Abstract
This paper presents a framework that integrates digital twin and virtual reality (VR) technologies to improve the efficiency and safety of human–robot collaborative systems in the disassembly domain. With the increasing complexity of the handling of end-of-life electronic products and as the related disassembly tasks are characterized by variabilities such as rust, deformation, and diverse part geometries, traditional industrial robots face significant challenges in this domain. These challenges require adaptable and flexible automation solutions that can work safely alongside human workers. We developed an architecture to address these challenges and support system configuration, training, and operational monitoring. Our framework incorporates a digital twin to provide a real-time virtual representation of the physical disassembly process, allowing for immediate feedback and dynamic adjustment of operations. In addition, VR is used to simulate and optimize the workspace layout, improve human–robot interaction, and facilitate safe and effective training scenarios without the need for physical prototypes. A unique case study is presented, where the collaborative system is specifically applied to the disassembly of antenna amplifiers, illustrating the potential of our comprehensive approach to facilitate engineering processes and enhance collaborative safety.
1. Introduction
The application of industrial robots in manufacturing is continuously rising due to their ability to execute tasks with speeds and accuracy that exceed humans’ capabilities. Particularly for the manufacturing of products that involve a high percentage of repeatable tasks, robots are an excellent resource. However, the deployment of robots is still challenging in processes that are not standardized, predetermined procedures and are characterized by extremely small batch sizes. Disassembly is one such process that is still very difficult to automate for several additional reasons. These factors are related to the high number of variants in product families, customization, mass personalization, product structure [1,2,3], as well as the state of the product, which can also be characterized by a variety of complications such as deformations, corrosion, and dust. In this context, it is crucial to focus on a hybrid robotic cell in which humans and robots can work collaboratively on disassembly tasks and support each other [4]. Humans are still better suited for tasks involving variability and fine physical movements and possess the ability to handle unpredictable changes in the environment. A composition of complementary strengths, which involve adaptability and automation, is necessary to make industrial robots more applicable for use cases such as disassembly.
1.1. Challenges within Human–Robot Collaboration
Despite its potential, human–robot collaboration in the disassembly domain also brings challenges related to appropriate task distribution and safety [4,5]. Such collaboration can be complex and dynamic, and collisions and possible injuries are, unfortunately, unpredictable sometimes. In this context, ensuring that safety aspects are respected is crucial for enabling robots to work in the immediate vicinity of humans. The challenge is organizing dynamic task sequencing and allocation while considering speed, capabilities, and safety issues while additionally reflecting the effectiveness of the actions. Consequently, there is a need for a unified representation of the involved entities and objects, as well as human and robot actions, in order to be more easily interpreted and integrated into heterogeneous environments such as collaborative systems [6,7]. Such a model can increase interoperability and can be used for system configuration as well as engineering purposes to reduce the amount of time and effort required for these activities. Additionally, it is important to provide new practical methods for the engineering and supervision of such environments that could provide convenience and flexibility as well as cover safety requirements and standards for specific industrial applications such as disassembly. Advanced human–robot interfaces are required to support the interaction between humans and robots, and facilitate their safe and efficient (co)operation. This kind of interface should enable users to communicate easily but also provide them with accurate information needed to oversee the current system behavior and accordingly react in dynamic situations [8]. Considering the conventional way of programming industrial robots, where each new task or process adjustment results in downtime that is not economically viable for smaller lot sizes, such interfaces should provide methods for simpler and economical robot programming not requiring comprehensive knowledge in the robotics domain [9]. Finally, it is essential that a solution provides cost-effective training for the personnel who will be operating the robotic system. Companies rely on robots or specialized software for training to understand robot operation, programming, and troubleshooting. Without this practical exercise, employees may lack the necessary skills, leading to potential operational inefficiencies and safety risks. However, considering that many small- and medium-sized companies (SMEs) cannot afford to acquire a robot specifically for training purposes, simulators are seen as an economical alternative [10]. Hence, the main obstacles for SMEs that prevent them from adopting robots on a massive scale are uncertainty about total cost and missing robotic competencies [11].
Realistic industrial system models are indispensable in enabling the early and efficient assessment of system design decisions as well as in improving a system’s operation performance [12]. Such a solution should be able to mirror the physical system and should enable the assessment of real scenarios, embodying and exactly showing the involved entities, as well as enabling the realistic validation of poses and movements [13].
1.2. Digital Twin
The digital twin is an emerging technology that offers a new perspective on supervising the operation of physical objects. It provides a virtual representation of real objects and facilitates interaction and data streaming between the physical process and the virtual space [14,15]. A digital twin is used to establish a virtual representation able to mimic the properties, behaviors, and processes of the real world. Due to the harmonized operation of the real and virtual counterparts, digital twins provide means that can be used to effectively test, observe, and evaluate the system but also propose changes and visualize potential corrections [16]. Being a digital replica of a physical system, the digital twin provides users with a reliable, high-fidelity, and real-time controllable instrument, which is particularly useful for situations that require safe and efficient human-0machine interaction [17]. However, the development of the virtual models is time-consuming and requires significant efforts for their physical and logical modeling as well as for modeling the coupling correlation between them [18]. Further challenges are related to better modeling and more accurate representation of the components and process, as well as improved data streams between the different parts of the digital twin [19]. Moreover, issues related to two-way connection and synchronization, the guidance of the physical entities in real time, and visualization should be addressed as well [15,20]. Finally, human–machine interactions and direct feedback control should be significantly improved to better integrate and involve humans in the manufacturing process [21]. In this context, digital twins lack human-centered focus, and the currently developed solutions have limited interaction and collaboration functionalities [22].
1.3. Virtual Reality
Virtual-reality-based industrial robotic systems have the potential to handle some of the challenges mentioned earlier. Virtual reality (VR) is a safe and cost-effective solution that can be used for offline robot programming, providing an authentic experience of a real situation [10,23]. It can be used to analyze a variety of concepts and layout designs in a trial-and-error manner with movement prediction and built-in collision checking. VR allows an operator to observe and walk through the environment and to use handheld controllers to interact/move robot arms or 3D objects virtually and make modifications when necessary [24]. Furthermore, it is possible to perform reachability tests to identify the locations that robots and humans can reach as well as placement tests to determine the placement range and working conditions. VR also supports virtual experimentation before transferring a scenario to a real system. However, even though research on VR has increased and significant technological progress has been made in the last years, the application of VR within robotics is still in the early stages, and applications have not substantially reached the production environment [25]. Additionally, the development of the virtual plant model requires a significant amount of time and effort, and new concepts should enable faster system development [26]. Finally, VR applications are often deployed in a laboratory or structured environment that can be easily managed. Therefore, it is important to test these systems in real-world conditions, which are often unpredictable and unstructured [27].
To bridge all the gaps mentioned above and contextualize our contributions, this work explored how digital twin and virtual reality technologies can address the challenges in human–robot collaboration by providing a unified representation and advanced interfaces for interaction, thereby enhancing safety, task distribution, and system integration. The contribution of this work is as follows:
- We developed a system architecture integrating digital twin and VR to enhance human–robot collaborative systems.
- We implemented a prototype that allows users to simulate and optimize disassembly tasks in a safe, virtual environment.
- We applied the framework in a case study to disassemble antenna amplifiers.
- We demonstrated important aspects of human–robot collaboration, such as task distribution and safety issues.
- We demonstrated the framework for use in system configuration, training, and operational monitoring.
This paper is structured as follows: The following State of the Art Section analyzes various aspects regarding human–robot collaboration and simulation, as well as digital twin and virtual reality technologies. Afterward, this paper describes the development of a framework that combines digital twin and VR technologies, as well as the software communication infrastructure and the provided functionalities. The Experiments Section presents the implementation and testing of the framework in a representative use case scenario. Subsequently, the Discussion Dection examines the potential of the developed digital twin and VR framework. In the final section, this paper concludes by summarizing the developments and outlining directions for future work.
2. State of the Art
Collaborative human–robot systems are complex and commonly integrate a large number of elements and aspects that have to be considered and optimized since they influence the safety and efficiency of the industrial process. In this context, it is important that robotic systems are able to not only manage uncertainties about the geometry and physical properties of objects but also partition the main task into primitive elements and synchronize the robot’s action with its human counterpart [28]. In order for a robotic system to function in an environment with a high degree of dynamic uncertainty and to ensure safety and continuous operation, it is crucial to obtain reliable and meaningful information about the state of the robotic system and the environment [29]. An important challenge is also reflected in usability, where user-friendly and effective interfaces should be provided to facilitate adaptability and the seamless interaction between humans and robots [30]. Because of these reasons, there is a strong need to verify these kinds of systems during the design and development phase and to optimize them once they are in operation. Simulation is a powerful means of developing various robot solutions and improving their quality during the design phase.
2.1. Robot Simulation Limitations
Robot simulation tools provide great means to design, program, and optimize a robotic cell without stopping the manufacturing process. Simulation can provide functions such as path and collision analysis, calibration, equipment placement, and reachability assessment [31]. Robot simulation can also be successfully used to test and validate control programs and algorithms. A general review of physics simulators covering various areas of robotics research such as learning, soft, aerial, and underwater robotics, and manipulation has been reported by Collins et al. [32]. Tsagaris et al. used RoboDK software to convert a CAD model into a controllable simulation of a 5DoF robotic arm [33]. Sekala et al. demonstrated the modeling and programming of robotic work cells using Siemens Process Simulate software [34]. Baizid et al. presented the IRoSim platform to assist users in designing and simulating robotic tasks [35]. There are also several available software solutions, such as RobotStudio (ABB), KUKA.Sim Pro (KUKA), and RoboGuide (FANUC), which have been developed by robot manufacturers and enable the offline programming and simulation of robots [36]. With these kinds of solutions, it is possible to develop a robot program in advance and immediately implement it on a real robotic cell. These kinds of tools have been successfully used in various manufacturing processes such as welding [37,38,39], palletizing operations [40,41], circuit board assembly [42], and painting [43]. Lukac conducted a comparative study of industrial robot simulation systems for educational needs [44]. A disadvantage of these solutions emerges in situations when robots from different manufacturers are used in production, having different programming characteristics and requiring specific software tools. In general, simulations have limited capabilities for assessing system performance since the direct link to the real system and the ability to track current and past system states are missing [14] and the user cannot preview motion replication in real time [17]. Additionally, the presence of human users in a collaborative workspace raises the level of unpredictability, which is not easy to cover with simulation tools [45]. In this context, the digital twin boosts the simulation ability using data from real systems, enabling real-time optimization and decision making. This is particularly necessary in environments such as collaborative human–robot systems, which require reliable and efficient operation and interaction [17].
2.2. Digital Twin Technologies
The idea of the digital twin has its roots in NASA’s Apollo space program, where it was used to mirror the conditions of the shuttles during the mission. NASA also contributed with the first definition of the digital twin [46]. Since then, the digital twin has been broadly applied in the entire product lifecycle, e.g., during the design phase for iterative optimization; during the manufacturing phase for production control, planning, real-time monitoring or evaluation; as well as in the service phase for predictive maintenance, fault detection, and diagnosis or performance prediction [47].
Given the omnipresence and increased deployment of robotics in industry, digital twin technology has also found broad application in the development and supervision of this kind of system. Digital twin implementations encompass Industry 4.0 [48], human–robot interaction, work-cell simulation, maintenance [49], as well as solutions driven by artificialiIntelligence to support control, energy modeling, or planning [45]. Considering the significant benefits, such as the ability to assess the safety of a system and assist in speed and configuration optimization as well as task planning and the training of personnel, digital twins have found wide application in human–robot collaboration. Ramasubramanian et al. reviewed related implementations and trends in human–robot collaboration. The identified challenges included the lack of a generic framework, high cost, limited training, and real-time connectivity issues, while future trends focus on AR/VR advances in realistic representation, generic frameworks, and modular AI hardware to improve the implementation and efficiency of DT in human–robot collaboration [19]. In this context, Malik and Brem presented the development of a digitaltTwin for collaborative robots and investigated its usefulness in an assembly use case [50]. Yao et al. proposed a digital-twin-based framework for task rescheduling in robotic assembly lines. This framework integrates physical entities, virtual entities, and a virtual reality interaction mechanism, and handles the dynamic disturbances and uncertainties that affect assembly processes by enabling real-time rescheduling. A mathematical model was developed, and an improved discrete fireworks algorithm was introduced to optimize task scheduling by minimizing computation time and improving solution quality [51].
2.3. Virtual Reality for Digital Twins
Virtual reality is seen as one of the main pillars of Industry 4.0, offering an effective way of modeling and studying industrial processes [52]. In this context, VR technology can be used complementary to the digital twin to enable users to better understand and assess a collaborative environment, with a particular focus on safety and ergonomics assessments [53], providing natural and effective training [52]. Recent research works have also focused on addressing different issues in the robotics domain using VR. Dimitrokalli et al. investigated human–robot collaboration in mechanical product assembly using virtual reality. The virtual environment was created using Unity 3D, with Leap Motion for hand tracking and an Oculus Rift DK2 headset for immersion and head motion detection [54]. Garg et al. presented a framework that facilitates online/remote programming of a robotic cell. It consists of the digital twin model developed with the Unity game engine, as well as VR and a real FANUC robot (model M-10ia/12) [55]. Burghardt et al. also used virtual reality and digital twins to program robots in the process of cleaning ceramic molds. The digital twin mimics a robotic cell, allowing the operator to perform tasks in a virtual environment, and then the robot replicates these movements in the real world [56]. Furthermore, Kuts et al. achieved synchronization between real and virtual industrial robots, enabling real-time control and programming of industrial robots through a VR interface [57]. Finally, Perez et al. developed a methodology for engineering and operating multirobot manufacturing cells using digital twin and virtual reality technologies in a real-world part assembly use case [58]. The use cases presented are challenging; however, to comprehensively demonstrate the potential of these technologies, it would be advantageous to investigate applications in more complex and unpredictable environments, such as during disassembly. In this context, better synchronization and interaction functionalities with the physical world are needed to handle this kind of dynamic use case.
2.4. Safety in Human–Robot Collaboration
Physical safety is a primary aspect of human–robot collaboration that must be ensured if it is to be widely accepted and effectively used. Hamad et al. analyzed various physical and cognitive safety aspects and presented a multilayered safety architecture, integrating both aspects for effective HRI [59]. Valori et al. presented the most relevant standards dealing with the safety requirements in human–robot collaboration [60], and Robla-Gómez et al. gave an overview of the progression of safety systems and their implementation in robotic environments [61]. Gualtieri et al. proposed guidelines for ensuring safety in collaborative human–robot assembly systems and validated them through a laboratory case study [62]. Lacevic et al. presented a method for ensuring safe human–robot collaboration by continuously monitoring and explicitly representing danger zones [63]. Effective HRC requires safe collaboration, explainable and predictable robot actions, as well as bidirectional communication with built-in safety mechanisms from design to deployment [30]. The consideration and integration of safety aspects and requirements in a way for the robot to understand the risks are desirable. Additionally, there is a need for the consolidated and unified modeling of human and robot actions to be easily integrated and generically reusable for various kinds of products to be disassembled. For this reason, the knowledge representation should be separated from the program logic to be used for different scenarios. Additionally, the developed applications should be usable for different purposes (for design, simulation, operation, or training), which can significantly speed up the realization of new applications. Finally, the focus should be on improving collaboration through real-time data processing and building trust through explainable robot actions and bidirectional communication.
3. System Overview
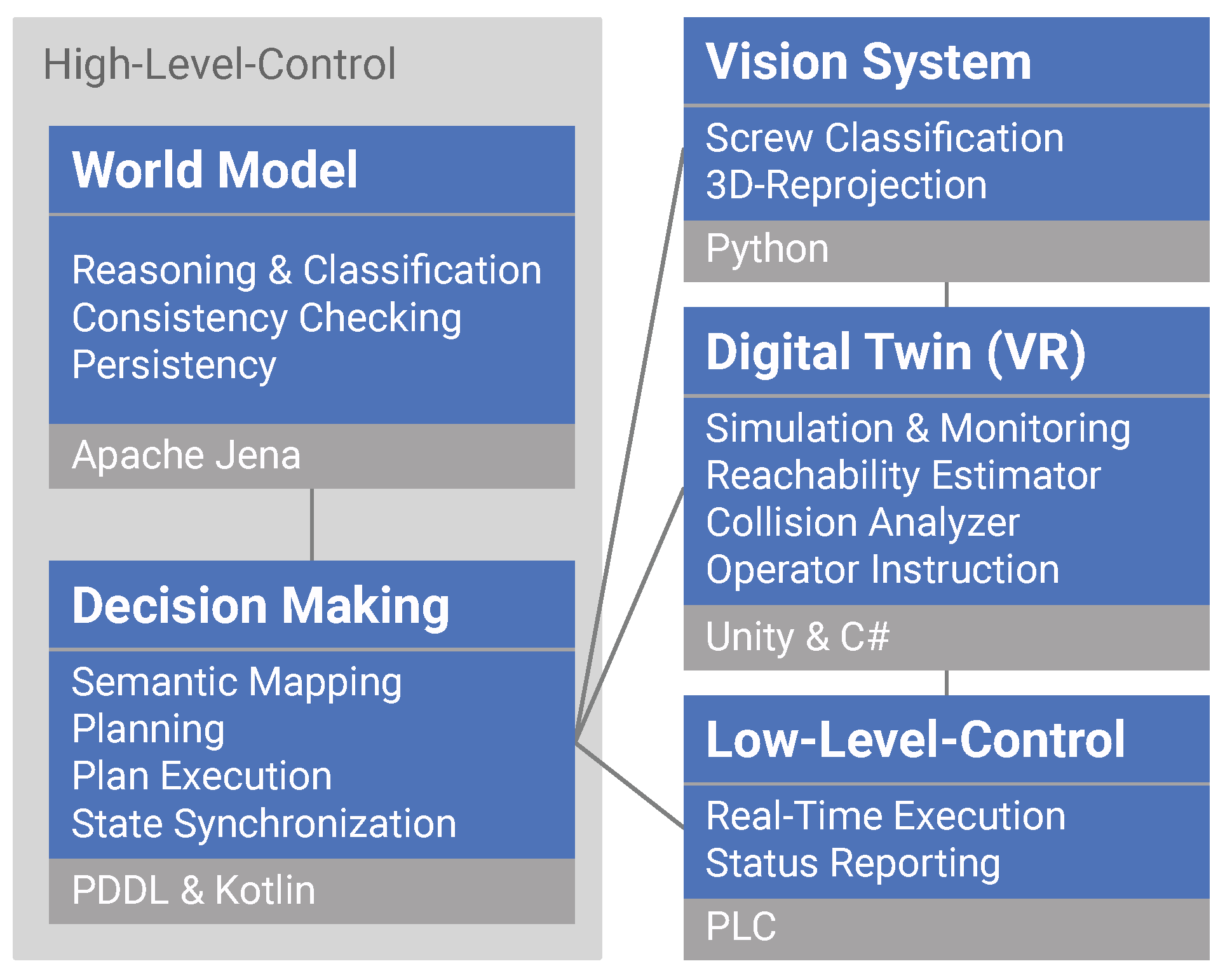
The main objective of this work was to develop oa framework that combines digital twin and VR technology in order to support the user during the engineering and supervision of industrial and collaborative robotics systems applied in the disassembly domain. The core components of the framework are the world model, the decision making, the vision system, the digital twin with a VR interface, and its execution components, which are responsible for moving the robots. The architecture has its origin in our previous work, which differentiated the control of a specific manufacturing unit into two levels: high-level control (HLC) and low-level control (LLC) [64,65]. The architecture incorporates the control system components into these two layers, as presented in Figure 1. The core functions of the world model, decision mkking, and execution component (i.e., the LLC) are explained more in detail in our previous research [66]. In this work, we extended the HLC, which generally consists of the world model and decision-making components, by adding a digital twin module with a VR Interface. In this way, the framework enhances functionality from pure controlling functions to enable use for broader engineering purposes such as commissioning, training, and supervision.
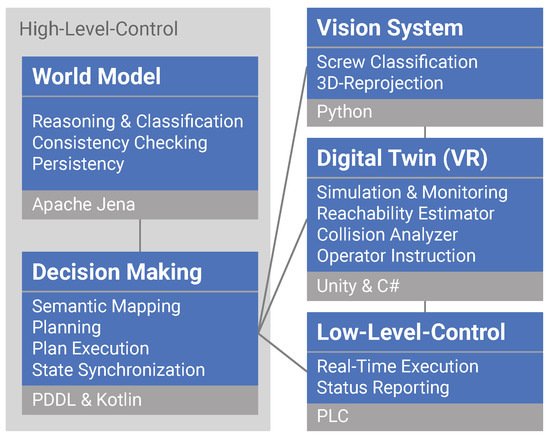
Figure 1.
The core components of the framework, each listed with their capabilities and implementation technologies: high-level control consisting of the world model and decision making, the vision system, digital twin with VR Interface, and the lowlLevel control. The interfaces between each component are shown as black lines.
3.1. World Model
The world model is a core component of the framework, with the role of centrally persisting all information and concepts of all interconnected components. These components can query and store information to/from it via the decision-making component. The world model maintains the exact model of the environment and delivers up-to-date information to all other associated elements. Ontologies are applied to express information models and store associated knowledge within the world model. Ontologies have recently been used in industry to enrich data with semantics and provide a common vocabulary, integrating different systems and making the content understandable to both humans and machines [67,68,69].
Two important duties of the ontology within the system are reasoning and classification as well as consistency checking. Reasoning and classification involve deriving new knowledge from the existing ontology by applying logical rules and categorizing information into predefined classes. This enhances the ability of the world model to make informed decisions based on the relationships and properties defined within the ontology. Consistency checking ensures that the information within the ontology does not contain contradictions and adheres to the defined rules and constraints. Consistency checking helps to identify and resolve conflicts within the ontology, thereby supporting the stability and coherence of the world model.
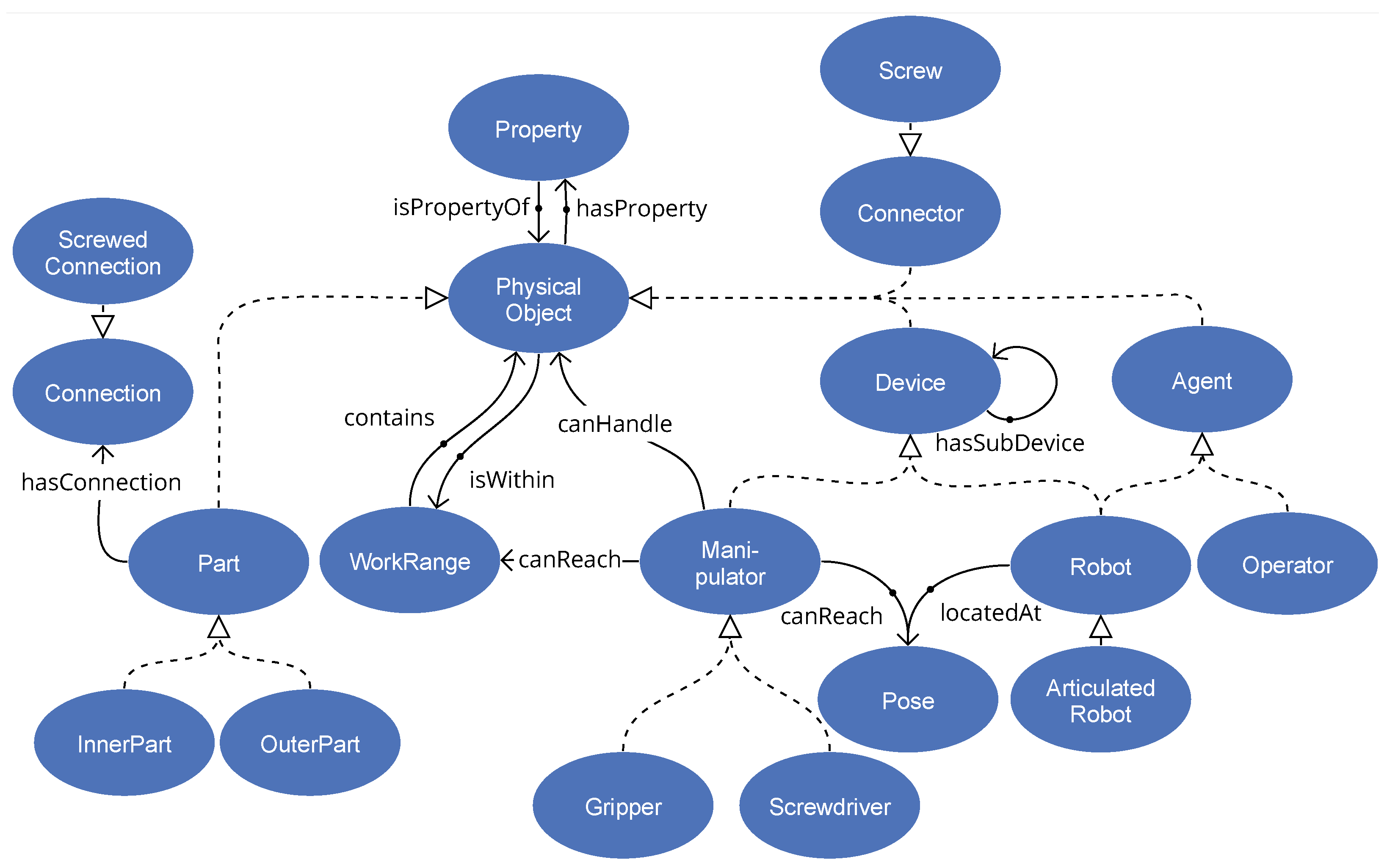
To be sufficiently exploitable for disassembly system configuration and function, the ontology should include an adequate model of the system environment, including human and robot capacities and limitations, tooling and other equipment, interfacing, and support services. Recognizing the relevance of previously developed ontologies, we reused some concepts associated with robotic devices and skills from the ROSETTA ontology [70] and concepts related to human–robot collaboration from the CCORA ontology [71]. We also extended our previously developed ontologies [66] further by inserting concepts related to disassembly processes, human–robot interaction, and safety requirements (see Figure 2). The central class concept is the PhysicalObject with its spatial properties of position, rotation, and scale. It is the parent class for most other concepts, e.g., devices, parts, connectors, manipulators, agents, etc.
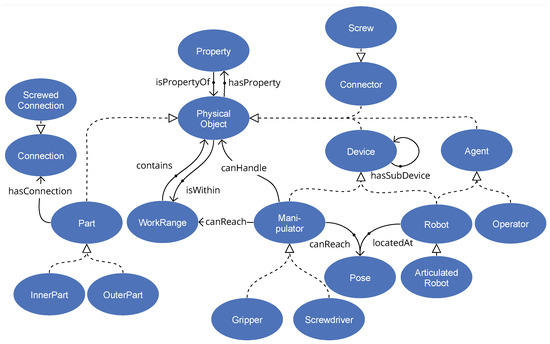
Figure 2.
The core classes of the world model of the disassembly robotics system and their relationships. The unnamed relationships are parent–child relationships (subClassOf).
3.2. Vision System
The vision system plays a critical role in the framework for accurate and reliable automated disassembly. The key function is to accurately identify the position and orientation of the screws and other components within the antenna amplifier. For this purpose, a neural network approach using fully convolutional one-stage object detection (FCOS) [72] was trained on synthetic screw data. An RGB-D camera, Intel Realsense 435 (Intel RealSense, available at https://www.intelrealsense.com/ (accessed on 31 May 2024)), detects screw heads in 2D images, which are reprojected back into the 3D point cloud, as explained more in detail in our previous work [73]. This detection functionality is triggered by the decision making and the recognized objects are stored in the world model. These data are used to calculate approach points and collision-free paths for the robot, as well as to optimize the robot’s trajectories. The vision system also plays an important role in continuously monitoring the disassembly process and detecting any deviations or errors, which are communicated to the decision-making component for dynamic rescheduling and adjustments.
3.3. Decision Making
The decision-making component was designed to generate a plan, based on input from the world model, to accomplish particular tasks and reach the final state. In our case, the initial state is defined by the working environment, with the robot and its hardware, and the product to be disassembled. The final state is defined as the extracted parts of the product.
The decision-making component uses a planner implementing the Planning Domain Definition Language (PDDL) [74] to generate sequences of actions (tasks) to reach the final state (goal). To transform the knowledge from the ontology into PDDL, we implemented a semantic mapping approach in our previous research [66]. During the design and development phase of the robotic system, these actions are shared with the digital twin and VR interface for validation. Once the system is operational, the actions are directly forwarded to the execution component, which integrates the planning system with the physical components (robots, tools, vision system, etc.). During the execution of the actions, their execution status is monitored and synchronized back into the ontology. If execution fails at a certain point, a replanning is triggered, which relies on the newly synchronized world model state.
3.4. Execution
The execution component interprets the action plan generated by the decision component and executes the code on the physical robot hardware in real time. To allow status monitoring and state synchronization back into the ontology, the execution component reports its execution status back to the decision-making component. The robot hardware incorporates the robot with its motion controller and its attached tools, e.g., an industrial screwdriver (nut runner).
3.5. Digital Twin
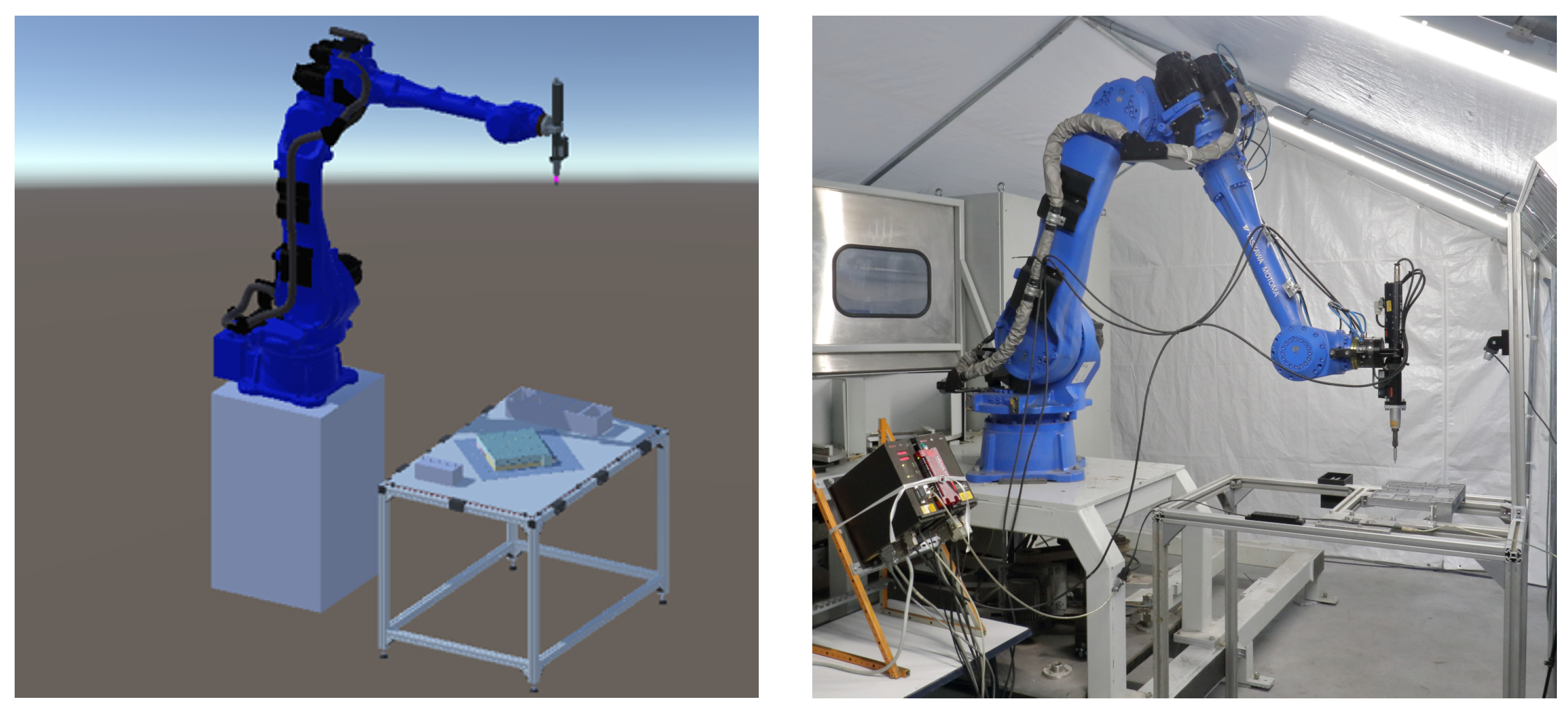
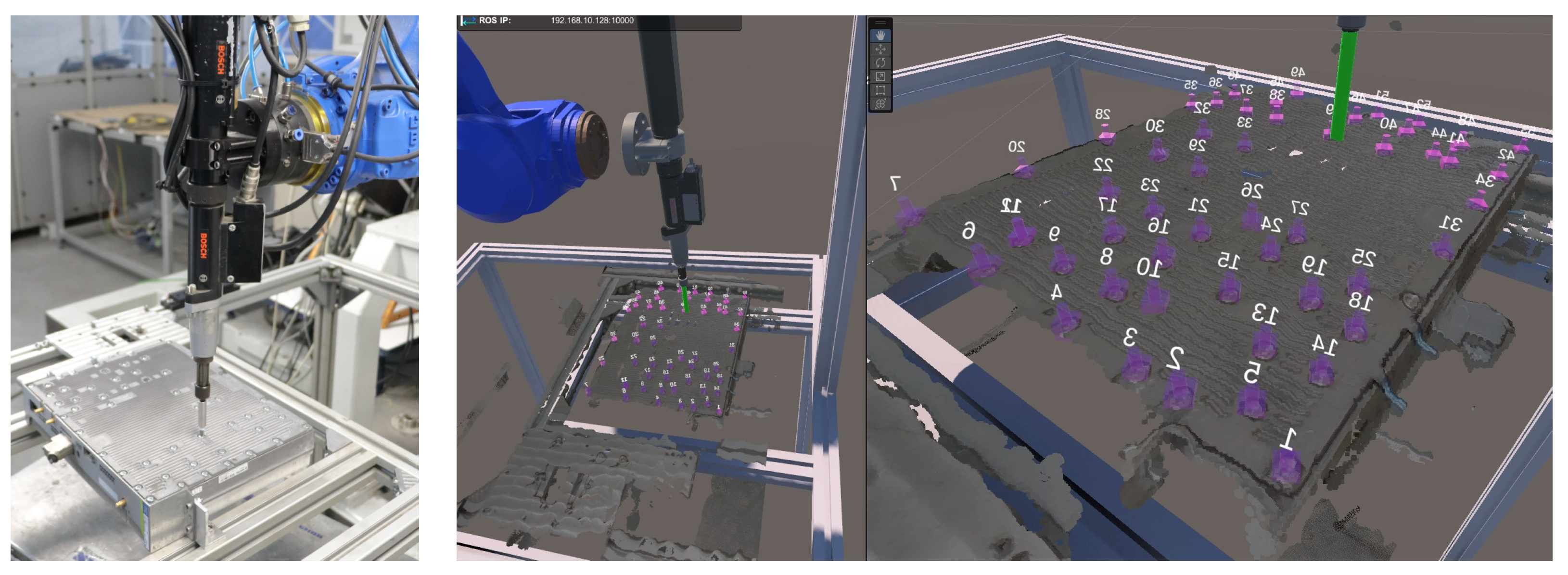
The purpose of the digital twin is to support the disassembly system during the engineering process and its operation. The digital twin is automatically configured based on the information from the world model via the decision making. This means the spatial information about the geometry and positioning of the product, robots, and other mechatronic components is transferred to the digital twin for the initial configuration [75]. Similarly, the robot’s environment is reflected in the digital twin to define its workspace. This type of automated configuration facilitates the rapid development of new production settings and makes it easy to modify them. This is particularly important for the disassembly domain, which is focused on disassembling different product types with potentially high uncertainties due to the end-of-life product phase. In addition, by synchronizing the objects of the physical system with their digital representation in the digital twin, it is possible to monitor the system conditions and visualize sensor data. Again, this is important to support the dynamic and collaborative nature of the disassembly environment. Figure 3 shows the digital twin of the disassembly robot cell and the corresponding real-world setup.
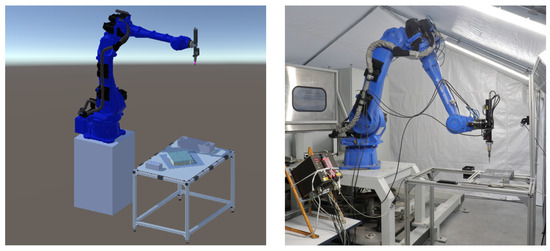
Figure 3.
The disassembly robotics cell in the virtual (left) and physical worlds (right).
Unity (available at https://unity.com/ (accessed on 31 May 2024)) was used to create visual representations of the disassembly environment and provide immersive physics simulations. Unity is a cross-platform game engine with intuitive design tools that facilitate the development of digital twins and advanced graphics rendering that supports VR devices. It integrates a robust physics engine capable of simulating real-world physics in the form of rigid body kinematics and collisions. The VR interface, as well as the human–machine interface (HMI) on a screen for the human worker, can be used to monitor the system.
3.6. Virtual Reality Interface
The VR interface is used to monitor and visualize the robot’s actions, including the position and orientation of its end effector, as well as the products and environment (table, boxes for storing parts or tools, etc.). It allows users to better gauge the depth of objects and their spatial relationships in contrast to regular display interfaces. This enhanced spatial perception helps in accurately identifying overlapping objects and potential collisions, leading to improved interaction and navigation in complex environments. We chose virtual reality (VR) over augmented reality (AR) due to the easier implementation, as it does not require costly robotics and is inherently safer.
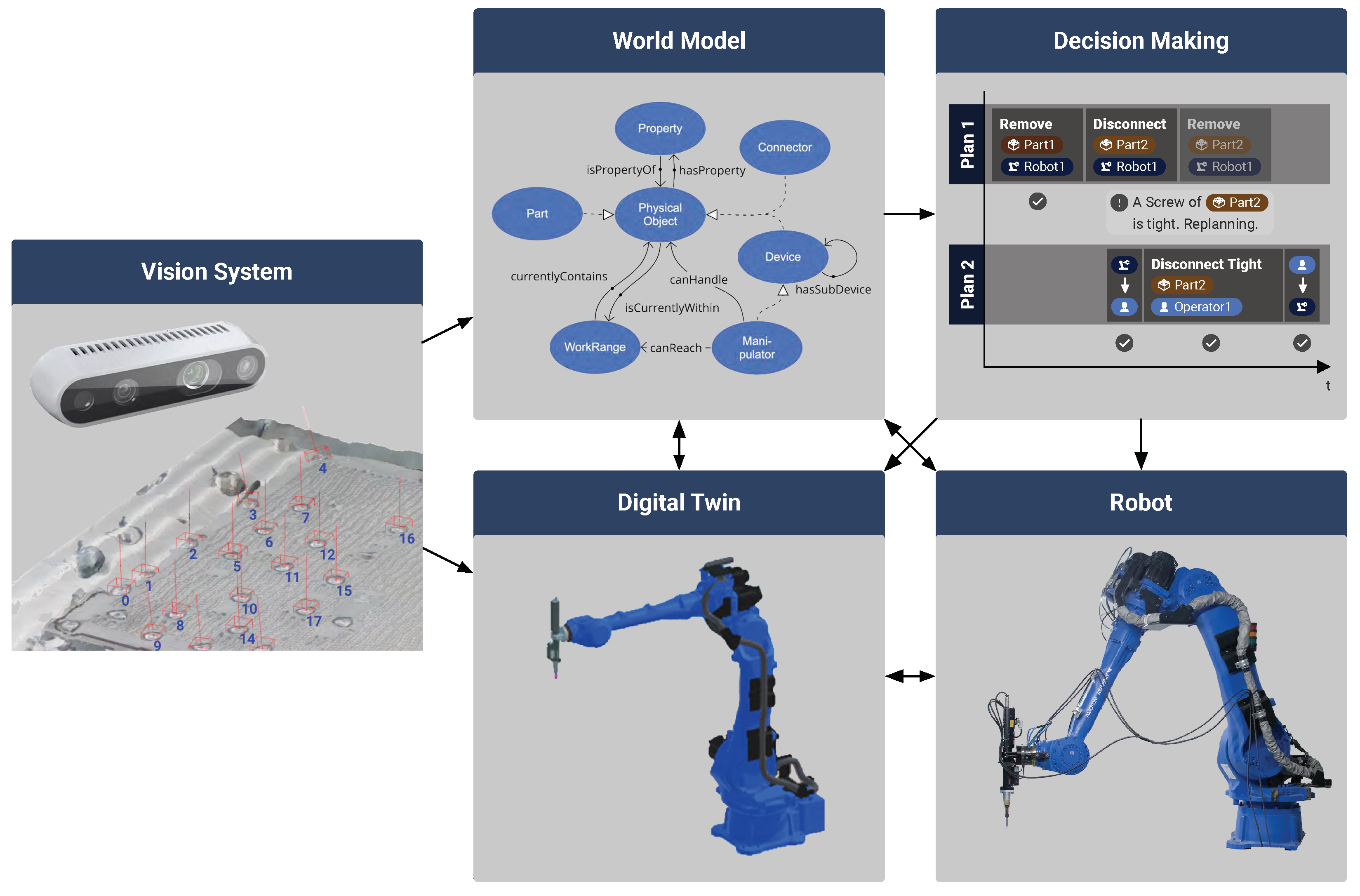
Using the VR interface, the human worker navigates through the virtual environment using two handheld controllers to move objects from one position to another. Once the layout is defined, the worker can start the dynamic simulation while still immersed in the VR scene. It is also possible to explore different object placements in the environment and analyze different disassembly scenarios and actions from different angles in certain situations. This is especially important given the collaborative nature of the disassembly process. Within the framework presented, the worker can adjust the environment as needed by moving equipment to a new position and specifying new feasible or safe paths. These new positions are then directly transmitted and synchronized with a real robot or its world model, as shown in Figure 4. They are immediately considered in the analysis and planning of actions and the automatic generation of robot execution code.
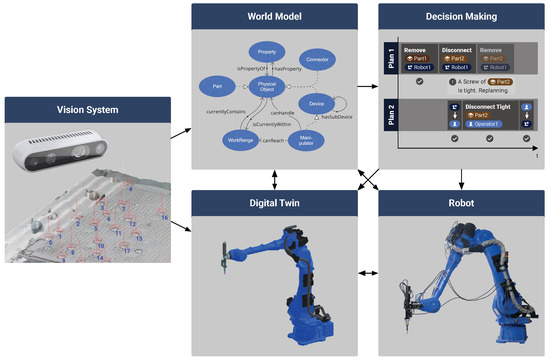
Figure 4.
Information synchronization and transfer (black arrows) between the system components of the physical and physical environments. The detected screws of the vision system are annotated using colored numbers.
During the design phase of the robotic work cell, we used this functionality to test and optimize different workspace layouts. The immersive experience, thanks to improved depth perception due to VR, opens up further possibilities for workspace design, improving communication with stakeholders and avoiding time-consuming conversions of the physical prototype. For each of the designs, we performed a reachability analysis, as described in Section 4.1, and simulated a disassembly, for example, of devices, which is further detailed in Section 4.2.
In addition, the virtual framework can receive information related to the motion in the environment (robot, product, people, etc.) using the point cloud information of the RGB-D camera and perform analysis based on the real data. This type of bidirectional connection ensures that all changes from the real world can be transferred to the virtual space and vice versa. Moreover, the subsequent integration with the PDDL planner of the decision-making component, which generates actions such as movements for the human worker and the robot, allows the visualization of the generated plans in cases where new layouts are tested and analyzed. Given that humans and robots have different capabilities, any planned disassembly operation can be evaluated against the process characteristics and physical constraints of the component. In this way, the approach can be used to validate robot movements for individual product parts and correct specific factors in the control strategy until the actions are feasible and effective. In addition, the verification of tooling, path planning, collision analysis, and safety considerations ensures safe operation and resolves critical issues. Finally, mirroring and linking the disassembly processes, once implemented and running, to the virtual space provides the ability to monitor and modify them in real-time.
The immersion of 3D perception provided by the additional depth dimension of VR also leads to advantages in the training and further education of operating personnel. Inexperienced operators can be safely and realistically introduced to the system’s operation using the digital twin and its visualization via VR. This avoids the considerable risk posed by moving objects on the real robot system if safety regulations are violated. In addition, the system does not have to be shut down to train new operators, which leads to further efficiency gains in the operation of the system. More experienced users can practice and further optimize changes in the workflow. The simulation functionality also makes it possible to safely test modifications to the robot system’s motion planning without endangering the operator or recognizing safety-critical situations at an early stage.
3.7. Message Middleware
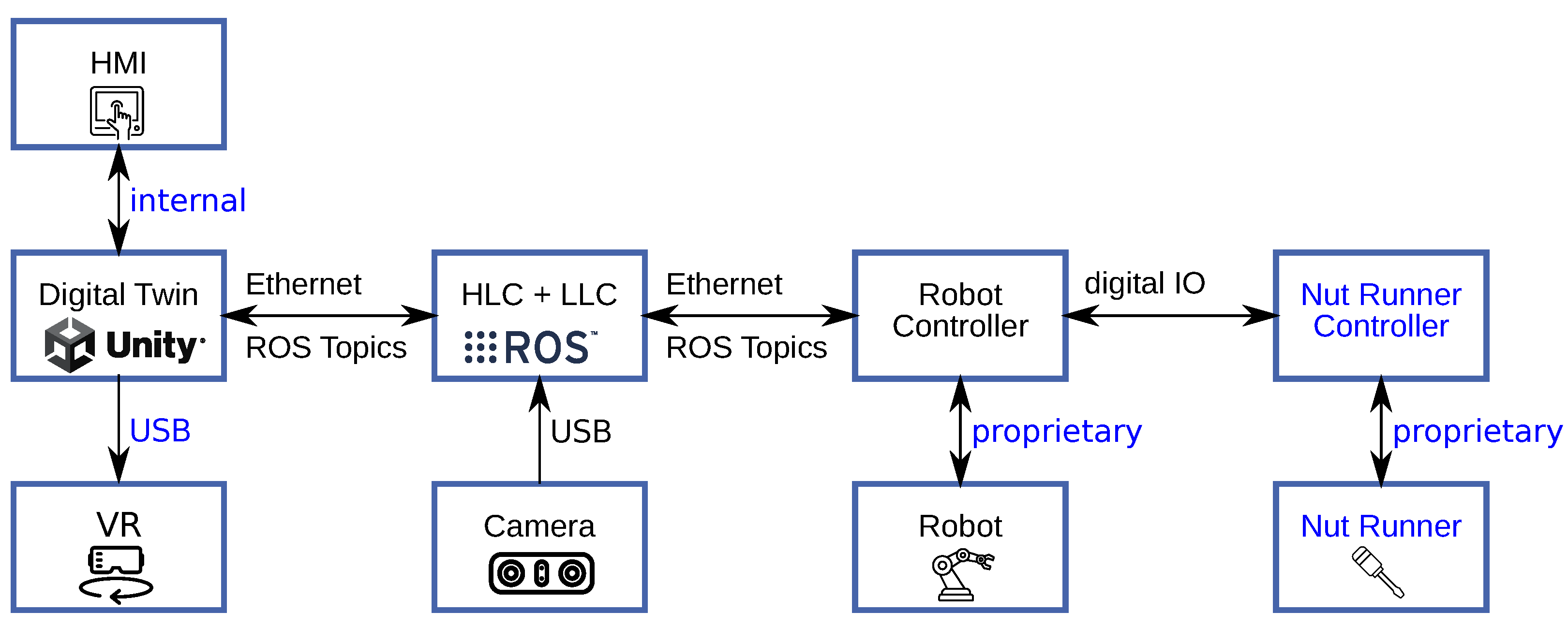
The system communication architecture was built on the Robot Operating System (ROS) [76], as presented in Figure 5. ROS is used as middleware for communication with the robot as well as between the different components of the system. ROS is an open-source framework that integrates a wide range of tools and libraries for robot operation. The ROS MoveIt library [77] is used to calculate collision-free trajectories, create pick-and-place paths, and compute the forward and inverse kinematics of the robot. The high number of established interfaces to robot systems and simulation environments in programming languages such as Python, C++, and MATLAB/Simulink supports a step-by-step integration of the components into an overall system and promotes the testing of the software in the context of a digital twin. ROS utilizes its modular publisher–subscriber architecture, where components (nodes), starting with task planning and ending with hardware commands, communicate with each other as the nodes of a network via extensible messages. The built-in parameter server and launch scripts handle different configurations. This enables a seamless switch from simulation to real-world execution. The communication infrastructure of the disassembly system is presented in [73].
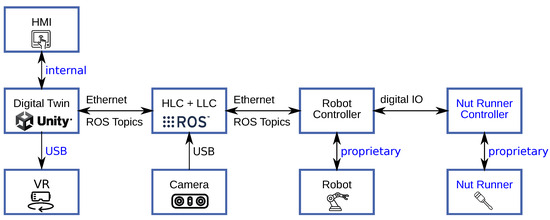
Figure 5.
Communication infrastructure between the different system components. (Image sources: ROS logo (https://www.ros.org/blog/media/ (accessed on 31 May 2024)) with permission from Open Source Robotics Foundation, Inc.; Unity logo (https://unity.com/en/legal/branding-trademarks (accessed on 31 May 2024)) with permission from Unity Technologies. HMI (https://thenounproject.com/icon/noun-hmi-5664890 (accessed on 31 May 2024)) by Eris Kusnadi (The Noun Project); Virtual Reality (https://thenounproject.com/icon/virtual-reality-4177349 (accessed on 31 May 2024)) by Abdulloh Fauzan (The Noun Project); Dual Camera (https://thenounproject.com/icon/noun-dual-camera-598787 (accessed on 31 May 2024)) by Nikita Cherednikov (The Noun Project); Robotic (https://thenounproject.com/icon/robotic-5610082 (accessed on 31 May 2024)) by Rukanicon (The Noun Project); Screwdriver (https://thenounproject.com/icon/screwdriver-4104291 (accessed on 31 May 2024)) by DinosoftLabs (The Noun Project). All icons from The Noun Project are licensed under CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/ (accessed on 31 May 2024))).
ROS provides computed sensor data and robot positioning to Unity, which are then presented in the HMI and visualized in the digital twin and available for handling in VR. The decision making generates a task and sends it to ROS to generate a collision-free motion path, which is then returned to Unity3D and visualized to the user for validation. Once the user confirms the generated motion, a message is sent to ROS to convert the motion plan to robot execution code. While the real robot performs the work, ROS communicates updated robot positions continuously to Unity, further visualizing the motion in the digital twin and the VR. Additionally, the robot controller’s digital IO controls an industrial screwdriver (nut runner) consisting of a nut runner controller and a nut runner drive. Its corresponding control and status monitoring are also handled by ROS.
4. System Functionalities
To facilitate the design and operation of the disassembly system, several functions are integrated into the robotic system. These functionalities are the result of the benefits offered by the synergies and interconnections between the virtual and real environments. On the one hand, the focus is on enhanced engineering of the work cell prior to system operation. On the other hand, the emphasis is on supporting supervision, simplifying programming, and ensuring efficient and safe operation.
4.1. Reachability and Placement Analysis
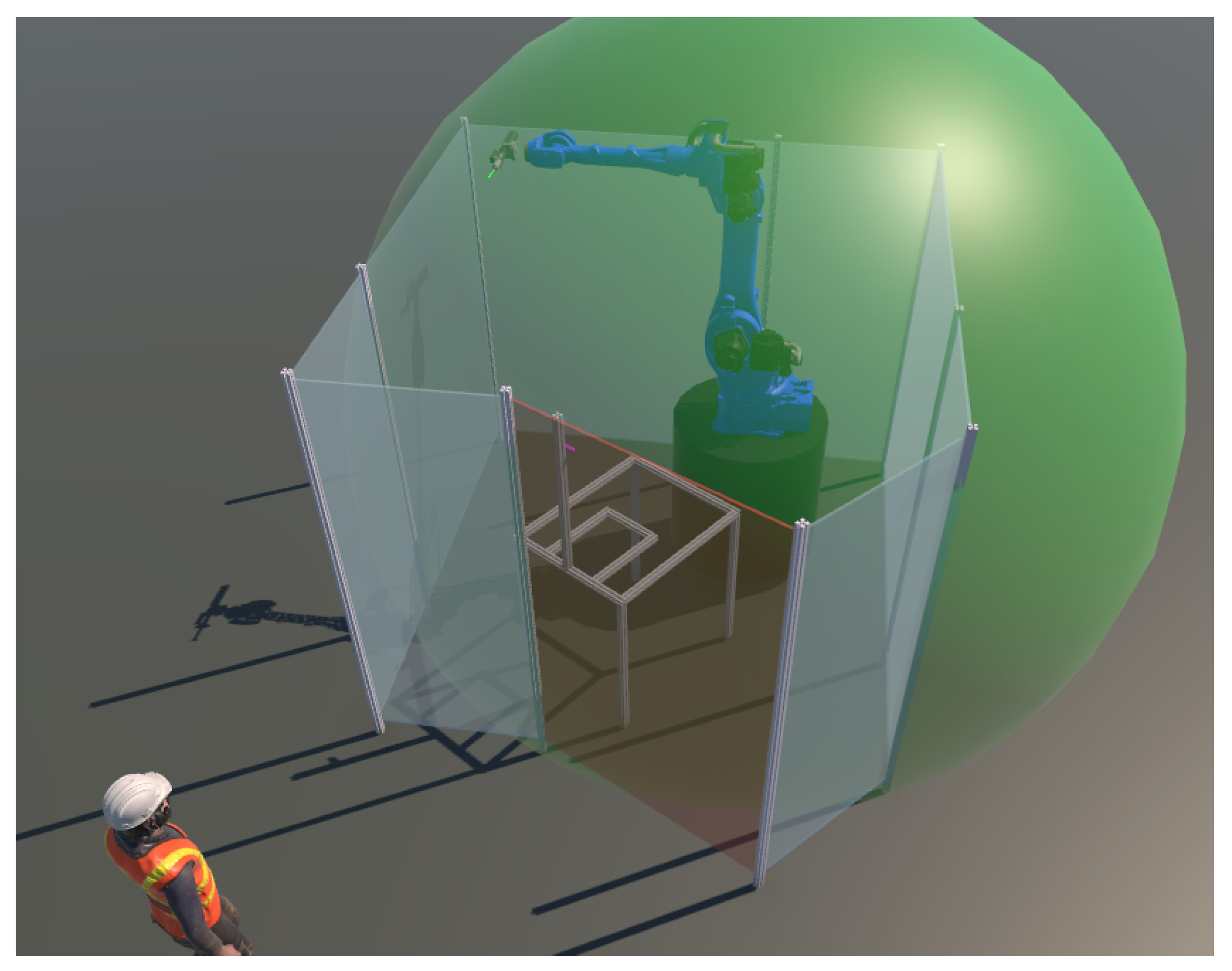
To investigate and improve the layout of a disassembly system, the placement of its entities can be visualized, taking into account various constraints and safety aspects. By creating a virtual reach envelope around the robot, its position in the virtual environment can be studied, and all reachable points can be determined and relevant safety issues addressed (see Figure 6). Using the VR controllers, the robot’s current position can be easily adjusted to place the robot in a position that allows it to reach all required locations. In this way, other entities such as people, tables, products to be disassembled, and boxes for disassembled parts can be placed in the most appropriate location in the work cell. With the same functionality, placement can also be investigated to optimize manipulation paths and improve safety measures. This is a cost-effective way to verify the manufacturing layout before it is physically implemented.
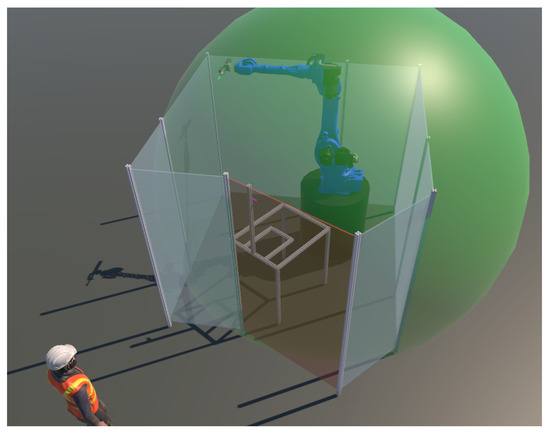
Figure 6.
The reachability simulation of the robot in the work cell shown in green.
4.2. Program Testing
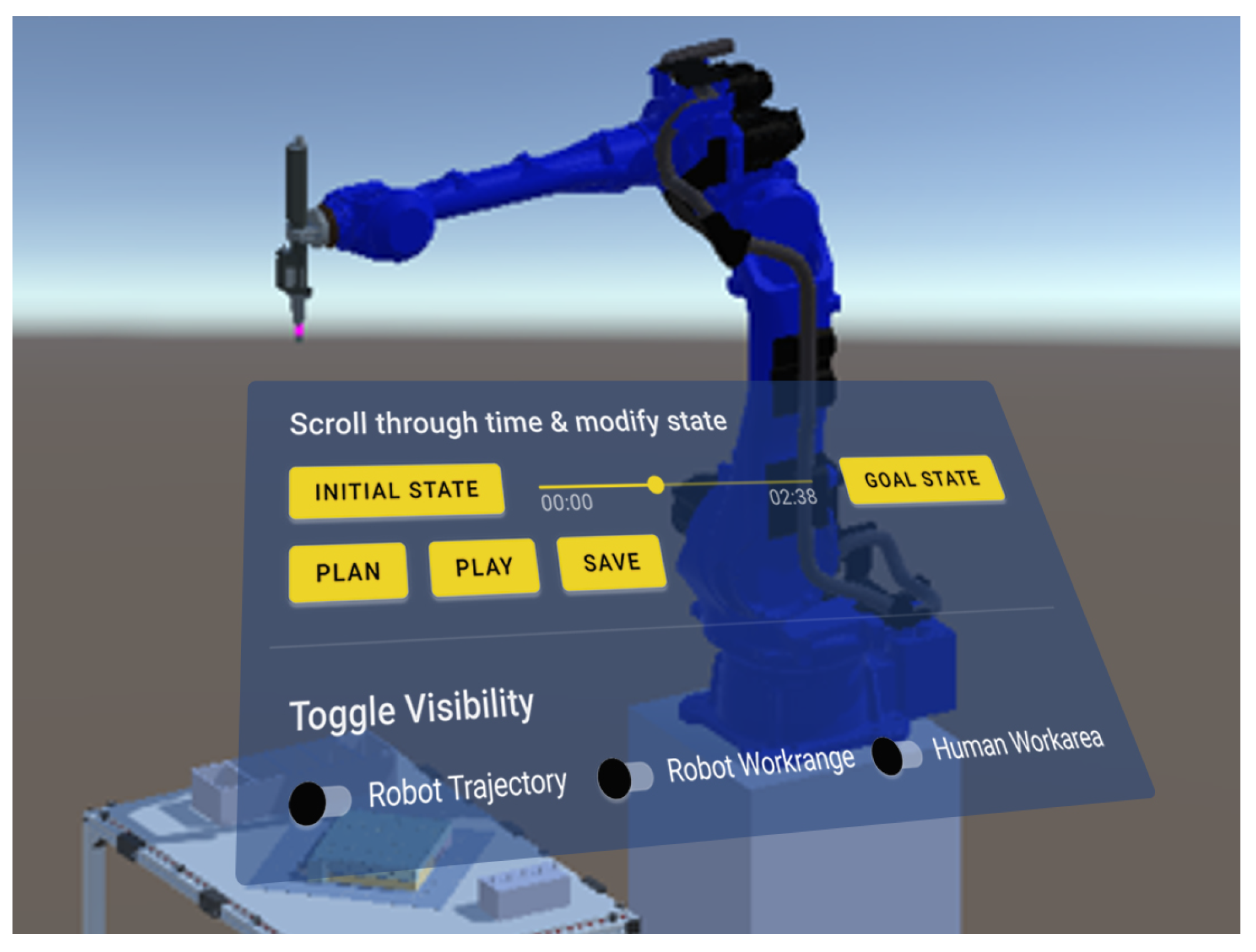
Program testing involves reviewing the set of generated actions using the PDDL planner, as detailed in our previous work [66]. Once the positions of the involved entities (humans and robots) and objects (products and parts) are defined, the planner calculates the actions of the human workers and the robots according to their capabilities, and the robot program is generated based on the defined virtual environment. We developed a GUI that allows the user to easily test the developed layout and generated program using the VR controllers, as shown in Figure 7. The planner specifies the movements between the start and target points, taking into account the operating conditions in the work environment in such a way that the generated paths are collision-free. The generated robot program can be tested by pressing the “Play” button, and the simulation of the generated robot program starts automatically. The user can also browse through the sequence of robot movements and scroll through time by moving the slider on the GUI to the left or right. If the user is not satisfied with the result of the generated trajectories, the positions of the involved entities can be changed, or the actions can be assigned differently. This process is repeated until the user is satisfied with the program, which can then be saved or executed. This kind of functionality enables a user to easily check for potential collisions or path failures of the robot in a virtual environment before it is deployed in the real system. Additionally, the human worker can understand the robot’s actions and workspace as well as observe specific sequences of the manipulation realistically without requiring the real robot hardware.
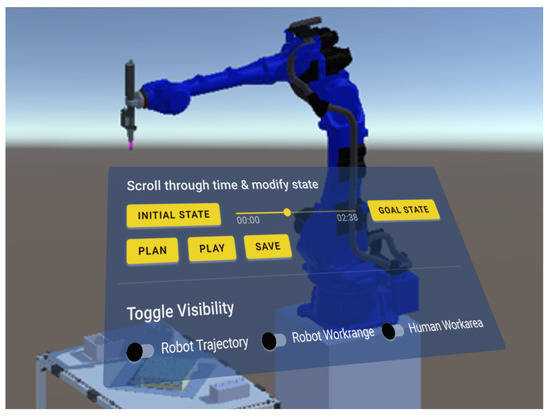
Figure 7.
Virtual reality interface for program testing. The user can spatially interact with each object and scroll through time between the initial state and the goal state computed by the planner.
4.3. Task Communication
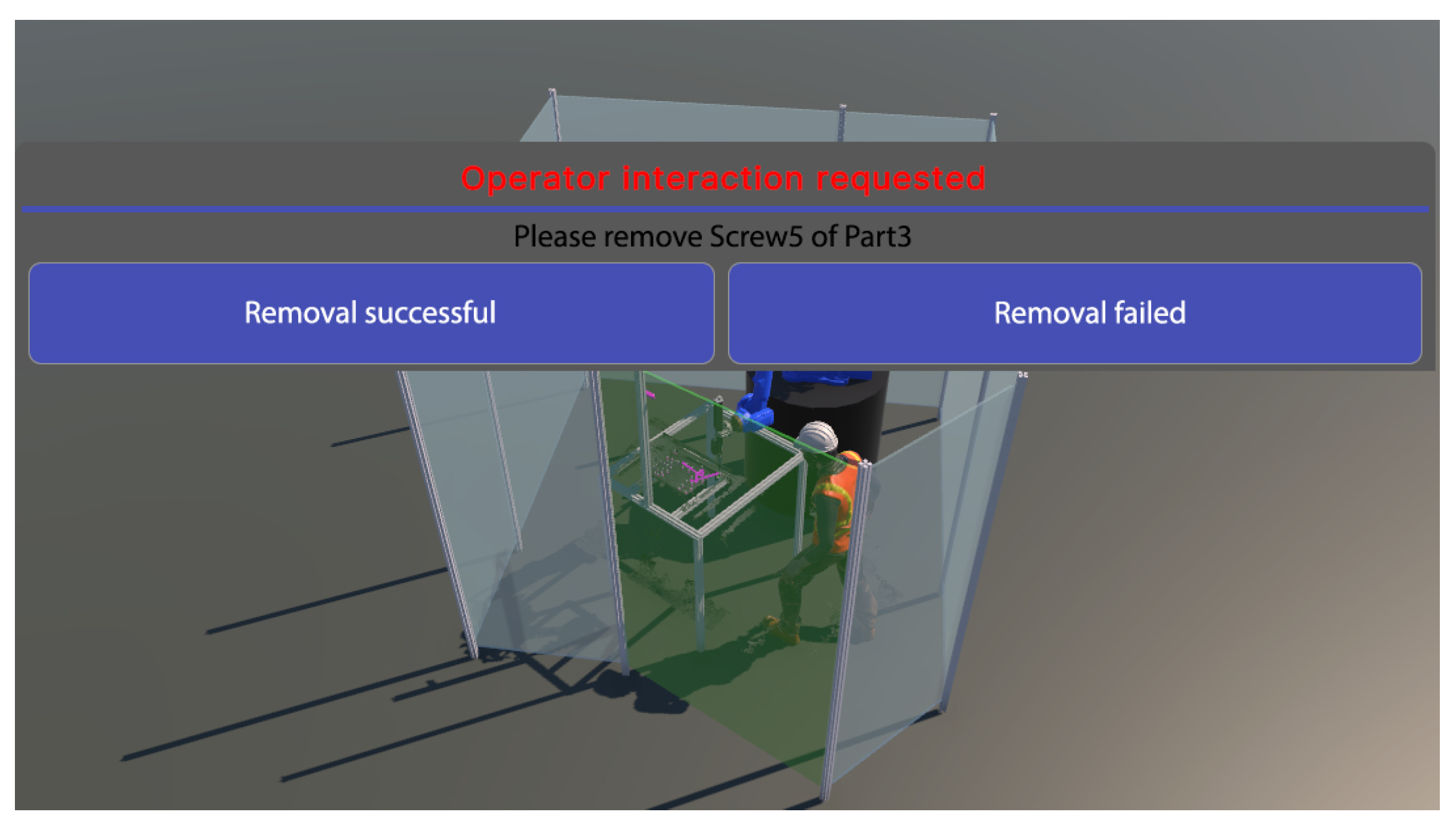
In order to ensure safe working conditions and effective task assignments between humans and robots, information about the upcoming action should be communicated appropriately. In this context, to support a human in a disassembly process, adequate instructions are of great help by guiding the human and extending the knowledge about the process. We developed the instruction generation function as an addition to the existing decision-making component, which previously only generated an action plan for robots. The planner reasons how to disassemble a product based on the available semantic model of the manufacturing environment and the available system capabilities represented in the world model. In this context, the planner considers different capabilities (time, accuracy, flexibility, etc.) that a human or a robot provides to perform an operation. Together with the disassembly models of the product, this information is fed into the assembly sequence planning module, where the required actions are evaluated based on specific parameters. The planner then generates a list of instructions for each resource, providing a description of how to perform a particular task. The information is provided in the form of multimodal text and visual animations. The generated actions could include the following characteristics: type of action (take, move, disconnect, unscrew, etc.), part name and location, targeted placement depending on the action, tools if required, etc. All origin/target locations of objects are also spatially visualized to support efficient handling. These instructions are displayed either in the VR or on the HMI on a monitor (see Figure 8). After each instruction, the worker is encouraged to confirm the successful action or report if effective finishing was not possible.
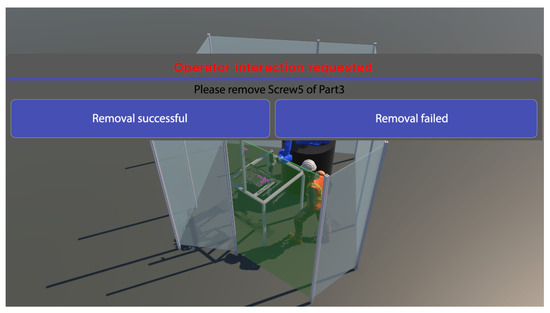
Figure 8.
Instructions generated for a human worker to remove a screw and report back if the removal was successful.
4.4. Collision Avoidance
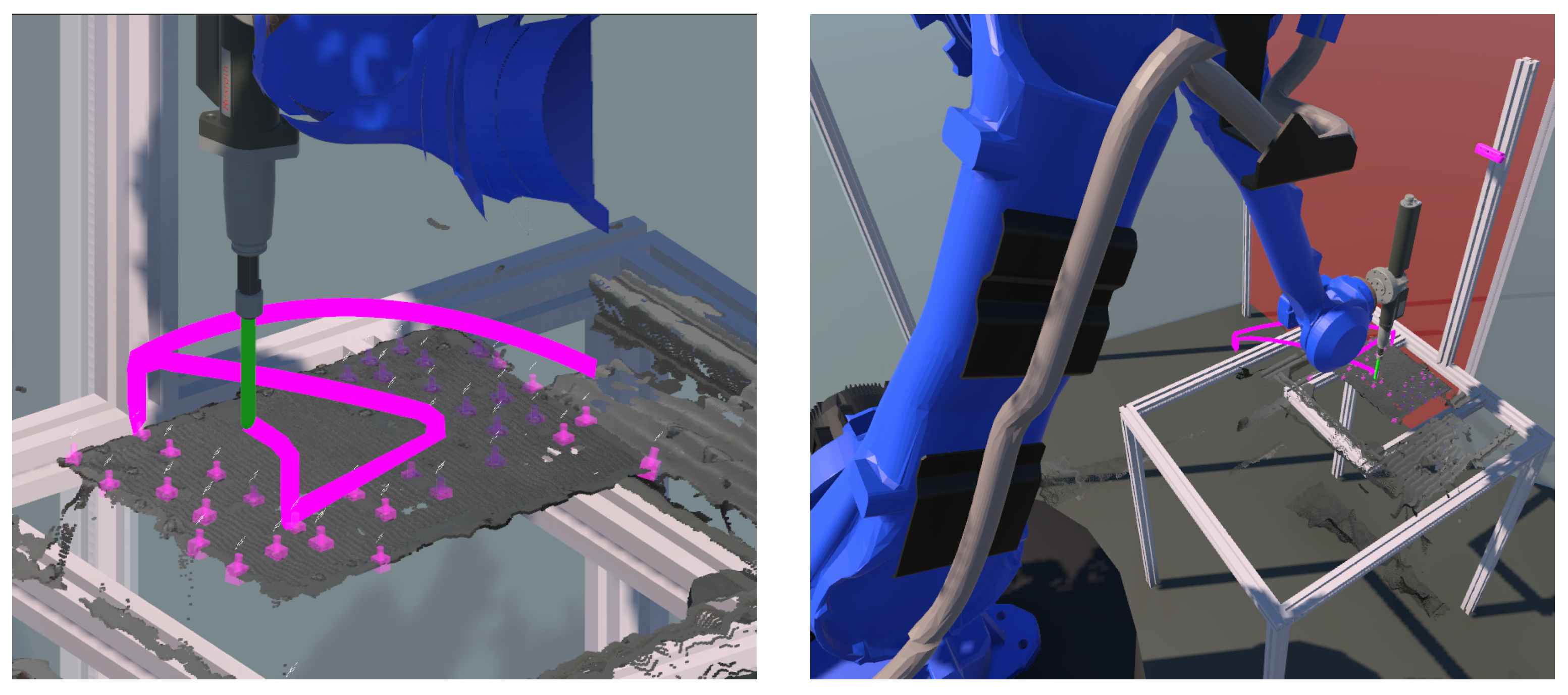
This functionality provides the ability to visualize and study robot trajectories. In a dynamic and collaborative robot disassembly environment, it is important to identify collision situations. Collisions are likely to occur when the human and the robot enter each other’s work area. In addition, collisions are possible when some elements of the environment (products, boxes containing parts, conveyors, etc.) are within the planned trajectory of the robot. However, continuous contact or the possibility of contact reduces the robot’s efficiency. Therefore, these situations must be avoided. Therefore, robot trajectories should be defined in such a way that the possibility of collisions is minimized. In this context, the ability of the system to examine possible contacts using the built-in collision detection functionality is of particular importance for the overall safety as well as for the productiveness of the collaborative disassembly environment. Additionally, we developed and integrated the trajectory visualization functionality, which should help the human worker avoid potential collision events and analyze the trajectories generated by the robot in advance. In this context, the planned robot trajectories are visualized in the digital twin to inspect and debug potentially dangerous movements and improve safety (see Figure 9). The quality of the visualization and the accuracy of the models integrated in the digital twin are essential to achieve reliable collision avoidance. The user can observe the current robot positions, and the framework draws the trajectory of the virtual robot along a sweep geometry. The integrated simulation of the trajectories allows the identification of likely points of impact and the optimization of the trajectory, e.g., by relocating the robot or equipment to avoid possible direct contact. The aim of this module is to reproduce movements for better error detection and accident prediction.
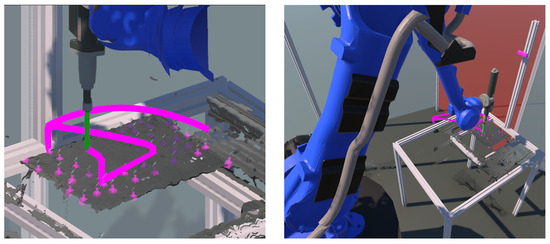
Figure 9.
Trajectory visualization functionality for collision avoidance. The spatial motion of the robot tool center point generates a pink sweep geometry to oversee possible collisions without monitoring all the robot’s movements.
5. Case Study
This system was implemented and tested in a representative use case with the goal of cooperatively disassembling antenna amplifiers. A video of the case study is available in [78], showing the semiautonomous disassembly process with the embedded visualization of the digital twin. Figure 10 shows the disassembly of the real antenna amplifier next to the visualization of the digital twin, highlighting the removed and remaining screws. In general, the system is designed to function without any prior knowledge regarding these antenna amplifiers since this information is not available for all possible antenna amplifier types, lacking both geometric models and detailed information about all possible antenna amplifiers. The presence of screws is presumed, yet there is no insight into their condition. Each antenna amplifier contains multiple hundred screws; therefore, the main objective of the robot is the automatic removal of the screws, while the human is expected to remove parts that require complex handling operations, such as the removal of front and back cases, cooling fins, and integrated printed circuit boards (PCBs). Once the robot completes its actions or is unable to complete them, the human user is notified and can safely approach and perform a specific task. However, before the real execution begins, the user can perform analysis and verification of the layout, testing the safety issues as well as the placement of components in the work cell. In addition, the user can simulate the sequence of robot operations and execution of robot actions to ensure optimal trajectories. During the execution, the current status of the robot is monitored on the digital twin. The robotic system was realized with a Yaskawa Motoman MH50 robot equipped with a screwdriver capable of changing bits for different types of screws.
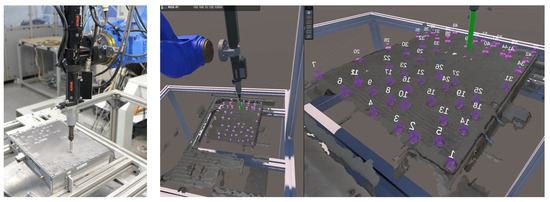
Figure 10.
Photo (left) and visualization (right) of the digital twin during the disassembly of an antenna amplifier at the same time instance. The antenna amplifier is represented as a point cloud from the RGB-D camera. The screws that have already been removed are shown in dark purple, and the screws still to be removed in bright purple.
5.1. Development of the Virtual Environment
To realize the system, a virtual environment was first developed and reconstructed. In this step, we reproduced the 3D environment, inserting the virtual models of all the other components of the disassembly system. The models of the additional components were derived from CAD drawings (end-effector, workbench, robot base), and the robot model was generated from a URDF description of its kinematic and link geometries. The effort required for this task depends on the number and quality of the existing CAD models. Finally, the virtual scene was completed by setting up the physical behavior of the elements so that the virtual elements behaved similarly to the real ones. In addition, a set of elements, such as buttons and text boxes, were integrated to facilitate immersive user interaction with the virtual environment.
The digital twin also allows the insertion of a virtual camera, which significantly simplified the debugging of the image processing system. For this purpose, an antenna amplifier was recreated as a CAD model and inserted into the work cell. A virtual camera captured a photorealistic image and transferred it to the image processing system. This was based on the same functionalities of the digital twin required to generate virtual reality. The recorded point clouds from the depth camera were also imported into the digital twin and visualized there. The positioning of the camera within the work cell was also optimized based on this approach.
5.2. Preparation Phase with Digital Twin
At the beginning of this phase, the digital twin was used to determine the disassembly process. This included identifying which steps the robot could perform and which required human intervention. In this context, the goal of the decision-making component was to automatically generate coherent plans based on the current state of the world model and the skills required for each operation in the disassembly process so that the product could be disassembled. For this purpose, the entire disassembly environment was initially represented in the world model, including the workpiece and tool types and positions, as well as the robot and human with their skills. The generated program was then tested in VR to determine if the generated plan was feasible to execute. Afterward, different layouts were investigated considering different parameters and constraints (working range, available production space, etc.) by using the provided VR features (see Figure 6). The human worker could consider all virtual positions that each robot could take at specific operation steps. During several iterations, the robot behaviors, as well as the accuracy of the performed actions for each specific layout, were analyzed. In each iteration, the current layout setting was virtually improved by the worker and tested again. Once all robot actions were validated, the system was implemented in the real environment.
5.3. Execution Phase
Once the program was tested in the virtual environment, the robot used its depth camera to identify the position and type of screws on the antenna amplifier. In the first step, only the captured 2D images were used to detect the screws using neuronal networks, whereas the detected 2D positions were reprojected into 3D coordinates. By reconstructing the surface from the point cloud in the vicinity of the screws, the robot tool approach vector was by using the normal vector. The mentioned screw detection process is described more in detail in our previous work [73].
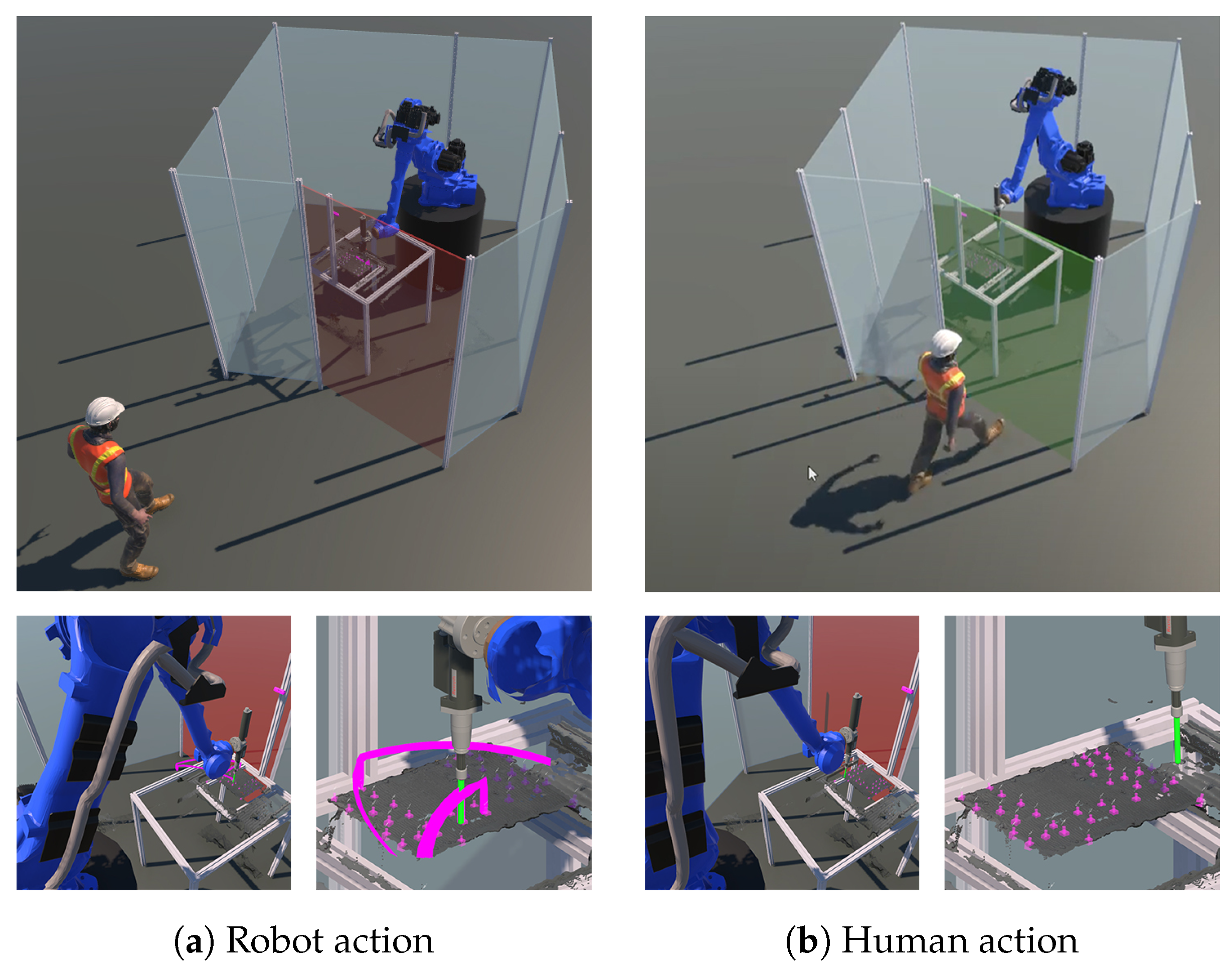
After detection, the robot automatically started loosening the screws. In case some screws could not be removed, or the screw removal was finished but parts needed to be removed manually, the human worker took over (see Figure 11). This could also include the removal of jammed or damaged components that require careful handling. During the disassembly process, the digital twin was used to monitor progress, as shown in Figure 10, and make adjustments as needed. For example, the digital twin could be used to validate that all steps were performed properly or if there were any discrepancies.
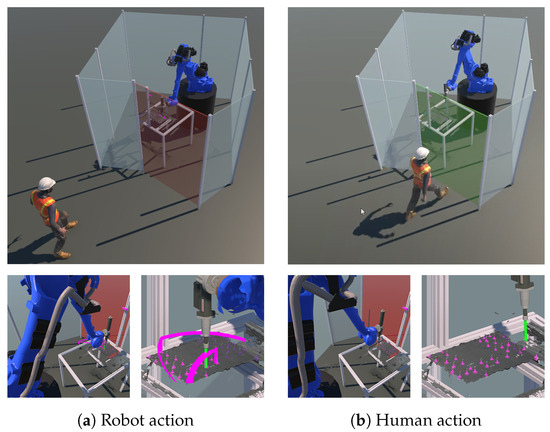
Figure 11.
Division of tasks in the disassembly use case: if the robot’s actions (left) for unscrewing and removal fail, the robot stops, and the human worker (right) is instructed to take over.
6. Discussion
This study aligns with the goals of Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0 by leveraging advanced technologies, such as digital twins and virtual reality, to enhance human–robot collaboration and sustainable development [79]. The provided industrial use case is representative and reflects the potential of the digital twin and VR system. As pointed out in Section 5.1, a number of CAD files and kinematic descriptions were required to create a virtual model of the work cell and the disassembly process. Although the initial setup of the digital twin requires some effort and expert knowledge, it is easy to adapt to different scenarios, such as repositioning the robot or replacing the robot model, as well as facilitating a quick assessment of the modifications. This allows the analysis of the reachability of poses in the workspace, the identification of singularities or joint limits of the robot, and optimizing the layout of the work cell during the preparation phase. It enables the identification of potential safety hazards in collaboration with human workers during different steps of the disassembly process and makes it possible to analyze and verify measures for risk reductions. Combined with task and trajectory planning, this enabled us to test safety interlocks and motion restrictions during different operation modes, such as automatic processing and the handover to the human worker for manual disassembly. The visualization of the planned trajectories in 3D allowed us to debug possibly dangerous motions and modify the parameters of the motion planner and the underlying collision avoidance accordingly. This currently manual process may be extended to integrate risk calculation for safety speed reductions in the future. We demonstrated the monitoring of the disassembly process in Section 5.3, where the digital twin tracked the current state of the antenna amplifier and the motion of the robot system. This was achieved by combining different data sources using ROS as a common message middleware. The VR functionality not only enhances immersion during the planning and operational phases but also delivers visual representations free from the depth perception inaccuracies of 2D screens. The exhaustive simulation capability of the digital twin and integration of motion planning allow for optimizing the workflow, task planning, and trajectory validation without extensive knowledge of automation and robotics. This also enables realistic training for employees to learn and improve their skills. Thus, the placement and program tests do not interrupt the service, which reduce system downtime and the associated costs.
Unity and ROS provided an ideal basis for setting up the digital twin due to their openness and rich ecosystem in robotics and visualization. This allows for a vendor-agnostic robot setup and enables the reuse and exchange of design data due to their support of common file formats and protocols. For the communication between the digital twin and the control system, various message types and services are provided and can be easily extended to fit the required needs. However, some drawbacks may be the partially poor documentation of some ROS packages, their lack of support by equipment vendors, and the missing standardization of protocols and interfaces. Currently, the digital twin considers only a kinematic model of the robot. This indicates the potential to benefit from integrating a dynamics model of the robot and the robot controller’s behavior to assess joint torques and interaction forces.
The described digital twin provides the basis to further unlock potential for different user groups, automation solution builders, system integrators, recycling companies, and human workers. It provides a living documentation of a plant and its machinery over their entire life cycle, which can be used during planning, commissioning, operation, and dismounting. This enables workers, supervisors, and service personnel to build a knowledge base. The monitoring merges sensor data and system states from different sources used for operation and diagnostics in case of faults. This provides the foundation for advanced features like anomaly detection and predictive maintenance, which will be addressed in future work. However, the initial effort to set up the digital twin might be substantial since the components for the world model have to be modeled, e.g., by creating CAD drawings and a survey of the actual equipment positions. Another problem is the lack of openness of component manufacturers, such as their support of only specific platforms, formats, or protocols. The missing relevant documentation, such as CAD data or control parameters, may complicate the generation of an exact model. Moreover, poorly documented and updated changes to the physical setup may cause the digital twin to become outdated, leading to deviations between the actual and displayed states. Therefore, a user-friendly and more intuitive user interface is required to ease the creation and updating of the digital twin.
7. Conclusions
In this paper, we presented a comprehensive framework integrating digital twin and VR technologies to enhance the engineering, supervision, and operation of industrial and collaborative robotic systems, specifically within the disassembly domain. The core components of the framework—the world model, decision making, vision system, digital twin with VR interface, and execution—were detailed, showcasing their roles in improving system flexibility, safety, and efficiency. The case study, involving the cooperative disassembly of antenna amplifiers, illustrated the practical application and benefits of this framework, such as improved layout planning, task simulation, collision avoidance, and enhanced human–robot interaction. The combination of digital twin and VR enabled a detailed and interactive virtual representation of the physical environment with enhanced spatial perception in contrast to that of the traditional display interface, providing significant advantages in system validation, training, and real-time monitoring.
The framework’s capability to dynamically simulate and visualize disassembly processes allowed for a more in-depth understanding and optimization of human–robot collaboration, addressing safety concerns and improving overall task efficiency. Additionally, the integration of ROS and Unity technologies provided a robust communication infrastructure, supporting modular and scalable system design. Despite the initial setup efforts and challenges related to component modeling and synchronization, the framework demonstrated substantial potential in reducing system downtime, enhancing operational safety, and offering realistic training opportunities.
Future work will focus on several key areas to further enhance the proposed framework. This will include adapting the system for other products to be disassembled, ensuring that it can handle a broader spectrum of items with varying complexities and conditions. Moreover, extending the framework to support a wider range of robotic applications, including those in unpredictable and variable environments, will demonstrate its versatility and scalability. Applying the system to related domains such as assembly and maintenance will showcase its adaptability and utility across different industrial contexts. For example, the framework could be utilized in assembly lines for complex machinery and predictive maintenance tasks for industrial equipment, highlighting its potential to improve efficiency and safety in various collaborative robotic applications. Finally, while usability testing with users was not conducted as part of this study, we recognize the importance of evaluating and validating the usability of the developed collaborative robotics system in its presented context. We plan to conduct extensive empirical studies and testing with end users as part of our future work to ensure the effectiveness and usability of the system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.H. and M.M.; methodology, T.H., M.M. and M.A.; software, T.H., S.S. and M.A.; validation, T.H. and M.A.; investigation, T.H., M.A. and S.S.; data curation, T.H. and M.A.; writing—original draft preparation, T.H., M.A. and M.M.; writing—review and editing, M.V. and S.S.; visualization, T.H., S.S. and M.A.; supervision, M.V.; project administration, M.M., M.V. and W.L.; funding acquisition, M.M., M.V. and W.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the “ICT of the Future DE-AT AI” program of the Austrian Ministry for Climate Action, Environment, Energy, Mobility, Innovation, and Technology under contract FFG 887636, and through the German Space Agency (DLR) with funds provided by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action (BMWK) due to an enactment of the German Bundestag under Grant No. 01MJ21005A.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Stephan Seibel was employed by the company Boxx IT Solutions. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Poschmann, H.; Brüggemann, H.; Goldmann, D. Disassembly 4.0: A Review on Using Robotics in Disassembly Tasks as a Way of Automation. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2020, 92, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, G.; Kara, S.; Pagnucco, M. Challenges of robotic disassembly in practice. Procedia CIRP 2022, 105, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aheleroff, S.; Mostashiri, N.; Xu, X.; Zhong, R.Y. Mass Personalisation as a Service in Industry 4.0: A Resilient Response Case Study. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2021, 50, 101438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjorth, S.; Chrysostomou, D. Human–robot collaboration in industrial environments: A literature review on non-destructive disassembly. Robot.-Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2022, 73, 102208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.L.; Liang, X.; Hu, B.; Onel, G.; Behdad, S.; Zheng, M. A Review of Prospects and Opportunities in Disassembly with Human–Robot Collaboration. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2023, 146, 020902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, J.; Weyer, S.; Quint, F. Plug-and-Simulate within Modular Assembly Line enabled by Digital Twins and the use of AutomationML. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2017, 50, 15904–15909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichhart, G.; Åkerman, M.; Akkaladevi, S.C.; Plasch, M.; Fast-Berglund, Å; Pichler, A. Models for Interoperable Human Robot Collaboration. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villani, V.; Pini, F.; Leali, F.; Secchi, C. Survey on human–robot collaboration in industrial settings: Safety, intuitive interfaces and applications. Mechatronics 2018, 55, 248–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krot, K.; Kutia, V. Intuitive Methods of Industrial Robot Programming in Advanced Manufacturing Systems. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Systems in Production Engineering and Maintenance; Burduk, A., Chlebus, E., Nowakowski, T., Tubis, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, L.; Diez, E.; Usamentiaga, R.; García, D.F. Industrial robot control and operator training using virtual reality interfaces. Comput. Ind. 2019, 109, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buerkle, A.; Eaton, W.; Al-Yacoub, A.; Zimmer, M.; Kinnell, P.; Henshaw, M.; Coombes, M.; Chen, W.H.; Lohse, N. Towards industrial robots as a service (IRaaS): Flexibility, usability, safety and business models. Robot.-Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2023, 81, 102484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Leng, J.; Yan, D.; Zhang, D.; Wei, L.; Yu, A.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X. Digital twin-based designing of the configuration, motion, control, and optimization model of a flow-type smart manufacturing system. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 58, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, P.; Silva, J.A.; Costa, P.; Veiga, G.; Moreira, A.P. Flexible Work Cell Simulator Using Digital Twin Methodology for Highly Complex Systems in Industry 4.0. In Proceedings of the ROBOT 2017: Third Iberian Robotics Conference; Ollero, A., Sanfeliu, A., Montano, L., Lau, N., Cardeira, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 11, pp. 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segovia, M.; Garcia-Alfaro, J. Design, Modeling and Implementation of Digital Twins. Sensors 2022, 22, 5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, T.; Deng, X.; Liu, Z.; Tan, J. Digital twin: A state-of-the-art review of its enabling technologies, applications and challenges. J. Intell. Manuf. Spec. Equip. 2021, 2, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihai, S.; Yaqoob, M.; Hung, D.V.; Davis, W.; Towakel, P.; Raza, M.; Karamanoglu, M.; Barn, B.; Shetve, D.; Prasad, R.V.; et al. Digital Twins: A Survey on Enabling Technologies, Challenges, Trends and Future Prospects. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2022, 24, 2255–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallala, A.; Kumar, A.A.; Hichri, B.; Plapper, P. Digital Twin for Human–Robot Interactions by Means of Industry 4.0 Enabling Technologies. Sensors 2022, 22, 4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.G.; Park, S.C. Survey on the virtual commissioning of manufacturing systems. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2014, 1, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasubramaniana, A.K.; Mathew, R.; Kelly, M.; Hargaden, V.; Papakostas, N. Digital Twin for Human–Robot Collaboration in Manufacturing: Review and Outlook. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, F.; Cachada, A.; Barbosa, J.; Moreira, A.P.; Leitão, P. Digital Twin in Industry 4.0: Technologies, Applications and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 17th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Helsinki, Finland, 22–25 July 2019; Volume 1, pp. 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, K.I.K.; Huang, H.; Xu, X. Digital Twin-driven smart manufacturing: Connotation, reference model, applications and research issues. Robot.-Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2020, 61, 101837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havard, V.; Jeanne, B.; Lacomblez, M.; Baudry, D. Digital twin and virtual reality: A co-simulation environment for design and assessment of industrial workstations. Prod. Manuf. Res. 2019, 7, 472–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, I.D.H.J.; Taha, Z.; Vui, L. VR-Based Robot Programming and Simulation System for an Industrial Robot. Int. J. Ind. Eng. Theory Appl. Pract. 2008, 15, 314–322. [Google Scholar]
- Dianatfar, M.; Latokartano, J.; Lanz, M. Review on existing VR/AR solutions in human–robot collaboration. Procedia CIRP 2021, 97, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyekan, J.O.; Hutabarat, W.; Tiwari, A.; Grech, R.; Aung, M.H.; Mariani, M.P.; López-Dávalos, L.; Ricaud, T.; Singh, S.; Dupuis, C. The effectiveness of virtual environments in developing collaborative strategies between industrial robots and humans. Robot.-Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2019, 55, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Berglund, J.; Fast-Berglund, Å.; Johansson, B.; Wang, Z.; Börjesson, T. Development of virtual reality support to factory layout planning. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. (Ijidem) 2019, 13, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonsick, M.; Padir, T. A Systematic Review of Virtual Reality Interfaces for Controlling and Interacting with Robots. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 9051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.; Silva, F.; Santos, V. Trends of human–robot Collaboration in Industry Contexts: Handover, Learning, and Metrics. Sensors 2021, 21, 4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galin, R.R.; Meshcheryakov, R.V. Human–robot Interaction Efficiency and human–robot Collaboration. In Robotics: Industry 4.0 Issues & New Intelligent Control Paradigms; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arents, J.; Abolins, V.; Judvaitis, J.; Vismanis, O.; Oraby, A.; Ozols, K. Human–Robot Collaboration Trends and Safety Aspects: A Systematic Review. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2021, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumičáková, D.; Rengevič, A. Automation of manufacturing technologies with utilisation of industrial robots. Appl. Comput. Sci. 2015, 11, 5–18. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, J.; Chand, S.; Vanderkop, A.; Howard, D. A Review of Physics Simulators for Robotic Applications. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 51416–51431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagaris, A.; Polychroniadis, C.; Tzotzis, A.; Kyratsis, P. Cost-effective Robotic Arm Simulation and System Verification. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. 2024, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekala, A.; Kost, G.; Banas, W.; Gwiazda, A.; Grabowik, C. Modelling and simulation of robotic production systems. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2198, 012065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baizid, K.; Ćuković, S.; Iqbal, J.; Yousnadj, A.; Chellali, R.; Meddahi, A.; Devedzic, G.; Ghionea, I. IRoSim: Industrial Robotics Simulation Design Planning and Optimization Platform based on CAD and Knowledgeware Technologies. Robot.-Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2016, 42, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Dai, X.; Li, D. Off-Line Programming Techniques for Multirobot Cooperation System. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2013, 10, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, P.L.; Morgado-Estévez, A.; Aparicio, J.L.; Bárcena, G.; Soto-Núñez, J.A.; Chavera, P.; Abad Fraga, F.J. Development of a Customized Interface for a Robotic Welding Application at Navantia Shipbuilding Company. In Proceedings of the ROBOT 2017: Third Iberian Robotics Conference; Ollero, A., Sanfeliu, A., Montano, L., Lau, N., Cardeira, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Borys, S.; Kaczmarek, W.; Laskowski, D.; Polak, R. Experimental Study of the Vibration of the Spot Welding Gun at a Robotic Station. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diprasetya, M.R.; Yuwono, S.; Löppenberg, M.; Schwung, A. Integration of ABB Robot Manipulators and Robot Operating System for Industrial Automation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 21st International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Lemgo, Germany, 18–20 July 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, Y.; Han, H. The Simulation Design of Robot Automatic Sorting and Palletizing Workstation Based on RobotStudio. In Proceedings of the 2022 5th International Conference on Robotics, Control and Automation Engineering (RCAE), Changchun, China, 28–30 October 2022; pp. 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, F.M.; Silva, M.F. Application for automatic programming of palletizing robots. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Autonomous Robot Systems and Competitions (ICARSC), Torres Vedras, Portugal, 25–27 April 2018; pp. 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragun, D.; Mascaro, S.; Blanchard, J.; Chauhan, V. Assembly Automation Using an Industrial Robot. In ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition; Volume 2B: Advanced Manufacturing; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.A.; Haladus, J.; Pereira, F.; Felgueiras, C.; Fazenda, R. Simulation Case Study for Improving Painting Tires Process Using the Fanuc Roboguide Software. In Proceedings of the Flexible Automation and Intelligent Manufacturing: Establishing Bridges for More Sustainable Manufacturing Systems; Silva, F.J.G., Pereira, A.B., Campilho, R.D.S.G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 517–524. [Google Scholar]
- Lukac, D. Comparative Selection of Industrial Robot Simulation Systems for Educational Purposes. In Proceedings of the XV International Scientific–Professional Symposium INFOTEH-JAHORINA 2016, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 20 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Li, J.; Fey, M.; Brecher, C. A Survey on AI-Driven Digital Twins in Industry 4.0: Smart Manufacturing and Advanced Robotics. Sensors 2021, 21, 6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafto, M.; Conroy, M.; Doyle, R.; Glaessgen, E.; Kemp, C.; LeMoigne, J.; Wang, L. Modeling, Simulation, Information Technology and Processing Roadmap. NASA 2010, 11, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Fang, S.; Dong, H.; Xu, C. Review of digital twin about concepts, technologies, and industrial applications. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 58, 346–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aheleroff, S.; Xu, X.; Zhong, R.Y.; Lu, Y. Digital Twin as a Service (DTaaS) in Industry 4.0: An Architecture Reference Model. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2021, 47, 101225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, A.; Sahed, M.; Tasneem, Z.; Das, P.; Badal, F.; Ali, M.; Ahamed, M.; Abhi, S.; Sarker, S.; Das, S.; et al. Towards next generation digital twin in robotics: Trends, scopes, challenges, and future. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.A.; Brem, A. Digital twins for collaborative robots: A case study in human–robot interaction. Robot.-Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2021, 68, 102092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Xu, W.; Shen, T.; Ye, X.; Tian, S. Digital twin-based multi-level task rescheduling for robotic assembly line. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottogalli, K.; Rosquete, D.; Amundarain, A.; Aguinaga, I.; Borro, D. Flexible Framework to Model Industry 4.0 Processes for Virtual Simulators. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weistroffer, V.; Keith, F.; Bisiaux, A.; Andriot, C.; Lasnier, A. Using Physics-Based Digital Twins and Extended Reality for the Safety and Ergonomics Evaluation of Cobotic Workstations. Front. Virtual Real. 2022, 3, 781830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrokalli, A.; Vosniakos, G.C.; Nathanael, D.; Matsas, E. On the assessment of human–robot collaboration in mechanical product assembly by use of Virtual Reality. Procedia Manuf. 2020, 51, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, G.; Kuts, V.; Anbarjafari, G. Digital Twin for FANUC Robots: Industrial Robot Programming and Simulation Using Virtual Reality. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burghardt, A.; Szybicki, D.; Gierlak, P.; Kurc, K.; Pietruś, P.; Cygan, R. Programming of Industrial Robots Using Virtual Reality and Digital Twins. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuts, V.; Otto, T.; Tähemaa, T.; Bondarenko, Y. Digital twin based synchronised control and simulation of the industrial robotic cell using virtual reality. J. Mach. Eng. 2019, 19, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, L.; Rodríguez-Jiménez, S.; Rodríguez, N.; Usamentiaga, R.; Garcia, F.D. Digital Twin and Virtual Reality Based Methodology for Multi-Robot Manufacturing Cell Commissioning. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, M.; Nertinger, S.; Kirschner, R.J.; Figueredo, L.; Naceri, A.; Haddadin, S. A Concise Overview of Safety Aspects in human–robot Interaction. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.09936. [Google Scholar]
- Valori, M.; Scibilia, A.; Fassi, I.; Saenz, J.; Behrens, R.; Herbster, S.; Bidard, C.; Lucet, E.; Magisson, A.; Schaake, L.; et al. Validating Safety in Human–Robot Collaboration: Standards and New Perspectives. Robotics 2021, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robla-Gómez, S.; Becerra, V.M.; Llata, J.R.; González-Sarabia, E.; Torre-Ferrero, C.; Pérez-Oria, J. Working Together: A Review on Safe human–robot Collaboration in Industrial Environments. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 26754–26773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, L.; Rauch, E.; Vidoni, R. Development and validation of guidelines for safety in human–robot collaborative assembly systems. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 163, 107801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacevic, B.; Zanchettin, A.M.; Rocco, P. Safe human–robot Collaboration via Collision Checking and Explicit Representation of Danger Zones. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2023, 20, 846–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepuschitz, W.; Zoitl, A.; Vallée, M.; Merdan, M. Toward Self-Reconfiguration of Manufacturing Systems Using Automation Agents. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part (Appl. Rev.) 2011, 41, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merdan, M.; Hoebert, T.; List, E.; Lepuschitz, W. Knowledge-based cyber-physical systems for assembly automation. Prod. Manuf. Res. 2019, 7, 223–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoebert, T.; Lepuschitz, W.; Vincze, M.; Merdan, M. Knowledge-driven framework for industrial robotic systems. J. Intell. Manuf. 2021, 34, 771–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath Kumar, V.R.; Khamis, A.; Fiorini, S.; Carbonera, J.L.; Olivares Alarcos, A.; Habib, M.; Goncalves, P.; Li, H.; Olszewska, J.I. Ontologies for Industry 4.0. Knowl. Eng. Rev. 2019, 34, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legat, C.; Seitz, C.; Lamparter, S.; Feldmann, S. Semantics to the Shop Floor: Towards Ontology Modularization and Reuse in the Automation Domain. Ifac Proc. Vol. 2014, 47, 3444–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, M.; Breslin, J.G.; Ali, M.I. Semantic Web and Knowledge Graphs for Industry 4.0. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenmark, M.; Malec, J. Knowledge-based instruction of manipulation tasks for industrial robotics. Robot.-Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2015, 33, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, D.; Bruno, G. Ontology-Based Framework to Design a Collaborative human–robotic Workcell. In Proceedings of the Collaboration in a Data-Rich World; Camarinha-Matos, L.M., Afsarmanesh, H., Fornasiero, R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Chen, H.; He, T. FCOS: Fully Convolutional One-Stage Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Kore, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9626–9635. [Google Scholar]
- Hoebert, T.; Neubauer, D.; Merdan, M.; Lepuschitz, W.; Thalhammer, S.; Vincze, M. ROS-driven Disassembly Planning Framework incorporating Screw Detection. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Computing Science and Automatic Control, CCE 2023, Mexico City, Mexico, 25–27 October 2023; IEEE: Mexico City, Mexico, 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghallab, M.; Knoblock, C.; Wilkins, D.; Barrett, A.; Christianson, D.; Friedman, M.; Kwok, C.; Golden, K.; Penberthy, S.; Smith, D.; et al. PDDL—The Planning Domain Definition Language; Technical Report Tech Report CVC TR-98-003/DCS TR-1165; Yale Center for Computational Vision and Control: New Haven, CT, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Hoebert, T.; Lepuschitz, W.; List, E.; Merdan, M. Cloud-Based Digital Twin for Industrial Robotics. In Proceedings of the Industrial Applications of Holonic and Multi-Agent Systems; Mařík, V., Kadera, P., Rzevski, G., Zoitl, A., Anderst-Kotsis, G., Tjoa, A.M., Khalil, I., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, M.; Gerkey, B.; Conley, K.; Faust, J.; Foote, T.; Leibs, J.; Berger, E.; Wheeler, R.; Ng, A. ROS: An Open-Source Robot Operating System. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Kobe, Japan, 2–17 May 2009; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, D.; Sucan, I.; Chitta, S.; Correll, N. Reducing the Barrier to Entry of Complex Robotic Software: A MoveIt! Case Study. J. Softw. Eng. Robot. 2014, 5, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amersdorfer, M.; Meurer, T. SmartDis—Semi-Automatic Disassembly of an Antenna Amplifier; Institut für Mechanische Verfahrenstechnik und Mechanik (MVM): Karlsruhe, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aheleroff, S.; Huang, H.; Xu, X.; Zhong, R.Y. Toward sustainability and resilience with Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0. Front. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 2, 951643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).