PI3K/mTOR Signaling Pathway Dual Inhibition for the Management of Neuroinflammation: Novel Insights from In Vitro Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Lines
2.2.1. C6
2.2.2. SH-SY5Y
2.2.3. BV-2
2.2.4. Mo3.13
2.3. Experimental Procedures
2.4. MTT Assay
2.5. ELISA Kit
2.6. Immunofluorescence
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
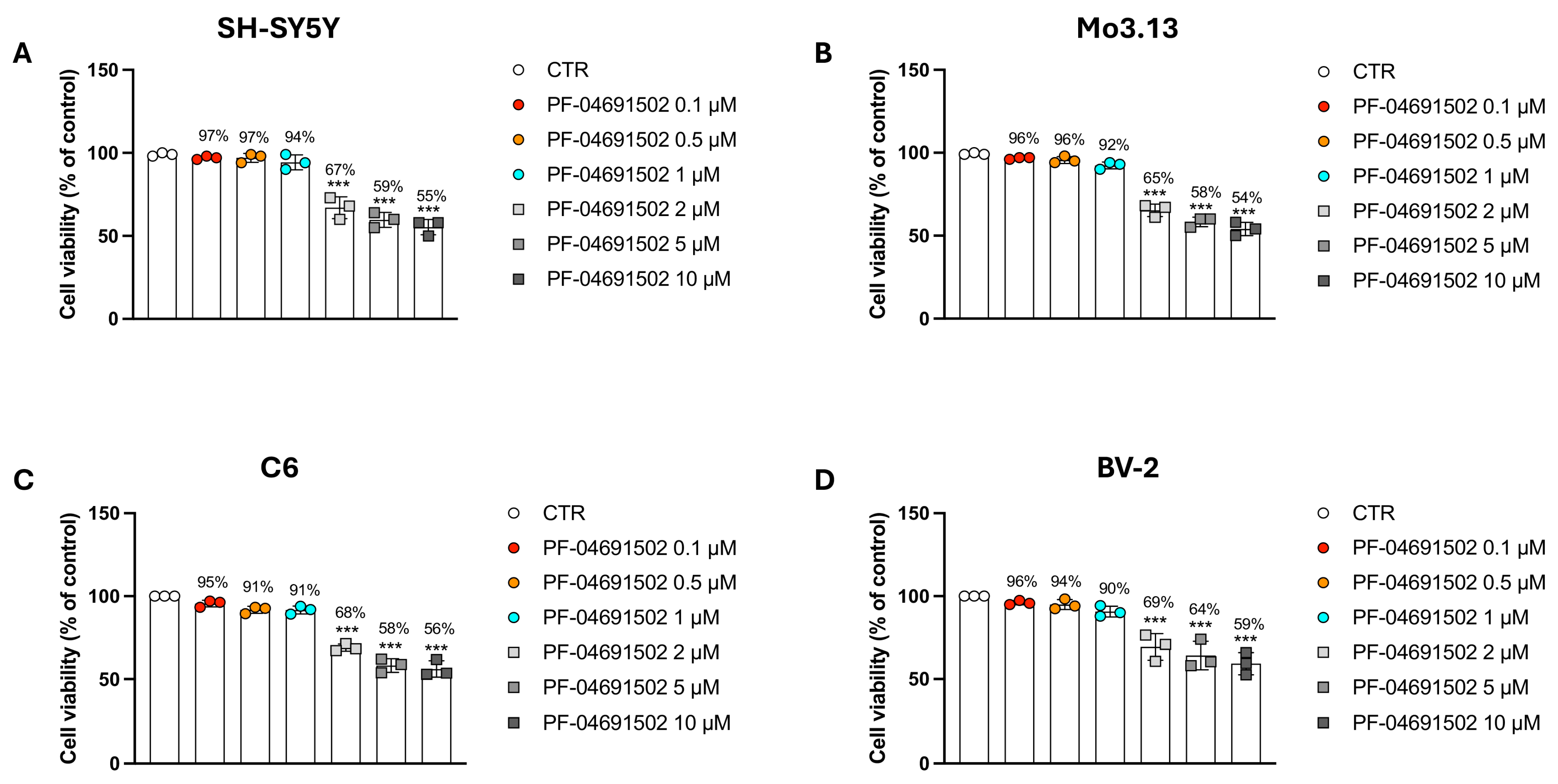
3.1. Evaluating the Concentration-Dependent Cytotoxic Effects of the Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor PF-04691502 in Neural and Glial Models
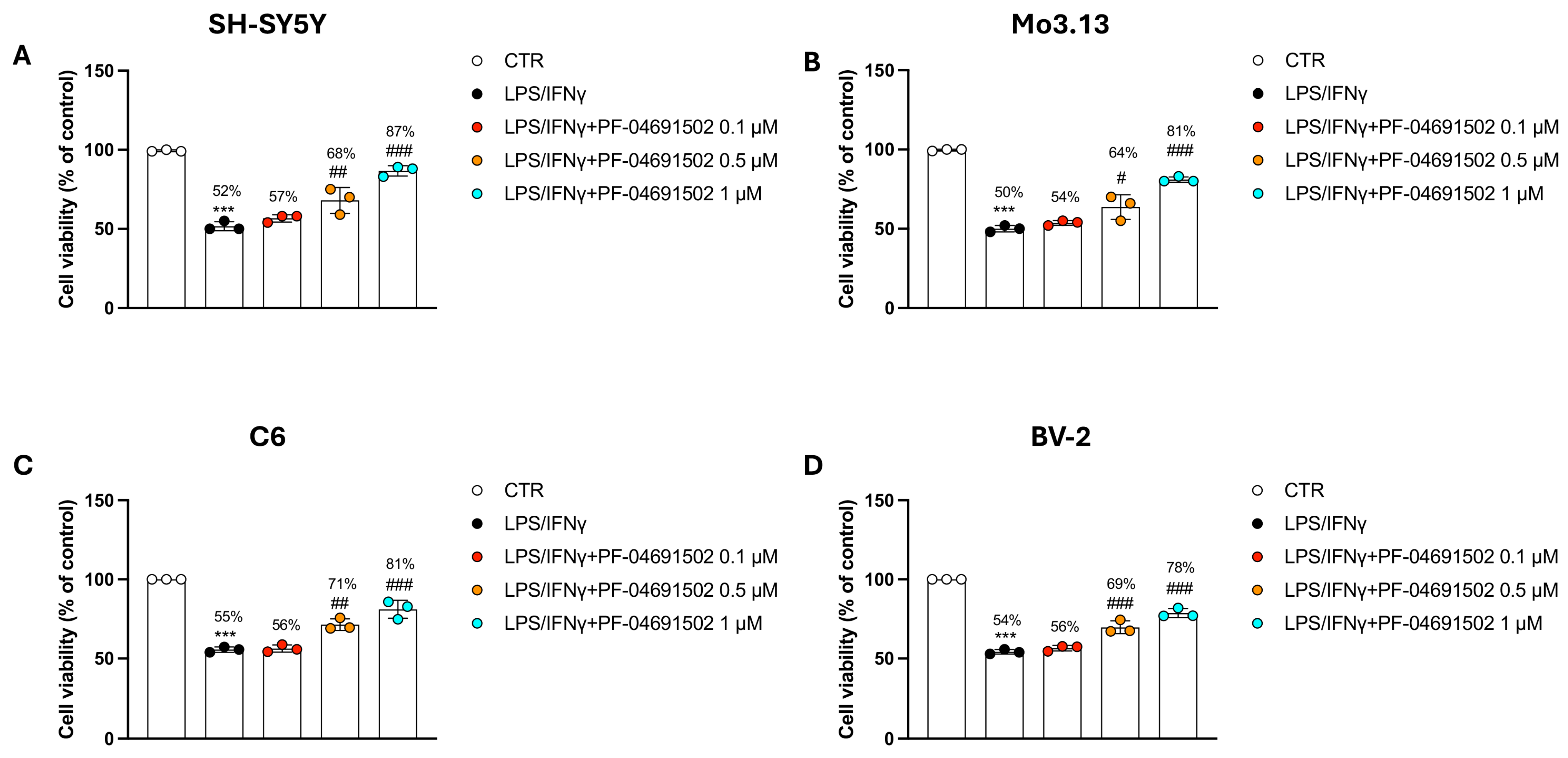
3.2. The Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor PF-04691502 Modulates Inflammation in Neural and Glial Cells Induced by LPS/IFNγ
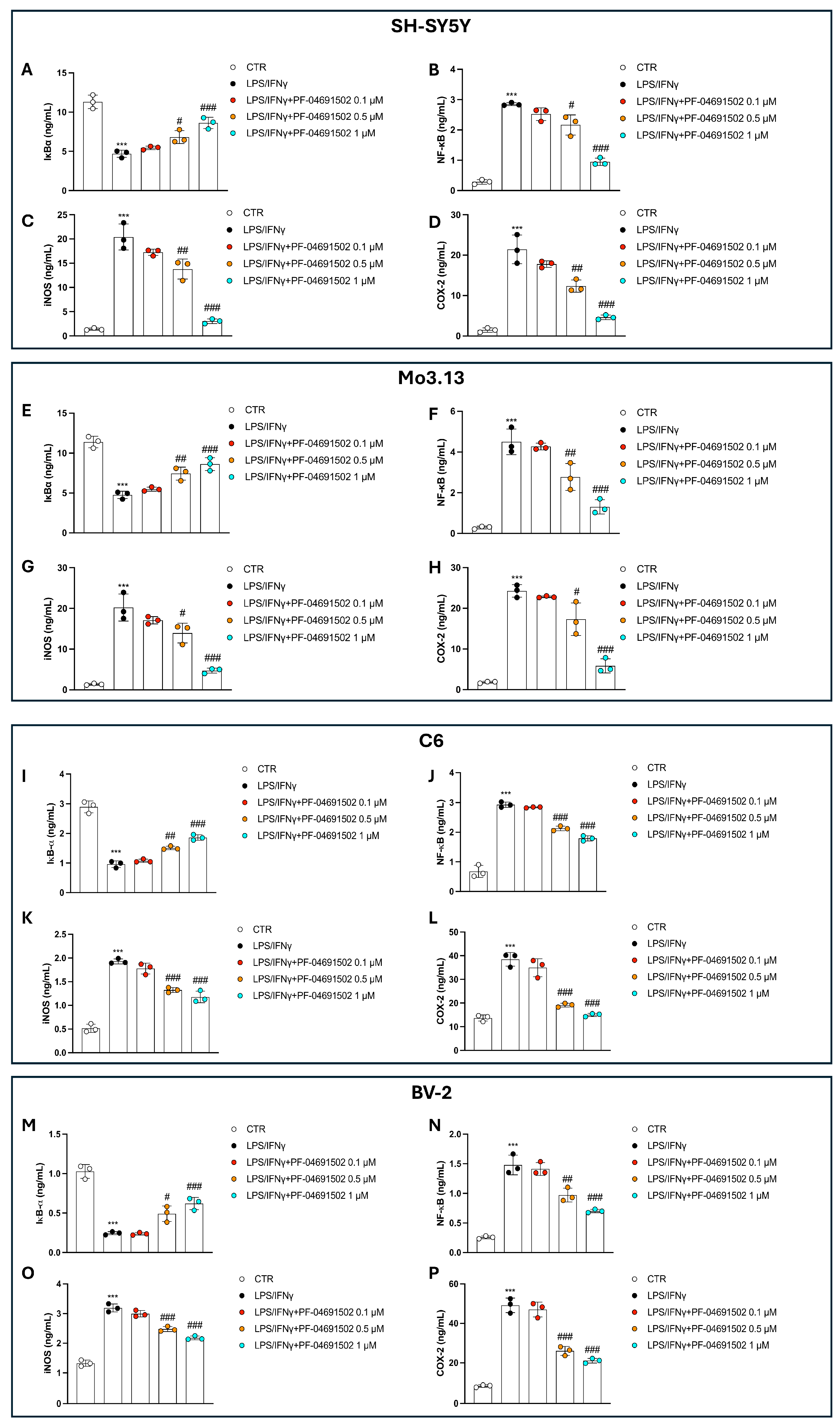
3.3. Dual Inhibition of PI3K/mTOR by PF-04691502 Modulates NF-κB Pathway, iNOS, and COX-2 Levels in a Concentration-Dependent Manner
3.4. PF-04691502 Reduces TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 Levels in a Concentration-Dependent Manner Through PI3K/mTOR Inhibition
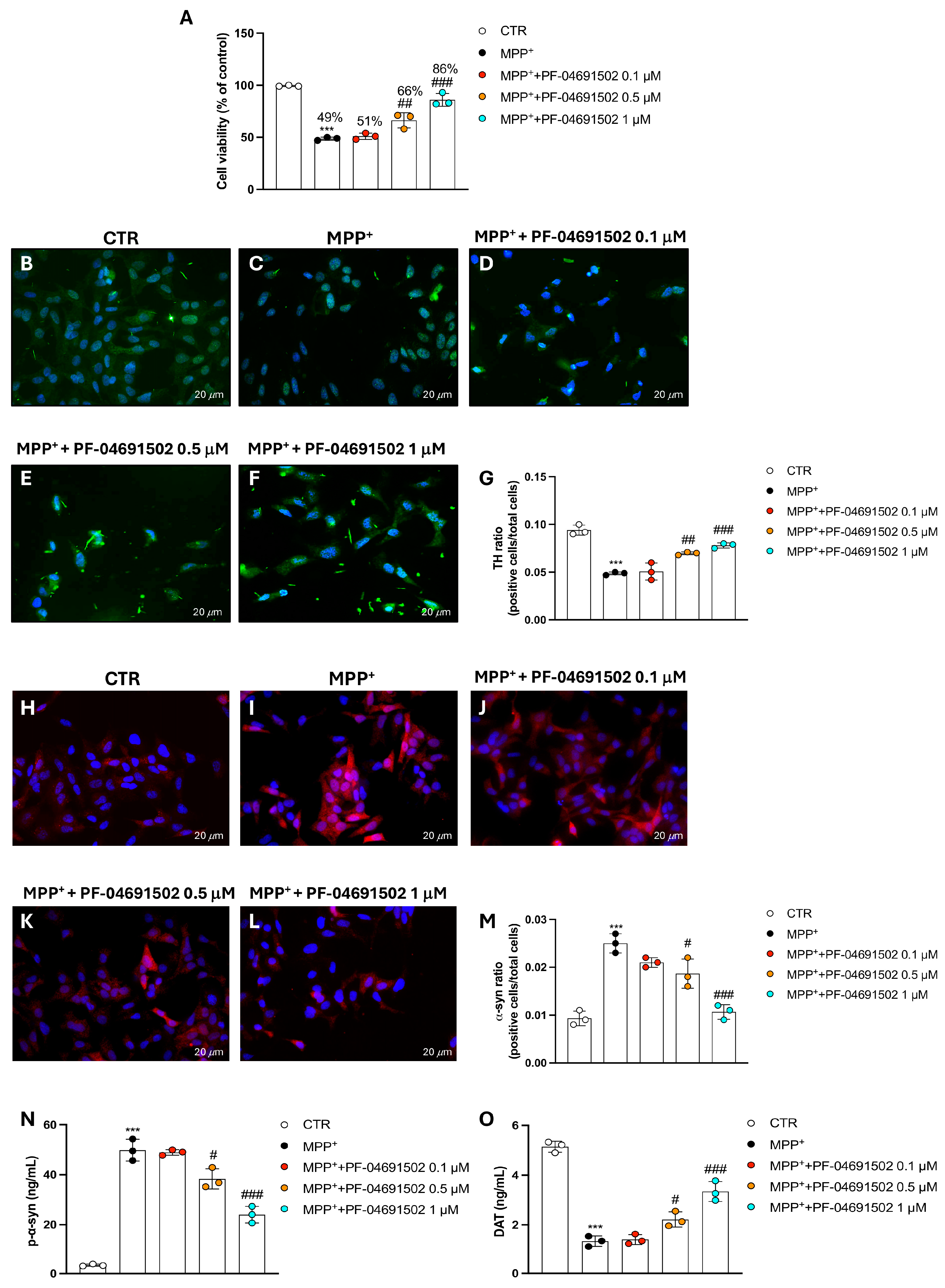
3.5. PF-04691502 Dual Inhibition of PI3K/mTOR Protects SH-SY5Y Cells from MPP+-Induced Neurodegeneration
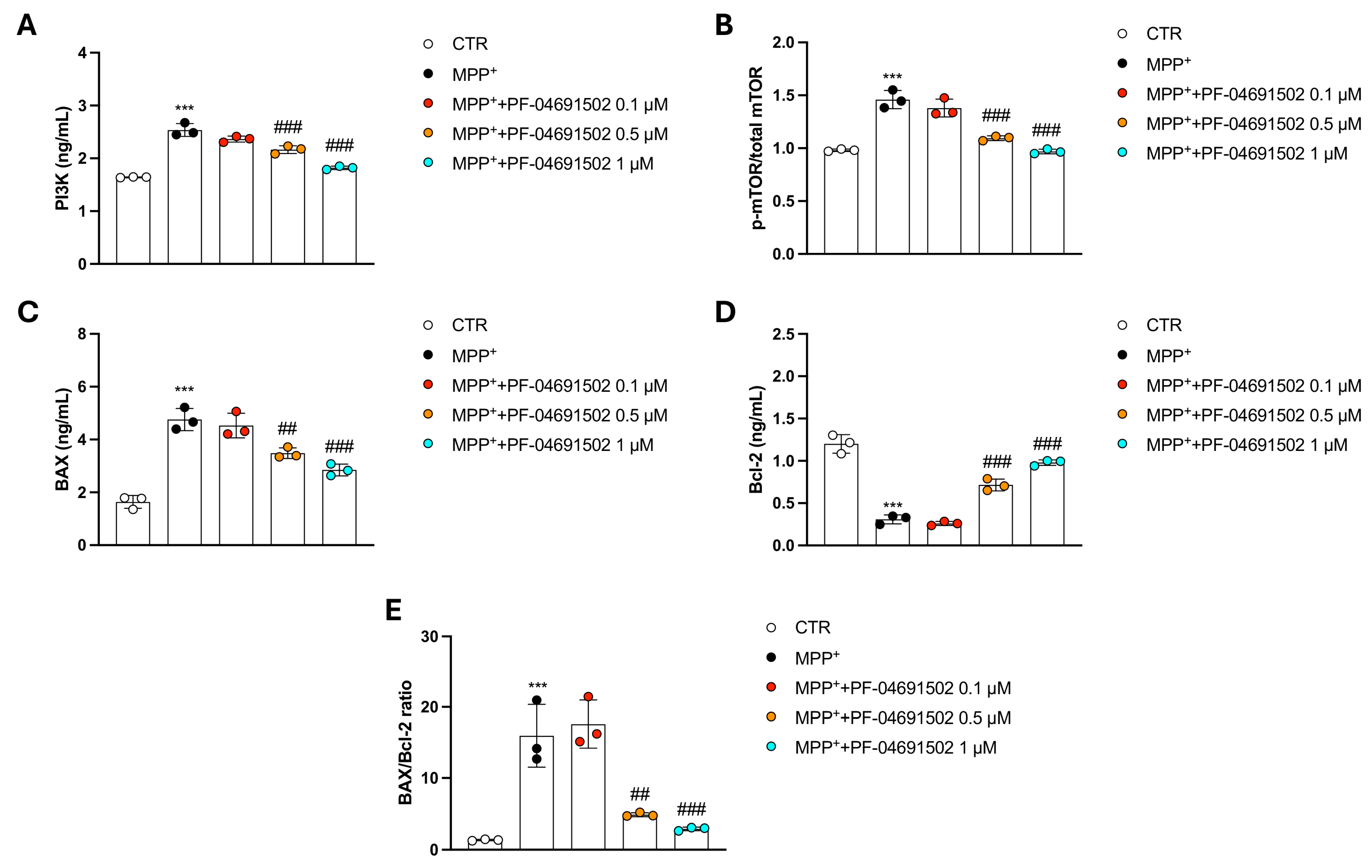
3.6. Modulation of PI3K/mTOR Signaling and Apoptotic Pathways by PF-04691502 in MPP+-Treated SH-SY5Y Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, W.; Xiao, D.; Mao, Q.; Xia, H. Role of neuroinflammation in neurodegeneration development. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Jiang, J.; Tan, Y.; Chen, S. Microglia in neurodegenerative diseases: Mechanism and potential therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, U.C.; Bhol, N.K.; Swain, S.K.; Samal, R.R.; Nayak, P.K.; Raina, V.; Panda, S.K.; Kerry, R.G.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Jena, A.B. Oxidative stress and inflammation in the pathogenesis of neurological disorders: Mechanisms and implications. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2025, 15, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlay, D.; Cantrell, D. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase and the mammalian target of rapamycin pathways control T cell migration. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1183, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panwar, V.; Singh, A.; Bhatt, M.; Tonk, R.K.; Azizov, S.; Raza, A.S.; Sengupta, S.; Kumar, D.; Garg, M. Multifaceted role of mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) signaling pathway in human health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perluigi, M.; Di Domenico, F.; Butterfield, D.A. mTOR signaling in aging and neurodegeneration: At the crossroad between metabolism dysfunction and impairment of autophagy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 84, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kma, L.; Baruah, T.J. The interplay of ROS and the PI3K/Akt pathway in autophagy regulation. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Yao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chang, S.; Li, C.; Wu, Y.; Shen, J.; Yang, R. The role of PI3K signaling pathway in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1459025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.K.; Jha, N.K.; Kar, R.; Ambasta, R.K.; Kumar, P. p38 MAPK and PI3K/AKT Signalling Cascades inParkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Cell Med. 2015, 4, 67–86. [Google Scholar]
- Cianciulli, A.; Porro, C.; Calvello, R.; Trotta, T.; Lofrumento, D.D.; Panaro, M.A. Microglia Mediated Neuroinflammation: Focus on PI3K Modulation. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heras-Sandoval, D.; Pérez-Rojas, J.M.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J. Novel compounds for the modulation of mTOR and autophagy to treat neurodegenerative diseases. Cell. Signal. 2020, 65, 109442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Xu, Y.; Liang, Q.; Yang, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Shi, J. Recent Advances in Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitors for Tumour Treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 875372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Q.W.; Knight, Z.A.; Goldenberg, D.D.; Yu, W.; Mostov, K.E.; Stokoe, D.; Shokat, K.M.; Weiss, W.A. A dual PI3 kinase/mTOR inhibitor reveals emergent efficacy in glioma. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britten, C.D.; Adjei, A.A.; Millham, R.; Houk, B.E.; Borzillo, G.; Pierce, K.; Wainberg, Z.A.; LoRusso, P.M. Phase I study of PF-04691502, a small-molecule, oral, dual inhibitor of PI3K and mTOR, in patients with advanced cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2014, 32, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Mehta, P.P.; Yin, M.-J.; Sun, S.; Zou, A.; Chen, J.; Rafidi, K.; Feng, Z.; Nickel, J.; Engebretsen, J. PF-04691502, a potent and selective oral inhibitor of PI3K and mTOR kinases with antitumor activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 2189–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espana-Serrano, L.; Chougule, M.B. Enhanced Anticancer Activity of PF-04691502, a Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor, in Combination With VEGF siRNA Against Non-small-cell Lung Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.H.; Loong, H.H.; Hui, C.W.; Lau, C.P.; Hui, E.P.; Ma, B.B.; Chan, A.T. Preclinical evaluation of the PI3K-mTOR dual inhibitor PF-04691502 as a novel therapeutic drug in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Investig. New Drugs 2013, 31, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, M.D.; Carter, M.J.; Larrayoz, M.; Smith, L.D.; Aguilar-Hernandez, M.; Cox, K.L.; Tipton, T.; Reynolds, M.; Murphy, S.; Lemm, E. The PI3K/mTOR inhibitor PF-04691502 induces apoptosis and inhibits microenvironmental signaling in CLL and the Eµ-TCL1 mouse model. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2015, 125, 4032–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casili, G.; Lanza, M.; Campolo, M.; Siracusa, R.; Paterniti, I.; Ardizzone, A.; Scuderi, S.A.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Esposito, E. Synergic Therapeutic Potential of PEA-Um Treatment and NAAA Enzyme Silencing In the Management of Neuroinflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Peng, S.; Zhu, X. Baicalein protects against MPP(+)/MPTP-induced neurotoxicity by ameliorating oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cells and mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotoxicology 2021, 87, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campolo, M.; Scuderi, S.A.; Filippone, A.; Bova, V.; Lombardo, S.P.; Colarossi, L.; Sava, S.; Capra, A.P.; De Gaetano, F.; Portelli, M.; et al. EZH2 Inhibition to Counteract Oral Cancer Progression through Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway Modulation. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campolo, M.; Casili, G.; Paterniti, I.; Filippone, A.; Lanza, M.; Ardizzone, A.; Scuderi, S.A.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Esposito, E. Effect of a Product Containing Xyloglucan and Pea Protein on a Murine Model of Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuderi, S.A.; Casili, G.; Lanza, M.; Ardizzone, A.; Pantaleo, L.; Campolo, M.; Paterniti, I.; Cucinotta, L.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Esposito, E. Efficacy of a Product Containing Xyloglucan and Pea Protein on Intestinal Barrier Function in a Partial Restraint Stress Animal Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakrakou, A.G.; Alexaki, A.; Brinia, M.-E.; Anagnostouli, M.; Stefanis, L.; Stathopoulos, P. The mTOR signaling pathway in multiple sclerosis; from animal models to human data. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, B.; King, S.; Suphioglu, C. The Importance of Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase in Neuroinflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike-Kumagai, M.; Fujimoto, M.; Wataya-Kaneda, M. Sirolimus relieves seizures and neuropsychiatric symptoms via changes of microglial polarity in tuberous sclerosis complex model mice. Neuropharmacology 2022, 218, 109203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fung, N.S.K.; Lam, W.-C.; Lo, A.C.Y. mTOR signalling pathway: A potential therapeutic target for ocular neurodegenerative diseases. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daei Sorkhabi, A.; Mohamed Khosroshahi, L.; Sarkesh, A.; Mardi, A.; Aghebati-Maleki, A.; Aghebati-Maleki, L.; Baradaran, B. The current landscape of CAR T-cell therapy for solid tumors: Mechanisms, research progress, challenges, and counterstrategies. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1113882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, P.; Tulsawani, R.; Vohora, D. Dual targeting by inhibition of phosphoinositide-3-Kinase and mammalian target of rapamycin attenuates the neuroinflammatory responses in murine hippocampal cells and seizures in C57BL/6 mice. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 739452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, K.; Cai, X.; Yang, B.; He, Q.; Wang, J.; Weng, Q. Targeting PI3K/AKT signaling for treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardizzone, A.; Capra, A.P.; Repici, A.; Lanza, M.; Bova, V.; Palermo, N.; Paterniti, I.; Esposito, E. Rebalancing NOX2/Nrf2 to limit inflammation and oxidative stress across gut-brain axis in migraine. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2024, 213, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhtar, I. Unravelling the critical role of neuroinflammation in epilepsy-associated neuropsychiatric comorbidities: A review. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2024, 136, 111135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypczak-Wiercioch, A.; Sałat, K. Lipopolysaccharide-induced model of neuroinflammation: Mechanisms of action, research application and future directions for its use. Molecules 2022, 27, 5481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Singh, T.G. Role of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signalling in neurodegenerative diseases: An mechanistic approach. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 18, 918–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: New insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kölliker-Frers, R.; Udovin, L.; Otero-Losada, M.; Kobiec, T.; Herrera, M.I.; Palacios, J.; Razzitte, G.; Capani, F. Neuroinflammation: An integrating overview of reactive-Neuroimmune cell interactions in health and disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 9999146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias-Carvalho, A.; Sá, S.I.; Carvalho, F.; Fernandes, E.; Costa, V.M. Inflammation as common link to progressive neurological diseases. Arch. Toxicol. 2024, 98, 95–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardizzone, A.; Bova, V.; Casili, G.; Filippone, A.; Campolo, M.; Lanza, M.; Esposito, E.; Paterniti, I. SUN11602, a bFGF mimetic, modulated neuroinflammation, apoptosis and calcium-binding proteins in an in vivo model of MPTP-induced nigrostriatal degeneration. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, G.; Giannoni, S.; Bellini, G.; Siciliano, G.; Ceravolo, R. Dopamine transporter imaging, current status of a potential biomarker: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramburu, J.; Ortells, M.C.; Tejedor, S.; Buxadé, M.; López-Rodríguez, C. Transcriptional regulation of the stress response by mTOR. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, re2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venderova, K.; Park, D.S. Programmed cell death in Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a009365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Yang, H. Balancing apoptosis and autophagy for Parkinson’s disease therapy: Targeting BCL-2. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 10, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghavami, S.; Shojaei, S.; Yeganeh, B.; Ande, S.R.; Jangamreddy, J.R.; Mehrpour, M.; Christoffersson, J.; Chaabane, W.; Moghadam, A.R.; Kashani, H.H. Autophagy and apoptosis dysfunction in neurodegenerative disorders. Prog. Neurobiol. 2014, 112, 24–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, P.P.; Hirsch, E.C.; Hunot, S. Understanding dopaminergic cell death pathways in Parkinson disease. Neuron 2016, 90, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, P.T.; Kumari, M.; Byran, G.; Gangadharappa, H.V.; Garikapati, K.K. Neuroprotective approaches to halt Parkinson’s disease progression. Neurochem. Int. 2022, 158, 105380. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Liu, W.; Ou, L.; Gao, F.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Wei, P.; Miao, F. Emodin Alleviates Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress via Mitochondrial Dysfunction by Inhibiting the PI3K/mTOR/GSK3beta Pathway in Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1562915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ardizzone, A.; Scuderi, S.A.; Casili, G.; Basilotta, R.; Esposito, E.; Lanza, M. PI3K/mTOR Signaling Pathway Dual Inhibition for the Management of Neuroinflammation: Novel Insights from In Vitro Models. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050677
Ardizzone A, Scuderi SA, Casili G, Basilotta R, Esposito E, Lanza M. PI3K/mTOR Signaling Pathway Dual Inhibition for the Management of Neuroinflammation: Novel Insights from In Vitro Models. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(5):677. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050677
Chicago/Turabian StyleArdizzone, Alessio, Sarah Adriana Scuderi, Giovanna Casili, Rossella Basilotta, Emanuela Esposito, and Marika Lanza. 2025. "PI3K/mTOR Signaling Pathway Dual Inhibition for the Management of Neuroinflammation: Novel Insights from In Vitro Models" Biomolecules 15, no. 5: 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050677
APA StyleArdizzone, A., Scuderi, S. A., Casili, G., Basilotta, R., Esposito, E., & Lanza, M. (2025). PI3K/mTOR Signaling Pathway Dual Inhibition for the Management of Neuroinflammation: Novel Insights from In Vitro Models. Biomolecules, 15(5), 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050677









