Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase Modulates Midgut Physiology in Aedes aegypti Through miRNA Regulation: Insights from Small RNA Sequencing and Gene Expression Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mosquito Rearing and Sample Collection
2.2. DsRNA Synthesis Analysis
2.3. Real-Time Fluorescence Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.4. Sample Preparation for Small RNA Sequencing
2.5. Small RNA Sequencing Analysis
2.5.1. Quality Control of Sequencing Data
2.5.2. Read Mapping to the Reference Genome
2.5.3. Differential Expression of miRNA
2.5.4. GO and KEGG Enrichment Analysis
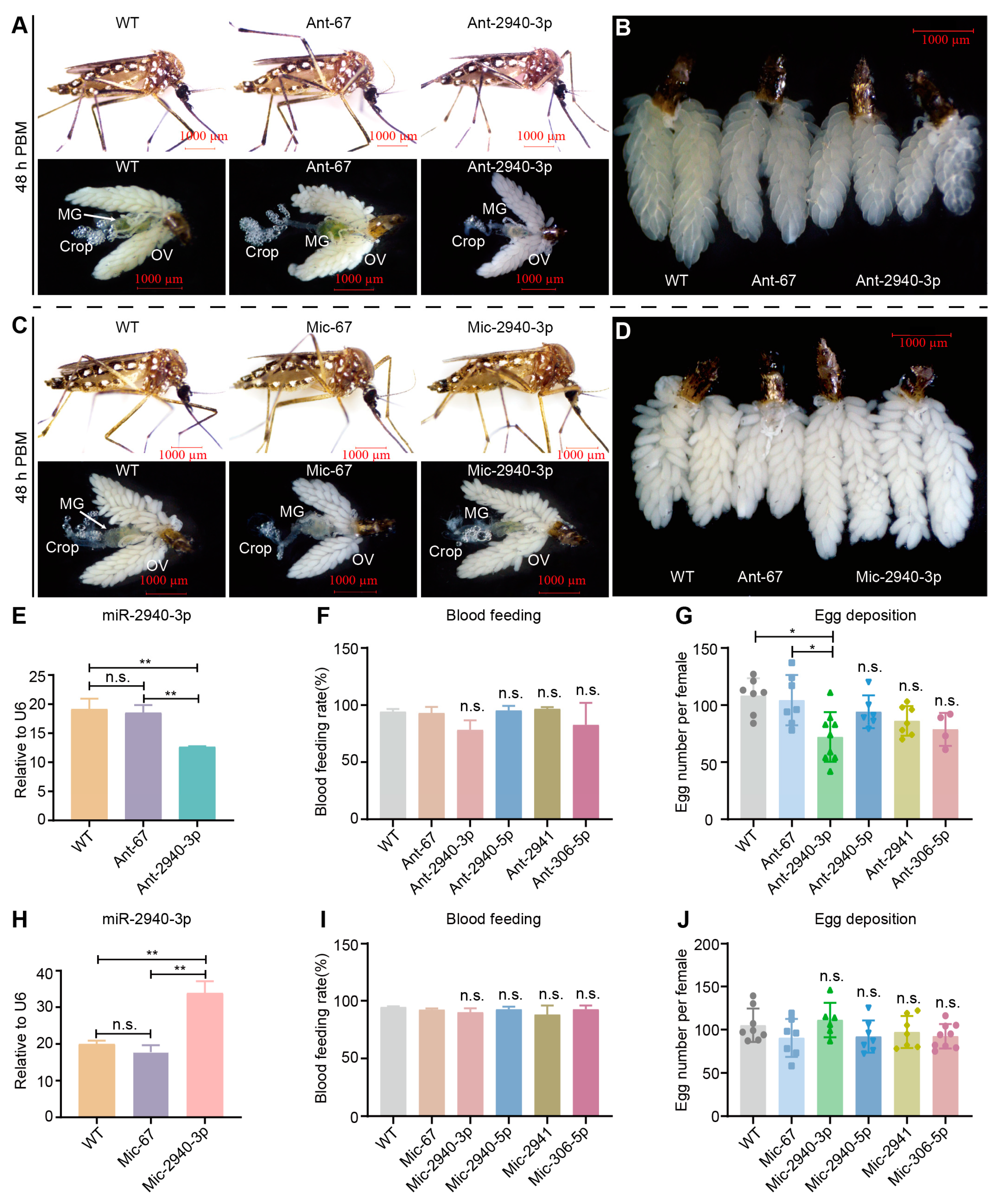
2.6. miRNA Antagomir and Mimic Treatment
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. SHMT-Mediated miRNAs Revealed via Small RNA Sequencing Analysis
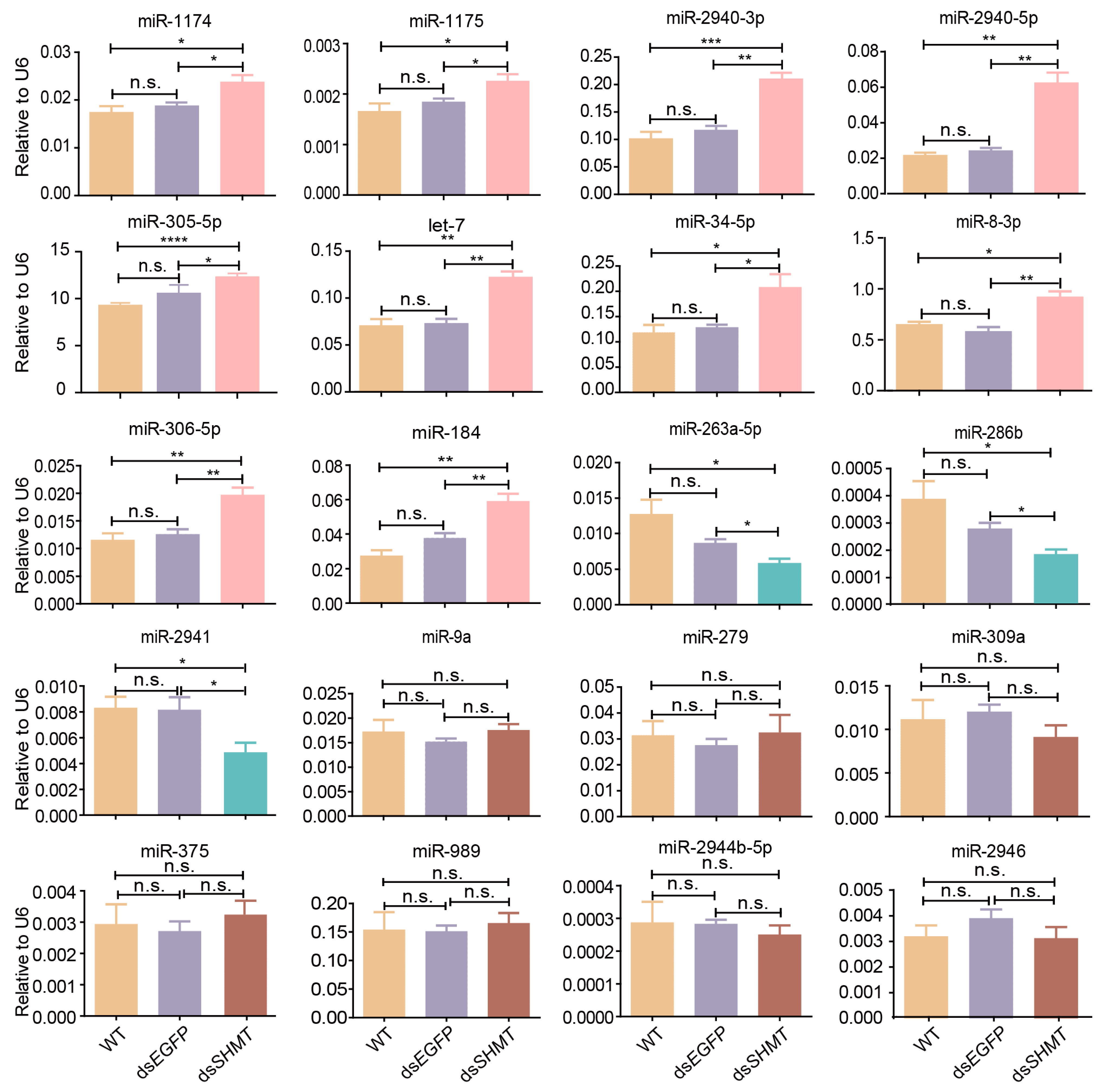
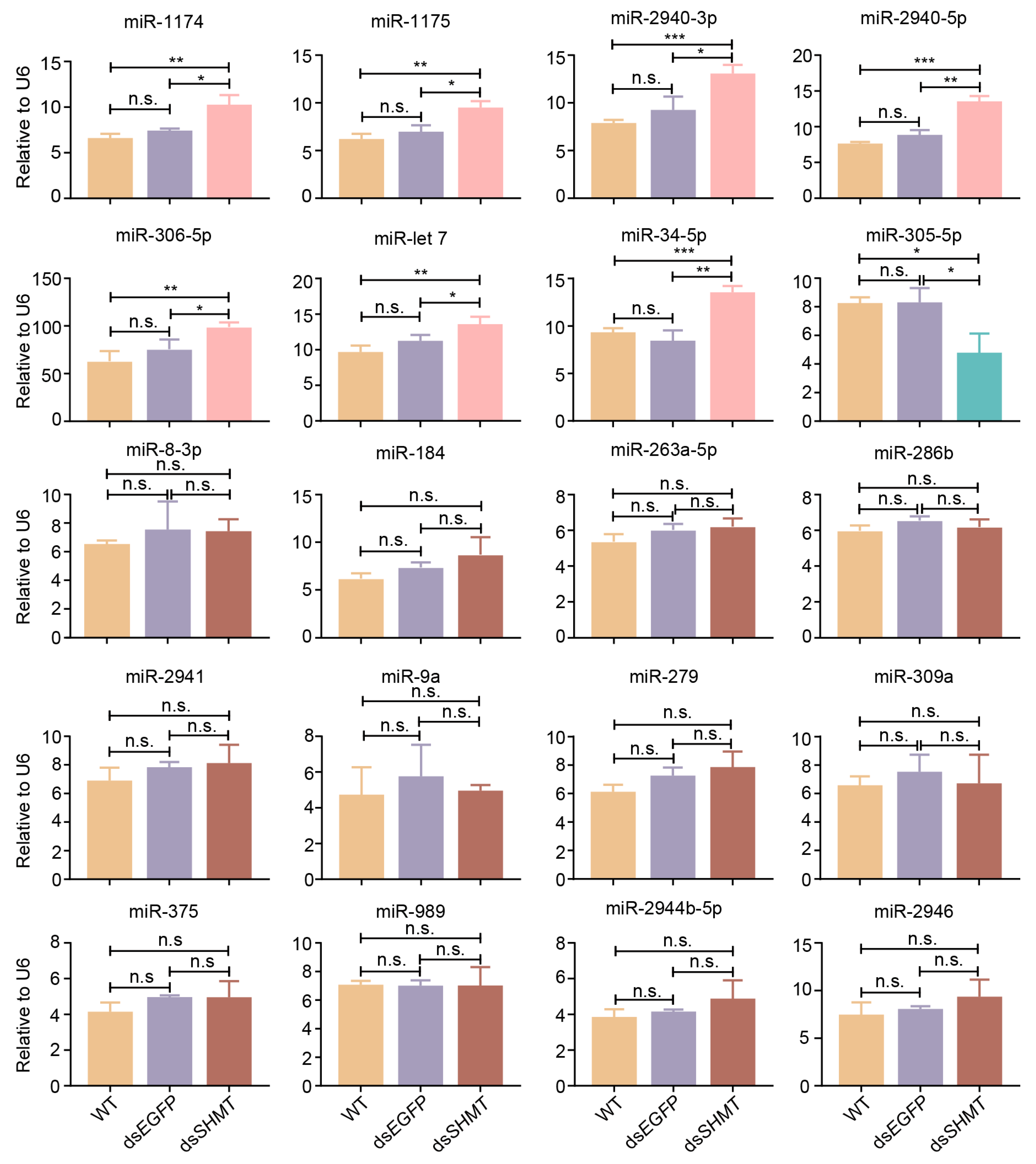
3.2. Validation of DEMs at 72 H PIJ Through Real-Time Quantitative PCR
3.3. Validation of DEMs at 15 H PBM Through Real-Time Quantitative PCR
3.4. Biological Roles of Differentially Expressed microRNAs
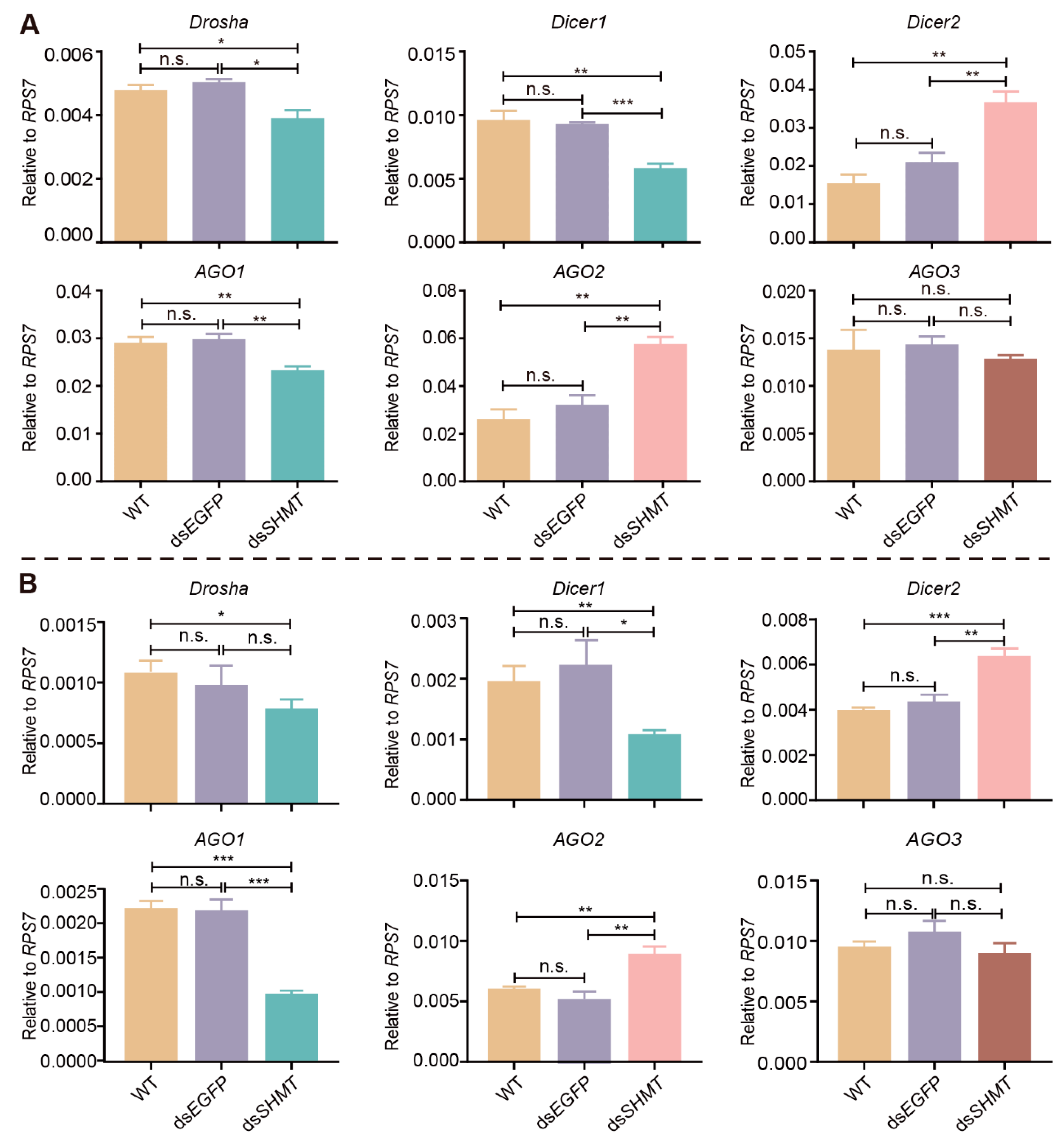
3.5. SHMT Knockdown Influences the miRNA Biosynthesis Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pajor, M.J.; Long, B.; Liang, S.Y. Dengue: A focused review for the emergency clinician. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2024, 82, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.F.; Long, C.M.; Poh, C.L. Current status of the development of dengue vaccines. Vaccine X 2025, 22, 100604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Yu, X.; Wang, P.; Cheng, G. Arbovirus lifecycle in mosquito: Acquisition, propagation and transmission. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2019, 21, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.J.; Higgs, S.; Horne, K.M.; Vanlandingham, D.L. Flavivirus-mosquito interactions. Viruses 2014, 6, 4703–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffman, E.B.; Kramer, L.D. Zika Virus Mosquito Vectors: Competence, Biology, and Vector Control. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216 (Suppl. 10), S976–S990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.P. Dengue fever and dengue virus in the People’s Republic of China. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo-Cortes, A.; Mejia-Jaramillo, A.M.; Granada, Y.; Coatsworth, H.; Lowenberger, C.; Triana-Chavez, O. The Midgut Microbiota of Colombian Aedes aegypti Populations with Different Levels of Resistance to the Insecticide Lambda-cyhalothrin. Insects 2020, 11, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comandatore, F.; Damiani, C.; Cappelli, A.; Ribolla, P.E.M.; Gasperi, G.; Gradoni, F.; Capelli, G.; Piazza, A.; Montarsi, F.; Mancini, M.V.; et al. Phylogenomics Reveals that Asaia Symbionts from Insects Underwent Convergent Genome Reduction, Preserving an Insecticide-Degrading Gene. mBio 2021, 12, e00106-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fan, J.; Yu, L.; Nie, M.; Zhang, Z.; Han, Q.; Liao, C. Analysis of Midgut Bacterial Communities in Larvae and Adult Mosquitoes of Aedes aegypti Invaded by Three Different Microorganisms. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Niu, G.; Hooker-Romera, D.; Shabani, S.; Ramelow, J.; Wang, X.; Butler, N.S.; James, A.A.; Li, J. Targeting plasmodium alpha-tubulin-1 to block malaria transmission to mosquitoes. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1132647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, H.M.; Crampton, J.M.; della Torre, A.; Sinden, R.; Crisanti, A. Members of a trypsin gene family in Anopheles gambiae are induced in the gut by blood meal. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 2891–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borovsky, D. Biosynthesis and control of mosquito gut proteases. IUBMB Life 2003, 55, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.N.; Shi, S.R.; Zhang, X.Y.; Xin, G.S.; Zou, X.; Li, W.L.; Guo, S.D. Targeting PDGF/PDGFR Signaling Pathway by microRNA, lncRNA, and circRNA for Therapy of Vascular Diseases: A Narrow Review. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciavarella, C.; Motta, I.; Capri, M.; Gargiulo, M.; Pasquinelli, G. Heterogeneity and Differentiation of the Human Arterial Tree: Focus on microRNA Expression in Vascular Disease. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanek, J.; Tretyn, A. MicroRNA-Mediated Regulation of Histone-Modifying Enzymes in Cancer: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puthiyakunnon, S.; Yao, Y.; Li, Y.; Gu, J.; Peng, H.; Chen, X. Functional characterization of three MicroRNAs of the Asian tiger mosquito, Aedes albopictus. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, B.; Macdonald, W.; Raikhel, A.S. microRNA miR-275 is indispensable for blood digestion and egg development in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 22391–22398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Lucas, K.J.; Saha, T.T.; Ha, J.; Ling, L.; Kokoza, V.A.; Roy, S.; Raikhel, A.S. MicroRNA-275 targets sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ adenosine triphosphatase (SERCA) to control key functions in the mosquito gut. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Kokoza, V.A.; Zhang, C.; Aksoy, E.; Raikhel, A.S. MicroRNA-277 targets insulin-like peptides 7 and 8 to control lipid metabolism and reproduction in Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8017–E8024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Roy, S.; Saha, T.T.; Kokoza, V.A.; Li, M.; Raikhel, A.S. microRNA-309 targets the Homeobox gene SIX4 and controls ovarian development in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E4828–E4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Ji, Y.; Chang, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zou, Z. The accumulation of modular serine protease mediated by a novel circRNA sponging miRNA increases Aedes aegypti immunity to fungus. BMC Biol. 2024, 22, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, L.; Shi, M.; Cao, T.; Yuan, H.; Wang, R.; Wang, W.; She, Y.; Wang, C.; Zeng, Q.; Mao, W.; et al. Wolbachia mediates crosstalk between miRNA and Toll pathways to enhance resistance to dengue virus in Aedes aegypti. PLoS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1012296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, K.J.; Roy, S.; Ha, J.; Gervaise, A.L.; Kokoza, V.A.; Raikhel, A.S. MicroRNA-8 targets the Wingless signaling pathway in the female mosquito fat body to regulate reproductive processes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1440–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzec, S.; Siperstein, A.; Zhou, A.; Holzapfel, C.M.; Bradshaw, W.E.; Meuti, M.E.; Armbruster, P.A. MicroRNA Expression Prior to Biting in a Vector Mosquito Anticipates Physiological Processes Related to Energy Utilization, Reproduction and Immunity. Insects 2023, 14, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Lucas, K.J.; Roy, S.; Ha, J.; Raikhel, A.S. Mosquito-specific microRNA-1174 targets serine hydroxymethyltransferase to control key functions in the gut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14460–14465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Xu, Y.; Pu, Q.; Zhao, L.; Wei, T.; Fan, T.; Lou, Y.; et al. Combined analysis of the proteome and metabolome provides insight into microRNA-1174 function in Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Parasites Vectors 2023, 16, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, M.J.; Hunter, C.J.; Zhang, Z.; TeSlaa, T.; Xu, X.; Ducker, G.S.; Rabinowitz, J.D. Glycine homeostasis requires reverse SHMT flux. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 103–115.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; He, R.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Wu, M.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, T. Elucidation of the Role of SHMT2 in L-Serine Homeostasis in Hypoxic Hepa1-6 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, Y.; Oe, C.; Iwama, K.; Suzuki, S.; Nishiyama, A.; Hasegawa, K.; Okuda, H.; Hirata, K.; Ueno, M.; Kawaji, K.; et al. Serine hydroxymethyltransferase as a potential target of antibacterial agents acting synergistically with one-carbon metabolism-related inhibitors. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, F.; Kriebel, M.; Clever, M.; Gröning, S.; Großhans, J. Essential Function of the Serine Hydroxymethyl Transferase (SHMT) Gene During Rapid Syncytial Cell Cycles in Drosophila. G3 2017, 7, 2305–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Situ, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liao, W.; Liang, Q.; Lu, L.; Xu, Q.; Chen, J.; Lu, X.; Cui, Y.; Shao, Z.; et al. SHMT as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Renal Cell Carcinoma. Front. Biosci. 2023, 28, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Jung, S.N.; Lim, M.A.; Oh, C.; Piao, Y.; Kim, H.J.; Nguyena, Q.; Kang, Y.E.; Chang, J.W.; Won, H.R.; et al. SHMT2 Induces Stemness and Progression of Head and Neck Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, M.; Du, T.; Hou, Z.; You, S.; Zhang, S.; Ji, M.; Xue, N.; Chen, X. SHMT2 Promotes Gastric Cancer Development through Regulation of HIF1alpha/VEGF/STAT3 Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, J.; Pu, Q.; Peng, X.; Xu, L.; Liu, S. Serine hydroxymethyltransferase controls blood-meal digestion in the midgut of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.D.; Wakefield, M.J.; Smyth, G.K.; Oshlack, A. Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: Accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Araki, M.; Goto, S.; Hattori, M.; Hirakawa, M.; Itoh, M.; Katayama, T.; Kawashima, S.; Okuda, S.; Tokimatsu, T.; et al. KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D480–D484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Cai, T.; Olyarchuk, J.G.; Wei, L. Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3787–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heid, C.A.; Stevens, J.; Livak, K.J.; Williams, P.M. Real time quantitative PCR. Genome Res. 1996, 6, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winer, J.; Jung, C.K.; Shackel, I.; Williams, P.M. Development and validation of real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction for monitoring gene expression in cardiac myocytes in vitro. Anal. Biochem. 1999, 270, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, Y.Y.; Kim, V.N. The biogenesis and regulation of animal microRNAs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2024, 26, 276–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Tang, X.; Yu, L.; Dong, L.; Chen, D. MiR-218-5p Suppresses the Killing Effect of Natural Killer Cell to Lung Adenocarcinoma by Targeting SHMT1. Yonsei Med. J. 2019, 60, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Kim, D.; Chun, C.H.; Jin, E.J. miR-370 and miR-373 regulate the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis by modulating one-carbon metabolism via SHMT-2 and MECP-2, respectively. Aging Cell 2015, 14, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Tayebi, H.M.; Hosny, K.A.; Esmat, G.; Breuhahn, K.; Abdelaziz, A.I. miR-615-5p is restrictedly expressed in cirrhotic and cancerous liver tissues and its overexpression alleviates the tumorigenic effects in hepatocellular carcinoma. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 3309–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Deng, L.; Tang, D.; Ying, G.; Yao, X.; Liu, F.; Liang, G. miR-615-5p prevents proliferation and migration through negatively regulating serine hydromethyltransferase 2 (SHMT2) in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 6813–6821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Tan, J.; Guo, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhan, Q. Exosome-mediated transfer of circ_0063526 enhances cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells via regulating miR-449a/SHMT2 axis. Anticancer Drugs 2022, 33, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, E.; Raikhel, A.S. Juvenile hormone regulation of microRNAs is mediated by E75 in the Dengue vector mosquito Aedes aegypti. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2102851118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Pu, Q.; Luo, C.; Xu, L.; Peng, X.; Liu, S. Genetic manipulation of microRNAs in the silk gland of silkworm, Bombyx mori. Biol. Proced. Online 2019, 21, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Luo, C.; Pu, Q.; Yin, Q.; Xu, L.; Peng, X.; Ma, S.; Xia, Q.; Liu, S. Let-7 microRNA is a critical regulator in controlling the growth and function of silk gland in the silkworm. RNA Biol. 2020, 17, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, F.; Yang, F.; Meng, Z.; Zeng, Y. Selectivity of Exportin 5 binding to human precursor microRNAs. RNA Biol. 2021, 18 (Suppl. 2), 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; Lee, S.; Senavirathne, G.; Lai, E.C. microRNAs in action: Biogenesis, function and regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2023, 24, 816–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Yu, X.; Hu, S.; Yu, J. A brief review on the mechanisms of miRNA regulation. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2009, 7, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhao, M.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, X.; Ding, C.; Ma, C.; Lu, J.; Yue, X. SHMT2 promotes papillary thyroid cancer metastasis through epigenetic activation of AKT signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, M.; Mihanfar, A.; Akbarzadeh, S.; Yousefi, B.; Majidinia, M. Crosstalk between miRNA and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in cancer. Life Sci. 2021, 285, 119984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, S. SHMT2 regulates esophageal cancer cell progression and immune Escape by mediating m6A modification of c-myc. Cell Biosci. 2023, 13, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghrayeb, A.; Finney, A.C.; Agranovich, B.; Peled, D.; Anand, S.K.; McKinney, M.P.; Sarji, M.; Yang, D.; Weissman, N.; Drucker, S.; et al. Serine synthesis via reversed SHMT2 activity drives glycine depletion and acetaminophen hepatotoxicity in MASLD. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 116–129.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadotto, V.; Giambruno, R.; Massignani, E.; Mihailovich, M.; Maniaci, M.; Patuzzo, F.; Ghini, F.; Nicassio, F.; Bonaldi, T. PRMT1-mediated methylation of the microprocessor-associated proteins regulates microRNA biogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 96–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Yu, X.; Duan, M.; Shi, N. Recent advances in methylation modifications of microRNA. Genes Dis. 2025, 12, 101201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
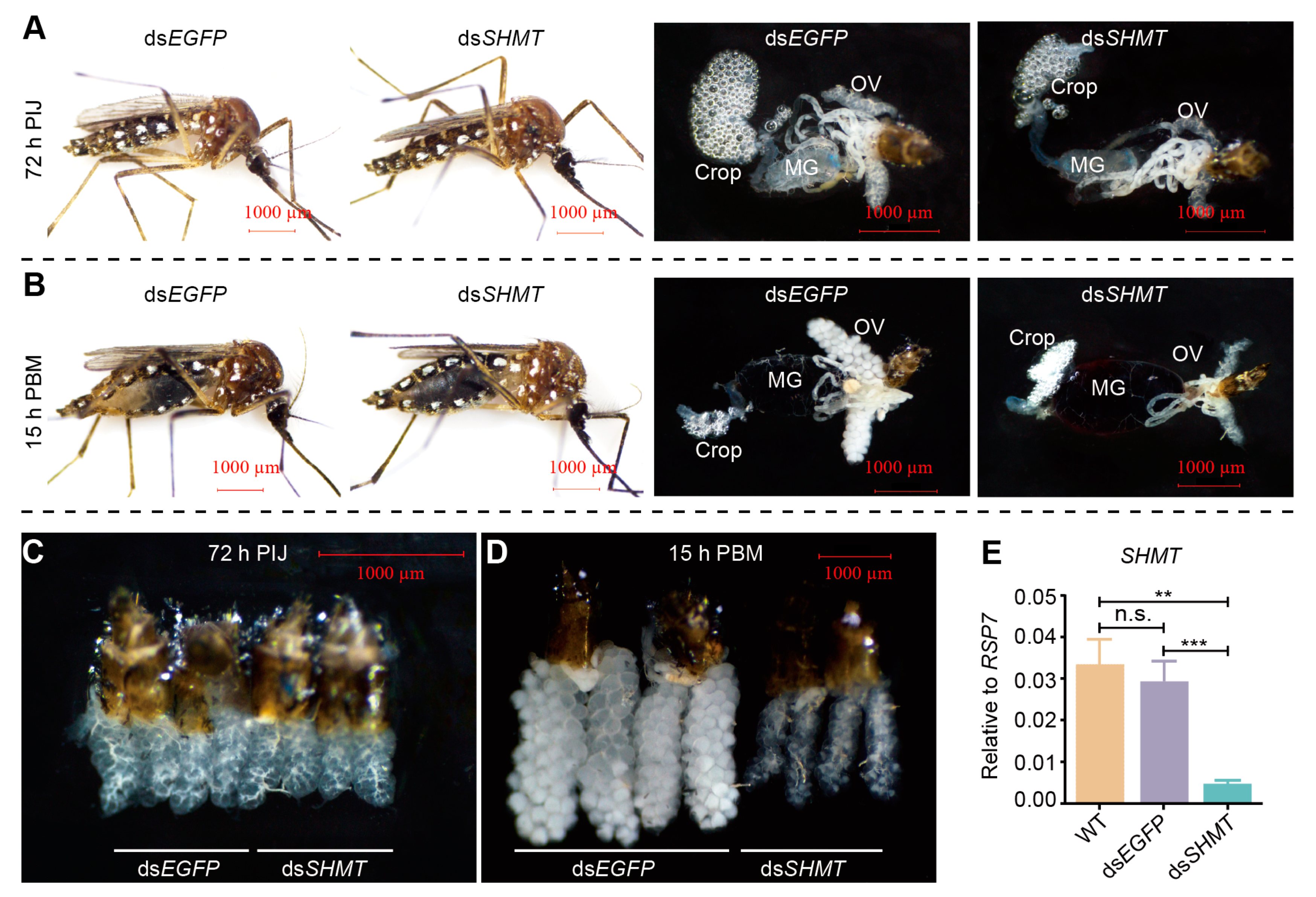
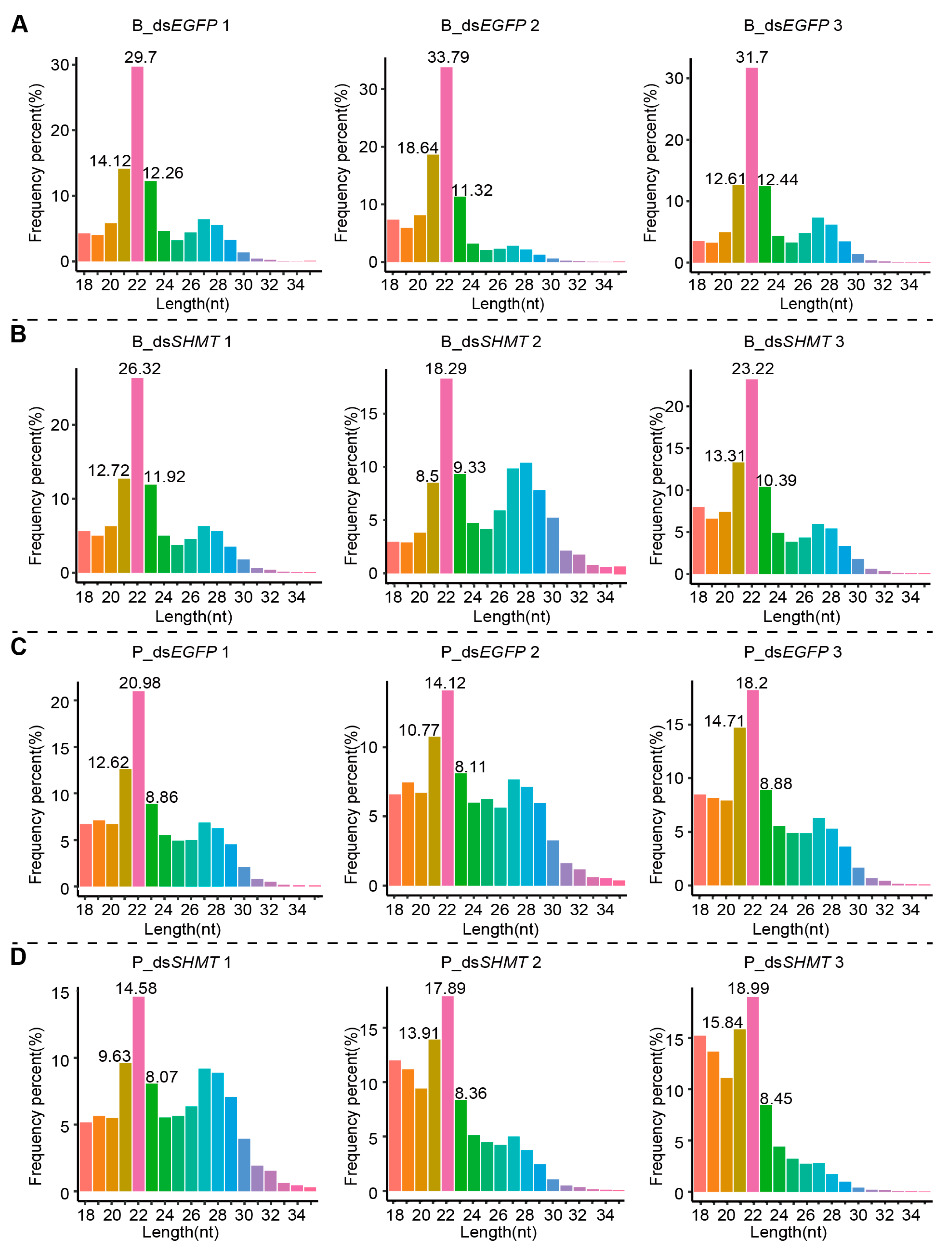
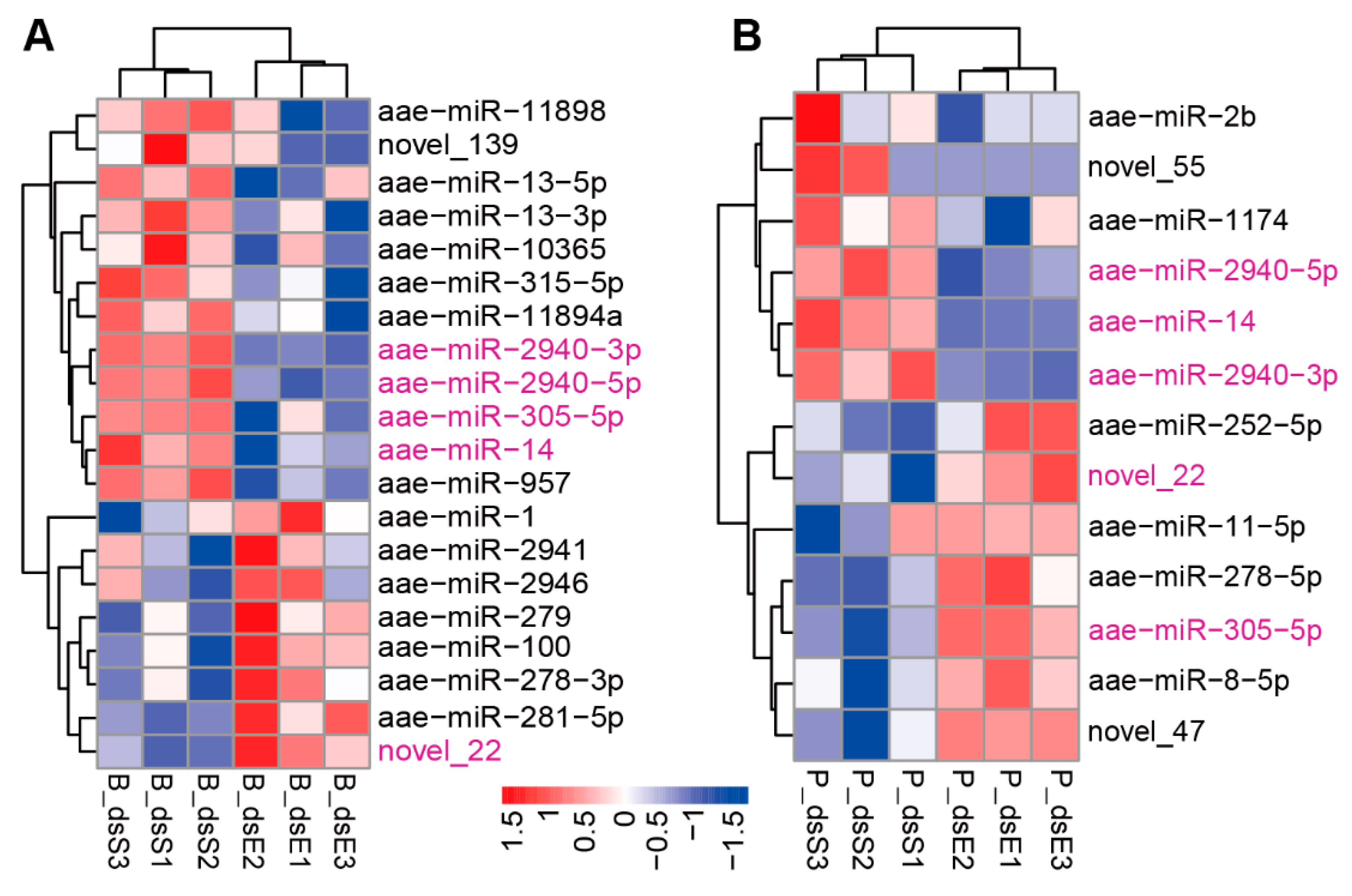
| miRNA | B_dsS_Readcount | B_dsE_Readcount | Log2foldchange | p-Val | p-Adj | Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aae-miR-2940-3p | 38,503.96064 | 17,963.88509 | 1.099846276 | 1.27 × 10−22 | 2.75 × 10−20 | up |
| aae-miR-2940-5p | 28,776.17523 | 14,239.18183 | 1.015030016 | 1.31 × 10−15 | 1.42 × 10−13 | up |
| aae-miR-10365 | 1672.989849 | 1303.784612 | 0.358497771 | 0.038818301 | 0.479559669 | up |
| aae-miR-11894a | 1222.489078 | 887.4538831 | 0.46232103 | 0.003855015 | 0.118954763 | up |
| aae-miR-11898 | 41.06098255 | 21.5461849 | 0.95894345 | 0.021603411 | 0.40864567 | up |
| aae-miR-13-3p | 22,546.40415 | 18,133.37452 | 0.314187719 | 0.011490061 | 0.248185318 | up |
| aae-miR-13-5p | 349.6802822 | 246.7725908 | 0.496899458 | 0.024177837 | 0.40864567 | up |
| aae-miR-14 | 74,719.97782 | 58,674.92568 | 0.348711384 | 0.008823778 | 0.211770679 | up |
| aae-miR-305-5p | 11,070.20678 | 6645.786433 | 0.735803189 | 5.85 × 10−5 | 0.003160797 | up |
| aae-miR-315-5p | 15,999.77039 | 13,614.42772 | 0.232868934 | 0.040695943 | 0.479559669 | up |
| aae-miR-957 | 13,867.09344 | 11,558.02215 | 0.262582036 | 0.024594415 | 0.40864567 | up |
| aae-miR-1 | 372,756.3313 | 436,433.1172 | −0.227531884 | 0.046939287 | 0.479559669 | down |
| aae-miR-100 | 226,244.2959 | 263,694.4811 | −0.22098482 | 0.033555478 | 0.472595793 | down |
| aae-miR-278-3p | 5759.313951 | 7506.544882 | −0.382049339 | 0.001315148 | 0.056814412 | down |
| aae-miR-279 | 15,401.80793 | 19,926.74112 | −0.371521561 | 0.002496829 | 0.089885837 | down |
| aae-miR-281-5p | 80,276.02829 | 100,106.3372 | −0.318492468 | 0.004670184 | 0.126094959 | down |
| aae-miR-2941 | 6771.211175 | 8089.190071 | −0.256322377 | 0.048873163 | 0.479559669 | down |
| aae-miR-2946 | 2113.090291 | 2587.873342 | −0.292018987 | 0.035007096 | 0.472595793 | down |
| novel_22 | 73.83129566 | 166.6737009 | −1.167479519 | 1.76 × 10−6 | 0.000126948 | down |
| miRNA | P_dsS_Readcount | P_dse_Readcount | Log2foldchange | p-Val | p-Adj | Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aae-miR-11-5p | 1664.66266 | 2356.000046 | −0.498733975 | 0.041077109 | 0.680571033 | up |
| aae-miR-1174 | 6353.65955 | 4130.419729 | 0.621354561 | 0.013352252 | 0.299683875 | up |
| aae-miR-14 | 1,9701.04808 | 15,953.54525 | 0.30438114 | 0.003283273 | 0.132644239 | up |
| aae-miR-2940-3p | 10,621.09158 | 7665.246502 | 0.470924008 | 9.40 × 10−6 | 0.000949497 | up |
| aae-miR-2940-5p | 9800.348606 | 7564.805556 | 0.373575047 | 0.005986621 | 0.201549588 | up |
| aae-miR-2b | 2862.942607 | 2230.901831 | 0.35811565 | 0.043799126 | 0.680571033 | up |
| novel_55 | 4.104653461 | 0 | 4.622962489 | 0.031714775 | 0.64063846 | up |
| aae-miR-252-5p | 3330.881667 | 3923.49034 | −0.236519613 | 0.036052746 | 0.662059515 | down |
| aae-miR-278-5p | 125.7710599 | 185.1747529 | −0.547435742 | 0.009131322 | 0.239686085 | down |
| aae-miR-305-5p | 15,072.75569 | 26176.11006 | −0.796115398 | 1.59 × 10−9 | 3.20 × 10−7 | down |
| aae-miR-8-5p | 4121.121114 | 4987.051375 | −0.27482532 | 0.009492518 | 0.239686085 | down |
| novel_22 | 363.33811 | 595.7105685 | −0.717321745 | 0.00058874 | 0.0396418 | down |
| novel_47 | 36.58597513 | 72.55578887 | −0.957760648 | 0.002476551 | 0.125065816 | down |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pu, Q.; Han, Y.; Su, Z.; Ren, H.; Ou, Q.; Kashyap, S.; Liu, S. Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase Modulates Midgut Physiology in Aedes aegypti Through miRNA Regulation: Insights from Small RNA Sequencing and Gene Expression Analysis. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050644
Pu Q, Han Y, Su Z, Ren H, Ou Q, Kashyap S, Liu S. Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase Modulates Midgut Physiology in Aedes aegypti Through miRNA Regulation: Insights from Small RNA Sequencing and Gene Expression Analysis. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(5):644. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050644
Chicago/Turabian StylePu, Qian, Yujiao Han, Zhuanzhuan Su, Houming Ren, Qingshan Ou, Symphony Kashyap, and Shiping Liu. 2025. "Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase Modulates Midgut Physiology in Aedes aegypti Through miRNA Regulation: Insights from Small RNA Sequencing and Gene Expression Analysis" Biomolecules 15, no. 5: 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050644
APA StylePu, Q., Han, Y., Su, Z., Ren, H., Ou, Q., Kashyap, S., & Liu, S. (2025). Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase Modulates Midgut Physiology in Aedes aegypti Through miRNA Regulation: Insights from Small RNA Sequencing and Gene Expression Analysis. Biomolecules, 15(5), 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050644







