Effects of Testosterone and Its Major Metabolites upon Different Stages of Neuron Survival in the Dentate Gyrus of Male Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
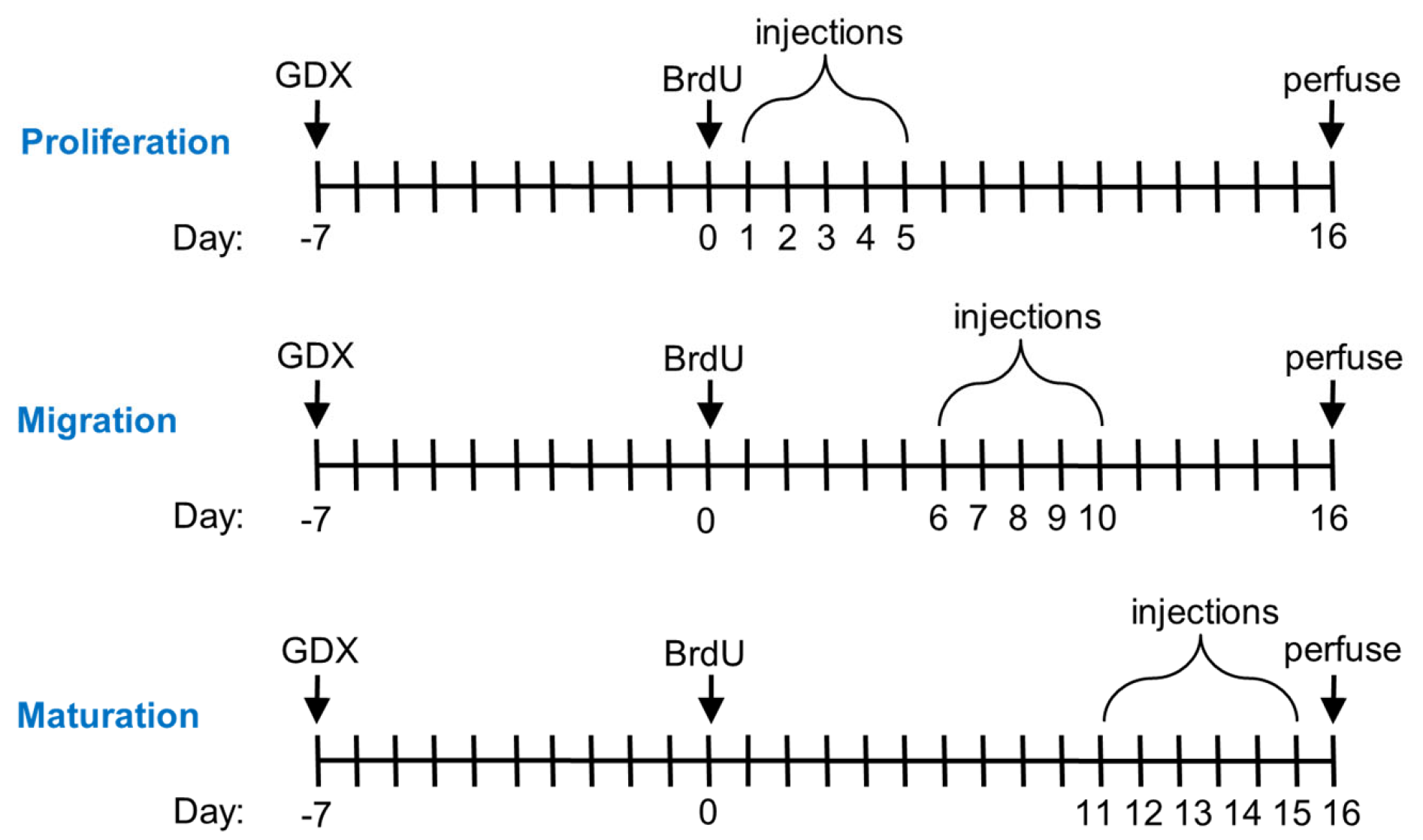
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Microscopy
2.5. Statistical Analysis
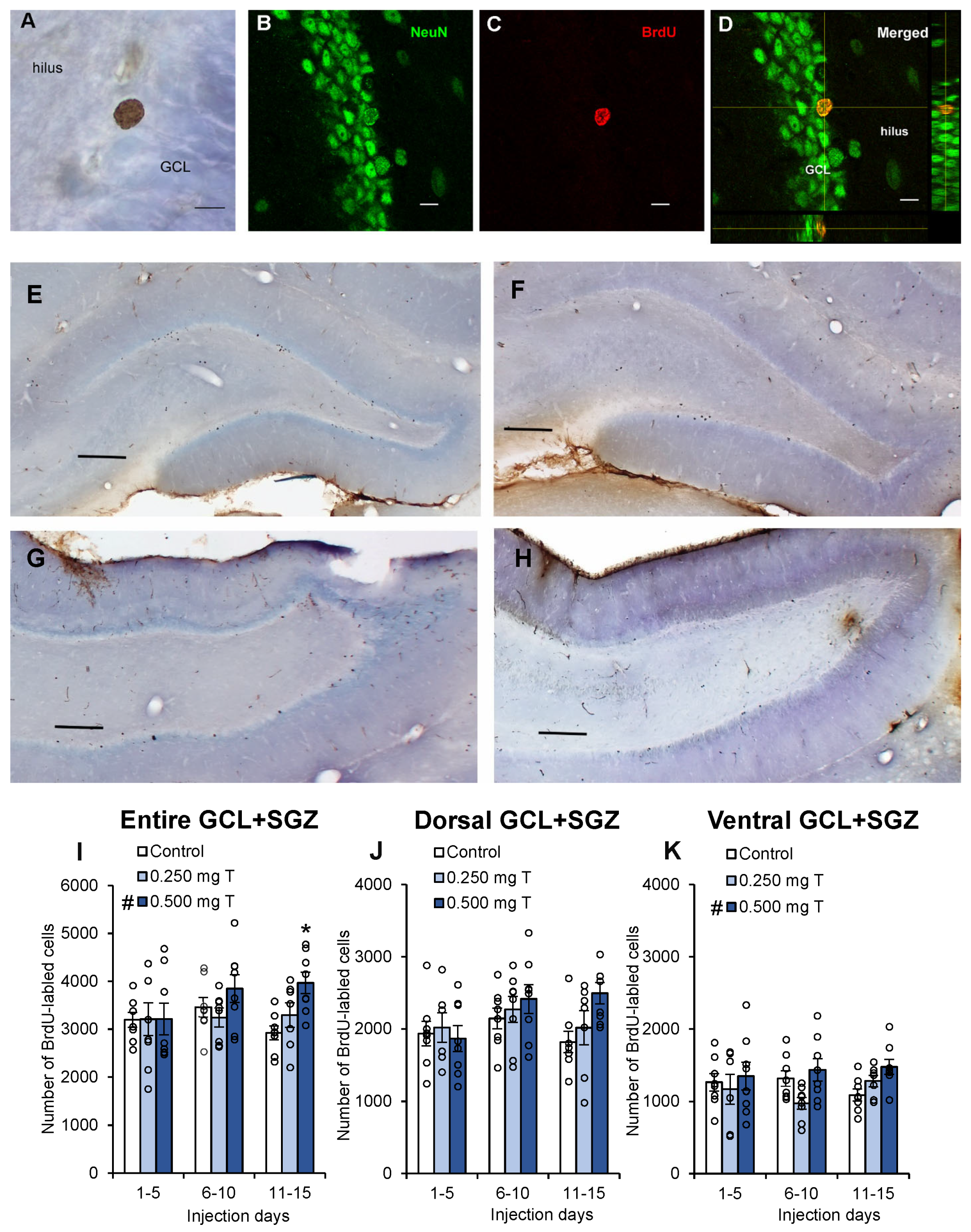
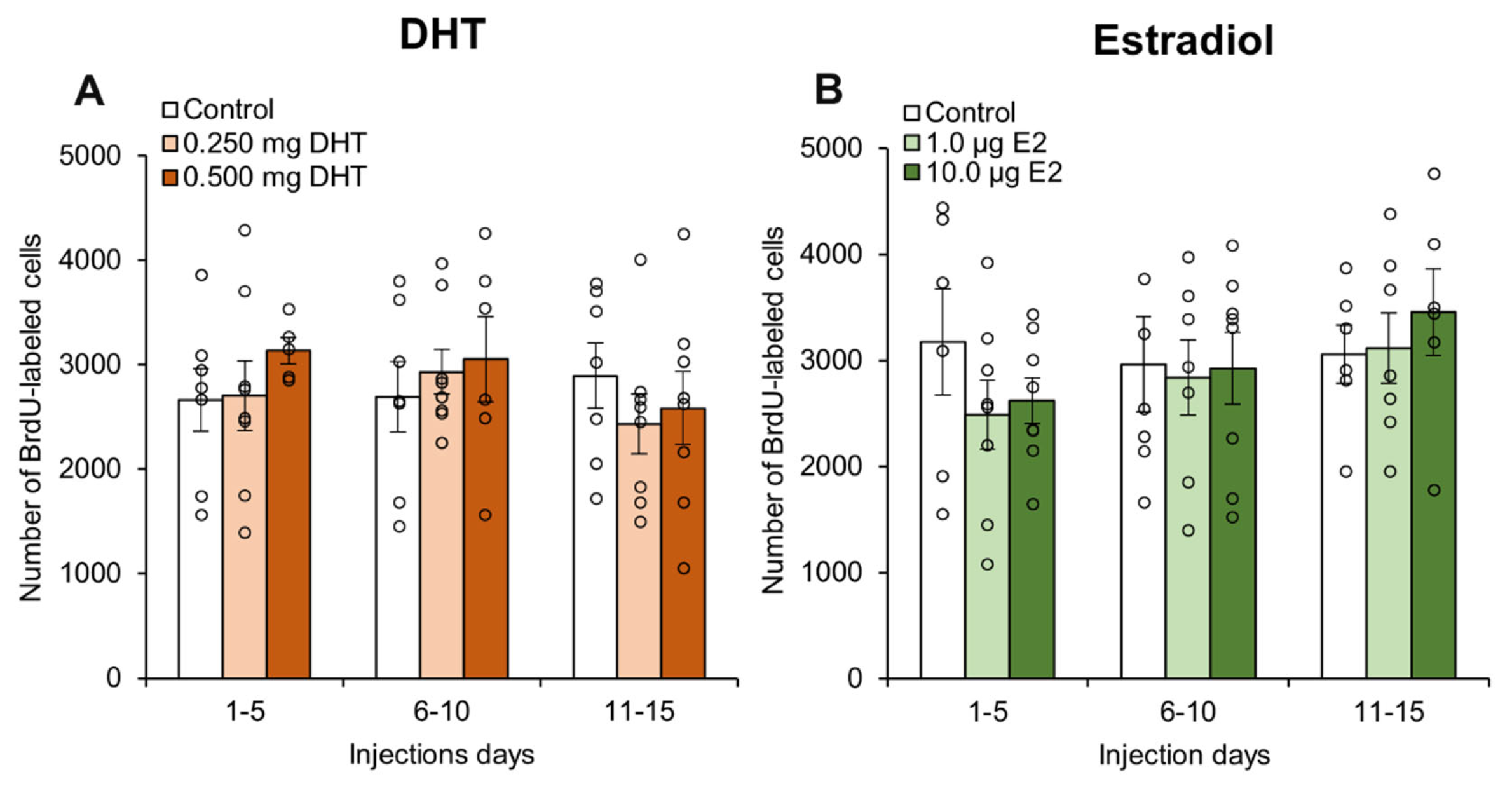
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Testosterone May Enhance Neurogenesis During a Critical Period
4.2. Estradiol and DHT Had No Effect on Neurogenesis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feldman, H.A.; Longcope, C.; Derby, C.A.; Johannes, C.B.; Araujo, A.B.; Coviello, A.D.; Bremner, W.J.; McKinlay, J.B. Age Trends in the Level of Serum Testosterone and Other Hormone in Middle-Aged Men: Longitudinal Results from the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harman, S.M.; Metter, E.J.; Tobin, J.D.; Pearson, J.; Blackman, M.R. Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging Longitudinal Effects of Aging on Serum Total and Free Testosterone Levels in Healthy Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanabar, R.; Mazur, A.; Plum, A.; Schmied, J. Correlates of Testosterone Change as Men Age. Aging Male 2022, 25, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, J.; Bandelow, S.; Hogervorst, E. Testosterone Levels and Cognition in Elderly Men: A Review. Maturitas 2011, 69, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulubaev, A.; Lee, D.M.; Purandare, N.; Pendleton, N.; Wu, F.C.W. Activational Effects of Sex Hormones on Cognition in Men. Clin. Endocrinol. 2009, 71, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazova, I.; Vlcek, K.; Laczó, J.; Nedelska, Z.; Hyncicova, E.; Mokrisova, I.; Sheardova, K.; Hort, J. Spatial Navigation-a Unique Window into Physiological and Pathological Aging. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2012, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, I.; Kastuk, D.; Choi, J.; Phillips, K. Testosterone Levels and Spatial Ability in Men. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1999, 24, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Silverman, I. The Relationship between Testosterone and Route-Learning Strategies in Humans. Brain Cogn. 2002, 50, 116–120. [Google Scholar]
- Hooven, C.K.; Chabris, C.F.; Ellison, P.T.; Kosslyn, S.M. The Relationship of Male Testosterone to Components of Mental Rotation. Neuropsychologia 2004, 42, 782–790. [Google Scholar]
- Thilers, P.P.; MacDonald, S.W.S.; Herlitz, A. The Association between Endogenous Free Testosterone and Cognitive Performance: A Population-Based Study in 35 to 90 Year-Old Men and Women. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2006, 31, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherrier, M.M.; Rose, A.L.; Higano, C. The Effects of Combined Androgen Blockade on Cognitive Function during the First Cycle of Intermittent Androgen Suppression in Patients with Prostate Cancer. J. Urol. 2003, 170, 1808–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherrier, M.M.; Aubin, S.; Higano, C.S. Cognitive and Mood Changes in Men Undergoing Intermittent Combined Androgen Blockade for Non-Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Psychooncology 2009, 18, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherrier, M.; Borghesani, P.; Shelton, A.; Higano, C. Changes in Neuronal Activation Patterns in Response to Androgen Deprivation Therapy: A Pilot Study. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, T.M.; Bland, L.B.; Bussiere, J.R.; Neiss, M.B.; Wersinger, E.M.; Garzotto, M.; Ryan, C.W.; Janowsky, J.S. Testosterone Loss and Estradiol Administration Modify Memory in Men. J. Urol. 2006, 175, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, E.K.; Portin, R.I.; Koskinen, A.; Helenius, H.; Nurmi, M. Associations between Serum Testosterone Fall and Cognitive Function in Prostate Cancer Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 7575–7582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lašaitė, L.; Čeponis, J.; Preikša, R.T.; Žilaitienė, B. Effects of Two-Year Testosterone Replacement Therapy on Cognition, Emotions and Quality of Life in Young and Middle-Aged Hypogonadal Men. Andrologia 2017, 49, e12633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spritzer, M.D.; Jaeger, E.C.B.; Guo, J.D. Testosterone and Spatial Memory: Rodent Models and Clinical Applications. Androg. Clin. Res. Ther. 2021, 2, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.B.; Johnson, D.A. Sex-Specific Effects of Gonadectomy and Hormone Treatment on Acquisition of a 12-Arm Radial Maze Task by Sprague Dawley Rats. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 3176–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, J.M.; Winsauer, P.J.; Moerschbaecher, J.M. Castration in Rats Impairs Performance during Acquisition of a Working Memory Task and Exacerbates Deficits in Working Memory Produced by Scopolamine and Mecamylamine. Psychopharmacology 2003, 170, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, N.; Mochizuki, M. Improved Effect of Pycnogenol on Impaired Spatial Memory Function in Partial Androgen Deficiency Rat Model. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 840–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritzer, M.F.; McLaughlin, P.J.; Smirilis, T. Gonadectomy Impairs T-Maze Acquisition in Adult Male Rats. Horm. Behav. 2001, 39, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locklear, M.N.; Bhamidipaty, S.; Kritzer, M.F. Local N-Methyl-d-Aspartate Receptor Antagonism in the Prefrontal Cortex Attenuates Spatial Cognitive Deficits Induced by Gonadectomy in Adult Male Rats. Neuroscience 2015, 288, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locklear, M.N.; Kritzer, M.F. Assessment of the Effects of Sex and Sex Hormones on Spatial Cognition in Adult Rats Using the Barnes Maze. Horm. Behav. 2014, 66, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spritzer, M.D.; Daviau, E.D.; Coneeny, M.K.; Engelman, S.M.; Prince, W.T.; Rodriguez-Wisdom, K.N. Effects of Testosterone on Spatial Learning and Memory in Adult Male Rats. Horm. Behav. 2011, 59, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, B.A.; Braddick, V.C.; Batson, C.G.; Cullen, B.H.; Miller, L.E.; Spritzer, M.D. Effects of Testosterone Dose on Spatial Memory among Castrated Adult Male Rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 89, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacome, L.F.; Barateli, K.; Buitrago, D.; Lema, F.; Frankfurt, M.; Luine, V.N. Gonadal Hormones Rapidly Enhance Spatial Memory and Increase Hippocampal Spine Density in Male Rats. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, S.E.A.; Alla, J.; Wheat, E.; Romeo, R.D.; McEwen, B.; Thornton, J.E. The Role of Testicular Hormones and Luteinizing Hormone in Spatial Memory in Adult Male Rats. Horm. Behav. 2012, 61, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourrabi, S.; Hossini, S.; Nayebi, A.M. A Behavioral and Molecular Study of Androgen Effects on Memory Impairments in Mature Male Rats Afflicted by Alzheimer’s Disease. Clin. Schizophr. Relat. Psychoses 2021, 15, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Abrous, D.N.; Koehl, M.; Le Moal, M. Adult Neurogenesis: From Precursors to Network Physiology. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 523–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, G.; Song, H. Adult Neurogenesis in the Mammalian Brain: Significant Answers and Significant Questions. Neuron 2011, 70, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdissa, D.; Hamba, N.; Gerbi, A. Review Article on Adult Neurogenesis in Humans. Transl. Res. Anat. 2020, 20, 100074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrein, I. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Natural Populations of Mammals. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a021295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalding, K.L.; Bergmann, O.; Alkass, K.; Bernard, S.; Salehpour, M.; Huttner, H.B.; Boström, E.; Westerlund, I.; Vial, C.; Buchholz, B.A.; et al. Dynamics of Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Adult Humans. Cell 2013, 153, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldrini, M.; Fulmore, C.A.; Tartt, A.N.; Simeon, L.R.; Pavlova, I.; Poposka, V.; Rosoklija, G.B.; Stankov, A.; Arango, V.; Dwork, A.J.; et al. Human Hippocampal Neurogenesis Persists throughout Aging. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 589–599.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, M.K.; Musaraca, K.; Disouky, A.; Shetti, A.; Bheri, A.; Honer, W.G.; Kim, N.; Dawe, R.J.; Bennett, D.A.; Arfanakis, K.; et al. Human Hippocampal Neurogenesis Persists in Aged Adults and Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 24, 974–982.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Su, Y.; Li, S.; Kennedy, B.C.; Zhang, D.Y.; Bond, A.M.; Sun, Y.; Jacob, F.; Lu, L.; Hu, P.; et al. Molecular Landscapes of Human Hippocampal Immature Neurons across Lifespan. Nature 2022, 607, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrells, S.F.; Paredes, M.F.; Cebrian-Silla, A.; Sandoval, K.; Qi, D.; Kelley, K.W.; James, D.; Mayer, S.; Chang, J.; Auguste, K.I.; et al. Human Hippocampal Neurogenesis Drops Sharply in Children to Undetectable Levels in Adults. Nature 2018, 555, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Jiménez, E.P.; Flor-García, M.; Terreros-Roncal, J.; Rábano, A.; Cafini, F.; Pallas-Bazarra, N.; Ávila, J.; Llorens-Martín, M. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis Is Abundant in Neurologically Healthy Subjects and Drops Sharply in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, H.A.; Woolley, C.A.; McEwen, B.S.; Gould, E. Differentiation of Newly Born Neurons and Glia in the Dentate Gyrus of the Adult Rat. Neuroscience 1993, 56, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Praag, H.; Schinder, A.F.; Christie, B.R.; Toni, N.; Palmer, T.D.; Gage, F.H. Functional Neurogenesis in the Adult Hippocampus. Nature 2002, 415, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Teng, E.M.; Summers, R.G.; Ming, G.; Gage, F.H. Distinct Morphological Stages of Dentate Granule Neuron Maturation in Adult Mouse Hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastings, N.B.; Gould, E. Rapid Extension of Axons into the CA3 Region by Adult-Generated Granule Cells. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 413, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, G.; Song, H. Adult Neurogenesis in the Mammalian Central Nervous System. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 28, 223–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrogini, P.; Cuppini, R.; Ciuffoli, S.; Frontini, A.; Fanelli, M. Synaptogenesis in Adult-Generated Hippocampal Granule Cells Is Affected by Behavioral Experiences. Hippocampus 2010, 20, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmidt-Hieber, C.; Jones, P.; Bischofberger, J. Enhanced Synaptic Plasticity in Newly Generated Granule Cells of the Adult Hippocampus. Nature 2004, 429, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Yang, C.-H.; Hsu, K.-S.; Ming, G.-L.; Song, H. A Critical Period for Enhanced Synaptic Plasticity in Newly Generated Neurons of the Adult Brain. Neuron 2007, 54, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberwirth, C.; Pan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z. Hippocampal Adult Neurogenesis: Its Regulation and Potential Role in Spatial Learning and Memory. Brain Res. 2016, 1644, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, J.S.; Hong, N.S.; McDonald, R.J.; Wojtowicz, J.M. A Role for Adult Neurogenesis in Spatial Long-Term Memory. Neuroscience 2005, 130, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupret, D.; Revest, J.-M.; Koehl, M.; Ichas, F.; De Giorgi, F.; Costet, P.; Abrous, D.N.; Piazza, P.V. Spatial Relational Memory Requires Hippocampal Adult Neurogenesis. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clelland, C.D.; Choi, M.; Romberg, C.; Clemenson, G.D.; Fragniere, A.; Tyers, P.; Jessberger, S.; Saksida, L.M.; Barker, R.A.; Gage, F.H.; et al. A Functional Role for Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Spatial Pattern Separation. Science 2009, 325, 213. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W.; Saxe, M.D.; Gallina, I.S.; Gage, F.H. Adult-Born Hippocampal Dentate Granule Cells Undergoing Maturation Modulate Learning and Memory in the Brain. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 13532–13542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessberger, S.; Clark, R.E.; Broadbent, N.J.; Clemenson, G.D.; Copnsiglio, A.; Lie, D.C.; Squire, L.R.; Gage, F.H. Dentate Gyrus-Specific Knockdown of Adult Neurogenesis Impairs Spatial and Object Recognition Memory in Adult Rats. Learn. Mem. 2009, 16, 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, T.; Trouche, S.; Massou, I.; Verret, L.; Zerwas, M.; Roullet, P.; Rampon, C. Young Hippocampal Neurons Are Critical for Recent and Remote Spatial Memory in Adult Mice. Neuroscience 2010, 171, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lensu, S.; Waselius, T.; Mäkinen, E.; Kettunen, H.; Virtanen, A.; Tiirola, M.; Penttonen, M.; Pekkala, S.; Nokia, M.S. Irradiation of the Head Reduces Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Impairs Spatial Memory, but Leaves Overall Health Intact in Rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 53, 1885–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, T.P.; Askari, B.; Lee, B.H.; Darby, K.; Knudson, C.; Ash, A.M.; Seib, D.R.; Espinueva, D.F.; Snyder, J.S. Sex Differences in the Spatial Behavior Functions of Adult-bornnNeurons in Rats. eNeuro 2022, 9, ENEURO.0054-22.2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdugo-Vega, G.; Lee, C.-C.; Garthe, A.; Kempermann, G.; Calegari, F. Adult-Born Neurons Promote Cognitive Flexibility by Improving Memory Precision and Indexing. Hippocampus 2021, 31, 1068–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bohlen und Halbach, O. Immunohistological Markers for Proliferative Events, Gliogenesis, and Neurogenesis within the Adult Hippocampus. Cell Tissue Res. 2011, 345, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, H.A.; McKay, R.D.G. Adult Neurogenesis Produces a Large Pool of New Granule Cells in the Dentate Gyrus. J. Comp. Neurol. 2001, 435, 406–417. [Google Scholar]
- Dayer, A.G.; Ford, A.A.; Cleaver, K.M.; Yassaee, M.; Cameron, H.A. Short-Term and Long-Term Survival of New Neurons in the Rat Dentate Gyrus. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 460, 563–572. [Google Scholar]
- Epp, J.R.; Spritzer, M.D.; Galea, L.A.M. Hippocampus-Dependent Learning Promotes Survival of New Neurons in the Dentate Gyrus at a Specific Time during Cell Maturation. Neuroscience 2007, 149, 273–285. [Google Scholar]
- Epp, J.R.; Haack, A.K.; Galea, L.A.M. Activation and Survival of Immature Neurons in the Dentate Gyrus with Spatial Memory Is Dependent on Time of Exposure to Spatial Learning and Age of Cells at Examination. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2011, 95, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, E.; Beylin, A.; Tanapat, P.; Reeves, A.; Shors, T.J. Learning Enhances Adult Neurogenesis in the Hippocampal Formation. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrogini, P.; Cuppini, R.; Cuppini, C.; Ciaroni, S.; Cecchini, T.; Ferri, P.; Sartini, S.; Del Grande, P. Spatial Learning Affects Immature Granule Cell Survival in Adult Rat Dentate Gyrus. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 286, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupret, D.; Fabre, A.; Dobrossy, M.D.; Panatier, A.; Rodriguez, J.J.; Lamarque, S.; Lemaire, V.; Oliet, S.H.R.; Piazza, P.-V.; Abrous, D.N. Spatial Learning Depends on Both the Addition and Removal of New Hippocampal Neurons. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, 1683–1694. [Google Scholar]
- Sisti, H.M.; Glass, A.L.; Shors, T.J. Neurogenesis and the Spacing Effect: Learning over Time Enhances Memory and the Survival of New Neurons. Learn. Mem. 2007, 14, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, A.; Makino, H.; Gage, F.H. Experience-Specific Functional Modification of the Dentate Gyrus through Adult Neurogenesis: A Critical Period during the Immature Stage. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 3252–3259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lods, M.; Pacary, E.; Mazier, W.; Farrugia, F.; Mortessagne, P.; Masachs, N.; Charrier, V.; Massa, F.; Cota, D.; Ferreira, G.; et al. Adult-Born Neurons Immature during Learning Are Necessary for Remote Memory Reconsolidation in Rats. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.P.; Couillard-Despres, S.; Cooper-Kuhn, C.; Winkler, J.; Aigner, L.; Kuhn, H.G. Transient Expression of Doublecortin during Adult Neurogenesis. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 467, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, H.Y.; Wojtowicz, J.M. Dynamics of Neurogenesis in the Dentate Gyrus of Adult Rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 385, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, R.; Wainwright, S.R.; Galea, L.A.M. Sex Hormones and Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis: Regulation, Implications, and Potential Mechanisms. Front. Neuroendocr. 2016, 41, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberden, C. Sex Steroids and Neurogenesis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 141, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, C.; Wang, Z. Hormonal Regulation of Mammalian Adult Neurogenesis: A Multifaceted Mechanism. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankers, S.A.; Galea, L.A.M. Androgens and Adult Neurogenesis in the Hippocampus. Androg. Clin. Res. Ther. 2021, 2, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spritzer, M.D.; Galea, L.A.M. Testosterone and Dihydrotestosterone, but Not Estradiol, Enhance Survival of New Hippocampal Neurons in Adult Male Rats. Dev. Neurobiol. 2007, 67, 1321–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Benice, T.S.; Raber, J. Castration and Training in a Spatial Task Alter the Number of Immature Neurons in the Hippocampus of Male Mice. Brain Res. 2010, 1329, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, M.; Hojo, Y.; Inoue, K.; Matsui, T.; Kawato, S.; McEwen, B.S.; Soya, H. Mild Exercise Increases Dihydrotestosterone in Hippocampus Providing Evidence for Androgenic Mediation of Neurogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13100–13105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, S.R.; Lieblich, S.E.; Galea, L.A.M. Hypogonadism Predisposes Males to the Development of Behavioural and Neuroplastic Depressive Phenotypes. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2011, 36, 1327–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spritzer, M.D.; Ibler, E.; Inglis, W.; Curtis, M.G. Testosterone and Social Isolation Influence Adult Neurogenesis in the Dentate Gyrus of Male Rats. Neuroscience 2011, 195, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, S.R.; Workman, J.L.; Tehrani, A.; Hamson, D.K.; Chow, C.; Lieblich, S.E.; Galea, L.A.M. Testosterone Has Antidepressant-like Efficacy and Facilitates Imipramine-Induced Neuroplasticity in Male Rats Exposed to Chronic Unpredictable Stress. Horm. Behav. 2016, 79, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrier, N.; Kabbaj, M. Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 2 Signaling in the Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus Mediates the Antidepressant Effects of Testosterone. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 71, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrier, N.; Kabbaj, M. Testosterone and Imipramine Have Antidepressant Effects in Socially Isolated Male but Not Female Rats. Horm. Behav. 2012, 61, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannan, A.J.; Ransome, M.I. Deficits in Spermatogenesis but Not Neurogenesis Are Alleviated by Chronic Testosterone Therapy in R6/1 Huntington’s Disease Mice. J. Neuroendocr. 2012, 24, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, C.D.; Freeman, M.E.; Wang, Z.X. Newly Proliferated Cells in the Adult Male Amygdala Are Affected by Gonadal Steroid Hormones. J. Neurobiol. 2003, 57, 257–269. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, F.G.N.; Fernandes, J.; Campos, D.V.; Cassilhas, R.C.; Viana, G.M.; D’almeida, V.; Rêgo, M.K.d.M.; Buainain, P.I.; Cavalheiro, E.A.; Arida, R.M. The Beneficial Effects of Strength Exercise on Hippocampal Cell Proliferation and Apoptotic Signaling Is Impaired by Anabolic Androgenic Steroids. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2014, 50, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamson, D.K.; Wainwright, S.R.; Taylor, J.R.; Jones, B.A.; Watson, N.V.; Galea, L.A.M. Androgens Increase Survival of Adult-Born Neurons in the Dentate Gyrus by an Androgen Receptor-Dependent Mechanism in Male Rats. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 3294–3304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Swift-Gallant, A.; Duarte-Guterman, P.; Hamson, D.K.; Ibrahim, M.; Monks, D.A.; Galea, L.A.M. Neural Androgen Receptors Affect the Number of Surviving New Neurones in the Adult Dentate Gyrus of Male Mice. J. Neuroendocr. 2018, 30, e12578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Guterman, P.; Lieblich, S.E.; Wainwright, S.R.; Chow, C.; Chaiton, J.A.; Watson, N.V.; Galea, L.A.M. Androgens Enhance Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Males but Not Females in an Age-Dependent Manner. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 2128–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, J.M.; Galea, L.A.M. Repeated Estradiol Administration Alters Different Aspects of Neurogenesis and Cell Death in the Hippocampus of Female, but Not Male, Rats. Neuroscience 2008, 152, 888–902. [Google Scholar]
- Ormerod, B.K.; Lee, T.T.-Y.; Galea, L.A.M. Estradiol Enhances Neurogenesis in the Dentate Gyri of Adult Male Meadow Voles by Increasing the Survival of Young Granule Neurons. Neuroscience 2004, 128, 645–654. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, M.S.; Piatti, V.C.; Laplagne, D.A.; Morgenstern, N.A.; Ferrari, C.C.; Pitossi, F.J.; Schinder, A.F. Neuronal Differentiation in the Adult Hippocampus Recapitulates Embryonic Development. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 10074–10086. [Google Scholar]
- McCloskey, D.P.; Hintz, T.M.; Pierce, J.P.; Scharfman, H.E. Stereological Methods Reveal the Robust Size and Stability of Ectopic Hilar Granule Cells after Pilocarpine-Induced Status Epilepticus in the Adult Rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 2203–2210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scharfman, H.; Goodman, J.; McCloskey, D. Ectopic Granule Cells of the Rat Dentate Gyrus. Dev. Neurosci. 2007, 29, 14–27. [Google Scholar]
- Banasr, M.; Soumier, A.; Hery, M.; Mocaër, E.; Daszuta, A. Agomelatine, a New Antidepressant, Induces Regional Changes in Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanselow, M.S.; Dong, H.-W. Are the Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus Functionally Distinct Structures? Neuron 2010, 65, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundersen, H.J.; Bendtsen, T.F.; Korbo, L.; Marcussen, N.; Moller, A.; Nielsen, K.; Nyengaard, J.R.; Pakkenberg, B.; Sorensen, F.B.; Besterby, A. Some New, Simple and Efficient Stereological Methods and Their Use in Pathological Research and Diagnosis. APMIS 1988, 96, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saravia, F.; Beauquis, J.; Pietranera, L.; De Nicola, A.F. Neuroprotective Effects of Estradiol in Hippocampal Neurons and Glia of Middle Age Mice. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2007, 32, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buwalda, B.; van der Borght, K.; Koolhass, J.M.; McEwen, B.S. Testosterone Decrease Does Not Play a Major Role in the Suppression of Hippocampal Cell Proliferation Following Social Defeat Stress in Rats. Physiol. Behav. 2010, 101, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibbe, M.; Kulik, A. GABAergic Regulation of Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 5497–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieni, C.V.; Chancey, J.H.; Overstreet-Wadiche, L.S. Dynamic Functions of GABA Signaling during Granule Cell Maturation. Front. Neural Circuits 2012, 6, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagasia, R.; Steib, K.; Englberger, E.; Herold, S.; Faus-Kessler, T.; Saxe, M.; Gage, F.H.; Song, H.; Lie, D.C. GABA-cAMP Response Element-Binding Protein Signaling Regulates Maturation and Survival of Newly Generated Neurons in the Adult Hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 7966–7977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Pradhan, D.A.; Ming, G.-L.; Song, H. GABA Sets the Tempo for Activity-Dependent Adult Neurogenesis. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, D.S.; Jian, K. The Testosterone-Derived Neurosteroid Androstanediol Is a Positive Allosteric Modulator of GABAA Receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 334, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, T.; Bisgaard, C.F.; Nielsen, H.B.; Wiborg, O. Transcriptome Differentiation along the Dorso-Ventral Axis in Laser-Captured Microdissected Rat Hippocampal Granular Cell Layer. Neuroscience 2010, 170, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheirbek, M.A.; Drew, L.J.; Burghardt, N.S.; Costantini, D.O.; Tannenholz, L.; Ahmari, S.E.; Zeng, H.; Fenton, A.A.; Hen, R. Differential Control of Learning and Anxiety along the Dorsoventral Axis of the Dentate Gyrus. Neuron 2013, 77, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, O.F.; Cryan, J.F. A Ventral View on Antidepressant Action: Roles for Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis along the Dorsoventral Axis. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pothuizen, H.H.J.; Zhang, W.-N.; Jongen-Rêlo, A.L.; Feldon, J.; Yee, B.K. Dissociation of Function between the Dorsal and the Ventral Hippocampus in Spatial Learning Abilities of the Rat: A within-Subject, within-Task Comparison of Reference and Working Spatial Memory. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, D.F.; Leasure, J.L. Region-Specific Response of the Hippocampus to Chronic Unpredictable Stress. Hippocampus 2012, 22, 1338–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanti, A.; Rainer, Q.; Minier, F.; Surget, A.; Belzung, C. Differential Environmental Regulation of Neurogenesis along the Septo-Temporal Axis of the Hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 2012, 63, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opendak, M.; Offit, L.; Monari, P.; Schoenfeld, T.J.; Sonti, A.N.; Cameron, H.A.; Gould, E. Lasting Adaptations in Aocial Behavior Produced by Social Disruption and Inhibition of Adult Neurogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 7027–7038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.V.; Hen, R. Functional Dissociation of Adult-Born Neurons along the Dorsoventral Axis of the Dentate Gyrus. Hippocampus 2014, 24, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viau, V.; Meaney, M.J. The Inhibitory Effect of Testosterone on Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Responses to Stress in Mediated by the Medial Preoptic Area. J. Neurobiol. 1996, 16, 1866–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, R.E.; Maclusky, N.J.; Diaz, S.E.; Zrull, M.C.; Luine, V.N. Aged Rats: Sex Differences and Responses to Chronic Stress. Brain Res. 2006, 1126, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Guasti, A.; Martínez-Mota, L. Anxiolytic-like Actions of Testosterone in the Burying Behavior Test: Role of Androgen and GABA-Benzodiazepine Receptors. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2005, 30, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edinger, K.L.; Frye, C.A. Intrahippocampal Administration of an Androgen Receptor Antagonist, Flutamide, Can Increase Anxiety-like Behavior in Intact and DHT-Replaced Rats. Horm. Behav. 2006, 50, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirescu, C.; Gould, E. Stress and Adult Neurogenesis. Hippocampus 2006, 16, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podgorny, O.V.; Gulyaeva, N.V. Glucocorticoid-Mediated Mechanisms of Hippocampal Damage: Contribution of Subgranular Neurogenesis. J. Neurochem. 2021, 157, 370–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, R.; Zhou, R.; Li, L.; Sakobe, M.; Chen, L. Progesterone Promotes Survival of Newborn Neurons in the Dentate Gyrus of Adult Male Mice. Hippocampus 2010, 20, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, J.S.; Choe, J.S.; Clifford, M.A.; Jeurline, S.I.; Hurley, P.; Brown, A.; Kamhi, F.; Cameron, H.A. Adult-Born Hippocampal Neurons Are More Numerous, Faster Maturing, and More Involved in Behavior in Rats than in Mice. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 14484–14495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marbouti, L.; Zahmatkesh, M.; Riahi, E.; Sadr, S.S. Inhibition of Brain 17β-Estradiol Synthesis by Letrozole Induces Cognitive Decline in Male and Female Rats. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2020, 175, 107300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spritzer, M.D.; Roy, E.A. Testosterone and Adult Neurogenesis. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojo, Y.; Kawato, S. Neurosteroids in Adult Hippocampus of Male and Female Rodents: Biosynthesis and Actions of Sex Steroids. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hojo, Y.; Higo, S.; Ishii, H.; Ooishi, Y.; Mukai, H.; Murakami, G.; Kominami, T.; Kimoto, T.; Honma, S.; Poirier, D.; et al. Comparison between Hippocampus-Synthesized and Circulation-Derived Sex Steroids in the Hippocampus. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 5106–5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kee, N.; Teixeira, C.M.; Wang, A.H.; Frankland, P.W. Preferential Incorporation of Adult-Generated Granule Cells into Spatial Memory Networks in the Dentate Gyrus. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Hormone | Days | Dose | n | Percent Cells Co-Labeled |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Testosterone | Control | 8 | 83.00 ± 5.38 | |
| 1–5 | 0.250 mg/rat | 6 | 78.67 ± 9.42 | |
| 0.500 mg/rat | 8 | 76.88 ± 5.24 | ||
| Control | 8 | 75.38 ± 5.92 | ||
| 6–10 | 0.250 mg/rat | 8 | 87.75 ± 4.18 | |
| 0.500 mg/rat | 8 | 74.13 ± 9.76 | ||
| Control | 8 | 87.11 ± 2.35 | ||
| 11–15 | 0.250 mg/rat | 7 | 89.43 ± 2.78 | |
| 0.500 mg/rat | 8 | 86.75 ± 4.09 | ||
| DHT | Control | 7 | 80.14 ± 4.40 | |
| 1–5 | 0.250 mg/rat | 8 | 81.38 ± 3.70 | |
| 0.500 mg/rat | 5 | 82.80 ± 8.00 | ||
| Control | 7 | 80.57 ± 7.50 | ||
| 6–10 | 0.250 mg/rat | 8 | 85.63 ± 3.89 | |
| 0.500 mg/rat | 6 | 82.17 ± 7.02 | ||
| Control | 7 | 87.14 ± 4.41 | ||
| 11–15 | 0.250 mg/rat | 8 | 80.25 ± 4.31 | |
| 0.500 mg/rat | 8 | 82.88 ± 4.45 | ||
| Estradiol | Control | 6 | 92.00 ± 1.26 | |
| 1–5 | 1.0 μg/rat | 6 | 91.25 ± 1.31 | |
| 10.0 μg/rat | 8 | 91.25 ± 3.16 | ||
| Control | 7 | 92.29 ± 1.48 | ||
| 6–10 | 1.0 μg/rat | 8 | 82.86 ± 6.98 | |
| 10.0 μg/rat | 8 | 92.25 ± 1.78 | ||
| Control | 6 | 91.33 ± 3.00 | ||
| 11–15 | 1.0 μg/rat | 8 | 93.71 ± 2.16 | |
| 10.0 μg/rat | 6 | 93.33 ± 1.76 |
| Hormone | Days | Dose | GCL+SGZ (mm3) | Hilus (mm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Testosterone | Control | 2.074 ± 0.252 | 5.141 ± 0263 | |
| 1–5 | 0.250 mg/rat | 1.725 ± 0.182 | 4.806 ± 0.545 | |
| 0.500 mg/rat | 2.150 ± 0.085 | 4.984 ± 0.116 | ||
| Control | 1.847 ± 0.138 | 5.305 ± 0.321 | ||
| 6–10 | 0.250 mg/rat | 1.857 ± 0.120 | 4.578 ± 0.286 | |
| 0.500 mg/rat | 2.044 ± 0.197 | 4.989 ± 0.440 | ||
| Control | 1.956 ± 0.135 | 5.168 ± 0.194 | ||
| 11–15 | 0.250 mg/rat | 1.960 ± 0.090 | 5.576 ± 0.334 | |
| 0.500 mg/rat | 1.996 ± 0.116 | 5.734 ± 0.268 | ||
| DHT | Control | 1.835 ± 0.106 | 3.997 ± 0.209 | |
| 1–5 | 0.250 mg/rat | 1.829 ± 0.068 | 4.303 ± 0.320 | |
| 0.500 mg/rat | 1.996 ± 0.128 | 3.756 ± 0.122 | ||
| Control | 1.841 ± 0.103 | 3.633 ± 0.202 | ||
| 6–10 | 0.250 mg/rat | 1.935 ± 0.114 | 4.397 ± 0.247 | |
| 0.500 mg/rat | 2.117 ± 0.063 | 4.538 ± 0.388 | ||
| Control | 1.834 ± 0.124 | 4.049 ± 0.190 | ||
| 11–15 | 0.250 mg/rat | 1.938 ± 0.101 | 4.278 ± 0.260 | |
| 0.500 mg/rat | 1.866 ± 0.130 | 4.229 ± 0.164 | ||
| Estradiol | Control | 1.670 ± 0.060 | 3.724 ± 0.169 | |
| 1–5 | 1.0 μg/rat | 1.641 ± 0.055 | 3.771 ± 0.212 | |
| 10.0 μg/rat | 1.751 ± 0.063 | 3.919 ± 0.220 | ||
| Control | 1.612 ± 0.078 | 3.881 ± 0.169 | ||
| 6–10 | 1.0 μg/rat | 1.596 ± 0.104 | 3.804 ± 0.327 | |
| 10.0 μg/rat | 1.650 ± 0.118 | 3.681 ± 0.146 | ||
| Control | 1.558 ± 0.087 | 3.355 ± 0.164 | ||
| 11–15 | 1.0 μg/rat | 1.540 ± 0.223 | 3.601 ± 0.348 | |
| 10.0 μg/rat | 1.730 ± 0.099 | 3.884 ± 0.180 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spritzer, M.D.; Roy, E.A.; Calhoun, K.M.K.; Schneider-Lynch, Z.E.; Panella, L.; Michaelcheck, C.; Qian, A.; Kelly, E.D.; Barr, H.; Hall, E.; et al. Effects of Testosterone and Its Major Metabolites upon Different Stages of Neuron Survival in the Dentate Gyrus of Male Rats. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040542
Spritzer MD, Roy EA, Calhoun KMK, Schneider-Lynch ZE, Panella L, Michaelcheck C, Qian A, Kelly ED, Barr H, Hall E, et al. Effects of Testosterone and Its Major Metabolites upon Different Stages of Neuron Survival in the Dentate Gyrus of Male Rats. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(4):542. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040542
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpritzer, Mark D., Ethan A. Roy, Kelsey M. K. Calhoun, Zachary E. Schneider-Lynch, Leslie Panella, Charlotte Michaelcheck, April Qian, Evan D. Kelly, Hadley Barr, Emma Hall, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Testosterone and Its Major Metabolites upon Different Stages of Neuron Survival in the Dentate Gyrus of Male Rats" Biomolecules 15, no. 4: 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040542
APA StyleSpritzer, M. D., Roy, E. A., Calhoun, K. M. K., Schneider-Lynch, Z. E., Panella, L., Michaelcheck, C., Qian, A., Kelly, E. D., Barr, H., Hall, E., Cunningham, B., Nguyen, H. H. M., Xu, D., Barker, J. M., & Galea, L. A. M. (2025). Effects of Testosterone and Its Major Metabolites upon Different Stages of Neuron Survival in the Dentate Gyrus of Male Rats. Biomolecules, 15(4), 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040542






