Inhibition of Astrocyte Reactivity by Mdivi-1 After Status Epilepticus in Rats Exacerbates Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation and Impairs Limbic–Cortical Glucose Metabolism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
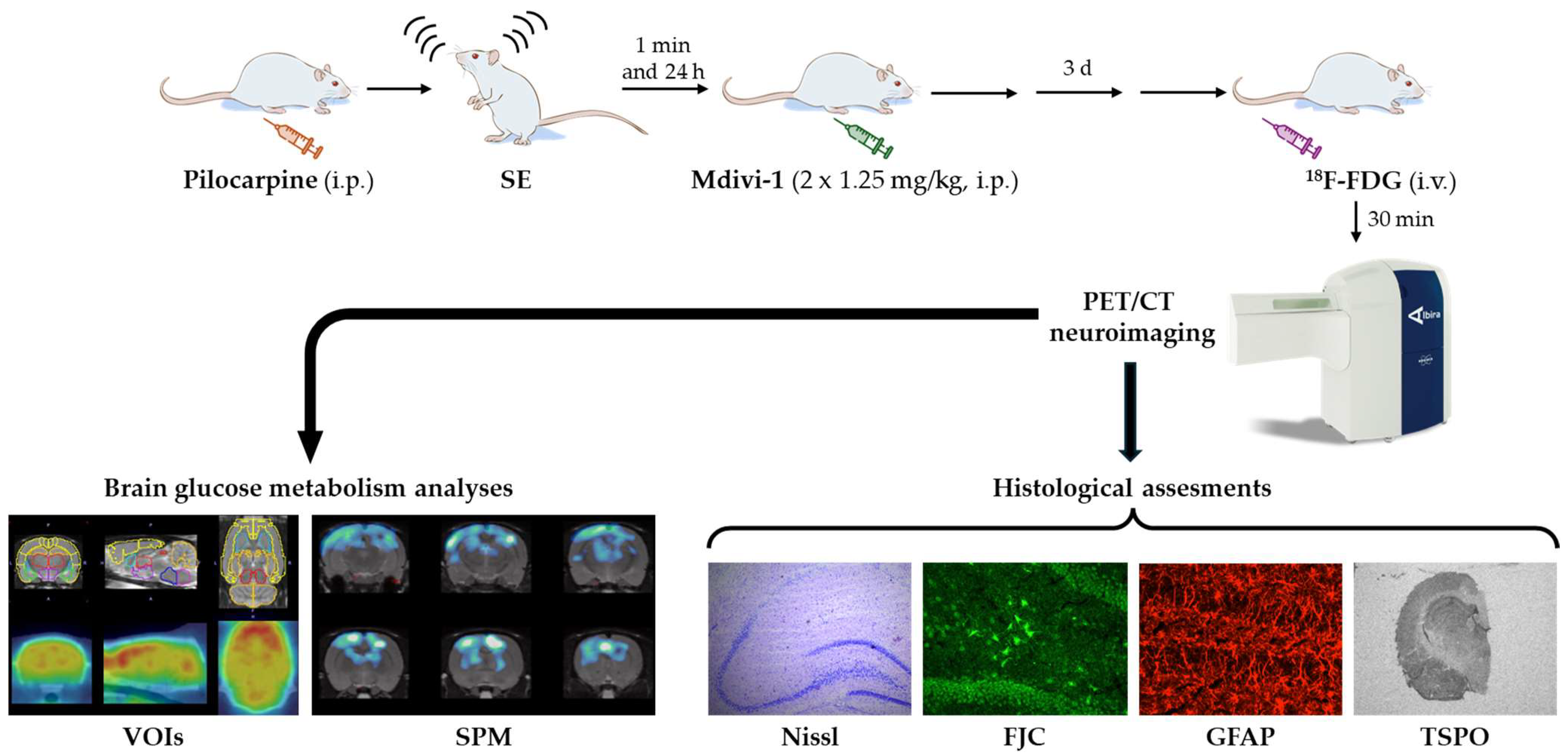
2.2. Lithium–Pilocarpine SE Model and Mdivi-1 Administration
2.3. Body Weight (BW) Measurements
2.4. [18F]FDG PET/CT Imaging
2.4.1. PET Image Analysis by Volume-of-Interest (VOI) Analysis
2.4.2. PET Evaluation by Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM)
2.5. Brain Collection and Processing for Neurohistochemical Studies
2.6. Nissl Staining
2.7. Fluoro-Jade C (FJC) Labeling
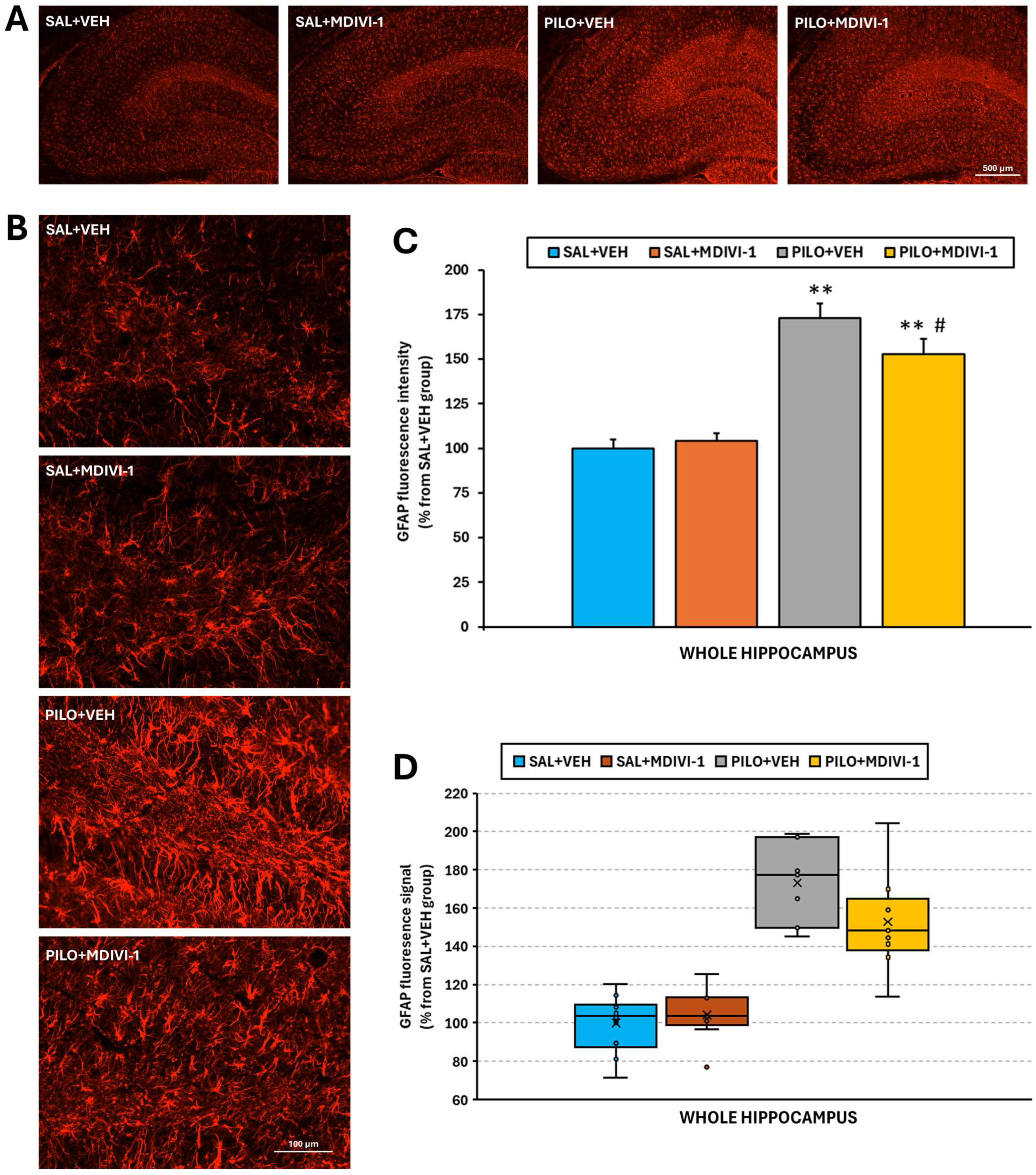
2.8. Reactive Astrogliosis Analysis by Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP) Immunofluorescence Staining
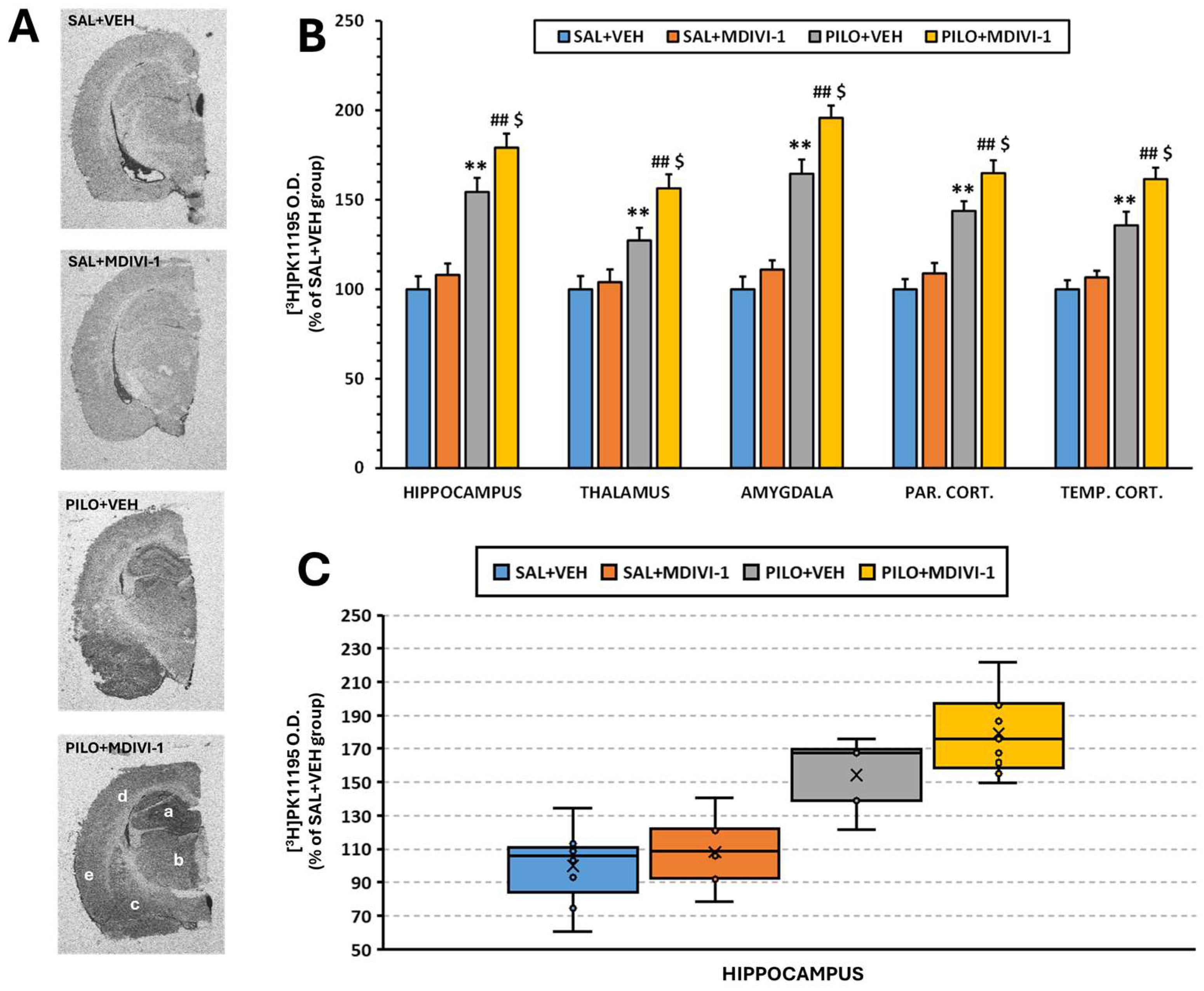
2.9. Analysis of Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation by [3H]PK11195 Autoradiography
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
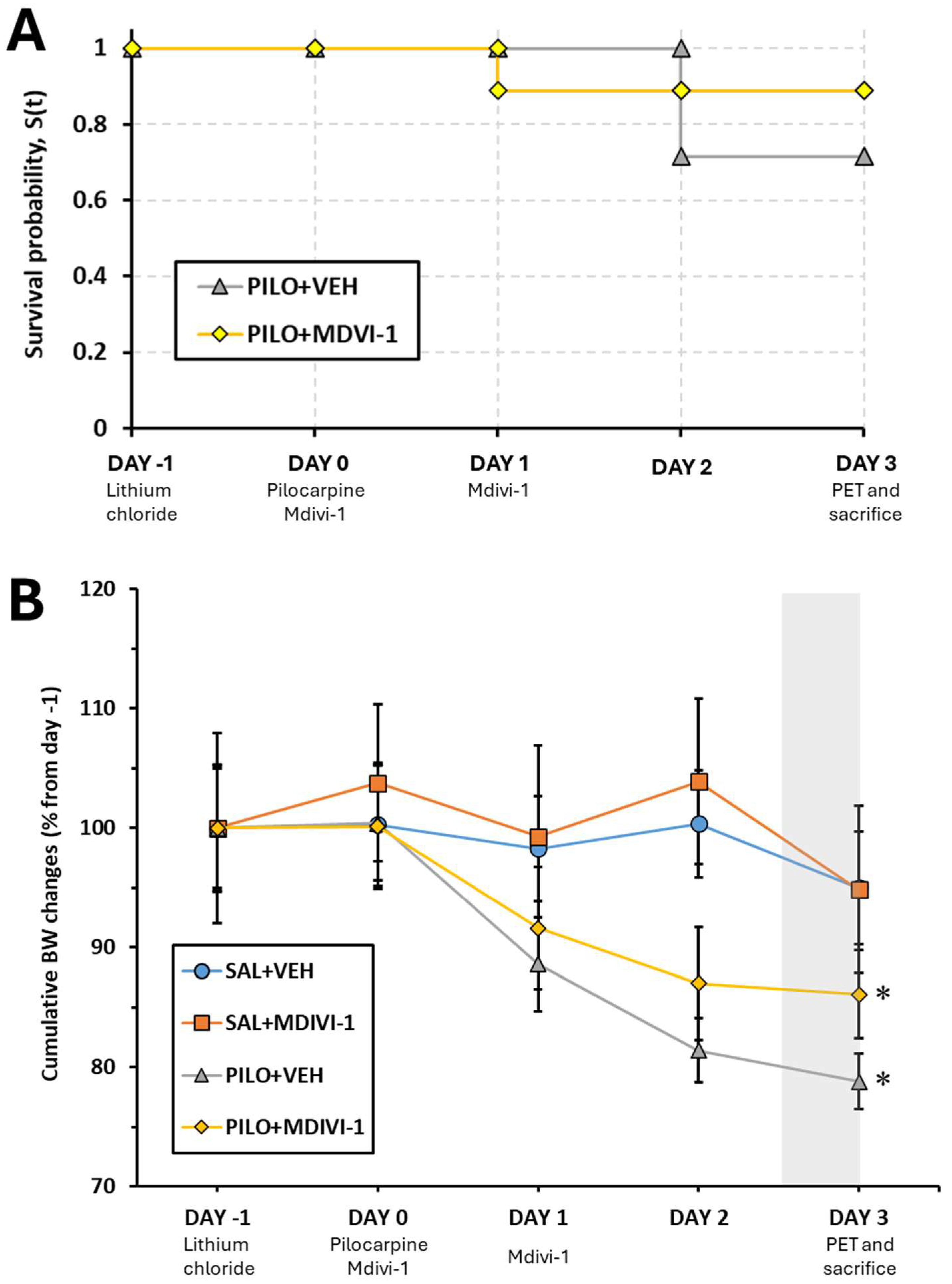
3.1. Mortality Rate
3.2. Overall BW Changes
3.3. Brain Glucose Metabolism Assessed by [18F]FDG PET
3.3.1. VOI-Based Quantitative Analysis (SUV Measurements)
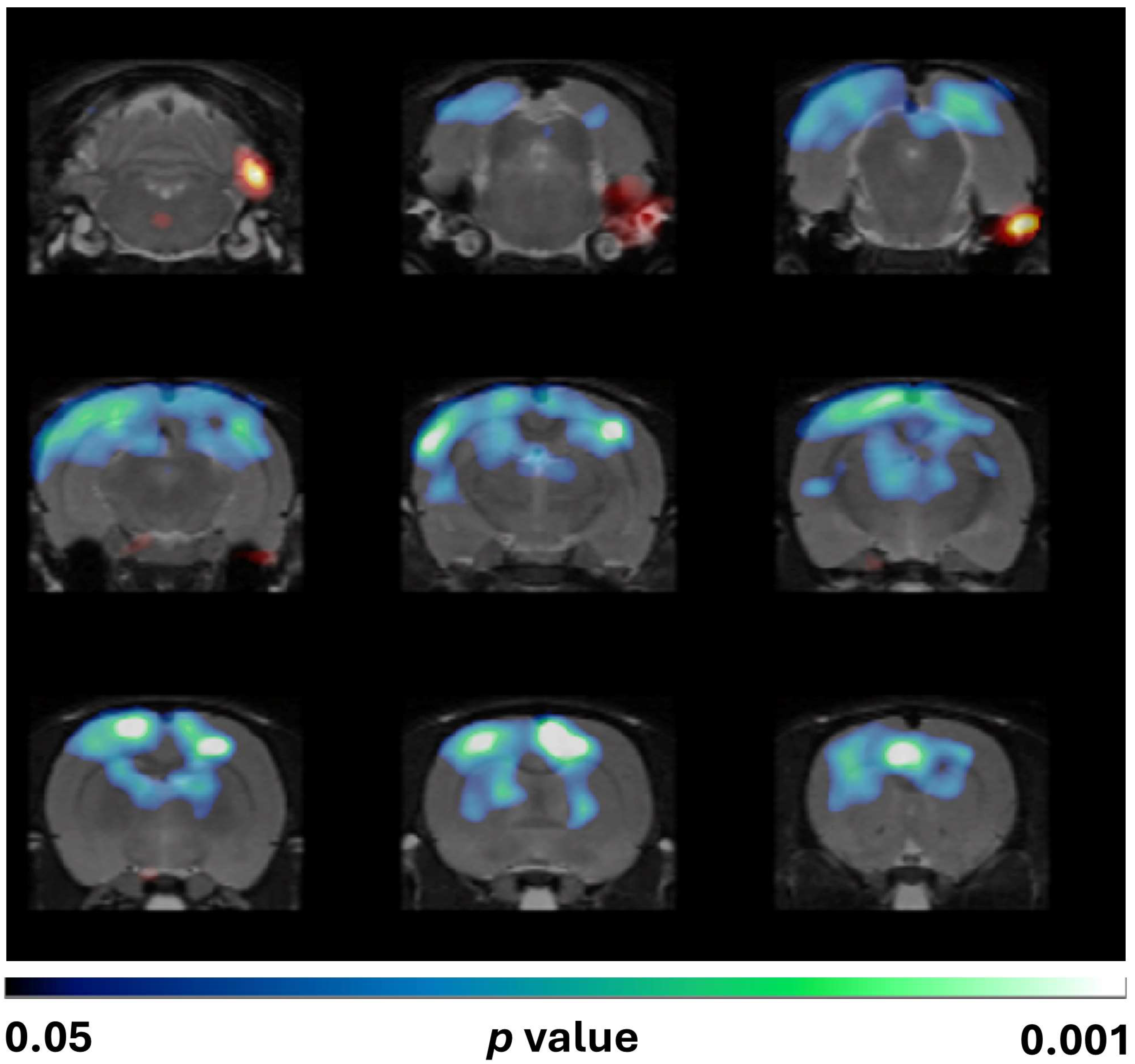
3.3.2. Voxel-Wise Analysis (SPM)
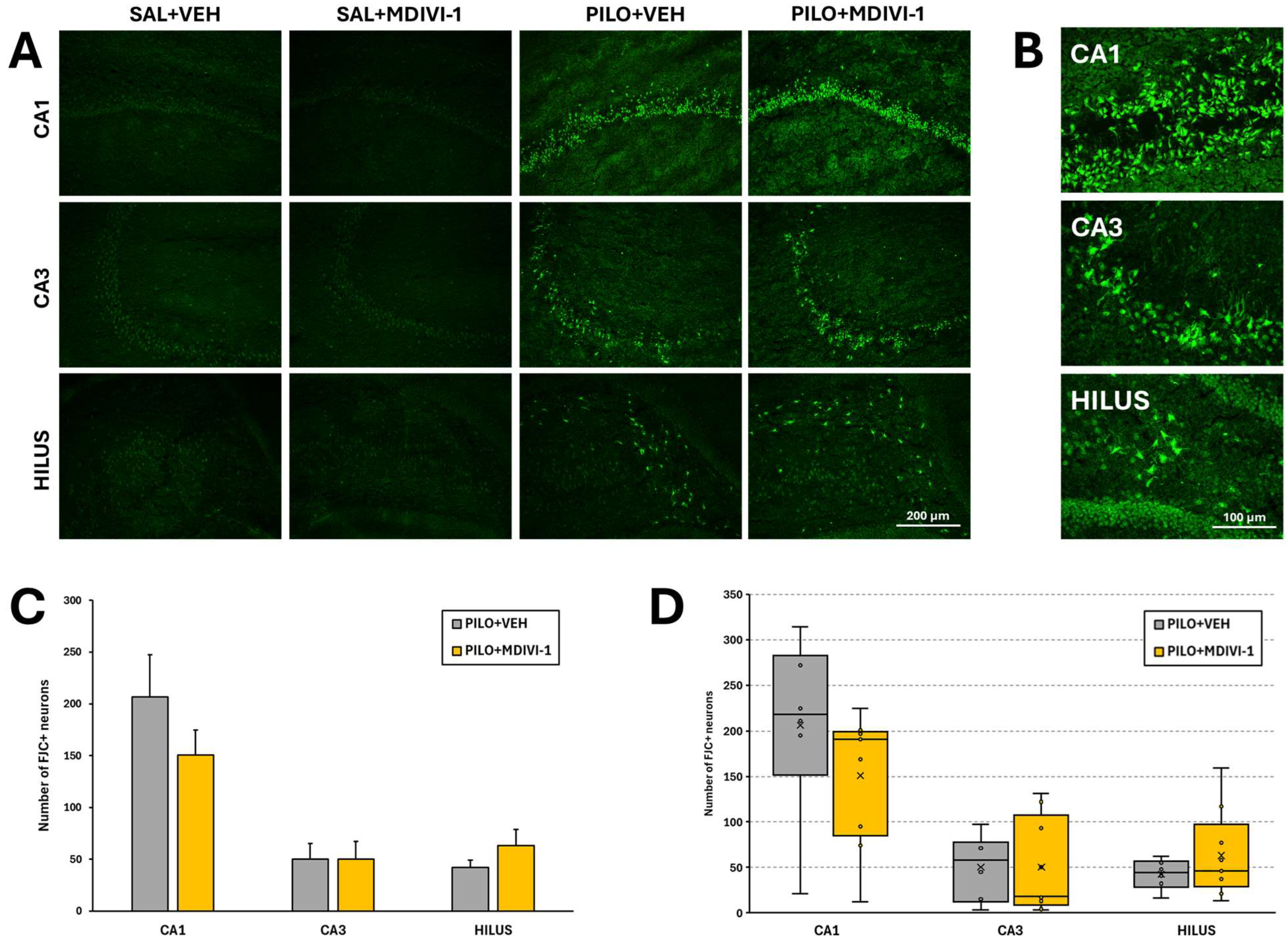
3.4. Histopathological Evaluation: Neurodegeneration
3.5. Astrocyte Reactivity (GFAP Immunofluorescence Staining)
3.6. Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation ([3H]PK11195 Autoradiography)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| [18F]FDG | 2-Deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-D-glucose |
| BW | Body weight |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Drp1 | Dynamin-related protein 1 |
| EEG | Electroencephalography |
| FBP | Filtered back projection |
| FJC | Fluoro Jade C |
| GFAP | Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| GS | Glutamine synthetase |
| Mdivi-1 | Mitochondrial division inhibitor-1 |
| MLEM | Maximum likelihood expectation maximization |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| O.D. | Optical density |
| PET | Positron emission tomography |
| SE | Status epilepticus |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
| SPM | Statistical parametric mapping |
| SRS | Spontaneous recurrent seizures |
| SUV | Standardized uptake value |
| TLE | Temporal lobe epilepsy |
| TSPO | 18 kDa translocator protein |
| VOI | Volume of interest |
References
- Fisher, R.S.; Cross, J.H.; French, J.A.; Higurashi, N.; Hirsch, E.; Jansen, F.E.; Lagae, L.; Moshé, S.L.; Peltola, J.; Roulet Perez, E.; et al. Operational Classification of Seizure Types by the International League Against Epilepsy: Position Paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Hartz, A.M.S.; Bauer, B. Drug-Resistant Epilepsy: Multiple Hypotheses, Few Answers. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janszky, J.; Janszky, I.; Schulz, R.; Hoppe, M.; Behne, F.; Pannek, H.W.; Ebner, A. Temporal Lobe Epilepsy with Hippocampal Sclerosis: Predictors for Long-Term Surgical Outcome. Brain 2005, 128, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Chugani, H.T. The Role of Radionuclide Imaging in Epilepsy, Part 1: Sporadic Temporal and Extratemporal Lobe Epilepsy. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2017, 45, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Chugani, H.T. The Role of Radionuclide Imaging in Epilepsy, Part 2: Epilepsy Syndromes. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2017, 45, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, T.J.; Miles, K.; Ware, R.; Cook, M.J.; Binns, D.S.; Hicks, R.J. The Cost-Effective Use of 18F-FDG PET in the Presurgical Evaluation of Medically Refractory Focal Epilepsy. J. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verger, A.; Lagarde, S.; Maillard, L.; Bartolomei, F.; Guedj, E. Brain Molecular Imaging in Pharmacoresistant Focal Epilepsy: Current Practice and Perspectives. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 174, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turski, W.A.; Cavalheiro, E.A.; Schwarz, M.; Czuczwar, S.J.; Kleinrok, Z.; Turski, L. Limbic Seizures Produced by Pilocarpine in Rats: Behavioural, Electroencephalographic and Neuropathological Study. Behav. Brain Res. 1983, 9, 315–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, C.; Töllner, K.; Klee, R.; Bröer, S.; Löscher, W. Effective Termination of Status Epilepticus by Rational Polypharmacy in the Lithium–Pilocarpine Model in Rats: Window of Opportunity to Prevent Epilepsy and Prediction of Epilepsy by Biomarkers. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 75, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed Juvale, I.I.; Che Has, A.T. The Evolution of the Pilocarpine Animal Model of Status Epilepticus. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitkänen, A. Drug-Mediated Neuroprotection and Antiepileptogenesis: Animal Data. Neurology 2002, 59, S27–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.M.; Park, G.Y.; Im, K.C.; Kim, S.T.; Woo, C.W.; Chung, J.H.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, J.S.; Shon, Y.M.; Kim, Y.I.; et al. Changes in Glucose Metabolism and Metabolites during the Epileptogenic Process in the Lithium-Pilocarpine Model of Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2012, 53, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Martín, N.; Gomez, F.; Silván, Á.; de la Rosa, R.F.; Delgado, M.; Bascuñana, P.; Pozo, M.Á.; García-García, L. A Single High Dose of Flufenamic Acid in Rats Does Not Reduce the Damage Associated with the Rat Lithium-Pilocarpine Model of Status Epilepticus but Leads to Deleterious Outcomes. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2023, 22, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-García, L.; Shiha, A.A.; Fernández de la Rosa, R.; Delgado, M.; Silván, Á.; Bascuñana, P.; Bankstahl, J.P.; Gomez, F.; Pozo, M.A. Metyrapone Prevents Brain Damage Induced by Status Epilepticus in the Rat Lithium-Pilocarpine Model. Neuropharmacology 2017, 123, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Martín, N.; Pozo-Cabanell, I.; Fernández de la Rosa, R.; García-García, L.; Gómez-Oliver, F.; Pozo, M.Á.; Brackhan, M.; Bascuñana, P. Preclinical PET Imaging in Epileptogenesis: Towards Identification of Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets. EJNMMI Res. 2025, 15, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-García, L.; Gomez, F.; Delgado, M.; Fernández de la Rosa, R.; Pozo, M.Á. The Vasodilator Naftidrofuryl Attenuates Short-Term Brain Glucose Hypometabolism in the Lithium-Pilocarpine Rat Model of Status Epilepticus without Providing Neuroprotection. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 939, 175453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-García, L.; Gómez-Oliver, F.; Fernández de la Rosa, R.; Pozo, M.Á. Dantrolene Paradoxically Exacerbates Short-Term Brain Glucose Hypometabolism, Hippocampal Damage and Neuroinflammation Induced by Status Epilepticus in the Rat Lithium-Pilocarpine Model. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 985, 177073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, Y.; Hu, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Gao, F. FDG-PET and NeuN-GFAP Immunohistochemistry of Hippocampus at Different Phases of the Pilocarpine Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 12, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.R.; Angelo, M.F.; Villarreal, A.; Lukin, J.; Ramos, A.J. Gabapentin Administration Reduces Reactive Gliosis and Neurodegeneration after Pilocarpine-Induced Status Epilepticus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bascuñana, P.; Wolf, B.J.; Jahreis, I.; Brackhan, M.; García-García, L.; Ross, T.L.; Bengel, F.M.; Bankstahl, M.; Bankstahl, J.P. 99mTc-HMPAO SPECT Imaging Reveals Brain Hypoperfusion during Status Epilepticus. Metab. Brain Dis. 2021, 36, 2597–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami Alkafaas, S.; Obeid, O.K.; Ali Radwan, M.; Elsalahaty, M.I.; Samy ElKaffas, S.; Hafez, W.; Janković, N.; Hessien, M. Novel Insight into Mitochondrial Dynamin-Related Protein-1 as a New Chemo-Sensitizing Target in Resistant Cancer Cells. Bioorg Chem. 2024, 150, 107574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Song, L.; Yu, J.; Huang, F.; Li, Y.; Ma, C. Mdivi-1: A Promising Drug and Its Underlying Mechanisms in the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Histol. Histopathol. 2022, 37, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Yang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z. ERK1/2 Regulates Epileptic Seizures by Modulating the DRP1-Mediated Mitochondrial Dynamic. Synapse 2024, 78, e22309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Wang, C.; Lian, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Q. A Selective Inhibitor of Drp1, Mdivi-1, Protects against Cell Death of Hippocampal Neurons in Pilocarpine-Induced Seizures in Rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 545, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, J.; Tang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Tian, F.; Xu, Z. Dynamic-Related Protein 1 Inhibitor Eases Epileptic Seizures and Can Regulate Equilibrative Nucleoside Transporter 1 Expression. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Cao, L.; Yang, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, X.; Han, Y.; Xue, Y.; Jiang, H.; Chi, Z. Role of Mitochondrial Fission in Neuronal Injury in Pilocarpine-Induced Epileptic Rats. Neuroscience 2013, 245, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Córdova-Dávalos, L.; Carrera-Calvo, D.; Solís-Navarrete, J.; Mercado-Gómez, O.F.; Arriaga-Ávila, V.; Agredano-Moreno, L.T.; Jiménez-García, L.F.; Guevara-Guzmán, R. Status Epilepticus Triggers Early Mitochondrial Fusion in the Rat Hippocampus in a Lithium-Pilocarpine Model. Epilepsy Res. 2016, 123, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Q.; Zheng, S.; Chen, Q.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J. The Protective Effect of Inhibiting Mitochondrial Fission on the Juvenile Rat Brain Following PTZ Kindling through Inhibiting the BCL2L13/LC3 Mitophagy Pathway. Metab. Brain Dis. 2023, 38, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.; Alberdi, E.; Matute, C. Mitochondrial Division Inhibitor 1 (Mdivi-1) Protects Neurons against Excitotoxicity through the Modulation of Mitochondrial Function and Intracellular Ca2+ Signaling. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Rui, T.; Luo, C.; Li, Q. Mdivi-1 Alleviates Brain Damage and Synaptic Dysfunction after Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Mice. Exp. Brain Res. 2021, 239, 1581–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.H.; Manczak, M.; Yin, X. Mitochondria-Division Inhibitor 1 Protects Against Amyloid-β Induced Mitochondrial Fragmentation and Synaptic Damage in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 58, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motori, E.; Puyal, J.; Toni, N.; Ghanem, A.; Angeloni, C.; Malaguti, M.; Cantelli-Forti, G.; Berninger, B.; Conzelmann, K.K.; Götz, M.; et al. Inflammation-Induced Alteration of Astrocyte Mitochondrial Dynamics Requires Autophagy for Mitochondrial Network Maintenance. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 844–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.U.; Mochly-Rosen, D. Mortal Engines: Mitochondrial Bioenergetics and Dysfunction in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 138, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordt, E.A.; Clerc, P.; Roelofs, B.A.; Saladino, A.J.; Tretter, L.; Adam-Vizi, V.; Cherok, E.; Khalil, A.; Yadava, N.; Ge, S.X.; et al. The Putative Drp1 Inhibitor Mdivi-1 Is a Reversible Mitochondrial Complex I Inhibitor That Modulates Reactive Oxygen Species. Dev. Cell 2017, 40, 583–594.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy-Stone, A.; Chipuk, J.E.; Ingerman, E.; Song, C.; Yoo, C.; Kuwana, T.; Kurth, M.J.; Shaw, J.T.; Hinshaw, J.E.; Green, D.R.; et al. Chemical Inhibition of the Mitochondrial Division Dynamin Reveals Its Role in Bax/Bak-Dependent Mitochondrial Outer Membrane Permeabilization. Dev. Cell 2008, 14, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, L.L.; Nunnari, J. Small Molecule Inhibitors of Mitochondrial Division: Tools That Translate Basic Biological Research into Medicine. Chem. Biol. 2010, 17, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racine, R.J. Modification of Seizure Activity by Electrical Stimulation: II. Motor Seizure. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1972, 32, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Oliver, F.; Fernández de la Rosa, R.; Brackhan, M.; Bascuñana, P.; Pozo, M.Á.; García-García, L. Seizures Triggered by Systemic Administration of 4-Aminopyridine in Rats Lead to Acute Brain Glucose Hypometabolism, as Assessed by [18F]FDG PET Neuroimaging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirrione, M.M.; Schiffer, W.K.; Fowler, J.S.; Alexoff, D.L.; Dewey, S.L.; Tsirka, S.E. A Novel Approach for Imaging Brain–Behavior Relationships in Mice Reveals Unexpected Metabolic Patterns during Seizures in the Absence of Tissue Plasminogen Activator. Neuroimage 2007, 38, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jupp, B.; O’Brien, T.J. Application of Coregistration for Imaging of Animal Models of Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2007, 48, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto, E.; Collantes, M.; Delgado, M.; Juri, C.; García-García, L.; Molinet, F.; Fernández-Valle, M.E.; Pozo, M.A.; Gago, B.; Martí-Climent, J.M.; et al. Statistical Parametric Maps of 18F-FDG PET and 3-D Autoradiography in the Rat Brain: A Cross-Validation Study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2011, 38, 2228–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiha, A.A.; de la Rosa, R.F.; Delgado, M.; Pozo, M.A.; García-García, L. Subacute Fluoxetine Reduces Signs of Hippocampal Damage Induced by a Single Convulsant Dose of 4-Aminopyridine in Rats. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2017, 16, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Schmued, L.C.; Sarkar, S.; Paule, M.G.; Raymick, B. One-Step Labeling of Degenerative Neurons in Unfixed Brain Tissue Samples Using Fluoro-Jade C. J. Neurosci. Methods 2012, 208, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitkänen, A.; Engel, J. Past and Present Definitions of Epileptogenesis and Its Biomarkers. Neurotherapeutics 2014, 11, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffin, K.; Van Paesschen, W.; Dupont, P.; Laere, K. Van Longitudinal MicroPET Imaging of Brain Glucose Metabolism in Rat Lithium-Pilocarpine Model of Epilepsy. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 217, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Gao, F.; Wang, S.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Ding, M.P. In Vivo Mapping of Temporospatial Changes in Glucose Utilization in Rat Brain during Epileptogenesis: An 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose-Small Animal Positron Emission Tomography Study. Neuroscience 2009, 162, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, L.A.; Wang, L.; Ribak, C.E. Rapid Astrocyte and Microglial Activation Following Pilocarpine-Induced Seizures in Rats. Epilepsia 2008, 49, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Su, Q.; Zhou, F. Drp1 Mitochondrial Fission in Astrocyte Modulates Behavior and Neuroinflammation during Morphine Addiction. J. Neuroinflamm. 2025, 22, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; McIntyre, R.L.; Janssens, G.E.; Houtkooper, R.H. Mitochondrial Fission and Fusion: A Dynamic Role in Aging and Potential Target for Age-Related Disease. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2020, 186, 111212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manczak, M.; Kandimalla, R.; Yin, X.; Hemachandra Reddy, P. Mitochondrial Division Inhibitor 1 Reduces Dynamin-Related Protein 1 and Mitochondrial Fission Activity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 177–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Middleton, A.; Carmichael, P.L.; et al. Doxorubicin-Induced Mitophagy and Mitochondrial Damage Is Associated with Dysregulation of the PINK1/Parkin Pathway. Toxicol. In Vitro 2018, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Cao, Y.; Shen, F.; Wang, Y.; Bai, L.; Guo, W.; Bi, Y.; Lv, G.; Fan, Z. Mdivi-1. Inhibits Astrocyte Activation and Astroglial Scar Formation and Enhances Axonal Regeneration after Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2016, 10, 216062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Wang, J.; Roginskaya, V.; McDermott, L.A.; Edwards, R.P.; Stolz, D.B.; Llambi, F.; Green, D.R.; Van Houten, B. Novel Combination of Mitochondrial Division Inhibitor 1 (Mdivi-1) and Platinum Agents Produces Synergistic pro-Apoptotic Effect in Drug Resistant Tumor Cells. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 4180–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.; Gallo, G. To Mdivi-1 or Not to Mdivi-1: Is That the Question? Dev. Neurobiol. 2017, 77, 1260–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Ding, H.; Chen, F.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Q.; Dong, Q. Mdivi-1 Protects Against Ischemic Brain Injury via Elevating Extracellular Adenosine in a CAMP/CREB-CD39-Dependent Manner. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Jung, S.; Lee, S.Y.; Yang, H.; Kim, B.S.; Choi, J.; Bang, M.; Shin, H.S.; Jeon, D. Early Deficits in Social Behavior and Cortical Rhythms in Pilocarpine-Induced Mouse Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 241, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assenza, G.; Lanzone, J.; Insola, A.; Amatori, G.; Ricci, L.; Tombini, M.; Di Lazzaro, V. Thalamo-Cortical Network Dysfunction in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 131, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, N.; Ritter, N.; Disse, P.; Seebohm, G.; Busch, K.B. Detailed Analysis of Mdivi-1 Effects on Complex I and Respiratory Supercomplex Assembly. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, K.J.; Kim, W.H.; Roh, G.S. A Mitochondrial Division Inhibitor, Mdivi-1, Inhibits Mitochondrial Fragmentation and Attenuates Kainic Acid-Induced Hippocampal Cell Death. BMC Neurosci. 2016, 17, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nhu, N.T.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Xiao, S.Y.; Lee, S. Da Effects of Mdivi-1 on Neural Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury After Stroke: A Systematic Review of Preclinical Studies. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 778569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Yang, H.Y.; Tang, P.Y.; Liu, W.; Luo, Y.J.; Lv, B.; Yin, J.; Jiang, T.; Chen, J.; Cai, W.H.; et al. Mitochondrial Division Inhibitor 1 Protects Cortical Neurons from Excitotoxicity: A Mechanistic Pathway. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1552–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Gao, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Gu, Z.; Shi, X.; Cui, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, X.; et al. Mdivi-1 Alleviates Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption and Cell Death in Experimental Traumatic Brain Injury by Mitigating Autophagy Dysfunction and Mitophagy Activation. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 94, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chi, L.; Liu, Y. Inhibition of Drp1 after Traumatic Brain Injury Provides Brain Protection and Improves Behavioral Performance in Rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 304, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavi, M.A.; Toutounchian, S.; Afsahi, S.; Ebrahim Soltani, Z.; Mohammad Jafari, R.; Dehpour, A.R. Ivermectin Exerts Anticonvulsant Effects Against Status Epilepticus Induced by Lithium-Pilocarpine in Rats via GABAA Receptor and Neuroinflammation Modulation: Possible Interaction of Opioidergic Pathways and KATP Channel with Nitrergic System. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 61, 7627–7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirtas, C.; Akca, M.; Aykin, U.; Surmeneli, Y.E.; Yildirim, H.; Yildirim, M. Effective Protection Against Status Epilepticus Caused by Lithium–Pilocarpine: Combination of Midazolam and Lacosamide. Brain Behav. 2025, 15, e70546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascuñana, P.; Javela, J.; Delgado, M.; Fernández de la Rosa, R.; Shiha, A.A.; García-García, L.; Pozo, M.Á. [18F]FDG PET Neuroimaging Predicts Pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) Kindling Outcome in Rats. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2016, 18, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devinsky, O.; Vezzani, A.; Najjar, S.; De Lanerolle, N.C.; Rogawski, M.A. Glia and Epilepsy: Excitability and Inflammation. Trends Neurosci. 2013, 36, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzani, A.; Aronica, E.; Mazarati, A.; Pittman, Q.J. Epilepsy and Brain Inflammation. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 244, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzani, A.; French, J.; Bartfai, T.; Baram, T.Z. The Role of Inflammation in Epilepsy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 7, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofroniew, M.V. Molecular Dissection of Reactive Astrogliosis and Glial Scar Formation. Trends Neurosci. 2009, 32, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burda, J.E.; Sofroniew, M.V. Reactive Gliosis and the Multicellular Response to CNS Damage and Disease. Neuron 2014, 81, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brackhan, M.; Bascun ana, P.; Postema, J.M.; Ross, T.L.; Bengel, F.M.; Bankstahl, M.; Bankstahl, J.P. Serial Quantitative TSPO-Targeted PET Reveals Peak Microglial Activation up to 2 Weeks after an Epileptogenic Brain Insult. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1302–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escartin, C.; Galea, E.; Lakatos, A.; O’Callaghan, J.P.; Petzold, G.C.; Serrano-Pozo, A.; Steinhäuser, C.; Volterra, A.; Carmignoto, G.; Agarwal, A.; et al. Reactive Astrocyte Nomenclature, Definitions, and Future Directions. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Guttenplan, K.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Bennett, F.C.; Bohlen, C.J.; Schirmer, L.; Bennett, M.L.; Münch, A.E.; Chung, W.S.; Peterson, T.C.; et al. Neurotoxic Reactive Astrocytes Are Induced by Activated Microglia. Nature 2017, 541, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Barres, B.A. Reactive Astrocytes: Production, Function, and Therapeutic Potential. Immunity 2017, 46, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, D.; Ravizza, T.; Maroso, M.; Carcak, N.; Eryigit, T.; Vanzulli, I.; Aker, R.G.; Vezzani, A.; Onat, F.Y. IL-1β Is Induced in Reactive Astrocytes in the Somatosensory Cortex of Rats with Genetic Absence Epilepsy at the Onset of Spike-and-Wave Discharges, and Contributes to Their Occurrence. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 44, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, D.K.; Steinhäuser, C. Functional Changes in Astroglial Cells in Epilepsy. Glia 2006, 54, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetherington, J.; Serrano, G.; Dingledine, R. Astrocytes in the Epileptic Brain. Neuron 2008, 58, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avignone, E.; Ulmann, L.; Levavasseur, F.; Rassendren, F.; Audinat, E. Status Epilepticus Induces a Particular Microglial Activation State Characterized by Enhanced Purinergic Signaling. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 9133–9144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyo, U.B.; Murugan, M.; Wu, L.J. Microglia–Neuron Communication in Epilepsy. Glia 2017, 65, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernhorst, K.; Herms, S.; Hoffmann, P.; Cichon, S.; Schulz, H.; Sander, T.; Schoch, S.; Becker, A.J.; Grote, A. TLR4, ATF-3 and IL8 Inflammation Mediator Expression Correlates with Seizure Frequency in Human Epileptic Brain Tissue. Seizure 2013, 22, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Chen, T.; Bosco, D.B.; Xie, M.; Zheng, J.; Dheer, A.; Ying, Y.; Wu, Q.; Lennon, V.A.; Wu, L.J. The Complement C3-C3aR Pathway Mediates Microglia–Astrocyte Interaction Following Status Epilepticus. Glia 2021, 69, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, L.; Antony, H.; Breuer, A.; Müller, J.; Seifert, G.; Audinat, E.; Singh, P.; Brosseron, F.; Heneka, M.T.; Steinhäuser, C.; et al. Reactive Microglia Are the Major Source of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha and Contribute to Astrocyte Dysfunction and Acute Seizures in Experimental Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Glia 2023, 71, 168–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zattoni, M.; Mura, M.L.; Deprez, F.; Schwendener, R.A.; Engelhardt, B.; Frei, K.; Fritschy, J.M. Brain Infiltration of Leukocytes Contributes to the Pathophysiology of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 4037–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Martín, N.; Martínez, M.G.; Bascuñana, P.; Fernández de la Rosa, R.; García-García, L.; Gómez, F.; Solas, M.; Martín, E.D.; Pozo, M.A. Astrocytic Ca2+ Activation by Chemogenetics Mitigates the Effect of Kainic Acid-Induced Excitotoxicity on the Hippocampus. Glia 2024, 72, 2217–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thergarajan, P.; Hudson, M.R.; Carmichael, I.; Clasadonte, J.; Dedeurwaerdere, S.; O’Brien, T.J.; Jones, N.C.; Ali, I. Characterising Seizure Development, Behavioural Comorbidities and Neuroinflammation in a Self-Sustained Electrical Status Epilepticus Model of Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy in C57BL/6J Mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2022, 168, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jupp, B.; Williams, J.; Binns, D.; Hicks, R.J.; Cardamone, L.; Jones, N.; Rees, S.; O’Brien, T.J. Hypometabolism Precedes Limbic Atrophy and Spontaneous Recurrent Seizures in a Rat Model of TLE. Epilepsia 2012, 53, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizuete, A.F.K.; Hennemann, M.M.; Gonçalves, C.A.; de Oliveira, D.L. Phase-Dependent Astroglial Alterations in Li–Pilocarpine-Induced Status Epilepticus in Young Rats. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 2730–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, J.; Alvestad, S.; Osen, K.K.; Skare, Ö.; Sonnewald, U.; Ottersen, O.P. Expression of Glutamine Synthetase and Glutamate Dehydrogenase in the Latent Phase and Chronic Phase in the Kainate Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Glia 2008, 56, 856–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, I.E.; Valous, N.A.; Lahrmann, B.; Janova, H.; Klaft, Z.J.; Koch, A.; Schneider, U.C.; Vajkoczy, P.; Heppner, F.L.; Grabe, N.; et al. Astrocytic Glutamine Synthetase Is Expressed in the Neuronal Somatic Layers and Down-Regulated Proportionally to Neuronal Loss in the Human Epileptic Hippocampus. Glia 2018, 66, 920–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gómez-Oliver, F.; Fernández de la Rosa, R.; Brackhan, M.; Bascuñana, P.; Pozo, M.Á.; García-García, L. Inhibition of Astrocyte Reactivity by Mdivi-1 After Status Epilepticus in Rats Exacerbates Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation and Impairs Limbic–Cortical Glucose Metabolism. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091242
Gómez-Oliver F, Fernández de la Rosa R, Brackhan M, Bascuñana P, Pozo MÁ, García-García L. Inhibition of Astrocyte Reactivity by Mdivi-1 After Status Epilepticus in Rats Exacerbates Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation and Impairs Limbic–Cortical Glucose Metabolism. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(9):1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091242
Chicago/Turabian StyleGómez-Oliver, Francisca, Rubén Fernández de la Rosa, Mirjam Brackhan, Pablo Bascuñana, Miguel Ángel Pozo, and Luis García-García. 2025. "Inhibition of Astrocyte Reactivity by Mdivi-1 After Status Epilepticus in Rats Exacerbates Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation and Impairs Limbic–Cortical Glucose Metabolism" Biomolecules 15, no. 9: 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091242
APA StyleGómez-Oliver, F., Fernández de la Rosa, R., Brackhan, M., Bascuñana, P., Pozo, M. Á., & García-García, L. (2025). Inhibition of Astrocyte Reactivity by Mdivi-1 After Status Epilepticus in Rats Exacerbates Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation and Impairs Limbic–Cortical Glucose Metabolism. Biomolecules, 15(9), 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091242






