[18F]Mefway: Imaging Serotonin 5HT1A Receptors in Human Postmortem Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Anterior Cingulate. Potential Applications to Human Positron Emission Tomography Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Methods
2.2. Postmortem Human Brain
2.3. [3H]WAY 100635 for Serotonin 5HT-1AR Imaging
2.4. [18F]Mefway for Serotonin 5HT-1AR Imaging
2.5. [18F]Fallypride for Dopamine D2/D3 Receptor Imaging
2.6. Immunohistochemistry
2.7. Image Analysis
2.7.1. [3H]WAY 100635
2.7.2. [18F]Mefway
2.7.3. [18F]Fallypride
2.7.4. [18F]FAZIN3
2.7.5. [125I]IBETA and [125I]IPPI
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Postmortem Human CN, PD and AD Brains
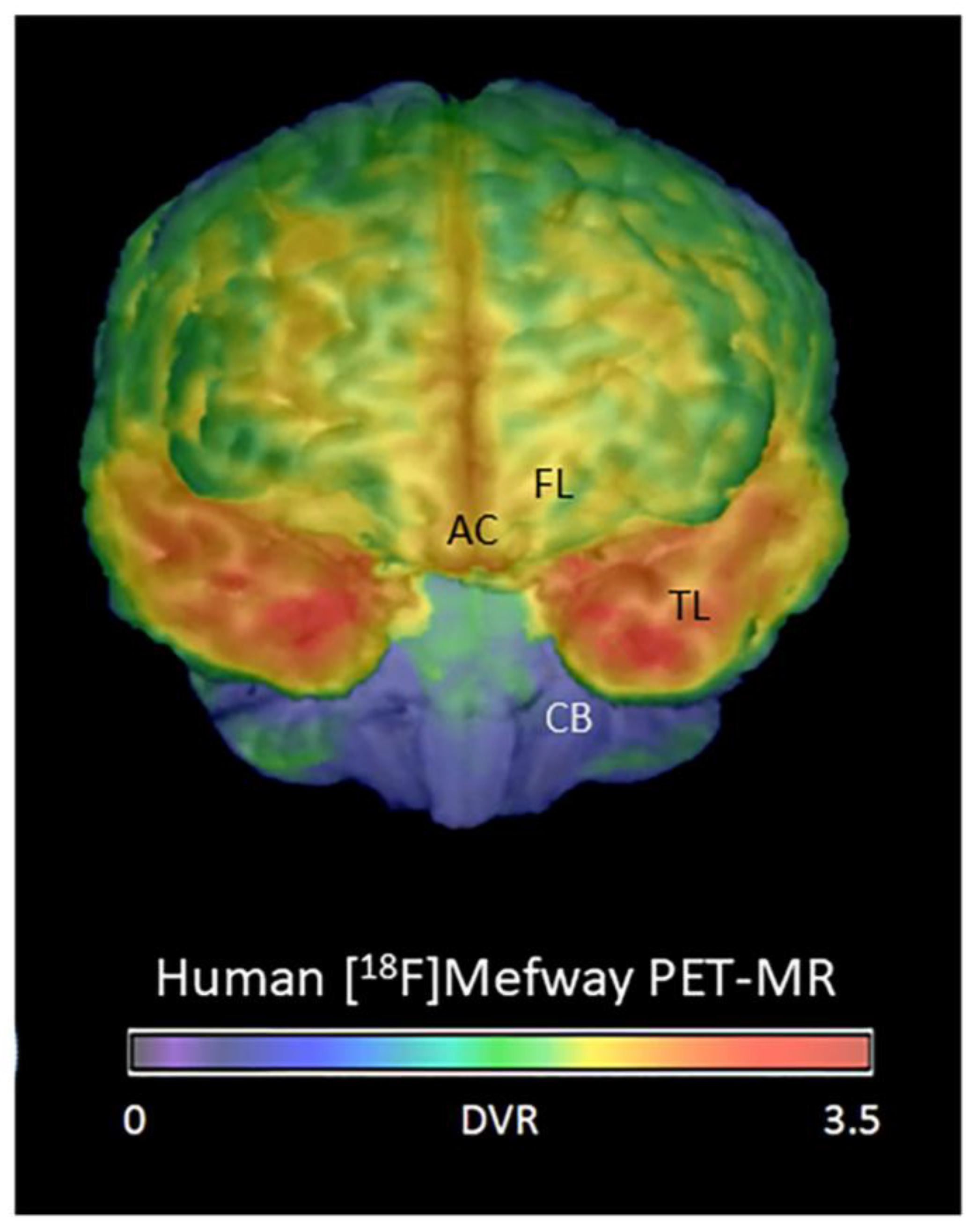
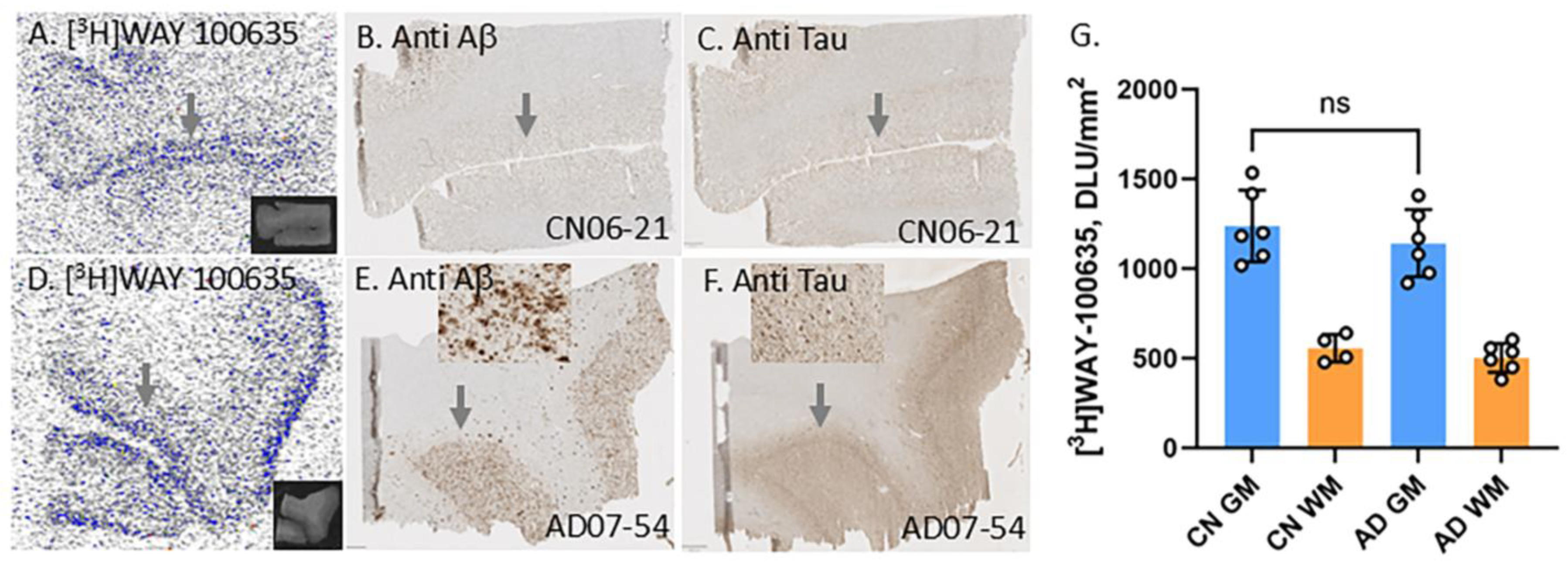
3.2. Frontal Cortex Serotonin 5HT1A Receptors
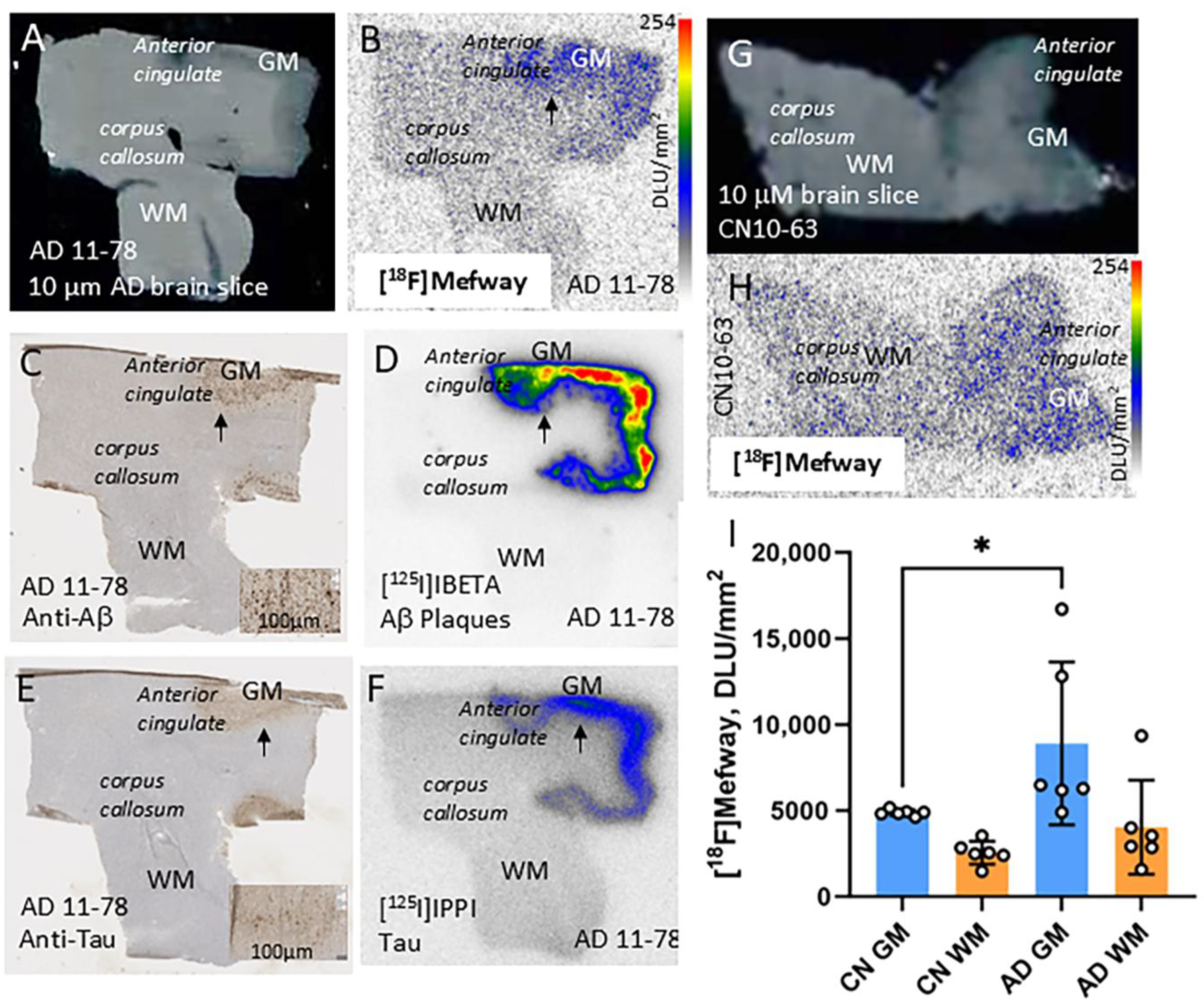
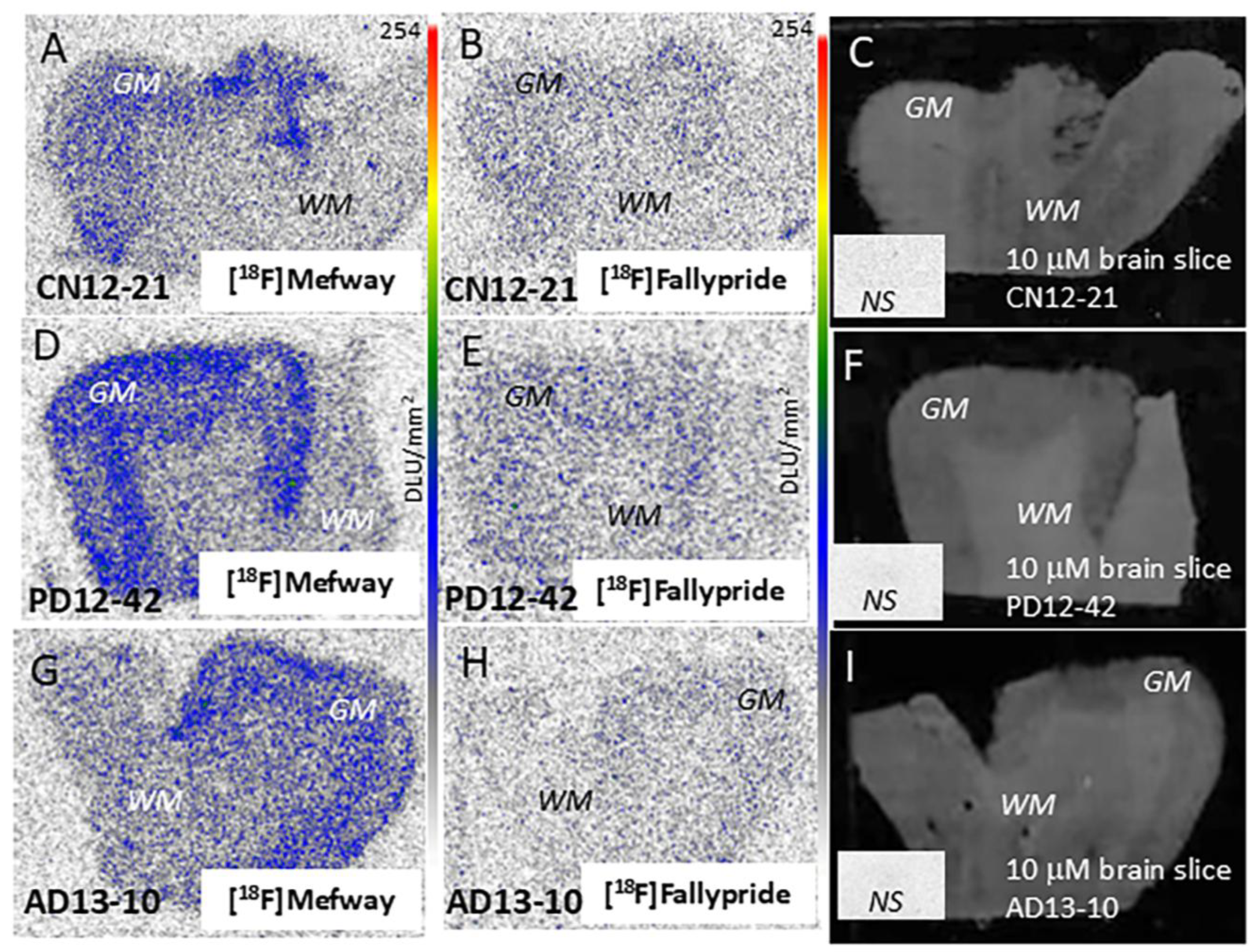
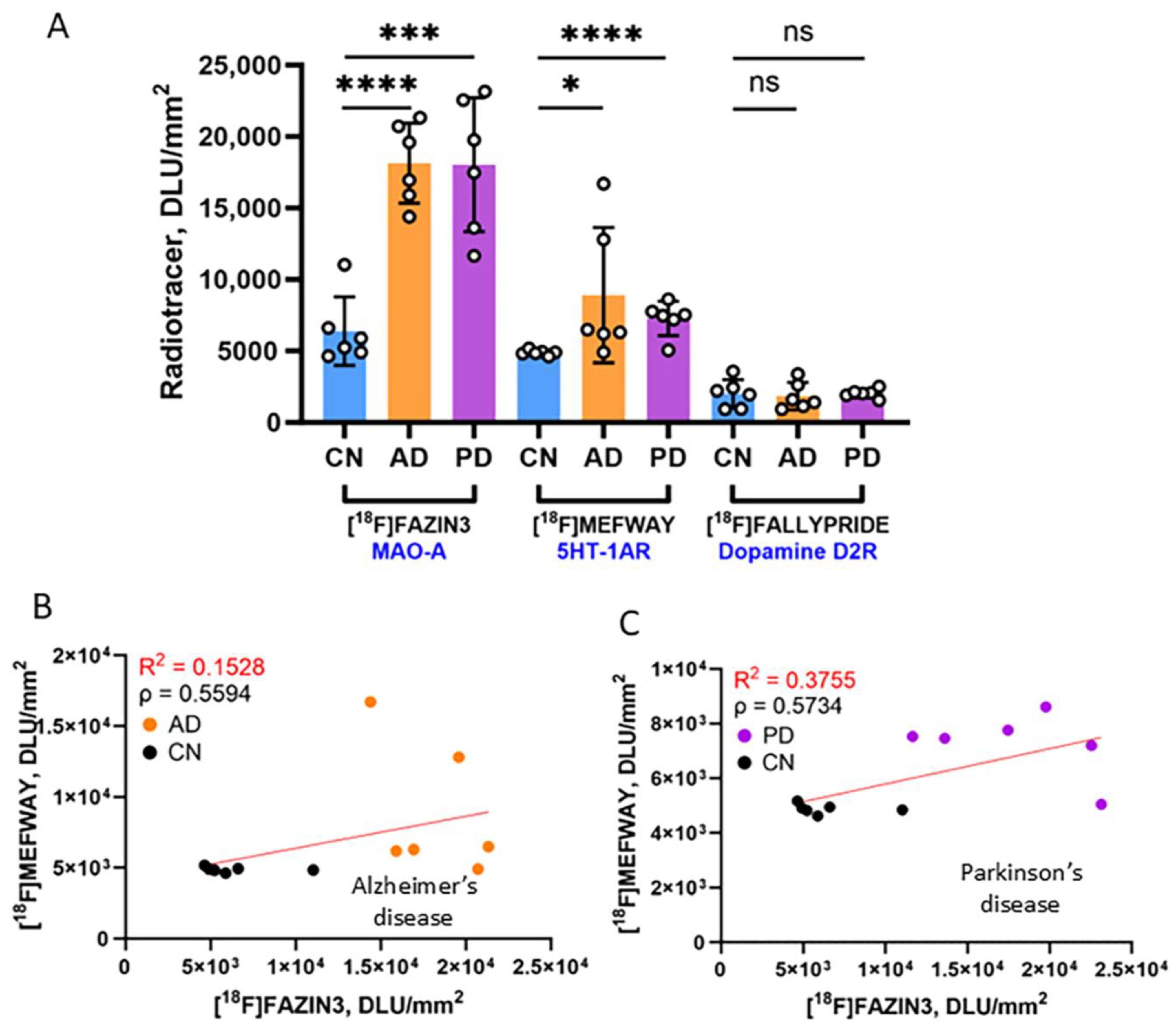
3.3. [18F]Mefway Imaging in AD Anterior Cingulate
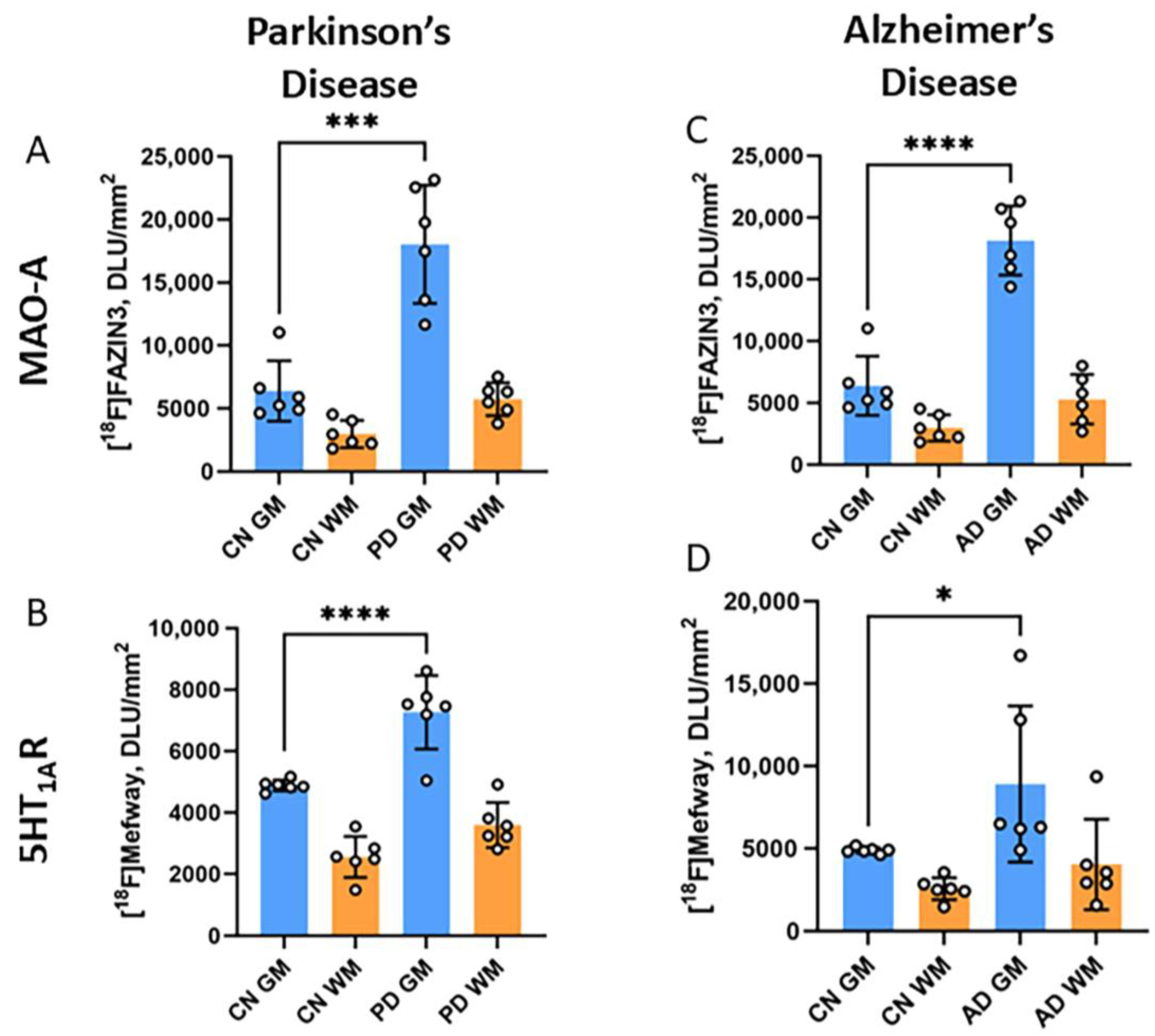
3.4. [18F]Mefway Imaging in PD Anterior Cingulate
3.5. [18F]Mefway and [18F]FAZIN3 Comparison in PD and AD Anterior Cingulate
3.6. [18F]Fallypride Imaging in PD and AD Anterior Cingulate
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caligiore, D.; Giocondo, F.; Silvetti, M. The neurodegenerative elderly syndrome (NES) hypothesis: Alzheimer and Parkinson are two faces of the same disease. IBRO Neurosci. Rep. 2022, 13, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.-S.; Li, G.; Gao, W.; Chen, G.; Gan, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, H.; Wu, S.; Du, Y. G protein-coupled receptors in neurodegenerative disease and psychiatric disorders. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azargoonjahromi, A. Serotonin enhances neurogenesis biomarkers, hippocampal volumes, and cognitivie functions in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Brain 2024, 17, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaldijk, E.; Vermeiren, Y. The role of serotonin within the microbiota-gut-brain axis in the development of Alzheimer’s disease: A narrative review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 75, 101556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyuz, E.; Arulsamy, A.; Aslan, F.S.; Sarisozen, B.; Guney, B.; Hekimoglu, A.; Yilmaz, B.N.; Retinasamy, T.; Shaikh, M.F. An expanded narrative review of neurotransmitter on Alzheimer’s disease: The role of therapeutic interventions on neurotransmission. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 62, 1631–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, S.H.; Chuang, R.; Brotchie, J.M. Serotonin and Parkinson’s disease: On movement, mood, and Madness. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacson, S.H.; Goldstein, M.; Pahwa, R.; Singer, C.; Klos, K.; Pucci, M.; Zhang, Y.; Crandall, D.; Koblan, K.S.; Navia, B.; et al. Ulotaront, a trace amine-associated receptor 1/serotonin 5HT1A agonist, in patients with Parkinsons disease psychosis. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2023, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinna, A.; Parekh, P.; Morelli, M. Serotonin 5HT1A receptors and their inteactions with adenosine A2A receptors in Parkinson’s disease and dyskinesia. Neuropharmacology 2023, 226, 109411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.; Hikima, A.; Morris, R.; Jackson, M.J.; Rose, S.; Varney, M.A.; Depoortere, R.; Newman-Tancredi, A. The selective HT1A receptor agonist, NLX-112, exerts anti-dyskinetic and anti-parkinsonian-like effects in MPTP-treated marmosets. Neuropharmacology 2020, 167, 107997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, G.; Streichenberger, N.; Billard, T.; Newman-Tancredi, A.; Zimmer, L. A postmortem study to compare agonist and antagonist 5HT1A receptor-binding sites in Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2014, 20, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdurand, M.; Zimmer, L. Hippocampal 5HT1A receptor expression changes in prodromal stages of Alzheimers disease: Beneficial or deleterious. Neuropharmacology 2017, 123, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billard, T.; Le Bars, D.; Zimmer, L. PET radiotracers for molecular imaging of serotonin 5HT1A receptors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keep, V.; Barrio, J.R.; Huang, S.C.; Huang, S.C.; Ercoli, L.; Siddarth, P.; Shoghi-Jadid, K.; Cole, G.M.; Satyamurthy, N.; Cummings, J.L.; et al. Serotonin 1A receptors in the living brain of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truchot, L.; Costes, S.N.; Zimmer, L.; Laurent, B.; Le Bars, D.; Thomas-Anterion, C.; Croisile, B.; Mercier, B.; Hermier, M.; Vighetto, A.; et al. Up-regulation of hippocampal serotonin metabolism in mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 2007, 69, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truchot, L.; Costes, S.N.; Zimmer, L.; Laurent, B.; Le Bars, D.; Thomas-Anterion, C.; Mercier, B.; Hermier, M.; Vighetto, A.; Krolak-Salmon, P. A distinct [18F]MPPF PET profile in amnestic mild cognitive impairment compared to mild Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 2008, 40, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doder, M.; Rabiner, E.A.; Turjanski, N.; Lees, A.J.; Brooks, D.J. Tremor in Parkinson’s disease and serotonergic dysfunction: An 11C-WAY 100635 PET study. Neurology 2003, 60, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.V.; Marsden, C.A.; Fone, K.C. A role for the 5HT1A, 5HT4 and 5HT6 receptors in learning and memory. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 29, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelsen, K.A.; Prickaerts, J.; Steinbusch, H.W.M. The dorsal raphe nucleus and serotonin: Implications for neuroplasticity linked to major depression and Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Brain Res. 2008, 172, 233–264. [Google Scholar]
- Borg, J. Molecular imaging of the 5HT1A receptor in relation to human cognition. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 195, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsey, R.V. Serotonin receptor imaging: Clinically useful? J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 1495–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, P.C.; Surace, E.; Bérgamo, Y.; Calandri, I.; Vázquez, S.; Sevlever, G.; Allegri, R.F. Biomarkers for Alzheimers disease. Where we stand and where we are headed. Medicina 2019, 79, 546–551. [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu, Y.K.; Bath, H.S.; Shergill, J.; Liang, C.; Syed, A.U.; Ngo, A.; Karim, F.; Serrano, G.E.; Beach, T.G.; Mukherjee, J. [18F]Flotaza for Ab plaque diagnostic imaging: Evaluation in postmortem human Alzheimer’s disease brain hippocampus and PET/CT imaging in 5xFAD transgenic mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, J.; Aisen, P.; Lemere, C.; Atri, A.; Sabbagh, M.; Salloway, S. Aducanumab produced a clinically meaningful benefit in association with amyloid lowering. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Paclibar, C.G.; Gonzaga, N.L.; Sison, S.A.; Bath, H.S.; Biju, A.P.; Mukherjee, J. [125I]IPC-Lecanemab: Synthesis and Evaluation of Ab plaque binding antibody and comparison with small molecule [18F]Flotaza and [125I]IBETA in postmortem human Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol. Int. 2024, 16, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, A.U.; Liang, C.; Patel, K.K.; Mondal, R.; Kamalia, V.M.; Moran, T.R.; Ahmed, S.T.; Mukherjee, J. Comparison of Monoamine oxidase-A, Ab plaques, Tau and Translocator protein in postmortem human Alzheimer’s disease brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, J.; Ladwa, R.M.; Liang, C.; Syed, A.U. Elevated monoamine oxidase-A in anterior cingulate of postmortem human Parkinson’s disease: A potential surrogate biomarker for Lewy bodies? Cells 2022, 11, 4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, J.; Bajwa, A.K.; Wooten, D.W.; Hillmer, A.T.; Pan, M.-L.; Pandey, S.K.; Saigal, N.; Christian, B.T. Comparative assessment of 18F-Mefway as a serotonin 5-HT1A receptor PET imaging agent across species-rodents, nonhuman primates and humans. J. Comp. Neurol. 2016, 524, 1457–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, M.; Dunzinger, A.; Wimmer, J.; Rittmannsberger, H.; Nader, M.; Pichler, R. Serotonin 1A receptor density measured by F-18 mefway PT/CT in mesolimbic cortex and raphe does not discriminate therapeutic response in patients with major depressive episode. Ed. Minerva Medica 2020, 64, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.J.; Lyoo, C.H.; Ryu, Y.H.; Choi, J.U. Assessing the applicability of PMOD residence times model for PET image-based radiation dosimetry. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, H.; Lundkvist, C.; Halldin, C.; Farde, L.; Pike, V.W.; McCarron, J.A.; Fletcher, A.; Cliffe, I.A.; Barf, T.; wikstrom, H.; et al. Autoradiographic localization of 5HT1A receptors in the post-mortem human brain using [3H]WAY-100635 and [11C]WAY-100635. Brain Res. 1997, 745, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, J.; Christian, B.T.; Dunigan, K.; Shi, B.; Narayanan, T.K.; Satter, M.; Mantil, J. Brain Imaging of 18F-fallypride in normal volunteers: Blood analysis, distribution, test-retest studies and preliminary assessment of sensitivity to aging effects on dopamine D-2/D-3 receptors. Synapse 2002, 46, 170–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, J.; Liang, C.; Patel, K.K.; Lam, P.Q.; Mondal, R. Development and evaluation [125I]IPPI for tau imaging in post-mortem human Alzheimer’s disease brain. Synapse 2021, 74, e22183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzoli, S.; Giorgio, J.; Martersteck, A.; Dobyns, L.; Harrison, T.M.; Jagust, W.J. Successful cognitive aging is associated with thicker anterior cingulate cortex and lower tau deposition compared to typical aging. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 20, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmqvist, S.; Scholl, M.; Strandberg, O.; Mattson, N.; Stomrud, E.; Zetterburg, H.; Blennow, K.; Landau, S.; Jagust, W.; Hansson, O. Earliest accumulation of b-amyloid occurs within the default-mode network and concurrently affects brain connectivity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 8, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnadas, N.; Huang, K.; Schultz, S.A.; Dore, V.; Bourgeat, P.; Goh, A.M.Y.; Lamb, F.; Bozinovski, S.; Burnham, S.C.; Robertson, J.S.; et al. Visually identified Tau 18F-MK6240 PET patterns in symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 88, 1627–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, J.D.; Liu, L.; Poirier, S.E.; Schaefer, B.; Poolacheria, R.; Burham, A.M.; Sabesan, P.; Lawrence, K.S.; Thebarge, J.; Hicks, J.W.; et al. The functional and structural associations of aberrant microglial activity in major depressive disorder. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2022, 47, E197–E208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, F.L.; Hurley, R.A.; Taber, K.H. Anterior cingulate cortex: Unique role in cognition and emotion. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 23, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saigal, N.; Pichika, R.; Easwaramoorthy, B.; Collins, D.; Christian, B.T.; Shi, B.; Narayanan, T.K.; Potkin, S.G.; Mukherjee, J. Synthesis and biological evaluation of a novel serotonin 5-HT1a receptor radioligand, N-{2-[4-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperazinyl]ethyl}-N-(2-pyridyl)-N-(4-18F-fluoromethylcyclohexane)carboxamide in rodents and imaging by PET in non-human primate. J. Nucl. Med. 2006, 47, 1697–1706. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, J.; Yang, Z.Y.; Das, M.K.; Brown, T. Fluorinated benzamide neuroleptics 3. Development of (S)-N-[(1-allyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl]-5-(3[F-18]-fluoropropyl)-2,3-dimethoxy-benzamide as an improved dopamine D-2 receptor tracer. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1995, 22, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, T.G.; Adler, C.H.; Sue, L.I.; Serrano, G.; Shill, H.A.; Walker, D.G.; Lue, L.; Roher, A.E.; Dugger, B.N.; Maarouf, C.; et al. Arizona study of aging and neurodegenerative disorders and brain and body donation program. Neuropathology 2015, 35, 354–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Thal, D.R.; Ghebremedhin, E.; Tredici, K.D. Stages of the pathologic process in Alzheimer’s disease age categories from 1 to 100 years. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 70, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, R.; Sandhu, Y.K.; Kamalia, V.M.; Delaney, B.A.; Syed, A.U.; Nguyen, G.A.H.; Moran, T.R.; Limpengco, R.R.; Liang, C.; Mukherjee, J. Measurement of Ab amyloid and Tau in postmortem human Alzheimer’s disease brain by immunohistochemistry analysis using QuPath and autoradiography using [18F]flotaza, [125I]IBETA and [124/125I]IPPI. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villemagne, V.L.; Harada, R.; Doré, V.; Furumoto, S.; Mulligan, R.; Kudo, Y.; Burnham, S.; Krishnadas, N.; Bozinovski, S.; Huang, K.; et al. First-in-humans evaluation of 18F-SMBT-1, a novel 18F-labeled monoamine oxidase-B PET tracer for imaging reactive astrogliosis. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.N.; Raghanti, M.A. The role of monoamine oxidase enzymes in the pathophysiology of neurological disorders. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2021, 114, 101957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanderigo, F.; D’Agostino, A.E.; Josh, N.; Schain, M.; Kumar, D.; Parsey, R.V.; DeLorenzo, C.; Mann, J.J. [11C]Harmine binding to brain monoamine oxidase A: Test-retest properties and noninvasive quantification. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2018, 20, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.S.; Protas, H.; Kuwabara, H.; Savonenko, A.; Nassery, N.; Gould, N.F.; Kraut, M.; Avramopoulous, D.; Holt, D.; Dannals, R.F.; et al. Moelcular imaging of the association between serotonin degeneration and beta-amyloid deposition in mild cognitive impairment. Neuroimage Clin. 2023, 37, 103322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaasinen, V.; Vahlberg, T.; Stoessl, A.J.; Strafella, A.P.; Antonini, A. Dopamine receptors in Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis of imaging studies. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 1781–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, A.J.; Smith, C.T.; Peterson, K.J.; Trujillo, P.; van Wouwe, N.C.; Donahue, M.J.; Kessler, R.M.; Deutch, A.Y.; Zald, D.H.; Claassen, D.O. [18F]Fallypride characterization of striatal and extrastriatal D2/3 receptors in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroimage Clin. 2018, 18, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.T.; Clark-Papasavas, C.; Marsden, P.; Baker, S.; Cleij, M.; Kapur, S.; Kessler, R.; Howard, R.; Reeves, S.J. Establishing test-retest reliability of an adapted [18F]fallypride imaging protocol. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Duin, E.D.A.; Ceccarini, J.; Booij, J.; Kasanova, Z.; Vingerhoets, C.; Huijstee, J.V.; Heinzel, A.; Mohammadkhani-Shali, S.; Winz, O.; Mottaghy, F.; et al. Lower [18F]fallypride binding to dopamine D2/D3 receptors in frontal brain areas in adults with 22q11.2 deletion syndrome: A positron emission tomography study. Psychol. Med. 2019, 50, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumme, V.; Aalto, S.; Ilonen, T.; Nagren, K.; Hietala, J. Dopamine D2/D3 receptor binding in the anterior cingulate cortex and executive functioning. Psychiatry Res. 2007, 156, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Hu, S.H.; Shi, Y.; Li, B.-M. The roles of the anterior cingulate cortex and its dopamine receptors in self-paced cost-benefit decision making in rats. Learn. Behav. 2017, 45, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhara, T.; Okubo, Y.; Yasuno, F.; Sudo, Y.; Inoue, M.; Ichimiya, T.; Nakashima, Y.; Nakayama, K.; Tanada, S.; Suzuki, K.; et al. Decreased dopamine D2 receptor binding in the anterior cingulate cortex in schizophrenia. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2002, 59, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martorana, A.; Koch, G. Is dopamine involved in Alzheimer’s disease? Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, A.S.; Vale, N. Antidepressants in Alzheimer’s disease: A focus on the role of mirtazapine. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, W.; Li, W.; Sun, A.; Li, X.; et al. Discovery of novel dual RAGE/SERT inhibitors for the potential treatment of the comorbidity of Alzheimer’s disease and depression. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 236, 114347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Okun, M.S. Diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson disease. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 323, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suescun, J.; Chandra, S.; Schiess, M.C. Chapter 13. The role of neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders. In Translational Inflammation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 241–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Chaney, A.M.; Carlson, M.L.; Jackson, I.M.; Rao, A.; James, M.L. Neuroinflammation PET imaging: Current opinion and future directions. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Subjects, N | CERAD Pathology | Gender | Age Range, Mean ± SD | PMI, hrs | Brain Region 1 | Plaque Total | Tangle Total | LB | Braak Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | CN | 5 Male 1 Female | 73–92 (85.2 ± 7.03) | 2–5.4 | FC | 0–5.5 | 0–6 | 0 | II-III |
| 6 | AD | 3 Male 3 Female | 75–90 (81.3 ± 6.12) | 1.8–5 | FC | 10–15 | 12–15 | 0 | V-VI |
| 6 | CN | 4 Male 2 Female | 71–97 (79.9 ± 8.55) | 2–5.4 | AC | 0–5.5 | 0–6 | 0 | I-III |
| 6 | AD | 5 Male 1 Female | 70–91 (80.4 ± 5.98) | 2.3–4.8 | AC | 14–15 | 10–15 | 0 | V-VI |
| 6 | PD | 4 Male 2 Female | 53–95 (80.4 ± 13.1) | 2.1–4.8 | AC | 0–10 | 0.5–6.5 | 0 | I-III |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonzaga, N.L.; Karim, F.; Liang, C.; Mukherjee, J. [18F]Mefway: Imaging Serotonin 5HT1A Receptors in Human Postmortem Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Anterior Cingulate. Potential Applications to Human Positron Emission Tomography Studies. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040592
Gonzaga NL, Karim F, Liang C, Mukherjee J. [18F]Mefway: Imaging Serotonin 5HT1A Receptors in Human Postmortem Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Anterior Cingulate. Potential Applications to Human Positron Emission Tomography Studies. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(4):592. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040592
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzaga, Noresa L., Fariha Karim, Christopher Liang, and Jogeshwar Mukherjee. 2025. "[18F]Mefway: Imaging Serotonin 5HT1A Receptors in Human Postmortem Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Anterior Cingulate. Potential Applications to Human Positron Emission Tomography Studies" Biomolecules 15, no. 4: 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040592
APA StyleGonzaga, N. L., Karim, F., Liang, C., & Mukherjee, J. (2025). [18F]Mefway: Imaging Serotonin 5HT1A Receptors in Human Postmortem Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Anterior Cingulate. Potential Applications to Human Positron Emission Tomography Studies. Biomolecules, 15(4), 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040592








