Disaster Image Classification by Fusing Multimodal Social Media Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A novel multimodal fusion model was proposed to efficiently extract useful disaster information from massive social media data.
- An optimized model architecture was adopted to process disaster images smaller parameter sizes.
- The accuracy of the disaster image classification on the representative real-world disaster datasets, generated from different disaster events (e.g., earthquakes, and hurricanes), was further improved.
- The code of the project was released to researchers in order to reproduce research and for conducting further research. The code is available at https://github.com/GanHY97/Classification-by-Fusing-Multimodal-Data(accessed on 2 July 2021).
2. Related Work
3. Dataset and Models
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Model
3.2.1. Image Feature Extractor
3.2.2. Text Feature Extractor
3.2.3. Multimodal Fusion
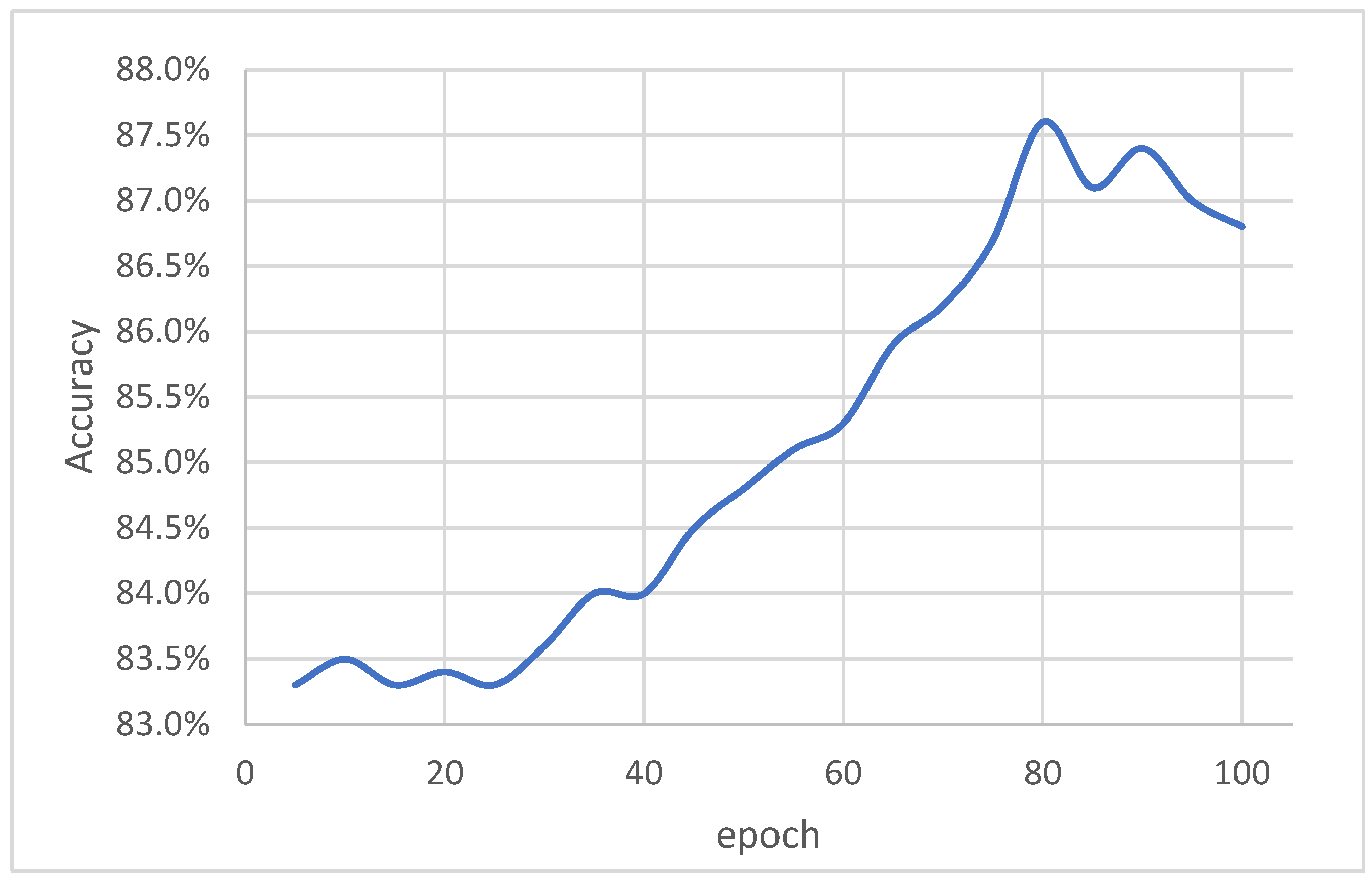
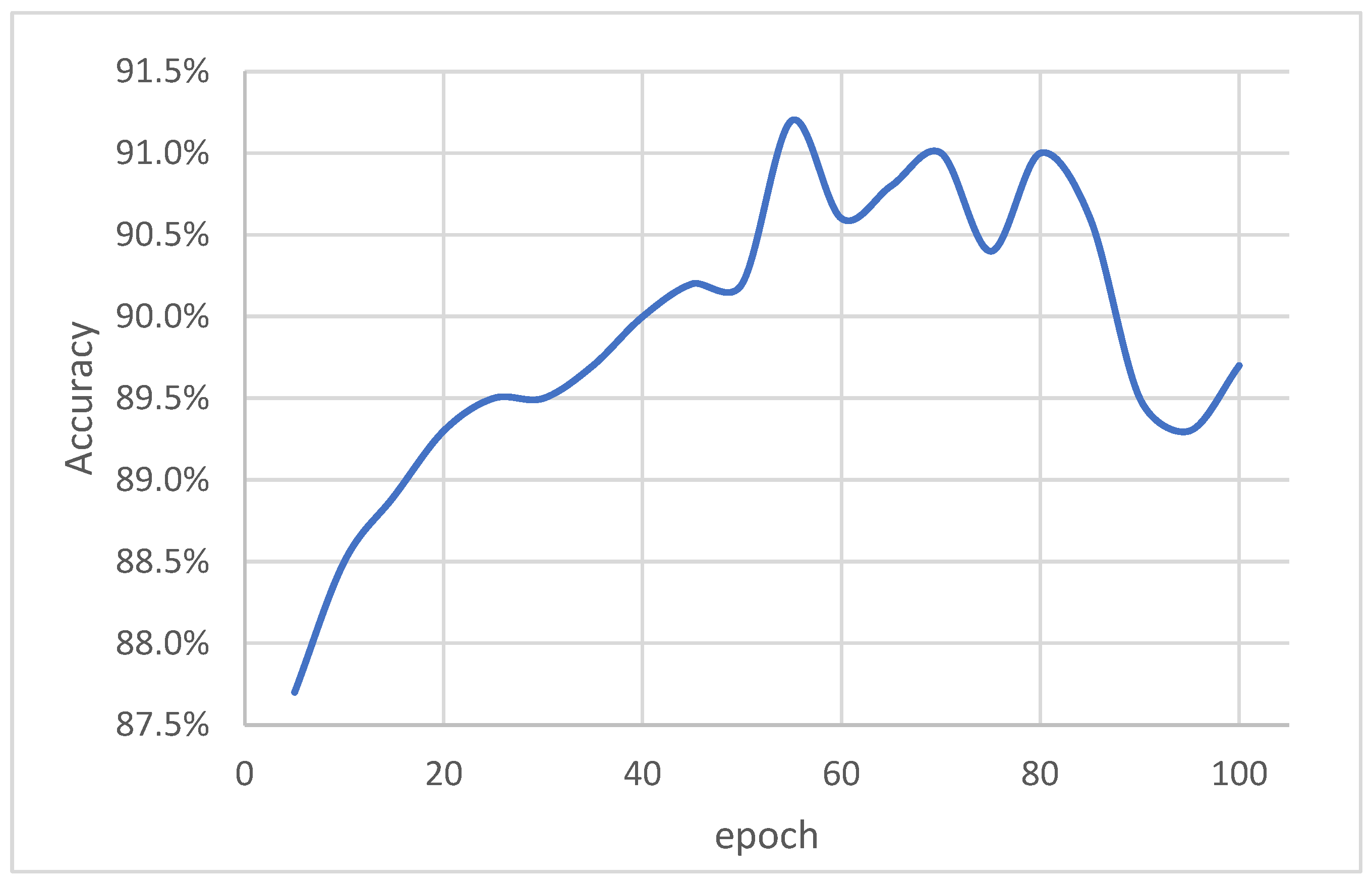
4. Experiments and Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Q.; Xiao, Y. Geographic Situational Awareness: Mining Tweets for Disaster Preparedness, Emergency Response, Impact, and Recovery. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2015, 4, 1549–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Sangwan, S.R.; Nayyar, A. Multimedia Social Big Data: Mining; Springer: Singapore, 2020; ISBN 9789811387593. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Kar, B.; Zhang, C.; Cochran, D.M. Assessing relevance of tweets for risk communication. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2019, 12, 781–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Resnick, P.; Mei, Q. Enquiring Minds: Early Detection of Rumors in Social Media from Enquiry Posts Categories and Subject Descriptors Detection Problems in Social Media. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on World Wide Web, Florence, Italy, 18–22 May 2015; pp. 1395–1405. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, K.; Mahudeswaran, D.; Wang, S.; Lee, D.; Liu, H. FakeNewsNet: A Data Repository with News Content, Social Context, and Spatiotemporal Information for Studying Fake News on Social Media. Big Data 2020, 8, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubiaga, A.; Liakata, M.; Procter, R. Learning Reporting Dynamics during Breaking News for Rumour Detection in Social Media. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1610.07363. [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza, M.; Poblete, B.; Castillo, C. Twitter under crisis: Can we trust what we RT? In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Social Media Analytics—SOMA’10, Washington, DC, USA, 25–28 July 2010; pp. 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Burnap, P.; Williams, M.L. Cyber hate speech on twitter: An application of machine classification and statistical modeling for policy and decision making. Policy Internet 2015, 7, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Shukla, N.; Mishra, N. Social media data analytics to improve supply chain management in food industries. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2018, 114, 398–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, N.; Cortez, P.; Areal, N. The impact of microblogging data for stock market prediction: Using Twitter to predict returns, volatility, trading volume and survey sentiment indices. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 73, 125–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganesan, T.; Anuradha, S.; Harika, A.; Nikitha, N.; Nalajala, S. Analyzing Social Media Data for Better Understanding Students’ Learning Experiences. Lect. Notes Data Eng. Commun. Technol. 2021, 57, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailunaz, K.; Alhajj, R. Emotion and sentiment analysis from Twitter text. J. Comput. Sci. 2019, 36, 101003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Garadi, M.A.; Hussain, M.R.; Khan, N.; Murtaza, G.; Nweke, H.F.; Ali, I.; Mujtaba, G.; Chiroma, H.; Khattak, H.A.; Gani, A. Predicting Cyberbullying on Social Media in the Big Data Era Using Machine Learning Algorithms: Review of Literature and Open Challenges. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 70701–70718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, S.; Xu, H. Detecting Offensive Language in Social Media to Protect Adolescent Online Safety. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Privacy, Security, Risk and Trust and 2012 International Confernece on Social Computing, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 3–5 September 2012; pp. 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Ding, G.; Huang, Q.; Chua, T.S.; Schuller, B.W.; Keutzer, K. Affective image content analysis: A comprehensive survey. IJCAI Int. Jt. Conf. Artif. Intell. 2018, 2018, 5534–5541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Xu, M. Multi-level region-based Convolutional Neural Network for image emotion classification. Neurocomputing 2019, 333, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltrušaitis, T.; Ahuja, C.; Morency, L.P. Multimodal machine learning: A survey and taxonomy. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 41, 423–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuhas, B.P.; Goldstein, M.H.; Sejnowski, T.J. Integration of Acoustic and Visual Speech Signals Using Neural Networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 1989, 27, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodosh, M.; Young, P.; Hockenmaier, J. Framing image description as a ranking task: Data, models and evaluation metrics. IJCAI Int. Jt. Conf. Artif. Intell. 2015, 2015, 4188–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lienhart, R. Comparison of Automatic Shot Boundary Detection Algorithms. Event Electron. Imaging 1999, 3656, 290–301. [Google Scholar]
- Evangelopoulos, G.; Zlatintsi, A.; Potamianos, A.; Maragos, P.; Rapantzikos, K.; Skoumas, G.; Avrithis, Y. Multimodal saliency and fusion for movie summarization based on aural, visual, and textual attention. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2013, 15, 1553–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, Z.; He, X.; Zhu, A. An Automatic Annotation Method for Discovering Semantic Information of Geographical Locations from Location-Based Social Networks. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ofli, F.; Alam, F.; Imran, M. Analysis of Social Media Data Using Multimodal Deep Learning for Disaster Response. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.11838. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015—Conference Track Proceedings, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Joulin, A.; Grave, E.; Bojanowski, P.; Mikolov, T. Bag of Tricks for Efficient Text Classification. In Proceedings of the 15th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Volume 2, Short Papers; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2017; Volume 2, pp. 427–431. [Google Scholar]
- Vongkusolkit, J.; Huang, Q. Situational awareness extraction: A comprehensive review of social media data classification during natural hazards. Ann. GIS 2021, 27, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Castillo, C.; Diaz, F.; Vieweg, S. Processing Social Media Messages in Mass Emergency: Survey Summary. In Proceedings of the Companion of the The Web Conference 2018 on The Web Conference 2018—WWW’18, Lyon, France, 23–27 April 2018; Volume 2, pp. 507–511. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Kar, B.; Montiel Ishino, F.A.; Zhang, C.; Williams, F. Assessing the Reliability of Relevant Tweets and Validation Using Manual and Automatic Approaches for Flood Risk Communication. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Xie, J.; Li, G.; Mou, N.; Li, Z.; Tian, C.; Zhao, J. Social Media Big Data Mining and Spatio-Temporal Analysis on Public Emotions for Disaster Mitigation. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, H.; Yu, G. A Weibo-based approach to disaster informatics: Incidents monitor in post-disaster situation via Weibo text negative sentiment analysis. Nat. Hazards 2016, 83, 1177–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragini, J.R.; Anand, P.M.R.; Bhaskar, V. Big data analytics for disaster response and recovery through sentiment analysis. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2018, 42, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Shen, Y.; Wang, H. Assessing Urban Areas’ Vulnerability to Flood Disaster Based on Text Data: A Case Study in Zhengzhou City. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alam, F.; Imran, M.; Ofli, F. Image4Act: Online social media image processing for disaster response. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining 2017, Sydney, Australia, 31 July–3 August 2017; pp. 601–604. [Google Scholar]
- Said, N.; Ahmad, K.; Riegler, M.; Pogorelov, K.; Hassan, L.; Ahmad, N.; Conci, N. Natural disasters detection in social media and satellite imagery: A survey. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 31267–31302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, S.Z.; Ahmad, K.; Hicks, S.; Halvorsen, P.; Al-Fuqaha, A.; Conci, N.; Riegler, M. Visual Sentiment Analysis from Disaster Images in Social Media. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.03051. [Google Scholar]
- Dao, M.-S.; Quang Nhat Minh, P.; Kasem, A.; Haja Nazmudeen, M.S. A Context-Aware Late-Fusion Approach for Disaster Image Retrieval from Social Media. In Proceedings of the 2018 ACM on International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, Yokohama, Japan, 11–14 June 2018; pp. 266–273. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, A.K.; Misra, L.; Kumar, A.; Misra, K.; Aggarwal, S.; Shah, R.R. Multimodal Analysis of Disaster Tweets. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Fifth International Conference on Multimedia Big Data (BigMM), Singapore, 11–13 September 2019; pp. 94–103. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, F.; Ofli, F.; Imran, M. CrisisMMD: Multimodal twitter datasets from natural disasters. In Proceedings of the 12th International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, ICWSM 2018, Palo Alto, CA, USA, 25–28 June 2018; pp. 465–473. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, S.J.; Yang, Q. A Survey on Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2010, 22, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilon, S.; Nex, F.; Kerle, N.; Vosselman, G. Post-Disaster Building Damage Detection from Earth Observation Imagery Using Unsupervised and Transferable Anomaly Detecting Generative Adversarial Networks. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Crisis Name | Images | Text Messages |
|---|---|---|
| Hurricane Irma | 4504 | 4021 |
| Hurricane Harvey | 4434 | 3992 |
| Hurricane Maria | 4556 | 3995 |
| California wildfires | 1589 | 1486 |
| Mexico earthquake | 1380 | 1238 |
| Iraq–Iran earthquake | 597 | 496 |
| Sri Lanka floods | 1022 | 830 |
| Total | 18,082 | 16,058 |
| Crisis Name | Images | Text Messages | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Informative | Not Informative | Informative | Not Informative | |
| Hurricane Irma | 2018 | 766 | 1836 | 678 |
| Hurricane Harvey | 2258 | 906 | 2082 | 800 |
| Hurricane Maria | 1813 | 1295 | 1594 | 1139 |
| California wildfires | 923 | 282 | 873 | 261 |
| Mexico earthquake | 806 | 315 | 732 | 285 |
| Iraq–Iran earthquake | 398 | 102 | 330 | 83 |
| Sri Lanka floods | 229 | 632 | 184 | 527 |
| Total | 8445 | 4298 | 7631 | 3773 |
| 12,743 | 11,404 | |||
| Crisis Name | Images | Text Messages | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | D | R | O | P | D | R | O | |
| Hurricane Irma | 6 | 207 | 214 | 657 | 6 | 174 | 187 | 623 |
| Hurricane Harvey | 22 | 233 | 402 | 397 | 21 | 194 | 367 | 385 |
| Hurricane Maria | 11 | 173 | 276 | 478 | 11 | 141 | 230 | 446 |
| California wildfires | 8 | 83 | 52 | 96 | 8 | 80 | 47 | 89 |
| Mexico earthquake | 9 | 37 | 166 | 64 | 9 | 32 | 154 | 62 |
| Iraq–Iran earthquake | 28 | 22 | 26 | 51 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 47 |
| Sri Lanka floods | 6 | 18 | 56 | 16 | 6 | 15 | 36 | 16 |
| Total | 90 | 773 | 1192 | 1759 | 88 | 656 | 1038 | 1668 |
| 3814 | 3450 | |||||||
| Crisis Name | Images | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| S | M | L | |
| Hurricane Irma | 316 | 229 | 250 |
| Hurricane Harvey | 556 | 220 | 116 |
| Hurricane Maria | 509 | 273 | 80 |
| California wildfires | 465 | 51 | 15 |
| Mexico earthquake | 148 | 25 | 5 |
| Iraq–Iran earthquake | 158 | 11 | 4 |
| Sri Lanka floods | 60 | 30 | 5 |
| Total | 2212 | 839 | 475 |
 |  |  |  |
| Astros pummel Harvey in his return, top Mets 12-8 | Not always good when your city shows up on a severe weather map. #HurricaneHarvey #ItAintOverYet | Three people, two dogs ride out Hurricane Harvey in ‘pod’ at Holiday Beach | #HurricaneHarvey Victim Relief-Ways you can help those effected by the storm. Click HERE: https://t.co/m13Lj10an2, accessed on 19 November 2017 https://t.co/lEf3HDxCyQ, accessed on 19 November 2017 |
| Not informative | Informative Other relevant information | Informative Affected individuals | Informative Rescue volunteering or donation effort |
 |  |  |  |
| RT @Nairametrics: Reports suggest Hurricane Harvey cars could be on its way to Nigeria | RT @stephentpaulsen: My street in SE #Houston is now a river. That light is from lightning; it’s 10pm #Harvey | RT @worldonalert: #Texas: Photos show destruction in #Bayside after hurricane #Harvey. | The hurricane “Harvey” in the USA: first victims and destructions-RIA Novosti, 8/27/20... |
| Informative Vehicle damage | Informative Infrastructure and utility damage Little or no damage | Informative Infrastructure and utility damage Mild damage | Informative Infrastructure and utility damage Severe damage |
| Layer | Output Size |
|---|---|
| conv3-64 | 224 × 224 × 64 |
| conv3-64 | 224 × 224 × 64 |
| max-pooling | 112 × 112 × 64 |
| conv3-128 | 112 × 112 × 128 |
| conv3-128 | 112 × 112 × 128 |
| max-pooling | 56 × 56 × 128 |
| conv3-256 | 56 × 56 × 256 |
| conv3-256 | 56 × 56 × 256 |
| conv3-256 | 56 × 56 × 256 |
| max-pooling | 28 × 28 × 256 |
| conv3-512 | 28 × 28 × 512 |
| conv3-512 | 28 × 28 × 512 |
| conv3-512 | 28 × 28 × 512 |
| max-pooling | 14 × 14 × 512 |
| conv3-512 | 14 × 14 × 512 |
| conv3-512 | 14 × 14 × 512 |
| conv3-512 | 14 × 14 × 512 |
| max-pooling | 7 × 7 × 512 |
| FC-4096 | 1 × 1 × 4096 |
| FC-500 | 1 × 1 × 500 |
| FC-Num_Classes | 1 × 1 × Num_Classes |
| SoftMax | 1 × 1 × Num_Classes |
| Text Sample | Segmentation | Cleaning | Normalization |
|---|---|---|---|
| RT @worldonalert: #Texas: Photos show destruction in #Bayside after hurricane #Harvey. | [‘RT’, ‘@worldonalert’, ‘:’, ‘Texas’, ‘:’, ‘Photos’, ‘show’, ‘destruction’, ‘in’, ‘Bayside’, ‘after’, ‘hurricane’, ‘Harvey’] | [‘texas’, ‘photos’, ‘show’, ‘destruction’, ‘bayside’, ‘hurricane’, ‘harvey’] | [‘texa’, ‘photo’, ‘show’, ‘destruct’, ‘baysid’, ‘hurrican’, ‘harvey’] |
| Layer | Output Size |
|---|---|
| FC | 1 × 1 × 1000 |
| FC | 1 × 1 × 500 |
| FC | 1 × 1 × Num_Classes |
| SoftMax | 1 × 1 × Num_Classes |
| Task | Models | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Task 1 | Only Text | 0.852 | 0.863 | 0.852 | 0.858 | |
| Only Images | 0.833 | 0.831 | 0.833 | 0.832 | ||
| Text and Images | 0.876 | 0.875 | 0.876 | 0.875 | ||
| Task 2 | Step 1 | Only Text | 0.907 | 0.908 | 0.906 | 0.907 |
| Only Images | 0.922 | 0.922 | 0.922 | 0.922 | ||
| Text and Images | 0.926 | 0.927 | 0.926 | 0.926 | ||
| Step 2 | Only Text | 0.922 | 0.922 | 0.920 | 0.918 | |
| Only Images | 0.885 | 0.847 | 0.885 | 0.864 | ||
| Text and Images | 0.9125 | 0.872 | 0.911 | 0.891 | ||
| Task 3 | Images | 0.689 | 0.663 | 0.669 | 0.670 | |
| Sample | Task | Model | Classification | Annotation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Task1 | OT | Informative | Informative | |
| OI | Informative | ||||
| TI | Informative | ||||
| Task2 | Step 1 | OT | P+D+R | D | |
| OI | P+D+R | ||||
| RT @worldonalert: #Texas: Photos show destruction in #Bayside after hurricane #Harvey. | TI | P+D+R | |||
| Step 2 | OT | D | |||
| OI | D | ||||
| TI | D | ||||
| Task 3 | TI | Mild damage | Mild damage | ||
| Data | Label | Predicted | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inf | Not-Inf | ||
| Only Text | Inf | 737 | 138 |
| Not-Inf | 58 | 396 | |
| Only Images | Inf | 1135 | 137 |
| Not-Inf | 183 | 470 | |
| Text + Images | Inf | 1186 | 86 |
| Not-Inf | 151 | 502 | |
| Data | Label | Predicted | |
|---|---|---|---|
| P + D + R | O | ||
| Only Text | P + D + R | 248 | 26 |
| O | 22 | 222 | |
| Only Image | P + D + R | 252 | 22 |
| O | 18 | 226 | |
| Text + Image | P + D + R | 254 | 20 |
| O | 18 | 226 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, Z.; Gan, H.; Huang, Q.; Cai, T.; Cao, K. Disaster Image Classification by Fusing Multimodal Social Media Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10100636
Zou Z, Gan H, Huang Q, Cai T, Cao K. Disaster Image Classification by Fusing Multimodal Social Media Data. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2021; 10(10):636. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10100636
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Zhiqiang, Hongyu Gan, Qunying Huang, Tianhui Cai, and Kai Cao. 2021. "Disaster Image Classification by Fusing Multimodal Social Media Data" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 10, no. 10: 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10100636
APA StyleZou, Z., Gan, H., Huang, Q., Cai, T., & Cao, K. (2021). Disaster Image Classification by Fusing Multimodal Social Media Data. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 10(10), 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10100636







