Function and Mechanism of Small Nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) and Their Host Genes (SNHGs) in Malignant Tumors
Abstract
1. Background
1.1. Classification, Biogenesis, and Non-Canonical Roles of snoRNAs
1.2. Biogenesis and Function of sdRNAs
1.2.1. Biogenesis of sdRNAs Associating with Argonaute 2 (AGO2)
1.2.2. Biogenesis of PIWI-Associated RNA (piRNA)-like sdRNAs
1.3. A Compendium of Common Human Small Nucleolar RNAs
2. In-Depth Elaboration on Key Examples
2.1. Functions of snoRNAs and SNHGs in Various Types of Malignancies
2.1.1. Neurologic Malignancies
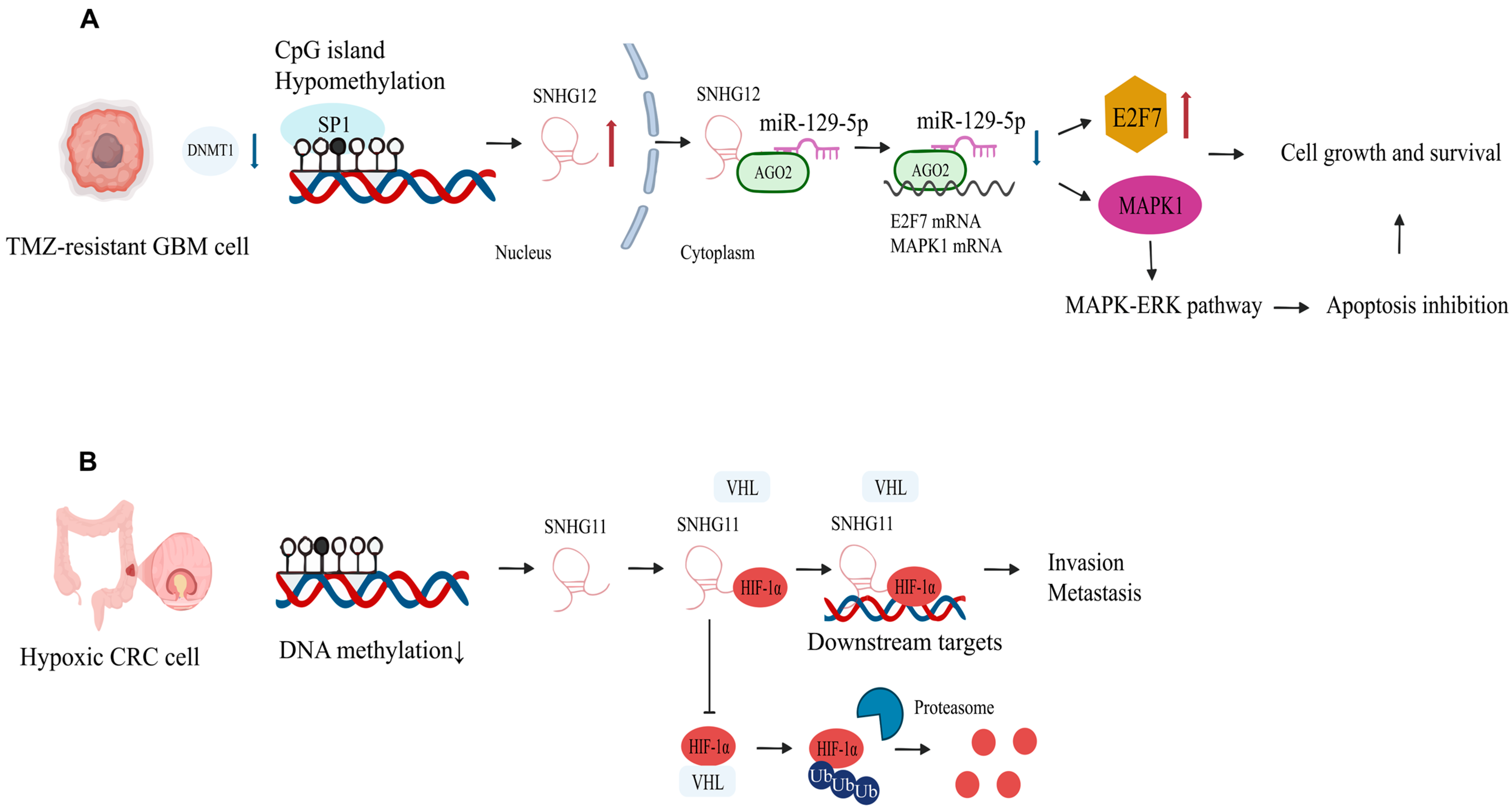
- Glioblastoma
- 2.
- Neuroblastoma
2.1.2. Bone Malignancies
2.1.3. Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC)
2.1.4. Digestive System Malignancies
- Esophageal cancer
- 2.
- Gastric cancer
- 3.
- Colorectal cancer
- 4.
- Liver malignancies
- 5.
- Pancreatic cancer
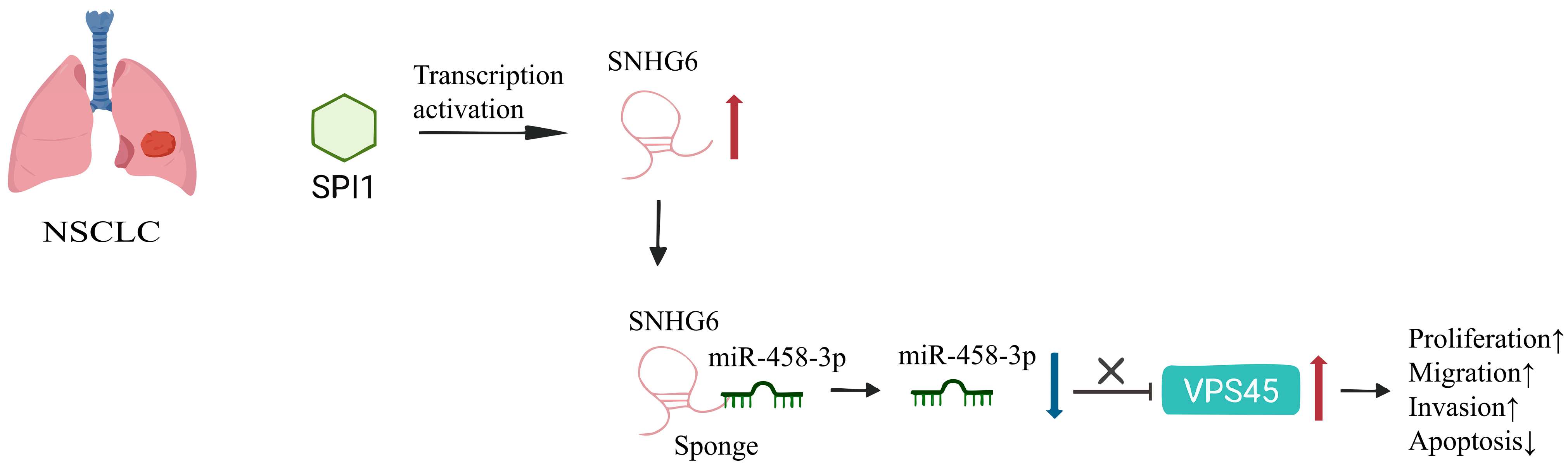
2.1.5. Lung Cancer
2.1.6. Breast Cancer
2.1.7. Urinary System Malignancies
- Bladder cancer
- 2.
- Renal cell carcinoma
- 3.
- Prostate cancer
2.1.8. Gynecological Malignancies
- Cervical cancer
- 2.
- Endometrial cancer
- 3.
- Ovarian cancer
2.1.9. Hematological Malignancies
Hallmarks of snoRNA-Mediated Cancer Regulation
3. Mechanisms of snoRNAs and SNHGs
- (I)
- ceRNA Regulatory Network (Figure 1)
- (II)
- Epigenetic regulation (Figure 2)
- (III)
- Exosome-mediated intercellular communication (Figure 3)
- (IV)
- Ribosomal RNA modification and translational regulation (Figure 4)
4. Clinical Application Potential of snoRNAs and SNHGs
- (I)
- Diagnostic and prognostic markers
- (II)
- Therapeutic targets
5. Summary and Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, J.; Li, G.; Liao, J.; Huang, Z.; Wen, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Cai, G.; Xu, W.; Ding, Z.; et al. Non-coding small nucleolar RNA SNORD17 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through a positive feedback loop upon p53 inactivation. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 988–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.H.; Du, Y.P.; Wen, J.T.; Lu, B.F.; Zhao, Y. snoRNAs: Functions and mechanisms in biological processes, and roles in tumor pathophysiology. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporali, A.; Emanueli, C. Unraveling the epitranscriptome of small non-coding RNAs in vascular cells. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2022, 30, 477–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorjani, H.; Kehr, S.; Jedlinski, D.J.; Gumienny, R.; Hertel, J.; Stadler, P.F.; Zavolan, M.; Gruber, A.R. An updated human snoRNAome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 5068–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.Z.; Wu, Z.; Chen, W.J.; Fang, Z.X.; Yu, X.N.; Wu, H.T.; Liu, J. Small nucleolar RNA and its potential role in the oncogenesis and development of colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, P.; Darzacq, X.; Bertrand, E.; Jády, B.E.; Verheggen, C.; Kiss, T. A common sequence motif determines the Cajal body-specific localization of box H/ACA scaRNAs. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 4283–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, U.T. RNA modification in Cajal bodies. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tycowski, K.T.; Shu, M.D.; Steitz, J.A. A mammalian gene with introns instead of exons generating stable RNA products. Nature 1996, 379, 464–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.M.; Steitz, J.A. Classification of gas5 as a multi-small-nucleolar-RNA (snoRNA) host gene and a member of the 5′-terminal oligopyrimidine gene family reveals common features of snoRNA host genes. Mol. Cell Biol. 1998, 18, 6897–6909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, G.T.; Farzaneh, F. Are snoRNAs and snoRNA host genes new players in cancer? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Sun, W.; Wang, Z.; Dong, W.; He, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, H. Long Non-Coding Small Nucleolar RNA Host Genes (SNHGs) in Endocrine-Related Cancers. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 7699–7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens-Uzunova, E.S.; Olvedy, M.; Jenster, G. Beyond microRNA--novel RNAs derived from small non-coding RNA and their implication in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013, 340, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coley, A.B.; DeMeis, J.D.; Chaudhary, N.Y.; Borchert, G.M. Small Nucleolar Derived RNAs as Regulators of Human Cancer. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Ruan, X.; Liu, L.; Xue, Y.; Ma, T.; E, T.; Wang, D.; Yang, C.; et al. U3 snoRNA-mediated degradation of ZBTB7A regulates aerobic glycolysis in isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 wild-type glioblastoma cells. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 2811–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Chen, G.; Yu, B.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Cheng, S.Y.; Li, Y.; et al. TRIM24 Cooperates with Ras Mutation to Drive Glioma Progression through snoRNA Recruitment of PHAX and DNA-PKcs. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2400023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Wei, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, J.; Li, W.; Chen, L.; Lyu, X.; Shi, Z.; Yan, W.; et al. DNA-methylation-mediated activating of lncRNA SNHG12 promotes temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Zhao, G.; Yang, H.; Wang, J. Long non-coding RNA SNHG7 promotes neuroblastoma progression through sponging miR-323a-5p and miR-342-5p. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, D.; Sun, H.; Liu, X. SNHG16 promotes tumorigenesis and cisplatin resistance by regulating miR-338-3p/PLK4 pathway in neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, F.F.; Shi, D.Y.; Chen, T.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhong, B.L.; Zhang, Z.C.; Liu, W.J.; Wu, Q.; Wang, B.C.; Shao, Z.W.; et al. SP1-induced long non-coding RNA SNHG6 facilitates the carcinogenesis of chondrosarcoma through inhibiting KLF6 by recruiting EZH2. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Cai, H.; Hong, Y.; Yao, M.; Ye, W.; Li, W.; Liang, W.; Feng, S.; Lv, Y.; Ye, H.; et al. Implications of m(5)C modifications in ribosomal proteins on oxidative stress, metabolic reprogramming, and immune responses in patients with mid-to-late-stage head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Insights from nanopore sequencing. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; He, X.; Wang, W.; Hu, X.; Wang, K.; Wang, M. Long noncoding RNA SNHG12 induces proliferation, migration, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and stemness of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells via post-transcriptional regulation of BMI1 and CTNNB1. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 2332–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Shi, L.; Zhao, H.; Huang, C. LncRNA SNHG17 regulates cell proliferation and invasion by targeting miR-338-3p/SOX4 axis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Beeharry, M.K.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Li, J.; Li, C. YY1-modulated long non-coding RNA SNHG12 promotes gastric cancer metastasis by activating the miR-218-5p/YWHAZ axis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 1629–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Guo, C.; Cao, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lv, S. Gastric cancer cell-derived extracellular vesicles elevate E2F7 expression and activate the MAPK/ERK signaling to promote peritoneal metastasis through the delivery of SNHG12. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Ji, T.; Liu, A.; Weng, Y. ELK4-mediated lncRNA SNHG22 promotes gastric cancer progression through interacting with EZH2 and regulating miR-200c-3p/Notch1 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Lin, C.; Lu, W.; He, J.; Wang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Z. Involvement of the oncogenic small nucleolar RNA SNORA24 in regulation of p53 stability in colorectal cancer. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2023, 39, 1377–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Tang, D.; Li, M.; Zhao, P.; Yang, W.; Shu, L.; Wang, J.; He, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. SNHG17 promotes the proliferation and migration of colorectal adenocarcinoma cells by modulating CXCL12-mediated angiogenesis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Zhou, M.; Cui, K.; Yang, F.; Cao, Y.; Sun, S.; Liu, B.; Gong, L.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; et al. SNHG17 promotes colorectal tumorigenesis and metastasis via regulating Trim23-PES1 axis and miR-339-5p-FOSL2-SNHG17 positive feedback loop. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, L.; Liu, P.; Li, K.; Zhang, Z.; He, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, P.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Z.; et al. The C/D box small nucleolar RNA SNORD52 regulated by Upf1 facilitates Hepatocarcinogenesis by stabilizing CDK1. Theranostics 2020, 10, 9348–9363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, S.; Shen, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Yu, J.; Huang, L.; Liu, N.; Lu, H.; Xu, M. SNHG1, interacting with SND1, contributes to sorafenib resistance of liver cancer cells by increasing m6A-mediated SLC7A11 expression and promoting aerobic glycolysis. Environ. Toxicol. 2024, 39, 1269–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Chen, H.; Li, H.Y.; Chen, R.; He, L.; Yang, J.L.; Xiao, L.L.; Chen, J.L. Long non-coding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 6 aggravates pancreatic cancer through upregulation of far upstream element binding protein 1 by sponging microRNA-26a-5p. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Yao, W.; Zhu, N.; Miao, R.; Liu, Z.; Song, X.; Xue, C.; Cai, C.; Cheng, M.; et al. RRP9 promotes gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer via activating AKT signaling pathway. Cell Commun. Signal 2022, 20, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Liu, Y.; Gerloff, D.; Rohde, C.; Pauli, C.; Köhn, M.; Misiak, D.; Oellerich, T.; Schwartz, S.; Schmidt, L.H.; et al. NOP10 predicts lung cancer prognosis and its associated small nucleolar RNAs drive proliferation and migration. Oncogene 2021, 40, 909–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, N.; Wang, L.; Wei, B.; Chen, J.; Gao, Y. lncRNA SNHG11 promotes lung cancer cell proliferation and migration via activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 7541–7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, P. Long non-coding RNA SNHG22 facilitates the malignant phenotypes in triple-negative breast cancer via sponging miR-324-3p and upregulating SUDS3. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Feng, C.; Wang, S.; Shi, L.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Lan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Qiang, W.; Ji, M.; et al. The noncoding RNAs SNORD50A and SNORD50B-mediated TRIM21-GMPS interaction promotes the growth of p53 wild-type breast cancers by degrading p53. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 2450–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, D.G.; Roberts, J.T.; King, V.M.; Houserova, D.; Barnhill, E.C.; Crucello, A.; Polska, C.J.; Brantley, L.W.; Kaufman, G.C.; Nguyen, M.; et al. Human snoRNA-93 is processed into a microRNA-like RNA that promotes breast cancer cell invasion. npj Breast Cancer 2017, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Pan, Q.; Gong, H.; Zhai, X.; Wan, Z.; Ge, M.; Gu, J.; Zhang, D.; Chen, X.; Xu, D. Super-enhancer-associated SNHG15 cooperating with FOSL1 contributes to bladder cancer progression through the WNT pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 197, 106940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, M.; Sun, N.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, P.; Hu, Y.; Wu, S.; Zheng, Z.; Lu, Y.; Jin, H. SNHG18 inhibits bladder cancer cell proliferation by increasing p21 transcription through destabilizing c-Myc protein. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liu, T.; Sun, L.; Zhang, S.; Dong, G. Long noncoding RNA SNHG4 promotes renal cell carcinoma tumorigenesis and invasion by acting as ceRNA to sponge miR-204-5p and upregulate RUNX2. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Deng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Guo, Q.; Zhou, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, C. Long noncoding RNA SNHG6 promotes carcinogenesis by enhancing YBX1-mediated translation of HIF1α in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Duan, Y.; Wang, P. SP1-mediated upregulation of lncRNA SNHG4 functions as a ceRNA for miR-377 to facilitate prostate cancer progression through regulation of ZIC5. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 3916–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Sun, G.; Liu, C. Long non-coding RNA SNHG6 regulates the sensitivity of prostate cancer cells to paclitaxel by sponging miR-186. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coley, A.B.; Stahly, A.N.; Kasukurthi, M.V.; Barchie, A.A.; Hutcheson, S.B.; Houserova, D.; Huang, Y.; Watters, B.C.; King, V.M.; Dean, M.A.; et al. MicroRNA-like snoRNA-Derived RNAs (sdRNAs) Promote Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cells 2022, 11, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xie, B.; Chen, X.; Lu, B.; Chen, S.; Sheng, X.; Zhao, Y. SNORD6 promotes cervical cancer progression by accelerating E6-mediated p53 degradation. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Li, R. LncRNA SNHG6 enhances the radioresistance and promotes the growth of cervical cancer cells by sponging miR-485-3p. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Qin, H.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y. C/D box small nucleolar RNA SNORD104 promotes endometrial cancer by regulating the 2′-O-methylation of PARP1. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Xu, S.; Qi, Y.; Tian, J.; Xu, F. Long noncoding RNA SNHG25 promotes the malignancy of endometrial cancer by sponging microRNA-497-5p and increasing FASN expression. J. Ovarian Res. 2021, 14, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Shen, L.; Lin, Q.; Dong, C.; Maswela, B.; Illahi, G.S.; Wu, X. SNHG5 enhances Paclitaxel sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells through sponging miR-23a. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 123, 109711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, W.; Jia, Y.; Wang, J.; Duan, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Hao, S.; Liu, L. Long non-coding RNA SNHG10 upregulates BIN1 to suppress the tumorigenesis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of epithelial ovarian cancer via sponging miR-200a-3p. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, C.; Liu, Y.; Rohde, C.; Cui, C.; Fijalkowska, D.; Gerloff, D.; Walter, C.; Krijgsveld, J.; Dugas, M.; Edemir, B.; et al. Site-specific methylation of 18S ribosomal RNA by SNORD42A is required for acute myeloid leukemia cell proliferation. Blood 2020, 135, 2059–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gao, Q.; Wang, M.; Xin, H. LncRNA SNHG1 contributes to the regulation of acute myeloid leukemia cell growth by modulating miR-489-3p/SOX12/Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J. Cell Physiol. 2021, 236, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Xia, S.; Xiao, F.; Peng, J.; Gao, Y.; Yu, F.; Wang, C.; Chen, X. The emerging role of snoRNAs in human disease. Genes. Dis. 2023, 10, 2064–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falaleeva, M.; Welden, J.R.; Duncan, M.J.; Stamm, S. C/D-box snoRNAs form methylating and non-methylating ribonucleoprotein complexes: Old dogs show new tricks. Bioessays 2017, 39, 1600264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, W.; Sudharshan, S.; Kafle, S.; Zennadi, R. SnoRNAs: Exploring Their Implication in Human Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massenet, S.; Bertrand, E.; Verheggen, C. Assembly and trafficking of box C/D and H/ACA snoRNPs. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godang, N.L.; DeMeis, J.D.; Houserova, D.; Chaudhary, N.Y.; Salter, C.J.; Xi, Y.; McDonald, O.G.; Borchert, G.M. Global Switch from DICER-dependent MicroRNA to DICER-independent SnoRNA-derived RNA Biogenesis in Malignancy. MicroPubl Biol. 2023, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemus-Diaz, N.; Ferreira, R.R.; Bohnsack, K.E.; Gruber, J.; Bohnsack, M.T. The human box C/D snoRNA U3 is a miRNA source and miR-U3 regulates expression of sortin nexin 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 8074–8089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestrade, L.; Weber, M.J. snoRNA-LBME-db, a comprehensive database of human H/ACA and C/D box snoRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D158–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.P.; Liao, J.P.; Shen, J.; Yu, L.; Liu, B.L.; Liu, L.; Li, R.Y.; Ji, L.; Dorsey, S.G.; Jiang, Z.R.; et al. Small nucleolar RNA 42 acts as an oncogene in lung tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2012, 31, 2794–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens-Uzunova, E.S.; Hoogstrate, Y.; Kalsbeek, A.; Pigmans, B.; Vredenbregt-van den Berg, M.; Dits, N.; Nielsen, S.J.; Baker, A.; Visakorpi, T.; Bangma, C.; et al. C/D-box snoRNA-derived RNA production is associated with malignant transformation and metastatic progression in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17430–17444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Chu, L. An Oncolytic Adenovirus Expressing SNORD44 and GAS5 Exhibits Antitumor Effect in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Hum. Gene Ther. 2017, 28, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.X.; Qiao, X.J.; Xing, Z.W.; Hou, M.X. The SNORA21 expression is upregulated and acts as a novel independent indicator in human gastric cancer prognosis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 5519–5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ge, A.; Chang, L.; Shi, H.; Fu, Y.; Luo, Q. Overexpression of SNORA21 suppresses tumorgenesis of gallbladder cancer in vitro and in vivo. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Shi, Q.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, X. Dicer-independent snRNA/snoRNA-derived nuclear RNA 3 regulates tumor-associated macrophage function by epigenetically repressing inducible nitric oxide synthase transcription. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yin, W.; Kuang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Huang, H.; Liu, W.; Jiang, X.; Ren, C. A prognostic signature based on snoRNA predicts the overall survival of lower-grade glioma patients. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1138363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Gao, Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Guo, Q.; Xue, H.; Zhao, R.; Guo, X.; Li, G. Identification and validation of SNHG gene signature to predict malignant behaviors and therapeutic responses in glioblastoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 986615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.L.; Yin, C.F.; Chang, Y.W.; Fan, Y.C.; Lin, S.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Huang, H.C.; Juan, H.F. LncRNA SNHG1 regulates neuroblastoma cell fate via interactions with HDAC1/2. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Pan, J.; Hu, C.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Tan, T.; Zheng, M.; Shen, Y.; Yang, T.; Deng, Y.; et al. SNHG25 facilitates SNORA50C accumulation to stabilize HDAC1 in neuroblastoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cai, G.; Yu, F.; Li, D.; Wang, C.; Ma, D.; Han, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; He, J. Changes in the small noncoding RNA transcriptome in osteosarcoma cells. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Tong, D. Expression scoring of a small-nucleolar-RNA signature identified by machine learning serves as a prognostic predictor for head and neck cancer. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 8071–8084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, N.; Song, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xie, M.; Wang, B.; Hua, H.; Shen, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Oncogenic SNORD12B activates the AKT-mTOR-4EBP1 signaling in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via nucleus partitioning of PP-1α. Oncogene 2021, 40, 3734–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Wang, L.; Yi, S.; Liu, G. Long non-coding RNA SNHG1/microRNA-195-5p/Yes-associated protein axis affects the proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer via the Hippo signaling pathway. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2022, 22, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.H.; Wang, Y.X.; Song, J.J.; Zhao, L.Q.; Zhai, Y.J.; Liu, Y.F.; Guo, W.J. LncRNA SNHG26 promotes gastric cancer progression and metastasis by inducing c-Myc protein translation and an energy metabolism positive feedback loop. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Bian, Z.; Wang, X.; Niu, N.; Liu, L.; Xiao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Huang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. SNORA56-mediated pseudouridylation of 28 S rRNA inhibits ferroptosis and promotes colorectal cancer proliferation by enhancing GCLC translation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Fan, Y.; Cai, D.; Lei, R.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Shen, L.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; et al. SNORA28 Promotes Proliferation and Radioresistance in Colorectal Cancer Cells through the STAT3 Pathway by Increasing H3K9 Acetylation in the LIFR Promoter. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2405332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Qin, W.; Lu, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Sun, T.; Hu, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; et al. Long noncoding RNA ZFAS1 promoting small nucleolar RNA-mediated 2′-O-methylation via NOP58 recruitment in colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Matas, J.; Duran-Sanchon, S.; Lozano, J.J.; Ferrero, G.; Tarallo, S.; Pardini, B.; Naccarati, A.; Castells, A.; Gironella, M. SnoRNA profiling in colorectal cancer and assessment of non-invasive biomarker capacity by ddPCR in fecal samples. iScience 2024, 27, 109283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Z.; Huang, G.; Wu, H.; He, Q.; Yang, C.; Dou, R.; Liu, Q.; Song, J.; Fang, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. SNHG16 upregulation-induced positive feedback loop with YAP1/TEAD1 complex in Colorectal Cancer cell lines facilitates liver metastasis of colorectal cancer by modulating CTCs epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 5291–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Gong, C.; Wu, Y.; Xie, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Shi, Q.; Liu, J.; Gao, N.; He, B.; et al. LncRNA SNHG1 facilitates colorectal cancer cells metastasis by recruiting HNRNPD protein to stabilize SERPINA3 mRNA. Cancer Lett. 2024, 604, 217217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, L.; He, F.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Cao, Z.; Xu, X.; Gong, J. Long noncoding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 1 as a potential novel biomarker for intraperitoneal free cancer cells in colorectal cancer. iScience 2024, 27, 110228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam Khan, M.Z.; Law, H.K.W. Suppression of small nucleolar RNA host gene 8 (SNHG8) inhibits the progression of colorectal cancer cells. Noncoding RNA Res. 2023, 8, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Huan, L.; Guo, T.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Huang, S.; Xu, Y.; Liang, L.; He, X. LncRNA SNHG11 facilitates tumor metastasis by interacting with and stabilizing HIF-1α. Oncogene 2020, 39, 7005–7018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Lan, Z.; Lai, Q.; Li, A.; Liu, S.; Wang, X. LncRNA SNHG6 plays an oncogenic role in colorectal cancer and can be used as a prognostic biomarker for solid tumors. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 7620–7634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Wang, C.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, L. lncRNA SNHG22 sponges miR-128-3p to promote the progression of colorectal cancer by upregulating E2F3. Int. J. Oncol. 2021, 59, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Feng, H.H.; Chen, Z.L.; Wang, Y.L.; Yang, J.E.; Zhuang, S.M. LncRNA SNHG17 interacts with LRPPRC to stabilize c-Myc protein and promote G1/S transition and cell proliferation. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xia, P.; Zhang, H.; Yin, M.; Qin, Z.; Ma, W.; Yuan, Y. Small nucleolar RNA 42 promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma through the p53 signaling pathway. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Wang, X.; Wei, B.; Sun, R.; Wu, C.; Yang, H.J. LncRNA SNHG6 promotes glycolysis reprogramming in hepatocellular carcinoma by stabilizing the BOP1 protein. Anim. Cells Syst. 2022, 26, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, X.; Lei, X.; Liu, Q.; Qian, K.; Tong, Q.; Qin, W.; Li, Z.; Cao, Z.; et al. TRPM8 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by inducing SNORA55 mediated nuclear-mitochondrial communication. Cancer Gene Ther. 2023, 30, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Mao, S.; Zhen, N.; Zhu, G.; Bian, Z.; Xie, Y.; Tang, X.; Ding, M.; Wu, H.; Ma, J.; et al. SNORA14A inhibits hepatoblastoma cell proliferation by regulating SDHB-mediated succinate metabolism. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Guo, D.; Ma, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, G.; He, S. LncRNA SNHG5 promotes the proliferation and cancer stem cell-like properties of HCC by regulating UPF1 and Wnt-signaling pathway. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022, 29, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhan, Y.; Lang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, J. LncRNA-SNHG5 mediates activation of hepatic stellate cells by regulating NF2 and Hippo pathway. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhou, X.; Zeng, H.; Yu, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Liao, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, L. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Potentiates the Immunosuppressive Microenvironment in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Promoting the Release of SNHG6-Enriched Small Extracellular Vesicles. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2024, 12, 1184–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Qi, Y.; Huang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Huang, T.; Jia, L. Exosome-derived SNHG16 sponging miR-4500 activates HUVEC angiogenesis by targeting GALNT1 via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 77, 667–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, N.; Zhu, J.; Mao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, S.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, M.; Li, H.; Huang, N.; et al. Alternative Splicing of lncRNAs From SNHG Family Alters snoRNA Expression and Induces Chemoresistance in Hepatoblastoma. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 16, 735–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallela, V.R.; Kasi, P.B.; Shetti, D.; Trailin, A.; Cervenkova, L.; Palek, R.; Daum, O.; Liska, V.; Hemminki, K.; Ambrozkiewicz, F. Small nucleolar RNA expression profiles: A potential prognostic biomarker for non-viral Hepatocellular carcinoma. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024, 9, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Yi, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Zhu, P.; Liu, N.; Xu, Y.; He, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. SNORD88B-mediated WRN nucleolar trafficking drives self-renewal in liver cancer initiating cells and hepatocarcinogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, L.; Song, X.; Song, X. SNORD88C guided 2′-O-methylation of 28S rRNA regulates SCD1 translation to inhibit autophagy and promote growth and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2023, 30, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; You, Q.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, Y. Serum exosomal small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) signatures as a predictive biomarker for benign and malignant pulmonary nodules. Cancer Cell Int. 2024, 24, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Feng, J.; Shi, T.; He, Y.; Mei, Z.; He, W.; et al. LncRNA SNHG3 is activated by E2F1 and promotes proliferation and migration of non-small-cell lung cancer cells through activating TGF-β pathway and IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 pathway. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 2891–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Ou, C.; Yan, A.; Zhu, K.; Xue, R.; Zhang, Y.; Lai, J. Long Noncoding RNA SNHG5 Induces the NF-κB Pathway by Regulating miR-181c-5p/CBX4 Axis to Promote the Progression of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2023, 59, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Pan, B.; Xia, G.; Zhu, J.; Li, C.; Feng, J. LncRNA SNHG15 regulates EGFR-TKI acquired resistance in lung adenocarcinoma through sponging miR-451 to upregulate MDR-1. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Yuan, Y.; Fang, S.; Liu, W.; Qian, Y.; Ma, J.; Chang, L.; Chen, F.; et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of SNHG7 enhances docetaxel resistance in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2022, 526, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xia, L.; Tan, X.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, W.; Tan, B.; Yu, X.; Fang, W.; Yang, Z. Molecular mechanism of lncRNA SNHG12 in immune escape of non-small cell lung cancer through the HuR/PD-L1/USP8 axis. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2022, 27, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.F.; He, Y.; Hu, L.Z.; Zhou, B.; Xu, H.Y.; Liu, X.Q. The Crosstalk between lncRNA-SNHG7/miRNA-181/cbx7 Modulates Malignant Character in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Lu, C.; Xia, Y.; Wu, L.; Song, J.; Chen, C.; Wang, Q. Small nucleolar RNA SNORA71A promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by maintaining ROCK2 mRNA stability in breast cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2022, 16, 1947–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.N.; Loh, Z.J.; Chen, H.W.; Lee, I.Y.; Tsai, J.H.; Chen, P.S. SnoRNA U50A mediates everolimus resistance in breast cancer through mTOR downregulation. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 48, 102062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrieri, A.N.; Zacchini, F.; Onofrillo, C.; Di Viggiano, S.; Penzo, M.; Ansuini, A.; Gandin, I.; Nobe, Y.; Taoka, M.; Isobe, T.; et al. DKC1 Overexpression Induces a More Aggressive Cellular Behavior and Increases Intrinsic Ribosomal Activity in Immortalized Mammary Gland Cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacchini, F.; Venturi, G.; De Sanctis, V.; Bertorelli, R.; Ceccarelli, C.; Santini, D.; Taffurelli, M.; Penzo, M.; Treré, D.; Inga, A.; et al. Human dyskerin binds to cytoplasmic H/ACA-box-containing transcripts affecting nuclear hormone receptor dependence. Genome Biol. 2022, 23, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Xie, L.; Song, X.; Song, X. Identification of four snoRNAs (SNORD16, SNORA73B, SCARNA4, and SNORD49B) as novel non-invasive biomarkers for diagnosis of breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2024, 24, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escuin, D.; Bell, O.; García-Valdecasas, B.; Clos, M.; Larrañaga, I.; López-Vilaró, L.; Mora, J.; Andrés, M.; Arqueros, C.; Barnadas, A. Small Non-Coding RNAs and Their Role in Locoregional Metastasis and Outcomes in Early-Stage Breast Cancer Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Lei, X.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Shi, J.; Jia, W.; et al. Long non-coding RNA SNHG8 enhances triple-negative breast cancer cell proliferation and migration by regulating the miR-335-5p/PYGO2 axis. Biol. Direct 2021, 16, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Wang, J.; Song, J.; Wu, Q.; Gong, Z.; Song, J.; Hou, L. Long noncoding RNA SNHG1 promotes breast cancer progression by regulating the miR-641/RRS1 axis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, W. Exosomal lncRNA SNHG12 promotes angiogenesis and breast cancer progression. Breast Cancer 2024, 31, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.H.; Tian, T.; Ge, Q.W.; He, X.Y.; Shi, C.Y.; Li, J.H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, F.Z.; Sang, L.J.; Yang, Z.Z.; et al. A phosphatidic acid-binding lncRNA SNHG9 facilitates LATS1 liquid-liquid phase separation to promote oncogenic YAP signaling. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 1088–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Ma, B.; Yuan, L.; Wang, G.; Tian, Y. Small nucleolar RNAs signature (SNORS) identified clinical outcome and prognosis of bladder cancer (BLCA). Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Ge, G.; Jia, Y.; Wu, D.; Ji, Y.; Wang, C. Silenced lncRNA SNHG14 restrains the biological behaviors of bladder cancer cells via regulating microRNA-211-3p/ESM1 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Huang, M.; Sun, N.; Hua, X.; Chen, R.; Xie, Q.; Huang, S.; Du, M.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, Q.; et al. Tumorigenesis of basal muscle invasive bladder cancer was mediated by PTEN protein degradation resulting from SNHG1 upregulation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grützmann, K.; Salomo, K.; Krüger, A.; Lohse-Fischer, A.; Erdmann, K.; Seifert, M.; Baretton, G.; Aust, D.; William, D.; Schröck, E.; et al. Identification of novel snoRNA-based biomarkers for clear cell renal cell carcinoma from urine-derived extracellular vesicles. Biol. Direct 2024, 19, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Powles, T.; Atkins, M.B.; Escudier, B.; McDermott, D.F.; Alekseev, B.Y.; Lee, J.L.; Suarez, C.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; De Giorgi, U.; et al. Final Overall Survival and Molecular Analysis in IMmotion151, a Phase 3 Trial Comparing Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab vs Sunitinib in Patients with Previously Untreated Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Zhao, S.; Kang, R.; Wang, X. lncRNA SNHG11 facilitates prostate cancer progression through the upregulation of IGF-1R expression and by sponging miR-184. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 48, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Song, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, H.; Ruan, H.; Cao, Q.; Wang, K.; Xiao, W.; Xiong, Z.; Liu, D.; et al. Long noncoding RNA SNHG12 indicates the prognosis of prostate cancer and accelerates tumorigenesis via sponging miR-133b. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Song, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ouyang, J. Small nucleolar RNA host gene 25 is a long non-coding RNA helps diagnose and predict outcomes in prostate cancer. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2023, 35, 100687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, H.J.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, W.; Li, Q.H.; Xian, J.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, S. Box C/D snoRNA SNORD89 influences the occurrence and development of endometrial cancer through 2′-O-methylation modification of Bim. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Cheng, H.; Wang, N.; Wang, C. SLERT, as a novel biomarker, orchestrates endometrial cancer metastasis via regulation of BDNF/TRKB signaling. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 21, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, M.L.; Zhao, Z.X.; Shuang, T. Dysregulation of lnc-SNHG1 and miR-216b-5p correlate with chemoresistance and indicate poor prognosis of serous epithelial ovarian cancer. J. Ovarian Res. 2020, 13, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Dong, Y.J. LncRNA SNHG20 promotes migration and invasion of ovarian cancer via modulating the microRNA-148a/ROCK1 axis. J. Ovarian Res. 2021, 14, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Huang, P.; Li, Q. Long noncoding RNA SNHG6 promotes the malignant phenotypes of ovarian cancer cells via miR-543/YAP1 pathway. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.; Zoller, J.; Zhou, F.; Rohde, C.; Liu, Y.; Blank, M.F.; Göllner, S.; Müller-Tidow, C. The landscape of RNA-chromatin interaction reveals small non-coding RNAs as essential mediators of leukemia maintenance. Leukemia 2024, 38, 1688–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Sun, Y.M.; Pan, Q.; Fang, K.; Chen, X.T.; Zeng, Z.C.; Chen, T.Q.; Zhu, S.X.; Huang, L.B.; Luo, X.Q.; et al. The snoRNA-like lncRNA LNC-SNO49AB drives leukemia by activating the RNA-editing enzyme ADAR1. Cell Discov. 2022, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zeng, T.; Lin, Z.; Yan, L.; Wang, F.; Tang, L.; Wang, L.; Tang, D.; Chen, P.; Yang, M. Long non-coding RNA SNHG5 regulates chemotherapy resistance through the miR-32/DNAJB9 axis in acute myeloid leukemia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 123, 109802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Cheng, J.; Song, Y.; Li, H.H.; Zheng, J.F. LncRNA SNHG5 upregulation induced by YY1 contributes to angiogenesis via miR-26b/CTGF/VEGFA axis in acute myelogenous leukemia. Lab. Investig. 2021, 101, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazan, J.M.; Amador, R.; Ali-Nasser, T.; Lahav, T.; Shotan, S.R.; Steinberg, M.; Cohen, Z.; Aran, D.; Meiri, D.; Assaraf, Y.G.; et al. Integration of transcription regulation and functional genomic data reveals lncRNA SNHG6’s role in hematopoietic differentiation and leukemia. J. Biomed. Sci. 2024, 31, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Cui, W.; Liu, M.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yin, Y.; Li, Y.; Che, Y.; Zhu, X.; et al. SnoRNAs: The promising targets for anti-tumor therapy. J. Pharm. Anal. 2024, 14, 101064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, E.D.S.; Matos, A.G.M.; Prata Da Silva, M.G.O.; Alves, M.S.; Teixeira-Júnior, A.A.L.; Duarte, W.E.; Mendonça, A.F.; Teixeira De Souza, C.R.; Andrade, M.S.; Khayat, A.S.; et al. What is the Role of SNORA42 in Carcinogenesis? A Systematic Review. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2023, 24, 2217–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Russo, G. Ribosomal Proteins Control or Bypass p53 during Nucleolar Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Lee, J.S.; Ni, C.; Guo, J.; Chen, E.; Wang, S.; Acharya, A.; Chang, T.C.; et al. A non-canonical role for a small nucleolar RNA in ribosome biogenesis and senescence. Cell 2024, 187, 4770–4789.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Werf, J.; Chin, C.V.; Fleming, N.I. SnoRNA in Cancer Progression, Metastasis and Immunotherapy Response. Biology 2021, 10, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Pang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Qin, Q.; Wang, R.; Li, W.; Jing, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, S. SNORA23 inhibits HCC tumorigenesis by impairing the 2′-O-ribose methylation level of 28S rRNA. Cancer Biol. Med. 2021, 19, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okugawa, Y.; Toiyama, Y.; Toden, S.; Mitoma, H.; Nagasaka, T.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y.; Kusunoki, M.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Clinical significance of SNORA42 as an oncogene and a prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. Gut 2017, 66, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wen, J.; Huang, Z.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, B.X.; Chu, L. Small Nucleolar RNAs: Insight Into Their Function in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.R.; Li, W.C.; Yu, Z.T.; Li, J.; Peng, C.Y.; Jin, L.; Yuan, G.L. Effects of small nucleolar RNA SNORD44 on the proliferation, apoptosis and invasion of glioma cells. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 153, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xie, W.; Meng, S.; Kang, X.; Liu, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, C. Small Nucleolar RNAs and Their Comprehensive Biological Functions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells 2022, 11, 2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Han, X.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, L.; Xu, H.; Bai, Y.; Xu, C.; et al. Downregulation of snoRNA SNORA52 and Its Clinical Significance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 7020637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Nakano, K.; Obchoei, S.; Setoguchi, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Obika, S.; Shimada, K.; Hiraoka, N. Small Nucleolar Noncoding RNA SNORA23, Up-Regulated in Human Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma, Regulates Expression of Spectrin Repeat-Containing Nuclear Envelope 2 to Promote Growth and Metastasis of Xenograft Tumors in Mice. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 292–306.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Ye, B. SPI1-induced upregulation of lncRNA SNHG6 promotes non-small cell lung cancer via miR-485-3p/VPS45 axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wu, D.; Jia, H.; Zhang, Z. Long non-coding RNA LRRC75A-AS1 facilitates triple negative breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion via functioning as a ceRNA to modulate BAALC. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Yan, Y.; Bai, S.; Kang, H.; Zhang, J.; Ma, W.; Gao, Y.; Hui, B.; Li, R.; et al. Long non-coding RNA SNHG1 stimulates ovarian cancer progression by modulating expression of miR-454 and ZEB1. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 1584–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, H.B.; Kurban, E.; Luo, H.W. LncRNA SNHG14 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via H3K27 acetylation activated PABPC1 by PTEN signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shang, X.; Yu, M.; Bi, Z.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, L.; Song, X.; Song, X. A three-snoRNA signature: SNORD15A, SNORD35B and SNORD60 as novel biomarker for renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, R.D.; Chen, S. Sno-derived RNAs are prevalent molecular markers of cancer immunity. Oncogene 2018, 37, 6442–6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Types of Cancer | Expression in Cancer | Expression | Regulatory Site | Function | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neurologic malignancies | |||||
| Glioblastoma | U3 snoRNA | Upregulated | ZBTB7A | Enhances aerobic glycolysis, proliferative capacity | [14] |
| Upregulated | TRIM24/DNA-PKcs | induces epigenetic remodeling and epithelioid transformation | [15] | ||
| SNHG12 | Upregulated | miR-129-5p/MAPK1/E2F7 | Activates MAPK/ERK cascade, drives cell cycle progression, promotes temozolomide resistance | [16] | |
| Neuroblastoma | SNHG7 | Upregulated | miR-323a-5p/miR-342-5p; CCND1 | Enhances migration, invasion, glycolytic activity | [17] |
| SNHG16 | Upregulated | miR-338-3p/PLK4; PI3K/AKT pathway | Promotes cisplatin resistance | [18] | |
| Bone malignancies | SNHG6 | Upregulated | EZH2/KLF6/SP1 | Promotes H3K27me3-mediated silencing of KLF6, drives proliferation, migration, and invasion | [19] |
| Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | SNHG3 | Downregulated | RPS27A/RPL8; ribosome biogenesis | Drives tumor progression via metabolic remodeling, immune regulation, and TME modulation | [20] |
| Digestive system malignancies | |||||
| Esophageal cancer | |||||
| SNHG12 | Upregulated | miR-6835-3p/BMI1; IGF2BP2/CTNNB1 | Induces EMT, reinforces stem-like properties, accelerates metastasis | [21] | |
| SNHG17 | Overexpressed | miR-338-3p/SOX4 | Promotes cellular proliferation and invasion | [22] | |
| Gastric cancer | |||||
| SNHG12 | Upregulated | miR-218-5p/YWHAZ/β-catenin | Promotes metastasis and EMT | [23] | |
| Overexpressed | miR-129-5p/E2F7/MAPK/ERK | Promotes peritoneal mesothelial cell apoptosis | [24] | ||
| SNHG22 | Upregulated | EZH2; miR-200c-3p/Notch1 | Enhances proliferation, invasion; silences tumor suppressors, upregulates Notch1 | [25] | |
| Colorectal cancer | |||||
| SNORA24 | Upregulated | p53 protein (proteasome pathway) | Promotes proliferation | [26] | |
| SNHG17 | Upregulated | miR-23a-3p/CXCL12 | Promotes proliferation and migration | [27] | |
| Upregulated | Trim23-PES1/miR-339-5p-FOSL2 | Promotes proliferation and metastasis | [28] | ||
| Hepatocellular Carcinoma | |||||
| SNORD52 | Upregulated | CDK1 | Promotes cell cycle progression and tumor growth | [29] | |
| SNHG1 | Upregulated | SND1/m6A/SLC7A11 | Sorafenib resistance | [30] | |
| Pancreatic cancer | |||||
| SNHG6 | Upregulated | miR-26a-5p/FUBP1/EMT markers | Promotes EMT (↑N-cadherin, vimentin, β-catenin; ↓E-cadherin), proliferation, and metastasis | [31] | |
| RRP9 (U3 snoRNA binder) | Upregulated | IGF2BP1/AKT signaling | Enhances DNA repair, inhibits apoptosis, induces gemcitabine resistance | [32] | |
| Lung cancer | |||||
| SNORA65, SNORA7A/B | Upregulated | Ribosomal pseudouridylation | Promotes proliferation/metastasis | [33] | |
| SNHG11 | Upregulated | miR-4436a/CTNNB1, activates Wnt/β-catenin | Promotes proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT | [34] | |
| Breast cancer | |||||
| SNHG22 | Upregulated | miR-324-3p/SUDS3 | Promotes proliferation and invasion | [35] | |
| SNORD50A/B | Downregulated | TRIM21-GMPS/p53 | Accelerates p53 degradation, drives tumor growth | [36] | |
| sdRNA-93 | Upregulated | Pipox 3′UTR | Enhances cellular invasion; specifically overexpressed in Luminal B Her2+ subtype | [37] | |
| Urinary system malignancies | |||||
| Bladder cancer | |||||
| SNHG15 | Upregulated | FOSL1/ADAM12; WNT/CTNNB1 pathway | Accelerates proliferation and metastasis | [38] | |
| SNHG18 | Downregulated | c-Myc/p21 | Induces G0-G1 arrest, inhibits proliferation | [39] | |
| Renal cell carcinoma | |||||
| SNHG4 | Upregulated | miR-204-5p/RUNX2 | Stimulates proliferation, invasion; inhibits apoptosis. | [40] | |
| SNHG6 | Upregulated | YBX1/HIF1α translation | Promotes tumor growth, metastasis. | [41] | |
| Prostate cancer | |||||
| SNHG4 | Upregulated | SP1/miR-377/ZIC5 | Drives proliferation, migration, invasion | [42] | |
| SNHG6 | Upregulated | miR-186/MRP1/MDR1 | Enhances paclitaxel resistance by upregulating multidrug resistance proteins | [43] | |
| sdRNA-D19b | Upregulated | CD44 | Promotes cell proliferation, migration, and paclitaxel resistance | [44] | |
| sdRNA-A24 | Upregulated | CDK12 | Promotes cell proliferation and dasatinib resistance | [44] | |
| Gynecological malignancies | |||||
| Cervical cancer | |||||
| SNORD6 | Upregulated | E6-mediated p53 ubiquitination | Inhibits apoptosis, drives tumor growth | [45] | |
| SNHG6 | Upregulated | miR-485-3p/STYX | Enhances radioresistance | [46] | |
| Endometrial cancer | |||||
| SNORD104 | Upregulated | PARP1 mRNA (2′-O-methylation) | Stabilizes PARP1 mRNA, drives tumor growth | [47] | |
| SNHG25 | Upregulated | miR-497-5p/fatty acid synthase | Promotes proliferation, migration; inhibits apoptosis | [48] | |
| Ovarian cancer | |||||
| SNHG5 | Downregulated | miR-23a/downstream targets | Enhances paclitaxel sensitivity | [49] | |
| SNHG10 | Downregulated | miR-200a-3p/BIN1 | Inhibits proliferation, migration, EMT | [50] | |
| Hematological malignancies | |||||
| SNORD42A | Upregulated | Ribosomal RNA modification | Sustains proliferation of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells | [51] | |
| SNHG1 | Upregulated | miR-489-3p/SOX12/Wnt/β-catenin pathway | Suppresses cell growth | [52] |
| snoRNA | Classification | Canonical Nucleolar Function | Disease Associations | Cancer Type(s) | Expression in Cancer | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNORA42 | H/ACA Box | rRNA pseudouridylation | Oncogene: Promotes proliferation, migration, invasion; inhibits apoptosis. High expression correlates with poor prognosis. | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) | Upregulated | [60] |
| SNORD44 | C/D Box | rRNA 2′-O-ribose methylation | Context-dependent role: In Prostate Cancer: Upregulated with its sdRNAs during malignant transformation. In Colorectal Cancer: Acts as a tumor suppressor in concert with its host gene GAS5. | Prostate Cancer (PCa), Colorectal Cancer (CRC) | PCa: Upregulated CRC: Downregulated | [61,62] |
| SNORA21 | H/ACA Box | rRNA pseudouridylation | Dual Role, highly context-dependent: In Gastric Cancer: Acts as an oncogene; high expression linked to metastasis and poor survival. In Gallbladder Cancer: Functions as a tumor suppressor; overexpression inhibits tumorigenesis. | Gastric Cancer (GC), Gallbladder Cancer (GBC) | GC: Upregulated GBC: Downregulated | [63,64] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, J.; Shao, Y.; Gu, W. Function and Mechanism of Small Nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) and Their Host Genes (SNHGs) in Malignant Tumors. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111625
Yu J, Shao Y, Gu W. Function and Mechanism of Small Nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) and Their Host Genes (SNHGs) in Malignant Tumors. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(11):1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111625
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Jiaji, Yingjie Shao, and Wendong Gu. 2025. "Function and Mechanism of Small Nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) and Their Host Genes (SNHGs) in Malignant Tumors" Biomolecules 15, no. 11: 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111625
APA StyleYu, J., Shao, Y., & Gu, W. (2025). Function and Mechanism of Small Nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) and Their Host Genes (SNHGs) in Malignant Tumors. Biomolecules, 15(11), 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111625







