Abstract
In this study, adaptive pincer grasping of soft pneumatic grippers (SPGs) is considered, and we propose how the performance of soft pneumatic actuators (SPAs) and the stiffness of grasped objects can be accounted for in modeling and control. The grasping kinetics was analyzed. The connection between grasping quality and SPA performance is discussed. We also devised a subjective definition of grasping quality due to SPA performance. A modeling technique was established, which makes dominant factors of grasping quality due to the SPA performance predictable over the gripper input. Later, a control architecture was developed. This architecture demonstrates how the grasping is implemented. The modeling technique was used to forecast grasping quality due to the SPA performance and its factors. An experiment was conducted to obtain actual results. The predicted and actual results were correspondingly compared. The results show minute deviation, thereby validating the reliability of the grasping. This study clarifies the association between grasping quality and SPA performance and contributes an advancement toward modellable and controllable task-level variables, such as grasping quality, in SPG pincer grasping.
1. Introduction
The gripper is one of the most common parts of robotic systems [1,2]. The main responsibility of grippers is to conduct grasping as the hands of the systems [3,4]. Grasping essentially leads to physical interaction between the systems and their environment, which is required to make the systems capable of mechanically manipulating objects [5,6,7]. Nowadays, available grippers can be categorized into a variety of types [8].
Soft robotics, a branch of robotics in which robots are structurally deformable, is currently gaining considerable attention globally [9,10]. This concept has been applied to a new group of grippers, called soft grippers. One of the widespread types of soft grippers is soft pneumatic grippers (SPGs). SPGs basically comprise two or more soft pneumatic actuators (SPAs). The main advantageous feature of SPAs is that their intrinsically flexible structures can provide admirable compliance, making SPGs able to grasp a variety of objects using simple gripper control [11,12,13]. Meanwhile, a main concern of operating SPAs is that the SPA structures have infinite degree of freedom (DOF) with nonlinear characteristics [14,15,16]. This concern leads to a significant challenge in the modeling and control of either SPAs or SPG grasping. Countless state variables are theoretically required to determine, examine, and handle the modeling and control.
The abovementioned complication has led the modeling and control of SPAs to become a main category of studies in soft robotics [17]. Suzumori et al. [18] pioneeringly proposed an empirical model of SPAs. Godage et al. [19] presented an analytical model of variable-length SPAs. Polygerinos et al. [20] proposed an analytical model and the feedback control of fiber-reinforced SPAs with rectangular, hemicircular, and circular shapes. Gerboni et al. [21] demonstrated feedback control using commercial flex sensors of SPAs. Hao et al. [22] developed an analytical model of amphibious SPAs. Wang and Hirai [23] proposed an analytical model of SPAs with parametric identification. Elgeneidy et al. [24] presented empirical models and model-based feedback control of SPAs. Hainsworth et al. [25] proposed analytical and empirical models of multi-material SPAs with their feedback control. Abbasi et al. [26] established an analytical model and feedforward control in the position and force of SPAs. Tian et al. [27] proposed an analytical model of fibrillar adhesive SPAs. Ibrahim et al. [28] presented an analytical model and observer-based feedback control of SPAs. Despite the presence of them, the modeling and control in such works only concerns actuator-level variables, such as bending angle and blocking force.
Previously, grasping quality was introduced to indicate the subjective satisfaction and outcome of grasping [29]. While its exact physical definition is still unclear, it is certainly a task-level variable. Most studies on grasping quality investigate grasping synthesis of mechanical grippers in the aspect of grasping stability [30,31]. In this consideration, the motion and force transformation between the actuator and task space is essential. Some sources also imply that grasping quality correlates with many other factors, such as gripper performance, manipulator motion, and geometrical compatibility [32]. With the comprehensive associations between grasping quality and these factors, grasping quality should be accurately modeled and controlled. Nevertheless, the exact number of factors has never been concluded. While the factors cannot be completely accounted for, the separate effects of each factor on grasping quality still can be examined to continue the approach toward modellable and controllable grasping quality.
A study on grasping quality in SPG grasping is rarely found. The work of Park et al. [33] highlights that the motion and force transformation is necessary in the consideration of grasping quality, and SPA performance is one of the impactful factors on grasping quality in SPG grasping. Studies on the associations between SPA performance and grasping quality should contribute to the development of the modeling and control of grasping quality in SPG grasping. Motion and force variables in existing models of SPAs cannot be simply translated into the task space, mainly due to the constant-curvature condition applied in the modeling process [34,35,36,37]. The connection between SPA performance and grasping quality is, hence, currently incomplete.
Adaptive SPG pincer grasping based on object stiffness is presented in this work. In the proposed grasping, SPA performance is considered at both actuator and task levels. The associations between grasping quality and SPA performance in SPG pincer grasping are also clarified here. The major demanding issue in this work is the modeling and control of SPG grasping. The main contribution of this work is advancing the development toward modellable and controllable task-level variables, such as grasping quality, in SPG pincer grasping.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pincer Grasping of SPG
Pincer grasping is plainly a kind of grasping, where grippers squeeze objects with their fingertips. In SPG pincer grasping, the objects are pressed by the ends of SPAs (Figure 1a). The interaction between the SPAs and objects is a mysterious issue that must be clarified to accomplish the transformation of motion and force between the actuator and task space. There are numerous factors in the interaction. To analyze the interaction due to SPA performance, the effects of other factors must be decoupled. The analysis then proceeded under the assumption that the effects of other factors can be ignored. Under this assumption, we proposed that the exerted force of SPAs on a grasped object, denoted by (Figure 1b), equals the withstanding force of the object on the SPAs, denoted by (Figure 1c), as follows:
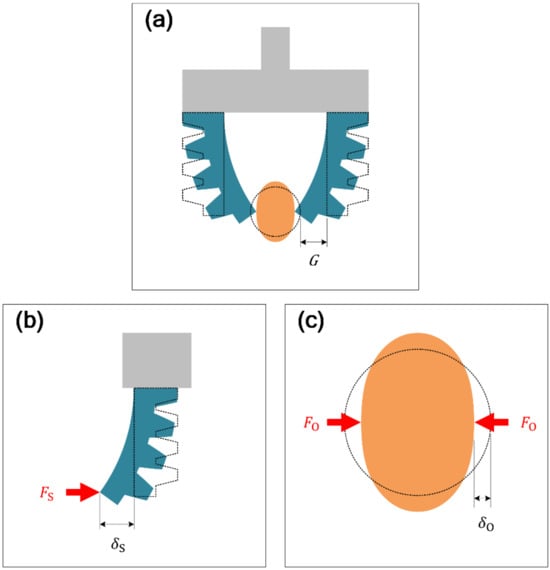
Figure 1.
(a) SPG pincer grasping and the gaps between SPAs and a grasped object; (b) deformation and withstanding force on an SPA; (c) deformation and exerted force on a grasped object.
The force transformation is then achievable using Equation (1). According to the geometrical constraint, the deformation of the SPAs, denoted by (Figure 1b), can be considered equivalent to the summation of the deformation of the objects due to , denoted by (Figure 1c), and the gap distance between them, denoted by (Figure 1a), as follows:
Equation (2) allows us to implement the motion transformation but is applicable only when the SPAs behave similarly throughout grasping. In cases when the SPAs nonidentically perform, the motion transformation should be proceeded with another correlation.
At the actuator level, the modeling of SPAs has been extensively studied. The most widespread approach to handle the infinite-DOF structures of SPAs has been exploiting the combined effects of local joints to represent the SPA configurations. Many models of SPAs in which the SPA configurations are represented by curvature angle have been elaborated and presented under the condition of constant curvature. Nevertheless, SPAs inconsistently curve along their length in SPG pincer grasping. A new concept of SPA modeling is therefore needed as part of the modeling of SPG pincer grasping. Equation (2) encourages us to employ to represent the SPA configurations. The equation of motion implies that we can initiate an SPA model as follows:
where denotes the input pressure of the SPA. Both and are the derivatives with respect to time of , and denotes a nonlinear function due to the SPA nonlinear characteristics. Equation (3) demonstrates that depends on , , , and . The SPAs are mainly in their steady state throughout grasping. Hence, and tend to be negligible. Equation (3) can be then revised as follows:
Equation (4) indicates that is repeatable under the identical conditions of and at the steady state.
2.2. Grasping Quality
Grasping quality, denoted by , is essentially a kind of matrix containing parameters of grasping satisfaction and outcome. The dimension of and its components are fundamentally subjective according to individual requirements. Different parameters and indexation can be employed to determine the physical definitions of . The dependence on the subjectivity of made a discussion of indexation beyond the scope of this study. However, it is well known that there are countless factors of . The mathematic expression of can be then written as a matrix function as follows:
where .denotes due to each factor. The understanding of will advance the opportunity of modeling and controlling . We focus on due to SPA performance, denoted by , in this work. From our observation, contact area and squeezing force are the most obvious factors of . In pincer grasping, contact area is empirically dominated by , and squeezing force is by its definition. In this sense, is a function of and as follows:
Equation (6) illustrates that can be controlled once and are intentionally programmable, and it also highlights that there is no specific physical definition of . Additionally, the factors of can be further added.
2.3. Modeling Technique
The modeling technique allows us to systematically forecast through and . The stiffness of an object, denoted by , is utilized in this technique. The correlation between and is governed by as follows:
Basically, is almost constant for rigid objects and decreases over and for soft objects. Equations (1) and (2) reveal that both and in Equation (7) can be replaced by and , respectively, as follows:
Equation (8) shows that significantly influences and throughout grasping. We suggest that and over can be forecast by solving Equations (4) and (8) together. The result of solving Equation (4) can be represented as performance curves, and the result of solving Equation (8) can be demonstrated as a stiffness curve. The solid lines in Figure 2 demonstrate the performance curves, and the dashed line in the same figure asymptotically illustrates the stiffness curve. Once we plot these curves on the same chart, the obtained intersections predictively indicate and at particular conditions of (Figure 2). The discrete results are then able to become continuous as and over using linear interpolation. Afterwards, and over can be obtained using Equations (1) and (2). Finally, over is forecastable using Equation (6).
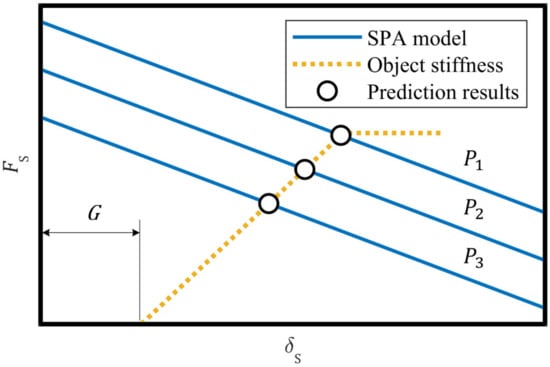
Figure 2.
A modeling technique of adaptive SPG pincer grasping based on object stiffness.
The proposed technique requires SPA performance curves. Nevertheless, solving Equation (4) is challenging. No standard analytical method is available for this purpose. We accordingly conducted an empirical inspection to acquire SPA performance curves for comprehensive demonstration. Two identical industrial SPAs, the operating of which ranges from –100 to 100 kPa., were employed in this inspection. The inspection proceeded using an experimental setup shown in Figure 3. The components of the setup included a motorized stage, load cell, and air supply. One of the SPAs was vertically hung, and the load cell was propelled in horizontal to adjust the limit of . The air supply was executed to provide . Once the SPA reached its steady state, was measured with the load cell. These procedures were iterated until was obtained under all conditions of and . The designated conditions of ranged from 0 to 8 mm with 200 µm intervals, whereas those of ranged from 10 to 100 kPa with 10 kPa intervals. The SPA was subsequently replaced by the other, and the whole process was repeated. The comparable results of both SPAs were averaged. Finally, the SPA performance curves were plotted.
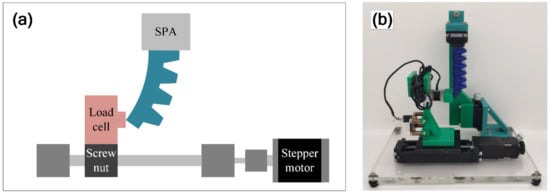
Figure 3.
An experimental setup for acquiring SPA performance curves: (a) schematic and (b) photograph.
Besides SPA performance curves, an object-stiffness curve is essential in this technique. An empirical investigation for an object-stiffness curve was then initiated. The specimen object was a flexible 3D-printed object with a cylindrical shape. The investigation was implemented using an experimental setup shown in Figure 4. The setup comprised a motorized stage, load cell, and bumper. By moving the load cell, was varied. Once the object was steadily squeezed, was measured with the load cell. This procedure was iterated until at all designated conditions of was obtained. The designated conditions of ranged from 0 to 5 mm with 100 µm intervals. The object-stiffness curve was finally plotted following result collection.
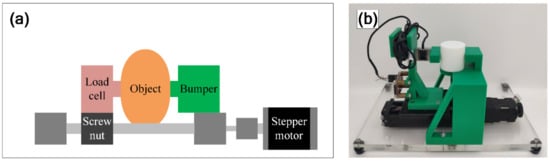
Figure 4.
An experimental setup for investigating an object-stiffness curve: (a) schematic and (b) photograph.
2.4. Control Architecture
The control architecture was elaborated to accommodate desirable , denoted by . It is essentially an open-loop architecture (Figure 5). First, is required to be indexed in the basis of preferable and , sequentially denoted by , and . The indexation of is the key in this step, but it is not within the scope of this work due to its subjectivity. Further studies on indexation are required to fulfill this architecture. Afterwards, suitable for , and is acquired using models produced using the presented modeling technique. Then, is supposed to be applied on SPAs. Both and are conducted. If the SPGs and grasped objects are in an appropriate position, pincer grasping is performed, and and are produced on the objects. Finally, is obtained. As an open-loop control architecture, accurate models at both actuator and task levels give more precise .
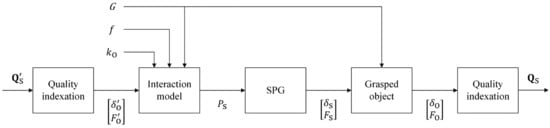
Figure 5.
A control architecture of adaptive SPG pincer grasping quality based on object stiffness.
2.5. Validation
Equation (6) shows that there is no exact physical definition of . The first step of validation is defining . We decided to define as the multiplication product of and . Thus, correlates to the elastic energy stored in grasped objects. The mathematic representation of can be written as follows:
Equation (9) was used to compute from and . We set the testing conditions of ranging from 25 to 85 kPa with 20 kPa intervals. The modeling technique was next implemented to forecast , , and over . The forecast results at the specified conditions were considered as , , and , respectively. Practical grasping was also implemented to observe actual under the same condition of , using an experimental setup shown in Figure 6. The main components of the setup included a binocular camera and air supply. The air supply was executed to provide . Once the grasping became steady, stereo images of the SPG and object were captured using the binocular camera. Image processing and computer vision were utilized to determine from the images. Afterwards, the object-stiffness curve was used to obtain from the determined values of . The actual results of and were employed to calculate . The deviation of from , denoted by , was exploited as the main criterion of the validation. It can be mathematically written as follows:
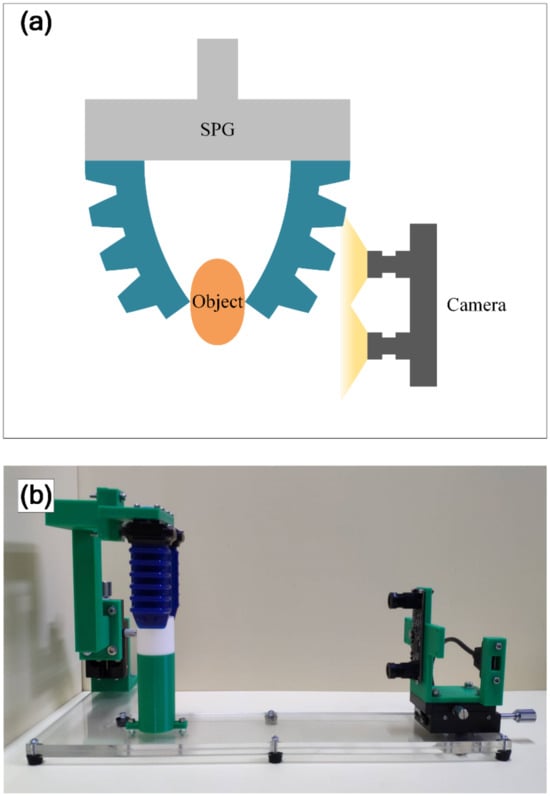
Figure 6.
An experimental setup for observing adaptive SPG pincer grasping: (a) schematic and (b) photograph.
The deviations of and , denoted by and , respectively, were also validation criteria. Their mathematical representations are similar to Equation (10).
3. Results and Discussion
The first obtained results were the SPA performance curves (Figure 7). Each performance curve reveals the correlation between and at a specific condition of . The performance curves reveal that experienced an almost linear decrease, while increased at every single condition of . Both and were amplified when increased. Moreover, the decrease of with respect to was invariant when increased. The maximum value of was 2.225 N when and were at 0 mm and 100 kPa, respectively. The curvature of the SPAs was constant along their length when was low and varied in larger magnitude when became greater, during the inspection process. This phenomenon remarks the necessity of a new concept of SPA modeling.
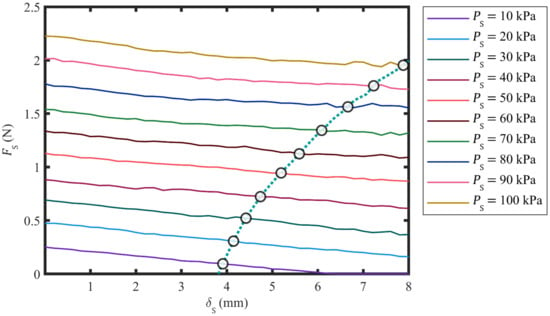
Figure 7.
Performance curves of an SPA, a stiffness curve of an object, and primary prediction deformation and force of SPG pincer grasping on the object.
A stiffness curve of the specimen object was the next result collected (Figure 7). The investigation results illustrate that parabolically declined, from 1.213 N/mm to 260 mN/mm, when and increased.
The performance and stiffness curves were used to forecast , , and over . The intersections in Figure 7 predictively indicate and at the SPA-inspection conditions of . Afterwards, , , and in the same conditions were achieved. Linear interpolation subsequently converted the discrete results into continuous , , and over ranging from 10 to 100 kPa (Figure 8a,c,e). Afterwards, , , and were determined from the prediction results. The validation experiment was then completed. The actual results of , , and were obtained (Figure 8a,c,e). The predicted and actual results had a similar trend in the comparable aspect. Next, , , and at the testing conditions of were acquired (Figure 8b,d,f). The comparison results show that and were below 464 µm and 410 mN, respectively. Furthermore, was under 451 µJ. Small results of , , and proved that can be reliably modeled and controlled. The proposed modeling technique and control architecture is credible. These findings clarify the association between and and, moreover, advance the development toward modellable and controllable .
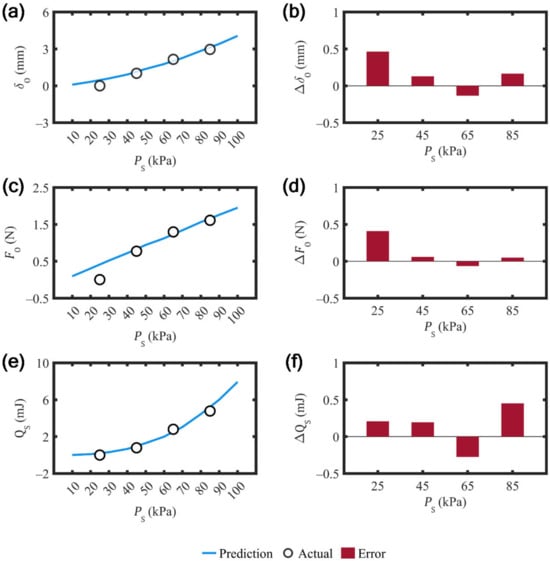
Figure 8.
Results of SPG pincer grasping on an object: (a) deformation of the object; (b) deviation in deformation; (c) exerted force on the object; (d) deviation in force; (e) grasping quality due to SPA performance; and (f) deviation in grasping quality due to SPA performance.
4. Conclusions
Adaptive pincer grasping of SPGs based on object stiffness is presented in this study. The main goal of this study was to clarify the association between grasping quality and SPA performance. SPA structures have infinite DOF, so the clarification is certainly not straightforward. We ignored the effects of other factors on grasping quality and focused only on grasping quality due to SPA performance. A modeling technique and control architecture were presented for the implementation of the proposed grasping. A validation of the established methods was conducted to evaluate their reliability. The validation results show that grasping quality correlates to the input air pressure of SPAs. The same results also reveal that grasping quality due to SPA performance is modellable and controllable using the established methods. These findings proceed the advancement on the modeling and control of grasping quality in SPG pincer grasping. This is a novel study of substantial duration that considers this issue. Further study on the correlations between grasping quality and other factors is strongly recommended. Therefore, grasping quality is expected to be modellable and controllable when the effects of all significant factors are determined and accounted for in its comprehensive modeling and control.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.S.; methodology, C.S.; software, C.S.; validation, C.S.; formal analysis, C.S.; investigation, C.S.; resources, C.S. and R.C.; data curation, C.S.; writing—original draft preparation, C.S.; writing—review and editing, C.S.; visualization, C.S.; supervision, R.C.; project administration, C.S. and R.C.; funding acquisition, R.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project is funded by National Research Council of Thailand (NRCT).
Acknowledgments
C.S. is supported by a scholarship from “The 100th Anniversary Chulalongkorn University Fund for Doctoral Scholarship”.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tsai, R.Y. A New Technique for Fully Autonomous and Efficient 3d Robotics Hand/Eye Calibration. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1989, 5, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, S.; Pastor, P.; Krizhevsky, A.; Ibarz, J.; Quillen, D. Learning Hand-Eye Coordination for Robotic Grasping with Deep Learning and Large-Scale Data Collection. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2018, 37, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, C.; Grioli, G.; Catalano, M.G.; Bicchi, A. A Century of Robotic Hands. Annu. Rev. Control Robot. Auton. Syst. 2019, 2, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwan, Q.M.; Chua, S.C.; Kwek, L.C. Comprehensive Review on Reaching and Grasping of Objects in Robotics. Robotica 2021, 39, 1849–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Trinkle, J.C.; Li, Z.X. Grasp Analysis as Linear Matrix Inequality Problems. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 2000, 16, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.T.; Allen, P.K. Graspit: A Versatile Simulator for Robotic Grasping. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2004, 11, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohg, J.; Morales, A.; Asfour, T.; Kragic, D. Data-Driven Grasp Synthesis-a Survey. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2014, 30, 289–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Z. State-of-the-Art Robotic Grippers, Grasping and Control Strategies, as Well as Their Applications in Agricultural Robots: A Review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 177, 105694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, G.; Fang, H.; Chen, L.; Wan, Y.; Xu, F.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, L. Soft Robotics: Academic Insights and Perspectives through Bibliometric Analysis. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyraz, P.; Runge, G.; Raatz, A. An Overview of Novel Actuators for Soft Robotics. Actuators 2018, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.; Culha, U.; Giardina, F.; Guenther, F.; Rosendo, A.; Iida, F. Soft Manipulators and Grippers: A Review. Front. Robot. AI 2016, 3, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, L.; Petersen, K.; Lum, G.Z.; Sitti, M. Soft Actuators for Small-Scale Robotics. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polygerinos, P.; Correll, N.; Morin, S.A.; Mosadegh, B.; Onal, C.D.; Petersen, K.; Cianchetti, M.; Tolley, M.T.; Shepherd, R.F. Soft Robotics: Review of Fluid-Driven Intrinsically Soft Devices; Manufacturing, Sensing, Control, and Applications in Human-Robot Interaction. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 19, 1700016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipson, H. Challenges and Opportunities for Design, Simulation, and Fabrication of Soft Robots. Soft Robot. 2014, 1, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Cao, L.; Liu, J. A Review of Soft Manipulator Research, Applications, and Opportunities. J. Field Robot. 2022, 39, 281–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Hou, X.; Zhang, X.; Qi, W.; Cai, S.; Xiong, X.; Guo, J. Pneumatic Soft Robots: Challenges and Benefits. Actuators 2022, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuruthel, T.G.; Ansari, Y.; Falotico, E.; Laschi, C. Control Strategies for Soft Robotic Manipulators: A Survey. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzumori, K.; Iikura, S.; Tanaka, H. Applying a Flexible Microactuator to Robotic Mechanisms. IEEE Control Syst. 1992, 12, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Godage, I.S.; Wirz, R.; Walker, I.D.; Webster, R.J. Accurate and Efficient Dynamics for Variable-Length Continuum Arms: A Center of Gravity Approach. Soft Robot. 2015, 2, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polygerinos, P.; Wang, Z.; Overvelde, J.T.B.; Galloway, K.C.; Wood, R.J.; Bertoldi, K.; Walsh, C.J. Modeling of Soft Fiber-Reinforced Bending Actuators. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerboni, G.; Diodato, A.; Ciuti, G.; Cianchetti, M.; Menciassi, A. Feedback Control of Soft Robot Actuators via Commercial Flex Bend Sensors. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Wang, T.; Ren, Z.; Gong, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Guan, S.; Wen, L. Modeling and Experiments of a Soft Robotic Gripper in Amphibious Environments. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2017, 14, 1729881417707148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hirai, S. Soft Gripper Dynamics Using a Line-Segment Model with an Optimization-Based Parameter Identification Method. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgeneidy, K.; Lohse, N.; Jackson, M. Bending Angle Prediction and Control of Soft Pneumatic Actuators with Embedded Flex Sensors—A Data-Driven Approach. Mechatronics 2018, 50, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainsworth, T.; Smith, L.; Alexander, S.; MacCurdy, R. A Fabrication Free, 3d Printed, Multi-Material, Self-Sensing Soft Actuator. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 4118–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, P.; Nekoui, M.A.; Zareinejad, M.; Abbasi, P.; Azhang, Z. Position and Force Control of a Soft Pneumatic Actuator. Soft Robot. 2020, 7, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, D.; Chen, C.; Zhang, J.; Duan, W. Theoretical Modelling of Soft Robotic Gripper with Bioinspired Fibrillar Adhesives. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 2250–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Krause, J.C.; Olbrich, A.; Raatz, A. Modeling and Reconstruction of State Variables for Low-Level Control of Soft Pneumatic Actuators. Front. Robot. AI 2021, 8, 557830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roa, M.A.; Suárez, R. Grasp Quality Measures: Review and Performance. Auton. Robot. 2015, 38, 65–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, D.; Tao, B.; Qi, J.; Jiang, G.; Yun, J.; Huang, L.; Tong, X.; Chen, B.; Li, G. Grasping Posture of Humanoid Manipulator Based on Target Shape Analysis and Force Closure. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 3959–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Tawk, C.; Alici, G. A 3d Printed Soft Robotic Hand with Embedded Soft Sensors for Direct Transition between Hand Gestures and Improved Grasping Quality and Diversity. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y. An Efficient Algorithm for a Grasp Quality Measure. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2013, 29, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.; Seo, S.; Oh, J.; Bae, J. A Sensorized Hybrid Gripper to Evaluate a Grasping Quality Based on a Largest Minimum Wrench. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 3243–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udupa, G.; Sreedharan, P.; Dinesh, P.S.; Kim, D. Asymmetric Bellow Flexible Pneumatic Actuator for Miniature Robotic Soft Gripper. J. Robot. 2014, 2014, 902625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Hao, L. A Novel Pneumatic Soft Sensor for Measuring Contact Force and Curvature of a Soft Gripper. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 266, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfiani, A.; Yi, X.; Shao, Z.; Zhao, H.; Parkestani, A.N. Analytical Modeling and Optimization of a Corrugated Soft Pneumatic Finger Considering the Performance of Pinch and Power Grasps. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2021, 44, 101215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alici, G.; Canty, T.; Mutlu, R.; Hu, W.; Sencadas, V. Modeling and Experimental Evaluation of Bending Behavior of Soft Pneumatic Actuators Made of Discrete Actuation Chambers. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).