Identification of Two Critical Contact Residues in a Pathogenic Epitope from Tetranectin for Monoclonal Antibody Binding and Preparation of Single-Chain Variable Fragments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. TN-P5-5 Complete Antigen Preparation
2.3. Epitope Prediction of P5-5
2.4. Sequence Analysis of 12F1 Monoclonal Antibody Variable Regions
2.5. 12F1 Monoclonal Antibody Homology Model and Docking with P5-5 Epitope
2.6. Purification of 12F1 mAb
2.7. TN-P5-5 Mutants Design and Synthesis
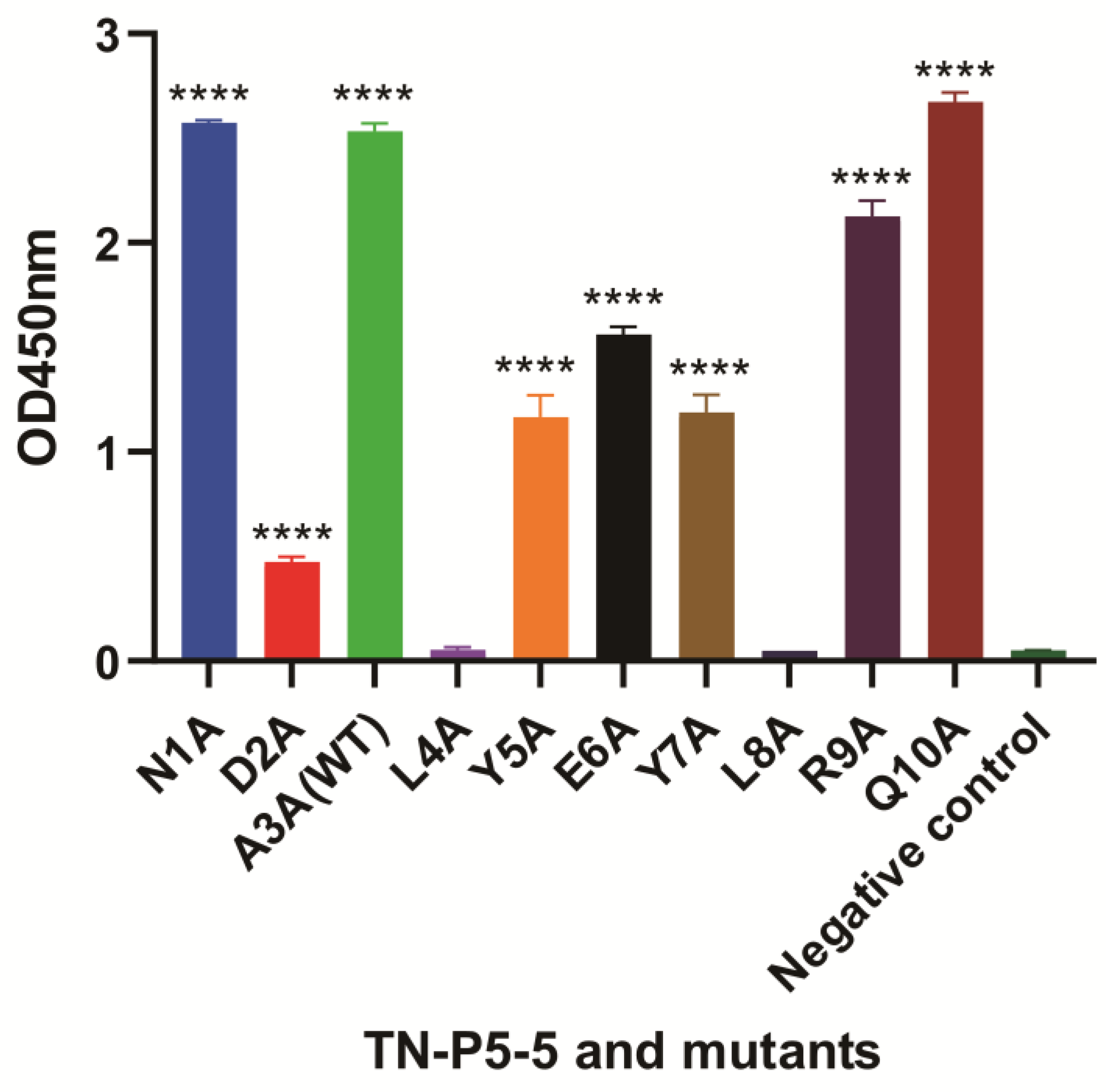
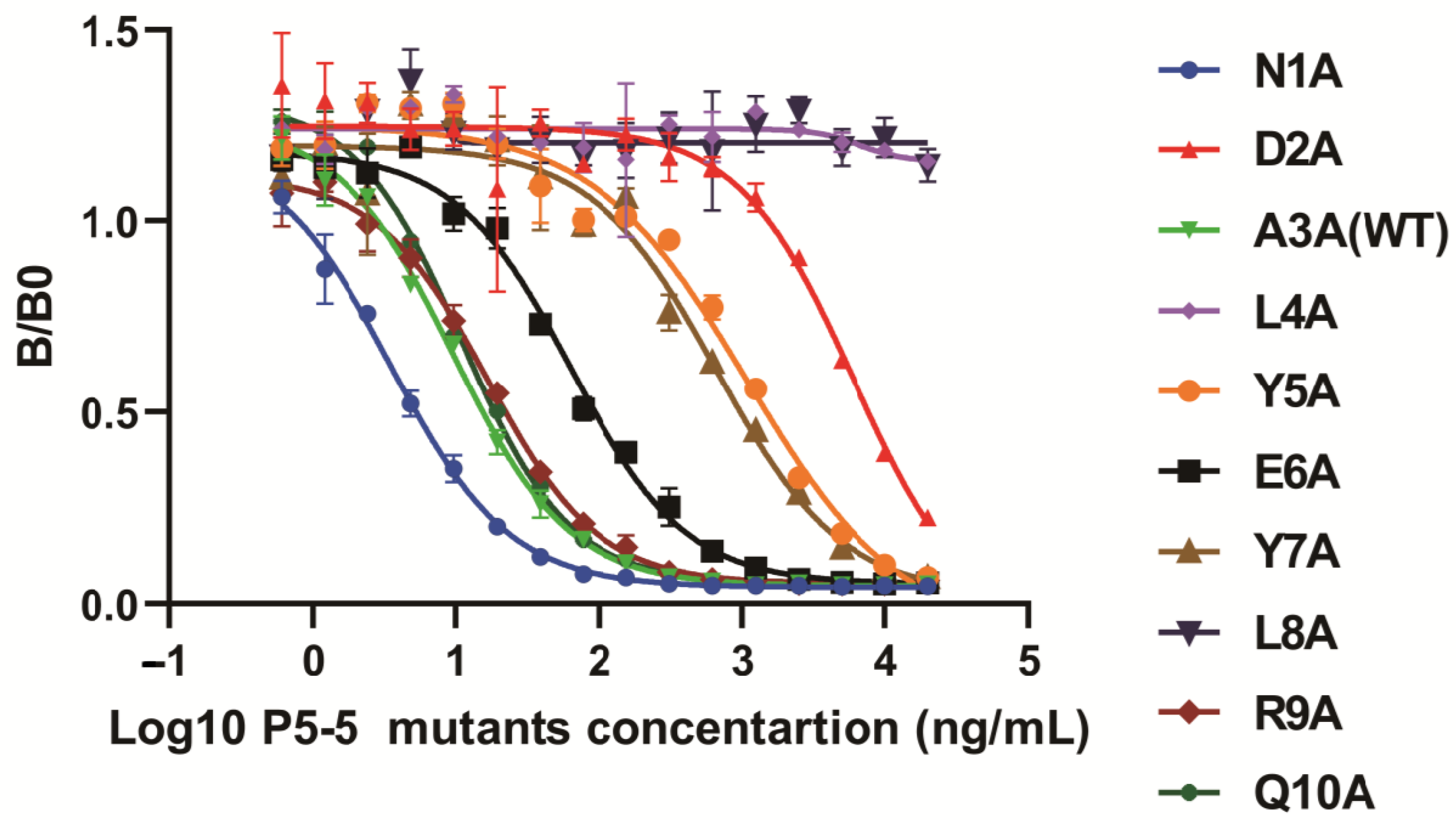
2.8. iELISA and icELISA to Identify the Specific Sites Between 12F1 mAb and TN-P5-5 Interaction
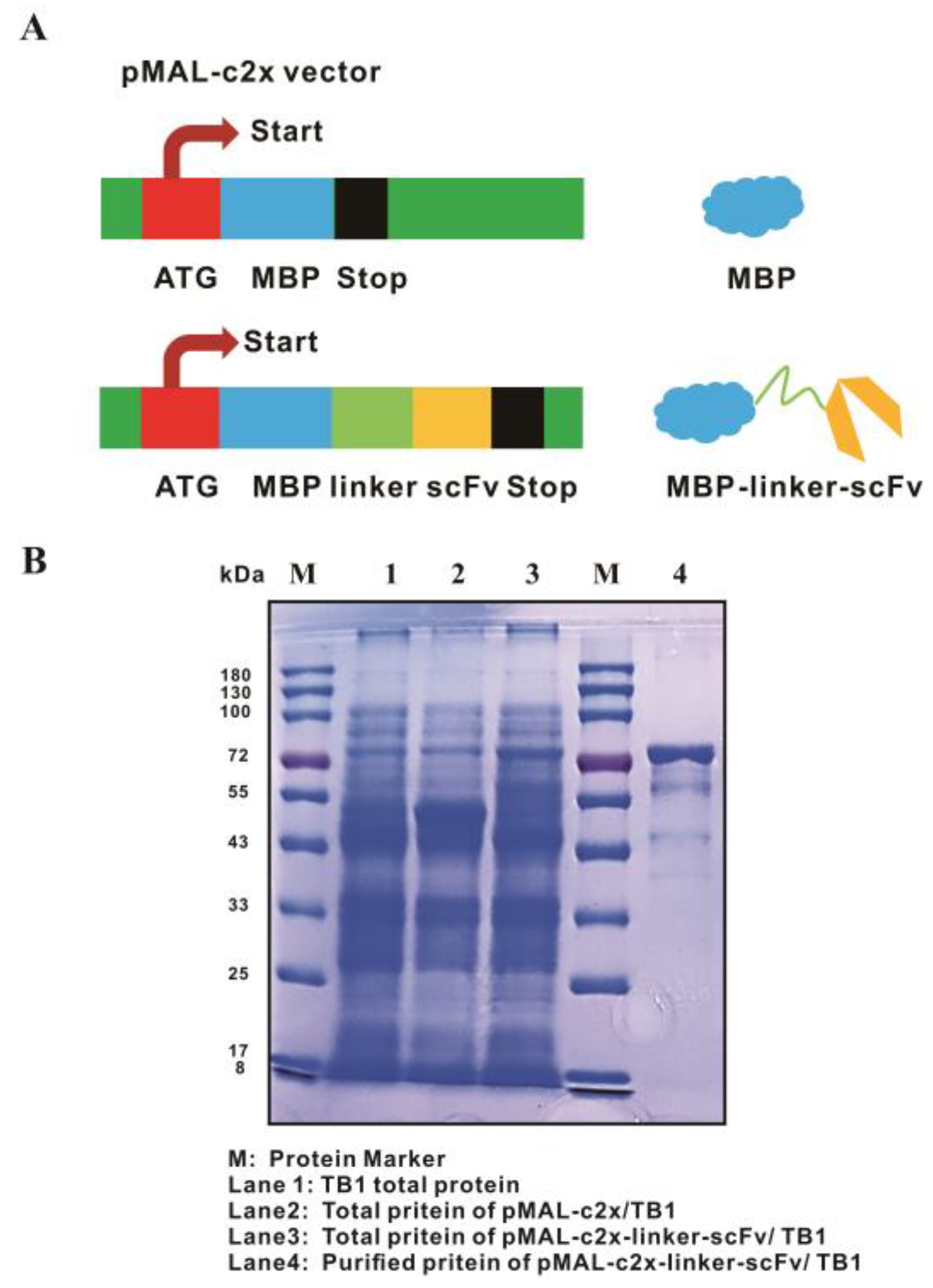
2.9. Construction of the MBP Fusion scFv Antibody, Soluble Expression, and Purification
2.10. Binding Activity Determination of Anti-P5-5 scFv by iELISA
2.11. The Sensitivity Determination of Anti-P5-5 scFv
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
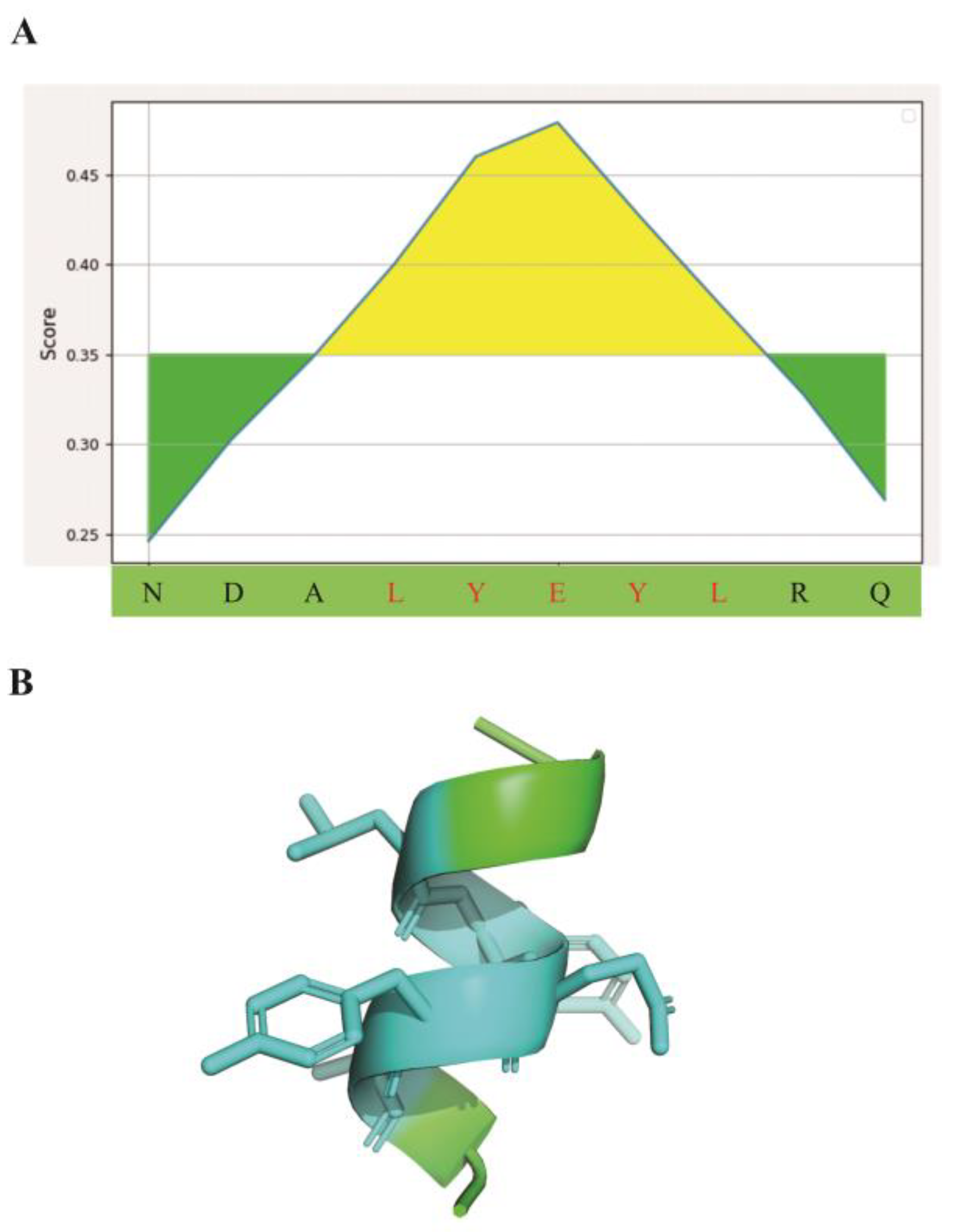
3.1. Epitope Binding Pattern Prediction
3.2. Antibody Variable Region Structure Prediction of 12F1 and Molecular Docking with P5-5 Epitope
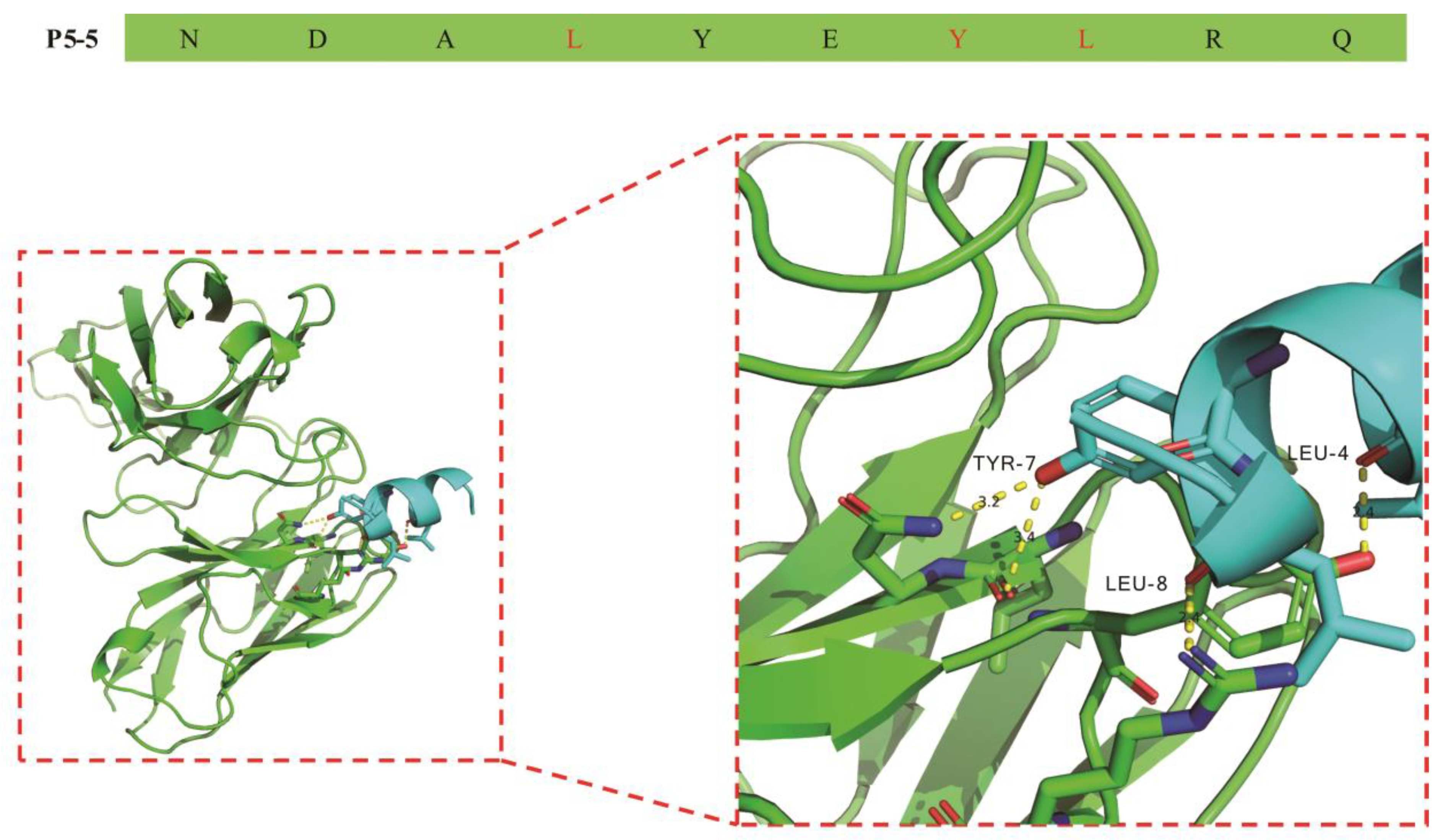
3.3. Molecular Recognition Mechanism of mAb 12F1 to P5-5
3.4. Bioinformatic Analysis of the Anti-P5-5 scFv
3.5. Expression, Purification, and Identification of Anti-P5-5 scFv
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, X.; Pu, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Fang, X.; Cui, J.; Deng, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Shao, M.; et al. A novel prognosis evaluation indicator of patients with sepsis created by integrating six microfluidic-based neutrophil chemotactic migration parameters. Talanta 2025, 281, 126801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Feng, M. Study on immune status alterations in patients with sepsis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 118, 110048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delano, M.J.; Ward, P.A. Sepsis-induced immune dysfunction: Can immune therapies reduce mortality? J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, H.R.; Yu, C.M.; Li, P.; Deng, X.M.; Wang, J.F. Dysregulation of neutrophil death in sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 963955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.T.; Yu, Y.H.; Yeh, Y.Y.; Mai, P.C.; Huang, T.T.; Huang, C.J.; Chau, L.K.; Chen, Y.L. Femtomolar-level detection of procalcitonin using a split aptamer-based fiber optic nanogold-linked sorbent assay for diagnosis of sepsis. Talanta 2025, 293, 128150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, K.; Syndergaard, C.; Damas, C.; Trubey, R.; Mukindaraj, A.; Qian, S.; Jin, X.; Breslow, S.; Niemz, A. Sepsis Pathogen Identification. J. Lab. Autom. 2015, 20, 539–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B., Jr.; Hassan, U.; Seymour, C.; Angus, D.C.; Isbell, T.S.; White, K.; Weir, W.; Yeh, L.; Vincent, A.; Bashir, R. Point-of-care sensors for the management of sepsis. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, Z.; Bhalla, N. Point-of-care diagnostics for sepsis using clinical biomarkers and microfluidic technology. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 227, 115181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Lei, Y.P.; Zhou, R.X. SIRS, SOFA, qSOFA, and NEWS in the diagnosis of sepsis and prediction of adverse outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2023, 21, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Qiang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Li, J.; Babaev, A.; Yang, H.; Gong, J.; Becker, L.; Wang, P.; et al. Identification of tetranectin-targeting monoclonal antibodies to treat potentially lethal sepsis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaz3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Bao, G.; Wang, H. Time to Develop Therapeutic Antibodies Against Harmless Proteins Colluding with Sepsis Mediators? Immunotargets Ther. 2020, 9, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, C.W.; Ford, M.L.; Coopersmith, C.M. Breaking the bond between tetranectin and HMGB1 in sepsis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eabb2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Cai, Z.; Zahid, R.; Zhang, W.; Ma, D.; Li, D.; Liang, Y.; Zha, L.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Pathogenic epitope-specific monoclonal antibody-based immunoassay for accurate diagnosis and monitoring of tetranectin in sepsis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 143, 113473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Liu, H.; Gao, Y.; Chen, R.; Dong, M.; Ling, S.; Wang, R.; Wang, S. Detection of alphaB-Conotoxin VxXXIVA (alphaB-CTX) by ic-ELISA Based on an Epitope-Specific Monoclonal Antibody. Toxins 2022, 14, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Wang, Q.; Yang, M.; Jia, R.; Yuan, J.; Wang, R. Development of sensitive immunoassay for identification and detection of mu-KIIIA-CTX: Insights into antibody discovery, molecular recognition, and immunoassay. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 310, 143346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Gu, X.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, S. Screening and Molecular Evolution of a Single Chain Variable Fragment Antibody (scFv) against Citreoviridin Toxin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7640–7648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Fang, S.; Wu, D.; Lian, J.; Fan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Lin, W. Screening for a single-chain variable-fragment antibody that can effectively neutralize the cytotoxicity of the Vibrio parahaemolyticus thermolabile hemolysin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 4967–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martviset, P.; Thanongsaksrikul, J.; Geadkaew-Krenc, A.; Chaimon, S.; Glab-Ampai, K.; Chaibangyang, W.; Sornchuer, P.; Srimanote, P.; Ruangtong, J.; Prathaphan, P.; et al. Production and immunological characterization of the novel single-chain variable fragment (scFv) antibodies against the epitopes on Opisthorchis viverrini cathepsin F (OvCatF). Acta Trop. 2024, 254, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilzadeh-Razin, S.; Mantegi, M.; Tohidkia, M.R.; Pazhang, Y.; Pourseif, M.M.; Barar, J.; Omidi, Y. Phage antibody library screening for the selection of novel high-affinity human single-chain variable fragment against gastrin receptor: An in silico and in vitro study. Daru 2019, 27, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Xiong, J.; Zheng, P.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H. Targeted preparation and recognition mechanism of broad-spectrum antibody specific to Aconitum alkaloids based on molecular modeling and its application in immunoassay. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1222, 340011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Liu, H.; Chen, R.; Gao, Y.; Dong, M.; Ling, S.; Wang, R.; Wang, S. Development of Immunochromatographic Strip for Detection of alphaB-VxXXIVA-Conotoxin Based on 5E4 Monoclonal Antibody. Toxins 2022, 14, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Ling, S.; Wang, S. Sensitive immunoassays based on specific monoclonal IgG for determination of bovine lactoferrin in cow milk samples. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 127820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.; Fang, J.; Han, S.; Sun, H.; Zhai, T.; Wang, L.; Qi, X.; Xue, Q.; Wang, J. Screening and identification of LSDV-specific monoclonal antibodies to establish a double-antibody sandwich ELISA for distinguishing LSDV from SPPV and GTPV. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 307, 142242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Lin, A.; Gu, Y.; Pan, X.; Ma, X.; Qing, Y.; Li, J. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting-based efficient screening of monensin monoclonal antibodies and applications in lateral flow immunoassay. Talanta 2025, 293, 128128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Jin, Z.; Sun, D.; Xu, B.; Lan, T.; Zhao, Q.; He, Y.; Li, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of hapten and monoclonal antibody of hesperetin and establishment of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Talanta 2025, 281, 126912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sun, C.; Hu, Z.; Wang, F.; Chang, J.; Gao, M.; Ye, D.; Jia, Q.; Zou, H.; Willems, L.; et al. Development of a novel monoclonal antibody-based competitive ELISA for antibody detection against bovine leukemia virus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 267, 131446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Jin, Y.; Sun, D.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, Q.; He, Y.; Jiao, B.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y. Monoclonal antibody-based icELISA for sensitive monitoring fenpyroximate residue by hydrolysis conversion. Talanta 2024, 268, 125288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; Yuan, J.; Wang, S. Development of an ic-ELISA and immunochromatographic strip based on IgG antibody for detection of omega-conotoxin MVIIA. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 378, 120510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Ling, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, R. Screening of a ScFv Antibody with High Affinity for Application in Human IFN-gamma Immunoassay. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Feng, C.; Huang, C.; Shi, Y.; Omar, S.M.; Zhang, B.; Cai, G.; Liu, P.; Guo, X.; Gao, X. Preparation of polyclonal antibodies to chicken P62 protein and its application in nephropathogenic infectious bronchitis virus-infected chickens. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 271, 132515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beatty, J.D.; Beatty, B.G.; Vlahos, W.G. Measurement of monoclonal antibody affinity by non-competitive enzyme immunoassay. J. Immunol. Methods 1987, 100, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Zeng, L.; Yang, H.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, J.; Ling, S.; Saeed, A.F.; Yuan, J.; Wang, S. Detection of okadaic acid (OA) using ELISA and colloidal gold immunoassay based on monoclonal antibody. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 339, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Jia, R.; Liu, Y.; Tang, H.; Wu, H.; Yuan, J.; Wang, R. High-sensitivity and rapid immunoassays for furosine detection based on monoclonal antibody 1C3. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 309, 143126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Sun, J.; Lu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X. A highly sensitive fluorescence immunochromatography strip for thiacloprid in fruits and vegetables using recombinant antibodies. Talanta 2023, 256, 124258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, M.; Ma, D.; Cai, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, L.; Zhai, C.; Xu, Y. Dendritic cell-expressed IDO alleviates atherosclerosis by expanding CD4+CD25+Foxp3+Tregs through IDO-Kyn-AHR axis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 116, 109758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, L.; Zhai, C.; Xu, Y. Gain-of-function of IDO in DCs inhibits T cell immunity by metabolically regulating surface molecules and cytokines. Exp. Ther. Med. 2023, 25, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondelinger, M.; Filee, P.; Sauvage, E.; Quinting, B.; Muyldermans, S.; Galleni, M.; Vandevenne, M.S. Understanding the Significance and Implications of Antibody Numbering and Antigen-Binding Surface/Residue Definition. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Dong, J.; Ueda, H.; Xiao, Z.; Shen, Y.; Xu, Z.; et al. An enhanced open sandwich immunoassay by molecular evolution for noncompetitive detection of Alternaria mycotoxin tenuazonic acid. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.; Wang, R.; Ling, S.; Wang, S. A high sensitive platinum-modified colloidal gold immunoassay for tenuazonic acid detection based on monoclonal IgG. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 130021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Huang, A.; Liu, L.; Xiang, S.; Li, X.; Ling, S.; Wang, L.; Lu, T.; Wang, S. Construction of a single chain variable fragment antibody (scFv) against tetrodotoxin (TTX) and its interaction with TTX. Toxicon 2014, 83, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Zahid, R.; Zhang, W.; Cai, Z.; Liang, Y.; Li, D.; Hao, J.; Xu, Y. Identification of Two Critical Contact Residues in a Pathogenic Epitope from Tetranectin for Monoclonal Antibody Binding and Preparation of Single-Chain Variable Fragments. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081100
Wang J, Liu M, Zahid R, Zhang W, Cai Z, Liang Y, Li D, Hao J, Xu Y. Identification of Two Critical Contact Residues in a Pathogenic Epitope from Tetranectin for Monoclonal Antibody Binding and Preparation of Single-Chain Variable Fragments. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(8):1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081100
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Juncheng, Meng Liu, Rukhshan Zahid, Wenjie Zhang, Zecheng Cai, Yan Liang, Die Li, Jiasheng Hao, and Yuekang Xu. 2025. "Identification of Two Critical Contact Residues in a Pathogenic Epitope from Tetranectin for Monoclonal Antibody Binding and Preparation of Single-Chain Variable Fragments" Biomolecules 15, no. 8: 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081100
APA StyleWang, J., Liu, M., Zahid, R., Zhang, W., Cai, Z., Liang, Y., Li, D., Hao, J., & Xu, Y. (2025). Identification of Two Critical Contact Residues in a Pathogenic Epitope from Tetranectin for Monoclonal Antibody Binding and Preparation of Single-Chain Variable Fragments. Biomolecules, 15(8), 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081100







