Changes in Artemin Correlate with Anxiety- and Depression-like Behaviors in a Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Rat Neuroinflammation Model †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Bodyweight Change, Mortality, Posture, and Piloerection Analysis
2.4. Open Field Test
2.5. Splash Test
2.6. Sucrose Preference Test
2.7. Animal Euthanasia and Tissue Collection
2.8. ELISA
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bodyweight Change, Mortality, Posture, and Piloerection Results
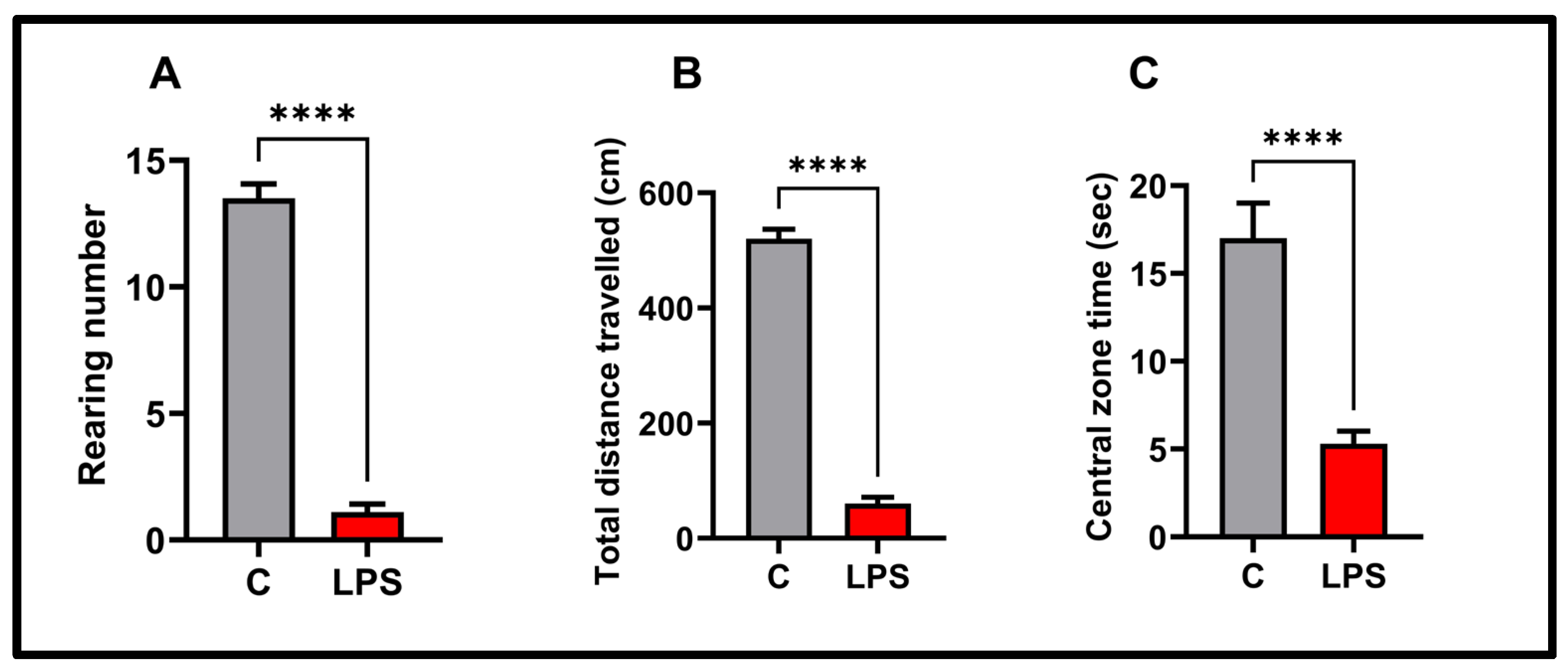
3.2. Open Field Results
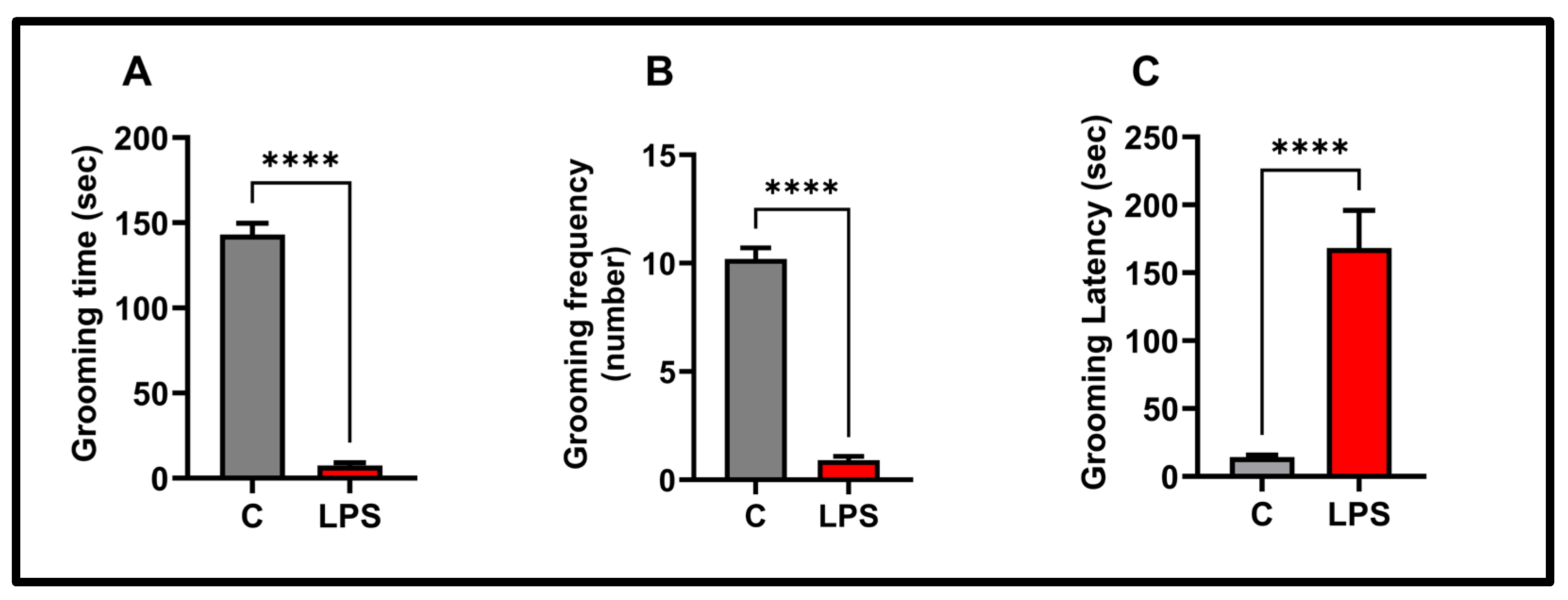
3.3. Splash Test Results
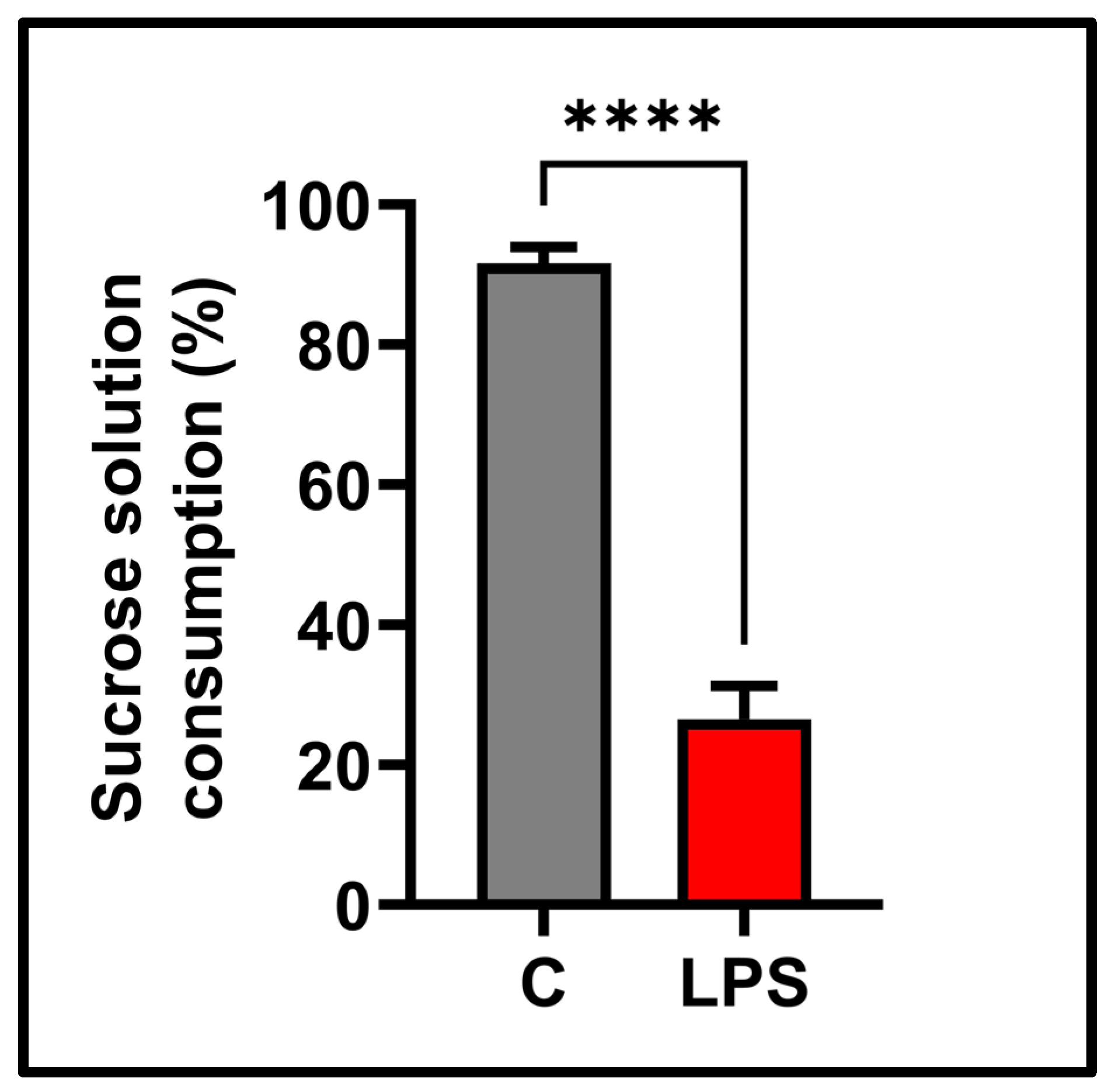
3.4. Sucrose Preference Test Result
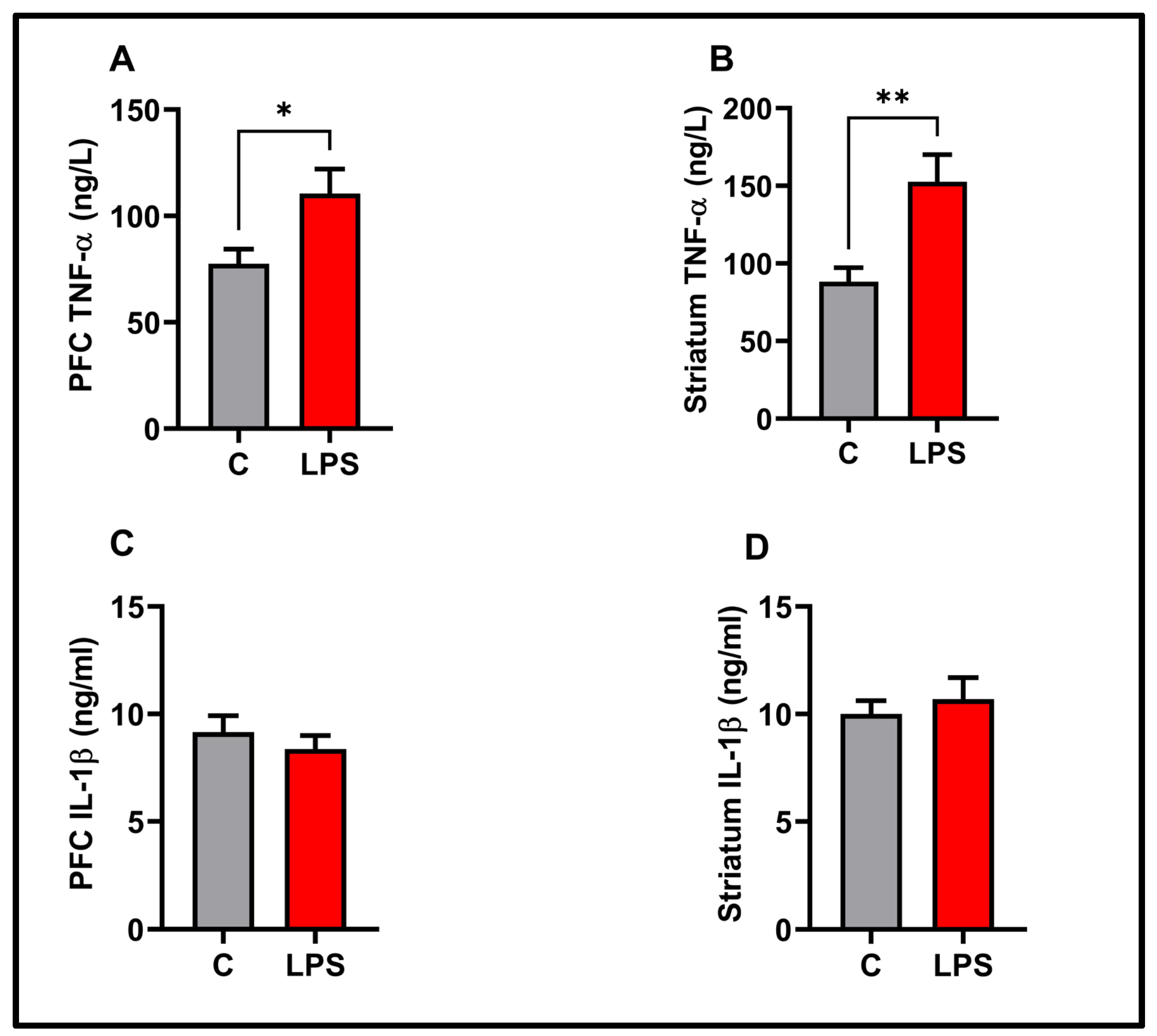
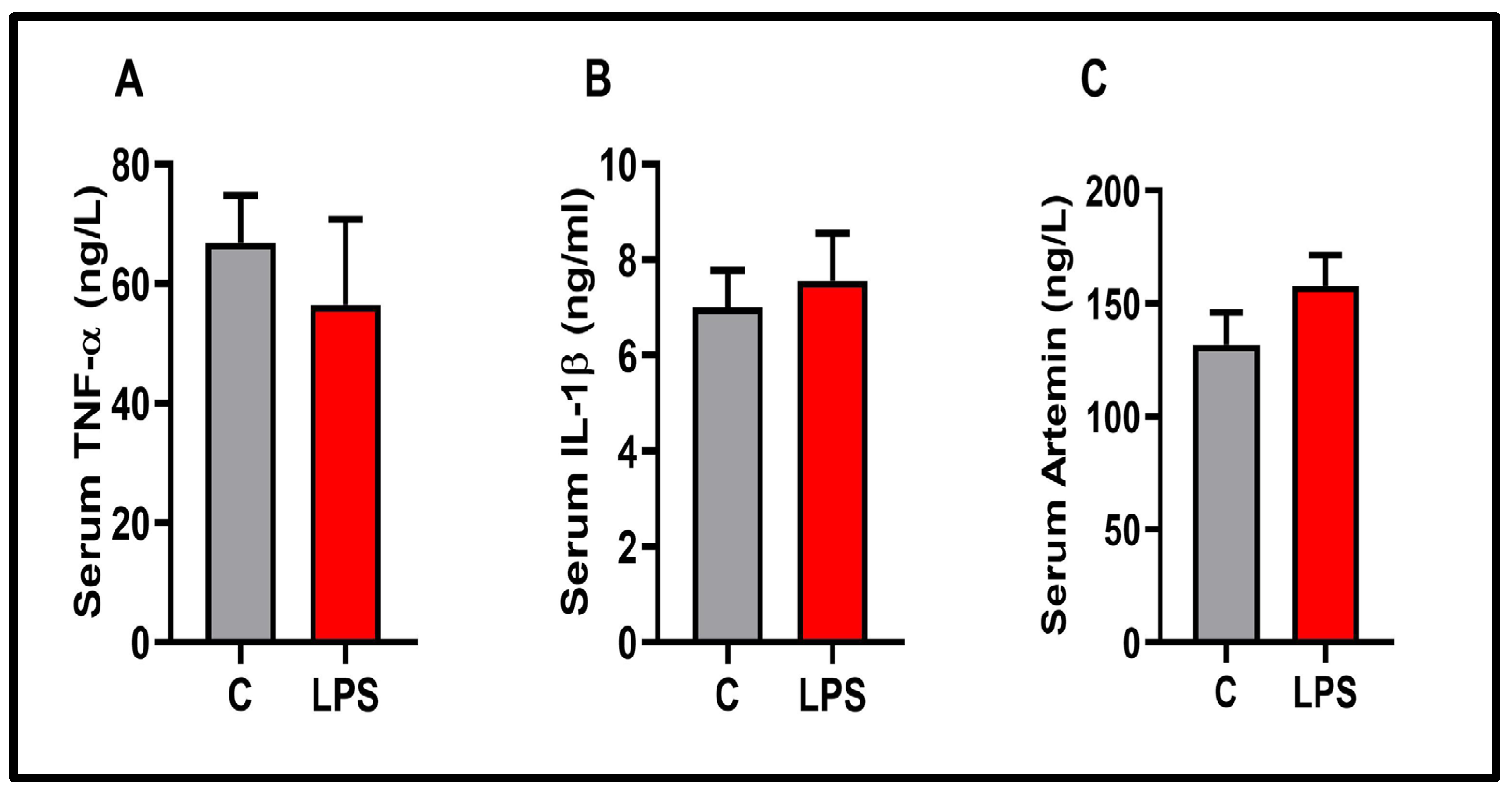
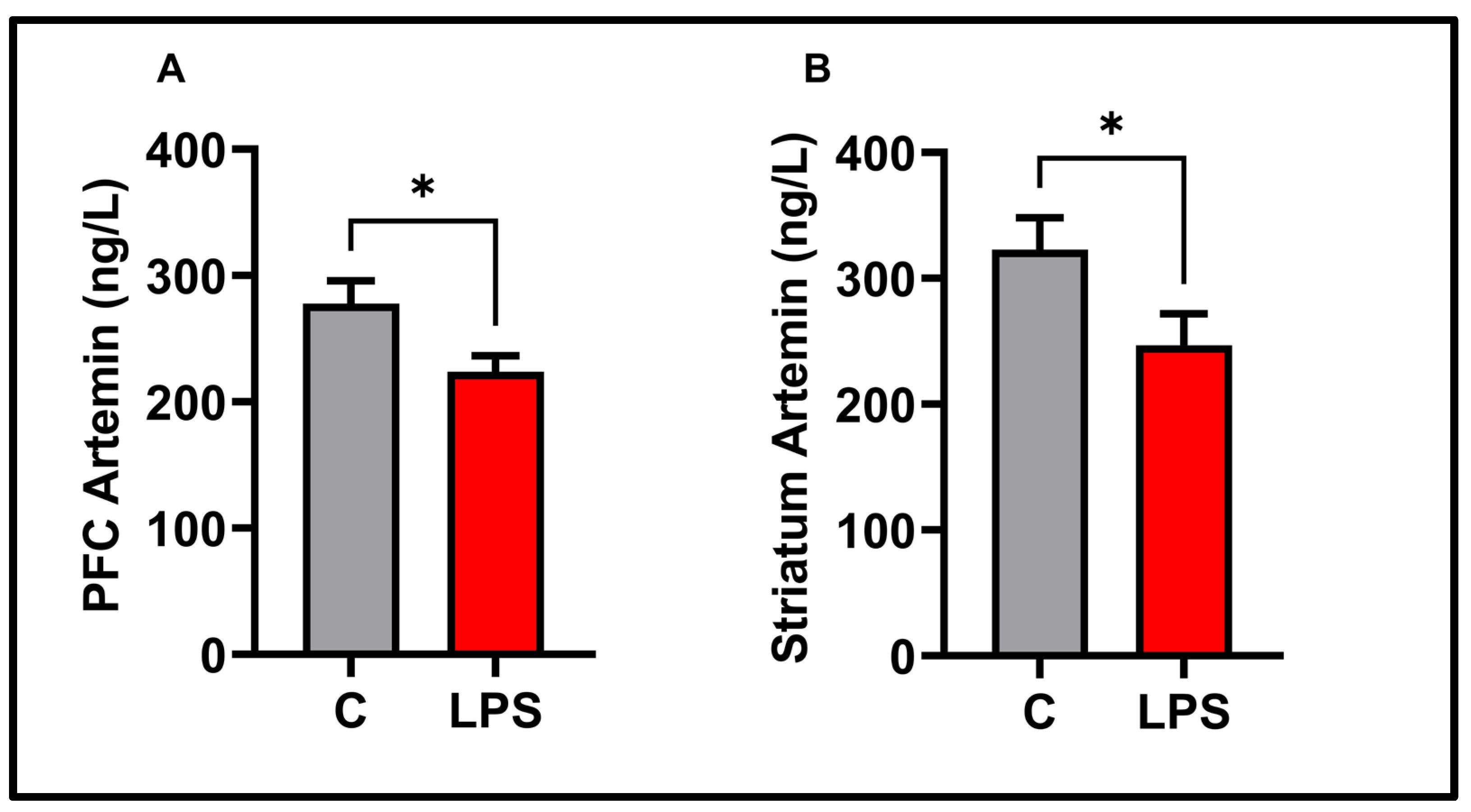
3.5. Molecular Results
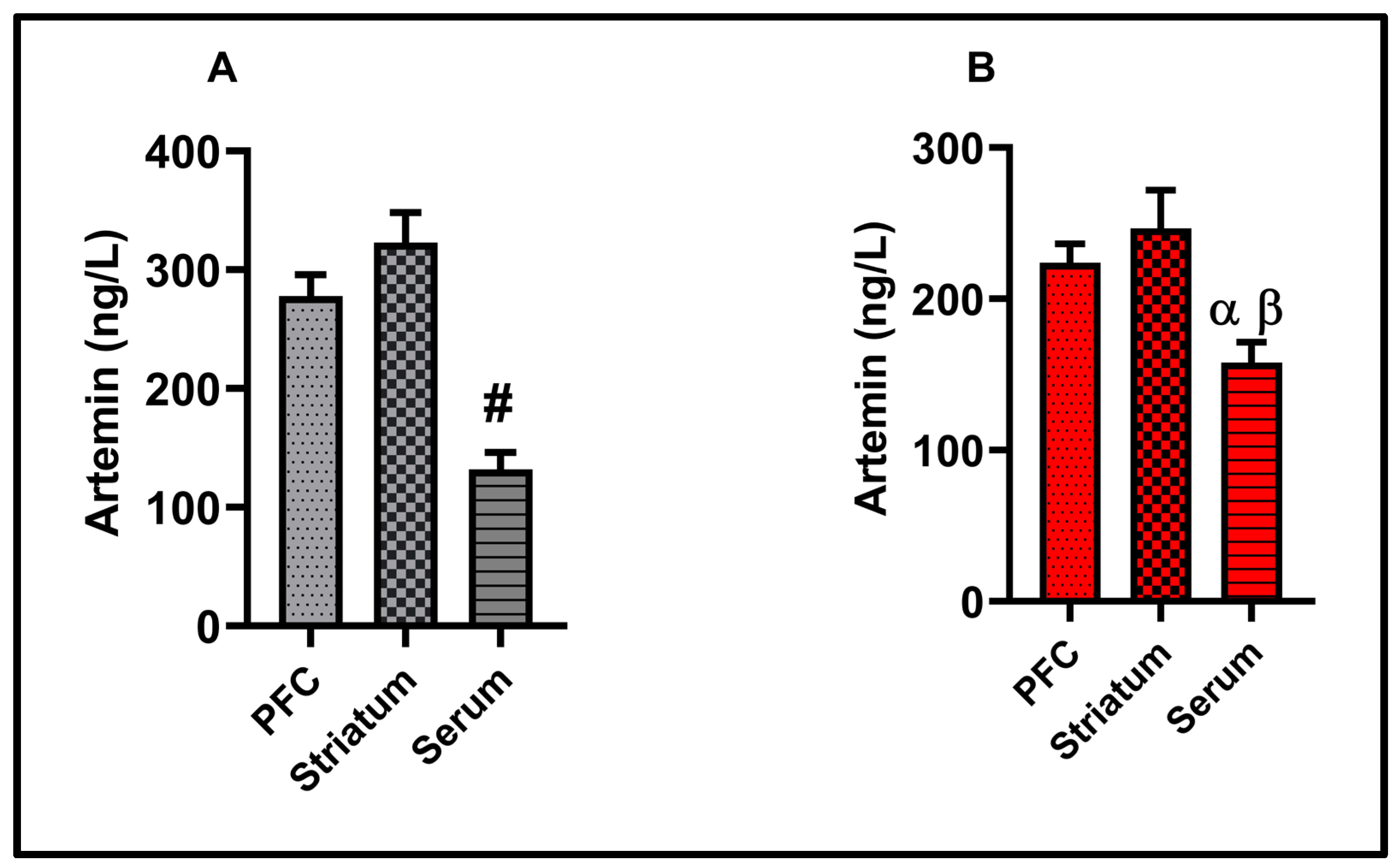
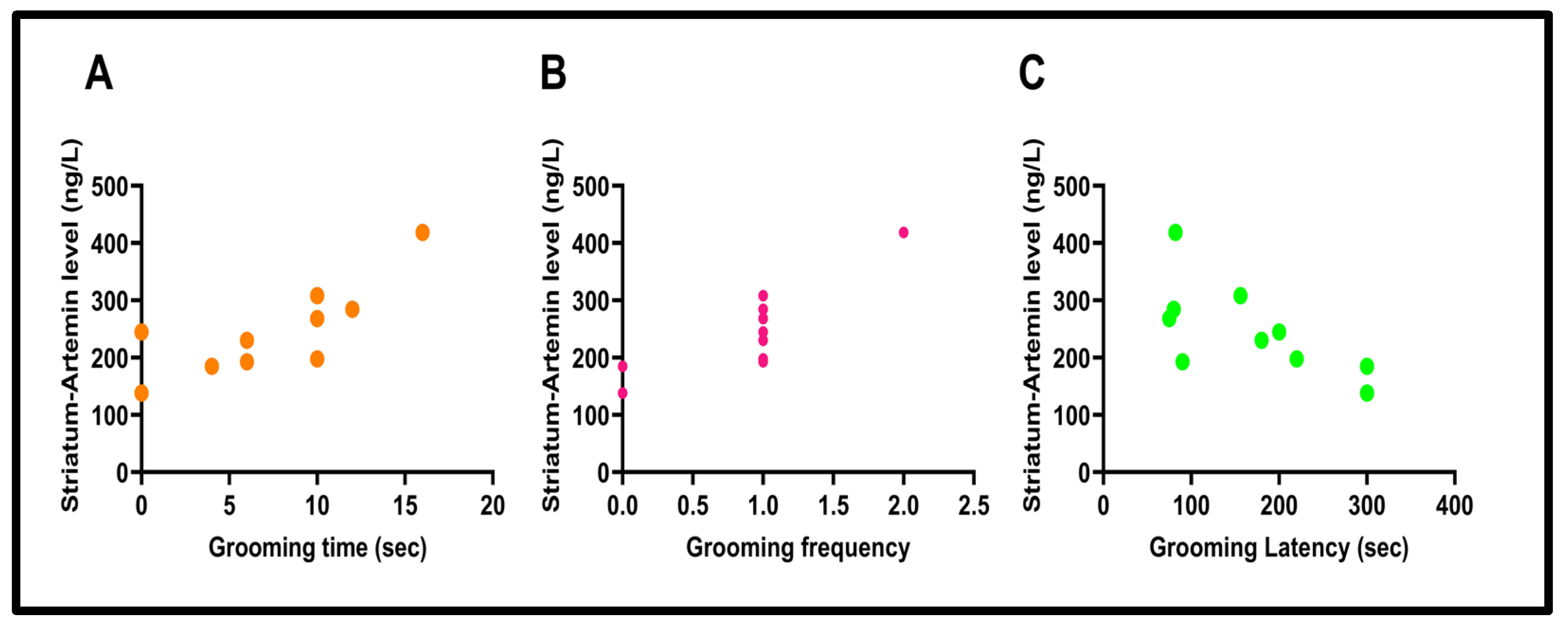
3.6. Correlation Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARTN | Artemin |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1beta |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| NTs | Neurotrophic factors |
| PFC | Prefrontal cortex |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
References
- Shabab, T.; Khanabdali, R.; Moghadamtousi, S.Z.; Kadir, H.A.; Mohan, G. Neuroinflammation pathways: A general review. Int. J. Neurosci. 2017, 127, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiSabato, D.J.; Quan, N.; Godbout, J.P. Neuroinflammation: The devil is in the details. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, M.; Lloyd, D.G.; Ji, X.; Vizcaychipi, M.P.; Ma, D. Neuroinflammation: The role and consequences. Neurosci. Res. 2014, 79, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, J.; Barak, Y.; Chengappa, K.; Rapoport, A.; Rebey, M.; Barak, V. Cerebrospinal cytokine levels in patients with acute depression. Neuropsychobiology 1999, 40, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, P.; Parveen, R.; Khan, M.A.; Kohli, S.; Agarwal, N.B. Interleucina-9 e interleucina-1β séricas aumentadas estão associadas à depressão em pacientes com diabetes tipo 2. Arq. De Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2020, 78, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, B.; Tawadros, N.; Scarr, E.; Gibbons, A.S. Regionally-specific changes in levels of tumour necrosis factor in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex obtained postmortem from subjects with major depressive disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2010, 120, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, K.; Li, H.-R.; Chen, X.-X.; Gao, X.-R.; Huang, L.-L.; Du, A.-Q.; Jiang, C.; Li, H.; Ge, J.-F. Quercetin alleviates LPS-induced depression-like behavior in rats via regulating BDNF-related imbalance of copine 6 and TREM1/2 in the hippocampus and PFC. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 10, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiergiel, A.H.; Dunn, A.J. Effects of interleukin-1β and lipopolysaccharide on behavior of mice in the elevated plus-maze and open field tests. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2007, 86, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulakhiya, K.; Keshavlal, G.P.; Bezbaruah, B.B.; Dwivedi, S.; Gurjar, S.S.; Munde, N.; Jangra, A.; Lahkar, M.; Gogoi, R. Lipopolysaccharide induced anxiety-and depressive-like behaviour in mice are prevented by chronic pre-treatment of esculetin. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 611, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.-C.; Shi, Z.; Qin, M.; Sha, N.-N.; Li, Y.; Liao, D.-F.; Lin, F.-H.; Shu, B.; Sun, Y.-L.; Yuan, T.-F. Muscone ameliorates LPS-induced depressive-like behaviors and inhibits neuroinflammation in prefrontal cortex of mice. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020, 48, 559–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaper, S.D. Neurotrophic factors: An overview. In Neurotrophic Factors: Methods and Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, C.E. Role of neurotrophic factors in neuronal development. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1996, 6, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Poo, M.-m. Neurotrophin regulation of neural circuit development and function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofroniew, M.V.; Howe, C.L.; Mobley, W.C. Nerve growth factor signaling, neuroprotection, and neural repair. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 1217–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, G.B.; Vasterling, J.J.; Vedak, P.C. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in traumatic brain injury, post-traumatic stress disorder, and their comorbid conditions: Role in pathogenesis and treatment. Behav. Pharmacol. 2010, 21, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çalışkan, H.; Önal, D.; Nalçacı, E. Darbepoetin alpha has an anxiolytic and anti-neuroinflammatory effect in male rats. BMC Immunol. 2024, 25, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hritcu, L.; Gorgan, L.D. Intranigral lipopolysaccharide induced anxiety and depression by altered BDNF mRNA expression in rat hippocampus. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 51, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Mizuno, M.; Nabeshima, T. Role for brain-derived neurotrophic factor in learning and memory. Life Sci. 2002, 70, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruinzeel, W.; Masure, S. Recombinant expression, purification and dimerization of the neurotrophic growth factor Artemin for in vitro and in vivo use. Protein Expr. Purif. 2012, 81, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloh, R.H.; Tansey, M.G.; Lampe, P.A.; Fahrner, T.J.; Enomoto, H.; Simburger, K.S.; Leitner, M.L.; Araki, T.; Johnson, E.M.; Milbrandt, J. Artemin, a novel member of the GDNF ligand family, supports peripheral and central neurons and signals through the GFRα3–RET receptor complex. Neuron 1998, 21, 1291–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Li, Y.; Bennett, S.; Chen, J.; Weng, I.Z.; Huang, L.; Xu, H.; Xu, J. The role of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor family member artemin in neurological disorders and cancers. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonde, C.; Kristensen, B.W.; Blaabjerg, M.; Johansen, T.E.; Zimmer, J.; Meyer, M. GDNF and neublastin protect against NMDA-induced excitotoxicity in hippocampal slice cultures. Neuroreport 2000, 11, 4069–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblad, C.; Grønborg, M.; Hansen, C.; Blom, N.; Meyer, M.; Johansen, J.; Dagø, L.; Kirik, D.; Patel, U.A.; Lundberg, C. In vivo protection of nigral dopamine neurons by lentiviral gene transfer of the novel GDNF-family member neublastin/artemin. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2000, 15, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sah, D.W.; Ossipov, M.H.; Rossomando, A.; Silvian, L.; Porreca, F. New approaches for the treatment of pain: The GDNF family of neurotrophic growth factors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2005, 5, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.E.; Gibson, M.E.; Arnold, H.M.; Pepinsky, B.; Frank, E. Artemin promotes functional long-distance axonal regeneration to the brainstem after dorsal root crush. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 6170–6175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Laboratory Animal Resources (US); Committee on Care & Use of Laboratory Animals. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals; US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1986.
- Değirmenci, M.D.; Çalışkan, H.; Güneş, E. Effects of chronic intermittent cold stress on anxiety-depression-like behaviors in adolescent rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2024, 472, 115130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çalışkan, H.; Karakaya, D.; Koçak, S.; Ömercioğlu, G.; Baştuğ, M. Effect of high-intensity interval training on self-care and anxiety-like behaviors in naive rats. Exp. Brain Res. 2024, 242, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çalışkan, H.; Akat, F.; Dursun, A.D.; Zaloğlu, N. Chronic pregabalin treatment reduced anxiety, and acute pregabalin treatment increased depression-like behaviors in rats. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2024, 25, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates: Hard Cover Edition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh, A.; Dhadde, S.B.; Durg, S.; Veerapur, V.P.; Badami, S.; Thippeswamy, B.S.; Patil, J.S. Effect of Embelin Against Lipopolysaccharide-induced Sickness Behaviour in Mice. Phytother Res. 2016, 30, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, M.M.; Galvao, M.C.; Cabral, D.; Coelho, C.P.; Queiroz Hazarbassanov, N.; Martins, M.F.; Bondan, E.F.; Bernardi, M.M.; Kirsten, T.B. Propentofylline Prevents Sickness Behavior and Depressive Like Behavior Induced by Lipopolysaccharide in Rats via Neuroinflammatory Pathway. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, B.M.; Godbout, J.P.; Chen, J.; Kelley, K.W.; Johnson, R.W. α-Tocopherol and Selenium Facilitate Recovery from Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sickness in Aged Mice12. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.T.; Tsai, Y.P.N.; Cherng, C.G.; Ke, J.J.; Ho, M.C.; Tsai, C.W.; Yu, L. Lipopolysaccharide mitagates methamphetamine-induced striatal dopamine depletion via modulating local TNF-α and dopamine transporter expression. J. Neural Transm. 2009, 116, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.R.D.; Castro, S.L.D.; Alves, M.C.D.S.; Batista, W.D.S.; Oliveira, G.M.D. Acute experimental Trypanosoma cruzi infection: Establishing a murine model that utilises non-invasive measurements of disease parameters. Memórias Do Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2012, 107, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, C.L. Microbial considerations in genetically engineered mouse research. ILAR J. 2006, 47, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuckeroth, R.O.; Enomoto, H.; Grider, J.R.; Golden, J.P.; Hanke, J.A.; Jackman, A.; Molliver, D.C.; Bardgett, M.E.; Snider, W.D.; Johnson, E.M., Jr.; et al. Gene targeting reveals a critical role for neurturin in the development and maintenance of enteric, sensory, and parasympathetic neurons. Neuron 1999, 22, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honma, Y.; Araki, T.; Gianino, S.; Bruce, A.; Heuckeroth, R.; Johnson, E.; Milbrandt, J. Artemin is a vascular-derived neurotropic factor for developing sympathetic neurons. Neuron 2002, 35, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuki, K.; Uchida, S.; Watanuki, T.; Wakabayashi, Y.; Fujimoto, M.; Matsubara, T.; Funato, H.; Watanabe, Y. Altered expression of neurotrophic factors in patients with major depression. J Psychiatr. Res. 2008, 42, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallanti, S.; Tofani, T.; Zanardelli, M.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Ghelardini, C. BDNF and Artemin are increased in drug-naïve non-depressed GAD patients: Preliminary data. Int. J. Psychiatry Clin. Pract. 2014, 18, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deberry, J.J.; Bielefeldt, K.; Davis, B.M.; Szigethy, E.M.; Hartman, D.J.; Coates, M.D. Abdominal pain and the neurotrophic system in ulcerative colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 2330–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheli, L.; Spitoni, S.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Bilia, A.R.; Ghelardini, C.; Pallanti, S. Bacopa monnieri as augmentation therapy in the treatment of anhedonia, preclinical and clinical evaluation. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 2331–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Vivoli, E.; Salvicchi, A.; Schiavone, N.; Koverech, A.; Messano, M.; Nicolai, R.; Benatti, P.; Bartolini, A.; Ghelardini, C. Antidepressant-like effect of artemin in mice: A mechanism for acetyl-L-carnitine activity on depression. Psychopharmacology 2011, 218, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yu, Y.; Tang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Xu, L. Differential expression of mRNAs of GDNF family in the striatum following 6-OHDA-induced lesion. Neuroreport 2000, 11, 3289–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cass, W.A.; Peters, L.E.; Harned, M.E.; Seroogy, K.B. Protection by GDNF and other trophic factors against the dopamine-depleting effects of neurotoxic doses of methamphetamine. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1074, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, J.F.; Morrison, P.F.; Chen, M.Y.; Harvey-White, J.; Pernaute, R.S.; Phillips, H.; Oldfield, E.; Bankiewicz, K.S. Heparin coinfusion during convection-enhanced delivery (CED) increases the distribution of the glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) ligand family in rat striatum and enhances the pharmacological activity of neurturin. Exp. Neurol. 2001, 168, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, X.; Wang, R.; Sakagami, M. Functional connectivity between prefrontal cortex and striatum estimated by phase locking value. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2016, 10, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchand, W.R. Cortico-basal ganglia circuitry: A review of key research and implications for functional connectivity studies of mood and anxiety disorders. Brain Struct. Funct. 2010, 215, 73–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbay, V.; Ely, B.A.; Li, Q.; Bangaru, S.D.; Panzer, A.M.; Alonso, C.M.; Castellanos, F.X.; Milham, M.P. Striatum-based circuitry of adolescent depression and anhedonia. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2013, 52, 628–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altar, C.A.; Cai, N.; Bliven, T.; Juhasz, M.; Conner, J.M.; Acheson, A.L.; Lindsay, R.M.; Wiegand, S.J. Anterograde transport of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its role in the brain. Nature 1997, 389, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Jiang, Y. How does peripheral lipopolysaccharide induce gene expression in the brain of rats? Toxicology 2004, 201, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Nakaoke, R.; Dohgu, S.; Banks, W.A. Release of cytokines by brain endothelial cells: A polarized response to lipopolysaccharide. Brain Behav. Immun. 2006, 20, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xaio, H.; Banks, W.A.; Niehoff, M.L.; Morley, J.E. Effect of LPS on the permeability of the blood–brain barrier to insulin. Brain Res. 2001, 896, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, H.E.; Tio, D.L.; Rahman, S.U.; Chiappelli, F.; Taylor, A.N. The glossopharyngeal nerve as a novel pathway in immune-to-brain communication: Relevance to neuroimmune surveillance of the oral cavity. J. Neuroimmunol. 2001, 115, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goehler, L.E.; Gaykema, R.P.; Nguyen, K.T.; Lee, J.E.; Tilders, F.J.; Maier, S.F.; Watkins, L.R. Interleukin-1β in immune cells of the abdominal vagus nerve: A link between the immune and nervous systems? J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 2799–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, W.A.; Robinson, S.M. Minimal penetration of lipopolysaccharide across the murine blood–brain barrier. Brain Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Caraveo, A.; Sayd, A.; Maus, S.R.; Caso, J.R.; Madrigal, J.L.; García-Bueno, B.; Leza, J.C. Lipopolysaccharide enters the rat brain by a lipoprotein-mediated transport mechanism in physiological conditions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, S.; Herkenham, M. Toll-like receptor 4 on nonhematopoietic cells sustains CNS inflammation during endotoxemia, independent of systemic cytokines. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 1788–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwatra, M.; Ahmed, S.; Gawali, B.; Panda, S.R.; Naidu, V.G.M. Hesperidin alleviates chronic restraint stress and lipopolysaccharide-induced Hippocampus and Frontal cortex damage in mice: Role of TLR4/NF-κB, p38 MAPK/JNK, Nrf2/ARE signaling. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 140, 104835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, H.; Shirokawa, T.; Isobe, K.; Ozaki, N. Shifting the balance of brain tryptophan metabolism elicited by isolation housing and systemic administration of lipopolysaccharide in mice. Stress 2009, 12, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, Z.J.; Miller, L.; Ruiz-Velasco, V.; Kunselman, A.R.; Karamchandani, K. In a model of neuroinflammation designed to mimic delirium, quetiapine reduces cortisol secretion and preserves reversal learning in the attentional set shifting task. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019, 14, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.W.; Jo, S.W.; Kim, D.E.; Paik, I.Y.; Balakrishnan, R. Aerobic exercise attenuates LPS-induced cognitive dysfunction by reducing oxidative stress, glial activation, and neuroinflammation. Redox Biol. 2024, 71, 103101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Xu, Q.; Guo, J.; Chen, Q.; Lv, Q.; Xiao, K.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y. Necroptosis Contributes to LPS-Induced Activation of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis in a Piglet Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, J.Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Shan, H.; Wang, S. Baicalin protects LPS-induced blood-brain barrier damage and activates Nrf2-mediated antioxidant stress pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 96, 107725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, A.H.; Xue, B.Y.; Li, C.Y.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, L. Inhibitory effect of artemin on endotoxin-induced nitric oxide synthesis. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2001, 26, 770–773. [Google Scholar]
- Giansante, G.; Marte, A.; Romei, A.; Prestigio, C.; Onofri, F.; Benfenati, F.; Baldelli, P.; Valente, P. Presynaptic L-type Ca2+ channels increase glutamate release probability and excitatory strength in the hippocampus during chronic neuroinflammation. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 6825–6841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.M. Glutamate: The Master Neurotransmitter and Its Implications in Chronic Stress and Mood Disorders. Front Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 722323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicosia, N.; Giovenzana, M.; Misztak, P.; Mingardi, J.; Musazzi, L. Glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity in the pathogenesis and treatment of neurodevelopmental and adult mental disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroon, E.; Miller, A.H.; Sanacora, G. Inflammation, Glutamate, and Glia: A Trio of Trouble in Mood Disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, B.; MacPherson, A.; Bambico, F. Neuroinflammation and neuroprogression in depression: Effects of alternative drug treatments. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2022, 26, 100554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peres, D.S.; Rodrigues, P.; Viero, F.T.; Frare, J.M.; Kudsi, S.Q.; Meira, G.M.; Trevisan, G. Prevalence of depression and anxiety in the different clinical forms of multiple sclerosis and associations with disability: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2022, 24, 100484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catorce, M.N.; Gevorkian, G. LPS-induced Murine Neuroinflammation Model: Main Features and Suitability for Pre-clinical Assessment of Nutraceuticals. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, C.R.A.; Gomes, G.F.; Candelario-Jalil, E.; Fiebich, B.L.; de Oliveira, A.C.P. Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation as a Bridge to Understand Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

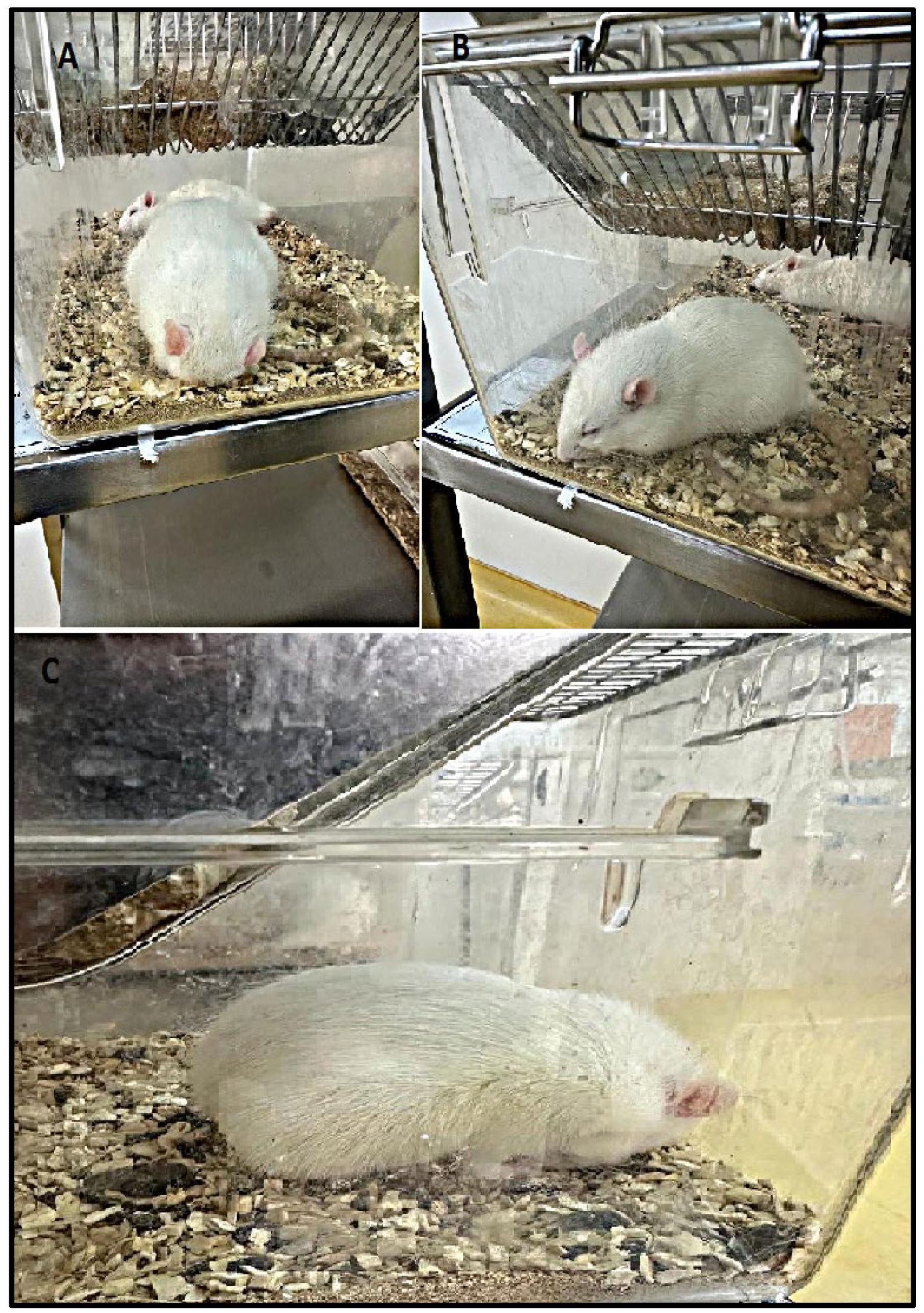


| Control Group | LPS Group | |
|---|---|---|
| Prostration posture | 0/10 | 9/10 ✦ |
| Piloerection | 0/10 | 10/10 # |
| Hunched posture | 0/10 | 10/10 # |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Çalışkan, H.; Koçak, S. Changes in Artemin Correlate with Anxiety- and Depression-like Behaviors in a Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Rat Neuroinflammation Model. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081192
Çalışkan H, Koçak S. Changes in Artemin Correlate with Anxiety- and Depression-like Behaviors in a Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Rat Neuroinflammation Model. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(8):1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081192
Chicago/Turabian StyleÇalışkan, Hasan, and Seda Koçak. 2025. "Changes in Artemin Correlate with Anxiety- and Depression-like Behaviors in a Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Rat Neuroinflammation Model" Biomolecules 15, no. 8: 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081192
APA StyleÇalışkan, H., & Koçak, S. (2025). Changes in Artemin Correlate with Anxiety- and Depression-like Behaviors in a Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Rat Neuroinflammation Model. Biomolecules, 15(8), 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081192







