Ashes to Rashes: An Exploration of the Intersection Between Smoking and Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
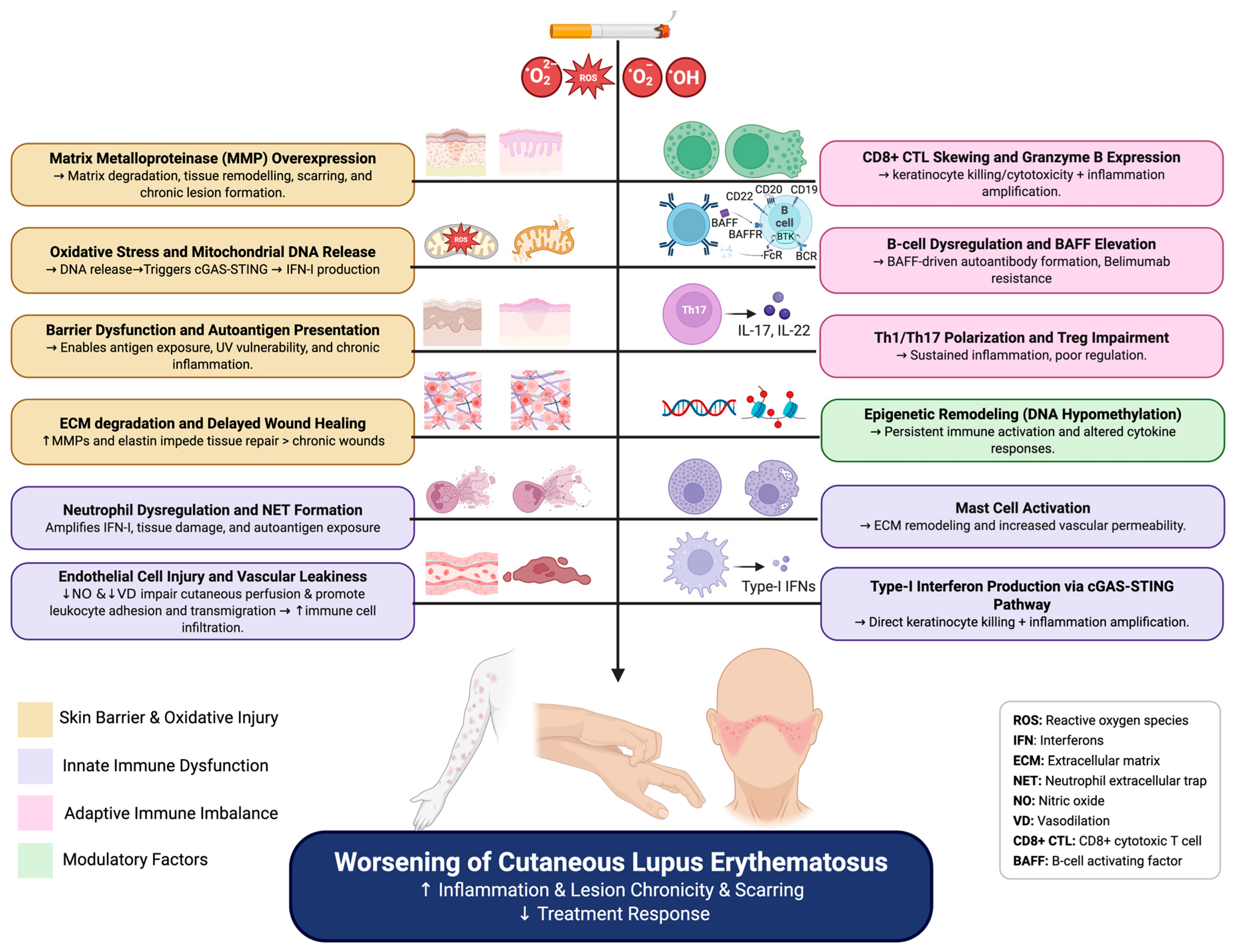
1. Introduction
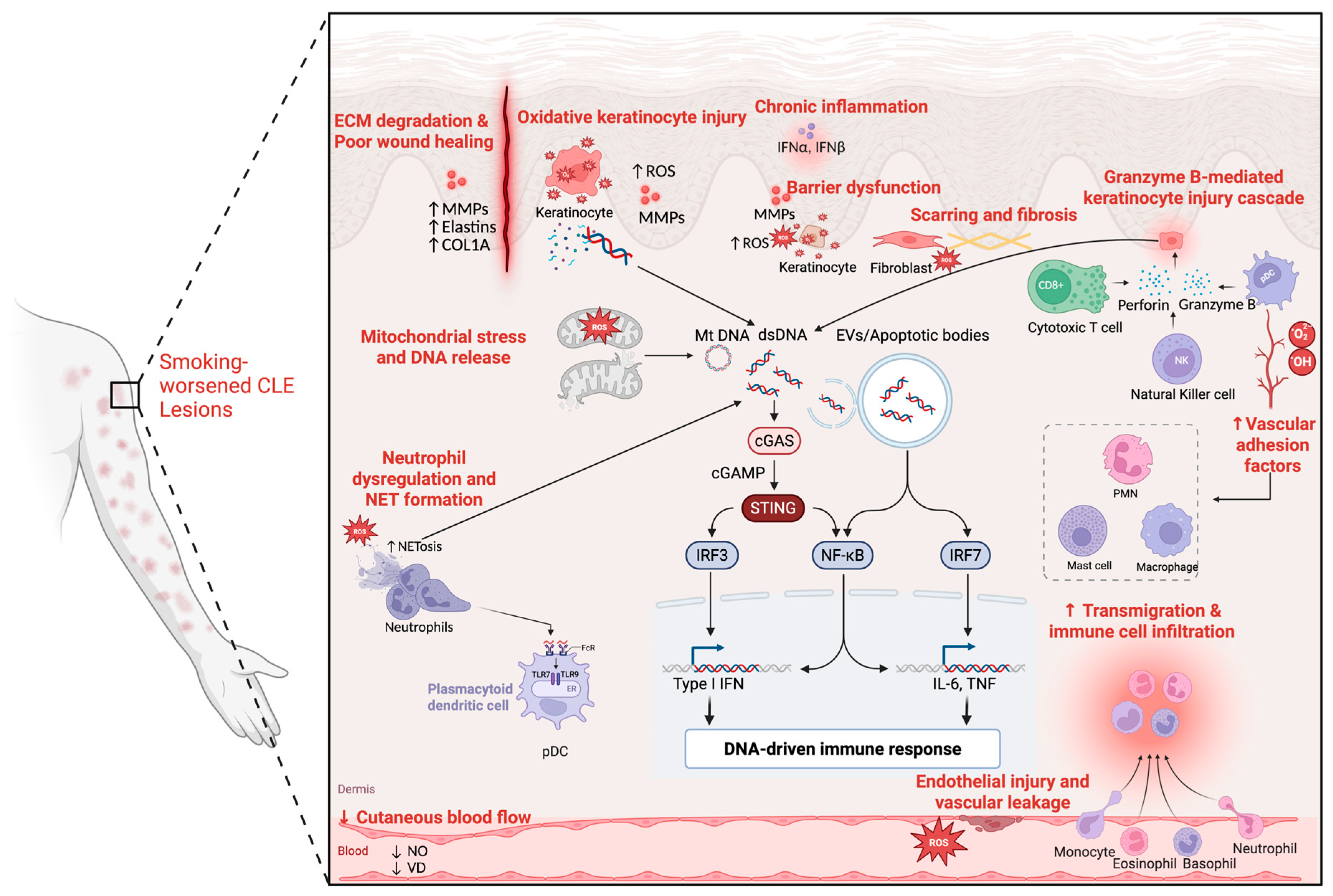
2. Initial Insults: Cigarette Smoke and Damage Induction in CLE Skin
2.1. Oxidative Stress and DNA Release
| Cell Type | Key Effects of Smoking/CS Exposure | Potential Impact on CLE Pathogenesis | Citation(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Keratinocytes | Induces oxidative stress, mitochondrial DNA release, and increased MMP-1 expression. | May trigger the cGAS-STING pathway to produce Type I IFN; degrades the extracellular matrix. | [16,47,48,49] |
| Fibroblasts | Causes oxidative stress, cellular senescence, and upregulation of MMP-1 in dermal fibroblasts. | May contribute to matrix remodeling and fibrosis seen in DLE; may participate in the inflammatory feedback loop. | [15,50,54] |
| Endothelial Cells | Increases ROS, reduces nitric oxide, enhances leukocyte adhesion and permeability. | May impair cutaneous blood flow and promotes the infiltration of inflammatory immune cells into the skin, fueling lesion formation. | [53,55,56] |
2.2. Formation of Extracellular Traps and Extracellular Vesicles
2.3. Barrier Dysfunction and Autoantigen Presentation
3. Amplification of Inflammation: The Interplay of Innate and Adaptive Immunity
3.1. Inflammatory Cell Recruitment and Activation
3.2. Cytotoxic Amplification of Inflammation
3.3. Type I Interferon Cascade: A CenBioRendertral Hub in CLE and Smoking
4. Dysregulation of Adaptive Immunity in Smoking-Related CLE
4.1. B-Cell Dysregulation and the B-Cell Activating Factor Axis
4.2. CD4+ T-Cell Polarization and Regulatory Imbalance
5. Epigenetic Implications of Smoking for CLE
6. Heat, Nicotine, and E-Cigarettes
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CLE | Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus |
| SHS | Secondhand Smoke |
| THS | Thirdhand Smoke |
| CS | Cigarette Smoke |
| ACLE | Acute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus |
| SCLE | Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus |
| DLE | Discoid Lupus Erythematosus |
| SLE | Systemic Lupus Erythematosus |
| EV | Extracellular Vesicle |
| CSE | Cigarette Smoke Extract |
| EC | Endothelial Cell |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| NET | Neutrophil Extracellular Trap |
| pDC | Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell |
| MMP | Matrix Metalloproteinases |
| TSE | Tobacco Smoke Extract |
| NK | Natural Killer |
| IFN | Interferon |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| CTL | Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte |
| BAFF | B-Cell Activating Factor |
| Treg | Regulatory T Cell |
| EC | Electronic Cigarette |
| ENDP | Electronic Nicotine Delivery Products |
References
- Yavuz, G.O.; Yavuz, I.H.; Bayram, I.; Aktar, R.; Bilgili, S.G. Clinic Experience in Discoid Lupus Erythematosus: A Retrospective Study of 132 Cases. Postep. Dermatol. Alergol. 2019, 36, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arévalo-Bermúdez, M.d.P.; Paradela, S.; Balboa-Barreiro, V.; Fonseca, E. Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus: Factors Related to Cutaneous Activity and Damage in a Cohort of 260 Patients from A Coruña, Spain. Lupus 2020, 29, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faden, D.F.; Xie, L.; Stone, C.; Lopes Almeida Gomes, L.; Le, T.; Ezeh, N.; Buckingham, W.R.; Kind, A.; Vleugels, R.A.; Werth, V.P.; et al. Area Deprivation and Disease Severity in Adult Patients with Discoid Lupus Erythematosus. JAMA Dermatol. 2024, 160, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskenmies, S.; Järvinen, T.M.; Onkamo, P.; Panelius, J.; Tuovinen, U.; Hasan, T.; Ranki, A.; Saarialho-Kere, U. Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics of Finnish Lupus Erythematosus Patients with Cutaneous Manifestations. Lupus 2008, 17, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miot, H.A.; Miot, L.D.B.; Haddad, G.R. Association between Discoid Lupus Erythematosus and Cigarette Smoking: A Case-Control Study. Dermatology 2005, 211, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeckler, P.; Milea, M.; Meyer, A.; Uring-Lambert, B.; Heid, E.; Hauptmann, G.; Cribier, B.; Lipsker, D. The Combination of Complement Deficiency and Cigarette Smoking as Risk Factor for Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus in Men; a Focus on Combined C2/C4 Deficiency. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 152, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeckler, P.; Cosnes, A.; Francès, C.; Hedelin, G.; Lipsker, D. Association of Cigarette Smoking but Not Alcohol Consumption with Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. Arch. Dermatol. 2009, 145, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuter, A.; Gaifullina, R.; Tigges, C.; Kirschke, J.; Altmeyer, P.; Gambichler, T. Lupus Erythematosus Tumidus Response to Antimalarial Treatment in 36 Patients with Emphasis on Smoking. Arch. Dermatol. 2009, 145, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, A.; Sigges, J.; Biazar, C.; Ruland, V.; Patsinakidis, N.; Landmann, A.; Amler, S.; Bonsmann, G. Influence of Smoking on Disease Severity and Antimalarial Therapy in Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus: Analysis of 1002 Patients from the EUSCLE Database. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 171, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobacco. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/tobacco (accessed on 13 July 2025).
- Health Risks of Secondhand Smoke|American Cancer Society. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/risk-prevention/tobacco/secondhand-smoke.html (accessed on 13 July 2025).
- Health Problems Caused by Secondhand Smoke|Smoking and Tobacco Use|CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/secondhand-smoke/health.html (accessed on 13 July 2025).
- United States Public Health Service Office of the Surgeon General; National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion (US) Office on Smoking and Health. Smoking Cessation: A Report of the Surgeon General; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2020.
- About Secondhand Smoke|Smoking and Tobacco Use|CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/secondhand-smoke/index.html (accessed on 13 July 2025).
- Hammer, T.R.; Fischer, K.; Mueller, M.; Hoefer, D. Effects of Cigarette Smoke Residues from Textiles on Fibroblasts, Neurocytes and Zebrafish Embryos and Nicotine Permeation through Human Skin. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2011, 214, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, R.; Kolci, K.; Yedikardes, E.N.; Coskun, G.P.; Uzuner, Y. Dermal Thirdhand Smoke Exposure Induced Epidermal Alterations in Human Keratinocyte Cells through Oxidative Damage and MMP-1 Expression. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 33, e15020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, J. Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus: New Insights into Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Strategies. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hile, G.A.; Werth, V.P. Understanding the Role of Type I Interferons in Cutaneous Lupus and Dermatomyositis: Toward Better Therapeutics. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025, 77, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchin, I.; Bernatsky, S.; Clarke, A.E.; St-Pierre, Y.; Pineau, C.A. Cigarette Smoking and Cutaneous Damage in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 2691–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourré-Tessier, J.; Peschken, C.A.; Bernatsky, S.; Joseph, L.; Clarke, A.E.; Fortin, P.R.; Hitchon, C.; Mittoo, S.; Smith, C.D.; Zummer, M.; et al. Association of Smoking with Cutaneous Manifestations in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Care Res. 2013, 65, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezeh, N.; McKown, T.; Garg, S.; Bartels, C.M. Smoking Exposure in Pack-Years Predicts Cutaneous Manifestations and Damage in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Lupus 2021, 30, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jewell, M.L.; McCauliffe, D.E. Patients with Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Who Smoke Are Less Responsive to Antimalarial Treatment. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2000, 42, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böckle, B.C.; Sepp, N.T. Smoking Is Highly Associated with Discoid Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Erythematosus Tumidus: Analysis of 405 Patients. Lupus 2015, 24, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piette, E.W.; Foering, K.P.; Chang, A.Y.; Okawa, J.; Ten Have, T.R.; Feng, R.; Werth, V.P. Impact of Smoking in Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. Arch. Dermatol. 2012, 148, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam-Kia, S.; Chilek, K.; Gaines, E.; Costlier, M.; Rose, M.E.; Okawa, J.; Werth, V.P. Cross-Sectional Analysis of a Collaborative Web-Based Database for Lupus Erythematosus-Associated Skin Lesions Prospective Enrollment of 114 Patients. Arch. Dermatol. 2009, 145, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayard, D.; Francès, C.; Amoura, Z.; Breillat, P.; Mathian, A.; Senet, P.; Barbaud, A.; Arnaud, L.; Chasset, F. Prevalence and Factors Associated with Long-Term Remission in Cutaneous Lupus: A Longitudinal Cohort Study of 141 Cases. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 87, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florez-Pollack, S.; Rizvi, S.K.; Hynan, L.S.; Chong, B.F. Discoid Lesions and Smoking History Are Negative Predictors of Disease Activity Remission in Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 87, 1135–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chasset, F.; Francès, C.; Arnaud, L. Smoking Enhances Toll-like Receptor-9 Responsiveness and Type i Interferon Production in Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells in Patients with Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 73, e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Placzek, M.; Kerkmann, U.; Bell, S.; Koepke, P.; Przybilla, B. Tobacco Smoke Is Phototoxic. Br. J. Dermatol. 2004, 150, 991–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.Q.; Capra, J.D.; Sontheimer, R.D. 4-Aminoquinoline Antimalarials Enhance UV-B Induced c-Jun Transcriptional Activation. Lupus 1998, 7, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniacka, A.; Lesiak, A.; Boncela, J.; Smolarczyk, K.; McCauliffe, D.P.; Sysa-Jedrzejowska, A. The Influence of Antimalarial Treatment on IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α MRNA Expression on UVB-Irradiated Skin in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 159, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.W.; Sprow, G.; Feng, R.; Werth, V.P.; Chong, B.F. Cigarette Smoking Is Associated with Decreased Long-Term Treatment Cessation of Mycophenolate Mofetil and Methotrexate in Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. Lupus 2023, 32, 1134–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hukkanen, J.; Jacob, P.; Peng, M.; Dempsey, D.; Benowitz, N.L. Effect of Nicotine on Cytochrome P450 1A2 Activity. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 72, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zevin, S.; Benowitz, N.L. Drug Interactions with Tobacco Smoking. An Update. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1999, 36, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.M.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, M.Z.; Li, Y.; Li, H.Q.; Li, W.Y. Effects of Long-Term Smoking on the Activity and MRNA Expression of CYP Isozymes in Rats. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 1725–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, G.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Hulot, J.-S.; Amoura, Z.; Francè, C.; Aymard, G.; Lechat, P.; Piette, J.-C. Relationship between Blood Hydroxychloroquine and Desethylchloroquine Concentrations and Cigarette Smoking in Treated Patients with Connective Tissue Diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 1547–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipa, K.; Zając, N.; Owczarek, W.; Ciechanowicz, P.; Szymańska, E.; Walecka, I. Does Smoking Affect Your Skin? Postȩpy Dermatol. Alergol. 2021, 38, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perricone, C.; Versini, M.; Ben-Ami, D.; Gertel, S.; Watad, A.; Segel, M.J.; Ceccarelli, F.; Conti, F.; Cantarini, L.; Bogdanos, D.P.; et al. Smoke and Autoimmunity: The Fire behind the Disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 354–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, D.; Jon Williams, K.; Liu, M.-L. Novel Proteolytic Microvesicles Released from Human Macrophages after Exposure to Tobacco Smoke. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 1552–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Liang, C.L.; Liu, H.; Zeng, Y.Q.; Hou, S.; Huang, S.; Lai, X.; Dai, Z. Impacts of Cigarette Smoking on Immune Responsiveness: Up and down or Upside Down? Oncotarget 2016, 8, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortaz, E.; Adcock, I.M.; Ito, K.; Kraneveld, A.D.; Nijkamp, F.P.; Folkerts, G. Cigarette Smoke Induces CXCL8 Production by Human Neutrophils via Activation of TLR9 Receptor. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 36, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brembach, T.C.; Sabat, R.; Witte, K.; Schwerdtle, T.; Wolk, K. Molecular and Functional Changes in Neutrophilic Granulocytes Induced by Nicotine: A Systematic Review and Critical Evaluation. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1281685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Lee, J.; Jeong, J.; Woo, J.; Lee, C.H.; Yoo, C.G. Cigarette Smoke Extract Enhances Neutrophil Elastase-Induced IL-8 Production via Proteinase-Activated Receptor-2 Upregulation in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milad, N.; Pineault, M.; Bouffard, G.; Maranda-Robitaille, M.; Lechasseur, A.; Beaulieu, M.J.; Aubin, S.; Jensen, B.A.H.; Morissette, M.C. Recombinant Human β-Defensin 2 Delivery Improves Smoking-Induced Lung Neutrophilia and Bacterial Exacerbation. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2022, 323, L37–L47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piaggeschi, G.; Rolla, S.; Rossi, N.; Brusa, D.; Naccarati, A.; Couvreur, S.; Spector, T.D.; Roederer, M.; Mangino, M.; Cordero, F.; et al. Immune Trait Shifts in Association With Tobacco Smoking: A Study in Healthy Women. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 637974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maz, M.P.; Martens, J.W.S.; Hannoudi, A.; Reddy, A.L.; Hile, G.A.; Kahlenberg, J.M. Recent Advances in Cutaneous Lupus. J. Autoimmun. 2022, 132, 102865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sticozzi, C.; Belmonte, G.; Pecorelli, A.; Arezzini, B.; Gardi, C.; Maioli, E.; Miracco, C.; Toscano, M.; Forman, H.J.; Valacchi, G. Cigarette Smoke Affects Keratinocytes SRB1 Expression and Localization via H2O2 Production and HNE Protein Adducts Formation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, P.; Nanjappa, V.; Raja, R.; Jain, A.P.; Mangalaparthi, K.K.; Sathe, G.J.; Babu, N.; Patel, K.; Cavusoglu, N.; Soeur, J.; et al. How Does Chronic Cigarette Smoke Exposure Affect Human Skin? A Global Proteomics Study in Primary Human Keratinocytes. OMICS A J. Integr. Biol. 2016, 20, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avezov, K.; Reznick, A.Z.; Aizenbud, D. Oxidative Damage in Keratinocytes Exposed to Cigarette Smoke and Aldehydes. Toxicol. Vitr. 2014, 28, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.Y.; Zhang, C.L.; Liu, X.C.; Qian, G.; Deng, D.Q. Effects of Cigarette Smoke Extracts on the Growth and Senescence of Skin Fibroblasts In Vitro. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kim, H.S.; Chung, J.H. Molecular Mechanisms of Mitochondrial DNA Release and Activation of the CGAS-STING Pathway. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, I.; Uchida, H.; Dai, Z.; Li, F.; Sanchez, T.; Locasale, J.W.; Cantley, L.C.; Zheng, H.; Paik, J. Cellular Stress Signaling Activates Type-I IFN Response through FOXO3-Regulated Lamin Posttranslational Modification. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saaoud, F.; Shao, Y.; Cornwell, W.; Wang, H.; Rogers, T.J.; Yang, X. Cigarette Smoke Modulates Inflammation and Immunity via Reactive Oxygen Species-Regulated Trained Immunity and Trained Tolerance Mechanisms. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2023, 38, 1041–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arredondo, J.; Hall, L.L.; Ndoye, A.; Nguyen, V.T.; Chernyavsky, A.I.; Bercovich, D.; Orr-Urtreger, A.; Beaudet, A.L.; Grando, S.A. Central Role of Fibroblast A3 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor in Mediating Cutaneous Effects of Nicotine. Lab. Investig. 2003, 83, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Pistelli, F.; Pesce, M.; Aquilini, F.; Franzoni, F.; Santoro, G.; Carrozzi, L. Impact of Long-Term Exposure to Cigarette Smoking on Skin Microvascular Function. Microvasc. Res. 2014, 93, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messner, B.; Bernhard, D. Smoking and Cardiovascular Disease: Mechanisms of Endothelial Dysfunction and Early Atherogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, T.; Patel, J.; Kodali, N.; Diaz, D.A.; Bashir, M.M.; Chin, F.; Keyes, E.; Sharma, M.; Sprow, G.; Grinnell, M.; et al. Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Are Not Major Producers of Type 1 IFN in Cutaneous Lupus: An In-Depth Immunoprofile of Subacute and Discoid Lupus. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 144, 1262–1272.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, D.S.; Flanders, W.D.; Barboriak, J.J.; Malarcher, A.M.; Gates, L. Cigarette Smoking and Leukocyte Subpopulations in Men. Ann. Epidemiol. 1996, 6, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.; Weiss, S.T. Cigarette Smoking and Peripheral Blood Leukocyte Differentials. Ann. Epidemiol. 1994, 4, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Effect of Smoking on Neutrophil/Lymphocyte and Platelet/Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet Indices: A Retrospective Study. Available online: https://www.europeanreview.org/article/11185 (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- White, P.C.; Hirschfeld, J.; Milward, M.R.; Cooper, P.R.; Wright, H.J.; Matthews, J.B.; Chapple, I.L.C. Cigarette Smoke Modifies Neutrophil Chemotaxis, Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation and Inflammatory Response-Related Gene Expression. J. Periodontal Res. 2018, 53, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.L.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Q.Y.; Bai, J.; He, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.Q.; Li, M.H.; Deng, J.M.; Liu, G.N.; Zhong, X.N. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Induced by Cigarette Smoke Activate Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells. Thorax 2017, 72, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.L.; Lyu, X.; Werth, V.P. Recent Progress in the Mechanistic Understanding of NET Formation in Neutrophils. FEBS J. 2021, 289, 3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, M.; Weigel, B.; Mall, M.; Werth, V.P.; Liu, M. Nuclear Envelope Rupture and NET Formation Is Driven by PKCα-mediated Lamin B Disassembly. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e48779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amulic, B.; Knackstedt, S.L.; Abu Abed, U.; Deigendesch, N.; Harbort, C.J.; Caffrey, B.E.; Brinkmann, V.; Heppner, F.L.; Hinds, P.W.; Zychlinsky, A. Cell-Cycle Proteins Control Production of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Dev. Cell 2017, 43, 449–462.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lyu, X.; Liao, J.; Werth, V.P.; Liu, M.L. Rho Kinase Regulates Neutrophil NET Formation That Is Involved in UVB-Induced Skin Inflammation. Theranostics 2022, 12, 2133–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dąbrowska, D.; Jabłońska, E.; Garley, M.; Ratajczak-Wrona, W.; Iwaniuk, A. New Aspects of the Biology of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Scand. J. Immunol. 2016, 84, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Boettcher, M.; Dölling, M.; Heuer, A.; Hohberger, B.; Leppkes, M.; Naschberger, E.; Schapher, M.; Schauer, C.; Schoen, J.; et al. Moonlighting Chromatin: When DNA Escapes Nuclear Control. Cell Death Differ. 2023, 30, 861–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoiber, W.; Obermayer, A.; Steinbacher, P.; Krautgartner, W.D. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in the Formation of Extracellular Traps (ETs) in Humans. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safi, R.; Al-Hage, J.; Abbas, O.; Kibbi, A.G.; Nassar, D. Investigating the Presence of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Cutaneous Lesions of Different Subtypes of Lupus Erythematosus. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 1348–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, N.E.; James, V.; Arkill, K.P.; Nizamudeen, Z.A.; Onion, D.; Fairclough, L.C. PBMC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in a Smoking-Related Inflammatory Disease Model. Eur. J. Immunol. 2023, 53, 2250143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, A.E.; Liao, Z.; Tkach, M.; Tarwater, P.M.; Ostrowski, M.; Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W. Cigarette Smoke-Induced Extracellular Vesicles from Dendritic Cells Alter T-Cell Activation and HIV Replication. Toxicol. Lett. 2022, 360, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkesson, M.; Li, C.; Frebelius, S.; Swedenborg, J.; Wågsäter, D.; Williams, K.J.; Eriksson, P.; Roy, J.; Liu, M.L. Proteolytically Active ADAM10 and ADAM17 Carried on Membrane Microvesicles in Human Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 114, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.M.; Zyulina, V.; Seltzer, E.S.; Dacic, M.; Chinenov, Y.; Daamen, A.R.; Veiga, K.R.; Schwartz, N.; Oliver, D.J.; Cabahug-Zuckerman, P.; et al. The Interferon-Rich Skin Environment Regulates Langerhans Cell ADAM17 to Promote Photosensitivity in Lupus. Elife 2024, 13, e85914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Baniel, A.; Diaz, D.A.; Ogawa-Momohara, M.; Ricco, C.; Eldaboush, A.; Bashir, M.; Sharma, M.; Liu, M.L.; Werth, V.P. Keratinocyte Derived Extracellular Vesicles Mediated Crosstalk between Epidermis and Dermis in UVB-Induced Skin Inflammation. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.L.; Williams, K.J.; Werth, V.P. Microvesicles in Autoimmune Diseases. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2016, 77, 125–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Xie, L.; Qin, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Lv, F.; Wang, L.; Zhu, X.; Xu, J. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 835566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricco, C.; Eldaboush, A.; Liu, M.L.; Werth, V.P. Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathogenesis, Clinical Characterization, and Management of Dermatomyositis: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wei, W.; Liu, M.L. Extracellular Vesicles and Lupus Nephritis—New Insights into Pathophysiology and Clinical Implications. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 115, 102540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fettig, J.; Callaghan, D.; Goldberg, L.J. Discoid Lupus Erythematosus. Alopecia 2019, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achtman, J.C.; Werth, V.P. Pathophysiology of Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoffner-Beck, S.K.; Abernathy-Close, L.; Lazar, S.; Ma, F.; Gharaee-Kermani, M.; Hurst, A.; Dobry, C.; Pandian, D.; Wasikowski, R.; Victory, A.; et al. Lupus Dermal Fibroblasts Are Proinflammatory and Exhibit a Profibrotic Phenotype in Scarring Skin Disease. JCI Insight 2024, 9, e173437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertugrul, G.; Keles, D.; Oktay, G.; Aktan, S. Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 and -9 Activity Levels Increase in Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Lesions and Correlate with Disease Severity. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2018, 310, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvinen, T.M.; Kanninen, P.; Jeskanen, L.; Koskenmies, S.; Panelius, J.; Hasan, T.; Ranki, A.; Saarialho-Kere, U. Matrix Metalloproteinases as Mediators of Tissue Injury in Different Forms of Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 157, 970–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nguyen, H.; Di Girolamo, N.; Jackson, N.; Hampartzoumian, T.; Bullpitt, P.; Tedla, N.; Wakefield, D. Ultraviolet Radiation-Induced Cytokines Promote Mast Cell Accumulation and Matrix Metalloproteinase Production: Potential Role in Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 40, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, A.; Torii, K.; Maeda, A.; Yamaguchi, Y. Molecular Basis of Tobacco Smoke-Induced Premature Skin Aging. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2009, 14, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahmann, C.; Bergemann, J.; Harrison, G.; Young, A.R. Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 and Skin Ageing in Smokers. Lancet 2001, 357, 935–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlstein, T.S.; Lee, R.T. Smoking, Metalloproteinases, and Vascular Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zigrino, P.; Brinckmann, J.; Niehoff, A.; Lu, Y.; Giebeler, N.; Eckes, B.; Kadler, K.E.; Mauch, C. Fibroblast-Derived MMP-14 Regulates Collagen Homeostasis in Adult Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarczyk-Sekuła, K.; Dyduch, G.; Kostański, M.; Wielowieyska-Szybińska, D.; Szpor, J.; Białas, M.; Okoń, K. Mast Cells in Systemic and Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. Pol. J. Pathol. 2015, 66, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellehsen, L.H. Cigarette Smoke Exposure Activates Human Mast Cells (MC) In Vitro. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 119, S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small-Howard, A.; Turner, H. Exposure to Tobacco-Derived Materials Induces Overproduction of Secreted Proteinases in Mast Cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 204, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugarte-Berzal, E.; Boon, L.; Martens, E.; Rybakin, V.; Blockmans, D.; Vandooren, J.; Proost, P.; Opdenakker, G. MMP-9/Gelatinase B Degrades Immune Complexes in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 427228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospelt, C.; Bang, H.; Feist, E.; Camici, G.; Keller, S.; Detert, J.; Krämer, A.; Gay, S.; Ghannam, K.; Burmester, G.R. Carbamylation of Vimentin Is Inducible by Smoking and Represents an Independent Autoantigen in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1176–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsalahy, M.M.; Nasser, H.S.; Hashem, M.M.; Elsayed, S.M. Effect of Tobacco Smoking on Tissue Protein Citrullination and Disease Progression in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Saudi Pharm. J. 2010, 18, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freemer, M.M.; King, T.E.; Criswell, L.A. Association of Smoking with DsDNA Autoantibody Production in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 65, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.A.; Terrell, D.R.; Guthridge, J.M.; Kamen, D.L.; Gilkeson, G.S.; Karp, D.R.; Ishimori, M.L.; Weisman, M.H.; Holers, V.M.; Harley, J.B.; et al. Smoking Is Not Associated with Autoantibody Production in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients, Unaffected First-Degree Relatives, nor Healthy Controls. Lupus 2014, 23, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbhaiya, M.; Tedeschi, S.K.; Lu, B.; Malspeis, S.; Kreps, D.; Sparks, J.A.; Karlson, E.W.; Costenbader, K.H. Cigarette Smoking and the Risk of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Overall and by Anti-Double Stranded DNA Antibody Subtype, in the Nurses’ Health Study Cohorts. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushima, K.; Yang, D.; Oppenheim, J.J. Interleukin-8: An Evolving Chemokine. Cytokine 2022, 153, 155828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortaz, E.; Lazar, Z.; Koenderman, L.; Kraneveld, A.D.; Nijkamp, F.P.; Folkerts, G. Cigarette Smoke Attenuates the Production of Cytokines by Human Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells and Enhances the Release of IL-8 in Response to TLR-9 Stimulation. Respir. Res. 2009, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Werth, V.P.; Williams, K.J.; Liu, M.L. Translocation of Endogenous Danger Signal HMGB1 From Nucleus to Membrane Microvesicles in Macrophages. J. Cell Physiol. 2016, 231, 2319–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labonte, A.C.; Kegerreis, B.; Geraci, N.S.; Bachali, P.; Madamanchi, S.; Robl, R.; Catalina, M.D.; Lipsky, P.E.; Grammer, A.C. Identification of Alterations in Macrophage Activation Associated with Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, B.F.; Tseng, L.C.; Hosler, G.A.; Teske, N.M.; Zhang, S.; Karp, D.R.; Olsen, N.J.; Mohan, C. A Subset of CD163+ Macrophages Displays Mixed Polarizations in Discoid Lupus Skin. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T. Role of Neutrophils in Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. J. Dermatol. 2024, 51, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, W.; Jinnin, M.; Makino, K.; Kajihara, I.; Makino, T.; Fukushima, S.; Sakai, K.; Inoue, Y.; Ihn, H. CD163 Expression Is Increased in the Involved Skin and Sera of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2012, 22, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, H.M.; van den Hoogen, L.L.; van Roon, J.A.G.; Adriaansen, E.J.M.; Fritsch-Stork, R.D.E.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Goldschmeding, R.; Radstake, T.R.D.J.; Bovenschen, N. Systemic and Local Granzyme B Levels Are Associated with Disease Activity, Kidney Damage and Interferon Signature in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 2129–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlap, G.S.; Billi, A.C.; Xing, X.; Ma, F.; Maz, M.P.; Tsoi, L.C.; Wasikowski, R.; Hodgin, J.B.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Michelle Kahlenberg, J.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomics Reveals Distinct Effector Profiles of Infiltrating T Cells in Lupus Skin and Kidney. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e156341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos, S.N.; Campbell, M.R.; Lozoya, O.A.; Wang, X.; Bennett, B.D.; Thompson, I.J.B.; Wan, M.; Pittman, G.S.; Bell, D.A. Single-Cell Analyses Identify Dysfunctional CD16+ CD8 T Cells in Smokers. Cell Rep. Med. 2020, 1, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubert, A.; Jung, K.; Hiroyasu, S.; Pardo, J.; Granville, D.J. Granzyme Serine Proteases in Inflammation and Rheumatic Diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2024, 20, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodge, S.; Hodge, G.; Nairn, J.; Holmes, M.; Reynolds, P.N. Increased Airway Granzyme b and Perforin in Current and Ex-Smoking COPD Subjects. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2006, 3, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousef, A.A.; Alsalahy, M.M.; Almahdy, M.A.; Essawy, T.S.; Belal, K.M. Study of Serum Granzyme B in Heavy Cigarette Smokers with and without Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Egypt. J. Chest Dis. Tuberc. 2014, 63, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morissette, M.C.; Parent, J.; Milot, J. Perforin, Granzyme B, and FasL Expression by Peripheral Blood T Lymphocytes in Emphysema. Respir. Res. 2007, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, V.; Vermi, W.; Cavani, A.; Lonardi, S.; Carbone, T.; Facchetti, F.; Bosisio, D.; Sozzani, S. IL-21 May Promote Granzyme B-Dependent NK/Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Functional Interaction in Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1493–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, J.; Uerlich, M.; Wörrenkämper, E.; Freutel, S.; Bieber, T.; Tüting, T. Scarring Skin Lesions of Discoid Lupus Erythematosus Are Characterized by High Numbers of Skin-homing Cytotoxic Lymphocytes Associated with Strong Expression of the Type I Interferon-induced Protein MxA. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 153, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Q.; Liu, X.F.; Liu, W.H.; Guo, W.; Yu, Q.; Wang, C.Y. Comparative Analysis of Dendritic Cell Numbers and Subsets between Smoking and Control Subjects in the Peripheral Blood. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2013, 6, 290. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhong, X.; Tang, H. IL-21 Is Increased in Peripheral Blood of Emphysema Mice and Promotes Th1/Tc1 Cell Generation in Vitro. Inflammation 2014, 37, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijl, M.; Horst, G.; Limburg, P.C.; Kallenberg, C.G.M. Effects of Smoking on Activation Markers, Fas Expression and Apoptosis of Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 31, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HuangFu, W.C.; Liu, J.; Harty, R.N.; Fuchs, S.Y. Cigarette Smoking Products Suppress Anti-Viral Effects of Type I Interferon via Phosphorylation-Dependent Downregulation of Its Receptor. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.; Vazquez, T.; Chin, F.; Keyes, E.; Yan, D.; Diaz, D.A.; Grinnell, M.; Sharma, M.; Li, Y.; Feng, R.; et al. Multidimensional Immune Profiling of Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus In Vivo Stratified by Patient Response to Antimalarials. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 1687–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-P.; Wu, J.; Han, Y.-F.; Shi, Z.-R.; Wang, L. Pathogenesis of Cutaneous Lupus Erythema Associated with and without Systemic Lupus Erythema. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholtissek, B.; Zahn, S.; Maier, J.; Klaeschen, S.; Braegelmann, C.; Hoelzel, M.; Bieber, T.; Barchet, W.; Wenzel, J. Immunostimulatory Endogenous Nucleic Acids Drive the Lesional Inflammation in Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, M.L.; Vargas, S.; Ramirez, E.; Bandaru, D.; Sha, J.; Wohlschlegel, J.; Talbot, P.; Hang, B.; Mao, J.-H.; Pozuelos, G.L.; et al. Nicotine Affects Multiple Biological Processes in EpiDermTM Organotypic Tissues and Keratinocyte Monolayers. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, V. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in the Second Decade. J. Innate Immun. 2018, 10, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannopoulos, V. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Immunity and Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 18, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lood, C.; Blanco, L.P.; Purmalek, M.M.; Carmona-Rivera, C.; De Ravin, S.S.; Smith, C.K.; Malech, H.L.; Ledbetter, J.A.; Elkon, K.B.; Kaplan, M.J. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Enriched in Oxidized Mitochondrial DNA Are Interferogenic and Contribute to Lupus-like Disease. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Romo, G.S.; Caielli, S.; Vega, B.; Connolly, J.; Allantaz, F.; Xu, Z.; Punaro, M.; Baisch, J.; Guiducci, C.; Coffman, R.L.; et al. Netting Neutrophils Are Major Inducers of Type I IFN Production in Pediatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 73ra20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, T.; Li, X.; Gao, L.; Wang, K.; Cheng, M.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, L.; Shen, Y.; Wen, F. DNA of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promote NF-ΚB-Dependent Autoimmunity via CGAS/TLR9 in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadigel, J.; Préfontaine, D.; Baglole, C.J.; Maltais, F.; Bourbeau, J.; Eidelman, D.H.; Hamid, Q. Cigarette Smoke Increases TLR4 and TLR9 Expression and Induces Cytokine Production from CD8+ T Cells in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Respir. Res. 2011, 12, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, M.W.; Shao, G.; Schlesinger, L.S.; Huang, Q.; Cosmar, D.G.; Bhatt, N.Y.; Culver, D.A.; Baughman, R.P.; Wood, K.L.; Crouser, E.D. Nicotine Treatment Improves Toll-like Receptor 2 and Toll-like Receptor 9 Responsiveness in Active Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. Chest 2013, 143, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dima, A.; Jurcut, C.; Chasset, F.; Felten, R.; Arnaud, L. Hydroxychloroquine in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Overview of Current Knowledge. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2022, 14, 1759720X211073001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamphier, M.; Zheng, W.; Latz, E.; Spyvee, M.; Hansen, H.; Rose, J.; Genest, M.; Yang, H.; Shaffer, C.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Novel Small Molecule Inhibitors of Tlr7 and Tlr9: Mechanism of Action and Efficacy in Vivo. Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 85, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwatra, S.G. Toll-like Receptor-9 Signaling and Decreased Efficacy of Antimalarial Drugs in Smokers with Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 73, e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, M.; Wu, H.; Lu, Q. The Pathological Role of B Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: From Basic Research to Clinical. Autoimmunity 2020, 53, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abernathy-Close, L.; Lazar, S.; Stannard, J.; Tsoi, L.C.; Eddy, S.; Rizvi, S.M.; Yee, C.M.; Myers, E.M.; Namas, R.; Lowe, L.; et al. B Cell Signatures Distinguish Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Subtypes and the Presence of Systemic Disease Activity. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 775353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerman, I.; Bawany, F.; Whitt, W.; Esaa, F.; Yon, J.; Babkowski, N.; Rapp, M.B.; Scott, G.A.; Anolik, J.H.; Richardson, C.T. Prominent B-Cell Signature Differentiates Discoid from Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 2885–2895.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, F.; Browning, J.L. BAFF: A Fundamental Survival Factor for B Cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, M.; Long, D.; Li, Q.; Zhao, M.; Wu, H.; Lu, Q. Abnormal Expression of BAFF and Its Receptors in Peripheral Blood and Skin Lesions from Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. Autoimmunity 2020, 53, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, J.; Landmann, A.; Vorwerk, G.; Kuhn, A. High Expression of B Lymphocyte Stimulator in Lesional Keratinocytes of Patients with Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, B.F.; Tseng, L.-C.; Kim, A.; Miller, R.T.; Yancey, K.B.; Hosler, G.A. Differential Expression of BAFF and Its Receptors in Discoid Lupus Erythematosus Patients. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2014, 73, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Ballesteros, F.J.; Oregon-Romero, E.; Franco-Topete, R.A.; Govea-Camacho, L.H.; Cruz, A.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F.; Bustos-Rodríguez, F.J.; Pereira-Suárez, A.L.; Palafox-Sánchez, C.A. B-Cell Activating Factor Receptor Expression Is Associated with Germinal Center B-Cell Maintenance. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morissette, M.C.; Gao, Y.; Shen, P.; Thayaparan, D.; Bérubé, J.C.; Paré, P.D.; Brandsma, C.A.; Hao, K.; Bossé, Y.; Ettinger, R.; et al. Role of BAFF in Pulmonary Autoantibody Responses Induced by Chronic Cigarette Smoke Exposure in Mice. Physiol. Rep. 2016, 4, e13057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, W.D.; Hamdorf, M.; Furfaro, M.; Eilertsen, G.O.; Nossent, J.C. Smoking Associates with Increased BAFF and Decreased Interferon-γ Levels in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Lupus Sci. Med. 2021, 8, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneeland, R.; Montes, D.; Endo, J.; Shields, B.; Bartels, C.M.; Garg, S. Improvement in Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus After Twenty Weeks of Belimumab Use: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arthritis Care Res. 2023, 75, 1838–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodis, I.; Sjöwall, C.; Jönsen, A.; Ramsköld, D.; Zickert, A.; Frodlund, M.; Sohrabian, A.; Arnaud, L.; Rönnelid, J.; Malmström, V.; et al. Smoking and Pre-Existing Organ Damage Reduce the Efficacy of Belimumab in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodis, I.; Gomez, A.; Frodlund, M.; Jönsen, A.; Zickert, A.; Sjöwall, C.; Bengtsson, A.A.; Gunnarsson, I. Smoking Reduces the Efficacy of Belimumab in Mucocutaneous Lupus. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2018, 18, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, J.; Leatherwood, C.; Malspeis, S.; Liu, X.; Lu, B.; Roberts, A.L.; Sparks, J.A.; Karlson, E.W.; Feldman, C.H.; Munroe, M.E.; et al. Associations Between Smoking and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus–Related Cytokines and Chemokines Among US Female Nurses. Arthritis Care Res. 2021, 73, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freutel, S.; Gaffal, E.; Zahn, S.; Bieber, T.; Tüting, T.; Wenzel, J. Enhanced CCR5+/CCR3+ T Helper Cell Ratio in Patients with Active Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. Lupus 2011, 20, 1300–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, A.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Gonzalez, J.; Cueto, I.; Franks, A.G.; Krueger, J.G. Dominant Th1 and Minimal Th17 Skewing in Discoid Lupus Revealed by Transcriptomic Comparison with Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Flores, S.; Hernández-Molina, G.; Enríquez, A.B.; Faz-Muñoz, D.; Esquivel, Y.; Pacheco-Molina, C.; Furuzawa-Carballeda, J. Cytokines and Effector/Regulatory Cells Characterization in the Physiopathology of Cutaneous Lupus Erythematous: A Cross-Sectional Study. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 7074829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Flores, S.; Hernández-Molina, G.; Azamar-Llamas, D.; Zúñiga, J.; Romero-Díaz, J.; Furuzawa-Carballeda, J. Inflammatory Chemokine Profiles and Their Correlations with Effector CD4 T Cell and Regulatory Cell Subpopulations in Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. Cytokine 2019, 119, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solé, C.; Gimenez-Barcons, M.; Ferrer, B.; Ordi-Ros, J.; Cortés-Hernández, J. Microarray Study Reveals a Transforming Growth Factor-β-dependent Mechanism of Fibrosis in Discoid Lupus Erythematosus. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 175, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seery, J.P.; Carroll, J.M.; Cattell, V.; Watt, F.M. Antinuclear Autoantibodies and Lupus Nephritis in Transgenic Mice Expressing Interferon Gamma in the Epidermis. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 186, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mande, P.; Zirak, B.; Ko, W.C.; Taravati, K.; Bride, K.L.; Brodeur, T.Y.; Deng, A.; Dresser, K.; Jiang, Z.; Ettinger, R.; et al. Fas Ligand Promotes an Inducible TLR-Dependent Model of Cutaneous Lupus-like Inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2966–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanigawa, T.; Araki, S.; Sata, F.; Nakata, A.; Araki, T. Effects of Smoking, Aromatic Amines, and Chromates on CD4+and CD8+T Lymphocytes in Male Workers. Environ. Res. 1998, 78, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsslund, H.; Mikko, M.; Karimi, R.; Grunewald, J.; Wheelock, Å.M.; Wahlström, J.; Sköld, C.M. Distribution of T-Cell Subsets in BAL Fluid of Patients with Mild to Moderate COPD Depends on Current Smoking Status and Not Airway Obstruction. Chest 2014, 145, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaberg, T.; Theilacker, C.; Nitschke, O.T.; Lode, H. Lymphocyte Subsets in Peripheral Blood and Smoking Habits. Lung 1997, 175, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qiu, S.-L.; Tang, Q.-Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.-Q.; He, Z.-Y.; Bai, J.; Li, M.-H.; Deng, J.-M.; Liang, Y.; et al. Erythromycin Suppresses Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Smoking-Related Chronic Pulmonary Inflammation. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejero, J.D.; Armand, N.C.; Finn, C.M.; Dhume, K.; Strutt, T.M.; Chai, K.X.; Chen, L.M.; McKinstry, K.K. Cigarette Smoke Extract Acts Directly on CD4 T Cells to Enhance Th1 Polarization and Reduce Memory Potential. Cell Immunol. 2018, 331, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Mu, Q.; Meng, Z.J. Cigarette Smoking Contributes to Th1/Th2 Cell Dysfunction via the Cytokine Milieu in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pharmacol. Dis. 2023, 18, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebane, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Aab, A.; Baurecht, H.; Koreck, A.; Karelson, M.; Abram, K.; Metsalu, T.; Pihlap, M.; Meyer, N.; et al. Mechanisms of IFN-γ-Induced Apoptosis of Human Skin Keratinocytes in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Tsoi, L.C.; Sarkar, M.K.; Xing, X.; Xue, K.; Uppala, R.; Berthier, C.C.; Zeng, C.; Patrick, M.; Billi, A.C.; et al. IFN-γ Enhances Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity against Keratinocytes via JAK2/STAT1 in Lichen Planus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaav7561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanasescu, C.; Balanescu, E.; Balanescu, P.; Olteanu, R.; Badea, C.; Grancea, C.; Vagu, C.; Bleotu, C.; Ardeleanu, C.; Georgescu, A. IL-17 in Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2010, 21, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Tajuelo, R.; Silván, J.; Pérez-Frías, A.; De La Fuente-Fernández, M.; Tejedor, R.; Espartero-Santos, M.; Vicente-Rabaneda, E.; Juarranz, Á.; Muñoz-Calleja, C.; Castañeda, S.; et al. P-Selectin Preserves Immune Tolerance in Mice and Is Reduced in Human Cutaneous Lupus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep41841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbour, S.N.; DiToro, D.F.; Witte, S.J.; Zindl, C.L.; Gao, M.; Schoeb, T.R.; Jones, G.W.; Jones, S.A.; Hatton, R.D.; Weaver, C.T. Th17 Cells Require Ongoing Classic IL-6 Receptor Signaling to Retain Transcriptional and Functional Identity. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eaaw2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stannard, J.N.; Reed, T.J.; Myers, E.; Lowe, L.; Sarkar, M.K.; Xing, X.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Kahlenberg, J.M. Lupus Skin Is Primed for IL-6 Inflammatory Responses through a Keratinocyte-Mediated Autocrine Type I Interferon Loop. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, P.S.; Aggarwal, R.; Levesque, M.C.; Maers, K.; Ramani, K. Type I Interferon and T Helper 17 Cells Co-Exist and Co-Regulate Disease Pathogenesis in Lupus Patients. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 18, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldaham, S.; Foote, J.A.; Chow, H.H.S.; Hakim, I.A. Smoking Status Effect on Inflammatory Markers in a Randomized Trial of Current and Former Heavy Smokers. Int. J. Inflam. 2015, 2015, 439396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abid, H.A.; Hameed, N.J.; Gomes, K.B.; Al-Tameemi, S.A. Cigarette Smoking Increases Plasma Levels of IL-6 and TNF-α. Baghdad J. Biochem. Appl. Biol. Sci. 2022, 3, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Fu, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, J.; Han, S.; Tian, Y.; Hou, H.; Hu, Q. Effects of Smoking on Inflammatory-Related Cytokine Levels in Human Serum. Molecules 2022, 27, 3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Peng, W.; Weng, Y.; Ying, H.; Li, H.; Xia, D.; Yu, W. Imbalance of Th17/Treg Cells in Mice with Chronic Cigarette Smoke Exposure. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 14, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, B.; Fritzsching, B.; Riehl, A.; Oberle, N.; Klemke, C.D.; Sykora, J.; Quick, S.; Stumpf, C.; Hartmann, M.; Enk, A.; et al. Low Number of Regulatory T Cells in Skin Lesions of Patients with Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 1910–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.W.; Barber, G.; Chong, B.F. The Genetic Landscape of Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 916011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryor, W.A.; Stone, K.; Zang, L.Y.; Bermúdez, E. Fractionation of Aqueous Cigarette Tar Extracts: Fractions That Contain the Tar Radical Cause DNA Damage. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1998, 11, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanata, C.M.; Chung, S.A.; Criswell, L.A. DNA Methylation 101: What Is Important to Know about DNA Methylation and Its Role in SLE Risk and Disease Heterogeneity. Lupus Sci. Med. 2018, 5, e000285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, D.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Ouyang, R.; Chen, P. The Role of Cigarette Smoke-Induced Epigenetic Alterations in Inflammation. Epigenet. Chromatin 2019, 12, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-André, V.; Charbit, B.; Biton, A.; Rouilly, V.; Possémé, C.; Bertrand, A.; Rotival, M.; Bergstedt, J.; Patin, E.; Albert, M.L.; et al. Smoking Changes Adaptive Immunity with Persistent Effects. Nature 2024, 626, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.A.; Padgett, J.K.; Mayo, K.B. Koebner Phenomenon. Consultant 2022, 51, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, E.; Robinson, M.; Patel, R.; Franks, A.G. Koebner Phenomenon to Heat in Cutaneous (Discoid) Lupus Erythematosus (Lupus Ab-Igne). Dermatol. Online J. 2012, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, E.; Ugonabo, N.; Franks, A.G.; Lo Sicco, K. Case Report of Discoid Lupus Erythematosus in Association with Electronic Cigarette Use. JAAD Case Rep. 2019, 5, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Homer, R.O.; Eldaboush, A.; Kang, D.; Ahmed, N.S.; Khosravi-Hafshejani, T.; Liu, M.-L.; Werth, V.P. Ashes to Rashes: An Exploration of the Intersection Between Smoking and Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091250
Homer RO, Eldaboush A, Kang D, Ahmed NS, Khosravi-Hafshejani T, Liu M-L, Werth VP. Ashes to Rashes: An Exploration of the Intersection Between Smoking and Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(9):1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091250
Chicago/Turabian StyleHomer, Rafael O., Ahmed Eldaboush, Darae Kang, Nada S. Ahmed, Touraj Khosravi-Hafshejani, Ming-Lin Liu, and Victoria P. Werth. 2025. "Ashes to Rashes: An Exploration of the Intersection Between Smoking and Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus" Biomolecules 15, no. 9: 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091250
APA StyleHomer, R. O., Eldaboush, A., Kang, D., Ahmed, N. S., Khosravi-Hafshejani, T., Liu, M.-L., & Werth, V. P. (2025). Ashes to Rashes: An Exploration of the Intersection Between Smoking and Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. Biomolecules, 15(9), 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091250






