Epibatidine: A Promising Natural Alkaloid in Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
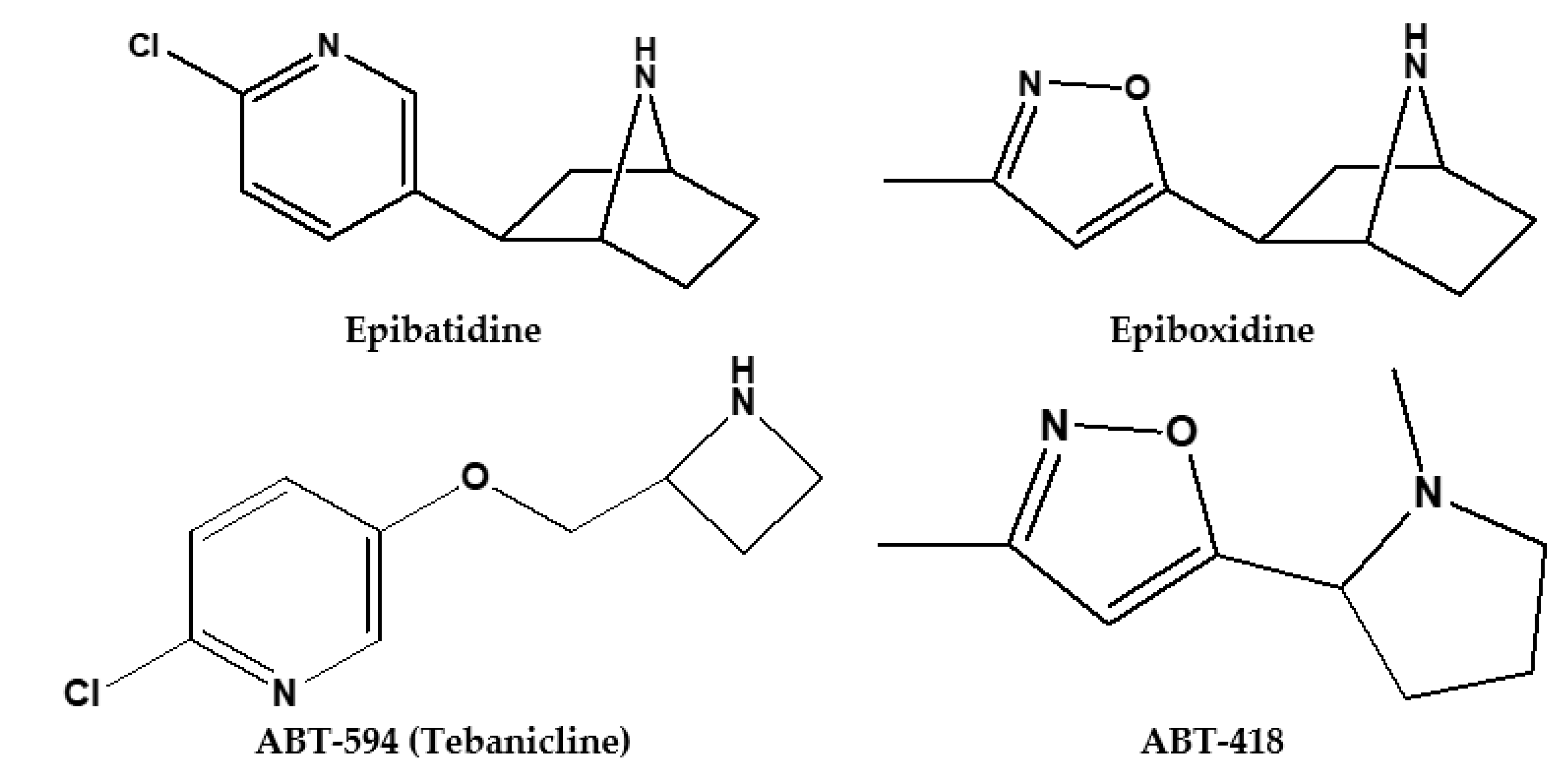
2. Pharmacokinetics of Epibatidine and Its Synthetic Derivatives
3. Role of Epibatidine in Health
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spande, T.F.; Garraffo, H.M.; Yeh, H.J.; Pu, Q.L.; Pannell, L.K.; Daly, J.W. A new class of alkaloids from a dendrobatid poison frog: A structure for alkaloid 251f. J. Nat. Prod. 1992, 55, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spande, T.F.; Garraffo, H.M.; Edwards, M.W.; Yeh, H.J.C.; Pannell, L.; Daly, J.W. Epibatidine: A novel (chloropyridyl)azabicycloheptane with potent analgesic activity from an Ecuadoran poison frog. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posadas, I.; Lopez-Hernandez, B.; Cena, V. Nicotinic receptors in neurodegeneration. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2013, 11, 298–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, J. Molecular biology of the cell, by b. Alberts, a. Johnson, j. Lewis, m. Raff, k. Roberts, and p. Walter. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2008, 36, 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, G.K.; Williams, M. Neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors as novel drug targets. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 292, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qian, C.; Li, T.; Shen, T.Y.; Libertine-Garahan, L.; Eckman, J.; Biftu, T. Epibatidine is a nicotinic analgesic. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 250, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, J.P.; Decker, M.W.; Brioni, J.D.; Donnelly-Roberts, D.; Anderson, D.J.; Bannon, A.W.; Kang, C.H.; Adams, P.; Piattoni-Kaplan, M.; Buckley, M.J. (+/−)-epibatidine elicits a diversity of in vitro and in vivo effects mediated by nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1994, 271, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.J.; Metzger, S.; Lochner, M.; Ruepp, M.-D. The binding orientation of epibatidine at α7 nach receptors. Neuropharmacology 2017, 116, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowska, U.; Wiśniewska, R.J. The α7-nach nicotinic receptor and its role in memory and selected diseases of the central nervous system. Postepy. Hig. Med. Dosw. 2017, 30, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly-Roberts, D.L.; Puttfarcken, P.S.; Kuntzweiler, T.A.; Briggs, C.A.; Anderson, D.J.; Campbell, J.E.; Piattoni-Kaplan, M.; McKenna, D.G.; Wasicak, J.T.; Holladay, M.W.; et al. Abt-594 [(r)-5-(2-azetidinylmethoxy)-2-chloropyridine]: A novel, orally effective analgesic acting via neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: I. In vitro characterization. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 285, 777–786. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, T.; Tanaka, K.; Hasegawa, T.; Yokotani, K. Brain α4β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are involved in the secretion of noradrenaline and adrenaline from adrenal medulla in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 654, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, B.T.; Lee, S.T.; Keele, J.W.; Welch, K.D.; Cook, D.; Pfister, J.A.; Kem, W.R. Complete inhibition of fetal movement in the day 40 pregnant goat model by the piperidine alkaloid anabasine but not related alkaloids. Toxicon 2018, 144, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traynor, J.R. Epibatidine and pain. Br. J. Anaesth. 1998, 81, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- London, E.D.; Scheffel, U.; Kimes, A.S.; Kellar, K.J. In vivo labeling of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in brain with [3h] epibatidine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 278, R1–R2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javors, M.A.; Sanchez, J.J.; King, T.S.; Rohde, A.R.; Wilson, S.G.; Flores, C.M. Extraction and quantification of epibatidine in plasma. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 2001, 755, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Suzuki, T. Simultaneous quantification of batrachotoxin and epibatidine in plasma by ultra-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Legal. Med. 2017, 25, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watt, A.P.; Hitzel, L.; Morrison, D.; Locker, K.L. Determination of the in vitro metabolism of (+)- and (−)-epibatidine. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 896, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heugebaert, T.S.A.; Van Overtveldt, M.; De Blieck, A. Synthesis of 1-substituted epibatidine analogues and their in vitro and in vivo evaluation as a4ß2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligands. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 2226–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patt, M.; Becker, G.A.; Grossmann, U. Evaluation of metabolism, plasma protein binding and other biological parameters after administration of (−)-[18f]flubatine in humans. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2014, 41, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, F.; Fischer, S.; Smits, R. Exploring the metabolism of (+)-[18f] flubatine in vitro and in vivo: Lc-ms/ms aided identification of radiometabolites in a clinical pet study. Molecules 2018, 23, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunnelle, W.H.; MJ Dart, M.; Schrimpf, M.R. Design of ligands for the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: The quest for selectivity. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2004, 4, 299–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yogeeswari, P.; Sriram, D.; Bal, T.R.; Thirumurugan, R. Epibatidine and its analogues as nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist: An update. Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 20, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, F.I. Epibatidine structure-activity relationships. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 5713. [Google Scholar]
- Seerden, J.G.; Tulp, M.T.; Scheeren, H.W.; Kruse, C.G. Synthesis and structure-activity data of some new epibatidine analogues. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 1998, 6, 2103–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badio, B.; Garraffo, H.M.; Plummer, C.V.; Padgett, W.L.; Daly, J.W. Synthesis and nicotinic activity of epiboxidine: An isoxazole analogue of epibatidine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 321, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, L.; Dallanoce, C.; Matera, C.; Magrone, P.; Pucci, L.; Gotti, C.; Clementi, F.; De Amici, M. Epiboxidine and novel-related analogues: A convenient synthetic approach and estimation of their affinity at neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 4651–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holladay, M.W.; Wasicak, J.T.; Lin, N.-H.; He, Y.; Ryther, K.B.; Bannon, A.W.; Buckley, M.J.; Kim, D.J.; Decker, M.W.; Anderson, D.J. Identification and initial structure—Activity relationships of (r)-5-(2-azetidinylmethoxy)-2-chloropyridine (abt-594), a potent, orally active, non-opiate analgesic agent acting via neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.D.; Anderson, D.J.; Campbell, J.E.; Carroll, S.; Marsh, K.C.; Rodrigues, A.D.; Decker, M.W. Preclinical pharmacology of abt-594: A nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist for the treatment of pain. CNS Drug Rev. 2000, 6, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowbotham, M.C.; Duan, W.R.; Thomas, J.; Nothaft, W.; Backonja, M.-M. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of abt-594 in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain 2009, 146, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, S.; Webb, J.K.; Shepheard, S.L.; Russell, M.G.; Hill, R.G.; Rupniak, N.M. Analgesic and toxic effects of abt-594 resemble epibatidine and nicotine in rats. Pain 2000, 85, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannon, A.W.; Decker, M.W.; Curzon, P.; Buckley, M.J.; Kim, D.J.; Radek, R.J.; Lynch, J.K.; Wasicak, J.T.; Lin, N.-H.; Arnold, W.H. Abt-594 [(r)-5-(2-azetidinylmethoxy)-2-chloropyridine]: A novel, orally effective antinociceptive agent acting vianeuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: Ii. In vivocharacterization. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 285, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Munro, G.; Dyhr, H.; Grunnet, M. Selective potentiation of gabapentin-mediated antinociception in the rat formalin test by the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist abt-594. Neuropharmacology 2010, 59, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, C.P. Mechanisms of action of gabapentin. Rev. Neurol. 1997, 153 (Suppl. 1), S39–S45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bitner, R.S.; Nikkel, A.L.; Curzon, P.; Arneric, S.P.; Bannon, A.W.; Decker, M.W. Role of the nucleus raphe magnus in antinociception produced by abt-594: Immediate early gene responses possibly linked to neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on serotonergic neurons. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 5426–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, T.; Katsuyama, S.; Orito, T.; Suzuki, T.; Sakurada, S. Antinociceptive effect of tebanicline for various noxious stimuli-induced behaviours in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 638, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hone, A.J.; McIntosh, J.M. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in neuropathic and inflammatory pain. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 1045–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sihver, W.; Nordberg, A.; Långström, B.; Mukhin, A.G.; Koren, A.O.; Kimes, A.S.; London, E.D. Development of ligands for in vivo imaging of cerebral nicotinic receptors. Behav. Brain Res. 2000, 113, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihver, W.; Långström, B.; Nordberg, A. Ligands for in vivo imaging of nicotinic receptor subtypes in alzheimer brain. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2000, 102, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belluardo, N.; Mudò, G.; Blum, M.; Cheng, Q.; Caniglia, G.; Dell’Albani, P.; Fuxe, K. The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist (±)-epibatidine increases fgf-2 mrna and protein levels in the rat brain. Mol. Brain Res. 1999, 74, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egea, J.; Rosa, A.O.; Cuadrado, A.; García, A.G.; López, M.G. Nicotinic receptor activation by epibatidine induces heme oxygenase-1 and protects chromaffin cells against oxidative stress. J. Neurochem. 2007, 102, 1842–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, A.; Corwin, J.; Lang, J.; Piasecki, M.; Lenox, R.; Newhouse, P.A. Acute effects of the selective cholinergic channel activator (nicotinic agonist) abt-418 in alzheimer’s disease. Psychopharmacology 1999, 142, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilens, T.E.; Biederman, J.; Spencer, T.J.; Bostic, J.; Prince, J.; Monuteaux, M.C.; Soriano, J.; Fine, C.; Abrams, A.; Rater, M. A pilot controlled clinical trial of abt-418, a cholinergic agonist, in the treatment of adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 1999, 156, 1931–1937. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perry, D.C.; Kellar, K.J. [3h] epibatidine labels nicotinic receptors in rat brain: An autoradiographic study. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995, 275, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
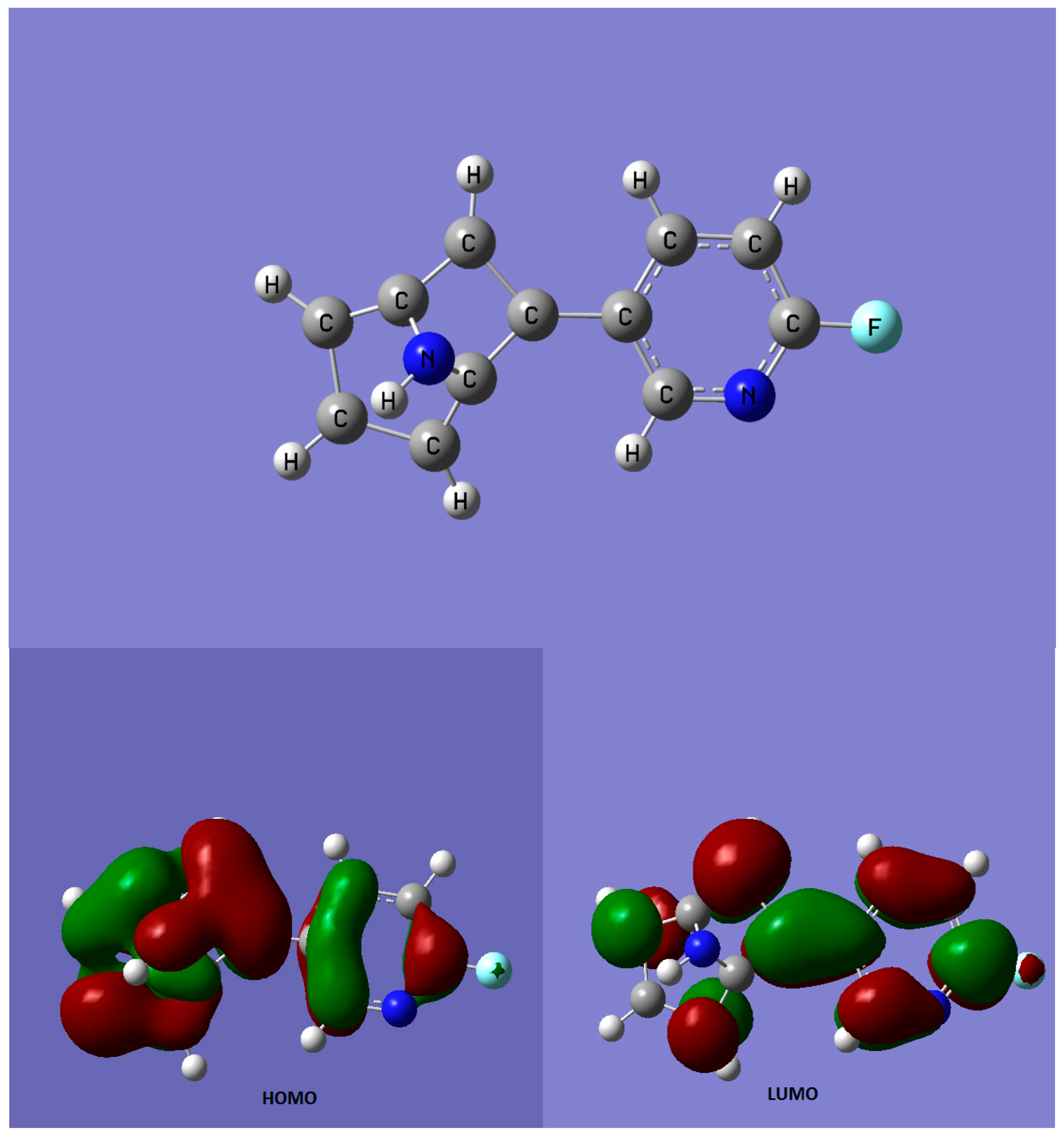
| Compound | Type of Study | References | |
|---|---|---|---|
| In Vivo Studies Using Animal Models | |||
| Epibatidine | Animal model | Primary outcomes | |
| Mice and rats | Antinociceptive | [6] | |
| Rats | Increased adrenaline and noradrenaline neuromediators | [12] | |
| Pregnant goats | Lack of completely inhibition of fetal movement | [11] | |
| Rats | Neuroprotective | [39] | |
| ABT-594 tebanicline | Rodent pain models (rats, mice) | Antinociceptive | [27,28,30,31,35] |
| Rat formalin test | Analgesic (multimodal analgesia) | [32] | |
| Epiboxidine | Rats | Cognitive disfunction treatment | [26] |
| Mice | Antinociceptive | ||
| In vitro studies using cell lines | |||
| Epibatidine | Bovine chromaffin cells | Antioxidant, antiapoptotic | [40] |
| Human clinical studies | |||
| ABT-594tebanicline | Study design | Primary outcomes | [29] |
| Randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (phase 2) | Analgesic in diabetic patients with neuropathic pain | ||
| ABT-418Epiboxidine | Double-blind, placebo-controlled study | Cognitive enhancement in moderate Alzheimer’s disease | [41] |
| Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial | Increased attention in deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults | [42] | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salehi, B.; Sestito, S.; Rapposelli, S.; Peron, G.; Calina, D.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Sharopov, F.; Martins, N.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Epibatidine: A Promising Natural Alkaloid in Health. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9010006
Salehi B, Sestito S, Rapposelli S, Peron G, Calina D, Sharifi-Rad M, Sharopov F, Martins N, Sharifi-Rad J. Epibatidine: A Promising Natural Alkaloid in Health. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalehi, Bahare, Simona Sestito, Simona Rapposelli, Gregorio Peron, Daniela Calina, Mehdi Sharifi-Rad, Farukh Sharopov, Natália Martins, and Javad Sharifi-Rad. 2019. "Epibatidine: A Promising Natural Alkaloid in Health" Biomolecules 9, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9010006
APA StyleSalehi, B., Sestito, S., Rapposelli, S., Peron, G., Calina, D., Sharifi-Rad, M., Sharopov, F., Martins, N., & Sharifi-Rad, J. (2019). Epibatidine: A Promising Natural Alkaloid in Health. Biomolecules, 9(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9010006












