Reduced Simulation: Real-to-Sim Approach toward Collision Detection in Narrowly Confined Environments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We tackled a collision detection problem in narrow or confined environments with a novel real-to-sim concept. This restricted environment has not been addressed in previous studies.
- We confirmed that the rendering style of reduced simulation does not reduce the performance of MAV control through the subject experiment.
- We evaluated our pipeline by carrying out similar experiments as those carried out in previous studies [4] on real experiment sites of the ceiling environments. By conducting experiments, we confirmed that our reduced simulation pipeline outperformed, within the adaptation capabilities, the traditional cost-saving simulation technique.
- Based on the results of our experiment, we provided guidelines for adopting a cost-saving reduced simulation for MAV collision detection in cluttered environments.
2. Related Works
2.1. Vision Based MAV Control
2.2. Sim-to-Real Approaches
2.3. Real-to-Sim Approach
3. Reduced Simulation Concept
4. User Study for Reduced Simulation
4.1. Hypothesis
4.2. Experiment Setup
4.3. Comparison among Types of Simulation
5. Collision Detection with Reduced Simulations
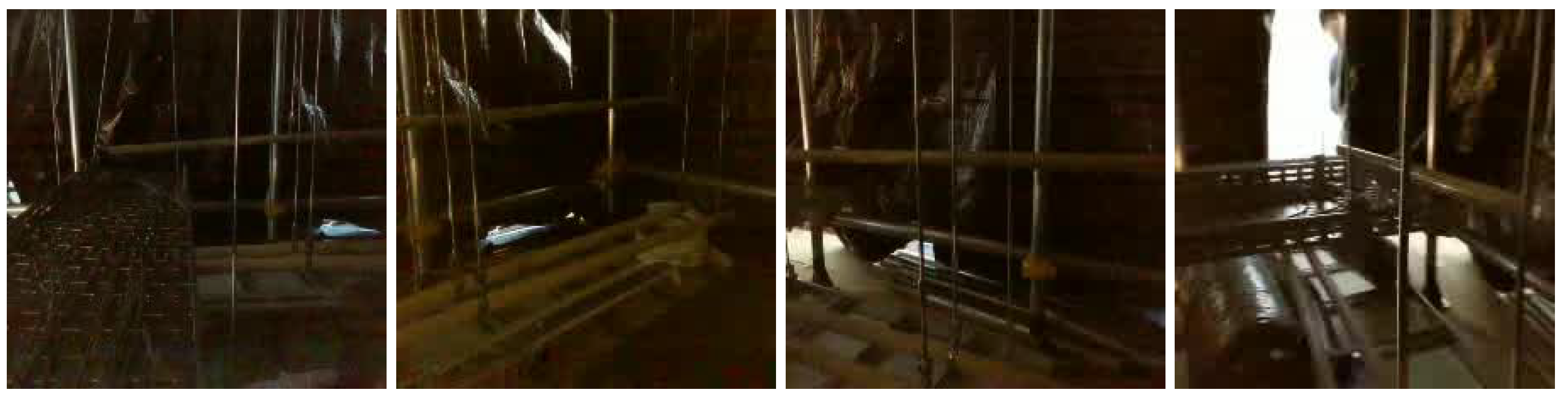
5.1. Dataset Generation
5.1.1. Low-Fidelity Simulation
5.1.2. Moderate-Fidelity Simulation
5.1.3. Real-World
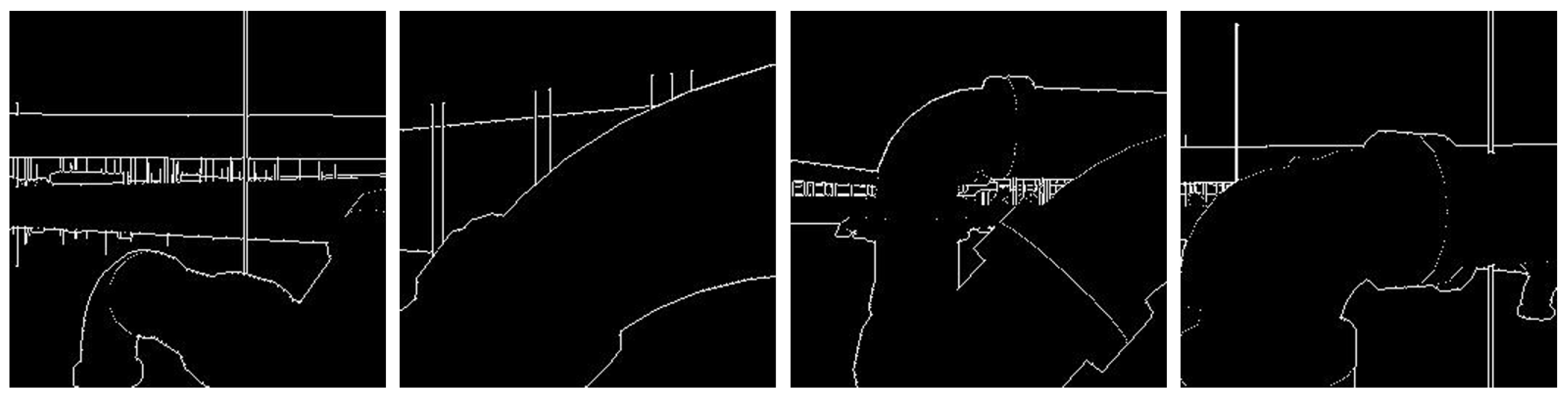
5.2. Image Based Collision Detection Model
5.3. Experimental Evaluation
5.4. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Faessler, M.; Fontana, F.; Forster, C.; Mueggler, E.; Pizzoli, M.; Scaramuzza, D. Autonomous, vision-based flight and live dense 3D mapping with a quadrotor micro aerial vehicle: Autonomous, vision-based flight and live dense 3D mapping. J. Field Robot. 2016, 33, 431–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakhatreh, H.; Sawalmeh, A.H.; Al-Fuqaha, A.; Dou, Z.; Almaita, E.; Khalil, I.; Othman, N.S.; Khreishah, A.; Guizani, M. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs): A Survey on Civil Applications and Key Research Challenges. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 48572–48634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, T.; Xia, G.; Zhang, L. Mini-Unmanned Aerial Vehicle-Based Remote Sensing: Techniques, applications, and prospects. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2019, 7, 29–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gandhi, D.; Pinto, L.; Gupta, A. Learning to fly by crashing. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 3948–3955. [Google Scholar]
- Loquercio, A.; Maqueda, A.I.; del Blanco, C.R.; Scaramuzza, D. DroNet: Learning to Fly by Driving. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.; Belkhale, S.; Kahn, G.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S. Generalization through Simulation: Integrating Simulated and Real Data into Deep Reinforcement Learning for Vision-Based Autonomous Flight. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 6008–6014. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, A.; Dai, A.; Funkhouser, T.; Halber, M.; Nießner, M.; Savva, M.; Song, S.; Zeng, A.; Zhang, Y. Matterport3D: Learning from RGB-D Data in Indoor Environments 2017. In Proceedings of the International Conference on 3D Vision 2017, Qingdao, China, 10–12 October 2017; pp. 667–676. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, M.; Paczan, N. Hypersim: A Photorealistic Synthetic Dataset for Holistic Indoor Scene Understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) 2021, Virtual, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10912–10922. [Google Scholar]
- Höfer, S.; Bekris, K.; Handa, A.; Gamboa, J.C.; Golemo, F.; Mozifian, M.; Atkeson, C.; Fox, D.; Goldberg, K.; Leonard, J.; et al. Perspectives on Sim2Real Transfer for Robotics: A Summary of the R:SS 2020 Workshop. 2020. Available online: http://xxx.lanl.gov/abs/2012.03806 (accessed on 6 December 2021).
- Xia, F.; Zamir, A.R.; He, Z.; Sax, A.; Malik, J.; Savarese, S. Gibson env: Real-world perception for embodied agents. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Tai, L.; Yun, P.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, M.; Boedecker, J.; Burgard, W. VR-Goggles for Robots: Real-to-Sim Domain Adaptation for Visual Control. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- James, S.; Wohlhart, P.; Kalakrishnan, M.; Kalashnikov, D.; Irpan, A.; Ibarz, J.; Levine, S.; Hadsell, R.; Bousmalis, K. Sim-to-real via sim-to-sim: Data-efficient robotic grasping via randomized-to-canonical adaptation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 12627–12637. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, K.; Harris, C.; Irpan, A.; Levine, S.; Ibarz, J.; Khansari, M. Rl-cyclegan: Reinforcement learning aware simulation-to-real. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Virtual, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 11157–11166. [Google Scholar]
- Beyeler, A.; Zufferey, J.C.; Floreano, D. Vision-based control of near-obstacle flight. Auton. Robot. 2009, 27, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bills, C.; Chen, J.; Saxena, A. Autonomous MAV flight in indoor environments using single image perspective cues. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 5776–5783. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, S.; Melik-Barkhudarov, N.; Shankar, K.S.; Wendel, A.; Dey, D.; Bagnell, J.A.; Hebert, M. Learning monocular reactive UAV control in cluttered natural environments. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 1765–1772. [Google Scholar]
- Giusti, A.; Guzzi, J.; Cireşan, D.C.; He, F.; Rodríguez, J.P.; Fontana, F.; Faessler, M.; Forster, C.; Schmidhuber, J.; Caro, G.D.; et al. A Machine Learning Approach to Visual Perception of Forest Trails for Mobile Robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2016, 1, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadeghi, F.; Levine, S. CAD2RL: Real Single-Image Flight without a Single Real Image. 2016. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems 2017, Cambridge, MA, USA, 12–16 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Straub, J.; Whelan, T.; Ma, L.; Chen, Y.; Wijmans, E.; Green, S.; Engel, J.J.; Mur-Artal, R.; Ren, C.; Verma, S.; et al. The Replica Dataset: A Digital Replica of Indoor Spaces 2019. Available online: http://xxx.lanl.gov/abs/1906.05797 (accessed on 2 August 2021).
- Armeni, I.; Sax, S.; Zamir, A.R.; Savarese, S. Joint 2D-3D-Semantic Data for Indoor Scene Understanding. 2017. Available online: http://xxx.lanl.gov/abs/1702.01105 (accessed on 2 August 2021).
- Savva, M.; Kadian, A.; Maksymets, O.; Zhao, Y.; Wijmans, E.; Jain, B.; Straub, J.; Liu, J.; Koltun, V.; Malik, J.; et al. Habitat: A platform for embodied ai research. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 9339–9347. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Naji, S.; Kaufmann, E.; Loquercio, A.; Scaramuzza, D. Flightmare: A Flexible Quadrotor Simulator. 2020. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL) 2020, Virtual, 16–18 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.; Dey, D.; Lovett, C.; Kapoor, A. AirSim: High-Fidelity Visual and Physical Simulation for Autonomous Vehicles. In Field and Service Robotics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 621–635. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, D.; Kadian, A.; Parikh, D.; Hoffman, J.; Batra, D. Splitnet: Sim2sim and task2task transfer for embodied visual navigation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27 Octobor–2 November 2019; pp. 1022–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wallach, H.; O’connell, D.N. The kinetic depth effect. J. Exp. Psychol. 1953, 45, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Bolya, D.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, F.; Lee, Y.J. YOLACT: Real-Time Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27 Octobor–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, J.V. Complete counterbalancing of immediate sequential effects in a Latin square design. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1958, 53, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.; Sendobry, A.; Kohlbrecher, S.; Klingauf, U.; von Stryk, O. Comprehensive Simulation of Quadrotor UAVs Using ROS and Gazebo. In Proceedings of the Simulation, Modeling, and Programming for Autonomous Robots, Tsukuba, Japan, 5–8 November 2012; pp. 400–411. [Google Scholar]
- DJI Tello Drone. Available online: https://www.ryzerobotics.com/jp/tello (accessed on 10 July 2021).
- Wen, H.; Shi, J.; Chen, W.; Liu, Z. Deep Residual Network Predicts Cortical Representation and Organization of Visual Features for Rapid Categorization. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

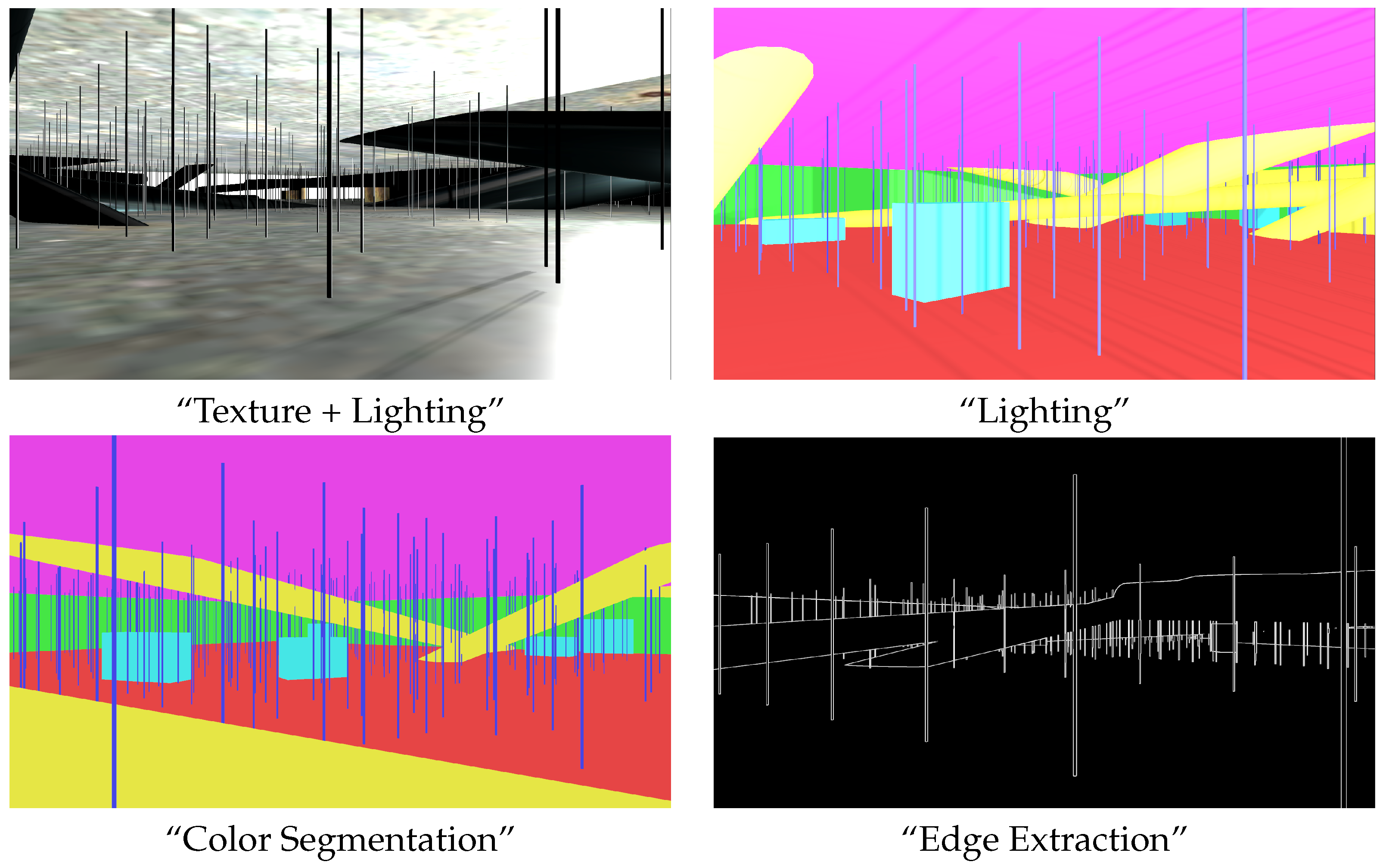


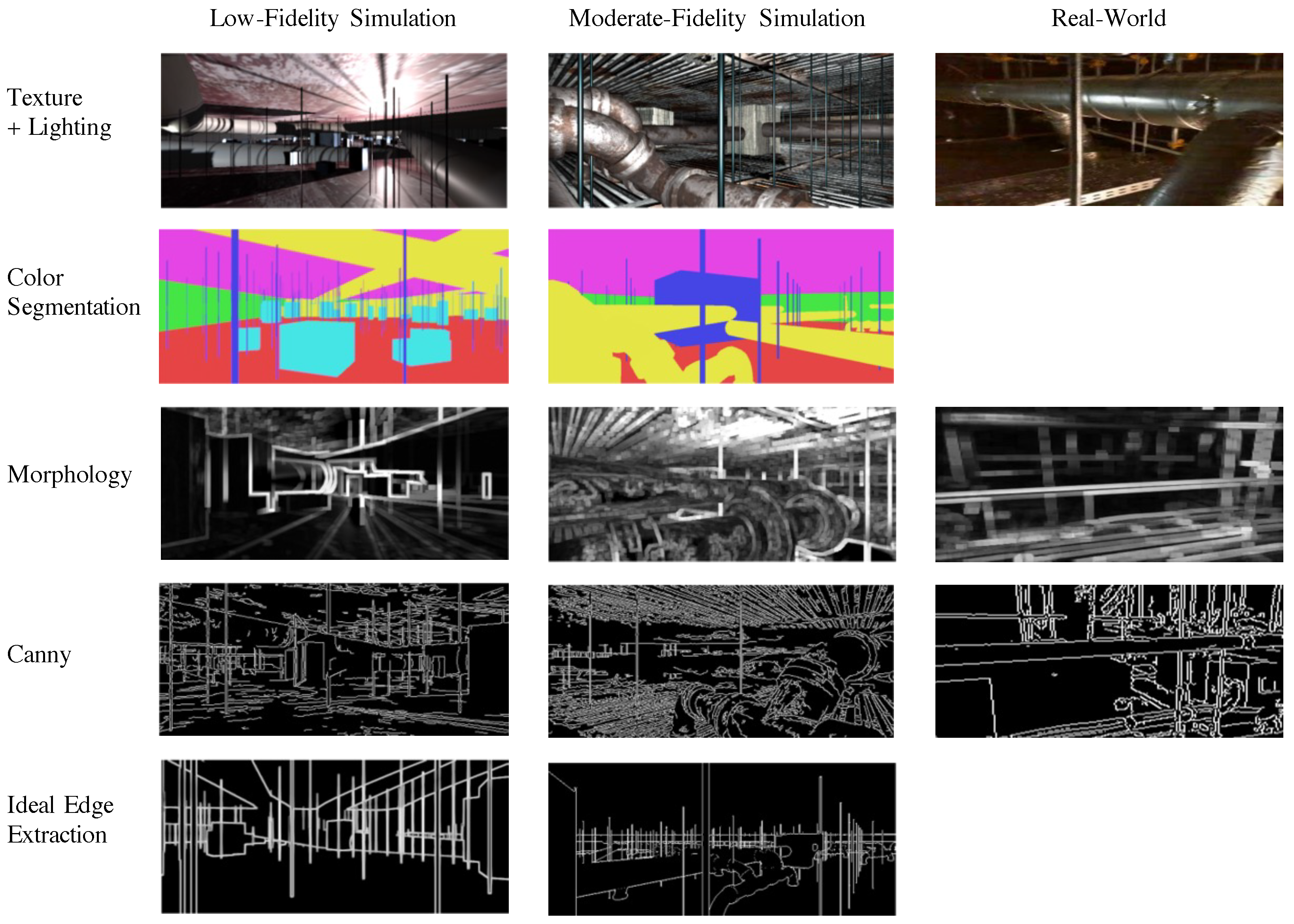




| Type | Number | Scale (x, y, z) |
|---|---|---|
| Box | 20 | (0.2~0.8, 0.2~0.6, 0.2~0.8) |
| Hanging Bolt | 800 | (0.01, 1, 0.001) |
| Pipe | 10 | (0.2~0.8, 1000, 0.2~0.8) |
| Texture + | Lighting | Color | Edge | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lighting | Segmentation | Extraction | ||
| p-value | 0.3776 | 0.0353 | 0.2228 | 0.62977 |
| Rendering Style | Low Fid. | Moderate Fid. | Real World |
|---|---|---|---|
| Texture + Lighting | 0.9360 | 0.8325 | 0.5050 |
| Color Segmentation | 0.9360 | 0.8825 | NaN |
| Morphology | 0.9160 | 0.6525 | 0.7200 |
| Canny | 0.8860 | 0.7850 | 0.6800 |
| Ideal Edge Extraction | 0.9480 | 0.8675 | (0.6650) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takayama, Y.; Ratsamee, P.; Mashita, T. Reduced Simulation: Real-to-Sim Approach toward Collision Detection in Narrowly Confined Environments. Robotics 2021, 10, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics10040131
Takayama Y, Ratsamee P, Mashita T. Reduced Simulation: Real-to-Sim Approach toward Collision Detection in Narrowly Confined Environments. Robotics. 2021; 10(4):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics10040131
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakayama, Yusuke, Photchara Ratsamee, and Tomohiro Mashita. 2021. "Reduced Simulation: Real-to-Sim Approach toward Collision Detection in Narrowly Confined Environments" Robotics 10, no. 4: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics10040131
APA StyleTakayama, Y., Ratsamee, P., & Mashita, T. (2021). Reduced Simulation: Real-to-Sim Approach toward Collision Detection in Narrowly Confined Environments. Robotics, 10(4), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics10040131







