Circulating Lipid Profiles Indicate Incomplete Metabolic Recovery After Weight Loss, Suggesting the Need for Additional Interventions in Severe Obesity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics and Participants
2.2. Liver Biopsies and Genotyping
2.3. Lipidomics Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analyses
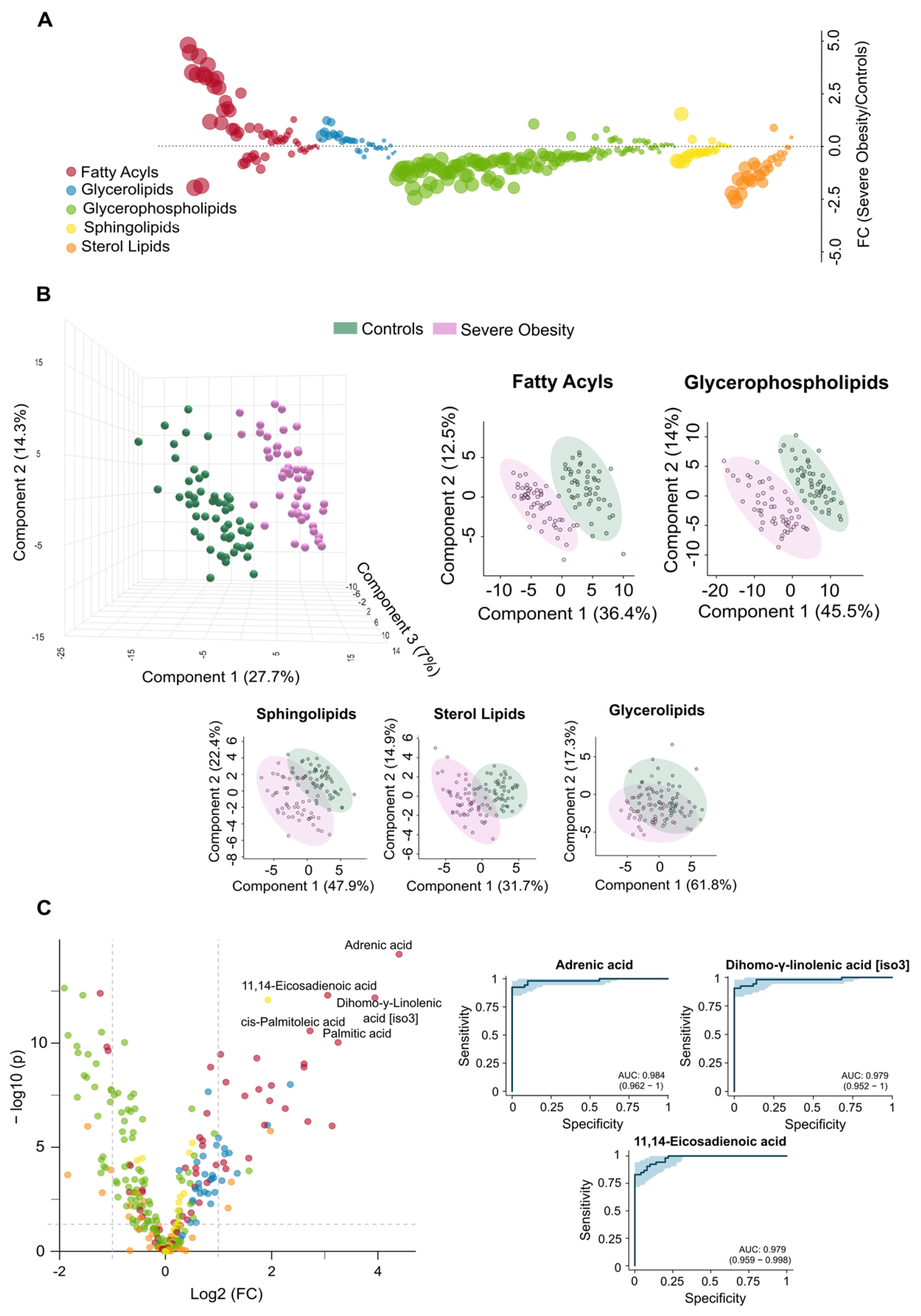
3. Results
3.1. LSG Is Effective in Inducing Weight Loss
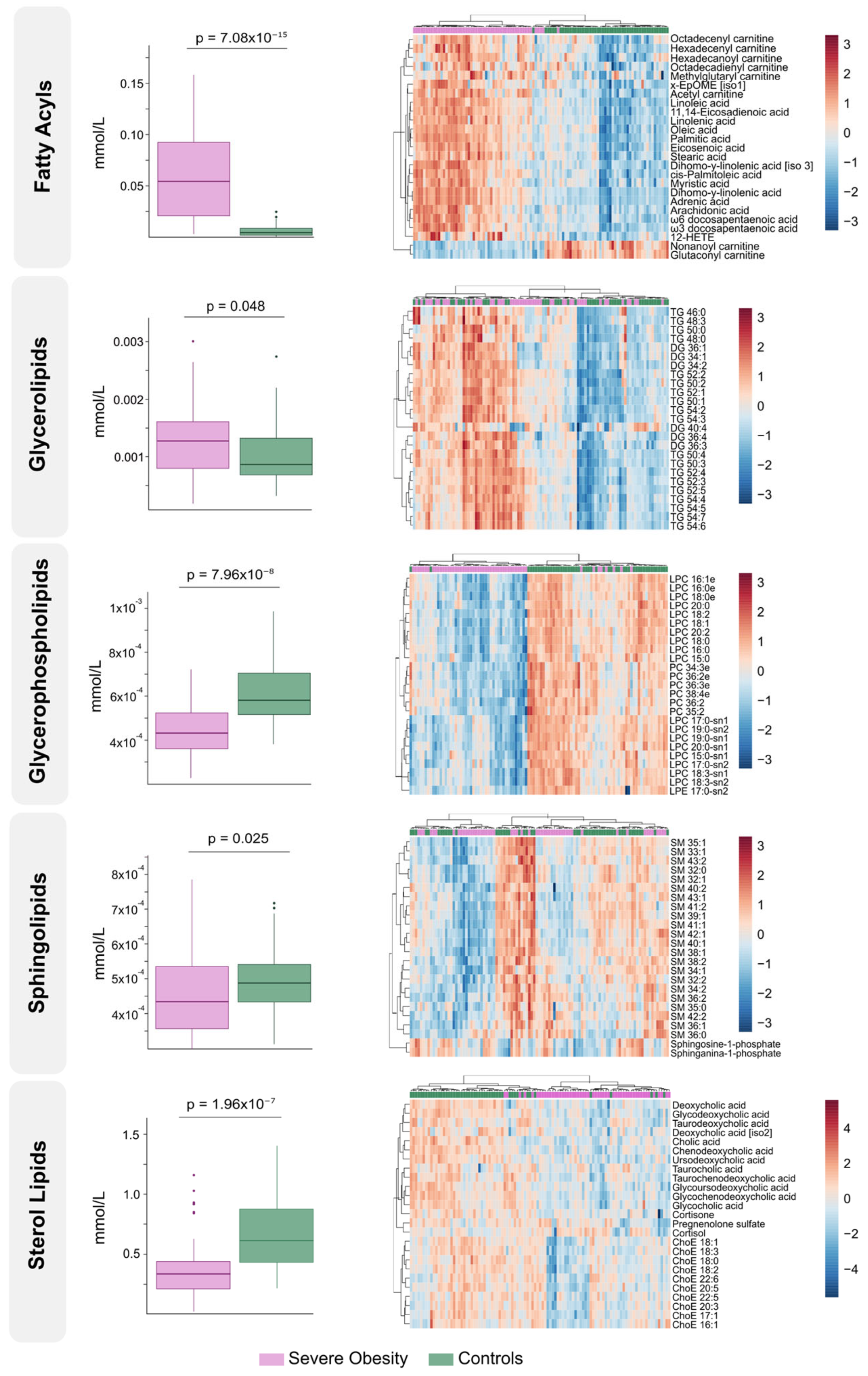
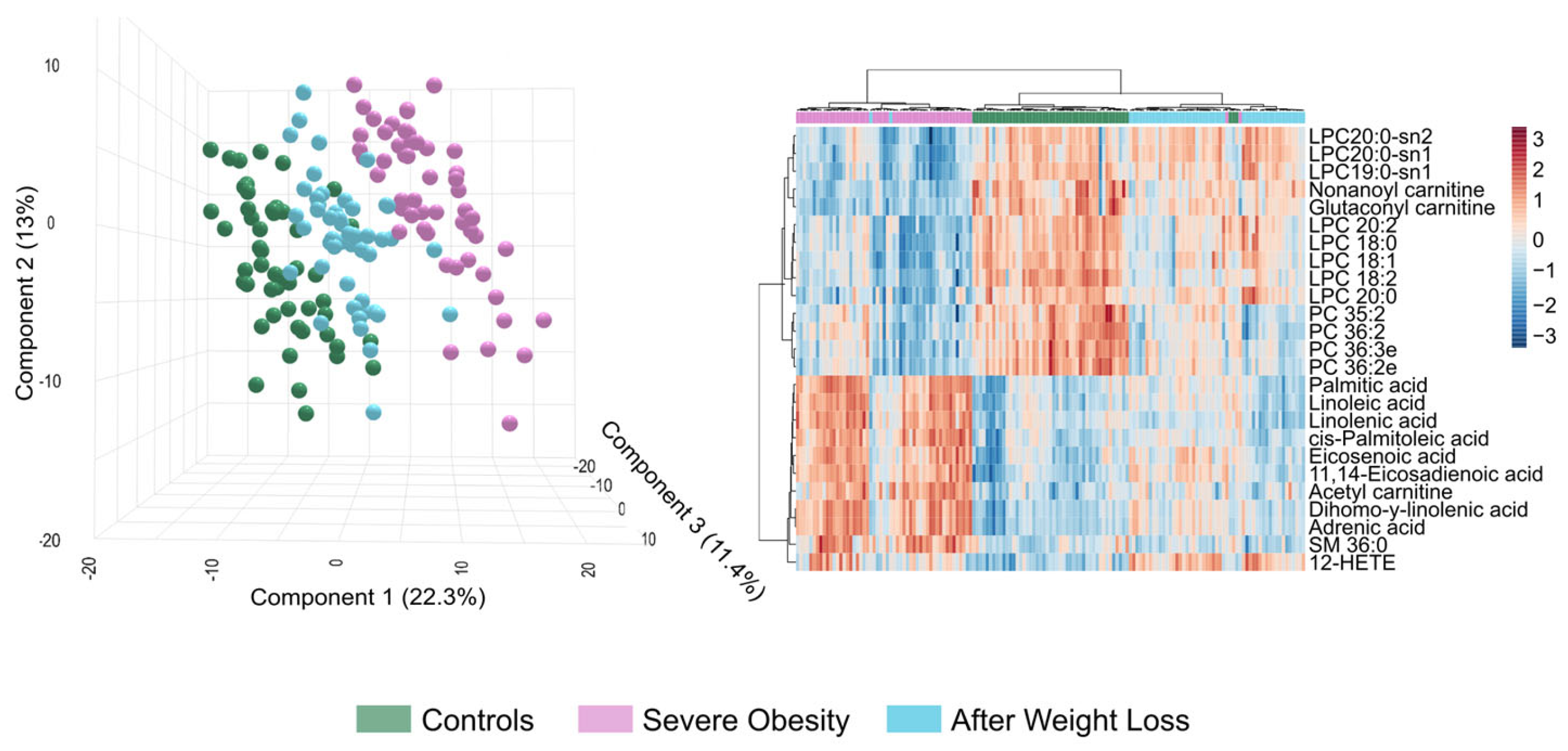
3.2. The Circulating Lipidome Captures the Systemic Metabolic Stress in Severe Obesity
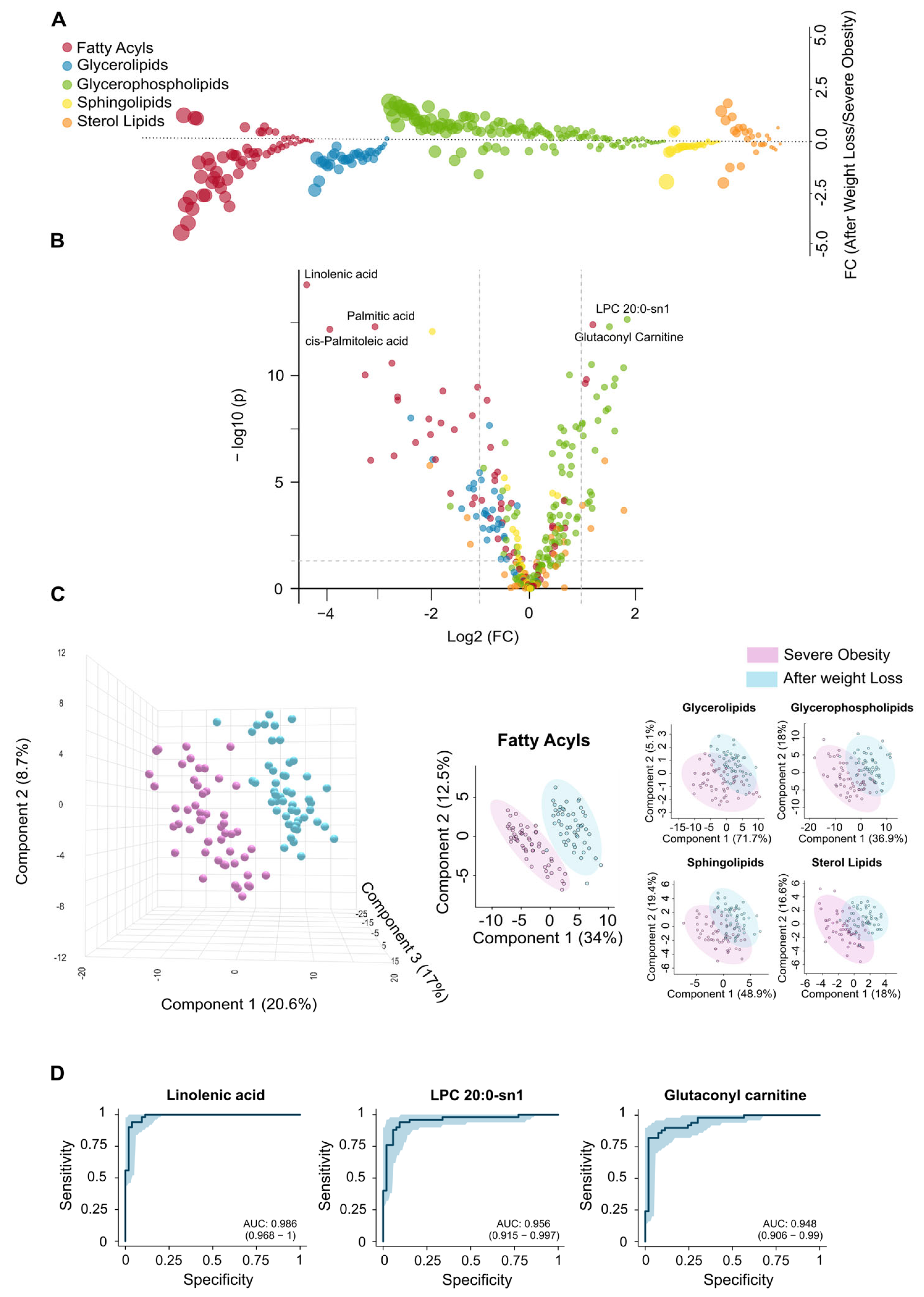
3.3. Extensive Weight Loss Causes Dynamic Changes in the Circulating Lipidome
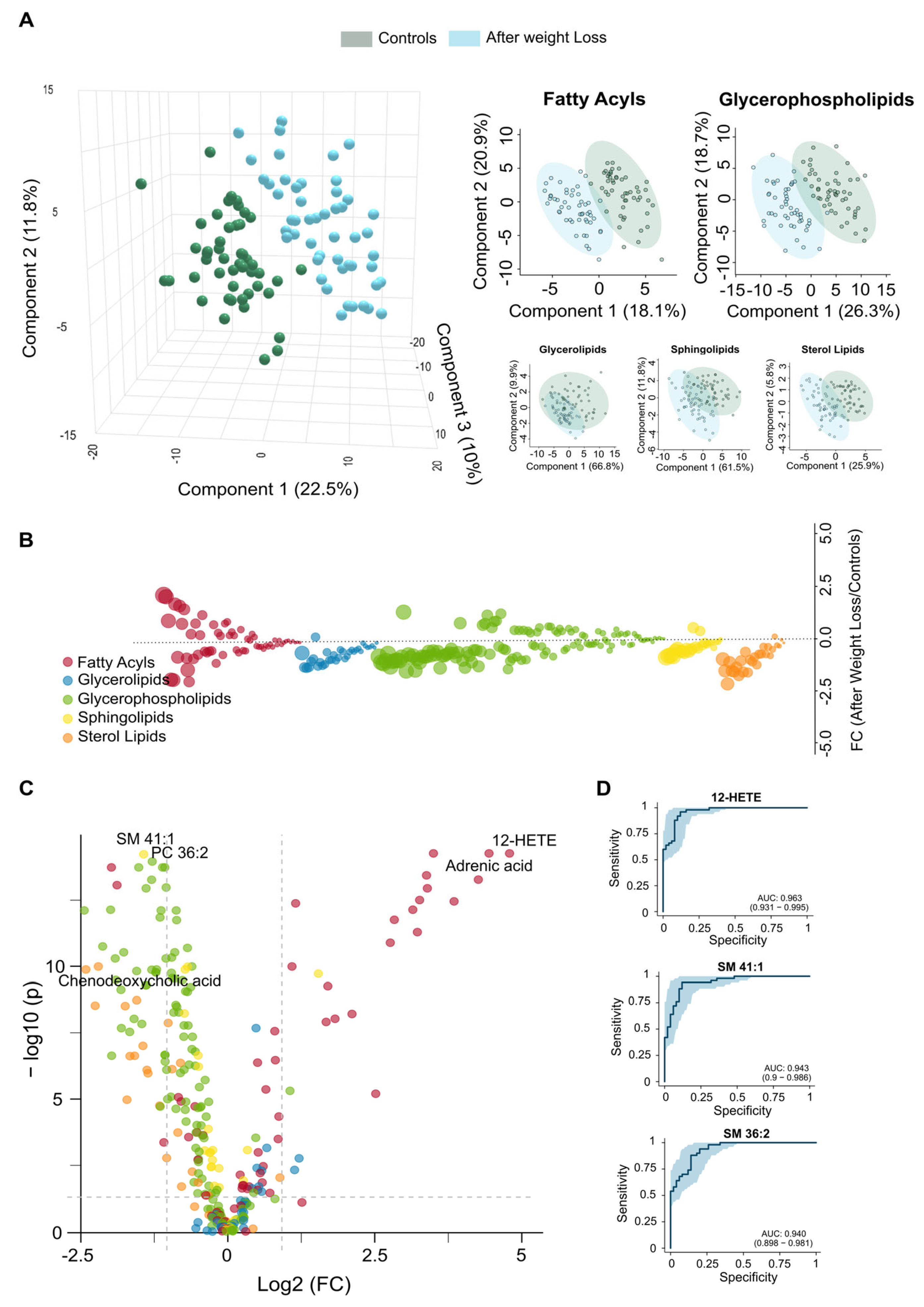
3.4. Lipidomic Signatures Indicate Persistent Dysregulation After Weight Loss
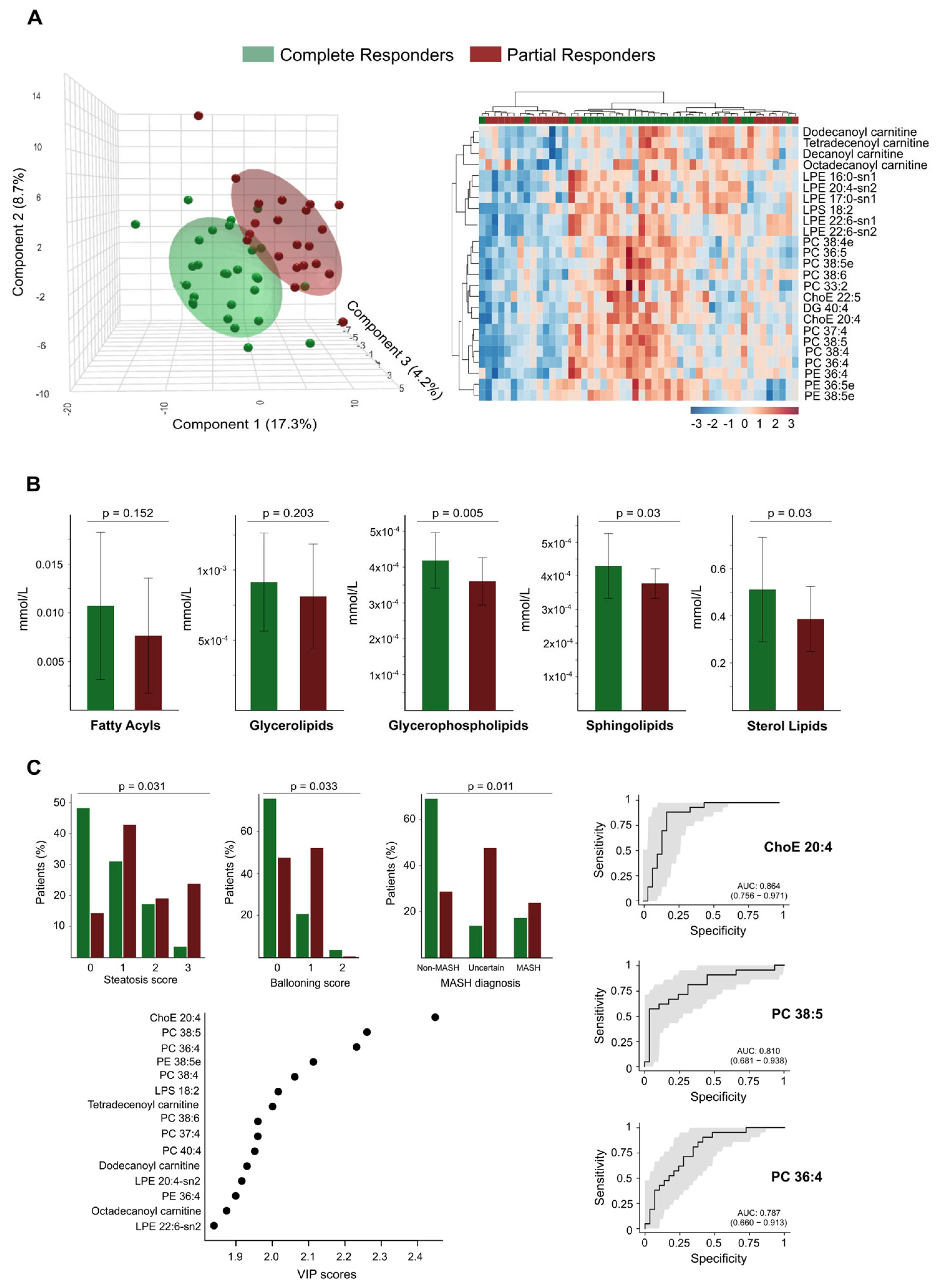
3.5. Residual Dysregulation Supports the Use of Lipidomic Biomarkers for Prediction of Outcomes and Long-Term Follow-Up
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body mass index |
| DG | Diacylglycerol |
| FDR | False discovery rate |
| HETE | Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid |
| HOME | Hydroxyoctadecenoic acid |
| LPC | Lysophosphatidylcholine |
| LPE | Lysophosphatidylethanolamine |
| LSG | Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy |
| PC | Phosphatidylcholine |
| PLS-DA | Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis |
| QTOF | Quadrupole-time-on-flight mass spectrometry |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| SM | Sphingomyelin |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| UHPLC | Ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography |
| VIP | Variable importance in projection |
References
- Ellison-Barnes, A.; Johnson, S.; Gudzune, K. Trends in obesity prevalence among adults aged 18 through 25 years, 1976–2018. JAMA 2021, 326, 2073–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UN. World Population Prospects 2024; Online Edition; United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division: New York, NY, USA, 2024; Available online: https://population.un.org/wpp/ (accessed on 17 June 2025).
- Rubino, F.; Cummings, D.E.; Eckel, R.H.; Cohen, R.V.; Wilding, J.P.H.; Brown, W.A.; Stanford, F.C.; Batterham, R.L.; Farooqi, I.S.; Farpour-Lambert, N.J.; et al. Definition and diagnostic criteria of clinical obesity. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2025, 13, 221–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanovski, S.Z.; Yanovski, J.A. Approach to obesity treatment in primary care: A review. JAMA Intern. Med. 2024, 184, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Li, H. Obesity: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and therapeutics. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 706978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cypess, A.M. Reassessing human adipose tissue. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 768–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME). GBD Results; IHME: Seattle, WA, USA; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2024; Available online: https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-results/ (accessed on 17 June 2025).
- Abdelaal, M.; le Roux, C.W.; Docherty, N.G. Morbidity and mortality associated with obesity. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Modica, S.; Dong, H.; Wolfrum, C. Plasticity and heterogeneity of thermogenic adipose tissue. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Sharma, A.K.; Wolfrum, C. Novel insights into adipose tissue heterogeneity. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Korf, H.; Vidal-Puig, A. An adipocentric perspective on the development and progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 1048–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carobbio, S.; Pellegrinelli, V.; Vidal-Puig, A. Adipose tissue dysfunction determines lipotoxicity and triggers the metabolic syndrome: Current challenges and clinical perspectives. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2024, 1460, 231–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronne, L.J.; Horn, D.B.; le Roux, C.W.; Ho, W.; Falcon, B.L.; Gomez Valderas, E.; Das, S.; Lee, C.J.; Glass, L.C.; Senyucel, C.; et al. Tirzepatide as compared with semaglutide for the treatment of obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 393, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabré, N.; Luciano-Mateo, F.; Chapski, D.J.; Baiges-Gaya, G.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Hernández-Aguilera, A.; Castañé, H.; Rodríguez-Tomàs, E.; París, M.; Sabench, F.; et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy in patients with severe obesity restores adaptive responses leading to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Han, B.; Zhang, X. Mechanisms through which laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy mitigates atherosclerosis risk: A focus on visceral adipose tissue. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2025, 30, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, D.; Magkos, F.; Klein, S. Effects of bariatric surgery on glucose homeostasis and type 2 diabetes. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 897–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Franco, A.; Castañé, H.; Martínez-Navidad, C.; Placed-Gallego, C.; Hernández-Aguilera, A.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Samarra, I.; Canela-Capdevila, M.; Arenas, M.; Zorzano, A.; et al. Metabolic adaptations in severe obesity: Insights from circulating oxylipins before and after weight loss. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinturel, F.; Chera, S.; Brulhart-Meynet, M.-C.; Montoya, J.P.; Lefai, E.; Jornayvaz, F.R.; D’aNgelo, G.; Jung, M.K.; Pataky, Z.; Riezman, H.; et al. Alterations of lipid homeostasis in morbid obese patients are partly reversed by bariatric surgery. iScience 2024, 27, 110820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruperez, C.; Madeo, F.; de Cabo, R.; Kroemer, G.; Abdellatif, M. Obesity accelerates cardiovascular ageing. Eur. Heart J. 2025, 46, 2161–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Alvarez, M.I.; Sebastián, D.; Vives, S.; Ivanova, S.; Bartoccioni, P.; Kakimoto, P.; Plana, N.; Veiga, S.R.; Hernández, V.; Vasconcelos, N.; et al. Deficient endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondrial phosphatidylserine transfer causes liver disease. Cell 2019, 177, 881–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Park, Y.S.; Cho, C.; Lee, H.; Park, J.; Park, D.J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.-J.; Ha, T.K.; Kim, Y.-J.; et al. Short-term changes in the serum metabolome after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Metabolomics 2021, 17, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayser, B.D.; Lhomme, M.; Dao, M.C.; Ichou, F.; Bouillot, J.-L.; Prifti, E.; Kontush, A.; Chevallier, J.-M.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Dugail, I.; et al. Serum lipidomics reveals early differential effects of gastric bypass compared with banding on phospholipids and sphingolipids independent of differences in weight loss. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabré, N.; Gil, M.; Amigó, N.; Luciano-Mateo, F.; Baiges-Gaya, G.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Rodríguez-Tomàs, E.; Hernández-Aguilera, A.; Castañé, H.; París, M.; et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy alters 1H-NMR-measured lipoprotein and glycoprotein profile in patients with severe obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köfeler, H.C.; Eichmann, T.O.; Ahrends, R.; Bowden, J.A.; Danne-Rasche, N.; Dennis, E.A.; Fedorova, M.; Griffiths, W.J.; Han, X.; Hartler, J.; et al. Quality control requirements for the correct annotation of lipidomics data. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castañé, H.; Baiges-Gaya, G.; Hernández-Aguilera, A.; Rodríguez-Tomàs, E.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Herrero, P.; Delpino-Rius, A.; Canela, N.; Menendez, J.A.; Camps, J.; et al. Coupling machine learning and lipidomics as a tool to investigate metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. A general overview. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañé, H.; Jiménez-Franco, A.; Hernández-Aguilera, A.; Martínez-Navidad, C.; Cambra-Cortés, V.; Onoiu, A.I.; Jiménez-Aguilar, J.M.; París, M.; Hernández, M.; Parada, D.; et al. Multi-omics profiling reveals altered mitochondrial metabolism in adipose tissue from patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis. eBioMedicine 2025, 111, 105532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertran, N.; Camps, J.; Fernandez-Ballart, J.; Arija, V.; Ferre, N.; Tous, M.; Simo, D.; Murphy, M.M.; Vilella, E.; Joven, J. Diet and lifestyle are associated with serum C-reactive protein concentrations in a population-based study. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2005, 145, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, R.A.; Hidalgo, M.R.; Castañé, H.; Jiménez-Franco, A.; Joven, J.; Burks, D.J.; Galán, A.; García-García, F. Landscape of sex differences in obesity and type 2 diabetes in subcutaneous adipose tissue: A systematic review and meta-analysis of transcriptomics studies. Metabolism 2025, 168, 156241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornier, M.A. A review of current guidelines for the treatment of obesity. Am. J. Manag. Care 2022, 28 (Suppl. 15), S288–S296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.-C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoiu, A.I.; Domínguez, D.P.; Joven, J. Digital pathology tailored for assessment of liver biopsies. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Du, X.; Kuppa, A.; Feitosa, M.F.; Bielak, L.F.; O’cOnnell, J.R.; Musani, S.K.; Guo, X.; Kahali, B.; Chen, V.L.; et al. Genome-wide association meta-analysis identifies 17 loci associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 1640–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Solingen, C.; Scacalossi, K.R.; Moore, K.J. Long noncoding RNAs in lipid metabolism. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2018, 29, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Hernández-Aguilera, A.; de Vries, M.A.; Burggraaf, B.; van der Zwan, E.; Pouw, N.; Joven, J.; Cabezas, M.C. Effect of vitamin D3 on the postprandial lipid profile in obese patients: A non-targeted lipidomics study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foguet-Romero, E.; Samarra, I.; Guirro, M.; Riu, M.; Joven, J.; Menendez, J.A.; Canela, N.; DelPino-Rius, A.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Herrero, P. Optimization of a GC-MS injection-port derivatization methodology to enhance metabolomics analysis throughput in biological samples. J. Proteome Res. 2022, 21, 2555–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köfeler, H.C.; Ahrends, R.; Baker, E.S.; Ekroos, K.; Han, X.; Hoffmann, N.; Holčapek, M.; Wenk, M.R.; Liebisch, G. Recommendations for good practice in MS-based lipidomics. J. Lipid Res. 2021, 62, 100138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowgiałło-Gornowicz, N.; Wityk, M.; Lech, P. Staying on track: Factors influencing 10-year follow-up adherence after sleeve gastrectomy. Obes. Surg. 2025, 35, 2711–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grönroos, S.; Helmiö, M.; Juuti, A.; Tiusanen, R.; Hurme, S.; Löyttyniemi, E.; Ovaska, J.; Leivonen, M.; Peromaa-Haavisto, P.; Mäklin, S.; et al. Effect of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy vs roux-en-y gastric bypass on weight loss and quality of life at 7 years in patients with morbid obesity: The SLEEVEPASS randomized clinical trial. JAMA Surg. 2021, 156, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.-Y.; Lin, X.; Xu, F.; Shan, S.-K.; Guo, B.; Li, F.-X.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, M.-H.; Xu, Q.-S.; Lei, L.-M.; et al. Ferroptosis and its potential role in metabolic diseases: A curse or revitalization? Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 701788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietraszek-Gremplewicz, K.; Olszańska, J.; Domagalski, M.; Simiczyjew, A.; Kot, M.; Skoniecka, A.; Tymińska, A.; Pikuła, M.; Nowak, D. Response of primary human adipocytes to fatty acid treatment. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2025, 29, e70622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amine, H.; Benomar, Y.; Taouis, M. Palmitic acid promotes resistin-induced insulin resistance and inflammation in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Tontonoz, P. Phospholipid remodeling in physiology and disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2019, 81, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, X.; Wang, B.; Dunham, M.M.; Hedde, P.N.; Wong, J.S.; Gratton, E.; Young, S.G.; Ford, D.A.; Tontonoz, P. Lpcat3-dependent production of arachidonoyl phospholipids is a key determinant of triglyceride secretion. eLife 2015, 4, e06557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, P.J.; Rong, X.; Maschek, J.A.; Verkerke, A.R.; Siripoksup, P.; Song, H.; Green, T.D.; Krishnan, K.C.; Johnson, J.M.; Turk, J.; et al. Lysophospholipid acylation modulates plasma membrane lipid organization and insulin sensitivity in skeletal muscle. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e135963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engler, M.M.; Bellenger-Germain, S.H.; Engler, M.B.; Narce, M.M.; Poisson, J.P. Dietary docosahexaenoic acid affects stearic acid desaturation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Lipids 2000, 35, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.G.; Song, Z.X.; Yin, H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Shu, G.F.; Lu, H.X.; Wang, S.K.; Sun, G.J. Low n-6/n-3 PUFA ratio improves lipid metabolism, inflammation, oxidative stress and endothelial function in rats using plant oils as n-3 fatty acid source. Lipids 2016, 51, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Montiel, V.R.-V.; Iftimie, S.; Montero-Calle, A.; Pingarrón, J.M.; Castro, A.; Camps, J.; Barderas, R.; Campuzano, S.; Joven, J. Contributing to the management of viral infections through simple immunosensing of the arachidonic acid serum level. Mikrochim. Acta 2024, 191, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.; Tanriverdi, K.; Iafrati, M.D.; Mosley, J.D.; Freedman, J.E.; Ferguson, J.F. Characterization of the plasma metabolome and lipidome in response to sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass surgeries reveals molecular patterns of surgical weight loss. Metabolism 2024, 158, 155955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanowicz, T.; Gutaj, P.; Plewa, S.; Spasenenko, I.; Olasińska-Wiśniewska, A.; Krasińska, B.; Tykarski, A.; Krasińska-Plachta, A.; Pilaczyńska-Szcześniak, Ł.; Krasiński, Z.; et al. Obesity and acylcarnitine derivates interplay with coronary artery disease. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 15676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vianello, E.; Ambrogi, F.; Kalousová, M.; Badalyan, J.; Dozio, E.; Tacchini, L.; Schmitz, G.; Zima, T.; Tsongalis, G.J.; Corsi-Romanelli, M.M. Circulating perturbation of phosphatidylcholine (PC) and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) is associated to cardiac remodeling and NLRP3 inflammasome in cardiovascular patients with insulin resistance risk. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2024, 137, 104895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grapov, D.; Fiehn, O.; Campbell, C.; Chandler, C.J.; Burnett, D.J.; Souza, E.C.; Casazza, G.A.; Keim, N.L.; Hunter, G.R.; Fernandez, J.R.; et al. Impact of a weight loss and fitness intervention on exercise-associated plasma oxylipin patterns in obese, insulin-resistant, sedentary women. Physiol. Rep. 2020, 8, e14547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauls, S.D.; Du, Y.; Clair, L.; Winter, T.; Aukema, H.M.; Taylor, C.G.; Zahradka, P. Impact of age, menopause, and obesity on oxylipins linked to vascular health. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 883–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrachina, M.N.; Hermida-Nogueira, L.; Moran, L.A.; Casas, V.; Hicks, S.M.; Sueiro, A.M.; Di, Y.; Andrews, R.K.; Watson, S.P.; Gardiner, E.E.; et al. Phosphoproteomic analysis of platelets in severe obesity uncovers platelet reactivity and signaling pathways alterations. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashti, M.; Kulik, W.; Hoek, F.; Veerman, E.C.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Rezaee, F. A phospholipidomic analysis of all defined human plasma lipoproteins. Sci. Rep. 2011, 1, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymańska, E.; van Dorsten, F.A.; Troost, J.; Paliukhovich, I.; van Velzen, E.J.J.; Hendriks, M.M.W.B.; Trautwein, E.A.; van Duynhoven, J.P.M.; Vreeken, R.J.; Smilde, A.K. A lipidomic analysis approach to evaluate the response to cholesterol-lowering food intake. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 894–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cho, Y.K.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Doh, J.; Park, J.-H.; Jung, Y.-S.; Lee, Y.-H. Lipid remodeling of adipose tissue in metabolic health and disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 1955–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellot, P.E.N.R.; Braga, E.S.; Omage, F.B.; Nunes, F.L.d.S.; Lima, S.C.V.C.; Lyra, C.O.; Marchioni, D.M.L.; Pedrosa, L.F.C.; Barbosa, F.; Tasic, L.; et al. Plasma lipid metabolites as potential biomarkers for identifying individuals at risk of obesity-induced metabolic complications. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Sulek, K.; Stinson, S.E.; Holm, L.A.; Kim, M.; Trost, K.; Hooshmand, K.; Lund, M.A.V.; Fonvig, C.E.; Juel, H.B.; et al. Lipid profiling identifies modifiable signatures of cardiometabolic risk in children and adolescents with obesity. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertran, L.; Capellades, J.; Abelló, S.; Aguilar, C.; Auguet, T.; Richart, C. Untargeted lipidomics analysis in women with morbid obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A comprehensive study. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0303569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.Y.; Highland, H.M.; Palmer, A.B.; Duong, T.; Lin, Z.; Zhu, W.; Sprinkles, J.; Kim, D.; Young, K.L.; Chen, H.-H. The circulating lipidome in severe obesity. MedRxiv, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertran, L.; Capellades, J.; Abelló, S.; Richart, C. Untargeted lipidomic analysis of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis in women with morbid obesity. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0318557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Mirza, I.; Metwally, E.; Morsy, M.H.; Scichilone, G.; Asada, M.C.; Mostafa, A.; Bianco, F.M.; Ali, M.M.; Masrur, M.A.; et al. Lipidomic profiling of human adiposomes identifies specific lipid shifts linked to obesity and cardiometabolic risk. JCI Insight 2025, 10, e191872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Cohort 1 (n = 50) | Cohort 2 (n = 50) | Cohort 3 (n = 50) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 47 [36–58] | 51 [43–57] | N/A |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 26.8 [23.0–28.9] | 46.3 [43.4–53.8] a | 33.9 [31.2–37.5] a,b |
| Waist circumference, cm | 89.5 [79.2–103.2] | 136.0 [127.0–145.0] a | 113.0 [104.5–121.6] b,c |
| SBP, mmHg | 125.0 [110.0–140.0] | 138.0 [128.7–153.2] a | 132.5 [117.0–146.7] |
| DBP, mmHg | 76.0 [70.0–85.0] | 85.5 [73.7–94.0] a | 75.5 [67.0–87.0] c |
| T2DM, n (%) | 5 (10.0) | 26 (52.0) a | 22 (44.0) b |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 7 (14.0) | 50 (80.0) a | 33 (66.0) b |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 3 (6.0) | 26 (52.0) a | 26 (52.0) b |
| Medication, n (%) | |||
| Metformin | 2 (4.0) | 26 (52.0) a | 16 (32.0) b |
| Sulfonylureas | 1 (2.0) | 7 (14.0) | 6 (12.0) |
| Other T2DM | 1 (2.0) | 12 (24.0) a | 5 (10.0) |
| Insulin | 1 (2.0) | 11 (22.0) a | 6 (12.0) |
| ACEIs + ARA-II | 2 (4.0) | 26 (52.0) a | 25 (50.0) b |
| Diuretics | 1 (2.0) | 12 (24.0) a | 13 (26.0) b |
| Other AHT medications | 0 | 15 (26.0) a | 14 (28.0) b |
| Statins | 1 (2.0) | 17 (34.0) a | 15 (30.0) b |
| Biochemical variables | |||
| Glucose, mmol/L | 4.8 [4.3–5.5] | 7.9 [6.0–10.6] a | 4.7 [4.4–5.3] c |
| Insulin, pmol/L | 51.8 [32.7–67.5] | 77.1 [55.6–145.1] a | 42.7 [27.8–67.7] c |
| HOMA-IR | 1.6 [1.0–2.4] | 4.1 [2.4–7.9] a | 1.4 [0.9–2.0] c |
| Triglycerides, mmol/L | 1.2 [0.8–1.6] | 1.8 [1.3–2.3] a | 1.0 [0.8–1.2] c |
| Cholesterol, mmol/L | 5.1 [4.5–6.0] | 3.9 [3.3–4.7] a | 4.8 [4.4–5.6] c |
| HDL, mmol/L | 1.5 [1.2–1.7] | 0.9 [0.7–1.0] a | 1.5 [1.3–1.8] c |
| LDL, mmol/L | 2.9 [2.5–3.9] | 2.1 [1.7–2.8] a | 2.9 [2.5–3.2] c |
| ALT, μKat/L | 0.3 [0.2–0.4] | 0.9 [0.5–1.2] a | 0.2 [0.2–0.3] b,c |
| AST, μKat/L | 0.3 [0.3–0.4] | 0.8 [0.5–1.0] a | 0.3 [0.2–0.3] b,c |
| GGT, μKat/L | 0.2 [0.1–0.4] | 0.5 [0.3–0.8] a | 0.2 [0.2–0.4] c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Onoiu, A.-I.; Cambra-Cortés, V.; Jiménez-Franco, A.; Hernández-Aguilera, A.; Parada, D.; Riu, F.; Zorzano, A.; Camps, J.; Joven, J. Circulating Lipid Profiles Indicate Incomplete Metabolic Recovery After Weight Loss, Suggesting the Need for Additional Interventions in Severe Obesity. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081112
Onoiu A-I, Cambra-Cortés V, Jiménez-Franco A, Hernández-Aguilera A, Parada D, Riu F, Zorzano A, Camps J, Joven J. Circulating Lipid Profiles Indicate Incomplete Metabolic Recovery After Weight Loss, Suggesting the Need for Additional Interventions in Severe Obesity. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(8):1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081112
Chicago/Turabian StyleOnoiu, Alina-Iuliana, Vicente Cambra-Cortés, Andrea Jiménez-Franco, Anna Hernández-Aguilera, David Parada, Francesc Riu, Antonio Zorzano, Jordi Camps, and Jorge Joven. 2025. "Circulating Lipid Profiles Indicate Incomplete Metabolic Recovery After Weight Loss, Suggesting the Need for Additional Interventions in Severe Obesity" Biomolecules 15, no. 8: 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081112
APA StyleOnoiu, A.-I., Cambra-Cortés, V., Jiménez-Franco, A., Hernández-Aguilera, A., Parada, D., Riu, F., Zorzano, A., Camps, J., & Joven, J. (2025). Circulating Lipid Profiles Indicate Incomplete Metabolic Recovery After Weight Loss, Suggesting the Need for Additional Interventions in Severe Obesity. Biomolecules, 15(8), 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081112








