RETRACTED: Evaluation of Anti-Obesity Activity, Acute Toxicity, and Subacute Toxicity of Probiotic Dark Tea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Tea Infusion Preparation
2.2.2. Acute Toxicity Studies
2.2.3. Subacute Toxicity Studies
2.2.4. The Anti-Obesity Effect of Probiotic Dark Tea in High-Fat Diet Sprague-Dawley Rats
2.2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
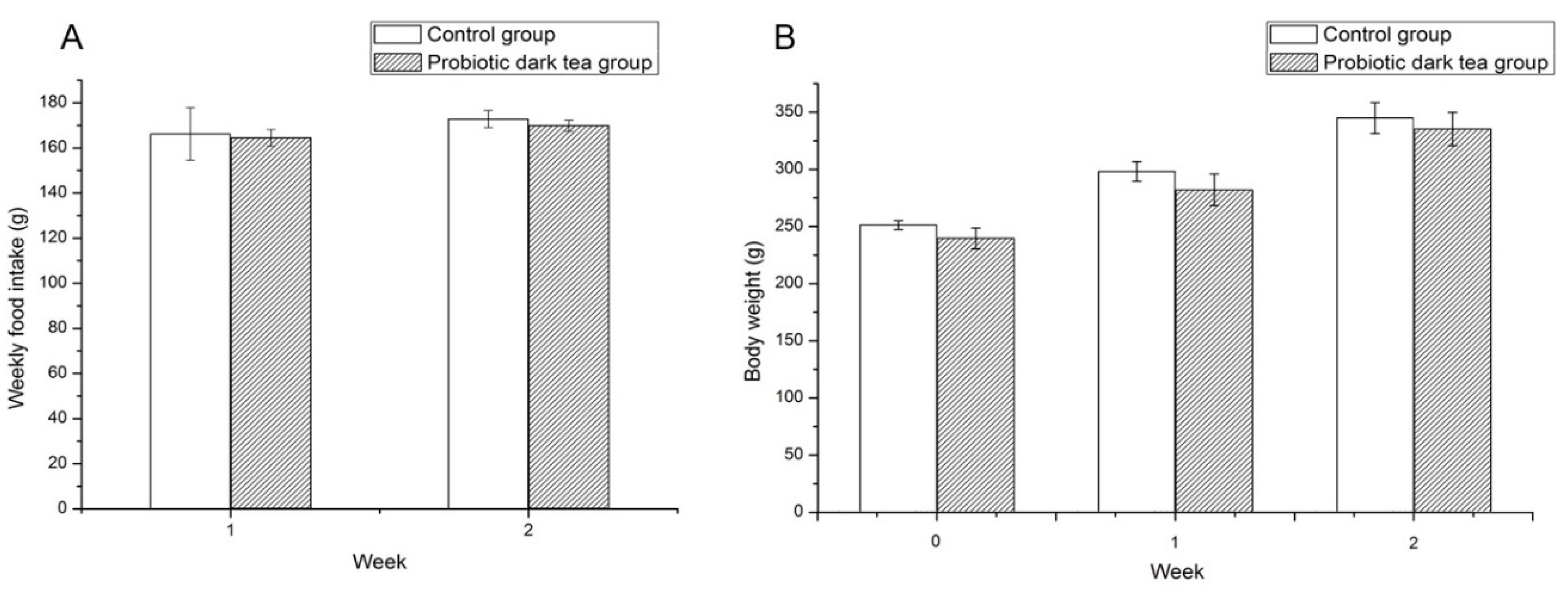
3.1. Acute Toxicity of Probiotic Dark Tea
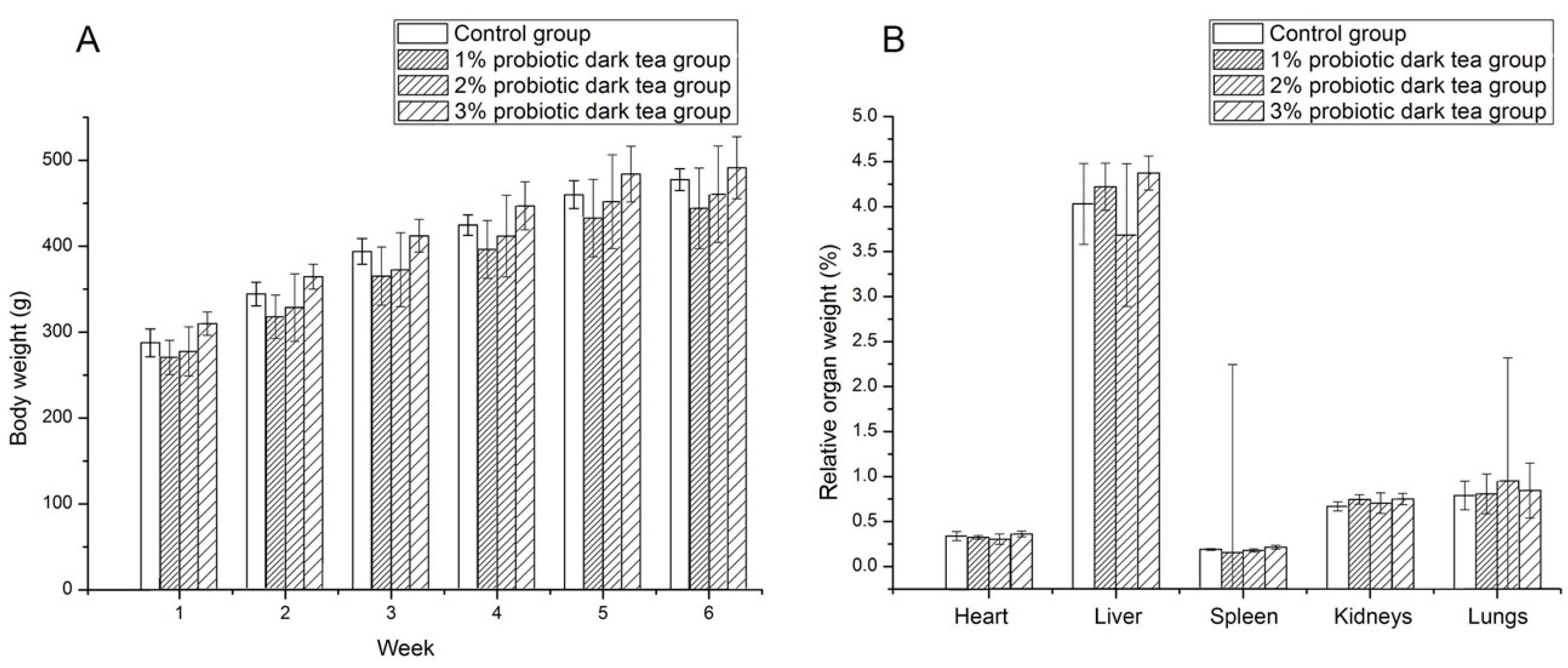
3.2. Subacute Toxicity of Probiotic Dark Tea
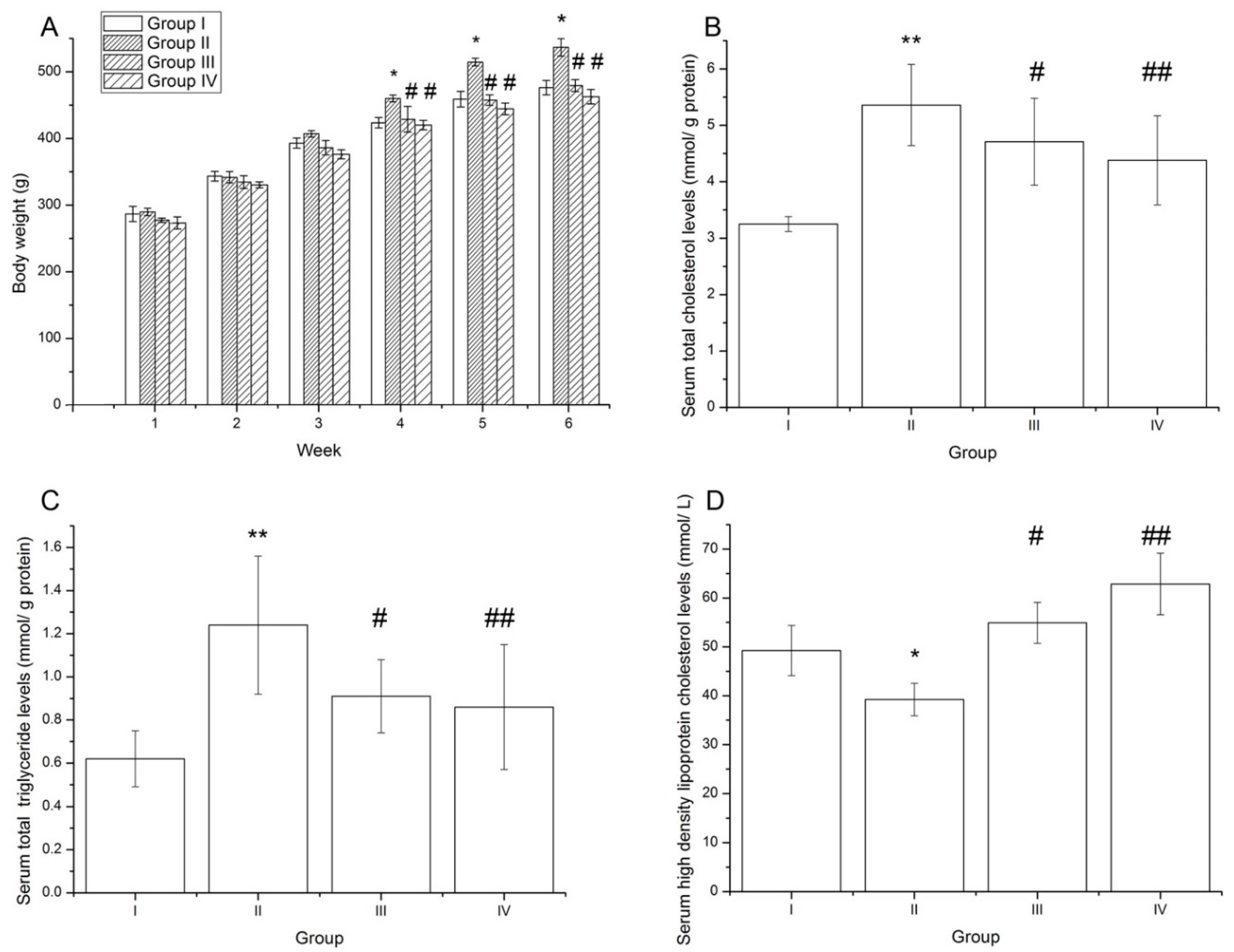
3.3. The Anti-Obesity Effect of Probiotic Dark Tea in High-Fat Diet Sprague-Dawley Rats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X. Tea and Cancer Prevention. J. Can. Res. Updat. 2015, 4, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Skaar, I.; Sulyok, M.; Liu, X.Z.; Rao, M.Y.; Taylor, J.W. The Microbiome and Metabolites in Fermented Pu-erh Tea as Revealed by High-Throughput Sequencing and Quantitative Multiplex Metabolite Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Jin, P.; Zhang, X.; Ravichandran, N.; Ying, H.; Yu, C.; Ying, H.; Xu, Y.; Yin, J.; Wang, K.; et al. New epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) nanocomplexes co-assembled with 3-mercapto-1-hexanol and β-lactoglobulin for improvement of antitumor activity. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2017, 13, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Shen, D.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shi, J.; Yin, J. Effect of Fermentation Conditions and Plucking Standards of Tea Leaves on the Chemical Components and Sensory Quality of Fermented Juice. J. Chem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Zhou, Y.B.; Ling, T.J.; Wan, X.C. Chinese dark teas: Postfermentation, chemistry and biological activities. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.J.; Wan, X.C.; Bao, G.H. Brick dark tea: A review of the manufacture, chemical constituents and bioconversion of the major chemical components during fermentation. Phytochem. Rev. 2015, 14, 499–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.P.; Zhang, Y.J.; Lin, Z.; Liang, Y.R. Processing and chemical constituents of Pu-erh tea: A review. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, K.C.; Chen, C.S.; Fang, Y.P.; Hou, R.C.; Chen, Y.S. Effect of microbial fermentation on content of statin, GABA, and polyphenols in Pu-Erh tea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8787–8792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.J.; Hwang, L.S. Study on the conversion of three natural statins from lactone forms to their corresponding hydroxy acid forms and their determination in Pu-Erh tea. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1119, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, J.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, H.J. Research Progress on the Hypolipidemic Effect and Ingredients of Pu-erh Tea. Chin. Agric. Bull. 2011, 27, 345–348. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, R.X.; Du, L.P.; Xu, R.X.; Xiao, D.G.; Wang, C. Correlations of enzymes and main quality components during the fermentation process of Pu’er tea. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2012, 33, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.H. Functional Appraisal of Blood Lipid Adjusted by Puer Tea and Study on Its Physiochemical Mechanism. Master’s Thesis, Southwest Agricultural University, Chongqing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y. MDG-1, an Ophiopogon polysaccharide, regulate gut microbiota in high-fat diet-induced obese C57BL/6 mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.H.; Huang, J.A.; Shi, Z.P. Dynamics of the major enzymes during the primary processing of dark green tea. J. Tea Sci. 1991, 11, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, D.; Pfeifer, B.; Reiterich, C.; Partenheimer, R.; Reck, B.; Buzina, W. Identification and quantification of fungi and mycotoxins from Pu-erh tea. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 166, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirogi, R.; Goyal, V.K.; Jana, S.; Pandey, S.K.; Gothi, A. What suits best for organ weight analysis: Review of relationship between organ weight and body/ brain weight for rodent toxicity studies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 5, 1525–1532. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.Y.; Guan, M.J.; Yang, W.J. The effect of brick tea on weight and the fat in blood of rats. J. Baotou Med. Coll. 2002, 18, 177–178. [Google Scholar]
- Du, M.; Chen, X.Q.; Han, X.L.; Di, X.Y. Effect of tea infusions with different concentrations on the blood lipids and body weight of rats. Chin. J. Health Lab. Technol. 2000, 10, 120. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, H.Z.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhu, P.P. Effect of tea infusions with different concentrations on the blood lipids and body weight of high-fat diet rats. China Public Health 2000, 16, 195. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T. Effect of Eurotium cristatum Fermented Dark Tea Extract on Body Weight and Blood Lipid in Rats. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, A77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, Y.; Swaisgood, M.H.; Ramos, B.V.; Steck, T.L. Plasma membranes contain half the phospholipid and 90% of the cholesterol and sphingomyelin in cultured human fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 3786–3793. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science 1986, 232, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Goldstein, J.L.; Anderson, D.D.; Brown, M.S. Use of mutant 125I-Perfringolysin O to probe transport and organization of cholesterol in membranes of animal cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 10580–10585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prospective Studies Collaboration; Lewington, S.; Whitlock, G.; Clarke, R.; Sherliker, P.; Emberson, J.; Halsey, J.; Qizilbash, N.; Peto, R.; Collins, R. Blood cholesterol and vascular mortality by age, sex, and blood pressure: A meta-analysis of individual data from 61 prospective studies with 55,000 vascular deaths. Lancet 2008, 370, 1829–1839. [Google Scholar]
- Kontush, A.; Chapman, M.J. Functionally defective high-density lipoprotein: A new therapeutic target at the crossroads of dyslipidemia, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 342–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.F.; Rader, D.J. New insights into the regulation of HDL metabolism and reverse cholesterol transport. Circ. Res. 2005, 96, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acheson, K.J.; Zahorska-Markiewicz, B.; Pittet, P.; Anantharaman, K.; Jéquier, E. Caffeine and coffee: Their influence on metabolic rate and substrate utilization in normal weight and obese individuals. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1980, 33, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.S.; Peng, C.X.; Chen, T.; Gao, B.; Zhou, H.J. Effects of Theabrownin from Pu-erh Tea on the Metabolism of Serum Lipids in Rats: Mechanism of Action. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, H182–H189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.K.; Lin-Shiau, S.Y. Mechanisms of hypolipidemic and anti-obesity effects of tea and tea polyphenols. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, C.; Nishimatsu, S.; Moriyama, T.; Ozasa, S.; Kawada, T.; Sayama, K. Catechins and Caffeine Inhibit Fat Accumulation in Mice through the Improvement of Hepatic Lipid Metabolism. J. Obes. 2012, 2012, 520510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wu, T.; Dai, S.; Xu, J.; Zhou, Z. The anti-obesity effect of green tea polysaccharides, polyphenols and caffeine in rats fed with a high-fat diet. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Group | WBC (109/L) | Lymph (%) | RBC (1012/L) | HGB (g/L) | MCV (Fl) | MCHC (g/L) | Mon (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 4.67 ± 0.78 | 75.38 ± 3.16 | 6.97 ± 0.65 | 140.00 ± 7.59 | 55.22 ± 1.50 | 307.33 ± 5.32 | 2.82 ± 0.29 |
| 1% PDT | 4.70 ± 1.04 | 75.80 ± 6.59 | 7.12 ± 0.65 | 134.33 ± 12.13 | 55.92 ± 0.70 | 316.33 ± 7.74 | 3.05 ± 0.73 |
| 2% PDT | 4.45 ± 1.45 | 75.47 ± 4.53 | 7.19 ± 0.28 | 138.33 ± 9.91 | 54.75 ± 1.71 | 320.50 ± 12.94 | 3.23 ± 0.93 |
| 3% PDT | 4.97 ± 1.01 | 74.73 ± 4.84 | 6.93 ± 0.96 | 136.67 ± 5.13 | 56.17 ± 1.61 | 309.67 ± 7.06 | 2.67 ± 0.66 |
| Group | ALT (U/L) | AST (U/L) | GGT (U/L) | TBIL (μmol/L) | TP (g/L) | CK (U/L) | BUN (mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 64.76 ± 14.77 | 42.98 ± 3.30 | 5.00 ± 0.71 | 4.54 ± 1.21 | 80.52 ± 2.08 | 160.40 ± 26.69 | 4.87 ± 0.57 |
| 1%PDT | 53.12 ± 16.34 | 36.80 ± 4.25 | 3.12 ± 2.07 | 6.60 ± 3.83 | 76.55 ± 3.07 | 138.17 ± 26.07 | 5.89 ± 0.82 |
| 2%PDT | 52.50 ± 15.27 | 40.32 ± 7.53 | 3.77 ± 1.30 | 4.77 ± 1.93 | 76.23 ± 3.77 | 128.83 ± 22.56 | 5.78 ± 0.73 |
| 3%PDT | 71.68 ± 16.29 | 38.18 ± 5.31 | 4.22 ± 1.65 | 6.67 ± 1.67 | 77.55 ± 4.08 | 167.67 ± 33.13 | 5.59 ± 1.96 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ling, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Du, Q.; Wang, G.; Fan, W.; Sun, K.; Bian, J. RETRACTED: Evaluation of Anti-Obesity Activity, Acute Toxicity, and Subacute Toxicity of Probiotic Dark Tea. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8040099
Ling W, Li S, Zhang X, Xu Y, Gao Y, Du Q, Wang G, Fan W, Sun K, Bian J. RETRACTED: Evaluation of Anti-Obesity Activity, Acute Toxicity, and Subacute Toxicity of Probiotic Dark Tea. Biomolecules. 2018; 8(4):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8040099
Chicago/Turabian StyleLing, Wang, Shungeng Li, Xingcai Zhang, Yongquan Xu, Ying Gao, Qizhen Du, Guangguang Wang, Wentong Fan, Kai Sun, and Jianchun Bian. 2018. "RETRACTED: Evaluation of Anti-Obesity Activity, Acute Toxicity, and Subacute Toxicity of Probiotic Dark Tea" Biomolecules 8, no. 4: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8040099
APA StyleLing, W., Li, S., Zhang, X., Xu, Y., Gao, Y., Du, Q., Wang, G., Fan, W., Sun, K., & Bian, J. (2018). RETRACTED: Evaluation of Anti-Obesity Activity, Acute Toxicity, and Subacute Toxicity of Probiotic Dark Tea. Biomolecules, 8(4), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8040099






