LIFR-Mediated ERBB2 Signaling Is Essential for Successful Embryo Implantation in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Histological Analysis
2.3. Immunostaining
2.4. Whole-Mount Staining
2.5. Measurement of Serum Hormone Levels
2.6. RNA Extraction and RNA Sequence (RNA-Seq)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Data Availability
3. Results
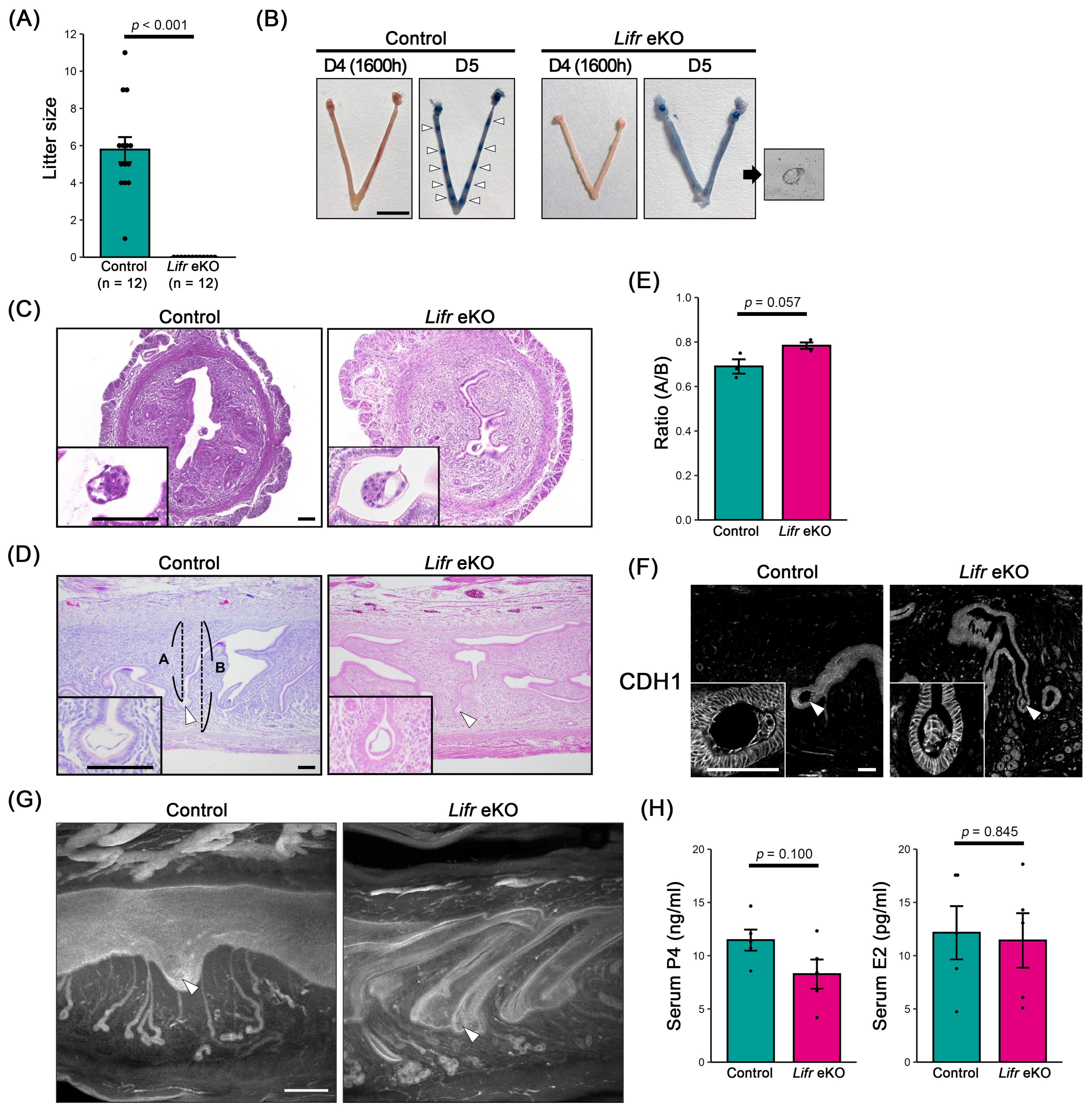
3.1. Epithelial-Specific Lifr-Deficient Females Are Infertile
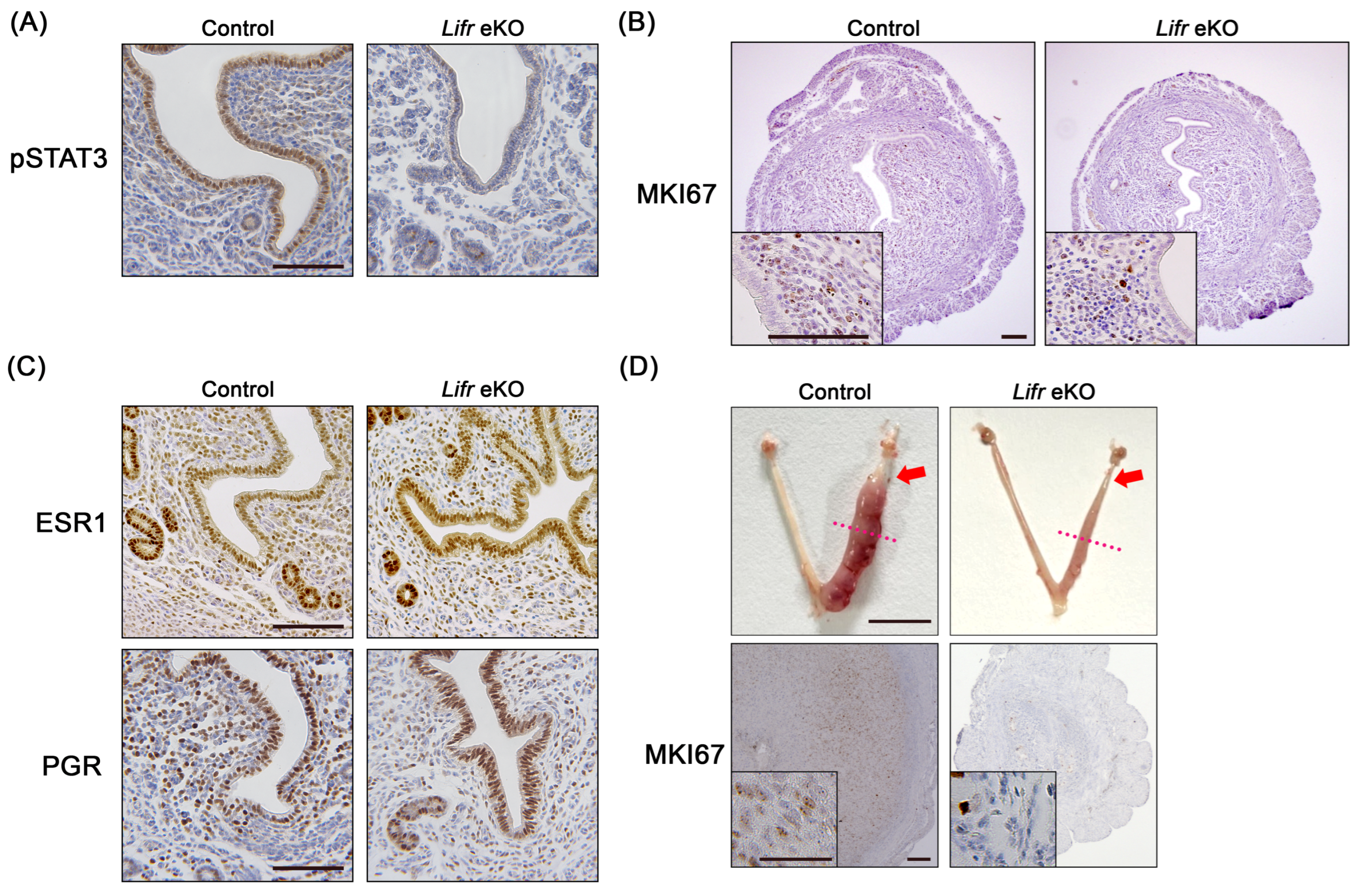
3.2. No Decidual Reaction in Epithelial-Specific Lifr-Deficient Females
3.3. Gene Expression Profiles in the Uterus of Epithelial-Specific Lifr-Deficient Mice During Embryo Implantation
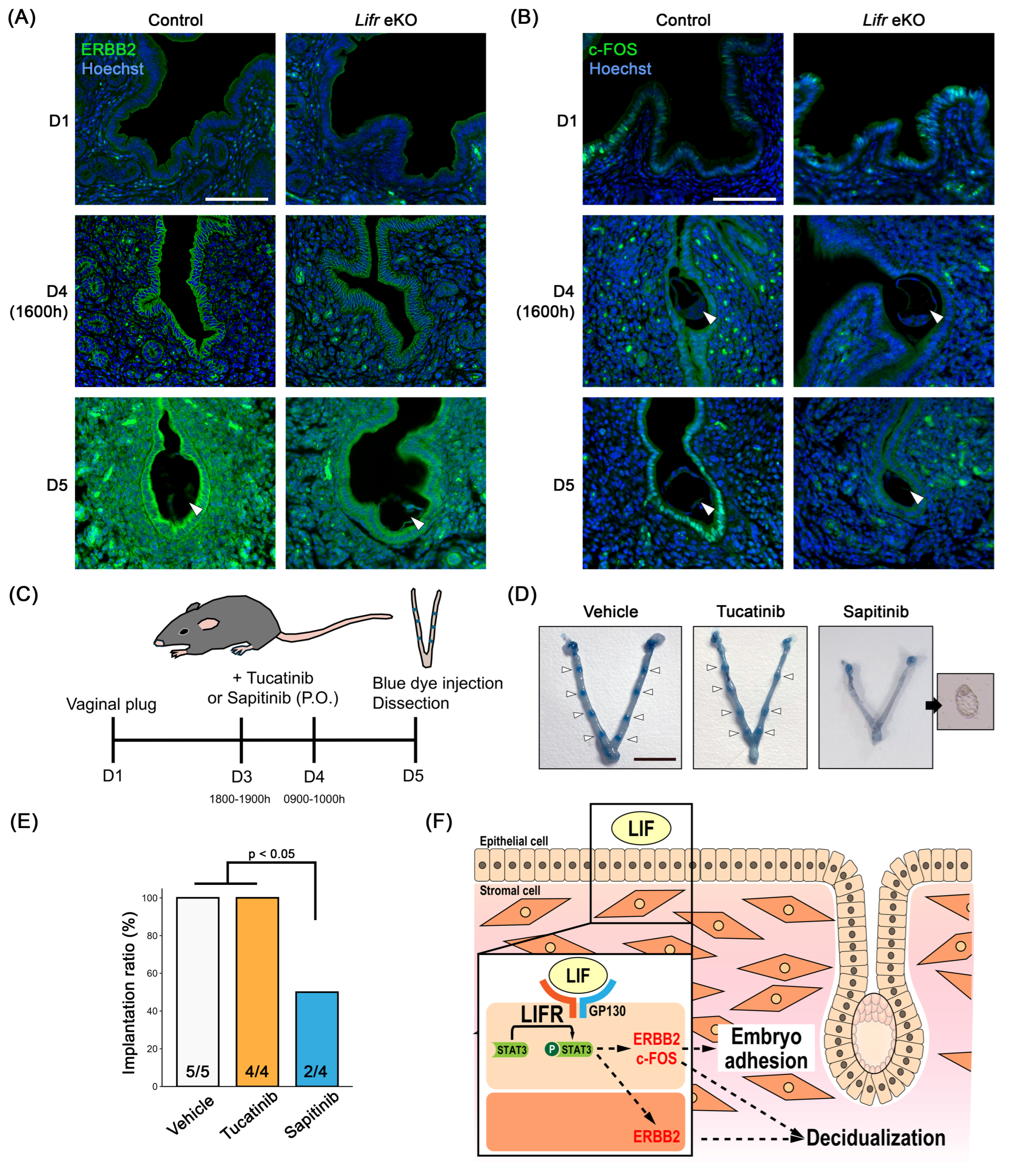
3.4. The Role of Erbb2 in Embryo Implantation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| P4 | Progesterone |
| E2 | 17β-estradiol |
| LIF | Leukemia inhibitory factor |
References
- Njagi, P.; Groot, W.; Arsenijevic, J.; Dyer, S.; Mburu, G.; Kiarie, J. Financial costs of assisted reproductive technology for patients in low- and middle-income countries: A systematic review. Hum. Reprod. Open 2023, 2023, hoad007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehring, J.; Beltsos, A.; Jeelani, R. Human implantation: The complex interplay between endometrial receptivity, inflammation, and the microbiome. Placenta 2022, 117, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinaga, K. Uterine Receptivity for Blastocyst Implantation. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 1988, 541, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazer, F.W.; Wu, G.; Spencer, T.E.; Johnson, G.A.; Burghardt, R.C.; Bayless, K. Novel pathways for implantation and establishment and maintenance of pregnancy in mammals. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2009, 16, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, J.; Sun, X.; Dey, S.K. Mechanisms of implantation: Strategies for successful pregnancy. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1754–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namiki, T.; Ito, J.; Kashiwazaki, N. Molecular mechanisms of embryonic implantation in mammals: Lessons from the gene manipulation of mice. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2018, 17, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Dey, S.K. Roadmap to embryo implantation: Clues from mouse models. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paria, B.C.; Huet-Hudson, Y.M.; Dey, S.K. Blastocyst’s state of activity determines the “window” of implantation in the receptive mouse uterus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1993, 90, 10159–10162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.L.; Kaspar, P.; Brunet, L.J.; Bhatt, H.; Gadi, I.; Köntgen, F.; Abbondanzo, S.J. Blastocyst implantation depends on maternal expression of leukaemia inhibitory factor. Nature 1992, 359, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimber, S.J. Leukaemia inhibitory factor in implantation and uterine biology. Reproduction 2005, 130, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, H.; Burdon, T.; Chambers, I.; Smith, A. Self-renewal of pluripotent embryonic stem cells is mediated via activation of STAT3. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 2048–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Behrmann, I.; Haan, S.; Hermanns, H.M.; Müller-Newen, G.; Schaper, F. Principles of interleukin (IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem. J. 2003, 374, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbers, C.; Hermanns, H.M.; Schaper, F.; Müller-Newen, G.; Grötzinger, J.; Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J. Plasticity and cross-talk of Interleukin 6-type cytokines. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012, 23, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, R.; Terakawa, J.; Kato, Y.; Azimi, S.; Inoue, N.; Ohmori, Y.; Hondo, E. The contribution of leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) for embryo implantation differs among strains of mice. Immunobiology 2014, 219, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraoka, T.; Hirota, Y.; Fukui, Y.; Gebril, M.; Kaku, T.; Aikawa, S.; Hirata, T.; Akaeda, S.; Matsuo, M.; Haraguchi, H.; et al. Differential roles of uterine epithelial and stromal STAT3 coordinate uterine receptivity and embryo attachment. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namiki, T.; Terakawa, J.; Karakama, H.; Noguchi, M.; Murakami, H.; Hasegawa, Y.; Ohara, O.; Daikoku, T.; Ito, J.; Kashiwazaki, N. Uterine epithelial Gp130 orchestrates hormone response and epithelial remodeling for successful embryo attachment in mice. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, Y.; Hirota, Y.; Saito-Fujita, T.; Aikawa, S.; Hiraoka, T.; Kaku, T.; Hirata, T.; Akaeda, S.; Matsuo, M.; Shimizu-Hirota, R.; et al. Uterine Epithelial LIF Receptors Contribute to Implantation Chamber Formation in Blastocyst Attachment. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Rosario, G.; Cohen, T.V.; Hu, J.; Stewart, C.L. Tissue-Specific Ablation of the LIF Receptor in the Murine Uterine Epithelium Results in Implantation Failure. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 1916–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daikoku, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Terakawa, J.; Ogawa, A.; DeFalco, T.; Dey, S.K. Lactoferrin-iCre: A New Mouse Line to Study Uterine Epithelial Gene Function. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 2718–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanki, H.; Suzuki, H.; Itohara, S. High-efficiency CAG-FLPe Deleter Mice in C57BL/6J Background. Exp. Anim. 2006, 55, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, R.; Fries, A.; Oelerich, K.; Marchuk, K.; Sabeur, K.; Giudice, L.C.; Laird, D.J. Insights from imaging the implanting embryo and the uterine environment in three dimensions. Development 2016, 143, 4749–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, M.; Suzuki, T.; Sato, R.; Sasaki, Y.; Kaneko, K. Artificial lactation by exogenous hormone treatment in non-pregnant sows. J. Reprod. Dev. 2020, 66, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopylova, E.; Noé, L.; Touzet, H. SortMeRNA: Fast and accurate filtering of ribosomal RNAs in metatranscriptomic data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3211–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. EdgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.X.; Jung, D.; Yao, R. ShinyGO: A graphical gene-set enrichment tool for animals and plants. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2628–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.-G.; Chen, J.R.; Hernandez, L.; Alvord, W.G.; Stewart, C.L. Dual control of LIF expression and LIF receptor function regulate Stat3 activation at the onset of uterine receptivity and embryo implantation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2001, 98, 8680–8685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantak, A.M.; Bagchi, I.C.; Bagchi, M.K. Role of uterine stromal-epithelial crosstalk in embryo implantation. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2014, 58, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, R.; Terakawa, J.; Omatsu, T.; Hengjan, Y.; Mizutani, T.; Ohmori, Y.; Hondo, E. The Window of Implantation Is Closed by Estrogen via Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Pathway. J. Reprod. Infertil. 2017, 18, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sirohi, V.K.I.; Medrano, T.; Mesa, A.M.; Kannan, A.; Bagchi, I.C.; Cooke, P.S. Regulation of AKT Signaling in Mouse Uterus. Endocrinology 2021, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Kannan, A.; DeMayo, F.J.; Lydon, J.P.; Cooke, P.S.; Yamagishi, H.; Srivastava, D.; Bagchi, M.K.; Bagchi, I.C. The Antiproliferative Action of Progesterone in Uterine Epithelium Is Mediated by Hand2. Science 2011, 331, 912–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, C.I.; Cheng, J.-G.; Liu, L.; Stewart, C.L. Cochlin, a Secreted von Willebrand Factor Type A Domain-Containing Factor, Is Regulated by Leukemia Inhibitory Factor in the Uterus at the Time of Embryo Implantation. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher, A.M.; Burns, G.W.; Behura, S.; Wu, G.; Spencer, T.E. Uterine glands impact uterine receptivity, luminal fluid homeostasis and blastocyst implantation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, H.; Xiao, S.; Li, R.; Zhao, F.; Ye, X. Distinct Spatiotemporal Expression of Serine Proteases Prss23 and Prss35 in Periimplantation Mouse Uterus and Dispensable Function of Prss35 in Fertility. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ni, H.; Ma, X.-H.; Hu, S.-J.; Luan, L.-M.; Ren, G.; Zhao, Y.-C.; Li, S.-J.; Diao, H.-L.; Xu, X.; et al. Global analysis of differential luminal epithelial gene expression at mouse implantation sites. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 37, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, J.; Wang, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, X. Microarray evaluation of endometrial receptivity in Chinese women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2008, 17, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, E.H.; Hewitt, S.C.; Liu, L.; del Rio, R.; Case, L.K.; Lin, C.; Korach, K.S.; Teuscher, C. Genetic control of estrogen-regulated transcriptional and cellular responses in mouse uterus. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 1874–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, D.; Zeng, Z.; Lin, M.; Hu, K.-L.; Zhou, P.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Yang, Y. Expression and Hormonal Regulation of Entpd3 at Various Estrous Cycle Stages in the Mouse Uterus. Reprod. Sci. 2024, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Nah, H.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J.W.; Gye, M.C.; Kim, C.H.; Kang, B.M.; Kim, M.K. Estrogen Regulates the Expression of the Small Proline-rich 2 Gene Family in the Mouse Uterus. Mol. Cells 2004, 17, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Jackson, L.; Dey, S.K.; Daikoku, T. In Pursuit of Leucine-Rich Repeat-Containing G Protein-Coupled Receptor-5 Regulation and Function in the Uterus. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 5065–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.C.; Sun, X. SLC26 anion exchangers in uterine epithelial cells and spermatozoa: Clues from the past and hints to the future. Cell Biol. Int. 2013, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, I.W.; Kirkwood, P.M.; Rebourcet, D.; Cousins, F.L.; Ainslie, R.J.; Livingstone, D.E.W.; Smith, L.B.; Saunders, P.T.; Gibson, D.A. A role for steroid 5 alpha-reductase 1 in vascular remodeling during endometrial decidualization. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1027164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krehelova, A.; Kovarikova, V.; Fabian, D.; Solar, P.; Curgali, K.; Neratzakis, I.; Hodorova, I.; Mihalik, J. Glutathione peroxidase 1 and 2 during preimplantation period of pregnancy in mouse. Bratisl. Med, J. 2023, 125, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Yuan, J.; Dewar, A.; Borg, J.-P.; Threadgill, D.W.; Sun, X.; Dey, S.K. An unanticipated discourse of HB-EGF with VANGL2 signaling during embryo implantation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2023, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, S.L.; Borges, V.F.; Baetz, T.; Mcspadden, T.; Fernetich, G.; Murthy, R.K.; Chavira, R.; Guthrie, K.; Barrett, E.; Chia, S.K. Phase I Study of ONT-380, a HER2 Inhibitor, in Patients with HER2+-Advanced Solid Tumors, with an Expansion Cohort in HER2+ Metastatic Breast Cancer (MBC). Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3529–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickinson, D.M.; Klinowska, T.; Speake, G.; Vincent, J.; Trigwell, C.; Anderton, J.; Beck, S.; Marshall, G.; Davenport, S.; Callis, R.; et al. AZD8931, an Equipotent, Reversible Inhibitor of Signaling by Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor, ERBB2 (HER2), and ERBB3: A Unique Agent for Simultaneous ERBB Receptor Blockade in Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, M.; Mezzogiorno, V.; Bresciani, F.; Weisz, A. Estrogen induces c-fos expression specifically in the luminal and glandular epithelia of adult rat uterus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 175, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitby, S.; Zhou, W.; Dimitriadis, E. Alterations in Epithelial Cell Polarity During Endometrial Receptivity: A Systematic Review. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 596324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Dey, S.K. Entosis Allows Timely Elimination of the Luminal Epithelial Barrier for Embryo Implantation. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daikoku, T.; Cha, J.; Sun, X.; Tranguch, S.; Xie, H.; Fujita, T.; Hirota, Y.; Lydon, J.; DeMayo, F.; Maxson, R.; et al. Conditional Deletion of MSX Homeobox Genes in the Uterus Inhibits Blastocyst Implantation by Altering Uterine Receptivity. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 1014–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Bartos, A.; Whitsett, J.A.; Dey, S.K. Uterine Deletion of Gp130 or Stat3 Shows Implantation Failure with Increased Estrogenic Responses. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 27, 1492–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uetzmann, L.; Burtscher, I.; Lickert, H. A mouse line expressing Foxa2-driven Cre recombinase in node, notochord, floorplate, and endoderm. Genesis 2008, 46, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher, A.M.; Allen, C.C.; Davis, D.J.; Spencer, T.E. Prss29 Cre recombinase mice are useful to study adult uterine gland function. Genesis 2022, 60, e23493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filant, J.; Spencer, T.E. Cell-Specific Transcriptional Profiling Reveals Candidate Mechanisms Regulating Development and Function of Uterine Epithelia in Mice. Biol. Reprod. 2013, 89, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messaoudi, S.; EL Kasmi, I.; Bourdiec, A.; Crespo, K.; Bissonnette, L.; Le Saint, C.; Bissonnette, F.; Kadoch, I.-J. 15 years of transcriptomic analysis on endometrial receptivity: What have we learnt? Fertil. Res. Pr. 2019, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajanova, L.; Altmäe, S.; Bjuresten, K.; Hovatta, O.; Landgren, B.-M.; Stavreus-Evers, A. Disturbances in the LIF pathway in the endometrium among women with unexplained infertility. Fertil. Steril. 2009, 91, 2602–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Target | Species | Source | Catalog No. | RRID | Dilution | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c-FOS | Rabbit | Abcam | ab222699 | AB_2891049 | 1:1000 | IF |
| ESR1 | Rabbit | Abcam | ab32063 | AB_732249 | 1:200 | IHC |
| PGR | Rabbit | Abcam | ab101688 | AB_10715248 | 1:200 | IHC |
| MKI67 | Rabbit | Abcam | ab16667 | AB_302459 | 1:200 | IHC |
| ERBB2 | Mouse | Santa Cruz | sc-33684 | AB_627996 | 1:200 | IF |
| CDH1 | Rabbit | Cell Signaling Technology | #3195 | AB_2066683 | 1:200 | IF |
| pSTAT3 | Rabbit | Cell Signaling Technology | #9145 | AB_2491009 | 1:200 | IHC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Terakawa, J.; Nakamura, S.; Ohtomo, M.; Uehara, S.; Kawata, Y.; Takarabe, S.; Sugita, H.; Namiki, T.; Kageyama, A.; Noguchi, M.; et al. LIFR-Mediated ERBB2 Signaling Is Essential for Successful Embryo Implantation in Mice. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050698
Terakawa J, Nakamura S, Ohtomo M, Uehara S, Kawata Y, Takarabe S, Sugita H, Namiki T, Kageyama A, Noguchi M, et al. LIFR-Mediated ERBB2 Signaling Is Essential for Successful Embryo Implantation in Mice. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(5):698. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050698
Chicago/Turabian StyleTerakawa, Jumpei, Sakura Nakamura, Mana Ohtomo, Saki Uehara, Yui Kawata, Shunsuke Takarabe, Hibiki Sugita, Takafumi Namiki, Atsuko Kageyama, Michiko Noguchi, and et al. 2025. "LIFR-Mediated ERBB2 Signaling Is Essential for Successful Embryo Implantation in Mice" Biomolecules 15, no. 5: 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050698
APA StyleTerakawa, J., Nakamura, S., Ohtomo, M., Uehara, S., Kawata, Y., Takarabe, S., Sugita, H., Namiki, T., Kageyama, A., Noguchi, M., Murakami, H., Kashiwazaki, N., & Ito, J. (2025). LIFR-Mediated ERBB2 Signaling Is Essential for Successful Embryo Implantation in Mice. Biomolecules, 15(5), 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050698





