Incretin-Related Pathology and Serum Exosome Detection in Experimental Alcohol-Related Brain Damage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Model
2.2. Tissue Homogenization for Immunoassays
2.3. Serum Exosome Isolation
2.4. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
2.5. Multiplex Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays (ELISAs)
2.6. Duplex ELISA
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Rat Model Characteristics
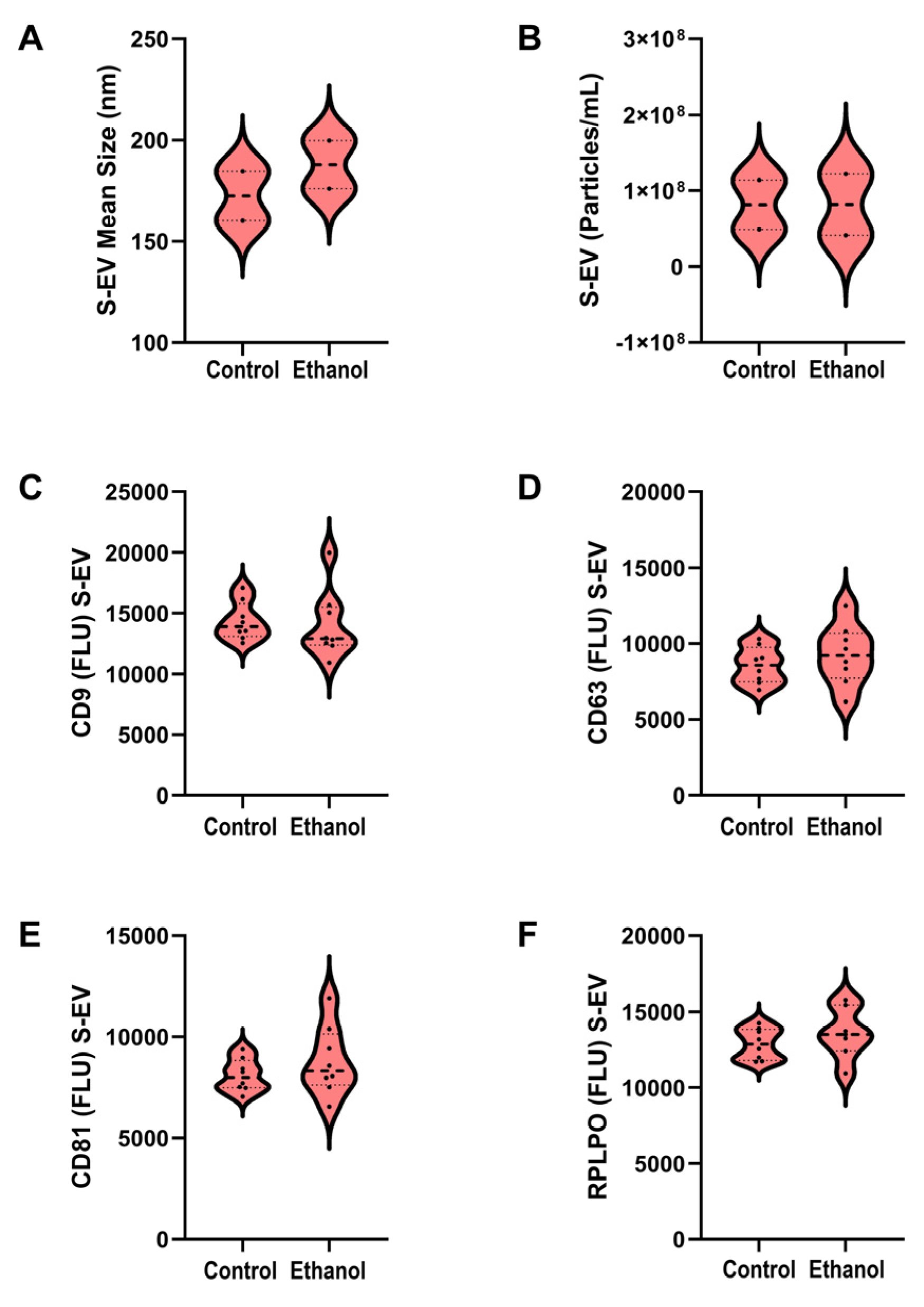
3.2. S-EV Characteristics
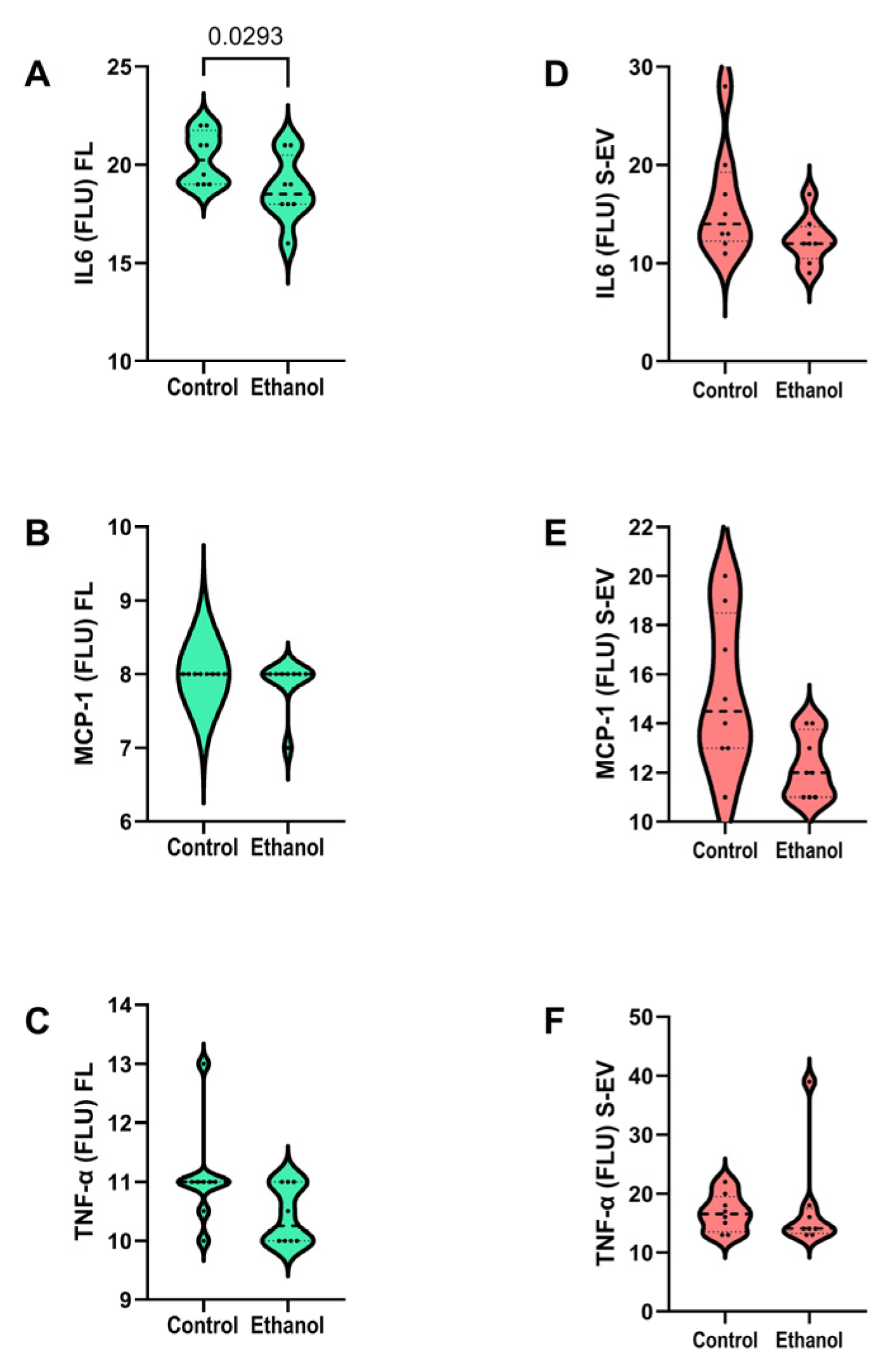
3.3. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
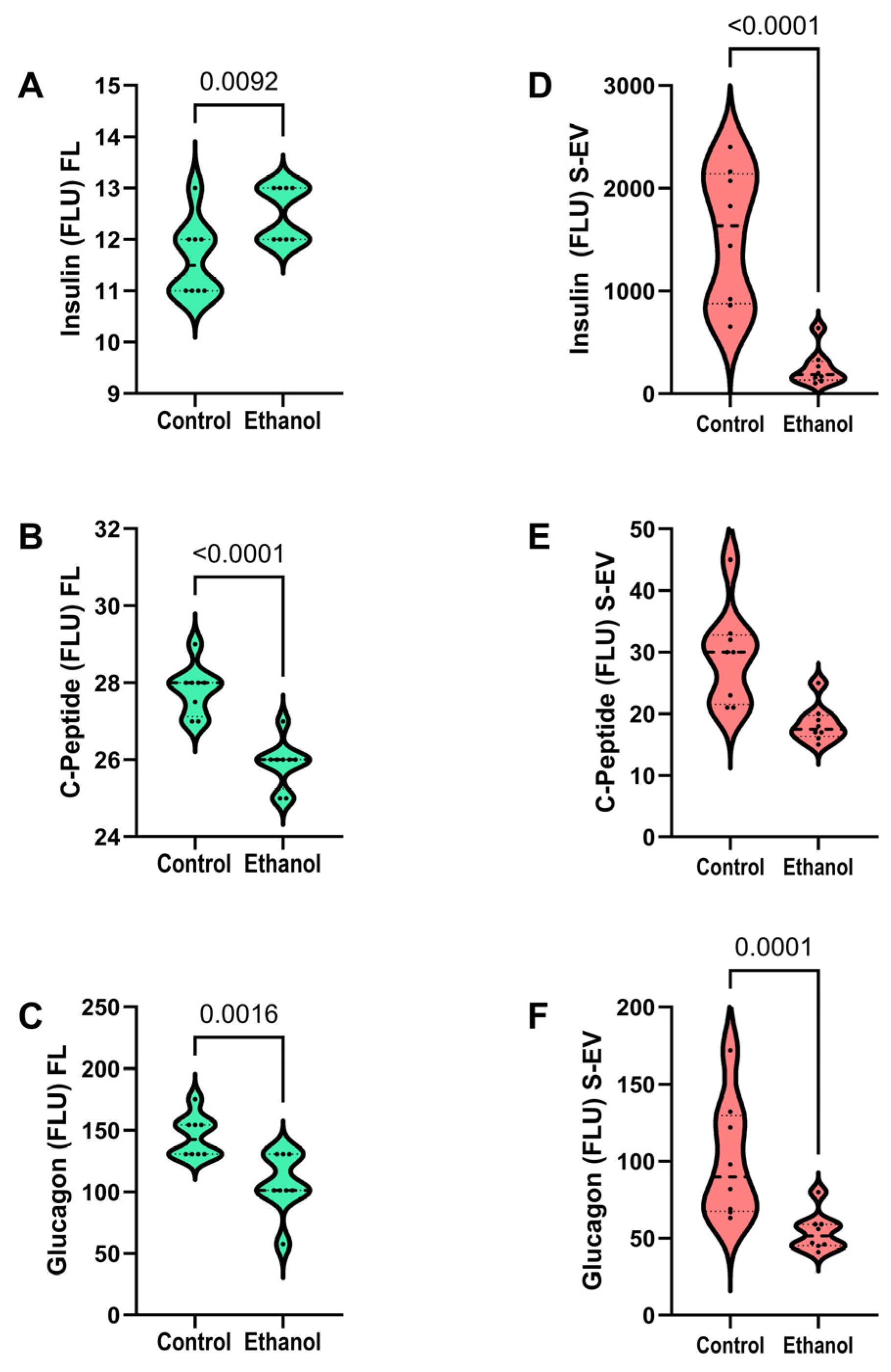
3.4. Insulin, C-Peptide, and Glucagon
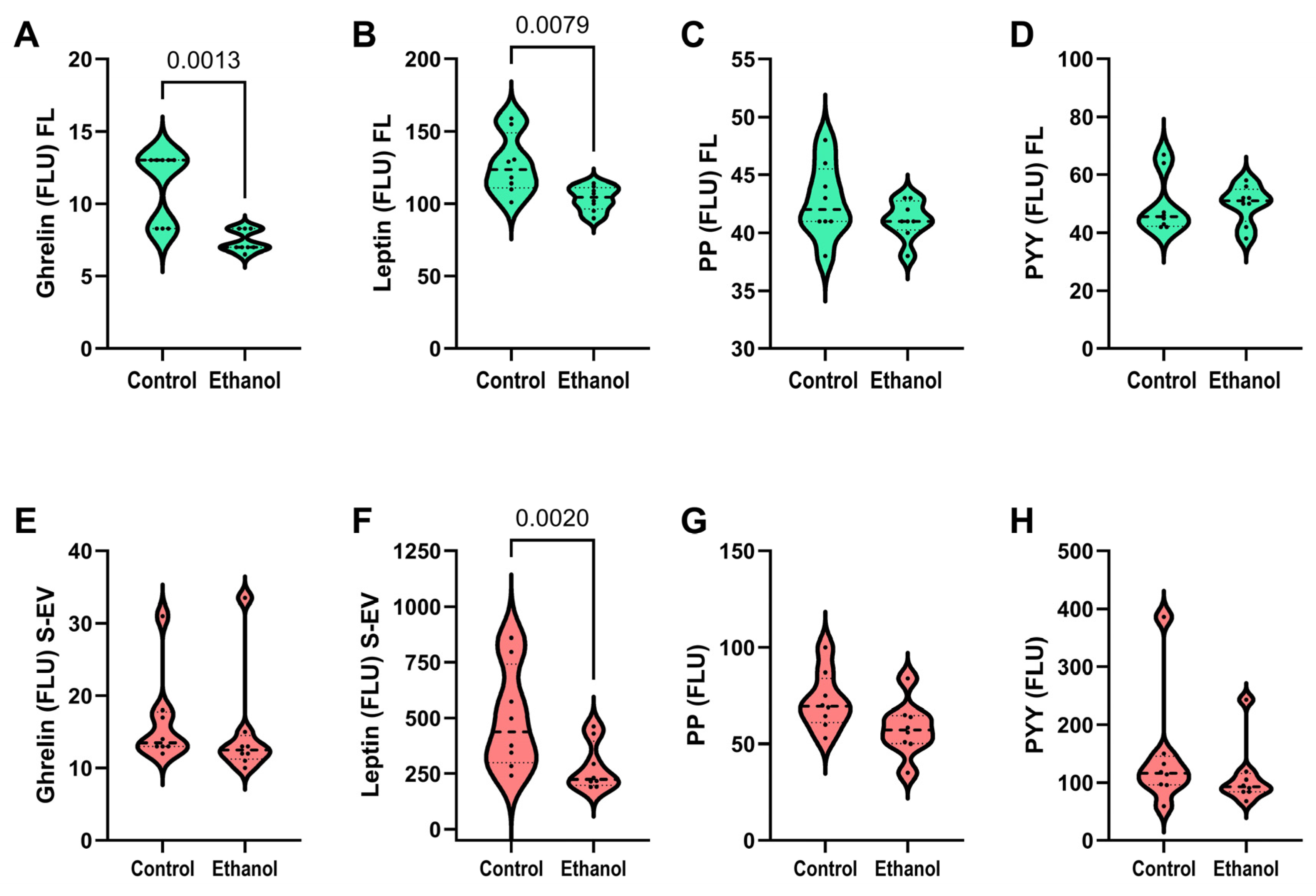
3.5. Ghrelin, Leptin, and Pancreatic Polypeptides
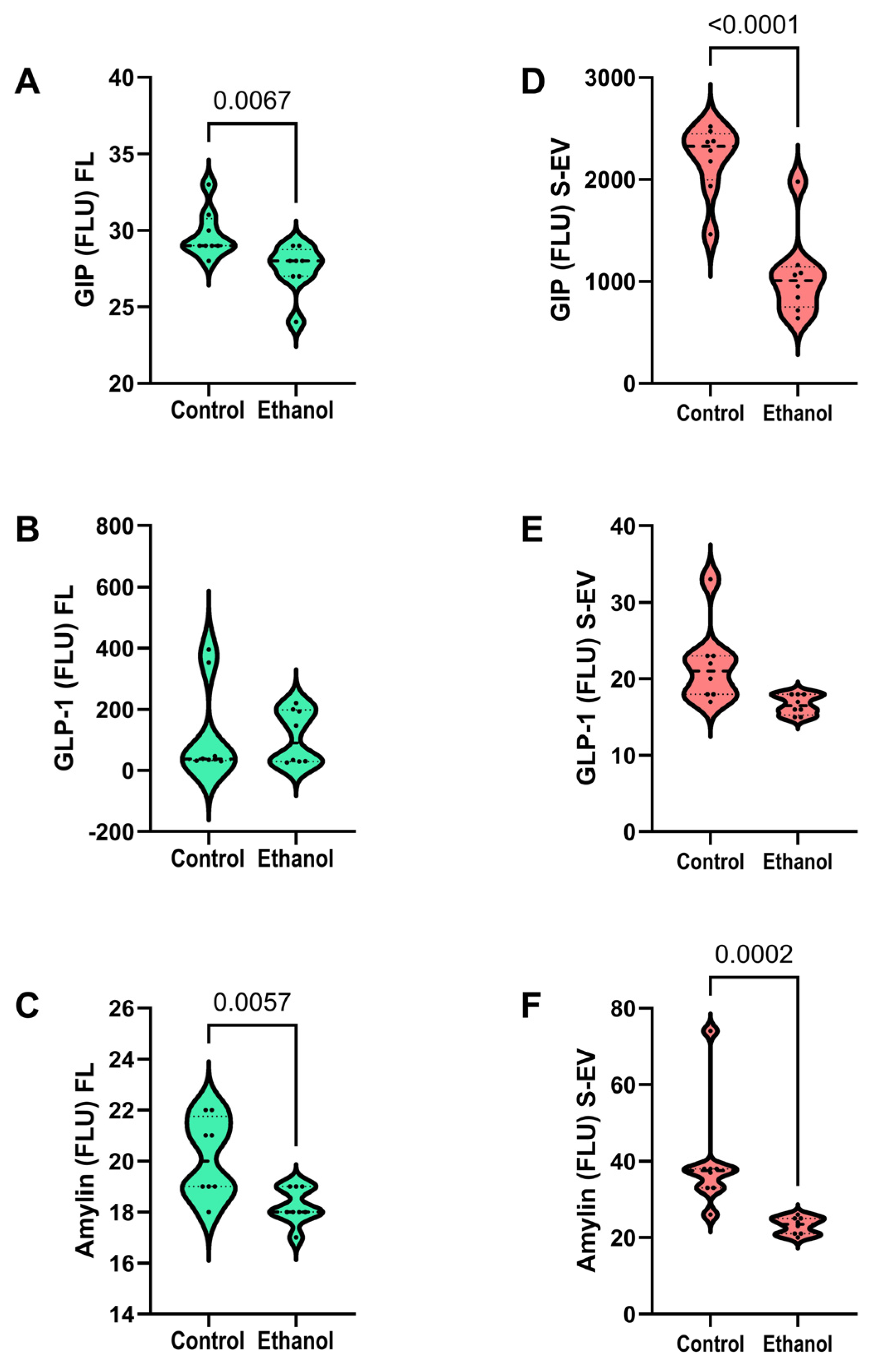
3.6. Incretin Network Cluster
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GIP | Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like peptide 1 |
| PP | Pancreatic polypeptide |
| PYY | Peptide YY/Neuropeptide Y |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| CD9 | Tetraspanin-29 |
| CD63 | Tetraspanin-30 |
| CD81 | Tetraspanin-28 |
| HSP70 | Heat shock protein 70 |
References
- de la Monte, S.M. Disproportionate atrophy of cerebral white matter in chronic alcoholics. Arch. Neurol. 1988, 45, 990–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Monte, S.M.; Kril, J.J. Human alcohol-related neuropathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 127, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kril, J.J.; Gundlach, A.L.; Dodd, P.R.; Johnston, G.A.; Harper, C.G. Cortical dihydropyridine binding sites are unaltered in human alcoholic brain. Ann. Neurol. 1989, 26, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kril, J.J.; Halliday, G.M. Brain shrinkage in alcoholics: A decade on and what have we learned? Prog. Neurobiol. 1999, 58, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, C.G.; Kril, J.J.; Holloway, R.L. Brain shrinkage in chronic alcoholics: A pathological study. Br. Med. J. (Clin. Res. Ed.) 1985, 290, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Monte, S.M.; Sutherland, G. Dual Stages of Alcohol-Related Cerebral White Matter Degeneration Reviewed: Early-Stage Stress/Neuroinflammation Versus Late-Stage Impaired Insulin/IGF Signaling Through Akt-mTOR-Review. ASN Neuro 2025, 17, 2573965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estruch, R.; Nicolas, J.M.; Salamero, M.; Aragon, C.; Sacanella, E.; Fernandez-Sola, J.; Urbano-Marquez, A. Atrophy of the corpus callosum in chronic alcoholism. J. Neurol. Sci. 1997, 146, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfefferbaum, A.; Adalsteinsson, E.; Sullivan, E.V. Dysmorphology and microstructural degradation of the corpus callosum: Interaction of age and alcoholism. Neurobiol. Aging 2006, 27, 994–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfefferbaum, A.; Lim, K.O.; Desmond, J.E.; Sullivan, E.V. Thinning of the corpus callosum in older alcoholic men: A magnetic resonance imaging study. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1996, 20, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, T.; Sullivan, E.V.; Muller-Oehring, E.M.; Adalsteinsson, E.; Pfefferbaum, A. Corpus callosal microstructural integrity influences interhemispheric processing: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Cereb. Cortex 2005, 15, 1384–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.S.; Gallo, J.L.; Ferri, C.; Giovannetti, T.; Sestito, N.; Libon, D.J.; Schmidt, P.S. The neuropsychological profile of alcohol-related dementia suggests cortical and subcortical pathology. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2005, 20, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elofson, J.; Gongvatana, W.; Carey, K.B. Alcohol use and cerebral white matter compromise in adolescence. Addict. Behav. 2013, 38, 2295–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobus, J.; Squeglia, L.M.; Bava, S.; Tapert, S.F. White matter characterization of adolescent binge drinking with and without co-occurring marijuana use: A 3-year investigation. Psychiatry Res. 2013, 214, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.C.; Tong, M.; Wands, J.R.; de la Monte, S.M. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor resistance with neurodegeneration in an adult chronic ethanol exposure model. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2007, 31, 1558–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Monte, S.M. Alcohol-Related Liver Disease: Roles of Insulin Resistance, Lipotoxic Ceramide Accumulation, and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. In Alcohol, Nutrition, and Health Consequences; Watson, R.R., Preedy, V.R., Zibadi, S., Eds.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 507–522. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, M.; Yu, R.; Deochand, C.; de la Monte, S.M. Differential Contributions of Alcohol and the Nicotine-Derived Nitrosamine Ketone (NNK) to Insulin and Insulin-Like Growth Factor Resistance in the Adolescent Rat Brain. Alcohol Alcohol. 2015, 50, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Monte, S.M.; Tong, M.; Cohen, A.C.; Sheedy, D.; Harper, C.; Wands, J.R. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor resistance in alcoholic neurodegeneration. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2008, 32, 1630–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corl, A.B.; Rodan, A.R.; Heberlein, U. Insulin signaling in the nervous system regulates ethanol intoxication in Drosophila melanogaster. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 18–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindtner, C.; Scherer, T.; Zielinski, E.; Filatova, N.; Fasshauer, M.; Tonks, N.K.; Puchowicz, M.; Buettner, C. Binge drinking induces whole-body insulin resistance by impairing hypothalamic insulin action. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 170ra14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, C.; Kril, J. An introduction to alcohol-induced brain damage and its causes. Alcohol Alcohol. Suppl. 1994, 2, 237–243. [Google Scholar]
- de la Monte, S.; Derdak, Z.; Wands, J.R. Alcohol, insulin resistance and the liver-brain axis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27 (Suppl. S2), 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.A.; Le, T.; Tong, M.; Silbermann, E.; Gundogan, F.; de la Monte, S.M. Impaired insulin/IGF signaling in experimental alcohol-related myopathy. Nutrients 2012, 4, 1058–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resnicoff, M.; Rubini, M.; Baserga, R.; Rubin, R. Ethanol inhibits insulin-like growth factor-1-mediated signalling and proliferation of C6 rat glioblastoma cells. Lab. Investig. 1994, 71, 657–662. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, C.J.; Flatt, P.R.; Conlon, J.M. Multifunctional incretin peptides in therapies for type 2 diabetes, obesity and associated co-morbidities. Peptides 2025, 187, 171380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggio, L.L.; Drucker, D.J. Biology of incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2131–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.; Patterson-Cross, R.; Woodward, O.; Lewis, J.; Chiarugi, D.; Merkle, F.; Gribble, F.; Reimann, F.; Adriaenssens, A. A comparative transcriptomic analysis of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor- and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor-expressing cells in the hypothalamus. Appetite 2022, 174, 106022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Monte, S.M. Conquering Insulin Network Dysfunctions in Alzheimer’s Disease: Where Are We Today? J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2024, 101, S317–S343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fessel, J. All GLP-1 Agonists Should, Theoretically, Cure Alzheimer’s Dementia but Dulaglutide Might Be More Effective Than the Others. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonthius, D.J.; Karacay, B.; Dai, D.; Pantazis, N.J. FGF-2, NGF and IGF-1, but not BDNF, utilize a nitric oxide pathway to signal neurotrophic and neuroprotective effects against alcohol toxicity in cerebellar granule cell cultures. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 2003, 140, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerlhag, E. Ghrelin system and GLP-1 as potential treatment targets for alcohol use disorder. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2024, 178, 401–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerlhag, E. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Promising Therapeutic Targets for Alcohol Use Disorder. Endocrinology 2025, 166, bqaf028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klausen, M.K.; Knudsen, G.M.; Vilsboll, T.; Fink-Jensen, A. Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Alcohol Use Disorder. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2025, 136, e70004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, R.S.; Rasgon, N.; Goldberg, J.; Wong, S.; Le, G.H.; Mansur, R.B.; Rosenblat, J.D.; Teopiz, K.M.; Stahl, S.M. The effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 and glucose dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor agonists on neurogenesis, differentiation, and plasticity (Neuro-GDP): Potential mechanistically informed therapeutics in the treatment and prevention of mental disorders. CNS Spectr. 2025, 30, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, J.H.; Franco, W.G.; O’Keefe, E.L. Anti-consumption agents: Tirzepatide and semaglutide for treating obesity-related diseases and addictions, and improving life expectancy. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2025, 89, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wu, K.J.; Yu, S.J.; Tamargo, I.A.; Wang, Y.; Greig, N.H. Neurotrophic and neuroprotective effects of oxyntomodulin in neuronal cells and a rat model of stroke. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 288, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wijerathne, H.; Godwin, A.K.; Soper, S.A. Isolation and analysis methods of extracellular vesicles (EVs). Extracell. Vesicles Circ. Nucl. Acids 2021, 2, 80–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, S.; Miras, M.C.M.; Pappolla, A.; Montalban, X.; Comabella, M. Liquid Biopsy in Neurological Diseases. Cells 2023, 12, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, Q.; Wu, L.; Pang, D.; Jiang, P. Exosomes in brain diseases: Pathogenesis and therapeutic targets. MedComm 2023, 4, e287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, C.; Liu, K. A new diagnostic tool for brain disorders: Extracellular vesicles derived from neuron, astrocyte, and oligodendrocyte. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1194210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Iqbal, Z.; Xu, L.; Wen, C.; Duan, L.; Xia, J.; Yang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, Y. Brain-derived extracellular vesicles: Potential diagnostic biomarkers for central nervous system diseases. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2023, 78, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de La Monte, S.M.; Yang, Y.; Tong, M. Brain and Serum Membrane Vesicle (Exosome) Profiles in Experimental Alcohol-Related Brain Degeneration: Forging the Path to Non-Invasive Liquid Biopsy Diagnostics. J. Mol. Pathol. 2024, 5, 360–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, E.B.; Tong, M.; Delikkaya, B.; Pelit, W.; Yang, Y.; de la Monte, S.M. Differential effects of moderate chronic ethanol consumption on neurobehavior, white matter glial protein expression, and mTOR pathway signaling with adolescent brain maturation. Am. J. Drug Alcohol. Abus. 2024, 50, 492–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Homans, C.; Pelit, W.; Delikkaya, B.; de la Monte, S.M. Progressive Alcohol-Related Brain Atrophy and White Matter Pathology Are Linked to Long-Term Inhibitory Effects on mTOR Signaling. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DaDalt, A.A.; Bonham, C.A.; Lotze, G.P.; Luiso, A.A.; Vacratsis, P.O. Src-mediated phosphorylation of the ribosome biogenesis factor hYVH1 affects its localization, promoting partitioning to the 60S ribosomal subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltanmohammadi, F.; Maghsoodi, M.; Alizadeh, E.; Adibkia, K.; Azarmi, Y.; Mahmoudi Gharehbaba, A.; Javadzadeh, Y. Bio fluid exosomes: Promises, challenges, and future directions in translational medicine. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Tong, M.; de la Monte, S.M. Early-Stage Moderate Alcohol Feeding Dysregulates Insulin-Related Metabolic Hormone Expression in the Brain: Potential Links to Neurodegeneration Including Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Rep. 2024, 8, 1211–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourgognon, J.M.; Cavanagh, J. The role of cytokines in modulating learning and memory and brain plasticity. Brain Neurosci. Adv. 2020, 4, 2398212820979802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorski, R.; Galiniak, S.; Mazur, A.; Domin, A.; Podgorska, D. Serum levels of leptin, ghrelin putative peptide YY-3 in patients with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinjyo, N.; Kita, K. Infection and Immunometabolism in the Central Nervous System: A Possible Mechanistic Link Between Metabolic Imbalance and Dementia. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2021, 15, 765217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrenho, D.; Santos, S.D.; Carvalho, A.L. The Role of Ghrelin in Regulating Synaptic Function and Plasticity of Feeding-Associated Circuits. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea Vega, M.L.; Sanchez, M.S.; Fernandez, G.; Paglini, M.G.; Martin, M.; de Barioglio, S.R. Ghrelin treatment leads to dendritic spine remodeling in hippocampal neurons and increases the expression of specific BDNF-mRNA species. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2021, 179, 107409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morissette, A.; Mulvihill, E.E. Obesity management for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: Emerging evidence and therapeutic approaches. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 27, 13065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panou, T.; Gouveri, E.; Popovic, D.S.; Papanas, N. Amylin analogs for the treatment of obesity without diabetes: Present and future. Expert. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2024, 17, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volcansek, S.; Koceva, A.; Jensterle, M.; Janez, A.; Muzurovic, E. Amylin: From Mode of Action to Future Clinical Potential in Diabetes and Obesity. Diabetes Ther. 2025, 16, 1207–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| 2-Week Model | Control | Ethanol | t-Test (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| # Rats (Male/Female) | 8 (4/4) | 8 (4/4) | |
| Body Weight (g) | 182.9 ± 22.72 | 170.6 ± 17.13 | N.S. |
| Blood Alcohol (mg/dL) | 25.76 ± 4.5 | 108.4 ± 11.2 | <0.0001 |
| Blood Glucose (mg/dL) | 194.6 ± 18.17 | 192.4 ± 28.99 | N.S. |
| Brain Weight (g) | 1.708 ± 0.08 | 1.702 ± 0.05 | N.S. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de la Monte, S.M.; Tong, M.; Yang, Y. Incretin-Related Pathology and Serum Exosome Detection in Experimental Alcohol-Related Brain Damage. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121670
de la Monte SM, Tong M, Yang Y. Incretin-Related Pathology and Serum Exosome Detection in Experimental Alcohol-Related Brain Damage. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(12):1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121670
Chicago/Turabian Stylede la Monte, Suzanne M., Ming Tong, and Yiwen Yang. 2025. "Incretin-Related Pathology and Serum Exosome Detection in Experimental Alcohol-Related Brain Damage" Biomolecules 15, no. 12: 1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121670
APA Stylede la Monte, S. M., Tong, M., & Yang, Y. (2025). Incretin-Related Pathology and Serum Exosome Detection in Experimental Alcohol-Related Brain Damage. Biomolecules, 15(12), 1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121670






