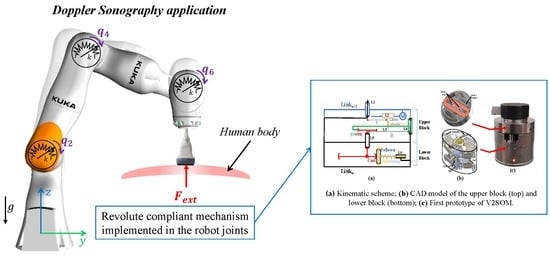
On the Design of a Safe Human-Friendly Teleoperated System for Doppler Sonography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
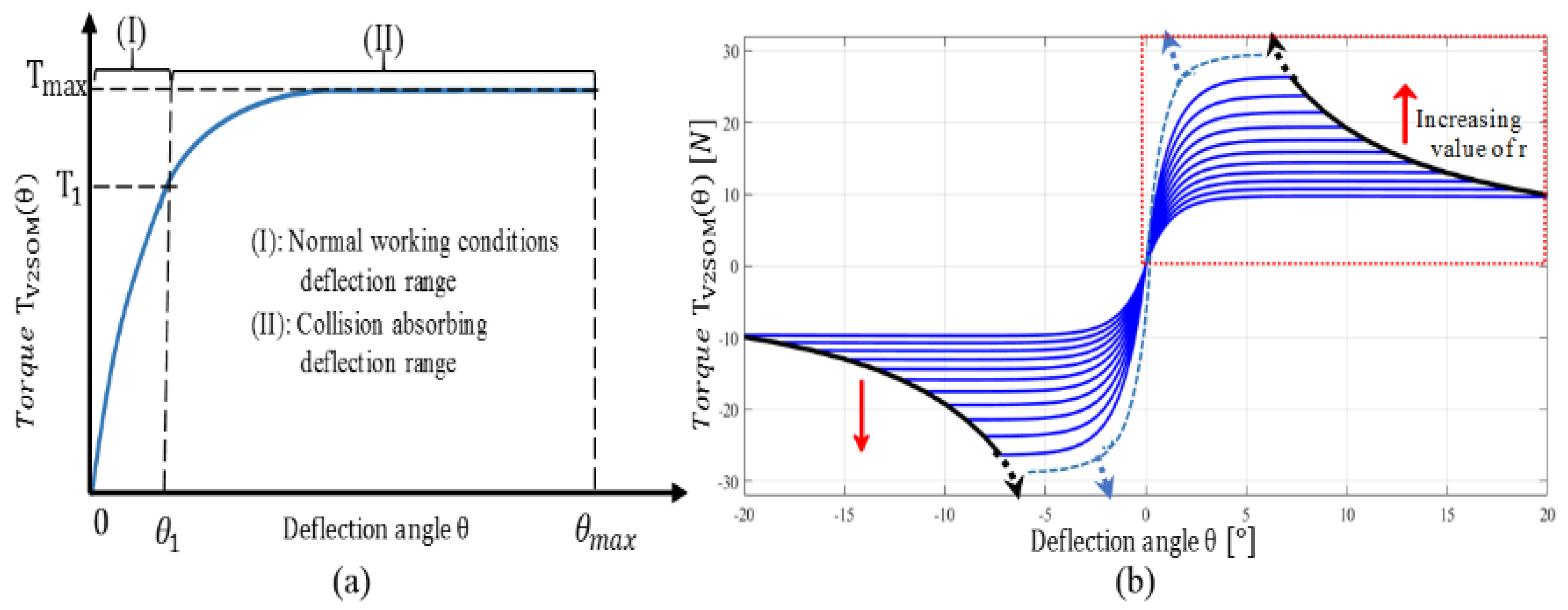
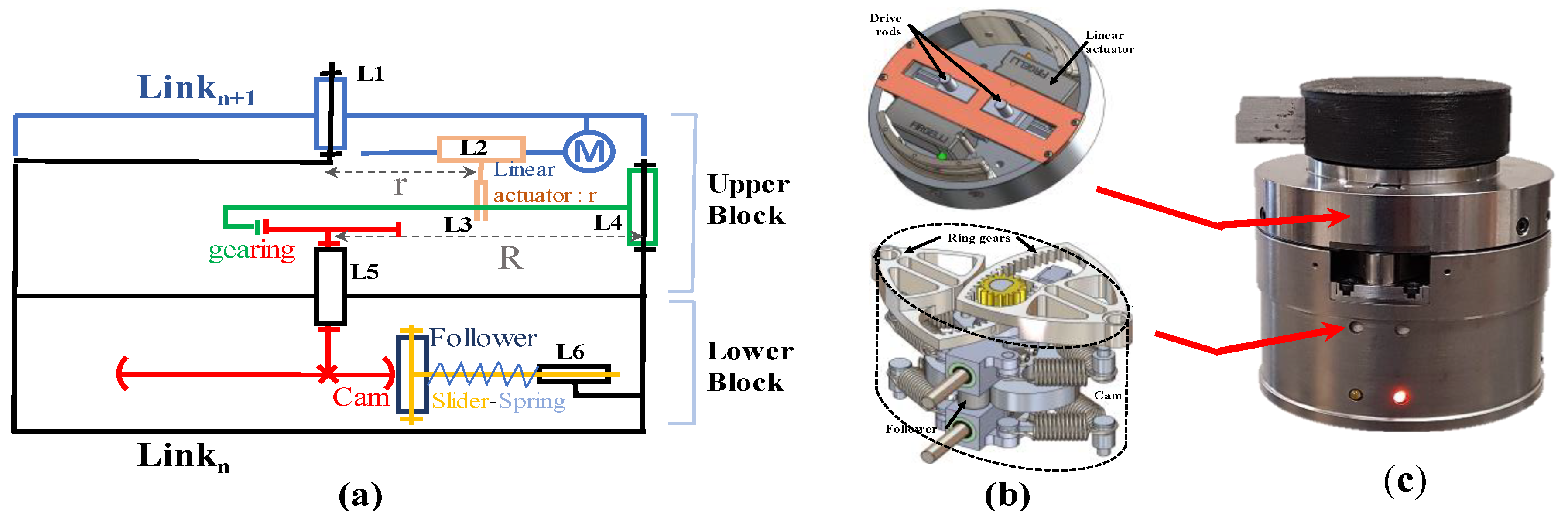
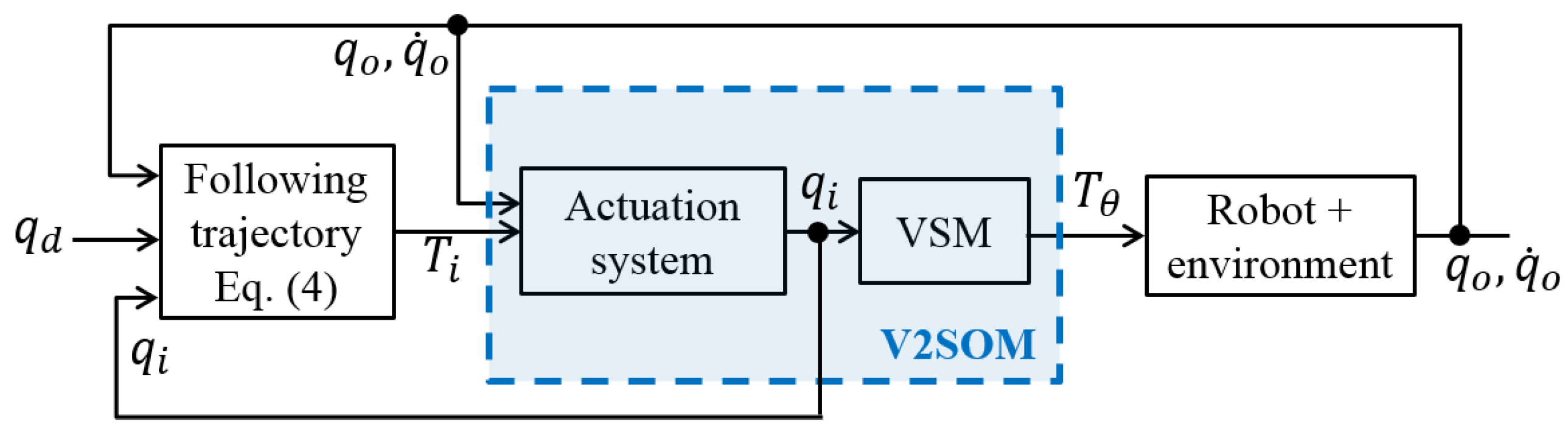
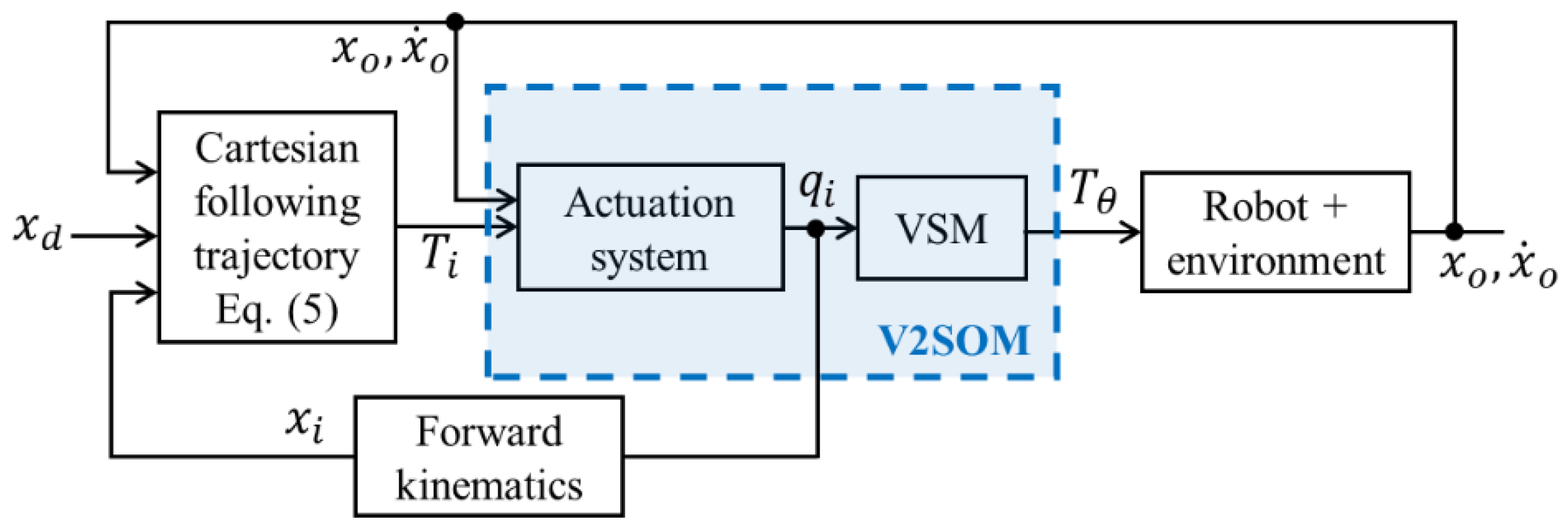
2.1. Working Principle of V2SOM
2.2. Joint Control Design
2.3. Cartesian Control Design
3. Implementation and Results
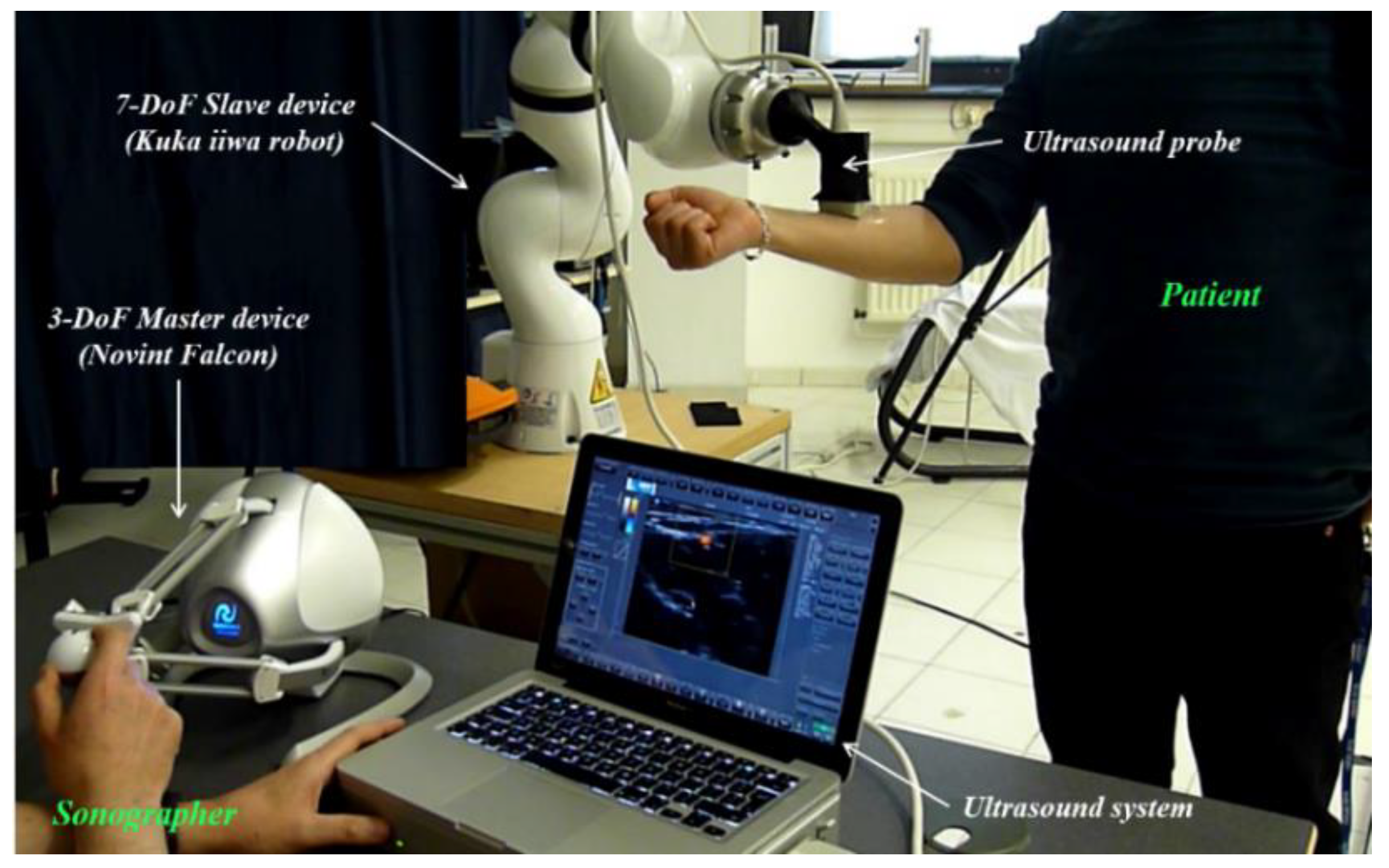
3.1. Robot-Assisted Doppler Sonography
3.2. Study Cases
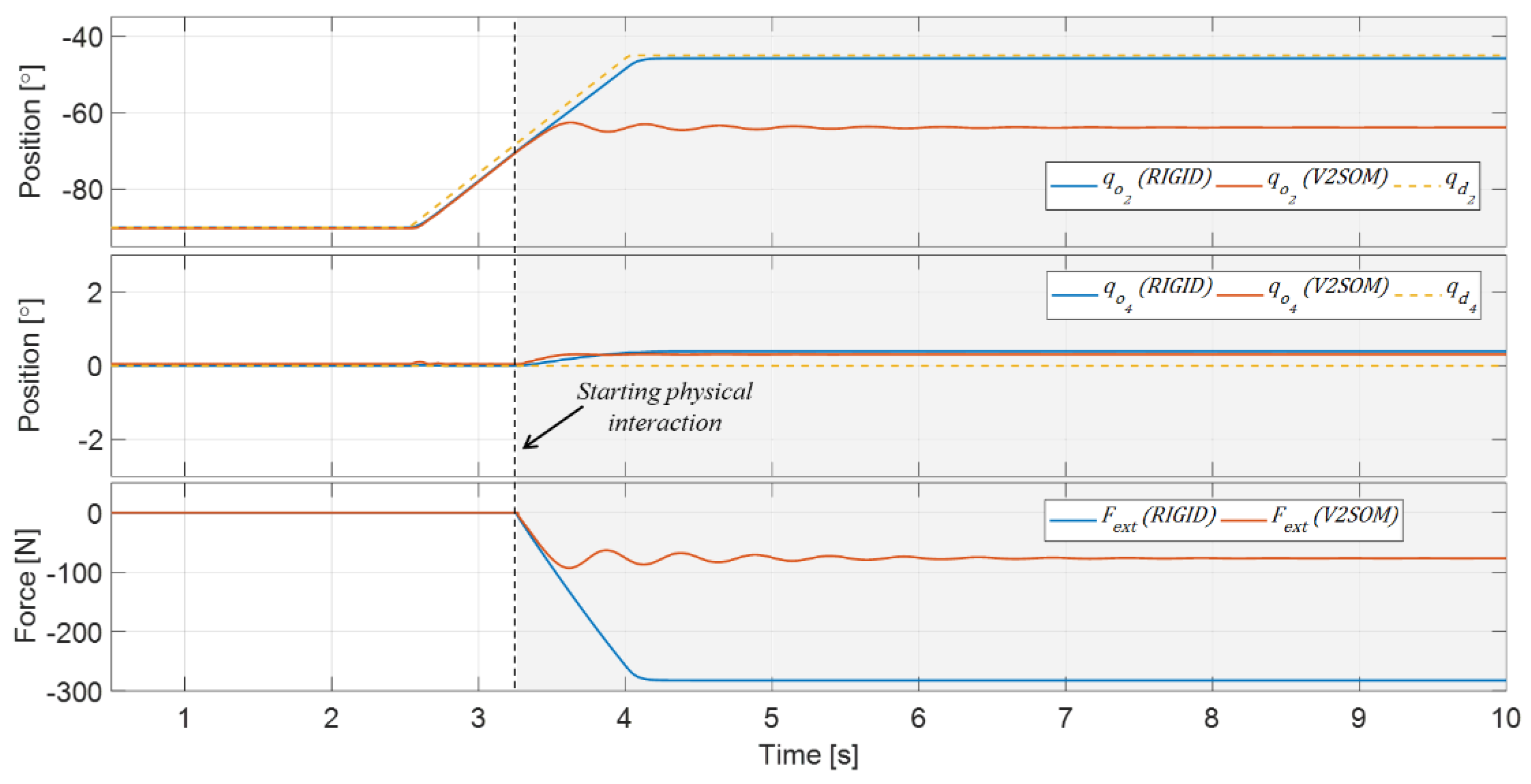
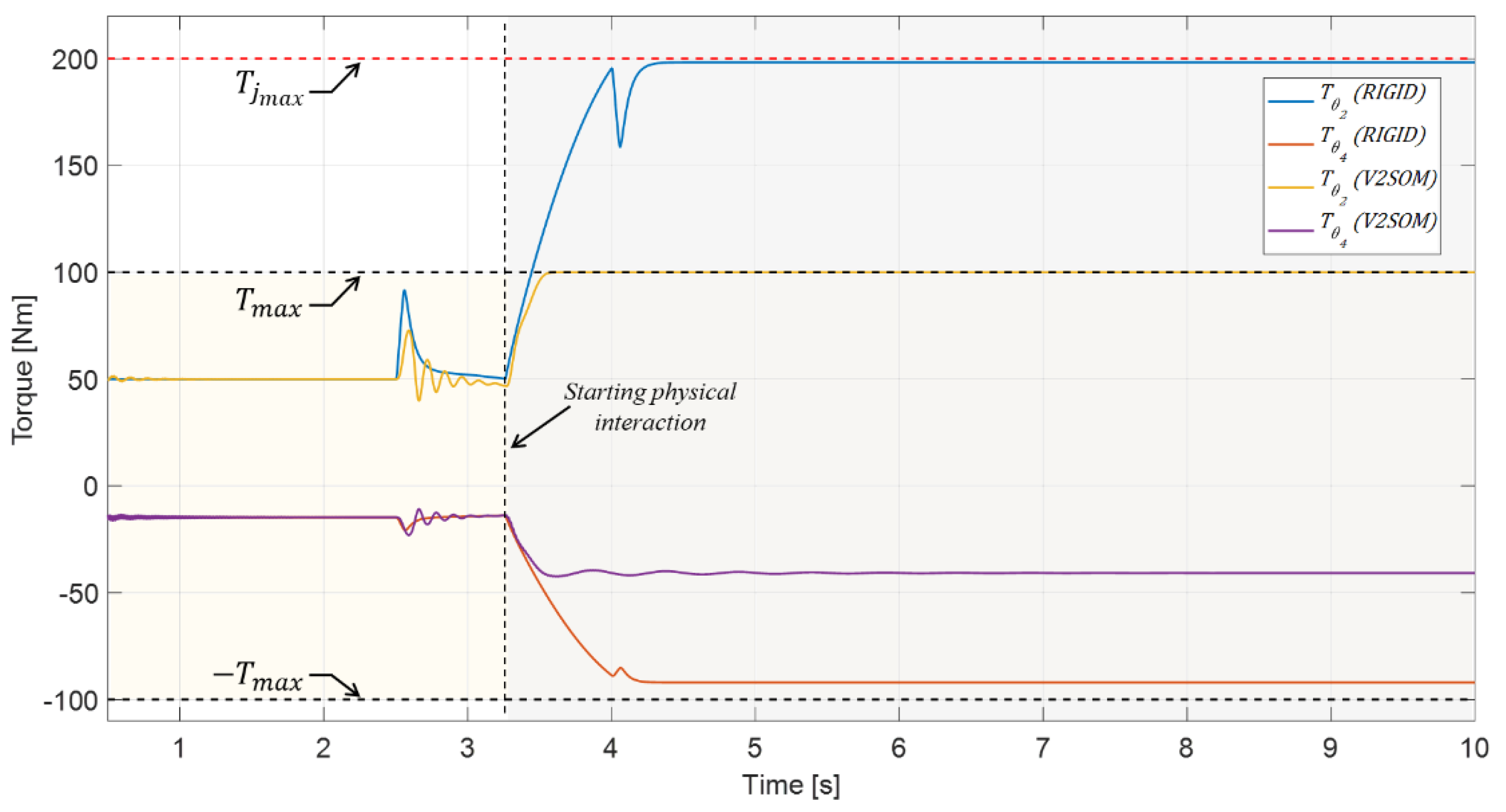
3.2.1. Joint Space Trajectory Task
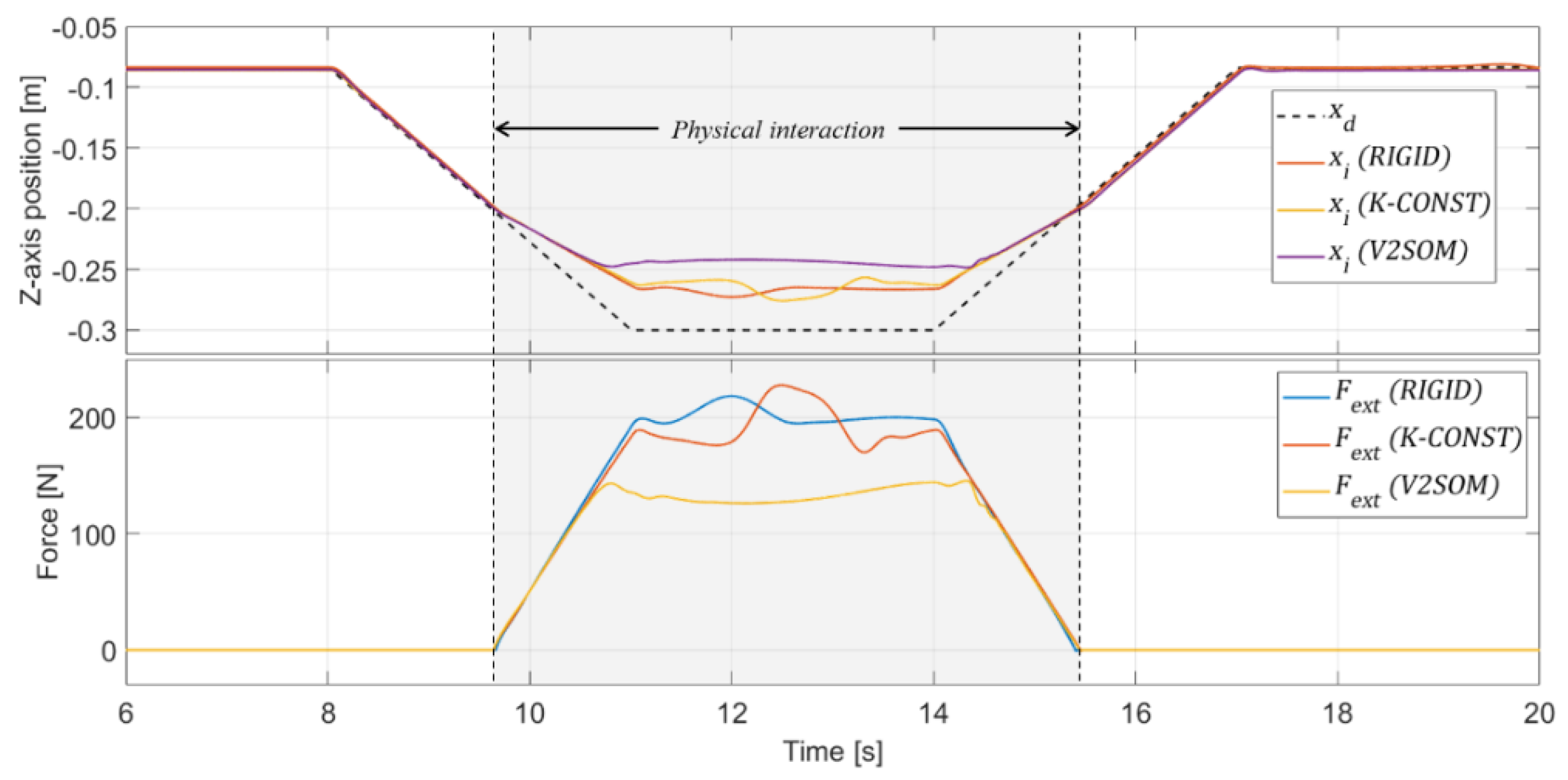
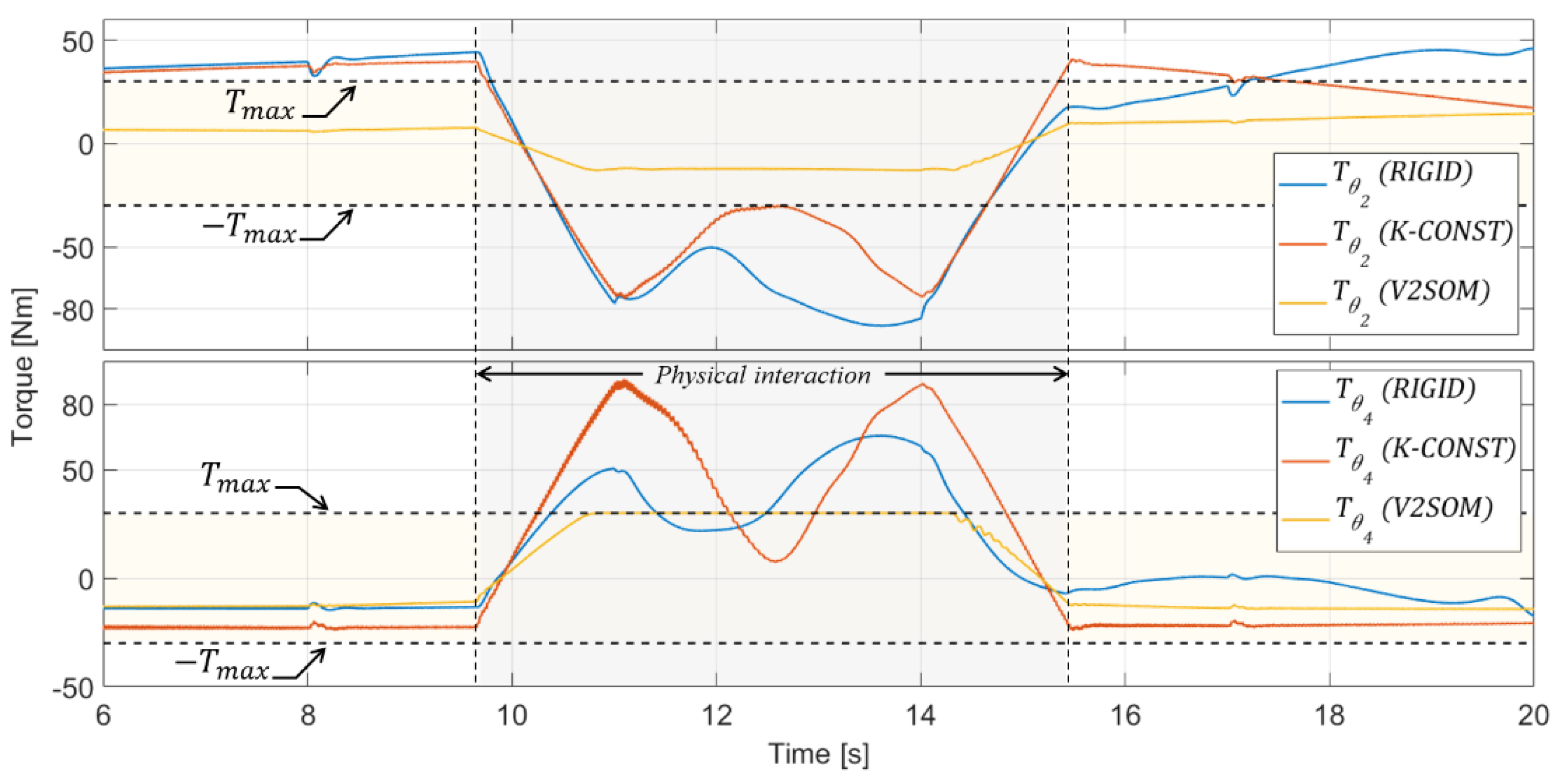
3.2.2. Cartesian Space Trajectory Task for Doppler Sonography
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gillespie, R.B.; Colgate, J.E.; Peshkin, M.A. A general framework for cobot control. IEEE Trans. Rob. Autom. 2001, 17, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, A.; Siciliano, B.; De Luca, A.; Bicchi, A. An atlas of physical human–robot interaction. Mech. Mach. Theory 2008, 43, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Haddadin, S.; Song, J.B.; Albu-Schäffer, A. Designing optimally safe robot surface properties for minimizing the stress characteristics of human-robot collisions. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 5413–5420. [Google Scholar]
- Fritzsche, M.; Elkmann, N.; Schulenburg, E. Tactile sensing: A key technology for safe physical human robot interaction. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction (HRI ‘11), Lausanne, Switzerland, 6–9 March 2011; pp. 139–140. [Google Scholar]
- Chiaverini, S.; Siciliano, B.; Villani, L. A survey of robot interaction control schemes with experimental comparison. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 1999, 4, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, C.; Mukherjee, R.; Nakamura, Y. A hybrid system framework for unified impedance and admittance control. J. Intell. Rob. Syst. 2014, 78, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, A.; Wimbock, T.; Albu-Schaffer, A.; Hirzinger, G. Integration of reactive, torque-based self-collision avoidance into a task hierarchy. IEEE Trans. Rob. 2012, 28, 1278–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghian, H.; Keshmiri, M.; Villani, L.; Siciliano, B. Null-space impedance control with disturbance observer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vila Moura, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; pp. 2795–2800. [Google Scholar]
- Pratt, G.A.; Williamson, M.M. Series elastic actuators. In Proceedings of the 1995 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Human Robot Interaction and Cooperative Robots, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 5–9 August 1995; pp. 399–406. [Google Scholar]
- Bicchi, A.; Tonietti, G.; Bavaro, M.; Piccigallo, M. Variable stiffness actuators for fast and safe motion control. Rob. Res. 2005, 15, 527–536. [Google Scholar]
- Grioli, G.; Wolf, S.; Garabini, M.; Catalano, M.; Burdet, E.; Caldwell, D.; Carloni, R.; Friedl, W.; Grebenstein, M.; Laffranchi, M.; et al. Variable stiffness actuators: The user’s point of view. Int. J. Rob. Res. 2015, 34, 727–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, T.; Sugano, S. Design and development of a new robot joint using a mechanical impedance adjuster. In Proceedings of the 1995 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Nagoya, Japan, 21–27 May 1995; pp. 2469–2475. [Google Scholar]
- Groothuis, S.; Carloni, R.; Stramigioli, S. A Novel Variable Stiffness Mechanism Capable of an Infinite Stiffness Range and Unlimited Decoupled Output Motion. Actuators 2014, 3, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.; Hirzinger, G. A new variable stiffness design: Matching requirements of the next robot generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2008), Pasadena, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2008; pp. 1741–1746. [Google Scholar]
- Schiavi, R.; Grioli, G.; Sen, S.; Bicchi, A. VSA-II: A novel prototype of variable stiffness actuator for safe and performing robots interacting with humans. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2008), Pasadena, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2008; pp. 2171–2176. [Google Scholar]
- Ayoubi, Y.; Laribi, M.A.; Arsicault, M.; Zeghloul, S.; Courreges, F. Mechanical device with variable compliance for rotary motion transmission. FR/IFBT17CNRCOB. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, Department of Transportation (DOT). Occupant Crash Protection—Head Injury Criterion S6.2 of MVSS 571.208; Docket 69-7, Notice 17; NHTSA: Washington, DC, USA, 1972.
- Newman, J.A.; Shewchenko, N.; Welbourne, E. A proposed new biomechanical head injury assessment function—the maximum power index’. In Proceedings of the 44th Stapp Car Crash Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 6–8 November 2000. SAE Paper No. 2000-01-SC16. [Google Scholar]
- López-Martínez, J.J.; García-Vallejo, D.D.; Giménez-Fernández, A.A.; Torres-Moreno, J.L. A Flexible Multibody Model of a Safety Robot Arm for Experimental Validation and Analysis of Design Parameters. ASME. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dynam. 2013, 9, 011003–011003-10. [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval, J.; Laribi, M.A.; Zeghloul, S.; Arsicault, M.; Poisson, G. Safety performance of a variable stiffness actuator for collaborative robots. In Advances in Service and Industrial Robotics; RAAD 2018, Ed.; Mechanisms and Machine Science. (In press)
- Spong, M. Modeling and control of elastic joint robots. ASME J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Contr. 1987, 109, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonietti, G.; Schiavi, R.; Bicchi, A. Design and Control of a Variable Stiffness Actuator for Safe and Fast Physical Human/Robot Interaction. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Barcelona, Spain, 18–22 April 2005; pp. 526–531. [Google Scholar]
- Albu-Schäffer, A.; Ott, C.; Hirzinger, G. A Unified Passivity-based Control Framework for Position, Torque and Impedance Control of Flexible Joint Robots. Int. J. Rob. Res. 2007, 26, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, H.; Allison, H. Work-related musculoskeletal disorders in ultrasound: Can you reduce risk? Ultrasound 2015, 23, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Village, J.; Trask, C. Ergonomic analysis of postural and muscular loads to diagnostic sonographers. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2007, 37, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoubi, Y.; Laribi, M.A.; Zeghloul, S.; Arsicault, M. V2SOM: A Novel Safety Mechanism Dedicated to a Cobot’s Rotary Joints. Robotics 2019, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoubi, Y.; Laribi, M.A.; Zeghloul, S.; Arsicault, M. Design of V2SOM: The Safety Mechanism for Cobot’s Rotary Joints. In Mechanism Design for Robotics. MEDER 2018. Mechanisms and Machine Science; Gasparetto, A., Ceccarelli, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 66. [Google Scholar]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sandoval Arévalo, J.S.; Laribi, M.A.; Zeghloul, S.; Arsicault, M. On the Design of a Safe Human-Friendly Teleoperated System for Doppler Sonography. Robotics 2019, 8, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics8020029
Sandoval Arévalo JS, Laribi MA, Zeghloul S, Arsicault M. On the Design of a Safe Human-Friendly Teleoperated System for Doppler Sonography. Robotics. 2019; 8(2):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics8020029
Chicago/Turabian StyleSandoval Arévalo, Juan Sebastián, Med Amine Laribi, Saïd Zeghloul, and Marc Arsicault. 2019. "On the Design of a Safe Human-Friendly Teleoperated System for Doppler Sonography" Robotics 8, no. 2: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics8020029
APA StyleSandoval Arévalo, J. S., Laribi, M. A., Zeghloul, S., & Arsicault, M. (2019). On the Design of a Safe Human-Friendly Teleoperated System for Doppler Sonography. Robotics, 8(2), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics8020029