Mechanistic Role of the Mdm2/MdmX Lid Domain in Regulating Their Interactions with p53
Abstract
1. Introduction
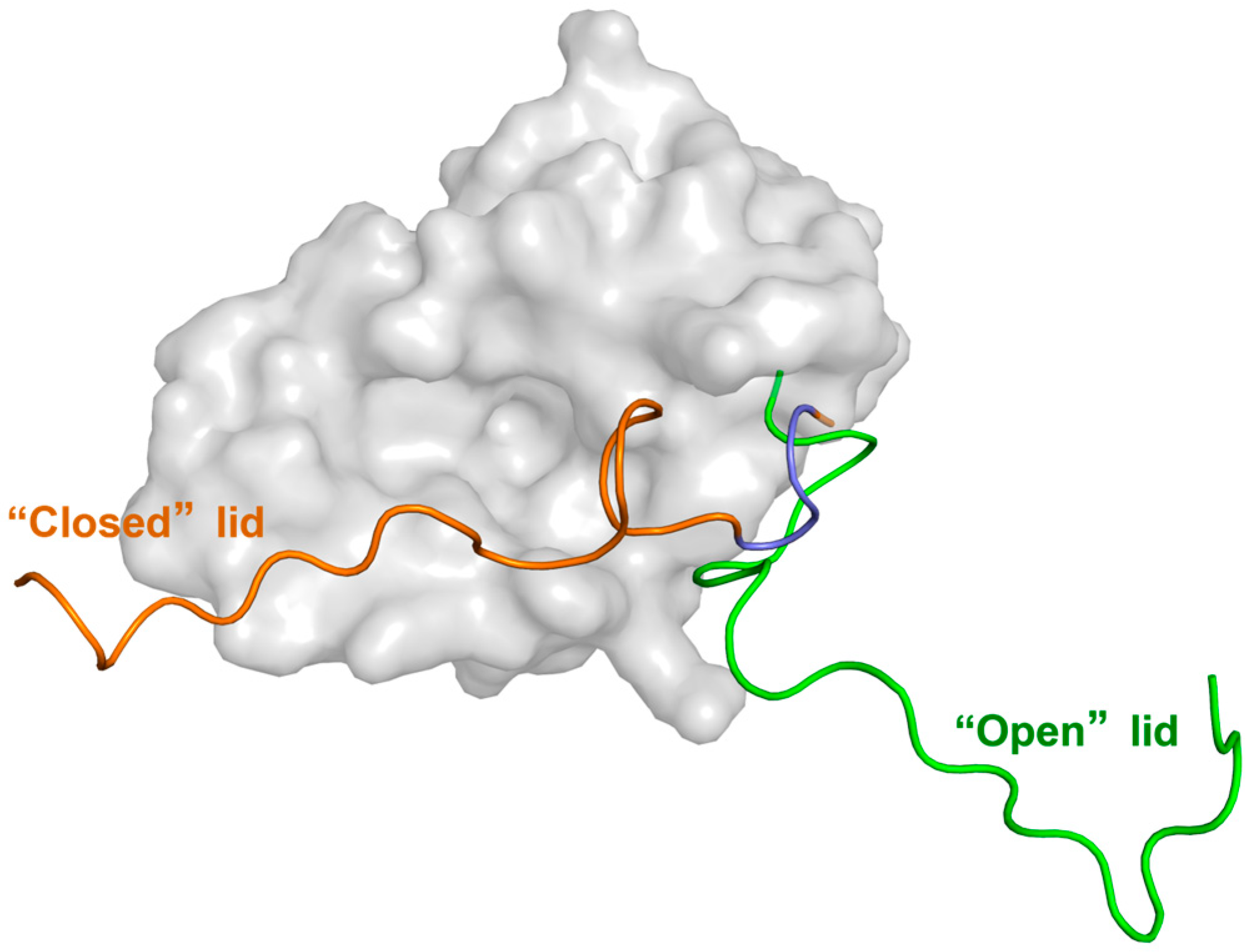
2. Conformational Behavior of the Lid in the Free (Apo) and p53-Bound (Holo) States
2.1. Detection of the Conformational Dynamics of the Lid Using NMR Method
2.2. Investigating the Function of the Lid Through MD Simulation
2.3. The Regulatory Mechanism of the Lid Investigated Through Affinity Assays
3. The Influence of Protein Phosphorylation Modifications on the Binding of Mdm2/MdmX to p53
3.1. The Impact of Lid Ser17 Phosphorylation on Mdm2-p53 Binding
3.2. The Effect of Tyr55/Tyr99 Phosphorylation on the Structure and Function of the MdmX Lid
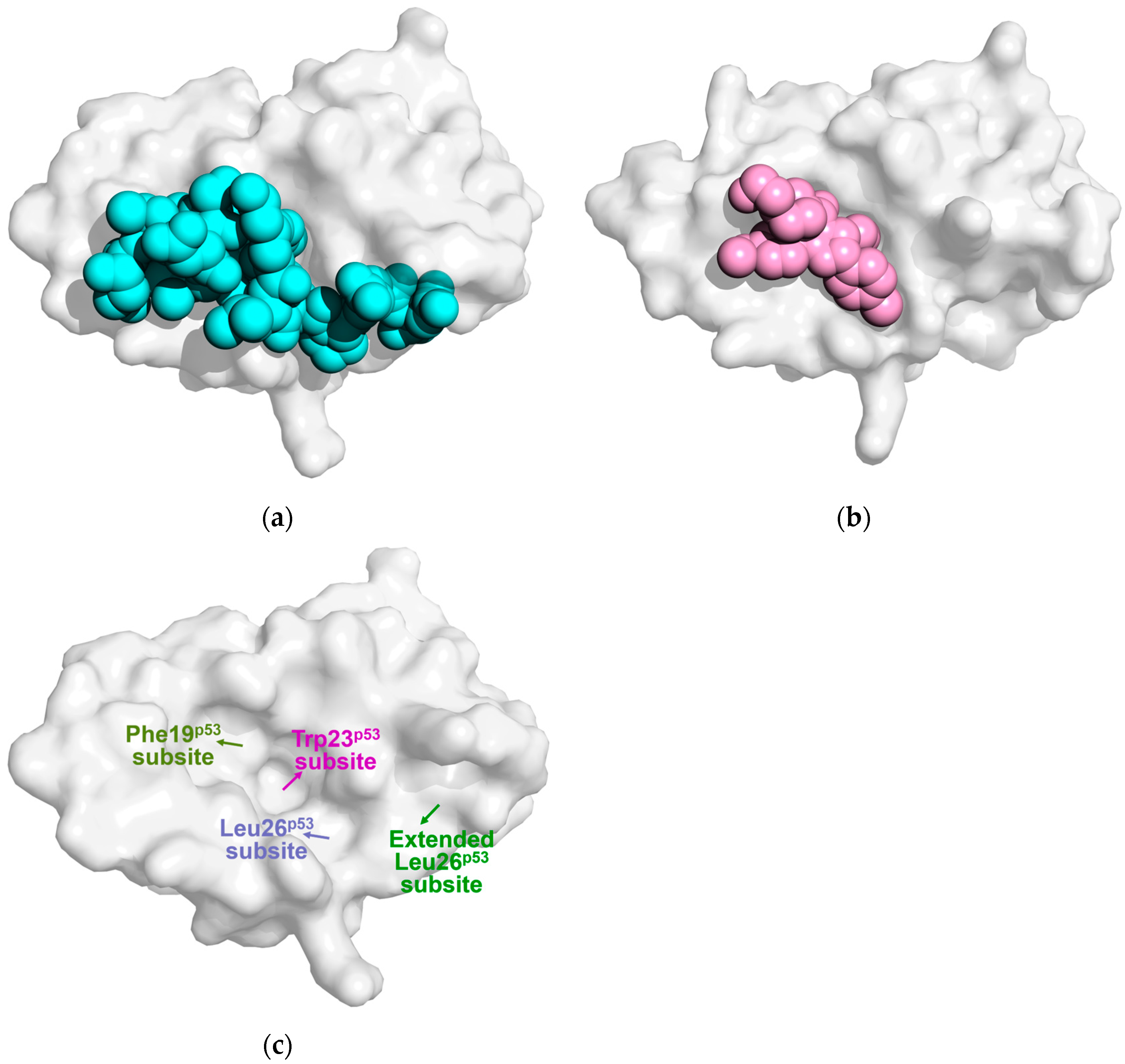
4. The Influence of the Lid on Mdm2/MdmX Protein Binding to Small Molecule Inhibitors
4.1. The Impact of the Lid on the Binding of the Porphyrin Compound Nutlin-3a
4.2. The Effect of the Lid on the Binding of Piperidone-Based Inhibitors
4.3. The Impact of the Lid on the Binding of Other Inhibitors
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Su, Z.; Tavana, O.; Gu, W. Understanding the complexity of p53 in a new era of tumor suppression. Cancer Cell 2024, 42, 946–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, M.; Li, Y.; Wahl, G.M. MDM2, MDMX and p53 in oncogenesis and cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macchiarulo, A.; Giacche, N.; Carotti, A.; Moretti, F.; Pellicciari, R. Expanding the horizon of chemotherapeutic targets: From MDM2 to MDMX (MDM4). Medchemcomm 2011, 2, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karni-Schmidt, O.; Lokshin, M.; Prives, C. The roles of MDM2 and MDMX in cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2016, 11, 617–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heltberg, M.L.; Chen, S.; Jimenez, A.; Jambhekar, A.; Jensen, M.H.; Lahav, G. Inferring leading interactions in the p53/mdm2/mdmx circuit through live-cell imaging and modeling. Cell Syst. 2019, 9, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, R.; Tanaka, H.; Yasuda, H. Oncoprotein MDM2 is a ubiquitin ligase e3 for tumor suppressor p53. FEBS Lett. 1997, 420, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Brooks, C.L.; Wu-Baer, F.; Chen, D.L.; Baer, R.; Gu, W. Mono-versus polyubiquitination: Differential control of p53 fate by mdm2. Science 2003, 302, 1972–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvarts, A.; Steegenga, W.T.; Riteco, N.; Vanlaar, T.; Dekker, P.; Bazuine, M.; Vanham, R.; Vanoordt, W.V.; Hateboer, G.; Vandereb, A.J.; et al. MDMX: A novel p53-binding protein with some functional properties of MDM2. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 5349–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, I.Y.; Lloyd, A.; Critchley, W.R.; Saikia, Q.; Jade, D.; Divan, A.; Zeqiraj, E.; Harrison, M.A.; Brown, C.J.; Ponnambalam, S. Structure and function of MDM2 and MDM4 in health and disease. Biochem. J. 2025, 482, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosztyu, P.; Slaninova, I.; Valcikova, B.; Verlande, A.; Mueller, P.; Palecek, J.J.; Uldrijan, S. A single conserved amino acid residue as a critical context-specific determinant of the differential ability of mdm2 and MdmX RING domains to dimerize. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Hu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Lu, J.; Wang, H. Cellular, structural basis, and recent progress for targeting murine double minute x (MDMX) in tumors. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 14723–14741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mccoy, M.A.; Gesell, J.J.; Senior, M.M.; Wyss, D.F. Flexible lid to the p53-binding domain of human mdm2: Implications for p53 regulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1645–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Li, H.; Luo, X.; Li, H.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Teng, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zuo, Z.; Ren, J. IBS 2.0: An upgraded illustrator for the visualization of biological sequences. Nucleic Acids. Res. 2022, 50, W420–W426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, N.; Khator, R.; Kulkarni, S.; Singh, Y.; Kumar, P.; Thareja, S. Recent advancements in the discovery of MDM2/MDM2-p53 interaction inhibitors for the treatment of cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2023, 30, 3668–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.J.; Kawai, H.; Nie, L.G.; Kitao, H.; Wiederschain, D.; Jochemsen, A.G.; Parant, J.; Lozano, G.; Yuan, Z.M. Mutual dependence of MDM2 and MDMX in their functional inactivation of p53. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 19251–19254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Albadari, N.; Du, Y.; Fowler, J.F.; Sang, H.T.; Xian, W.; Mckeon, F.; Li, W.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, R. MDM2 inhibitors for cancer therapy: The past, present, and future. Pharmacol. Rev. 2024, 76, 414–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kussie, P.H.; Gorina, S.; Marechal, V.; Elenbaas, B.; Moreau, J.; Levine, A.J.; Pavletich, N.P. Structure of the MDM2 oncoprotein bound to the p53 tumor suppressor transactivation domain. Science 1996, 274, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, P.; Brown, D.R.; Shivakumar, C.V.; Deb, S.; Deb, S.P. N-terminal 130 amino acids of MDM2 are sufficient to inhibit p53-mediated transcriptional activation. Oncogene 1995, 10, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Michelsen, K.; Jordan, J.B.; Lewis, J.; Long, A.M.; Yang, E.; Rew, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yakowec, P.; Schnier, P.D.; Huang, X.; et al. Ordering of the n-terminus of human MDM2 by small molecule inhibitors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 17059–17067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.V.; Ping Koh, D.X.; Liu, Y.; Joseph, T.L.; Lane, D.P.; Verma, C.S.; Tan, Y.S. Role of the n-terminal lid in regulating the interaction of phosphorylated MDMX with p53. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 112825–112840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, W. Functional interrogation of the n-terminal lid of MDMX in p53 binding via native chemical ligation. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 64, 1004–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Showalter, S.A.; Bruschweiler-Li, L.; Johnson, E.; Zhang, F.; Brüschweiler, R. Quantitative lid dynamics of MDM2 reveals differential ligand binding modes of the p53-binding cleft. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 6472–6478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueren-Calabuig, J.A.; Michel, J. Impact of ser17 phosphorylation on the conformational dynamics of the oncoprotein MDM2. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 2500–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhrinova, S.; Uhrin, D.; Powers, H.; Watt, K.; Zheleva, D.; Fischer, P.; Mcinnes, C.; Barlow, P.N. Structure of free MDM2 n-terminal domain reveals conformational adjustments that accompany p53-binding. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 350, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Zhao, Q.; Iwatsuki, R.; Fukui, R.; Ren, W.; Sugita, Y.; Nishida, N. Deciphering the multi-state conformational equilibrium of HDM2 in the regulation of p53 binding: Perspectives from molecular dynamics simulation and NMR analysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 9790–9800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.; Varney, K.; Yuan, W.; Zhao, L.; Lu, W. Interrogation of MDM2 phosphorylation in p53 activation using native chemical ligation: The functional role of ser17 phosphorylation in MDM2 reexamined. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6855–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantelopulos, G.A.; Mukherjee, S.; Voelz, V.A. Microsecond simulations of mdm2 and its complex with p53 yield insight into force field accuracy and conformational dynamics. Proteins 2015, 83, 1665–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Pantelopulos, G.A.; Voelz, V.A. Markov models of the apo-MDM2 lid region reveal diffuse yet two-state binding dynamics and receptor poses for computational docking. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastidar, S.G.; Lane, D.P.; Verma, C.S. Multiple peptide conformations give rise to similar binding affinities: Molecular simulations of p53-MDM2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 13514–13515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastidar, S.G.; Lane, D.P.; Verma, C.S. Modulation of p53 binding to MDM2: Computational studies reveal important roles of tyr100. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastidar, S.G.S.G.; Raghunathan, D.; Nicholson, J.; Hupp, T.R.; Lane, D.P.; Verma, C.S. Chemical states of the n-terminal “lid” of MDM2 regulate p53 binding: Simulations reveal complexities of modulation. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkhivker, G.M. Simulating molecular mechanisms of the MDM2-mediated regulatory interactions: A conformational selection model of the MDM2 lid dynamics. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueren-Calabuig, J.A.; Michel, J. Elucidation of ligand-dependent modulation of disorder-order transitions in the oncoprotein MDM2. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciemny, M.P.; Debinski, A.; Paczkowska, M.; Kolinski, A.; Kurcinski, M.; Kmiecik, S. Protein-peptide molecular docking with large-scale conformational changes: The p53-MDM2 interaction. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Martinez, C.; Papadourakis, M.; Llabres, S.; Gupta, A.A.; Barlow, P.N.; Michel, J. Energetics of a protein disorder-order transition in small molecule recognition. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 5220–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, L.D.; Turchi, J.J.; Berberich, S.J. Mdm-2 phosphorylation by DNA-dependent protein kinase prevents interaction with p53. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 5013–5016. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, A.L.; Burch, L.; Vojtesek, B.; Mikutowska, J.; Thompson, A.; Hupp, T.R. Novel phosphorylation sites of human tumour suppressor protein p53 at ser20 and thr18 that disrupt the binding of mdm2 (mouse double minute 2) protein are modified in human cancers. Biochem. J. 1999, 342, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, S.Y.; Taya, Y.; Prives, C. DNA damage-inducible phosphorylation of p53 at n-terminal sites including a novel site, ser20, requires tetramerization. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 1815–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Hupp, T.R. Intrasteric regulation of MDM2. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003, 28, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worrall, E.G.; Wawrzynow, B.; Worrall, L.; Walkinshaw, M.; Ball, K.L.; Hupp, T.R. Regulation of the e3 ubiquitin ligase activity of MDM2 by an n-terminal pseudo-substrate motif. J. Chem Biol. 2009, 2, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worrall, E.G. Novel Concepts in mdm2 Protein Regulation. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, Scotland, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Worrall, E.G.; Worrall, L.; Blackburn, E.; Walkinshaw, M.; Hupp, T.R. The effects of phosphomimetic lid mutation on the thermostability of the n-terminal domain of MDM2. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 398, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picksley, S.M.; Vojtesek, B.; Sparks, A.; Lane, D.P. Immunochemical analysis of the interaction of p53 with MDM2;--Fine mapping of the MDM2 binding site on p53 using synthetic peptides. Oncogene 1994, 9, 2523–2529. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wallace, M.; Worrall, E.; Pettersson, S.; Hupp, T.R.; Ball, K.L. Dual-site regulation of MDM2 e3-ubiquitin ligase activity. Mol. Cell 2006, 23, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.W.; Rudiger, S.; Veprintsev, D.; Freund, S.; Fernandez-Fernandez, M.R.; Fersht, A.R. The central region of HDM2 provides a second binding site for p53. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, H.; Burch, L.R.; Smith, A.J.; Dornan, D.; Wallace, M.; Ball, K.L.; Hupp, T.R. The conformationally flexible s9-s10 linker region in the core domain of p53 contains a novel MDM2 binding site whose mutation increases ubiquitination of p53 in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 28446–28458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, J.A.; Worrall, E.G.; Lin, Y.; Landre, V.; Pettersson, S.; Blackburn, E.; Walkinshaw, M.; Muller, P.; Vojtesek, B.; Ball, K.; et al. Phosphomimetic mutation of the n-terminal lid of MDM2 enhances the polyubiquitination of p53 through stimulation of e2-ubiquitin thioester hydrolysis. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 1728–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gohain, N.; Zhan, C.; Lu, W.; Pazgier, M.; Lu, W. Structural basis of how stress-induced MDMX phosphorylation activates p53. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1919–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuckerman, V.; Lenos, K.; Popowicz, G.M.; Silberman, I.; Grossman, T.; Marine, J.; Holak, T.A.; Jochemsen, A.G.; Haupt, Y. C-abl phosphorylates hdmx and regulates its interaction with p53. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 4031–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilev, L.T.; Vu, B.T.; Graves, B.; Carvajal, D.; Podlaski, F.; Filipovic, Z.; Kong, N.; Kammlott, U.; Lukacs, C.; Klein, C.; et al. In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2. Science 2004, 303, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilev, L.T. Small-molecule antagonists of p53-MDM2 binding—Research tools and potential therapeutics. Cell Cycle 2004, 3, 419–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schon, O.; Friedler, A.; Bycroft, M.; Freund, S.; Fersht, A.R. Molecular mechanism of the interaction between MDM2 and p53. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 323, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bista, M.; Petrovich, M.; Fersht, A.R. MDMX contains an autoinhibitory sequence element. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17814–17819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| p5319–26 (nM) | p5317–28 (nM) | p5315–29 (nM) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mdm21–109 | 88,300 ± 3700 | 2250 ± 100 | 1260 ± 70 |
| Mdm225–109 | 39,600 ± 2000 | 404 ± 19 | 184 ± 14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, Q.; Li, C.; Tang, Y.; Bai, J.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Su, Z.; Cheng, X. Mechanistic Role of the Mdm2/MdmX Lid Domain in Regulating Their Interactions with p53. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050642
Wei Q, Li C, Tang Y, Bai J, Li W, Liu J, Su Z, Cheng X. Mechanistic Role of the Mdm2/MdmX Lid Domain in Regulating Their Interactions with p53. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(5):642. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050642
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Qiuyin, Chenqi Li, Yibing Tang, Jinping Bai, Wang Li, Jidong Liu, Zhengding Su, and Xiyao Cheng. 2025. "Mechanistic Role of the Mdm2/MdmX Lid Domain in Regulating Their Interactions with p53" Biomolecules 15, no. 5: 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050642
APA StyleWei, Q., Li, C., Tang, Y., Bai, J., Li, W., Liu, J., Su, Z., & Cheng, X. (2025). Mechanistic Role of the Mdm2/MdmX Lid Domain in Regulating Their Interactions with p53. Biomolecules, 15(5), 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050642






