Structural and Functional Analysis of the Human IQSEC2 S1474Qfs*133 Mutation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Molecular Modeling of Wild-Type Human IQSEC2 and S1474Qfs*133 IQSEC2 3D Protein Structures
2.2. Molecular Dynamics Relaxation of Wild-Type Human IQSEC2 and Human Mutant IQSEC2 S1474Qfs*133
2.3. Functional Analysis of IQSEC2 S1474Qfs*133
2.4. Generation of a Conditional S1474Qfs*133 IQSEC2 Mouse Line
2.5. Assessment of Ultrasonic Vocalizations in Socially Interacting Mice
2.6. Quantitation of Endogenous Mouse IQSEC2
2.6.1. RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR
2.6.2. Western Blot of Brain IQSEC2
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
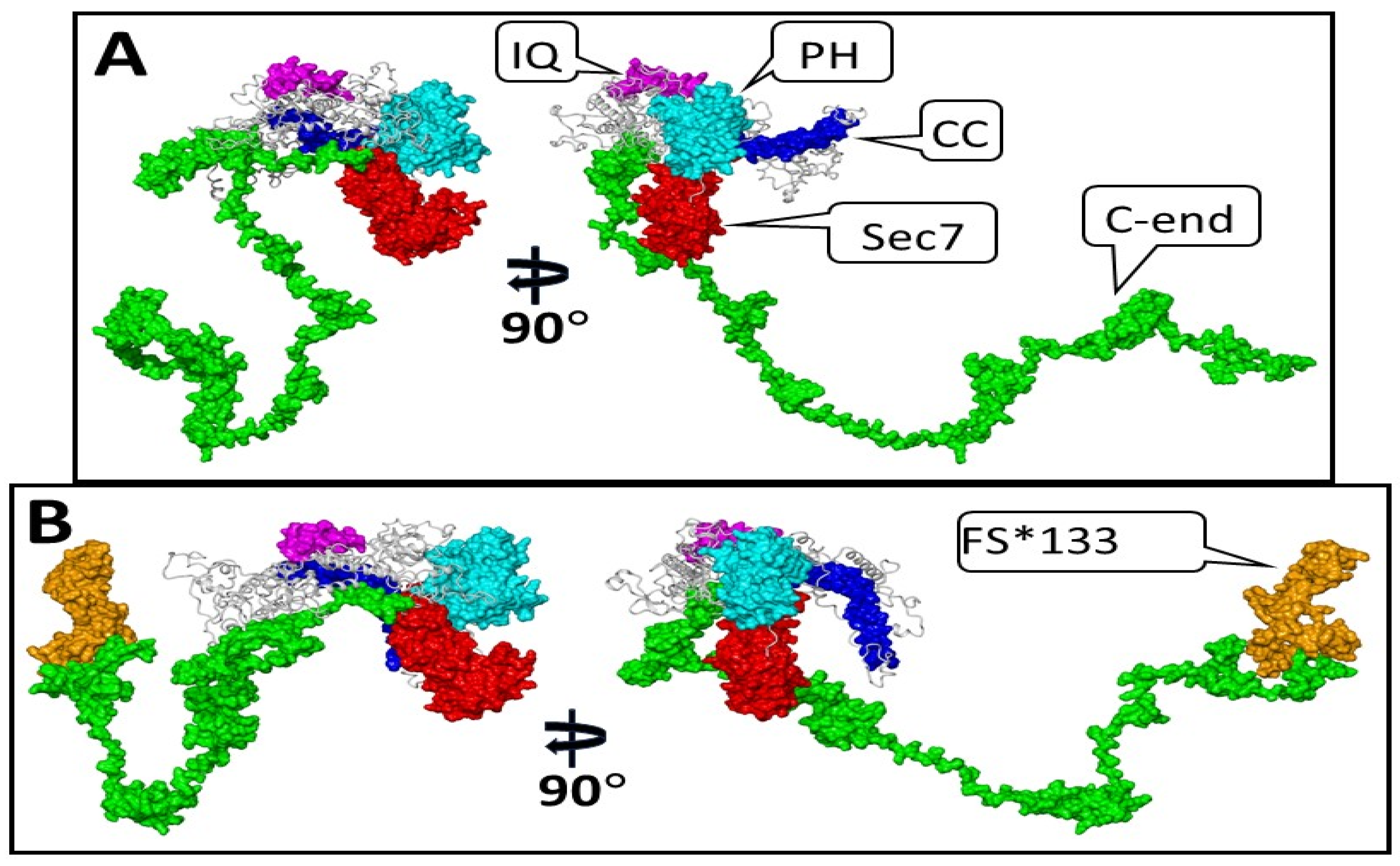
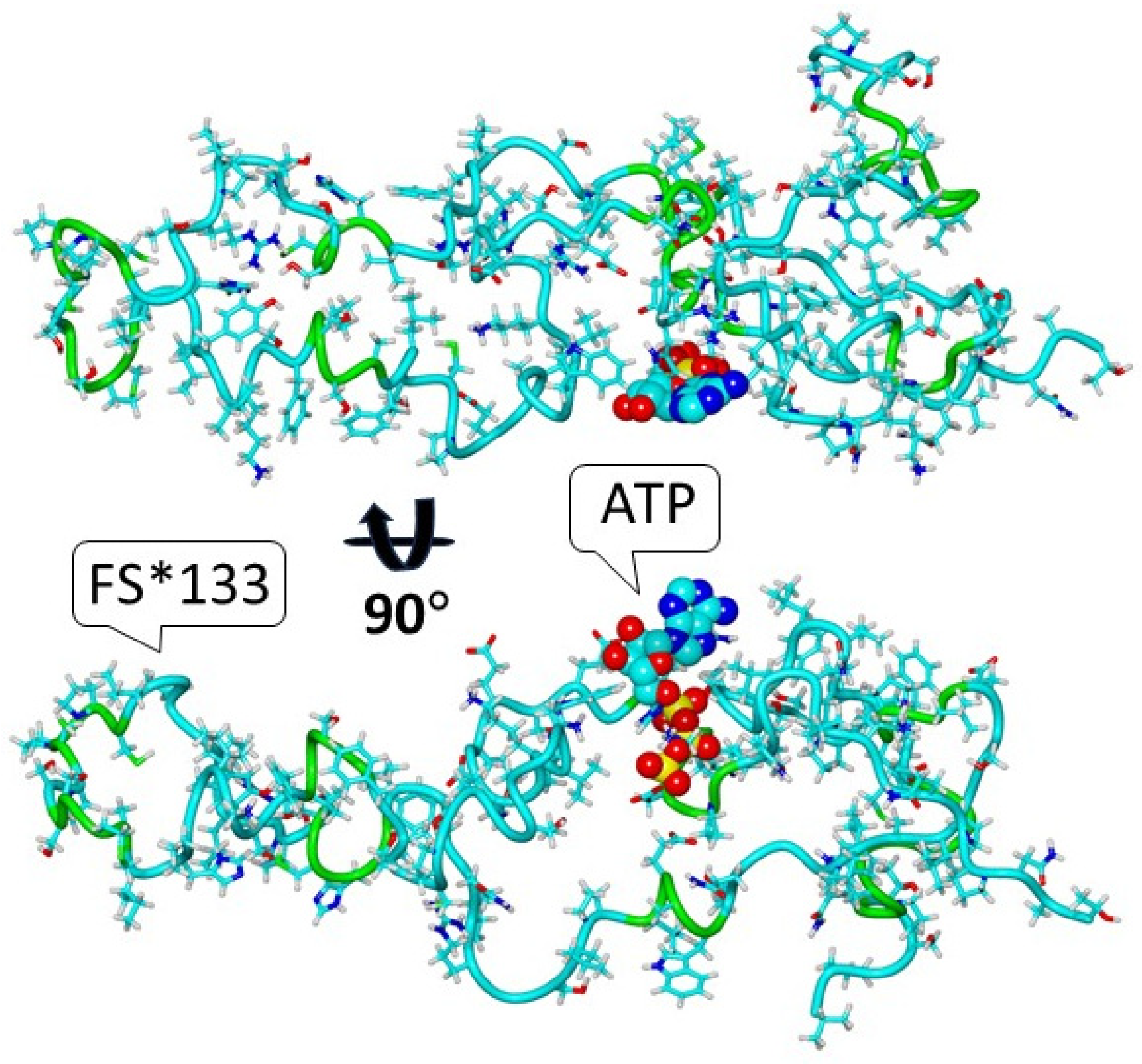
3.1. Modeling the Structure of the S1474Qfs*133 IQSEC2 Protein and the Possible Emergence of a New Functional Protein Domain in the Mutant Protein
3.2. Steady-State IQSEC2 S1474Qfs*133 Protein Is Decreased in 293T Cells and In Vivo as Compared to Wild-Type IQSEC2
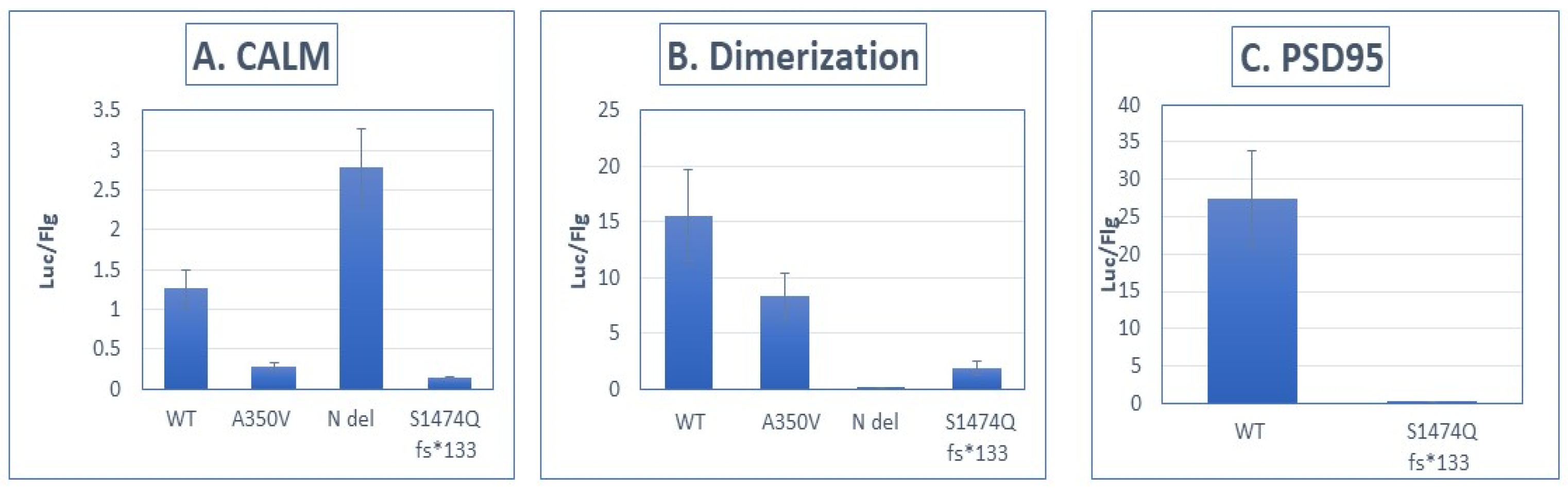
3.3. Impaired Protein Interactions of the S1474Qfs*133 Protein
- ₋
- Panel (A): Interaction strength between luciferase-tagged IQSEC2 and FLAG-tagged apocalmodulin [11]. WT—wild type IQSEC2. A350V—missense mutation of IQSEC2 in the IQ domain, previously demonstrated to impair binding of IQSEC2 to apocalmodulin [11]. N del—deletion of the N-terminal 213 amino acids of IQSEC2 [12]. S1474Qfs*133 mutant. There was an 89 ± 1% reduction in binding of the S1474Qfs*133 mutant to apocalmodulin as compared to WT IQSEC2 (n = 8 for each interacting pair, p < 0.01 between wild type and S1474Q).
- ₋
- Panel (B): Interaction strength between luciferase-tagged IQSEC2 and FLAG-tagged IQSEC2, assessing dimerization [11]. IQSEC2 has been demonstrated to dimerize as mediated by its N-terminal 213 amino acids [12]. Dimerization was assessed using the Lumier method [11]. There was an 87 ± 6% reduction in the ability of the S1474Qfs*133 mutant to dimerize as compared to WT IQSEC2 (n = 8 for each interacting pair, p < 0.01 between wild type and S1474Q).
- ₋
- Panel (C): Interaction strength between luciferase-tagged IQSEC2 and FLAG-tagged PSD-95 [11]. The interaction between IQSEC2 and PSD-95 is affected by the PDZ domain of IQSEC2, corresponding to the carboxy-terminal 4 amino acids of IQSEC2 [13]. The S1474Qfs*133 mutant had a 99 ± 0.1% reduction in binding to PSD-95 as compared to wild-type IQSEC2 (n = 8 for each interacting pair, p < 0.01 between wild type and S1474Q).
3.4. Early Mortality and Growth Retardation of S1474Qfs*133 Mice
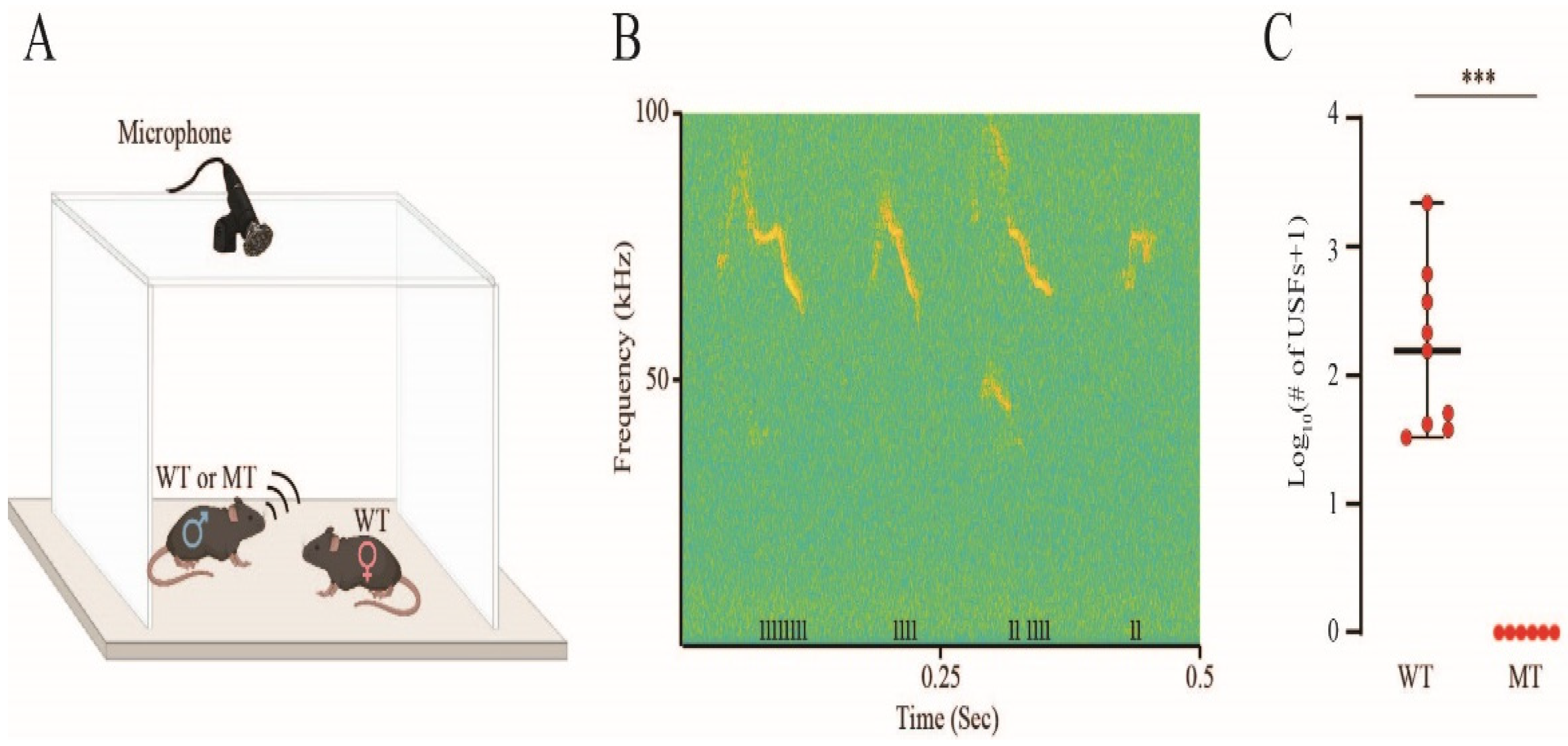
3.5. Impaired Ultrasonic Vocalizations in Socially Interacting S1474Qfs*133 Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Fs | frameshift |
| GEF | guanine exchange factor |
| 3D | three-dimensional |
| C-end | carboxy-terminal end |
| cMD | conventional molecular dynamics |
| USVs | ultrasonic vocalizations |
| USFs | ultrasonic fragments |
| ATP | adenosine triphosphate |
| CC | coiled coil |
| PH | plextrin homology |
| PSD | post-synaptic density |
| WT | wild type |
| MT | mutant |
| AAV | adeno-associated virus |
| shRNA | short hairpin RNA |
References
- Levy, N.S.; Borisov, V.; Lache, O.; Levy, A.P. Molecular insights into IQSEC2 disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoubridge, C.; Tarpey, P.S.; Abidi, F.; Ramsden, S.L.; Rujirabenjerd, S.; Murphy, J.A.; Boyle, J.; Shaw, M.; Gardner, A.; Proos, A.; et al. Mutations in the guanine nucleotide exchange factor gene IQSEC2 cause nonsyndromic intellectual disability. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 486–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, M.; Shiroshima, T.; Fukaya, M.; Sugawara, T.; Sakagami, H.; Yamazawa, K. C-terminal truncations in IQSEC2: Implications for synaptic localization, guanine nucleotide exchange factor activity, and neurological manifestations. J. Hum. Genet. 2024, 69, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radley, J.A.; O’Sullivan, R.B.G.; Turton, S.E.; Cox, H.; Vogt, J.; Morton, J.; Jones, E.; Smithson, S.; Lachlan, K.; Rankin, J.; et al. Deep phenotyping of 14 new patients with IQSEC2 variants; including monozygotic twins of discordant phenotype. Clin. Genet. 2019, 95, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokhen, M.; Albeck, A.; Borisov, V.; Israel, Y.; Levy, N.S.; Levy, A.P. Protein conformational analysis by statistical thermodynamics. Competing folding and dimerization of IQSEC2. Curr. Res. Struct. Biol. 2024, 8, 100158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, R.; Li, Y.; Omenn, G.S.; Zhang, Y. Fast and Accurate Ab Initio Protein Structure Prediction Using Deep Learning Potentials. PLoS Comp. Biol. 2022, 18, e101053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, E.; Vriend, G. YASARA view—Molecular graphics for all devices—From smartphones to workstations. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2981–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, E.; Vriend, G. New ways to boost molecular dynamics simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2015, 36, 996–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. ff14SB: Improving the accuracy of protein sidechain and backbone parameters from ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, D.A.; Aktulga, H.M.; Belfon, K.; Ben-Shalom, I.Y.; Brozell, S.R.; Cerutti, D.S. Amber 2024; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, E.J.; Jada, R.; Schagenheim-Rozales, K.; Sah, M.; Cortes, M.; Florence, M.; Levy, N.S.; Moss, R.; Walkonis, R.S.; Gerges, N.Z.; et al. An IQSEC2 mutation associated with intellectual disability and autism results in decreased surface AMPA receptors. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, K.R.; Wang, G.; Sheng, Y.; Conger, K.K.; Casanova, J.E.; Zhu, J.J. Arf6-GEF BRAG1 regulates JNK-mediated synaptic removal of GluA1-containing AMPA receptors: A new mechanism for nonsyndromic X-linked mental disorder. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 11716–11726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakagami, H.; Sanda, M.; Fukaya, M.; Myazaki, T.; Sukegawa, J.; Yanagisawa, T.; Suzuki, T.; Fukunaga, K.; Watanabe, M.; Kondo, H. IQ-ArfGEF/BRAG1 is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Arf6 that interacts with PSD-95 at post-synaptic density of excitatory synapses. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 60, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koentgen, F.; Lin, J.; Katidou, M.; Chang, I.; Khan, M.; Watts, J.; Mombaerts, P. Exclusive transmission of the embryonic stem cell derived genome through the mouse germline. Genesis 2016, 54, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabarin, R.; Levy, N.; Abergel, Y.; Berman, J.H.; Zag, A.; Netser, S.; Levy, A.P.; Wagner, S. Pharmacological modulation of AMPA receptors rescues specific impairments in social behavior associated with the A350V IQSEC2 mutation. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netser, S.; Nahardiya, G.; Weiss-Dicker, G.; Dadush, R.; Goussha, Y.; John, R.R.; Taub, M.; Werber, Y.; Sapir, N.; Yovel, Y.; et al. TrackUSF, a novel tool for automated ultrasonic vocalization analysis, reveals modified calls in a rat model of autism. BMC Biol. 2022, 20, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dautant, A.; Velours, J.; Giraud, M.F. Crystal structure of the Mg ADP-inhibited state of the yeast F1c10-ATP synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 29502–29510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.C.; Petersen, A.; Zhong, L.; Himelright, M.L.; Murphy, J.A.; Walikonis, R.S.; Gerges, N.Z. Bidirectional regulation of synaptic transmission by BRAG1/IQSEC2 and its requirement in long-term depression. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinze, S.J.; Jackson, M.R.; Lie, S.; Jolly, L.; Field, M.; Barry, S.C.; Harvey, R.J.; Shoubridge, C. Incorrect dosage of IQSEC2, a known intellectual disability and epilepsy gene, disrupts dendritic spine morphogenesis. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sah, M.; Shore, A.N.; Petri, S.; Kanber, A.; Yang, M.; Weston, M.C.; Frankel, W.N. Altered excitatory transmission onto hippocampal interneurons in the IQSEC2 mouse model of X linked neurodevelopmental disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 137, 104758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, A.; Shirai, Y.; Kouyama-Suzuki, E.; Zhou, N.; Yoshizawa, T.; Yanagawa, T.; Mori, T.; Tabuchi, K. IQSEC2 deficiency results in abnormal social behaviors relevant to autism by affecting functions of neural circuits in the medial prefrontal cortex. Cells 2021, 10, 2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Israel, Y.; Lowenkamp, A.; Shokhen, M.; Netser, S.; Wagner, S.; Zarowin, J.; Orth, S.; Borisov, V.; Lache, O.; Levy, N.S.; et al. Structural and Functional Analysis of the Human IQSEC2 S1474Qfs*133 Mutation. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 635. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050635
Israel Y, Lowenkamp A, Shokhen M, Netser S, Wagner S, Zarowin J, Orth S, Borisov V, Lache O, Levy NS, et al. Structural and Functional Analysis of the Human IQSEC2 S1474Qfs*133 Mutation. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(5):635. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050635
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsrael, Yonat, Aaron Lowenkamp, Michael Shokhen, Shai Netser, Shlomo Wagner, Joseph Zarowin, Shaun Orth, Veronika Borisov, Orit Lache, Nina S. Levy, and et al. 2025. "Structural and Functional Analysis of the Human IQSEC2 S1474Qfs*133 Mutation" Biomolecules 15, no. 5: 635. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050635
APA StyleIsrael, Y., Lowenkamp, A., Shokhen, M., Netser, S., Wagner, S., Zarowin, J., Orth, S., Borisov, V., Lache, O., Levy, N. S., & Levy, A. P. (2025). Structural and Functional Analysis of the Human IQSEC2 S1474Qfs*133 Mutation. Biomolecules, 15(5), 635. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050635





