The Meninges as CNS Interfaces and the Roles of Meningeal Macrophages
Abstract
1. Introduction
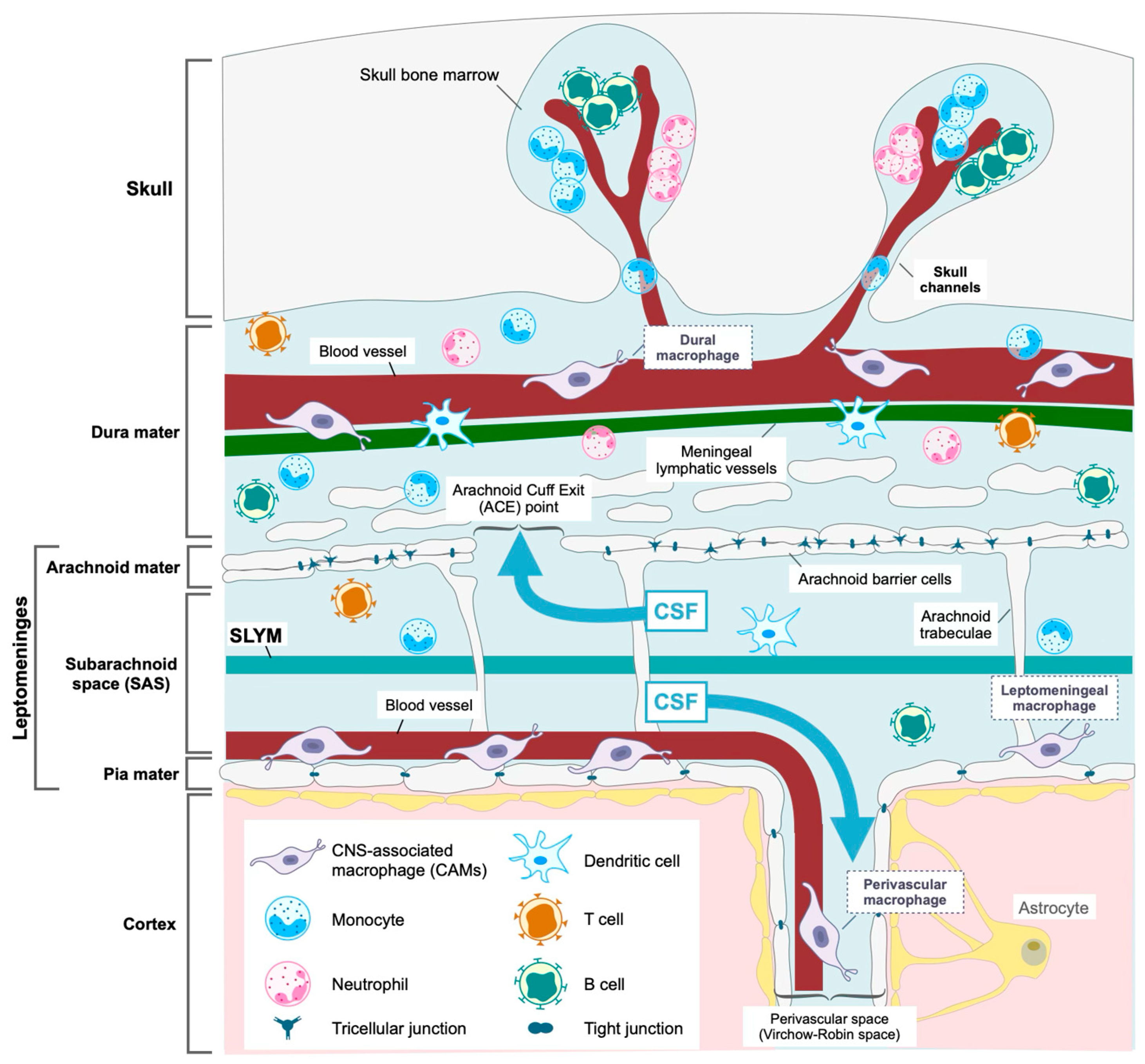
2. Structure and Function of the Meninges
2.1. The Leptomeninges
2.2. The Dura Mater
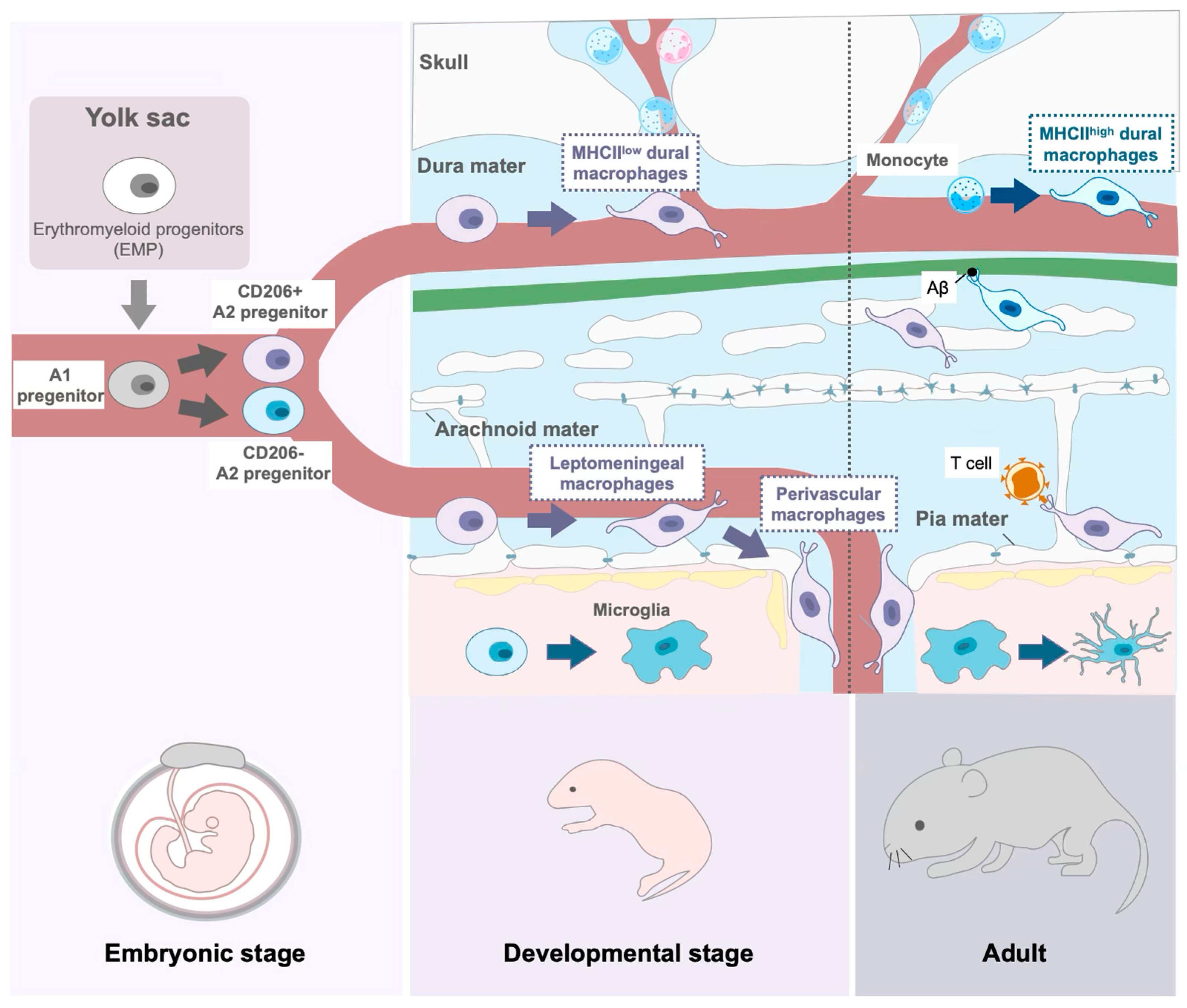
3. Macrophages in the Meninges
3.1. Development of CAMs
3.2. Function of CAMs in Meninges
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prinz, M.; Jung, S.; Priller, J. Microglia Biology: One Century of Evolving Concepts. Cell 2019, 179, 292–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmau Gasull, A.; Glavan, M.; Samawar, S.K.R.; Kapupara, K.; Kelk, J.; Rubio, M.; Fumagalli, S.; Sorokin, L.; Vivien, D.; Prinz, M. The Niche Matters: Origin, Function and Fate of CNS-Associated Macrophages during Health and Disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2024, 147, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvin, A.; Qian, J.; Ginhoux, F. Brain Macrophage Development, Diversity and Dysregulation in Health and Disease. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2023, 20, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kierdorf, K.; Masuda, T.; Jordão, M.J.C.; Prinz, M. Macrophages at CNS Interfaces: Ontogeny and Function in Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 20, 547–562. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, R.; Jiang, H. Border-Associated Macrophages in the Central Nervous System. J. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 21, 67. [Google Scholar]
- Muzio, L.; Perego, J. CNS Resident Innate Immune Cells: Guardians of CNS Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proulx, S.T.; Engelhardt, B. Central Nervous System Zoning: How Brain Barriers Establish Subdivisions for CNS Immune Privilege and Immune Surveillance. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 292, 47–67. [Google Scholar]
- Van Hove, H.; Martens, L.; Scheyltjens, I.; De Vlaminck, K.; Pombo Antunes, A.R.; De Prijck, S.; Vandamme, N.; De Schepper, S.; Van Isterdael, G.; Scott, C.L.; et al. A Single-Cell Atlas of Mouse Brain Macrophages Reveals Unique Transcriptional Identities Shaped by Ontogeny and Tissue Environment. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 1021–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Louveau, A.; Smirnov, I.; Keyes, T.J.; Eccles, J.D.; Rouhani, S.J.; Peske, J.D.; Derecki, N.C.; Castle, D.; Mandell, J.W.; Lee, K.S.; et al. Structural and Functional Features of Central Nervous System Lymphatic Vessels. Nature 2015, 523, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspelund, A.; Antila, S.; Proulx, S.T.; Karlsen, T.V.; Karaman, S.; Detmar, M.; Wiig, H.; Alitalo, K. A Dural Lymphatic Vascular System That Drains Brain Interstitial Fluid and Macromolecules. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herisson, F.; Frodermann, V.; Courties, G.; Rohde, D.; Sun, Y.; Vandoorne, K.; Wojtkiewicz, G.R.; Masson, G.S.; Vinegoni, C.; Kim, J.; et al. Direct Vascular Channels Connect Skull Bone Marrow and the Brain Surface Enabling Myeloid Cell Migration. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzitelli, J.A.; Smyth, L.C.D.; Cross, K.A.; Dykstra, T.; Sun, J.; Du, S.; Mamuladze, T.; Smirnov, I.; Rustenhoven, J.; Kipnis, J. Cerebrospinal Fluid Regulates Skull Bone Marrow Niches via Direct Access through Dural Channels. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 555–560. [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta, K.; Jeong, J. Developmental Biology of the Meninges. Genesis 2019, 57, e23288. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Møllgård, K.; Beinlich, F.R.M.; Kusk, P.; Miyakoshi, L.M.; Delle, C.; Plá, V.; Hauglund, N.L.; Esmail, T.; Rasmussen, M.K.; Gomolka, R.S.; et al. A Mesothelium Divides the Subarachnoid Space into Functional Compartments. Science 2023, 379, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Derk, J.; Jones, H.E.; Como, C.; Pawlikowski, B.; Siegenthaler, J.A. Living on the Edge of the CNS: Meninges Cell Diversity in Health and Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 703944. [Google Scholar]
- Pietilä, R.; Del Gaudio, F.; He, L.; Vázquez-Liébanas, E.; Vanlandewijck, M.; Muhl, L.; Mocci, G.; Bjørnholm, K.D.; Lindblad, C.; Fletcher-Sandersjöö, A.; et al. Molecular Anatomy of Adult Mouse Leptomeninges. Neuron 2023, 111, 3745–3764.e7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- DeSisto, J.; O’Rourke, R.; Jones, H.E.; Pawlikowski, B.; Malek, A.D.; Bonney, S.; Guimiot, F.; Jones, K.L.; Siegenthaler, J.A. Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analyses of the Developing Meninges Reveal Meningeal Fibroblast Diversity and Function. Dev. Cell 2020, 54, 43–59.e4. [Google Scholar]
- Saboori, P.; Sadegh, A. Histology and Morphology of the Brain Subarachnoid Trabeculae. Anat. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 279814. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, N.R.; Habgood, M.D.; Møllgård, K.; Dziegielewska, K.M. The Biological Significance of Brain Barrier Mechanisms: Help or Hindrance in Drug Delivery to the Central Nervous System? F1000Research 2016, 5, 313. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, N.J.; Patabendige, A.A.K.; Dolman, D.E.M.; Yusof, S.R.; Begley, D.J. Structure and Function of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Czarniak, N.; Kamińska, J.; Matowicka-Karna, J.; Koper-Lenkiewicz, O.M. Cerebrospinal Fluid-Basic Concepts Review. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliff, J.J.; Wang, M.; Liao, Y.; Plogg, B.A.; Peng, W.; Gundersen, G.A.; Benveniste, H.; Vates, G.E.; Deane, R.; Goldman, S.A.; et al. A Paravascular Pathway Facilitates CSF Flow through the Brain Parenchyma and the Clearance of Interstitial Solutes, Including Amyloid β. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 147ra111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hablitz, L.M.; Nedergaard, M. The Glymphatic System: A Novel Component of Fundamental Neurobiology. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 7698–7711. [Google Scholar]
- Shlobin, N.A.; Staple, B.L.; Sclafani, M.; Harter, D.H. The Glymphatic System and Subarachnoid Lymphatic-like Membrane: Recent Developments in Cerebrospinal Fluid Research. World Neurosurg. 2024, 190, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Betsholtz, C.; Engelhardt, B.; Koh, G.Y.; McDonald, D.M.; Proulx, S.T.; Siegenthaler, J. Advances and Controversies in Meningeal Biology. Nat. Neurosci. 2024, 27, 2056–2072. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smyth, L.C.D.; Xu, D.; Okar, S.V.; Dykstra, T.; Rustenhoven, J.; Papadopoulos, Z.; Bhasiin, K.; Kim, M.W.; Drieu, A.; Mamuladze, T.; et al. Identification of Direct Connections between the Dura and the Brain. Nature 2024, 627, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plá, V.; Bitsika, S.; Giannetto, M.J.; Ladron-de-Guevara, A.; Gahn-Martinez, D.; Mori, Y.; Nedergaard, M.; Møllgård, K. Structural Characterization of SLYM-a 4th Meningeal Membrane. Fluids Barriers CNS 2023, 20, 93. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, N.; Kimura, I. Podoplanin as a Marker for Mesothelioma. Pathol. Int. 2005, 55, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Adeeb, N.; Mortazavi, M.M.; Tubbs, R.S.; Cohen-Gadol, A.A. The Cranial Dura Mater: A Review of Its History, Embryology, and Anatomy. Childs. Nerv. Syst. 2012, 28, 827–837. [Google Scholar]
- Engelhardt, B.; Vajkoczy, P.; Weller, R.O. The Movers and Shapers in Immune Privilege of the CNS. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Louveau, A.; Harris, T.H.; Kipnis, J. Revisiting the Mechanisms of CNS Immune Privilege. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulous, F.E.; Cruz-Hernández, J.C.; Yang, C.; Kaya, Ζ.; Paccalet, A.; Wojtkiewicz, G.; Capen, D.; Brown, D.; Wu, J.W.; Schloss, M.J.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Can Exit into the Skull Bone Marrow and Instruct Cranial Hematopoiesis in Mice with Bacterial Meningitis. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzitelli, J.A.; Pulous, F.E.; Smyth, L.C.D.; Kaya, Z.; Rustenhoven, J.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Kipnis, J.; Nahrendorf, M. Skull Bone Marrow Channels as Immune Gateways to the Central Nervous System. Nat. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 2052–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Mesquita, S.; Fu, Z.; Kipnis, J. The Meningeal Lymphatic System: A New Player in Neurophysiology. Neuron 2018, 100, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Mesquita, S.; Louveau, A.; Vaccari, A.; Smirnov, I.; Cornelison, R.C.; Kingsmore, K.M.; Contarino, C.; Onengut-Gumuscu, S.; Farber, E.; Raper, D.; et al. Functional Aspects of Meningeal Lymphatics in Ageing and Alzheimer’s Disease. Nature 2018, 560, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Mesquita, S.; Papadopoulos, Z.; Dykstra, T.; Brase, L.; Farias, F.G.; Wall, M.; Jiang, H.; Kodira, C.D.; de Lima, K.A.; Herz, J.; et al. Meningeal Lymphatics Affect Microglia Responses and Anti-Aβ Immunotherapy. Nature 2021, 593, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korin, B.; Ben-Shaanan, T.L.; Schiller, M.; Dubovik, T.; Azulay-Debby, H.; Boshnak, N.T.; Koren, T.; Rolls, A. High-Dimensional, Single-Cell Characterization of the Brain’s Immune Compartment. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brioschi, S.; Wang, W.-L.; Peng, V.; Wang, M.; Shchukina, I.; Greenberg, Z.J.; Bando, J.K.; Jaeger, N.; Czepielewski, R.S.; Swain, A.; et al. Heterogeneity of Meningeal B Cells Reveals a Lymphopoietic Niche at the CNS Borders. Science 2021, 373, eabf9277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafflick, D.; Wolbert, J.; Heming, M.; Thomas, C.; Hartlehnert, M.; Börsch, A.-L.; Ricci, A.; Martín-Salamanca, S.; Li, X.; Lu, I.-N.; et al. Single-Cell Profiling of CNS Border Compartment Leukocytes Reveals That B Cells and Their Progenitors Reside in Non-Diseased Meninges. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Xu, D.; Huang, C.; Xing, R.; He, D.; Xu, H. Early Developing B Cells Undergo Negative Selection by Central Nervous System-Specific Antigens in the Meninges. Immunity 2021, 54, 2784–2794.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, Z.; Ghabdan Zanluqui, N.; Rosenblum, J.S.; Tuong, Z.K.; Lee, C.Y.C.; Chandrashekhar, V.; Negro-Demontel, M.L.; Stewart, A.P.; Posner, D.A.; Buckley, M.; et al. Venous-Plexus-Associated Lymphoid Hubs Support Meningeal Humoral Immunity. Nature 2024, 628, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cugurra, A.; Mamuladze, T.; Rustenhoven, J.; Dykstra, T.; Beroshvili, G.; Greenberg, Z.J.; Baker, W.; Papadopoulos, Z.; Drieu, A.; Blackburn, S.; et al. Skull and Vertebral Bone Marrow Are Myeloid Cell Reservoirs for the Meninges and CNS Parenchyma. Science 2021, 373, eabf7844. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cai, R.; Pan, C.; Ghasemigharagoz, A.; Todorov, M.I.; Förstera, B.; Zhao, S.; Bhatia, H.S.; Parra-Damas, A.; Mrowka, L.; Theodorou, D.; et al. Panoptic Imaging of Transparent Mice Reveals Whole-Body Neuronal Projections and Skull-Meninges Connections. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goldmann, T.; Wieghofer, P.; Jordão, M.J.C.; Prutek, F.; Hagemeyer, N.; Frenzel, K.; Amann, L.; Staszewski, O.; Kierdorf, K.; Krueger, M.; et al. Origin, Fate and Dynamics of Macrophages at Central Nervous System Interfaces. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 797–805. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez Perdiguero, E.; Klapproth, K.; Schulz, C.; Busch, K.; Azzoni, E.; Crozet, L.; Garner, H.; Trouillet, C.; de Bruijn, M.F.; Geissmann, F.; et al. Tissue-Resident Macrophages Originate from Yolk-Sac-Derived Erythro-Myeloid Progenitors. Nature 2015, 518, 547–551. [Google Scholar]
- Blériot, C.; Chakarov, S.; Ginhoux, F. Determinants of Resident Tissue Macrophage Identity and Function. Immunity 2020, 52, 957–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilliams, M.; Thierry, G.R.; Bonnardel, J.; Bajenoff, M. Establishment and Maintenance of the Macrophage Niche. Immunity 2020, 52, 434–451. [Google Scholar]
- Matcovitch-Natan, O.; Winter, D.R.; Giladi, A.; Vargas Aguilar, S.; Spinrad, A.; Sarrazin, S.; Ben-Yehuda, H.; David, E.; Zelada González, F.; Perrin, P.; et al. Microglia Development Follows a Stepwise Program to Regulate Brain Homeostasis. Science 2016, 353, aad8670. [Google Scholar]
- Butovsky, O.; Weiner, H.L. Microglial Signatures and Their Role in Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 622–635. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, T.; Sankowski, R.; Staszewski, O.; Prinz, M. Microglia Heterogeneity in the Single-Cell Era. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, P.S.; Dando, O.; Emelianova, K.; He, X.; McKay, S.; Hardingham, G.E.; Qiu, J. Microglial Identity and Inflammatory Responses Are Controlled by the Combined Effects of Neurons and Astrocytes. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108882. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borst, K.; Dumas, A.A.; Prinz, M. Microglia: Immune and Non-Immune Functions. Immunity 2021, 54, 2194–2208. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dzierzak, E.; Bigas, A. Blood Development: Hematopoietic Stem Cell Dependence and Independence. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 639–651. [Google Scholar]
- Ginhoux, F.; Greter, M.; Leboeuf, M.; Nandi, S.; See, P.; Gokhan, S.; Mehler, M.F.; Conway, S.J.; Ng, L.G.; Stanley, E.R.; et al. Fate Mapping Analysis Reveals That Adult Microglia Derive from Primitive Macrophages. Science 2010, 330, 841–845. [Google Scholar]
- Stremmel, C.; Schuchert, R.; Wagner, F.; Thaler, R.; Weinberger, T.; Pick, R.; Mass, E.; Ishikawa-Ankerhold, H.C.; Margraf, A.; Hutter, S.; et al. Yolk Sac Macrophage Progenitors Traffic to the Embryo during Defined Stages of Development. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Utz, S.G.; See, P.; Mildenberger, W.; Thion, M.S.; Silvin, A.; Lutz, M.; Ingelfinger, F.; Rayan, N.A.; Lelios, I.; Buttgereit, A.; et al. Early Fate Defines Microglia and Non-Parenchymal Brain Macrophage Development. Cell 2020, 181, 557–573.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Amann, L.; Monaco, G.; Sankowski, R.; Staszewski, O.; Krueger, M.; Del Gaudio, F.; He, L.; Paterson, N.; Nent, E.; et al. Specification of CNS Macrophage Subsets Occurs Postnatally in Defined Niches. Nature 2022, 604, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hattori, Y.; Kato, D.; Murayama, F.; Koike, S.; Asai, H.; Yamasaki, A.; Naito, Y.; Kawaguchi, A.; Konishi, H.; Prinz, M.; et al. CD206+ Macrophages Transventricularly Infiltrate the Early Embryonic Cerebral Wall to Differentiate into Microglia. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112092. [Google Scholar]
- Yano, S.; Asami, N.; Kishi, Y.; Takeda, I.; Kubotani, H.; Hattori, Y.; Kitazawa, A.; Hayashi, K.; Kubo, K.-I.; Saeki, M.; et al. Propagation of Neuronal Micronuclei Regulates Microglial Characteristics. Nat. Neurosci. 2025, 28, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kierdorf, K.; Erny, D.; Goldmann, T.; Sander, V.; Schulz, C.; Perdiguero, E.G.; Wieghofer, P.; Heinrich, A.; Riemke, P.; Hölscher, C.; et al. Microglia Emerge from Erythromyeloid Precursors via Pu.1- and Irf8-Dependent Pathways. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 273–280. [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki, A.; Imanishi, I.; Tanaka, K.; Ohkawa, Y.; Tsuda, M.; Masuda, T. IRF8 and MAFB Drive Distinct Transcriptional Machineries in Different Resident Macrophages of the Central Nervous System. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 896. [Google Scholar]
- Brioschi, S.; Belk, J.A.; Peng, V.; Molgora, M.; Rodrigues, P.F.; Nguyen, K.M.; Wang, S.; Du, S.; Wang, W.-L.; Grajales-Reyes, G.E.; et al. A Cre-Deleter Specific for Embryo-Derived Brain Macrophages Reveals Distinct Features of Microglia and Border Macrophages. Immunity 2023, 56, 1027–1045.e8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Benveniste, H.; Nedergaard, M.; Zlokovic, B.V.; Mestre, H.; Lee, H.; Doubal, F.N.; Brown, R.; Ramirez, J.; MacIntosh, B.J.; et al. Perivascular Spaces in the Brain: Anatomy, Physiology and Pathology. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 137–153. [Google Scholar]
- Drieu, A.; Du, S.; Storck, S.E.; Rustenhoven, J.; Papadopoulos, Z.; Dykstra, T.; Zhong, F.; Kim, K.; Blackburn, S.; Mamuladze, T.; et al. Parenchymal Border Macrophages Regulate the Flow Dynamics of the Cerebrospinal Fluid. Nature 2022, 611, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.V.; Latour, L.L.; McGavern, D.B. Distinct Myeloid Cell Subsets Promote Meningeal Remodeling and Vascular Repair after Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustenhoven, J.; Drieu, A.; Mamuladze, T.; de Lima, K.A.; Dykstra, T.; Wall, M.; Papadopoulos, Z.; Kanamori, M.; Salvador, A.F.; Baker, W.; et al. Functional Characterization of the Dural Sinuses as a Neuroimmune Interface. Cell 2021, 184, 1000–1016.e27. [Google Scholar]
- Benilova, I.; Karran, E.; De Strooper, B. The Toxic Aβ Oligomer and Alzheimer’s Disease: An Emperor in Need of Clothes. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, B.T.; Iliff, J.J.; Xia, M.; Wang, M.; Wei, H.S.; Zeppenfeld, D.; Xie, L.; Kang, H.; Xu, Q.; Liew, J.A.; et al. Impairment of Paravascular Clearance Pathways in the Aging Brain: Paravascular Clearance. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 76, 845–861. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, W.; Achariyar, T.M.; Li, B.; Liao, Y.; Mestre, H.; Hitomi, E.; Regan, S.; Kasper, T.; Peng, S.; Ding, F.; et al. Suppression of Glymphatic Fluid Transport in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 93, 215–225. [Google Scholar]
- Mildenberger, W.; Stifter, S.A.; Greter, M. Diversity and Function of Brain-Associated Macrophages. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2022, 76, 102181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hiraki, C.; Tsuruta, F. The Meninges as CNS Interfaces and the Roles of Meningeal Macrophages. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040497
Hiraki C, Tsuruta F. The Meninges as CNS Interfaces and the Roles of Meningeal Macrophages. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(4):497. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040497
Chicago/Turabian StyleHiraki, Chihiro, and Fuminori Tsuruta. 2025. "The Meninges as CNS Interfaces and the Roles of Meningeal Macrophages" Biomolecules 15, no. 4: 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040497
APA StyleHiraki, C., & Tsuruta, F. (2025). The Meninges as CNS Interfaces and the Roles of Meningeal Macrophages. Biomolecules, 15(4), 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040497




