Berberine Reveals Anticoccidial Activity by Influencing Immune Responses in Eimeria acervulina-Infected Chickens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Animals and Infection
2.3. Histopathological Examination
2.4. Library Construction and Transcriptome Sequencing
2.5. Transcriptome Data Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Berberine Positively Influences Gut Morphology in Chickens Infected with E. acervulina
3.2. Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis
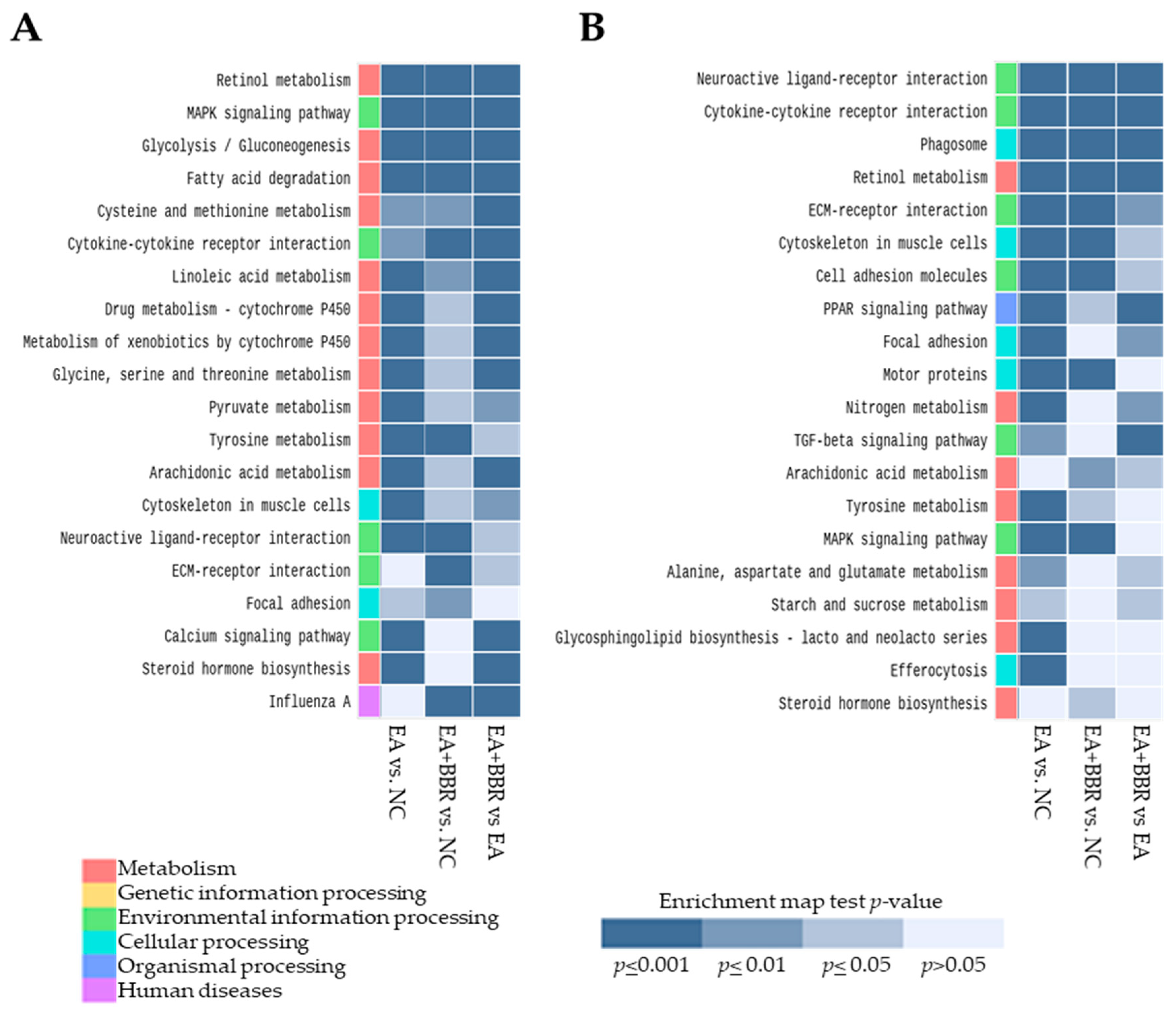
3.3. GO and KEGG Pathway Analyses
3.3.1. Pathway Analysis in E. acervulina Infection
3.3.2. Pathway Analysis in BBR Treatment and E. acervulina Infection
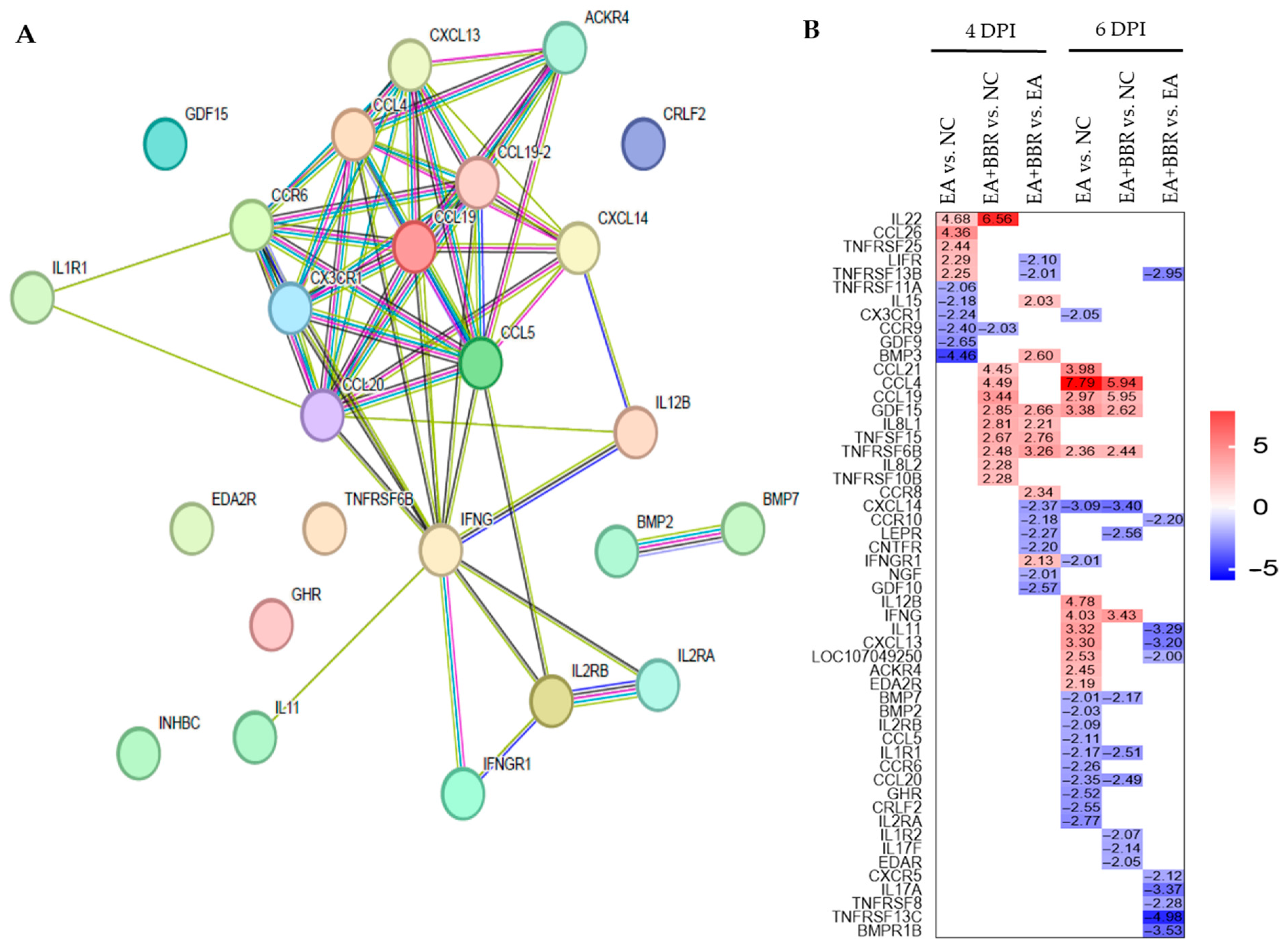
3.4. Effect of Berberine on Host Immune Changes in E. acervulina Infection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Suo, X. Live attenuated anticoccidial vaccines for chickens. Trends Parasitol. 2023, 39, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickramasuriya, S.S.; Park, I.; Lee, K.; Lee, Y.; Kim, W.H.; Nam, H.; Lillehoj, H.S. Role of Physiology, Immunity, Microbiota, and Infectious Diseases in the Gut Health of Poultry. Vaccines 2022, 10, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, W.; Kim, W.H.; Lillehoj, E.P.; Lillehoj, H.S. Recent progress in host immunity to avian coccidiosis: IL-17 family cytokines as sentinels of the intestinal mucosa. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 41, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesa-Pineda, C.; Navarro-Ruíz, J.L.; López-Osorio, S.; Chaparro-Gutiérrez, J.J.; Gómez-Osorio, L.M. Chicken Coccidiosis: From the Parasite Lifecycle to Control of the Disease. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 787653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Osorio, S.; Chaparro-Gutiérrez, J.J.; Gómez-Osorio, L.M. Overview of Poultry Eimeria Life Cycle and Host-Parasite Interactions. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.R.; Silva, L.J.G.; Pereira, A.M.P.T.; Esteves, A.; Duarte, S.C.; Pena, A. Coccidiostats and Poultry: A Comprehensive Review and Current Legislation. Foods 2022, 11, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, D.P.; Knox, J.; Dehaeck, B.; Huntington, B.; Rathinam, T.; Ravipati, V.; Ayoade, S.; Gilbert, W.; Adebambo, A.O.; Jatau, I.D.; et al. Re-calculating the cost of coccidiosis in chickens. Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.T.; Yim, D.; Flores, R.A.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, W.H.; Jung, S.-H.; Kim, S.; Min, W. Large-Scale Field Trials of an Eimeria Vaccine Induce Positive Effects on the Production Index of Broilers. Vaccines 2024, 12, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britez, J.D.; Rodriguez, A.E.; Di Ciaccio, L.; Marugán-Hernandez, V.; Tomazic, M.L. What Do We Know about Surface Proteins of Chicken Parasites Eimeria? Life 2023, 13, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lu, M.; Lillehoj, H.S. Coccidiosis: Recent Progress in Host Immunity and Alternatives to Antibiotic Strategies. Vaccines 2022, 10, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.H.; Kim, W.H.; Jeong, J.; Yoo, J.; Kwon, Y.-K.; Jung, B.Y.; Kwon, J.H.; Lillehoj, H.S.; Min, W. Prevalence and Cross-Immunity of Eimeria Species on Korean Chicken Farms. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2010, 72, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soutter, F.; Werling, D.; Tomley, F.M.; Blake, D.P. Poultry Coccidiosis: Design and Interpretation of Vaccine Studies. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, R.A.; Nguyen, B.T.; Cammayo, P.L.T.; Võ, T.C.; Naw, H.; Kim, S.; Kim, W.H.; Na, B.-K.; Min, W. Epidemiological investigation and drug resistance of Eimeria species in Korean chicken farms. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, D.P.; Pastor-Fernández, I.; Nolan, M.J.; Tomley, F.M. Recombinant anticoccidial vaccines—A cup half full? Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 55, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.T.; Flores, R.A.; Cammayo, P.L.T.; Kim, S.; Kim, W.H.; Min, W. Anticoccidial Activity of Berberine against Eimeria-Infected Chickens. Korean J. Parasitol. 2021, 59, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dkhil, M.A.; Metwaly, M.S.; Al-Quraishy, S.; Sherif, N.E.; Delic, D.; Al Omar, S.Y.; Wunderlich, F. Anti-Eimeria activity of berberine and identification of associated gene expression changes in the mouse jejunum infected with Eimeria papillata. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 1581–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Q.; Cao, F.; Liu, W.; Shi, P.; Yang, X. Effect of berberine on copper and zinc levels in chickens infected with Eimeria tenella. Mol. Biochem. Parasit. 2022, 249, 111478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriwilaijareon, N.; Petmitr, S.; Mutirangura, A.; Ponglikitmongkol, M.; Wilairat, P. Stage specificity of Plasmodium falciparum telomerase and its inhibition by berberine. Parasitol. Int. 2002, 51, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Fu, S.; Pi, R.; He, F. Neuropharmacological and pharmacokinetic properties of berberine: A review of recent research. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, Z.; Perna, S.; Al-Thawadi, S.; Alalwan, T.A.; Riva, A.; Petrangolini, G.; Gasparri, C.; Infantino, V.; Peroni, G.; Rondanelli, M. The effect of Berberine on weight loss in order to prevent obesity: A systematic review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 127, 110137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-C.; Xie, H.-Z.; Lu, B.; Xiang, R.-L.; Li, J.-Y.; Qian, H.; Zhang, S.-Y. Effect of berberine on global modulation of lncRNAs and mRNAs expression profiles in patients with stable coronary heart disease. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, B.; Qin, W.; Yan, Y.; Yin, B.; Xi, C.; Ma, L. Anti-inflammatory mechanism of berberine on lipopolysaccharide-induced IEC-18 models based on comparative transcriptomics. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 5163–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherif, N.E.; Metwaly, M.S.; Al-Quraishy, S.; Dkhil, M.A. In-vitro and in-vivo Anticoccidial Activities of Berberine against Murine Eimeria papillata Infection. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 8, 233–238. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Quraishy, S.; Sherif, N.E.; Metwaly, M.S.; Dkhil, M.A. Berberine-Induced Amelioration of the Pathological Changes in Nutrient’s Homeostasis During Murine Intestinal Eimeria papillata Infection. Pak. J. Zool. 2014, 46, 437–445. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, T.A.; Kamili, A.N.; Chishti, M.Z.; Tanveer, S.; Ahad, S.; Johri, R.K. In vivo anticoccidial activity of berberine [18,5,6-dihydro-9,10-dimethoxybenzo(g)-1,3-benzodioxolo(5,6-a) quinolizinium]—An isoquinoline alkaloid present in the root bark of Berberis lycium. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Liu, W.; Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z. Protective effect of berberine on the intestinal caecum in chicks with Eimeria tenella. Avian Biol. Res. 2016, 9, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, L.M.; Varga, E.; Coroian, M.; Nedișan, M.E.; Mircean, V.; Dumitrache, M.O.; Farczádi, L.; Fülöp, I.; Croitoru, M.D.; Fazakas, M.; et al. Efficacy of a commercial herbal formula in chicken experimental coccidiosis. Parasite Vector 2019, 12, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.; Reid, W.M. Anticoccidial drugs: Lesion scoring techniques in battery and floor-pen experiments with chickens. Exp. Parasitol. 1970, 28, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Tang, X.; Gu, X.; Chen, S.; Suo, X. Transcriptomic analysis uncovers a biphasic response to precocious Eimeria acervulina infection in chicken duodenal tissue. Vet. Parasitol. 2024, 331, 110245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandholt, A.K.S.; Wattrang, E.; Lilja, T.; Ahola, H.; Lundén, A.; Troell, K.; Svärd, S.G.; Söderlund, R. Dual RNA-seq transcriptome analysis of caecal tissue during primary Eimeria tenella infection in chickens. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, T.A.; Kamili, A.N.; Chishti, M.Z.; Tanveer, S.; Ahad, S.; Johri, R.K. Synergistic approach for treatment of chicken coccidiosis using berberine—A plant natural product. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 93, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Li, M.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, H.; Cui, L.; Wang, M. The Impact of Berberine on Intestinal Morphology, Microbes, and Immune Function of Broilers in Response to Necrotic Enteritis Challenge. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 1877075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehau, T.; Cherlet, M.; Croubels, S.; van Immerseel, F.; Goossens, E. A High Dose of Dietary Berberine Improves Gut Wall Morphology, Despite an Expansion of Enterobacteriaceae and a Reduction in Beneficial Microbiota in Broiler Chickens. Msystems 2023, 8, e0123922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.; Huang, Y.; Tian, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Lei, X.; Xu, Z.; Liu, D. Berberine enhances the function of intestinal stem cells in healthy and radiation-injured mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 136, 112278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Lambert, W.; Kiarie, E.G. Research Note: Impact of Eimeria on apparent retention of components and metabolizable energy in broiler chickens fed single or mixture of feed ingredients-based diets. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoluzzi, C.; Vieira, B.S.; Applegate, T.J. Influence of Dietary Zinc, Copper, and Manganese on the Intestinal Health of Broilers Under Eimeria Challenge. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Tang, X.; Suo, X.; Zhang, Y. Transcriptomic Insights into the Developmental Dynamics of Eimeria acervulina: A Comparative Study of a Precocious Line and the Wild Type. Genes 2024, 15, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinkels, W.J.; Post, J.; Cornelissen, J.B.; Engel, B.; Boersma, W.J.; Rebel, J.M. Immune responses to Eimeria acervulina an infection in different broilers lines. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2007, 117, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinkels, W.J.; Post, J.; Cornelissen, J.B.; Engel, B.; Boersma, W.J.; Rebel, J.M. Immune responses in Eimeria acervulina infected one-day-old broilers compared to amount of in the duodenum, measured by real-time PCR. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 138, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Lillehoj, H.; Zalenga, D. Changes in local IFN-γ and TGF-β4 mRNA expression and intraepithelial lymphocytes following Eimeria acervulina infection. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1999, 71, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloft, S.E.; Miska, K.B.; Jenkins, M.; Proszkowiec-Weglarz, M.; Kahl, S.; Wong, E.A. Temporal changes of genes associated with intestinal homeostasis in broiler chickens following a single infection with Eimeria acervulina. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.-H.; Lillehoj, H.S.; Hong, Y.-H.; Keeler, C.L.; Lillehoj, E.P. Comparison of global transcriptional responses to primary and secondary Eimeria acervulina infections in chickens. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Chung, Y.; Manjula, P.; Seo, D.; Cho, S.; Cho, E.; Ediriweera, T.K.; Yu, M.; Nam, S.; Lee, J.H. Time-series transcriptome analysis identified differentially expressed genes in broiler chicken infected with mixed Eimeria species. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 886781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jebessa, E.; Bello, S.F.; Xu, Y.; Cai, B.; Tuli, M.D.; Girma, M.; Bordbar, F.; Hanotte, O.; Nie, Q. Comprehensive analysis of differentially expressed mRNA profiles in chicken jejunum and cecum following Eimeria maxima infection. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, F. Berberine hydrochloride enhances innate immunity to protect against pathogen infection via p38 MAPK pathway. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1536143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakeri, F.; Kiani, S.; Rahimi, G.; Boskabady, M.H. Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory effects of Berberis vulgaris and its constituent berberine, experimental and clinical, a review. Phytother. Res. 2024, 38, 1882–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, A.; Kim, S.; Morris, K.M.; Nolan, M.J.; Borowska, D.; Wu, Z.; Tomley, F.; Blake, D.P.; Hawken, R.; Kaiser, P.; et al. Kinetics of the Cellular and Transcriptomic Response to Eimeria maxima in Relatively Resistant and Susceptible Chicken Lines. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 653085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


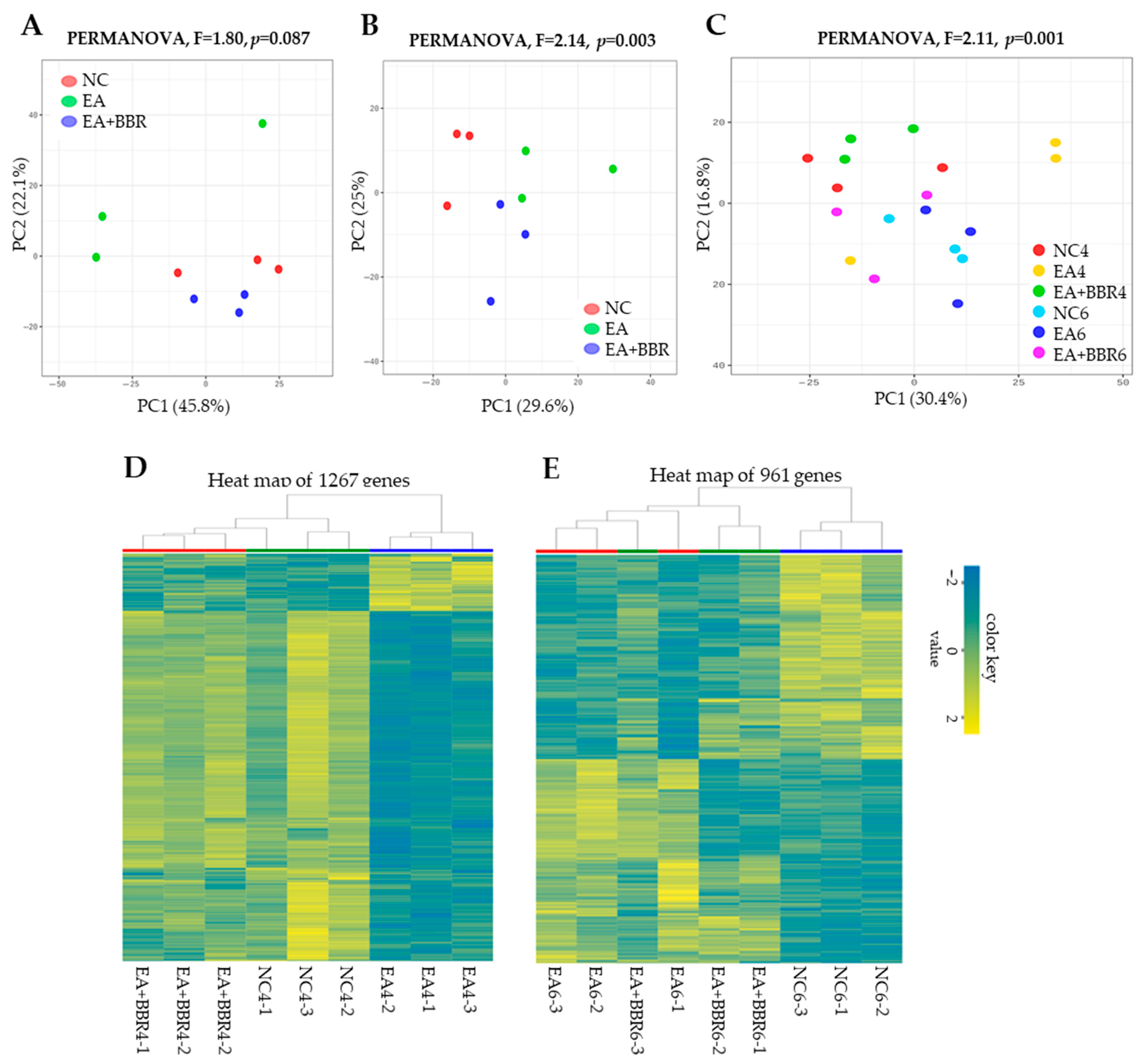


| Days | Numbers of Genes Qualifying the Criteria | Total DEGs | Up-Regulated DEGs | Down-Regulated DEGs | Groups |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 DPI | 15,408 | 441 | 62 | 379 | EA vs. NC |
| 112 | 47 | 65 | EA+BBR vs. NC | ||
| 714 | 534 | 180 | EA+BBR vs. EA | ||
| 6 DPI | 15,486 | 572 | 286 | 286 | EA vs. NC |
| 277 | 118 | 159 | EA+BBR vs. NC | ||
| 112 | 87 | 25 | EA+BBR vs. EA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, B.T.; Altanzul, B.; Flores, R.A.; Chang, H.; Kim, W.H.; Kim, S.; Min, W. Berberine Reveals Anticoccidial Activity by Influencing Immune Responses in Eimeria acervulina-Infected Chickens. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070985
Nguyen BT, Altanzul B, Flores RA, Chang H, Kim WH, Kim S, Min W. Berberine Reveals Anticoccidial Activity by Influencing Immune Responses in Eimeria acervulina-Infected Chickens. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(7):985. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070985
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Binh T., Bujinlkham Altanzul, Rochelle A. Flores, Honghee Chang, Woo H. Kim, Suk Kim, and Wongi Min. 2025. "Berberine Reveals Anticoccidial Activity by Influencing Immune Responses in Eimeria acervulina-Infected Chickens" Biomolecules 15, no. 7: 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070985
APA StyleNguyen, B. T., Altanzul, B., Flores, R. A., Chang, H., Kim, W. H., Kim, S., & Min, W. (2025). Berberine Reveals Anticoccidial Activity by Influencing Immune Responses in Eimeria acervulina-Infected Chickens. Biomolecules, 15(7), 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070985







