Structure of Salmonella Flagellar Hook Reveals Intermolecular Domain Interactions for the Universal Joint Function
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation and Electron Microscopy
2.2. Image Processing
2.3. Atomic Model Building
3. Results and Discussion
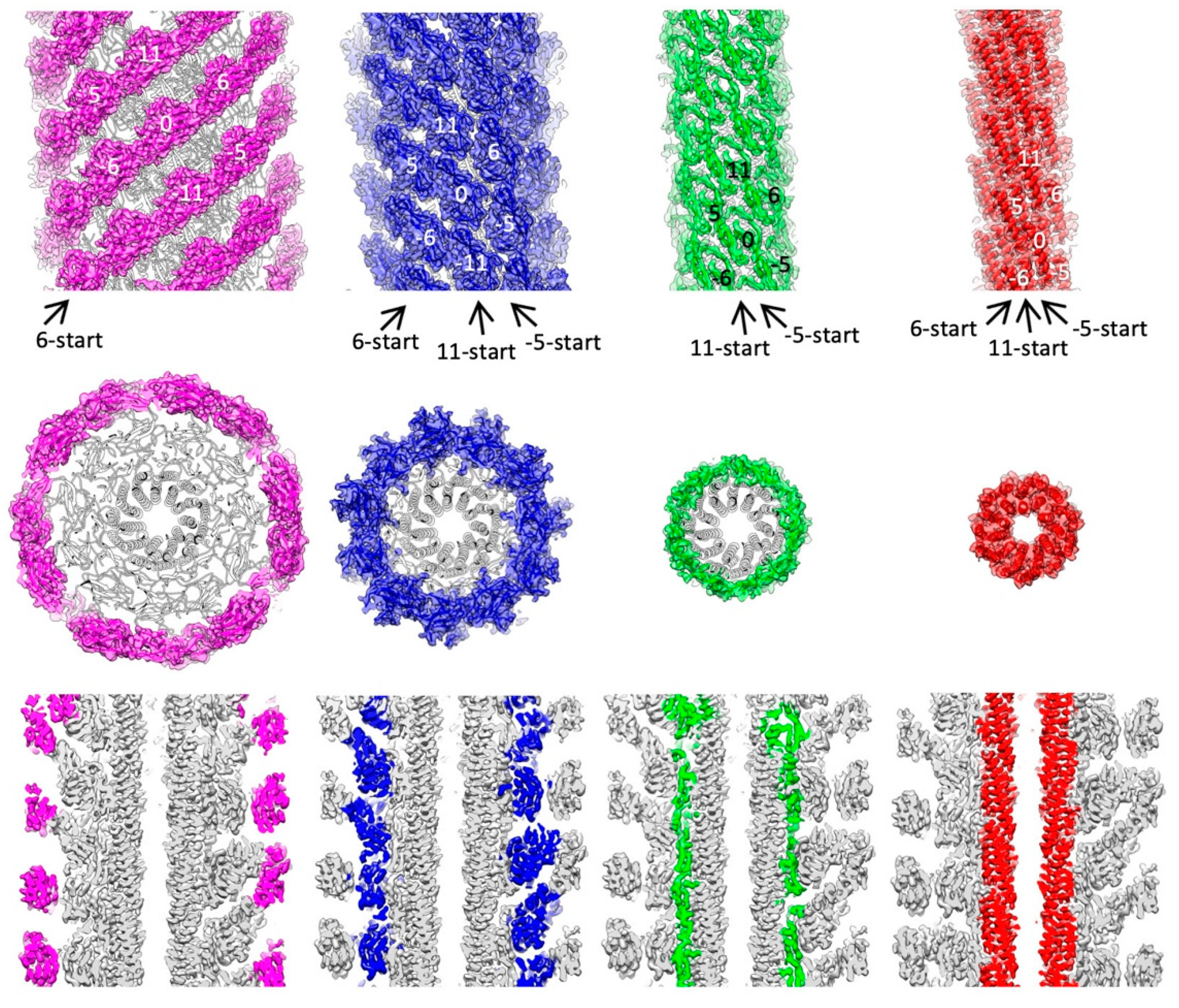
3.1. Structure Determination
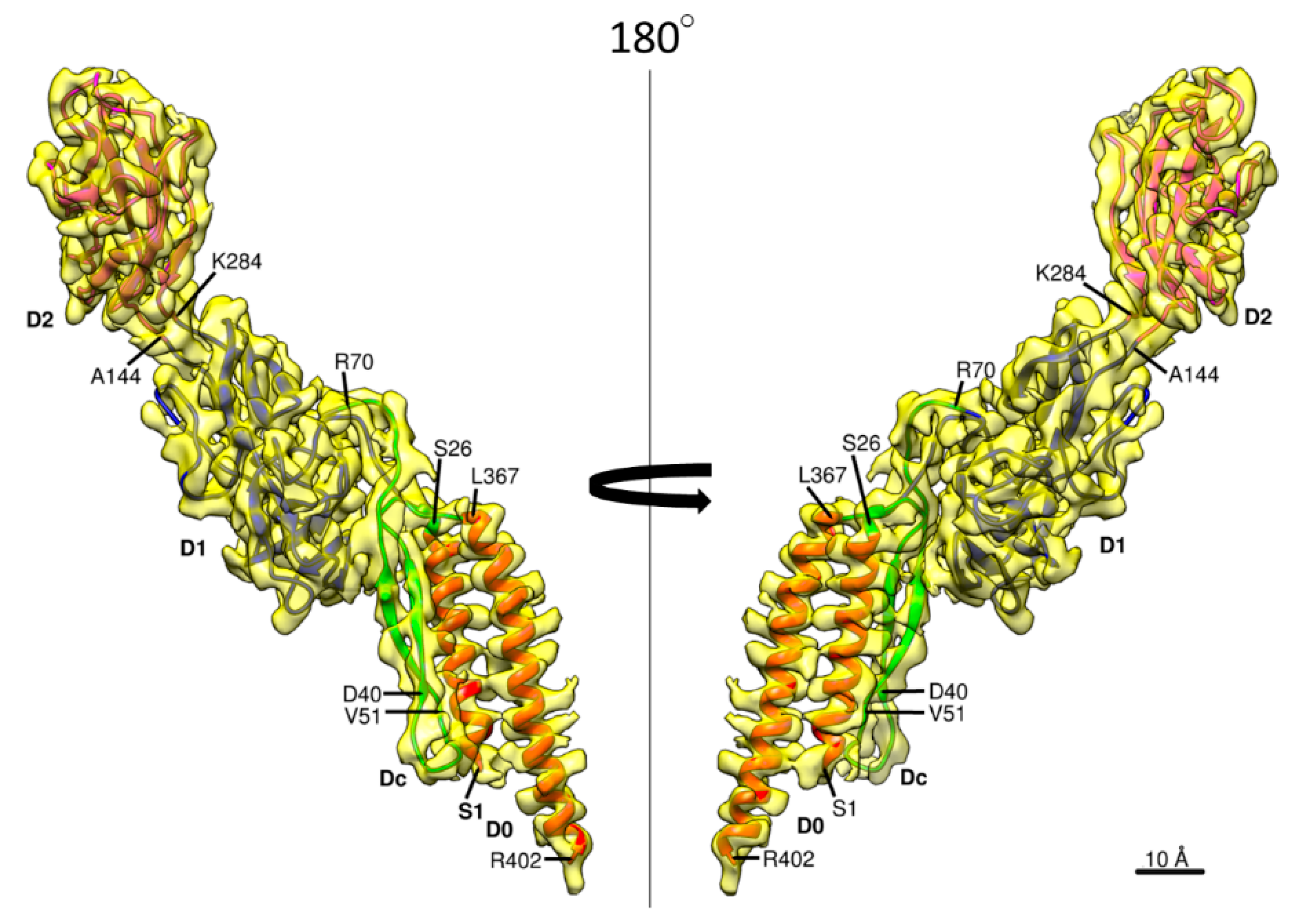
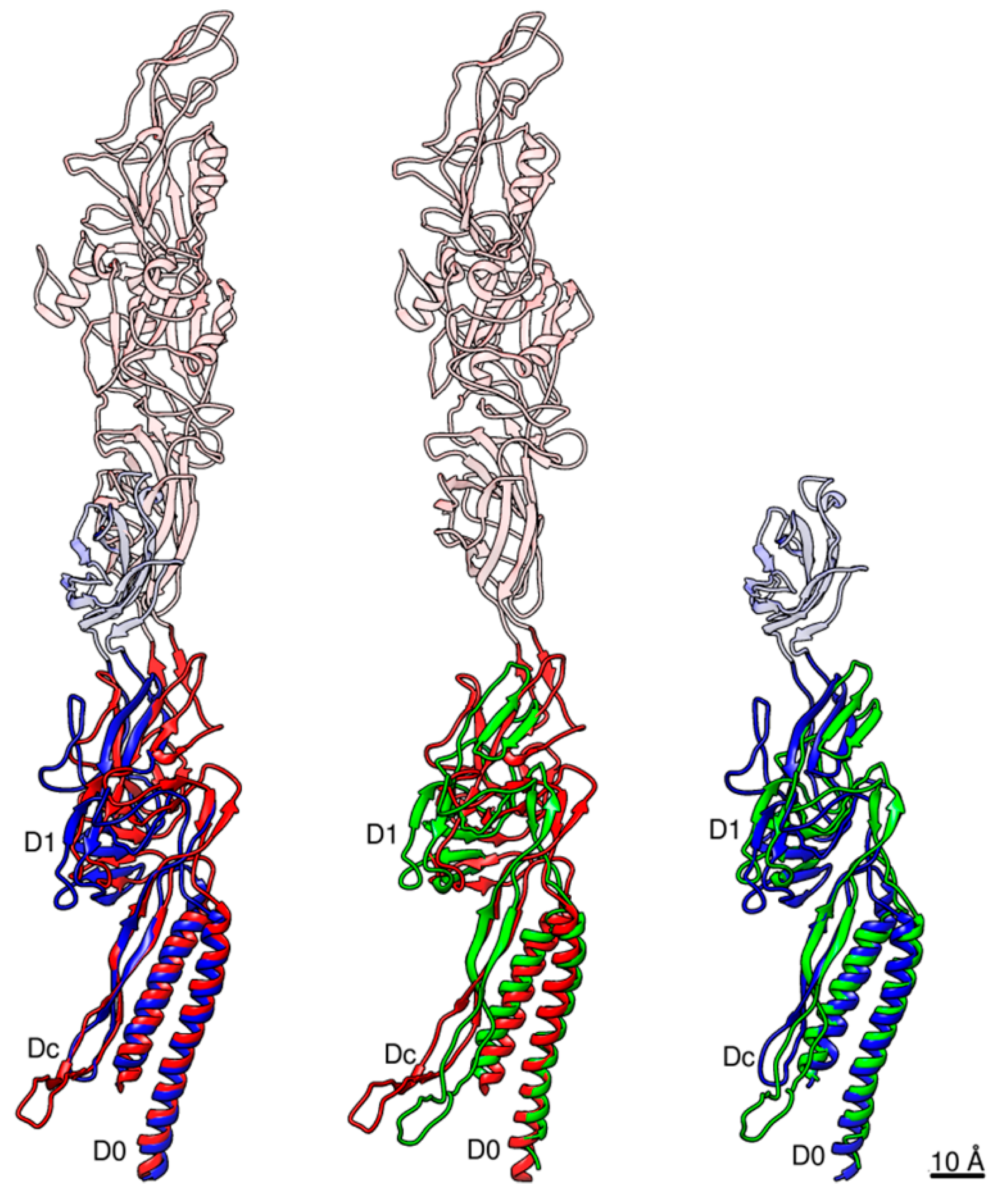
3.2. Structure of Salmonella Hook and FlgE in the Hook
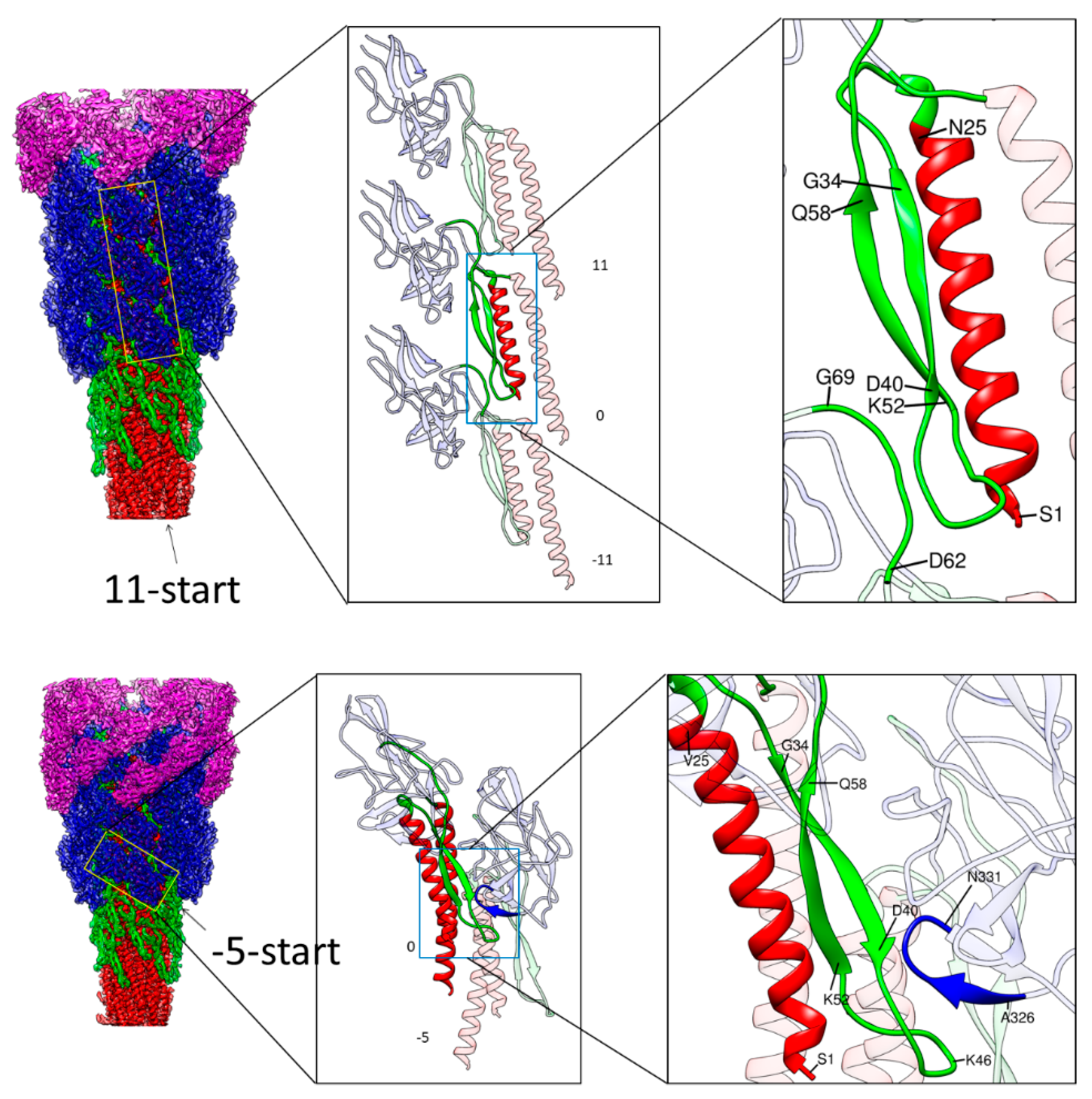
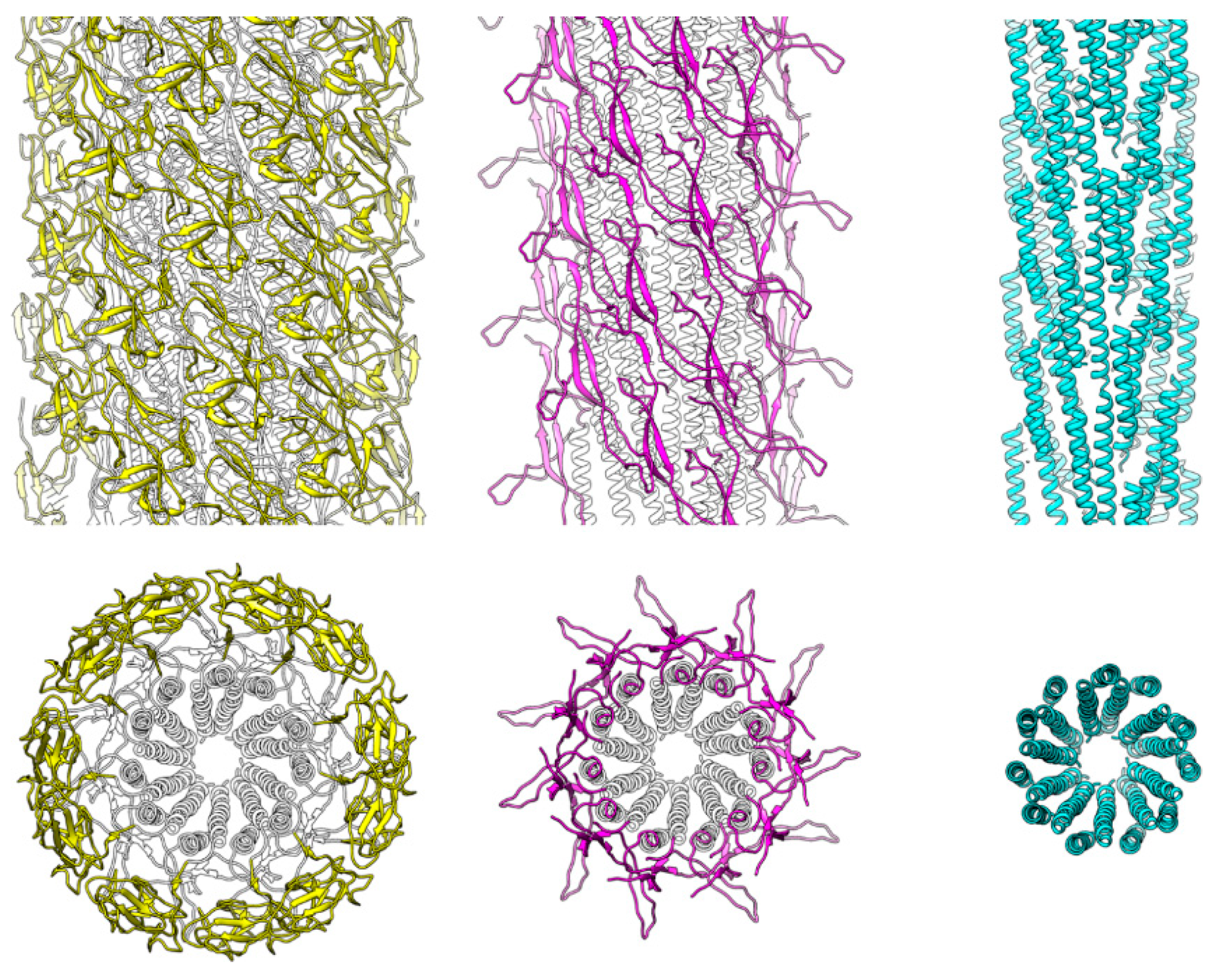
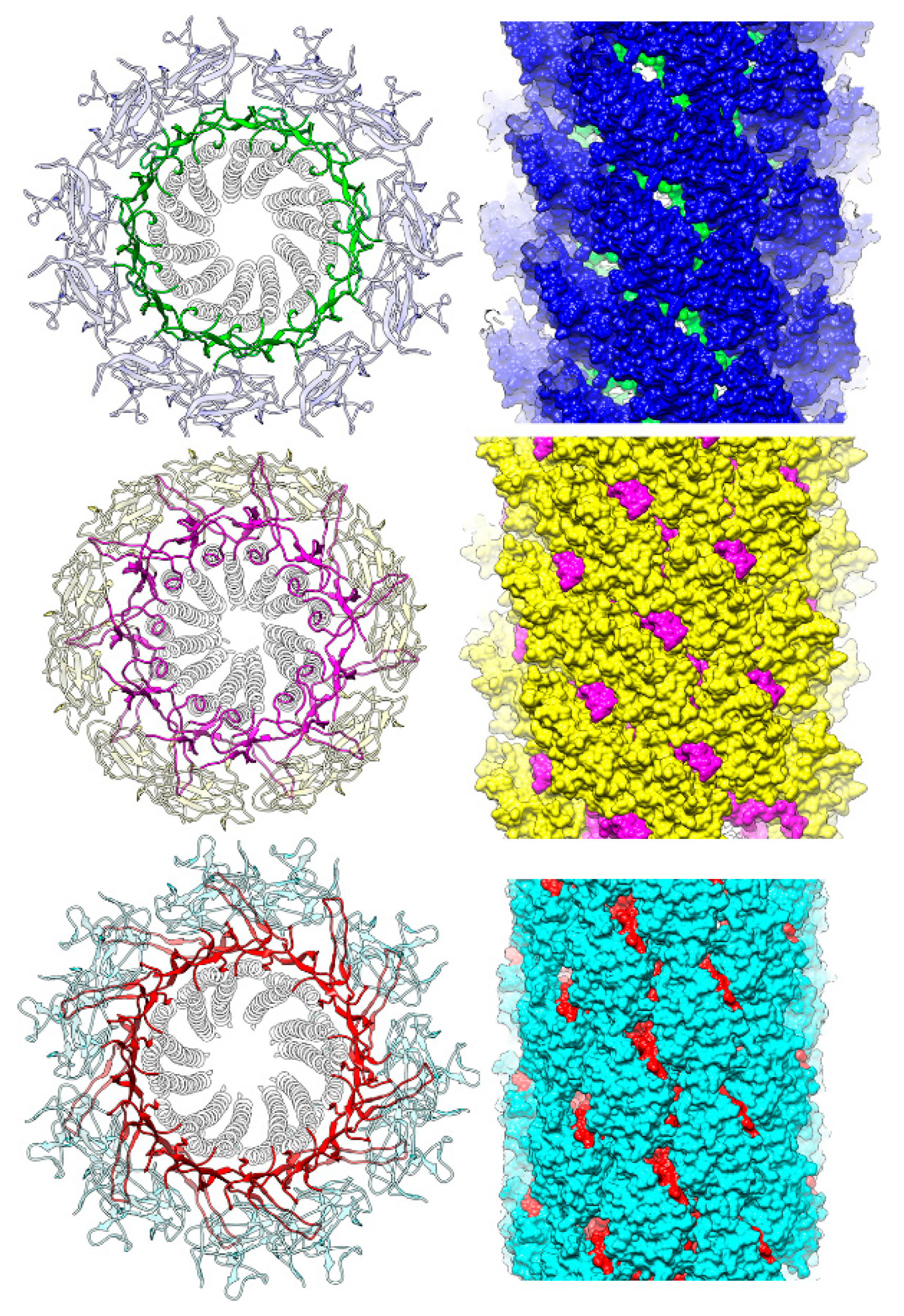
3.3. Intersubunit Interactions
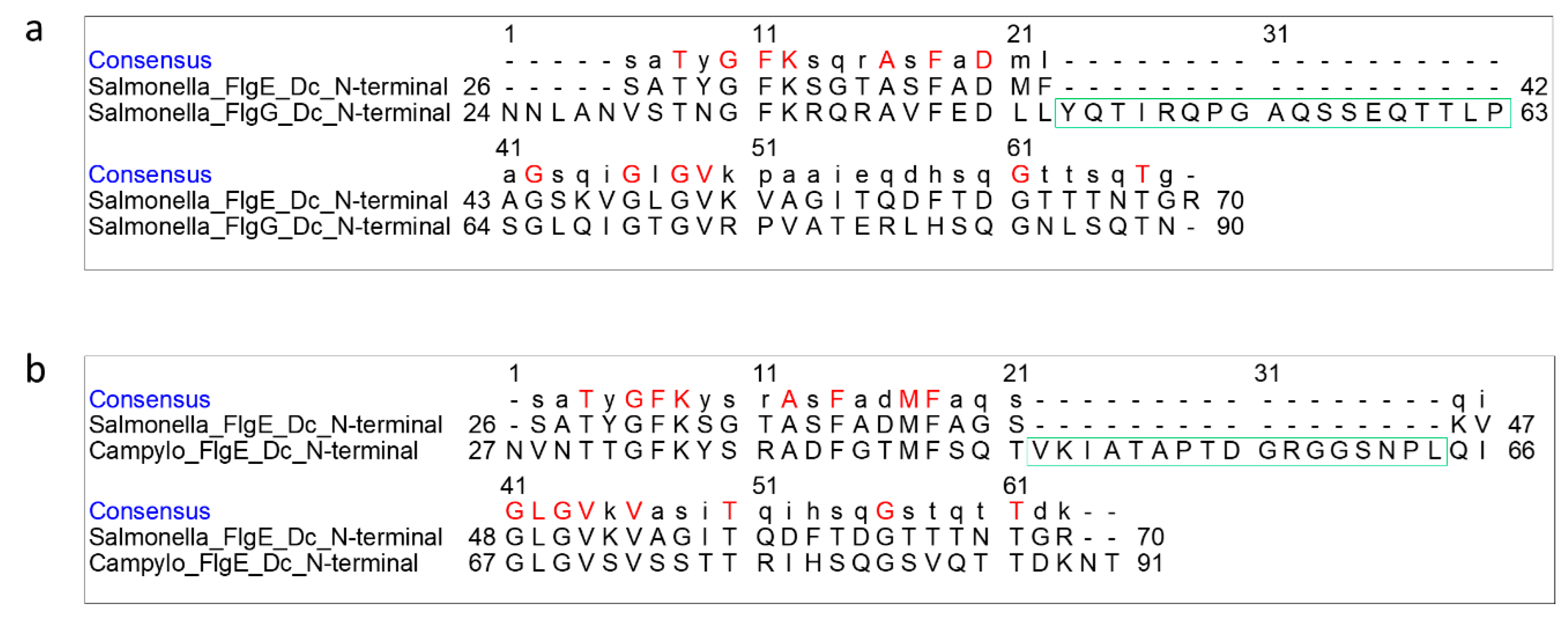
3.4. Role of the Longer β-Hairpin of Domain Dc in the Flagellar Rod Structure
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Namba, K.; Vonderviszt, F. Molecular architecture of bacterial flagellum. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1997, 30, 1–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macnab, R.M. How bacteria assemble flagella. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2003, 57, 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, H.C. The rotary motor of bacterial flagella. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003, 72, 19–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamino, T.; Imada, K.; Namba, K. Molecular motors of the bacterial flagella. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2008, 18, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, S.; Blair, D.F. The bacterial flagellar motor: Structure and function of a complex molecular machine. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2004, 233, 93–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, G.; Meister, M.; Berg, H.C. Rapid rotation of flagellar bundles in swimming bacteria. Nature 1987, 325, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, S.; Magariyama, Y.; Aizawa, S.-I. Abrupt changes in flagellar rotation observed by laser dark-field microscopy. Nature 1990, 346, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, H.C.; Anderson, R.A. Bacteria swim by rotating their flagellar filaments. Nature 1973, 245, 380–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, M.; Simon, M. Flagellar rotation and the mechanism of bacterial motility. Nature 1974, 249, 73–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakura, S. Polymerization of flagellin and polymorphism of flagella. Adv. Biophys. 1970, 1, 99–155. [Google Scholar]
- Macnab, R.M.; Ornston, M.K. Normal-to-curly flagellar transitions and their role in bacterial tumbling. Stabilization of an alternative quaternary structure by mechanical force. J. Mol. Biol. 1977, 112, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, L.; Ryu, W.S.; Berg, H.C. Real-time imaging of fluorescent flagellar filaments. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 2793–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DePamphilis, M.L.; Adler, J. Purification of intact flagella from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 1971, 105, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- DePamphilis, M.L.; Adler, J. Fine structure and isolation of the hook-basal body complex of flagella from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 1971, 105, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kagawa, H.; Aizawa, S.I.; Asakura, S. Transformations in isolated polyhooks. J. Mol. Biol. 1979, 129, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenknecht, T.; DeRosier, D.; Shapiro, L.; Weissborn, A. Three-dimensional reconstruction of the flagellar hook from Caulobacter crescentus. J. Mol. Biol. 1981, 151, 439–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Oosawa, K.; Aizawa, S. Roles of FliK and FlhB in determination of flagellar hook length in Salmonella typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 5439–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraoka, K.D.; Morimoto, Y.V.; Inoue, Y.; Fujii, T.; Miyata, T.; Makino, F.; Minamino, T.; Namba, K. Straight and rigid flagellar hook made by insertion of the FlgG specific sequence into FlgE. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Matsunami, H.; Inoue, Y.; Namba, K. Evidence for the hook supercoiling mechanism of the bacterial flagellum. Biophys. Physicobiol. 2018, 15, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, T.; Inoue, Y.; Terahara, N.; Namba, K.; Minamino, T. A triangular loop of domain D1 of FlgE is essential for hook assembly but not for the mechanical function. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 1789–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, M.; Kutsukake, K.; Hasebe, M.; Iino, T.; Macnab, R.M. FlgB, FlgC, FlgF and FlgG. A family of structurally related proteins in the flagellar basal body of Salmonella typhimurium. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 211, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.J.; Macnab, R.M.; Okino, H.; Aizawa, S. Stoichiometric analysis of the flagellar hook-(basal-body) complex of Salmonella typhimurium. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 212, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Kato, T.; Hiraoka, K.D.; Miyata, T.; Minamino, T.; Chevance, F.F.V.; Hughes, K.T.; Namba, K. Identical folds used for distinct mechanical functions of the bacterial flagellar rod and hook. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamino, T.; Kato, T.; Makino, F.; Horváth, P.; Miyata, T.; Namba, K. Electron microscopy of motor structure and possible mechanisms. In Encyclopedia of Biophysics, 2nd ed.; Roberts, G.C.K., Watts, A., Eds.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samatey, F.A.; Matsunami, H.; Imada, K.; Nagashima, S.; Shaikh, T.R.; Thomas, D.R.; Chen, J.Z.; DeRosier, D.J.; Kitao, A.; Namba, K. Structure of the bacterial flagellar hook and implication for the molecular universal joint mechanism. Nature 2004, 431, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, T.R.; Thomas, D.R.; Chen, J.Z.; Samatey, F.A.; Matsunami, H.; Imada, K.; Namba, K.; DeRosier, D.J. A partial atomic structure for the flagellar hook of Salmonella typhimurium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, T.; Kato, T.; Namba, K. Specific arrangement of alpha-helical coiled coils in the core domain of the bacterial flagellar hook for the universal joint function. Structure 2009, 17, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunami, H.; Barker, C.S.; Yoon, Y.-H.; Wolf, M.; Samatey, F.A. Complete structure of the bacterial flagellar hook reveals extensive set of stabilizing interactions. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizawa, S.I.; Dean, G.E.; Jones, C.J.; Macnab, R.M.; Yamaguchi, S. Purification and characterization of the flagellar hook-basal body complex of Salmonella typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 1985, 161, 836–849. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.Q.; Palovcak, E.; Armache, J.-P.; Verba, K.A.; Cheng, Y.; Agard, D.A. MotionCor2: Anisotropic correction of beam-induced motion for improved cryo-electron microscopy. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 331–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K. Gctf: Real-time CTF determination and correction. J. Struct. Biol. 2016, 193, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Scheres, S.H.W. Helical reconstruction in RELION. J. Struct. Biol. 2017, 198, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Protein structure modeling with MODELLER. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1137, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.Y.-R.; Song, Y.; Barad, B.A.; Cheng, Y.; Fraser, J.S.; DiMaio, F. Automated structure refinement of macromolecular assemblies from cryo-EM maps using Rosetta. eLife 2016, 5, e17219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.G.; Cowtan, K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson-Delafield, J.; Martinez, R.J.; Stocker, B.A.; Yamaguchi, S. A new fla gene in Salmonella typhimurium–flaR—And its mutant phenotype-superhooks. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973, 90, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, T.; Samatey, F.A.; Matsunami, H.; Imada, K.; Namba, K.; Kitao, A. Gap compression/extension mechanism of bacterial flagellar hook as the molecular universal joint. J. Struct. Biol. 2007, 157, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, N.; Minamino, T.; Ferris, H.U.; Morimoto, Y.V.; Ashihara, M.; Kato, T.; Namba, K. Role of the Dc domain of the bacterial hook protein FlgE in hook assembly and function. Biophysics 2013, 9, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Horváth, P.; Kato, T.; Miyata, T.; Namba, K. Structure of Salmonella Flagellar Hook Reveals Intermolecular Domain Interactions for the Universal Joint Function. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9090462
Horváth P, Kato T, Miyata T, Namba K. Structure of Salmonella Flagellar Hook Reveals Intermolecular Domain Interactions for the Universal Joint Function. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(9):462. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9090462
Chicago/Turabian StyleHorváth, Péter, Takayuki Kato, Tomoko Miyata, and Keiichi Namba. 2019. "Structure of Salmonella Flagellar Hook Reveals Intermolecular Domain Interactions for the Universal Joint Function" Biomolecules 9, no. 9: 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9090462
APA StyleHorváth, P., Kato, T., Miyata, T., & Namba, K. (2019). Structure of Salmonella Flagellar Hook Reveals Intermolecular Domain Interactions for the Universal Joint Function. Biomolecules, 9(9), 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9090462





