Dissecting the Emerging Regulatory and Mechanistic Paradigms of Transcribed Conserved Non-Coding Elements in Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preprocessing of Breast Cancer RNA-Seq Data
2.2. Extraction of Known CNEs, Excluded Regions, and Independent Transcribed Regions
2.3. Identification Pipeline for TCNEs
2.4. Validation of the Identified TCNEs
2.5. Construction of Shuffled Regions and Controlled Regions
2.6. Characterization of TCNEs with Known Annotations
2.7. Clinical Analysis of TCNEs with Enhancer Signatures
2.8. Motif Discovery and Enrichment Analysis
2.9. Integration of Gene Expression Data in Breast Cancer Tissues and NATs
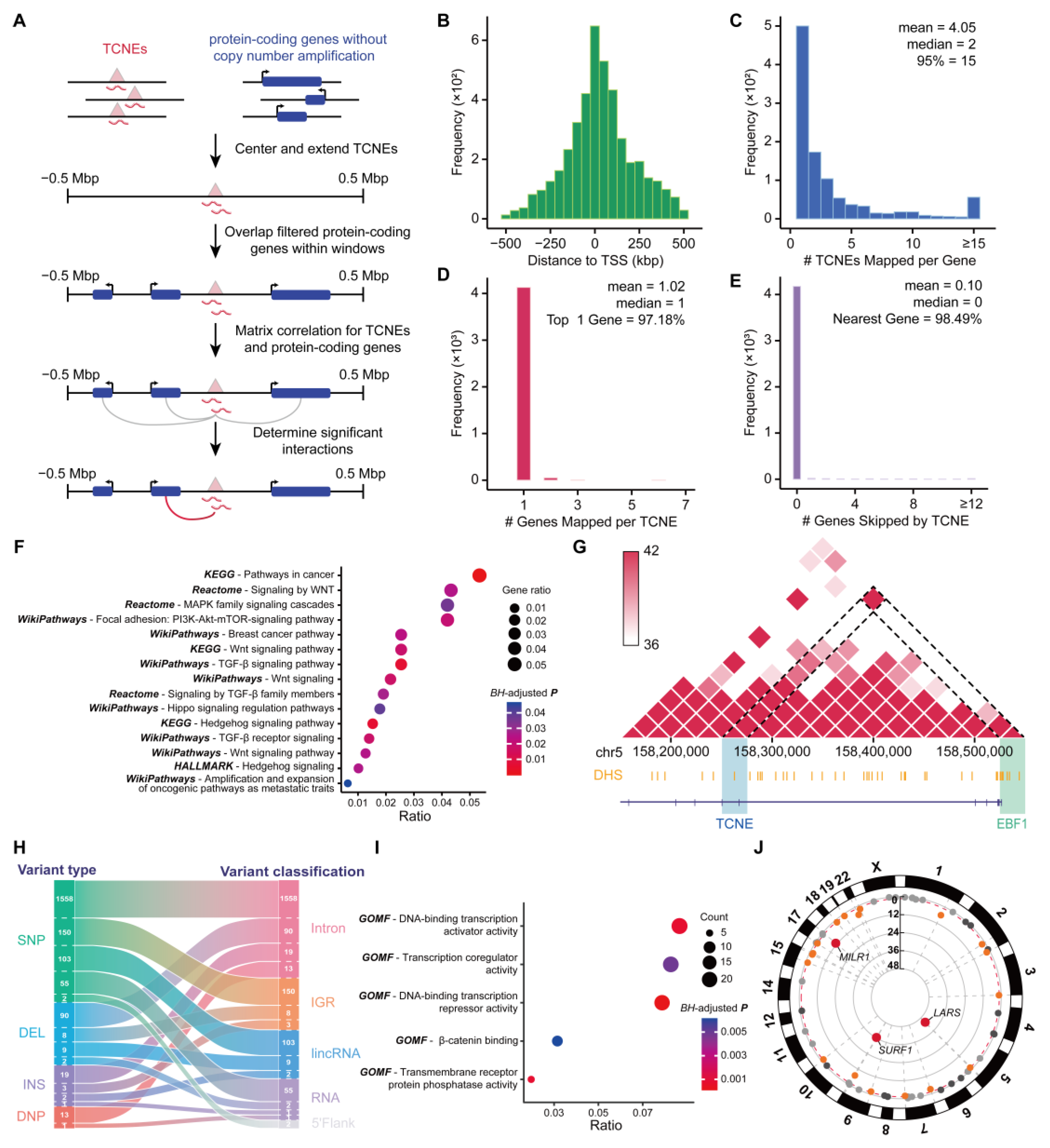
2.10. Prediction of Target Genes Associated with TCNEs
2.11. Pathway, GO, and GWAS Enrichment Analysis
2.12. Construction of Gene Regulatory Network
2.13. Variant Annotation and Analysis on TCNEs
2.14. Cell Culture and Quantitative PCR
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genome-Wide Identification and Validation of TCNEs in Breast Cancer
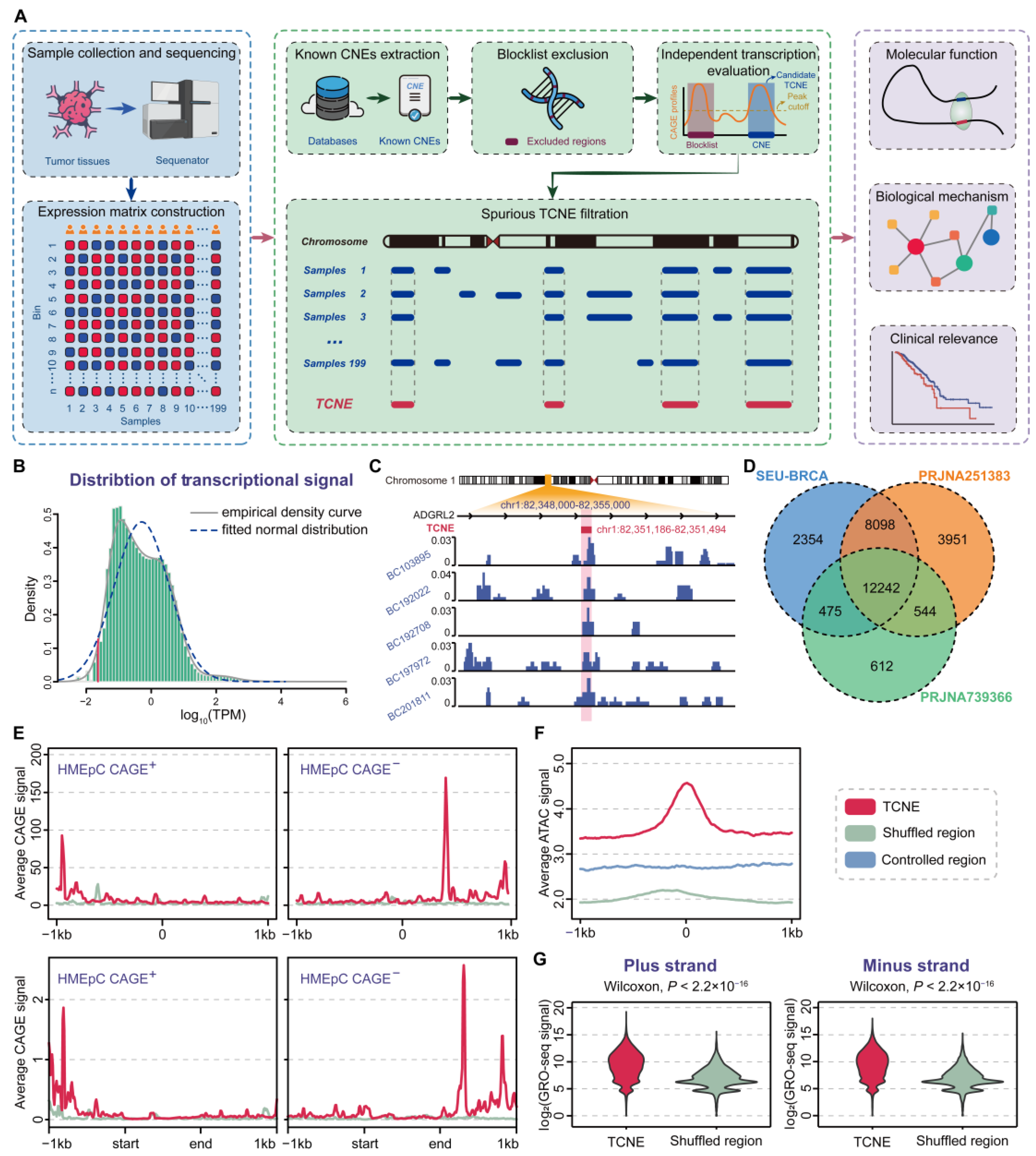
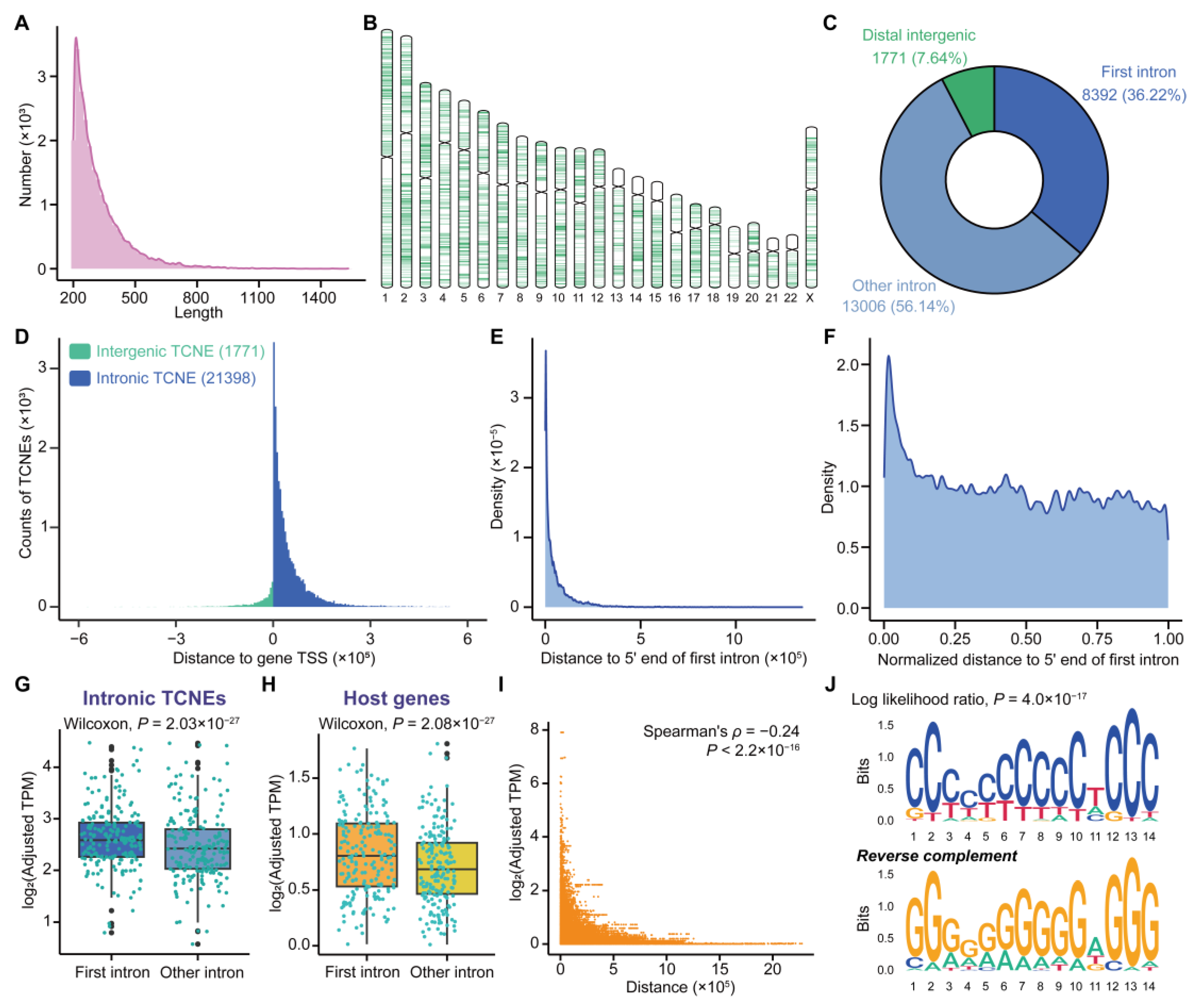
3.2. Characterization of TCNEs Reveals Their Functions in the Regulation of Host Genes
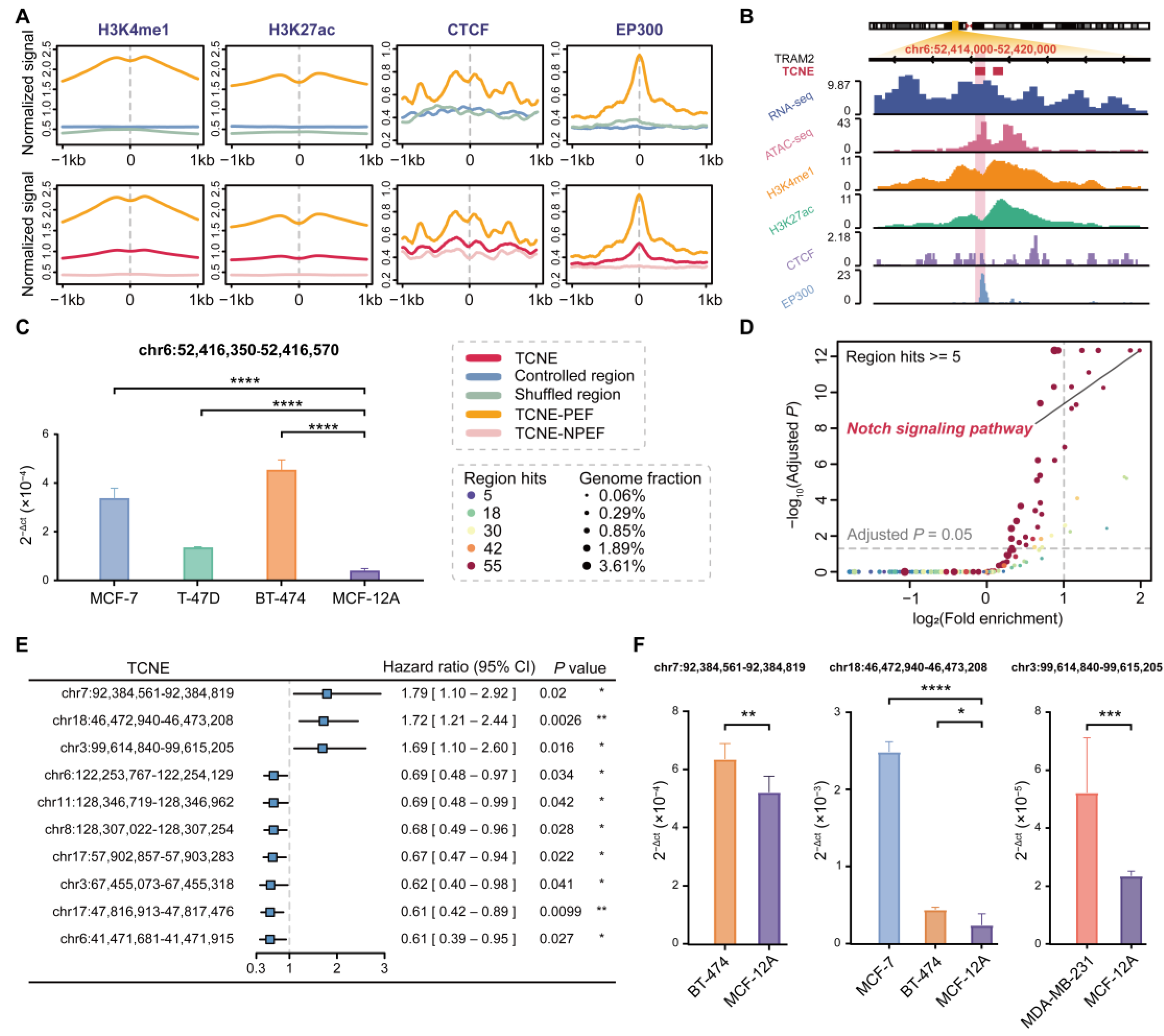
3.3. A Subset of TCNEs Serves as Putative Enhancers Active in Breast Cancer
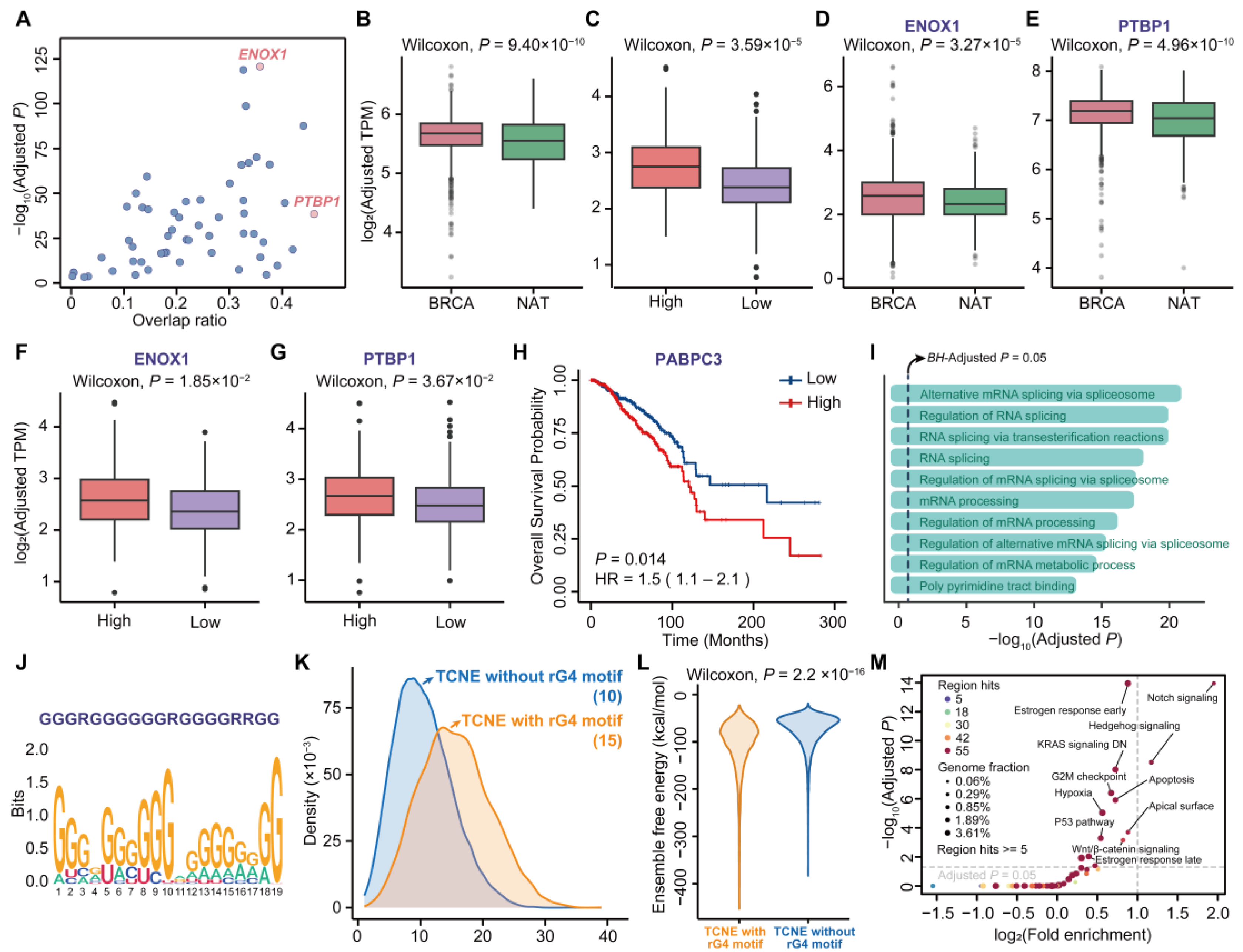
3.4. Sequence and Structure Signatures of TCNE Transcripts Relevant to Breast Carcinogenesis
3.5. TCNEs and Their Targeted Genes Construct the Cancer Biological Regulatory Networks
3.6. Variant-Containing TCNEs Induced Alterations of Gene Expression Related to Breast Cancer
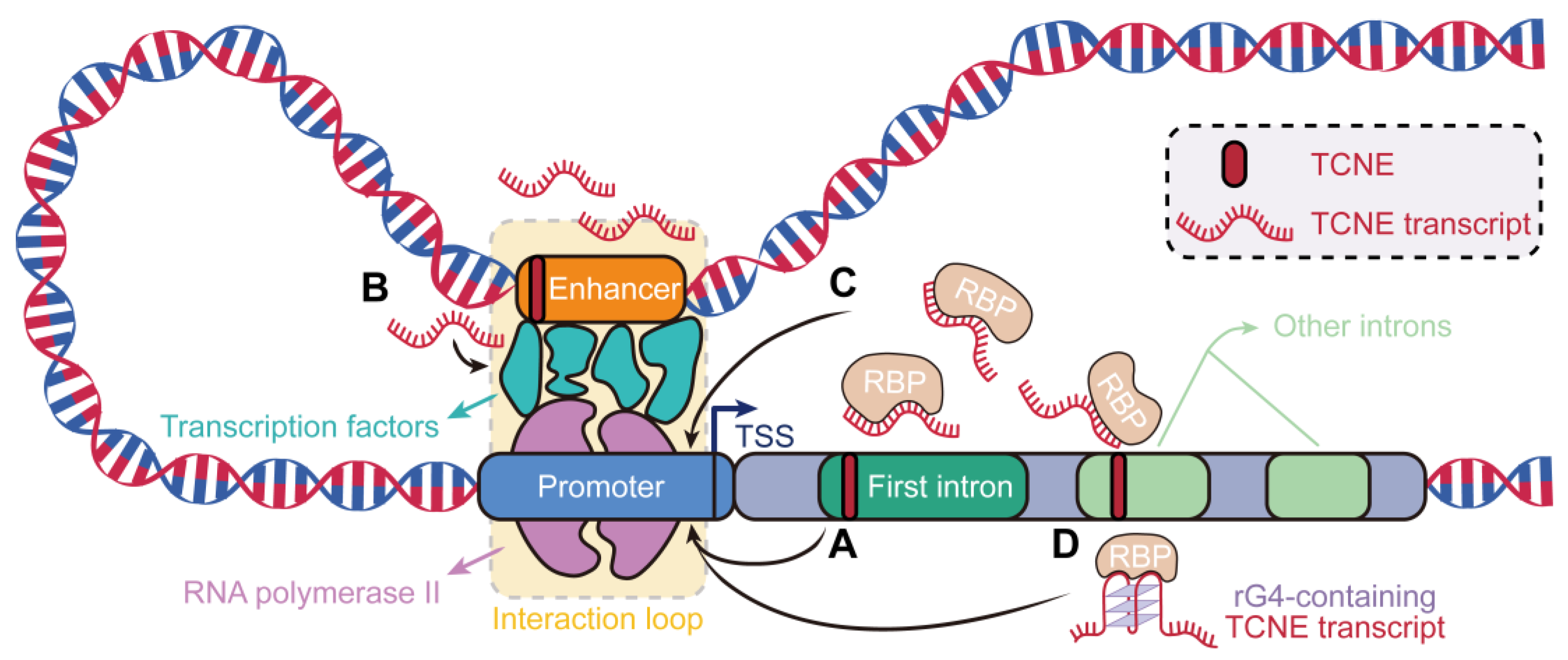
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TCNE | Transcribed conserved non-coding element |
| TSS | Transcription start site |
| NAT | Normal tissues adjacent to the tumor |
| RBP | RNA-binding protein |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| CNA | Copy number aberration |
| MCC | Maximal clique centrality |
| eQTL | Expression quantitative trait loci |
| eRNA | Enhancer RNA |
| rG4 | RNA G-quadruplex |
References
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2012, 490, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.-S.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, Z.-N.; Xu, F.; Lu, H.-J.; Zhu, Z.-Y.; Shi, W.; Jiang, J.; Yao, P.-P.; Zhu, H.-P. Risk factors and preventions of breast cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, A.C.; Korkut, A.; Kanchi, R.S.; Hegde, A.M.; Lenoir, W.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Fan, H.; Shen, H.; Ravikumar, V. A comprehensive pan-cancer molecular study of gynecologic and breast cancers. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 690–705.e699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolio, T.A.; Rowley, R.; Williams, M.S.; Roden, D.; Ginsburg, G.S.; Bult, C.; Chisholm, R.L.; Deverka, P.A.; McLeod, H.L.; Mensah, G.A. Opportunities, resources, and techniques for implementing genomics in clinical care. Lancet 2019, 394, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Hu, J.; Maryam, A.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Li, J.; Ma, H.; Ma, V.W.; Cheuk, W. Defining super-enhancer landscape in triple-negative breast cancer by multiomic profiling. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ghamrasni, S.; Quevedo, R.; Hawley, J.; Mazrooei, P.; Hanna, Y.; Cirlan, I.; Zhu, H.; Bruce, J.P.; Oldfield, L.E.; Yang, S.C. Mutations in Noncoding Cis-Regulatory Elements Reveal Cancer Driver Cistromes in Luminal Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2022, 20, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polychronopoulos, D.; King, J.W.; Nash, A.J.; Tan, G.; Lenhard, B. Conserved non-coding elements: Developmental gene regulation meets genome organization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 12611–12624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Huang, H.; Ming, W.; Zhang, R.; Gu, Y.; Bai, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Gu, W. Delineating highly transcribed noncoding elements landscape in breast cancer. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 4432–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Liao, Z.; Gritsch, D.; Hadzhiev, Y.; Bai, Y.; Locascio, J.J.; Guennewig, B.; Liu, G.; Blauwendraat, C.; Wang, T. Enhancers active in dopamine neurons are a primary link between genetic variation and neuropsychiatric disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1482–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, R.S.; Yi, M.; Volfovsky, N.; Prueitt, R.L.; Esposito, D.; Volinia, S.; Liu, C.-G.; Schetter, A.J.; Van Roosbroeck, K.; Stephens, R.M. Transcription signatures encoded by ultraconserved genomic regions in human prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambalde, E.P.; Adamoski, D.; Gradia, D.F.; Rabinovich, I.; Rodrigues, A.C.; Ivan, C.; Ribeiro, E.M.; Calin, G.A.; Carvalho de Oliveira, J. Transcribed ultraconserved regions are associated with clinicopathological features in breast cancer. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibert, M.K., Jr.; Sarkar, A.; Chagari, B.; Roig-Laboy, C.; Saha, S.; Bednarek, S.; Kefas, B.; Hanif, F.; Hudson, K.; Dube, C. Transcribed ultraconserved regions in cancer. Cells 2022, 11, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barshad, G.; Marom, S.; Cohen, T.; Mishmar, D. Mitochondrial DNA transcription and its regulation: An evolutionary perspective. Trends Genet. 2018, 34, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leypold, N.A.; Speicher, M.R. Evolutionary conservation in noncoding genomic regions. Trends Genet. 2021, 37, 903–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braconi, C.; Valeri, N.; Kogure, T.; Gasparini, P.; Huang, N.; Nuovo, G.J.; Terracciano, L.; Croce, C.M.; Patel, T. Expression and functional role of a transcribed noncoding RNA with an ultraconserved element in hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engström, P.G.; Fredman, D.; Lenhard, B. Ancora: A web resource for exploring highly conserved noncoding elements and their association with developmental regulatory genes. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrieva, S.; Bucher, P. UCNEbase—A database of ultraconserved non-coding elements and genomic regulatory blocks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D101–D109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The RNAcentral Consortium. RNAcentral: A hub of information for non-coding RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D221–D229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankish, A.; Diekhans, M.; Jungreis, I.; Lagarde, J.; Loveland, J.E.; Mudge, J.M.; Sisu, C.; Wright, J.C.; Armstrong, J.; Barnes, I. GENCODE 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D916–D923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro Gonzalez, J.; Zweig, A.S.; Speir, M.L.; Schmelter, D.; Rosenbloom, K.R.; Raney, B.J.; Powell, C.C.; Nassar, L.R.; Maulding, N.D.; Lee, C.M. The UCSC genome browser database: 2021 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1046–D1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djebali, S.; Davis, C.A.; Merkel, A.; Dobin, A.; Lassmann, T.; Mortazavi, A.; Tanzer, A.; Lagarde, J.; Lin, W.; Schlesinger, F. Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 2012, 489, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corces, M.R.; Granja, J.M.; Shams, S.; Louie, B.H.; Seoane, J.A.; Zhou, W.; Silva, T.C.; Groeneveld, C.; Wong, C.K.; Cho, S.W. The chromatin accessibility landscape of primary human cancers. Science 2018, 362, eaav1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundaje, A.; Meuleman, W.; Ernst, J.; Bilenky, M.; Yen, A.; Heravi-Moussavi, A.; Kheradpour, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Ziller, M.J.; et al. Integrative analysis of 111 reference human epigenomes. Nature 2015, 518, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizio, M.; Harshbarger, J.; Shimoji, H.; Severin, J.; Kasukawa, T.; Sahin, S.; Abugessaisa, I.; Fukuda, S.; Hori, F.; Ishikawa-Kato, S. Gateways to the FANTOM5 promoter level mammalian expression atlas. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.E.; Purcaro, M.J.; Pratt, H.E.; Epstein, C.B.; Shoresh, N.; Adrian, J.; Kawli, T.; Davis, C.A.; Dobin, A. Expanded encyclopaedias of DNA elements in the human and mouse genomes. Nature 2020, 583, 699–710. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, T.; Qian, J. EnhancerAtlas 2.0: An updated resource with enhancer annotation in 586 tissue/cell types across nine species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D58–D64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liang, H. A high-resolution map of human enhancer RNA loci characterizes super-enhancer activities in cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 701–715.e705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdon, S.; Herviou, P.; Dumas, L.; Destefanis, E.; Zen, A.; Cammas, A.; Millevoi, S.; Dassi, E. QUADRatlas: The RNA G-quadruplex and RG4-binding proteins database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D240–D247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig Lombardi, E.; Londoño-Vallejo, A. A guide to computational methods for G-quadruplex prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javierre, B.M.; Burren, O.S.; Wilder, S.P.; Kreuzhuber, R.; Hill, S.M.; Sewitz, S.; Cairns, J.; Wingett, S.W.; Várnai, C.; Thiecke, M.J. Lineage-specific genome architecture links enhancers and non-coding disease variants to target gene promoters. Cell 2016, 167, 1369–1384.e1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, J.L.; Hudson, T.J. International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC). Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.G.; Hannenhalli, S.; Choi, S.S. Conservation in first introns is positively associated with the number of exons within genes and the presence of regulatory epigenetic signals. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasiadi, D.; Esteve-Codina, A.; Piferrer, F. Consistent inverse correlation between DNA methylation of the first intron and gene expression across tissues and species. Epigenet. Chromatin 2018, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ugalde, A.P.; Scheele, C.L.; Dieter, S.M.; Nagel, R.; Ma, J.; Pataskar, A.; Korkmaz, G.; Elkon, R.; Chien, M.-P. A comprehensive enhancer screen identifies TRAM2 as a key and novel mediator of YAP oncogenesis. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-W.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, H. Emerging roles of m6A RNA modification in cancer therapeutic resistance. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikonomou, P.; Goodarzi, H.; Tavazoie, S. Systematic identification of regulatory elements in conserved 3′ UTRs of human transcripts. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nostrand, E.L.; Freese, P.; Pratt, G.A.; Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Xiao, R.; Blue, S.M.; Chen, J.-Y.; Cody, N.A.; Dominguez, D. A large-scale binding and functional map of human RNA-binding proteins. Nature 2020, 583, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Chen, J.-Y.; Liang, Z.; Luo, D.; Chen, G.; Lu, Z.J.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, B.; Li, H.; Du, X. Pervasive chromatin-RNA binding protein interactions enable RNA-based regulation of transcription. Cell 2019, 178, 107–121. e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.T.; Yang, Y.M.; Sun, M.M.; He, Y.; Liao, L.; Chen, K.S.; Li, B. New insights into the interplay between long non-coding RNAs and RNA-binding proteins in cancer. Cancer Commun. 2022, 42, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Qu, K.; Zhang, Q.C.; Flynn, R.A.; Manor, O.; Ouyang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Spitale, R.C.; Snyder, M.P.; Segal, E. Landscape and variation of RNA secondary structure across the human transcriptome. Nature 2014, 505, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Chung, C.-Y.; Uryu, S.; Petrovic, J.; Cao, J.; Rickard, A.; Nady, N.; Greasley, S.; Johnson, E.; Brodsky, O. Discovery of a highly potent, selective, orally bioavailable inhibitor of KAT6A/B histone acetyltransferases with efficacy against KAT6A-high ER+ breast cancer. Cell Chem. Biol. 2023, 30, 1191–1210.e1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, K.; Chow, E.Y.-C.; Mou, X.; Chan, T.-F.; Kwok, C.K. RNA G-quadruplexes (rG4s): Genomics and biological functions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 5426–5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, D.; Spiegel, J.; Zyner, K.; Tannahill, D.; Balasubramanian, S. The regulation and functions of DNA and RNA G-quadruplexes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknafs, Y.S.; Han, S.; Ma, T.; Speers, C.; Zhang, C.; Wilder-Romans, K.; Iyer, M.K.; Pitchiaya, S.; Malik, R.; Hosono, Y. The lncRNA landscape of breast cancer reveals a role for DSCAM-AS1 in breast cancer progression. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, P.; Chen, C.; Lu, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhang, M.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, F.; Huang, J.; Fan, L.; Ning, C. Genome-wide enhancer-gene regulatory maps link causal variants to target genes underlying human cancer risk. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Shen, H.; Laird, P.W.; Farnham, P.J.; Berman, B.P. Inferring regulatory element landscapes and transcription factor networks from cancer methylomes. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefnia, S.; Seyed Forootan, F.; Seyed Forootan, S.; Nasr Esfahani, M.H.; Gure, A.O.; Ghaedi, K. Mechanistic pathways of malignancy in breast cancer stem cells. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.X.; Polley, E.; Lipkowitz, S. New insights on PI3K/AKT pathway alterations and clinical outcomes in breast cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2016, 45, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Guo, W.; Dong, B.; Wang, Y.; Deng, P.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Grosschedl, R.; Yu, Z. EBF1 promotes triple-negative breast cancer progression by surveillance of the HIF1α pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2119518119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuderna, L.F.; Ulirsch, J.C.; Rashid, S.; Ameen, M.; Sundaram, L.; Hickey, G.; Cox, A.J.; Gao, H.; Kumar, A.; Aguet, F. Identification of constrained sequence elements across 239 primate genomes. Nature 2024, 625, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passarelli, M.C.; Pinzaru, A.M.; Asgharian, H.; Liberti, M.V.; Heissel, S.; Molina, H.; Goodarzi, H.; Tavazoie, S.F. Leucyl-tRNA synthetase is a tumour suppressor in breast cancer and regulates codon-dependent translation dynamics. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, P.; Kim, J.; Braunstein, L.Z.; Karlic, R.; Haradhavala, N.J.; Tiao, G.; Rosebrock, D.; Livitz, D.; Kübler, K.; Mouw, K.W.; et al. A mutational signature reveals alterations underlying deficient homologous recombination repair in breast cancer. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1476–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, H.L.; Nagari, A.; Malladi, V.S.; Li, W.; Xi, Y.; Richardson, D.; Allton, K.L.; Tanaka, K.; Li, J.; Murakami, S.; et al. Enhancer transcription reveals subtype-specific gene expression programs controlling breast cancer pathogenesis. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, B.; Hartonen, T.; Pihlajamaa, P.; Wei, B.; Dave, K.; Zhu, F.; Kaasinen, E.; Lidschreiber, K.; Lidschreiber, M.; Daub, C.O.; et al. Sequence determinants of human gene regulatory elements. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorev, M.; Carmel, L. The function of introns. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Mikkelsen, T.S.; Gnirke, A.; Lindblad-Toh, K.; Kellis, M.; Lander, E.S. Systematic discovery of regulatory motifs in conserved regions of the human genome, including thousands of CTCF insulator sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7145–7150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haudry, A.; Platts, A.E.; Vello, E.; Hoen, D.R.; Leclercq, M.; Williamson, R.J.; Forczek, E.; Joly-Lopez, Z.; Steffen, J.G.; Hazzouri, K.M.; et al. An atlas of over 90,000 conserved noncoding sequences provides insight into crucifer regulatory regions. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Mu, H. Alternative splicing and related RNA binding proteins in human health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Kharel, P.; Ivanov, P. RNA G-quadruplexes and stress: Emerging mechanisms and functions. Trends Cell Biol. 2024, 34, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgakopoulos-Soares, I.; Parada, G.E.; Wong, H.Y.; Medhi, R.; Furlan, G.; Munita, R.; Miska, E.A.; Kwok, C.K.; Hemberg, M. Alternative splicing modulation by G-quadruplexes. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endoh, T.; Kawasaki, Y.; Sugimoto, N. Stability of RNA quadruplex in open reading frame determines proteolysis of human estrogen receptor α. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 6222–6231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Zhang, H.; Kong, Q.; Jiang, Y. Mechanisms for estrogen receptor expression in human cancer. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oudelaar, A.M.; Higgs, D.R. The relationship between genome structure and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Mondragon, J.A.; Aure, M.R.; Lingjærde, O.C.; Langerød, A.; Martens, J.W.; Børresen-Dale, A.-L.; Kristensen, V.N.; Mathelier, A. Cis-regulatory mutations associate with transcriptional and post-transcriptional deregulation of gene regulatory programs in cancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 12131–12148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigau, M.; Juan, D.; Valencia, A.; Rico, D. Intronic CNVs and gene expression variation in human populations. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1007902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenta, T.; Hausmann, G.; Basler, K. The many faces and functions of β-catenin. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 2714–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Yu, C.; Li, F.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yao, L.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Ye, L. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in cancers and targeted therapies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, W.; Huang, H.; Li, Q.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Shu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, H.; Sun, X. Dissecting the Emerging Regulatory and Mechanistic Paradigms of Transcribed Conserved Non-Coding Elements in Breast Cancer. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050627
Zhu W, Huang H, Li Q, Gu Y, Zhang R, Shu H, Zhao Y, Liu H, Sun X. Dissecting the Emerging Regulatory and Mechanistic Paradigms of Transcribed Conserved Non-Coding Elements in Breast Cancer. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(5):627. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050627
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Wenyong, Hao Huang, Qiong Li, Yu Gu, Rongxin Zhang, Huiling Shu, Yunqi Zhao, Hongde Liu, and Xiao Sun. 2025. "Dissecting the Emerging Regulatory and Mechanistic Paradigms of Transcribed Conserved Non-Coding Elements in Breast Cancer" Biomolecules 15, no. 5: 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050627
APA StyleZhu, W., Huang, H., Li, Q., Gu, Y., Zhang, R., Shu, H., Zhao, Y., Liu, H., & Sun, X. (2025). Dissecting the Emerging Regulatory and Mechanistic Paradigms of Transcribed Conserved Non-Coding Elements in Breast Cancer. Biomolecules, 15(5), 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050627





