assessment between Air Pollution and Early-Stage COVID-19 Incidence: Evidence from 231 Countries and Regions. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2021; 10(6):401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10060401
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Yuan, Man Sing Wong, Hanfa Xing, Mei-Po Kwan, and Rui Zhu. 2021. "Yearly and Daily Relationship Assessment between Air Pollution and Early-Stage COVID-19 Incidence: Evidence from 231 Countries and Regions" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 10, no. 6: 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10060401
APA StyleMeng, Y., Wong, M. S., Xing, H., Kwan, M.-P., & Zhu, R. (2021). Yearly and Daily Relationship Assessment between Air Pollution and Early-Stage COVID-19 Incidence: Evidence from 231 Countries and Regions. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 10(6), 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10060401









