Exploring the Neuroprotective Potential of Astragalus membranaceus in Central Nervous System Diseases
Abstract
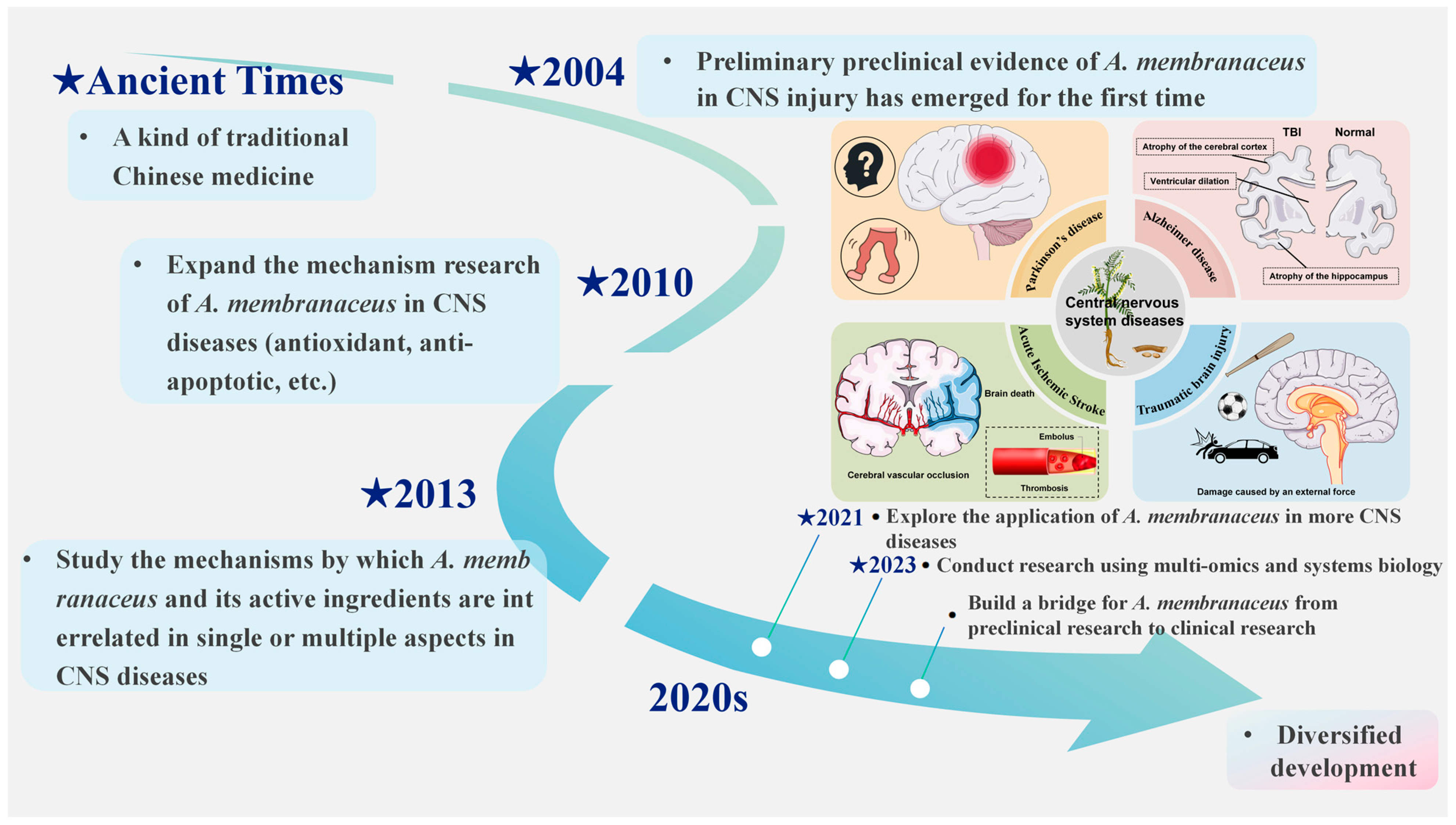
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
3. Results
4. Impact of A. membranaceus and Its Bioactive Components on the CNS
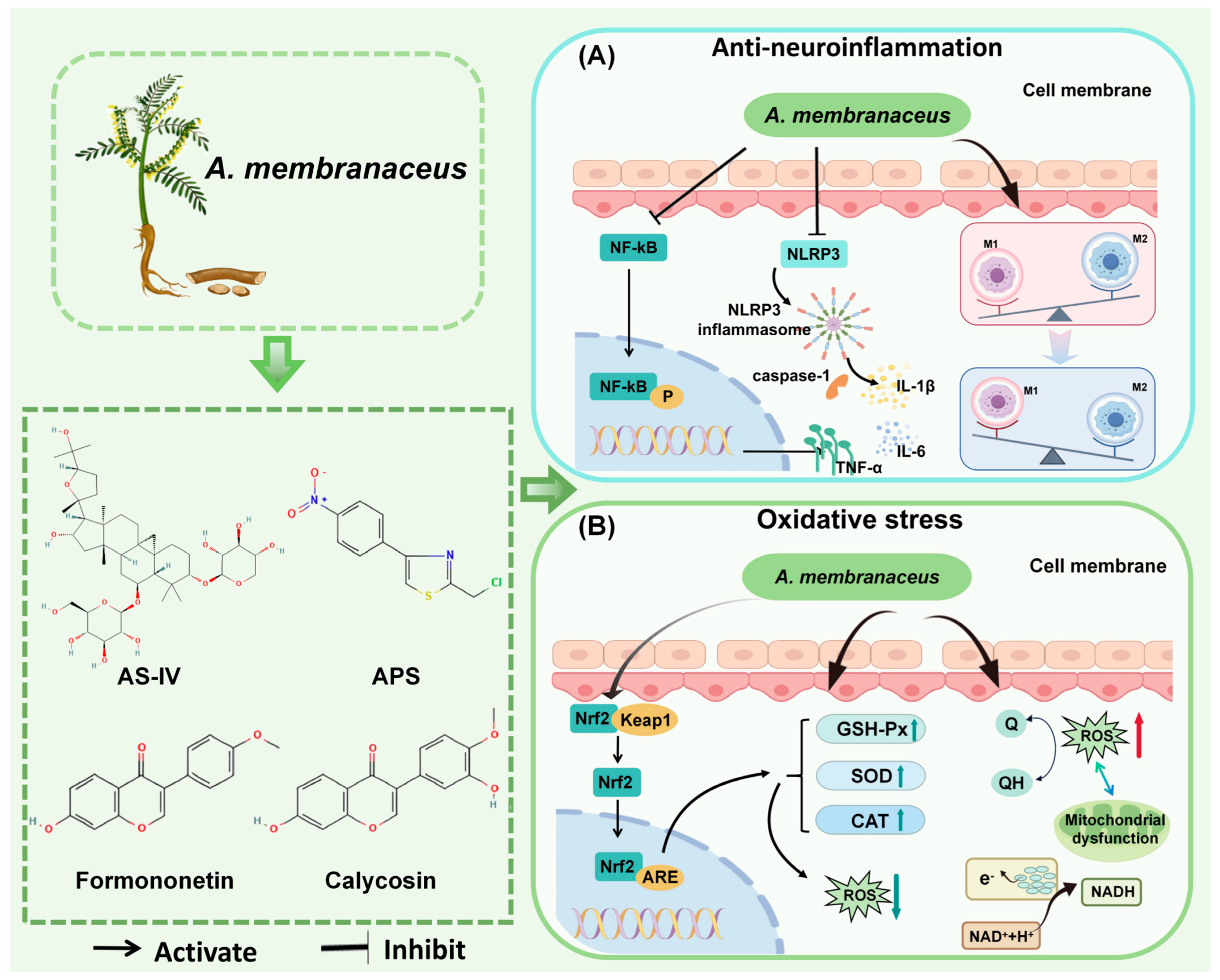
4.1. Anti-Neuroinflammation
4.1.1. Regulatory Effects of A. membranaceus Components (AS-IV, APS) on Microglia/Macrophages
4.1.2. Inhibitory Effect of AS-IV on NLRP3 Inflammatory Body and Related Damage
4.1.3. Regulatory Effect of A. membranaceus on Astrocytes
4.1.4. Regulatory Effect of A. membranaceus on Neutrophils
4.1.5. Regulatory Effects of A. membranaceus Through Multiple Inflammatory Signaling Pathways
4.2. Oxidative Stress
4.2.1. A. membranaceus Regulates the Expression Levels of Antioxidant Enzymes
4.2.2. The Regulation of Mitochondrial Function by A. membranaceus
4.2.3. Nrf2 Plays a Core Role in the Antioxidant Stress Resistance of A. membranaceus
4.3. Anti-Apoptosis
4.3.1. A. membranaceus Inhibits JNK Phosphorylation
4.3.2. A. membranaceus Regulates the Expression of CaSR
4.3.3. A. membranaceus Inhibits Apoptosis Through Other Pathways
4.4. Autophagy Regulation
A. membranaceus Regulates Autophagy via AMPK and mTOR
4.5. Anti-Ferroptosis
4.5.1. The Regulation of GPX4 by A. membranaceus
4.5.2. A. membranaceus Relies on NADPH to Function
4.6. Anti-Blood–Brain Barrier Damage
4.6.1. The Regulation of Tight Junction Proteins by Active Ingredients of A. membranaceus
4.6.2. The Regulation of ETS1 by A. membranaceus
4.6.3. A. membranaceus Combats the BBB Through Other Means
5. Pharmacognosy of A. membranaceus
5.1. Safety
5.2. Application of A. membranaceus in the Field of Food and Medicine
5.2.1. Application of A. membranaceus in Formulated Preparations
5.2.2. Application of A. membranaceus in Health Foods
Liquid Products
Semi-Liquid Products
Solid Products
6. Summary
6.1. Neuroprotective Potential and Mechanisms of A. membranaceus in CNS Disorders
6.2. The Limitations Faced in the Clinical Application and Promotion of A. membranaceus
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| AIS | Acute Ischemic Stroke |
| AMPK | Adenosine-activated protein kinase |
| APS | A. membranaceus polysaccharides |
| AS-IV | A. membranaceus IV |
| Astragalus membranaceus | A. membranaceus |
| BBB | blood–brain barrier |
| CA | Calycosin |
| CAG | Cycloastragenol |
| CaSR | calcium-sensitive receptor |
| CI | cerebral infarction |
| CIRI | cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| EAE | experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis |
| EBI | stroke-triggered early brain injury |
| FMN | Formononetin |
| GSH-Px | glutathione peroxidase |
| GPX4 | Glutathione peroxidase 4 |
| HGWD | Huangqi Guizhi WuWu Tang |
| I/R | ischemia/reperfusion |
| ISOI | Isoastragaloside I |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| LPO | Lipid Peroxidation |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharides |
| MCAO | middle cerebral artery occlusion |
| MS | multiple sclerosis |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-κB |
| NLRP3 | NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain-associated protein 3 |
| NOX2/4 | NADPH oxidase 2/4 |
| NOX4 | NADPH oxidase 4 |
| OGD/R | oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| p-ERK | phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| P-gp | P-glycoprotein |
| PPARγ | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ |
| PTZ | pentylenetetrazole |
| RAGE | receptor for advanced glycation end-products |
| Rg1 | Ginsenoside Rg1 |
| RNS | reactive nitrogen species |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| RRS | repeated restraint stress |
| SAE | sepsis-associated encephalopathy |
| SAH | subarachnoid hemorrhage |
| SCI | spinal cord injury |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| T-AOC | total antioxidant capacity |
| TBI | traumatic brain injury |
| TCM | traditional Chinese medicine |
| TFA | total flavonoids |
| TON | traumatic optic neuropathy |
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Stark, B.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Roth, G.A.; Bisignano, C.; Abady, G.G.; Abbasifard, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abedi, V.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 795–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Q.Q.; Zhu, F. Trends in Prevalence Cases and Disability-Adjusted Life-Years of Parkinson’s Disease: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Neuroepidemiology 2022, 56, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Guo, Y.; Fu, Y.; Ren, H.; Wang, H.; Yan, H.; Ge, Y. Trends of mitochondrial changes in AD: A bibliometric study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1136400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijdicks, E.F. Hepatic Encephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1660–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Yan, Y.; Long, T.; Xu, J.; Chang, C.; Kang, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, J. Ferroptosis: A potential therapeutic target in cardio-cerebrovascular diseases. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2025, 480, 4379–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Han, B.; Zhao, H.; Xu, C.; Xu, D.; Sieniawska, E.; Lin, X.; Kai, G. Biological active ingredients of Astragali Radix and its mechanisms in treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Phytomedicine 2022, 98, 153918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhao, M.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Y. Pharmacological potential of Astragali Radix for the treatment of kidney diseases. Phytomedicine 2024, 123, 155196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Elrahim Abd Elkader, H.T.; Essawy, A.E.; Al-Shami, A.S. Astragalus species: Phytochemistry, biological actions and molecular mechanisms underlying their potential neuroprotective effects on neurological diseases. Phytochemistry 2022, 202, 113293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, A.G.W.; Duan, R.; Wang, H.Y.; Kong, X.P.; Dong, T.T.X.; Tsim, K.W.K.; Chan, K. Evaluation of the Pharmaceutical Properties and Value of Astragali Radix. Medicines 2018, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Huang, H.; Fan, Y.; Xu, L.; Jin, X.; Xiao, B.; Ma, C.; Fan, H.; Chai, Z. Astragaloside IV ameliorates Parkinson’s disease by inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB-dependent neuroinflammation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 160, 114972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, W.; Lin, B.; Zheng, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Pan, X. Novel application of cycloastragenol target microglia for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: Evidence from single-cell analysis, network pharmacology and experimental assessment. Phytomedicine 2025, 139, 156502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ren, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y. A Review of the Pharmacological Action of Astragalus Polysaccharide. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Ding, G.; Gong, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yu, H.; Cheng, X. Microglia Polarization from M1 toward M2 Phenotype Is Promoted by Astragalus Polysaccharides Mediated through Inhibition of miR-155 in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 5753452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Gan, H.; Jin, H.; Fang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Chu, L. Astragaloside IV promotes microglia/macrophages M2 polarization and enhances neurogenesis and angiogenesis through PPARγ pathway after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 92, 107335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Mu, B.; Guo, M.; Liu, C.; Meng, T.; Yan, Y.; Song, L.; Yu, J.; Kumar, G.; Ma, C. Astragaloside IV inhibits experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by modulating the polarization of both microglia/macrophages and astrocytes. Folia. Neuropathol. 2023, 61, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Shi, H.; Jin, X.; Guo, S.; Zhou, X.; Gao, W. Mechanism of astragaloside IV regulating NLRP3 through LOC102555978 to attenuate cerebral ischemia reperfusion induced microglia pyroptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 131, 111862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.T.; Ruan, J.; Zhang, R.Y.; Deng, J.; Ma, Z.Q.; Ma, S.P. Astragaloside IV ameliorates neuroinflammation-induced depressive-like behaviors in mice via the PPARγ/NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome axis. Acta. Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhao, G.; Lang, J.; Sun, B.; Feng, S.; Li, D.; Sun, G. Astragaloside IV ameliorated neuroinflammation and improved neurological functions in mice exposed to traumatic brain injury by modulating the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 signaling pathway. J. Investig. Med. 2024, 72, 747–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Wang, X.; Siedlak, S.L.; Perry, G.; Smith, M.A.; Zhu, X. c-Jun phosphorylation in Alzheimer disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 85, 1668–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Wu, W.Y.; Gong, H.L.; Li, W.Z.; Yin, Y.Y. Astragalosides attenuate learning and memory impairment in rats following ischemia—Reperfusion injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 1319–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Pan, X.; Huang, C.; Gu, M.; Chen, X.; Zheng, X.; Shao, Z.; Hu, S.; Wang, B.; Lin, H.; et al. Dual regulation of microglia and neurons by Astragaloside IV-mediated mTORC1 suppression promotes functional recovery after acute spinal cord injury. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Du, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, T. GPX4-independent ferroptosis—A new strategy in disease’s therapy. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.M.; Guo, Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, H.Y.; Qin, X.Y.; Hu, Y.; Lan, R. Astragalin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior in mice by preserving blood-brain barrier integrity and suppressing neuroinflammation. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2025, 232, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Xie, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, T.; Yang, P.; Hu, J.; Peng, Z.; Luo, K.; Du, M.; Chen, C. Astragalus polysaccharide (APS) exerts protective effect against acute ischemic stroke (AIS) through enhancing M2 micoglia polarization by regulating adenosine triphosphate (ATP)/ purinergic receptor (P2X7R) axis. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 4468–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Jin, J.M.; Yang, C.; Wang, P.; Huang, F.; Wu, H.; Zhang, B.B.; Shi, H.L.; Wu, X.J. Isoastragaloside I suppresses LPS-induced tight junction disruption and monocyte adhesion on bEnd.3 cells via an activating Nrf2 antioxidant defense system. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, P.; Huang, F.; Jin, J.; Wu, H.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Shi, H.; Wu, X. Astragaloside IV protects blood-brain barrier integrity from LPS-induced disruption via activating Nrf2 antioxidant signaling pathway in mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 340, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Huan, Y.; Jiang, T.; He, Y.; Gao, Z. Rehabilitation training enhanced the therapeutic effect of calycosin on neurological function recovery of rats following spinal cord injury. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2024, 136, 102384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.; Walker, T.; Ayton, S. Neuroferroptosis in health and diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2025, 26, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Liu, R.; Wu, Y.; Huang, S. Astragaloside IV Reduces Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability in Rats by Inhibiting ER Stress-Mediated Apoptosis. Evid.-Based Complement Altern. 2020, 2020, 9087873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senapati, P.K.; Mahapatra, K.K.; Singh, A.; Bhutia, S.K. mTOR inhibitors in targeting autophagy and autophagy-associated signaling for cancer cell death and therapy. BBA Rev. Cancer 2025, 1880, 189342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, S.S.; Agrawal, Y.O.; Nakhate, K.T.; Meeran, M.F.N.; Ojha, S.; Goyal, S.N. Neuroinflammation in the Central Nervous System: Exploring the Evolving Influence of Endocannabinoid System. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherry, J.D.; Olschowka, J.A.; O’Banion, M.K. Neuroinflammation and M2 microglia: The good, the bad, and the inflamed. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunna, C.; Mengru, H.; Lei, W.; Weidong, C. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 877, 173090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Shi, Z.; Cao, X.; Dang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T. Research Progress on Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Related Mechanisms of Astragalin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haftcheshmeh, S.M.; Abedi, M.; Mashayekhi, K.; Mousavi, M.J.; Navashenaq, J.G.; Mohammadi, A.; Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A. Berberine as a natural modulator of inflammatory signaling pathways in the immune system: Focus on NF-κB, JAK/STAT, and MAPK signaling pathways. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 1216–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tak, P.P.; Firestein, G.S. NF-kappaB: A key role in inflammatory diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, R.C.; Schroder, K.; Pelegrín, P. NLRP3 and pyroptosis blockers for treating inflammatory diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 43, 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodi, T.; Sankhe, R.; Gopinathan, A.; Nandakumar, K.; Kishore, A. New Insights on NLRP3 Inflammasome: Mechanisms of Activation, Inhibition, and Epigenetic Regulation. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2024, 19, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Zhao, X.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB in inflammation and cancer. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2025, 22, 811–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Guo, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chai, Z.; Wang, Q.; Yan, Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, G.; et al. Astragaloside IV protects neurons from microglia-mediated cell damage through promoting microglia polarization. Folia. Neuropathol. 2019, 57, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Xu, T.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Qu, S.; Li, Q.; Gao, P.; Cong, Z. The molecular mechanism of polysaccharides in combating major depressive disorder: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Kouadir, M.; Song, H.; Shi, F. Recent advances in the mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and its inhibitors. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Yan, Z.; Wan, H.; Yang, J.; Ding, Z.; He, Y. A Combination of Astragaloside IV and Hydroxysafflor Yellow A Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via NF-κB/NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD Pathway. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, D.G.; Almeida, R.F.; Souza, D.O.; Zimmer, E.R. The astrocyte biochemistry. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 95, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tujula, I.; Hyvärinen, T.; Lotila, J.; Rogal, J.; Voulgaris, D.; Sukki, L.; Tornberg, K.; Korpela, K.; Jäntti, H.; Malm, T.; et al. Modeling neuroinflammatory interactions between microglia and astrocytes in a human iPSC-based coculture platform. Cell Commun. Signal 2025, 23, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Sun, Q.; Yang, J.; Wang, G.; Zhao, F.; Chen, Y.; Jin, Y. Reactive astrocytes induced by 2-chloroethanol modulate microglia polarization through IL-1β, TNF-α, and iNOS upregulation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 157, 112550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, Y.; Du, Y.; Wan, Q.; Xu, Y.; Wu, J. Astragaloside IV attenuates penicillin-induced epilepsy via inhibiting activation of the MAPK signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, M.L.; Xie, X.H.; Ding, J.H.; Du, R.H.; Hu, G. Astragaloside IV inhibits astrocyte senescence: Implication in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.T.; Shao, C.Y.; Huang, P.; Yu, D.; Yang, J.H.; Wan, H.T.; He, Y. Optimization, characterization of Astragalus polysaccharides, and evaluation of anti-inflammation effect in primary cultured astrocytes via HMGB1/RAGE/NF-κB/NLRP3 signal pathway. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2023, 197, 116594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, W.J.; Liu, K.; Wang, Y.; Xu, F.; Wang, D.M.; Yang, Y. Effects of neutrophil fate on inflammation. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 72, 2237–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagemann, N.; Mohamud Yusuf, A.; Martiny, C.; Zhang, X.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Gunzer, M.; Kolesnick, R.; Gulbins, E.; Hermann, D.M. Homozygous Smpd1 deficiency aggravates brain ischemia/reperfusion injury by mechanisms involving polymorphonuclear neutrophils, whereas heterozygous Smpd1 deficiency protects against mild focal cerebral ischemia. Basic. Res. Cardiol. 2020, 115, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Qu, Y.Z.; Zhao, Z.W.; Wu, S.X.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wei, X.Y.; Gao, L.; Gao, G.D. Astragaloside IV protects against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury correlating to suppression of neutrophils adhesion-related molecules. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 60, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.F.; Shi, M.M.; Luo, M.Y.; Liu, D.D.; Guo, D.M.; Ling, C.; Zhong, X.L.; Xu, Y.; Cao, W.Y. Targeting PERK mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress attenuates neuroinflammation and alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior in male mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 111, 109092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Shao, L.H.; Chen, X.; Wang, M.; Qin, Q.J.; Yang, Y.L.; Zhang, G.R.; Hai, Y.; Tian, Y.H. Anti-inflammatory and DNA Repair Effects of Astragaloside IV on PC12 Cells Damaged by Lipopolysaccharide. Curr. Med. Sci. 2024, 44, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Jiang, N.; Zheng, J.; Hu, H.; Yang, H.; Lin, A.; Hu, B.; Liu, H. Structural characterization and anti-inflammatory activity of polysaccharides from Astragalus membranaceus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 241, 124386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Liu, Y.; Meng, F.; Li, Q.; Wu, F.; Yuan, J.; Chen, H.; Lv, H.; Zhou, Y.; Chang, Y. Amplification of oxidative damage using near-infrared II-mediated photothermal/thermocatalytic effects for periodontitis treatment. Acta. Biomater. 2023, 171, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonian, N.A.; Coyle, J.T. Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1996, 36, 83–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teleanu, D.M.; Niculescu, A.G.; Lungu, I.I.; Radu, C.I.; Vladâcenco, O.; Roza, E.; Costăchescu, B.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Teleanu, R.I. An Overview of Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation, and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, K.; Sandoval, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Jaiswal, M.; Sanz, E.; Li, Z.; Hui, J.; Graham, B.H.; Quintana, A.; et al. Glial lipid droplets and ROS induced by mitochondrial defects promote neurodegeneration. Cell 2015, 160, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Han, X.; Zhang, T.; Tian, K.; Li, Z.; Luo, F. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging biomaterials for anti-inflammatory diseases: From mechanism to therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 16, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jomova, K.; Raptova, R.; Alomar, S.Y.; Alwasel, S.H.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Reactive oxygen species, toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: Chronic diseases and aging. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 2499–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Peng, T.; Shao, C.; Liu, Y.; Lin, H.; Liu, Y. The Antioxidant Action of Astragali radix: Its Active Components and Molecular Basis. Molecules 2024, 29, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, A.; Guo, S.; Tu, S.; Ammar, A.B.; Tang, J.; Hong, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, J. Astragaloside IV alleviates early brain injury following experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Du, M.; Gao, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, X.; Wang, Z. Astragaloside IV attenuates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis of mice by counteracting oxidative stress at multiple levels. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.G.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.L.; Yang, J.D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.H.; Xia, Y.; Yao, L.B.; Qin, H.Z.; et al. Astragaloside IV prevents MPP⁺-induced SH-SY5Y cell death via the inhibition of Bax-mediated pathways and ROS production. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2012, 364, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.X.; Du, M.; Shi, H.L.; Huang, F.; Liu, H.S.; Wu, H.; Zhang, B.B.; Dou, W.; Wu, X.J.; Wang, Z.T. Astragalosides from Radix Astragali benefits experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in C57BL /6 mice at multiple levels. BMC Complem. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Kan, P.; Yao, X.; Yang, P.; Wang, J.; Xiang, L.; Zhu, Y. Astragaloside IV reversed the autophagy and oxidative stress induced by the intestinal microbiota of AIS in mice. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biala, A.K.; Dhingra, R.; Kirshenbaum, L.A. Mitochondrial dynamics: Orchestrating the journey to advanced age. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2015, 83, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Lu, M.H.; Yuan, D.J.; Xu, D.E.; Yao, P.P.; Ji, W.L.; Chen, H.; Liu, W.L.; Yan, C.X.; Xia, Y.Y.; et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Neural Injury. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Jia, N.; Wang, W.; Jin, H.; Xu, J.; Hu, H. Protective effects of astragaloside IV against amyloid beta1-42 neurotoxicity by inhibiting the mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldarmaa, J.; Liu, Z.; Long, J.; Mo, X.; Ma, J.; Liu, J. Anti-convulsant effect and mechanism of Astragalus mongholicus extract in vitro and in vivo: Protection against oxidative damage and mitochondrial dysfunction. Neurochem. Res. 2010, 35, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahar, E.; Kim, J.Y.; Yoon, H. Quercetin Attenuates Manganese-Induced Neuroinflammation by Alleviating Oxidative Stress through Regulation of Apoptosis, iNOS/NF-κB and HO-1/Nrf2 Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Islas, C.A.; Maldonado, P.D. Canonical and non-canonical mechanisms of Nrf2 activation. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 134, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.M.; Lu, P.H.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Sun, M.; Chen, G.Q.; Wang, Q. EGFR mediates astragaloside IV-induced Nrf2 activation to protect cortical neurons against in vitro ischemia/reperfusion damages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 457, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.P.; Qiu, Y.Y.; Wang, B.; Ding, H.; Tang, Y.H.; Zeng, R.; Deng, C.Q. Effects of Astragaloside IV combined with the active components of Panax notoginseng on oxidative stress injury and nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2/heme oxygenase-1 signaling pathway after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in mice. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2014, 10, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Huang, Y.; Lin, L.; Jiang, X.; Wu, J.; Liao, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. Neuroprotective Effects of Formononetin on Traumatic Brain Injury Through miR-155 Modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Signalling Pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2025, 50, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Shen, J.; Gao, X.; Ruan, Y.; Ling, J.; Sun, R.; Dai, J.; Fan, H.; Cheng, X.; Cao, P. Herbal formula Huangqi Guizhi Wuwu decoction attenuates paclitaxel-related neurotoxicity via inhibition of inflammation and oxidative stress. Chin. Med. 2021, 16, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo Ferrer, C.; Berthenet, K.; Ichim, G. Apoptosis—Fueling the oncogenic fire. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 4445–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshi, L.; Wu, H.C.; Wu, J.L.; Wang, H.V.; Hong, J.R. GSIV serine/threonine kinase can induce apoptotic cell death via p53 and pro-apoptotic gene Bax upregulation in fish cells. Apoptosis 2016, 21, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Fang, K.; Liu, X.; Yao, R.; Wang, M.; Li, F.; Hao, S.; He, J.; Wang, Y.; Fan, M.; et al. QSER1 preserves the suppressive status of the pro-apoptotic genes to prevent apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2023, 30, 779–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, D.H.; Nafie, M.S. Design, synthesis, and docking studies of novel pyrazole-based scaffolds and their evaluation as VEGFR2 inhibitors in the treatment of prostate cancer. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 20443–20456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, B.; Liebermann, D.A. The proto-oncogene c-myc and apoptosis. Oncogene 1998, 17, 3351–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, L.E.; Soni, I.V.; Hardy, J.A.; Julien, O. Deorphanizing Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 Substrates In and Out of Apoptosis with Deep Substrate Profiling. ACS Chem. Biol. 2021, 16, 2280–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Chen, X.L.; Zheng, J.Y.; Zhou, J.W.; Ma, Z.L. Astragaloside IV protects new born rats from anesthesia-induced apoptosis in the developing brain. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 1829–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, F.; Zhou, H.; Fang, Y.; Li, C.; He, Y.; Yu, L.; Wan, H.; Yang, J. Astragaloside IV alleviates ischemia reperfusion-induced apoptosis by inhibiting the activation of key factors in death receptor pathway and mitochondrial pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 248, 112319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.M.; Dong, Y.J.; Tang, J.L.; Zhou, X.H.; Gao, W.J. Astragaloside IV attenuates cerebral ischemia—Reperfusion injury in rats through the inhibition of calcium-sensing receptor-mediated apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 47, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, K.M.; Alshehri, S.A.; Almarwani, W.A.; Aljohani, K.K.; Albalawi, A.Z.; Alatawi, A.S.; Al-Atwi, S.M.; Alhwyty, L.S.; Hassan, H.M.; Al-Gayyar, M.M.H. Effects of Cycloastragenol on Alzheimer’s Disease in Rats by Reducing Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2024, 21, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhang, W.; Yang, C.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; et al. Astragalin actives autophagy and inhibits apoptosis of astrocytes in AD mice via down-regulating Fas/Fasl-VDAC1 pathway. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2025, 232, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, W.; Chen, H.; Li, W.; Li, W.; Zhu, G. Astragaloside IV prevents Aβ(1-42) oligomers-induced memory impairment and hippocampal cell apoptosis by promoting PPARγ/BDNF signaling pathway. Brain Res. 2020, 1747, 147041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, J.; Gammoh, N.; Ryan, K.M. Autophagy and autophagy-related pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 560–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.M.; Hu, F. The role of autophagy and mitophagy in cancers. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 128, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapil, L.; Kumar, V.; Kaur, S.; Sharma, D.; Singh, C.; Singh, A. Role of Autophagy and Mitophagy in Neurodegenerative Disorders. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2024, 23, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Zhou, X.; Lu, J.H.; Yue, Z. Autophagy deficiency in neurodevelopmental disorders. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizama, B.N.; Chu, C.T. Neuronal autophagy and mitophagy in Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Aspects. Med. 2021, 82, 100972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, H.; Yuan, M.; Fan, H.; Cai, Z. Role of AMPK in autophagy. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1015500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.; Park, R.; Kim, H.; Namkoong, S.; Jo, D.; Huh, Y.H.; Jang, I.S.; Lee, J.I.; Park, J. AMPK contributes to autophagosome maturation and lysosomal fusion. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleyto-Seldas, N.; Efeyan, A. The mTOR-Autophagy Axis and the Control of Metabolism. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 655731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.Z.; Wang, S.H.; Zhang, R.H.; Lin, J.H.; Tian, Y.H.; Yang, Y.Q.; Liu, J.; Ma, Y.X. Neuroprotective effect of astragalin via activating PI3K/Akt-mTOR-mediated autophagy on APP/PS1 mice. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Yang, J.J.; Zhu, J.G. Astragaloside IV ameliorates cerebral ischemic damage by restraining adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase/mTOR-triggered autophagic process and apoptotic activity in neurons. Mater. Res. Express 2023, 13, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Chao, G.; Wu, Q.; Xia, Y.; Shang, M.; Wei, Q.; Zhou, J.; Liao, L. Astragaloside IV improves the survival rates of retinal ganglion cells in traumatic optic neuropathy by regulating autophagy mediated by the AMPK-MTOR-ULK signaling pathway. Mol. Vis. 2025, 31, 99–112. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, F.; Lane, D.; Nguyen, T.P.M.; Bush, A.I.; Ayton, S. In defence of ferroptosis. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadian, K.; Stockwell, B.R. SnapShot: Ferroptosis. Cell 2020, 181, 1188-1188.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.Y.; Yu, G.R. Cycloastragenol inhibits Aβ(1-42)-induced blood-brain barrier disruption and enhances soluble Aβ efflux in vitro. J. Asian. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 23, 556–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.T.; Wang, G.T.; Chen, Y.J.; Yuan, W.K.; Cai, J.; Feng, A.P.; Fang, J.; Xu, Q.; Wu, X.J. Total flavonoids of Astragalus membranaceus protect against 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced neurotoxicity in mice by inhibiting ferroptosis through SLC7A11/GPX-4 signaling pathway. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shi, Z.; Xu, Q.; He, J.; Chen, L.; Lu, Z.; Huan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cui, G. Astragaloside IV alleviates stroke-triggered early brain injury by modulating neuroinflammation and ferroptosis via the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Acta. Cir. Bras. 2023, 38, e380723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Ai, P.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y. Astragaloside IV attenuates ferroptosis after subarachnoid hemorrhage via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 924826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, L.; Liu, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, H.; Lin, Z.; Rao, S.; Sun, W.; Tan, A.; Lin, Y.; Chen, B. Enhanced inhibition of neuronal ferroptosis and regulation of microglial polarization with multifunctional traditional Chinese medicine active ingredients-based selenium nanoparticles for treating spinal cord injury. Mater. Today Bio. 2025, 32, 101758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, M.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Naseem, A.; Algradi, A.M.; Hao, Z.; Guan, W.; Chen, Q.; et al. Saponins from Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge Alleviated Neuronal Ferroptosis in Alzheimer’s Disease by Regulating the NOX4/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 7725–7740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patabendige, A.; Janigro, D. The role of the blood-brain barrier during neurological disease and infection. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2023, 51, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Ma, R.N.; Li, L.H.; Qu, Y.Z.; Gao, G.D. Astragaloside IV reduces cerebral edema post-ischemia/reperfusion correlating the suppression of MMP-9 and AQP4. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 715, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Pan, R.; Jia, X.; Li, Y.; Hou, Z.; Huang, R.Y.; Chen, X.; Huang, S.; Yang, G.Y.; Sun, J.; et al. The combination of astragalus membranaceus and ligustrazine ameliorates micro-haemorrhage by maintaining blood-brain barrier integrity in cerebrally ischaemic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 158 Pt A, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Ma, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, G.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, X.; Cheng, X. Disruption of blood-brain barrier and endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition are attenuated by Astragalus polysaccharides mediated through upregulation of ETS1 expression in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 180, 117521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Wan, G.; Jiang, R.; Zou, L.; Wan, D.; Zhu, H.; Feng, S. Astragalus injection ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced cognitive decline via relieving acute neuroinflammation and BBB damage and upregulating the BDNF-CREB pathway in mice. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 825–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.Y.; Ouyang, H.T.; Yang, J.Y.; Huang, X.L.; Yang, T.; Duan, J.P.; Cheng, J.P.; Chen, Y.X.; Yang, Y.J.; Qiong, P. Subchronic toxicity studies of Radix Astragali extract in rats and dogs. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 110, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.H.; Chen, Z.W.; Pan, Y.W.; Luo, D.M.; Su, Z.R.; Chen, H.M.; Qin, Z.; Huang, S.Q.; Lei, G. Evaluation of safety of modified-Danggui Buxue Tang in rodents:immunological, toxicity and hormonal aspects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 183, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Gao, W. Buyang Huanwu decoction alleviates oxidative injury of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion through PKCε/Nrf2 signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 303, 115953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tang, C. Gut microbiota: A new window for the prevention and treatment of neuropsychiatric disease. J. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Dis. 2025, 17, 11795735251322450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.X.; Li, Y.C.; Su, R.B.; Liu, C.X.; Wen, S.Y. Astragalus injection inhibits the growth of osteosarcoma by activating cytotoxic T lymphocyte and targeting CTSL. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 345, 119607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.D.; Liu, D.N.; Shang, Y.F.; Zhang, W.F.; Xu, S.; Feng, D.H.; Wang, Y.H. Neuroimmune modulators derived from natural products: Mechanisms and potential therapies. Pharmacol. Ther. 2025, 269, 108830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.G.; Lee, H.J.; Asatsuma, T.; Vento-Tormo, R.; Haque, A. An introduction to spatial transcriptomics for biomedical research. Genome. Med. 2022, 14, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Wetzel, I.; Marriott, I.; Dréau, D.; D’Avanzo, C.; Kim, D.Y.; Tanzi, R.E.; Cho, H. A 3D human triculture system modeling neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamek-Gliszczynski, M.J.; Sangha, V.; Shen, H.; Feng, B.; Wittwer, M.B.; Varma, M.V.S.; Liang, X.; Sugiyama, Y.; Zhang, L.; Bendayan, R. Transporters in Drug Development: International Transporter Consortium Update on Emerging Transporters of Clinical Importance. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 112, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Otto, M.; Piehl, F.; Sormani, M.P.; Gattringer, T.; Barro, C.; Kappos, L.; Comabella, M.; Fazekas, F.; et al. Neurofilaments as biomarkers in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Disease | Bioactive Compound | Major Molecular Targets/Pathways | Related Disease Models | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS | AS-IV | PPARγ | tMCAO rat model | [14] |
| EAE | AS-IV | TLR4/Myd88/NF-kB signalling pathway | EAE mice model | [15] |
| CIRI | AS-IV | NLRP3 | MCAO/R rat model | [16] |
| Depression | AS-IV | PPARγ/NF-kB/NLRP3 | RRS-induced mice model of depression | [17] |
| TBI | AS-IV | PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 signaling pathway | a mouse TBI model | [18] |
| Brain death induced by anesthesia | AS-IV | NF-kB, JNK | Rat model induced by isoflurane | [19] |
| ischemia/reperfusion damages | AS-IV | Fas, FasL, Caspase-8, and Bax/Bcl-2 | OGD/R rat model | [20] |
| AD | AS-IV | AMPK/mTOR | MCAO rat model | [21] |
| EBI | AS-IV | Nrf2/HO-1 | MCAO rat model | [22] |
| I/R | AS-IV | MMP-9 and AQP4 | I/R rat model | [23] |
| AIS | APS | P2X7R | MCAO rat model | [24] |
| EAE | APS | ETS1 and BBB | EAE mice model | [25] |
| AD | CAG | P-gp and RAGE | An immortalized endothelial cell line (bEnd.3) | [26] |
| SCI | CA | Hsp90-Akt/ASK1-p38 pathway | The vascular clamp compression SCI model | [27] |
| PD | TFA | SLC7A11/GPX-4 signaling pathway | MPTP/MPP-induced PD mouse model | [28] |
| AD | AST | Fas/Fasl-VDAC1 | AD mouse models induced by Aβ1-42 and Aβ25-35 | [29] |
| AD | AST | PI3K/Akt-mTOR-mediated autophagy | APP/PS1 mice | [30] |
| Product Category | Representative Product | Health Claims & Potential Benefits | Proposed Mechanisms & Scientific Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid Products | A. membranaceus Chicken Soup (with black-boned chicken, goji berries) | Alleviates fatigue, improves sub-health (e.g., qi and blood deficiency), and may support appetite in chronic conditions (e.g., PD). | Nourishes qi and blood in TCM theory. Modern research suggests AM’s active compounds (e.g., AS-IV, APS) may combat fatigue and modulate energy metabolism. The formulation provides easily absorbable nutrients. |
| Semi-Liquid Products | A. membranaceus Porridge (with Japonica rice) | Aids post-illness/surgery recovery, may help alleviate symptoms like memory loss in AD patients with spleen-kidney deficiency. | Easy to digest and absorb. A. membranaceus fortifies the spleen and kidney in TCM, which are considered fundamental to cognitive function. Provides stable energy release. |
| Solid Products | A. membranaceus Health Biscuits | Provides convenient nutritional support, enhances physical well-being for patients with CNS disorders. | Portable and palatable. Offers a functional snack option. The potential systemic anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of A. membranaceus may indirectly support brain health. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sang, J.; Gao, J.; Zuo, H.; Yu, H.; Qin, Y.; Hu, J.; Hao, F. Exploring the Neuroprotective Potential of Astragalus membranaceus in Central Nervous System Diseases. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121671
Sang J, Gao J, Zuo H, Yu H, Qin Y, Hu J, Hao F. Exploring the Neuroprotective Potential of Astragalus membranaceus in Central Nervous System Diseases. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(12):1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121671
Chicago/Turabian StyleSang, Jiajia, Jialin Gao, Hui Zuo, Haolu Yu, Yuqi Qin, Jun Hu, and Feng Hao. 2025. "Exploring the Neuroprotective Potential of Astragalus membranaceus in Central Nervous System Diseases" Biomolecules 15, no. 12: 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121671
APA StyleSang, J., Gao, J., Zuo, H., Yu, H., Qin, Y., Hu, J., & Hao, F. (2025). Exploring the Neuroprotective Potential of Astragalus membranaceus in Central Nervous System Diseases. Biomolecules, 15(12), 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121671







